Abstract
While understanding the dynamic urban network through the concept of regional centrality has provided various implications on the structure and hierarchy of cities, the macroscopic focus of previous studies has largely overlooked the small-scale physical and social urban entities in central places. Meanwhile, recent advances in real-time Point-of-Interest (POI) data have quickly replaced much of traditional urban facility data, emerging as a new representation of urban activities and demands. Therefore, this study proposes a method to identify the relationship between regional centrality and the distribution of POI facilities, particularly focused on the Seoul metropolitan area of South Korea. To this end, this study conducts a correlation analysis between regional centrality results derived from social network analysis and POI indices obtained from POI distribution analysis. The results indicate that a statistically significant relationship exists between regional centrality and the distribution of urban facilities, with a particularly strong correlation exhibited in specific POI categories. The results also demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in capturing disparities in the provision of facilities concerning growing commuting centers. The findings of the study provide pragmatic implications for prioritization and planning of facility development, as well as making informed decisions in real estate and facility investment.
1. Introduction
In the globalized modern world, the interconnectedness between nations, cities, and organizations is becoming ever complicated, like a neural structure [1], and the networked connectivity between cities has gained wide attention in regional development [2]. Consequently, urban studies have shifted their focus from evaluating the individual attributes and comparative measures of cities to understanding the relationships between them. In other words, the focal point of discussion is no longer about the nodes but the links of the urban network shaped by flows, linkages, connections, and relations [3]. Under such context, regional centrality refers to the relative importance of each region within the urban network, i.e., an indicator of the status, prestige, and significance of each nodal point in the network. The concept of regional centrality thus departs from the traditional definition of ‘urban centers’ measured through static indicators like population size and capital goods, arriving at the comprehensive understanding of network city through dynamic indices such as human and information flows between cities through social network analysis [4]. In this regard, no unanimity exists over what centrality should mean or how it should be measured due to its wide applications of various indices and acceptance of different interpretations, further diversifying the spatial implication of centrality throughout various research fields such as urban structures, transportation network, and economic geographies [5]. Among various indicators that represent linkages within the complex urban network, inter-regional commuting information is a pivotal factor in identifying the national transit network. Commuting data represent the daily movements of individuals between residential areas and employment centers, providing valuable insights into the identification of urban hierarchical structures and the formulation of strategic policies [6]. Notably, South Korea stands out as a country that has conducted population and housing censuses since 1980, facilitating comprehensive and precise analyses of regional networks and urban structures through the availability of commuting information. Within such background, studies on identifying urban networks using commuting flow data have been conducted actively, and centrality measures based on the workforce have gained significant attention in the field. Previous studies primarily focused on identifying the urban structure based on commuting networks, revealing pronounced concentration in the Seoul metropolitan area and imbalanced growth in other cities [2,6,7]. Furthermore, several studies have evaluated the effectiveness of balanced regional development policies, examining whether national strategies have effectively addressed urban concentration issues based on centrality measures [8,9]. In alignment with this active dialogue, this study also measures centrality using commuting flow, and regional centrality, in this case, thus represents the centers of the workforce with respect to complementary regions in the network.
The notion that central places have spatial privileges in social and economic amenities and facilities is rarely questioned [10]; however, with regional centrality’s macroscale scope of research and its inability to address small-scale physical and social urban entities, the specifics of these ‘spatial privileges’ remain largely unanswered. In other words, despite the valuable insights that the previous literature offers, the study of regional centrality has been limited as it falls short of identifying relationships with specific urban entities. This study is thus an attempt to uncover the dynamics of spatial, social, and economic interactions regarding commuting networks, with particular interest in the role of physical urban facilities. In light of this matter, urban facilities are a tangible representation of people’s daily needs, activities, and lives [9], developed and managed in response to the accelerated growth of cities and their constantly changing centrality [11].
Meanwhile, the rapid advancement of information technology has led to the availability of new applied data that serve as indicators of urban conditions and activities. In particular, the widespread expansion of open Application Programming Interface (API) services has greatly facilitated the acquisition of POI data, making it more accessible than ever before. POI data are new spatial data sources that indicate economic, industrial, and commercial urban facilities accumulated based on web navigation service. In comparison to conventional urban facility data, POI data offer significant advantages in terms of its abundance, ease of access, and high accuracy [12]. Due to these characteristics, POI data have been extensively employed across various research fields as a scientific representation of urban facilities and human activities [13,14].
In this context, we propose a method of identifying the relationship between regional centrality and urban facilities based on commuting origin–destination (OD) data and POI data over 77 administrative districts in the Seoul metropolitan area. The essential idea that underlies the study is to conduct a correlation analysis between variables that exhibit regional centrality and urban facilities—the degree and eigenvector centrality score representing the regional centrality of a region and the number and density of POI data representing the spatial distribution of urban facilities. The main contributions of this work are three-fold. By identifying the direct relationship between regional centrality and the distribution of POI, this study fills the academic gap that exists between centrality measures and urban entities. Second, through social network analysis and statistical analysis, this study constructs a research framework that can be applied and replicated in various urban settings. Third, by applying the up-to-date, real-time POI data for the findings, this study provides implications for facility management and decision-making processes that are responsive to rapid urban growth and dynamic transformations.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Regional Centrality
The notion of centrality surfaced with the central place theory, first proposed by Chrystaller and refined by Losch [15], understanding cities as nodal points for the distribution of goods and services in relation to complementary regions. Among many studies that followed this foundational work, Nysteun and Dacey applied mathematical graph theory to better explain the magnitude and direction of flow between cities [16]. The concept of centrality then took a major leap through the work of Cartwright and his team, as they successfully applied the graph theory to social network analysis [17]. First proposed by Barnes, social network theory identified a relationship between people, information, and regions through a networked structure constructed by nodal points and links [13,14]. In this regard, centrality became one of the more popular indicators of relationship in the network, referring to the influence of an actor or how central one actor is in the entire network [18]. Under this context, Freeman conducted an overarching review of published measures and reduced them to three basic concepts: degree centrality, closeness centrality, and betweenness centrality [19]. Moreover, Bonacich then proposed eigenvector centrality as well as Bonacich beta centrality to supplement the previous understanding of centrality measures and provide a more accurate understanding of centrality with consideration for influence [20,21]. Based on such prominent measures of centrality, Irwin presented a comprehensive understanding and application of these centrality indices, specifically utilizing airline and commuting data as its study of interest [22]. This understanding of regional centrality established through theoretical work provided solid ground for active discussion and applications across various fields of urban studies: land use [23,24], residential characteristics [25], R&D network [26], economy [11], and green space [27].
While its multifaceted nature allows for wide applications over various indices of interest, regional centrality especially proved to be an effective tool in identifying urban spatial structure and regional hierarchy [28]. Kim identified spatial structure in the Seoul metropolitan area through commuting OD data [29]. He measured the degree centrality of each administrative district for different time periods of the day and analyzed different network clusters within the metropolitan area. Lee conducted a comparative study of the spatial structure in the capital region between 1995 and 2005 [30]. By comparing the degree centrality result each year, he identified the transformation of urban spatial structure in the Seoul metropolitan region. Lee and Seo conducted a comparative analysis of regional centrality between different spatial scales of a dataset [4]. By comparing the degree centrality result of Seoul regional data and nationwide data, they proposed that regional centrality be measured using nationwide data for higher accuracy. Lee and Kim were among the first to apply eigenvector centrality in spatial structure analysis in South Korea, as they compared the regional centrality of the Seoul metropolitan area between 1980 and 2000 [31]. The study measured the change in eigenvector centrality between the twenty-year time period, identifying new commuting structures in the capital region. Lee and Ha analyzed migration and regional structural change in Jeju Island through eigenvector centrality [32]. Kim and Ahn studied the relationship between regional centrality and social factors such as population, jobs, and social capital [33]. They explained the impact of social factors on regional centrality by formulating the regression model between eigenvector centrality and social factors. Park, Lee, and Jo went further to implement eigenvector centrality in identifying traffic networks in the Seoul metropolitan area, concluding that eigenvector centrality is more useful than degree centrality in regard to traffic analysis [34]. Applying a similar process, several empirical studies have also utilized regional centrality measures to examine the effectiveness of national policies on balanced urban development [7,8].
However, previous studies have been conducted primarily on a large scale over wide geographic distances, overlooking much of the physical, social, economic urban entities in turn. In response, more studies in recent years have dedicated their attention to applying centrality measures on a more regional scale of street centrality. Yue and Zhu investigated the association between street centrality and urban vitality in Wuhan, China [35], and Al-Saaidy and Alobaydi applied street centrality to identify its relation to human density in different urban forms of Baghdad, Iraq [36]. In the same vein, there have been studies to incorporate the presence of physical urban facilities into centrality measures. Agryzkov et al. used geo-located data about buildings in the city of Murcia to provide a new model of centrality that represents a more accurate depiction of urban networks [37]. Similarly, Amen conducted research on establishing an urban centrality model based on buildings’ physical characteristics and positions in the network of Erbil City [38]. While these efforts are noteworthy for incorporating physical entities into regional centrality analysis, they predominantly rely on facility data as a supplementary source to augment centrality measures rather than establishing a direct relationship between the centrality and distinctive urban facilities.
2.2. POI Big Data
In recent years, a vast amount of big data regarding urban conditions has been accumulated and implemented to understand the urban spatial structure. Among these data sources, POI data have attracted considerable attention as they reflect daily urban activities [13,14]. Previous research on POI data and urban spatial structure can be largely categorized into two branches: (1) a study that identifies the center of urban activity based on the concentration of POI; (2) a study that distinguishes the functional area of the city based on the type of POI data.
Representatively, Deng et al. conducted a study to identify the polycentric urban structure in Beijing, China, using POI big data [13]. By applying kernel density analysis and contour tree methodology on POI big data, they proposed a new urban subcenter identification method that can overcome the shortcomings of previous studies. In a similar study, Han and Song analyzed the urban structure through the distribution of POI data on the accommodation and catering industry in Beijing [14]. They applied contour tree methodology and location coefficient analysis to identify the distribution and agglomeration characteristics of POI data. However, these studies have been conducted without regard to the centrality of commuting flow, focused solely on deriving the center of POI beyond the administrative boundaries. In a domestic study, Kim and Lee attempted a comparative analysis of the urban center between commute-based data and the POI big data, but it was limited to a visual comparison of the results derived from each analysis.
Furthermore, studies have been conducted to classify the functional areas of cities based on the types of POIs [39,40,41]. Hu and Han, for instance, divided the Guangzhou Economic Development Zone into grids and derived functional areas based on POI data for each grid [39]. They employed measures such as frequency density and the ratio of POI function types within each grid to determine the functional areas. In a similar context, Miao, Wang, and Li utilized POI data derived from social media location information to identify functional regions through hot spot analysis and cluster analysis [40]. While research on functional areas has incorporated the classification of POI types, these studies provide limited explanations regarding their relationship with regional centrality.
These empirical studies have utilized POI data to identify the urban structure beyond conventional administrative boundaries and classify functional areas based on POI categories. However, they have not adequately addressed the relationship with the daily commuting flow. Thus, this study is significant as it aims to establish a direct and practical connection between commuting centers and physical facilities. Therefore, it overcomes the limitations of previous POI research that did not consider regional centrality in their analysis. The findings of this study will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the relationship between commuting patterns and the distribution of urban facilities, providing valuable insights for urban planning and development.
3. Research Methods
3.1. Research Scope
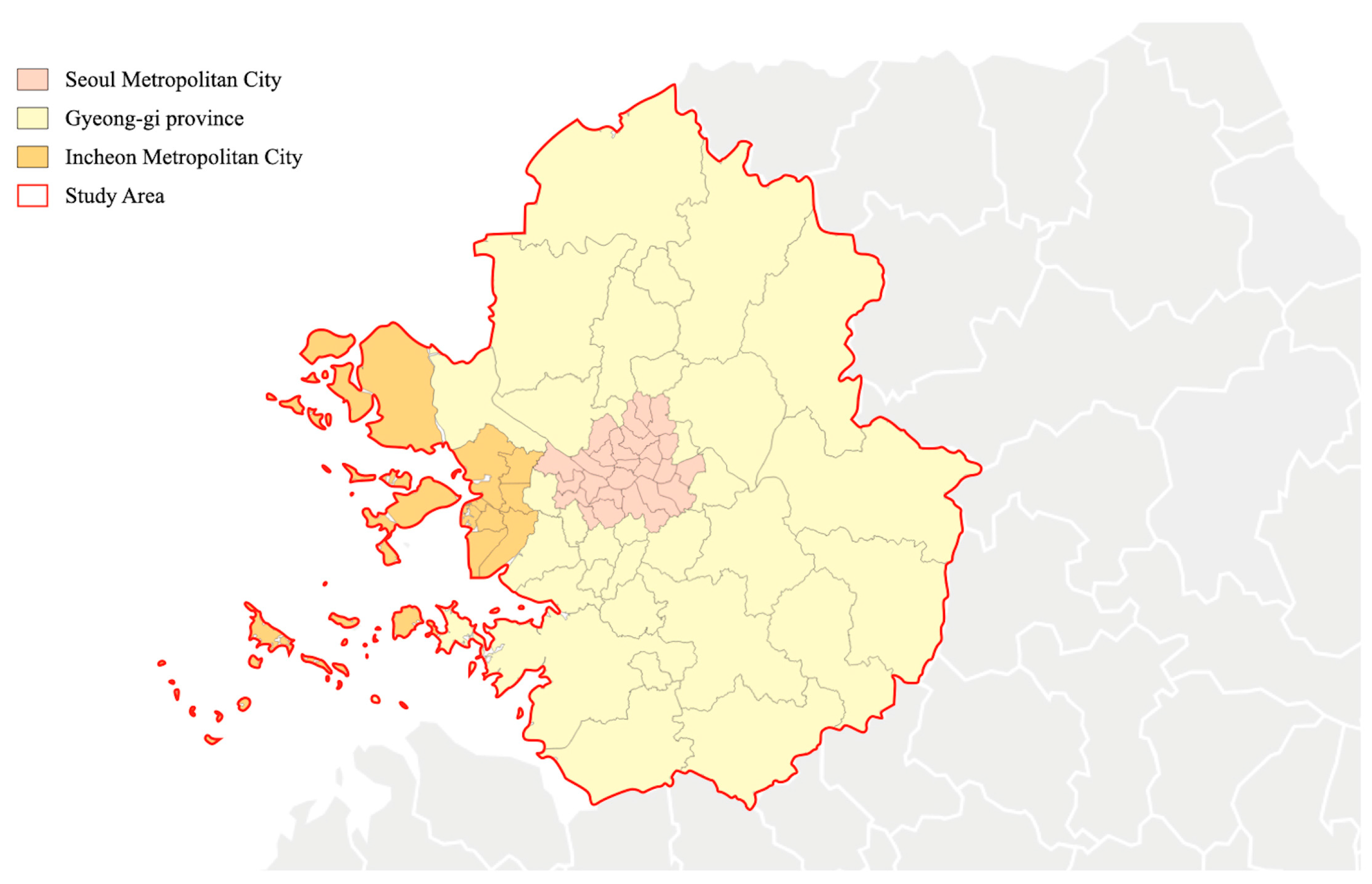
The spatial scope of the study is the metropolitan area of Seoul, including Seoul Metropolitan City, Incheon Metropolitan City, and Gyeonggi Province (see Figure 1). Seventy-seven administrative subdivisions—cities (“Si”), counties (“Gun”), districts (“Gu”)—within the metropolitan area were used as analysis units, for this spatial delineation constitutes the administrative boundary for much of the economic, legislative, and political decisions in South Korea. The metropolitan area of Seoul occupies approximately 11.8% of the total land area in South Korea and is characterized by a high concentration of population, with over 50% of the country’s population. As of March 2023, the population in this area was recorded as 26,053,000, according to Statistics Korea [42]. The Seoul Metropolitan area is known for its significant presence of labor and diverse types of facilities [43]. Regarding the temporal scope, the origin–destination (OD) data and POI big data used in the analysis were collected between 2020 and 2022, and the most up-to-date data provided were employed to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the findings.
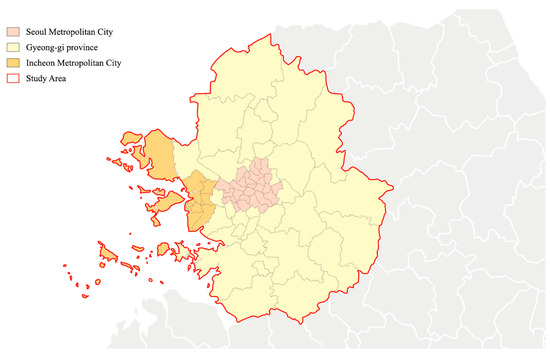
Figure 1.
Administrative boundaries of Seoul metropolitan area.
3.2. Data Collection and Rearrangement
3.2.1. OD Data
In this study, OD data for commuting flow was obtained from the National Transportation DB [44] to measure the centrality of different regions. In social network analysis, various types of data, such as phone calls, commuter traffic, and data transmission and reception, are used to understand the inter-regional flow patterns. Among them, commuting data play an important role in understanding urban spatial structure, as they represent the daily flow between residential and workplace [45]. Particularly, the OD matrix used in this study documents the average volume of traffic between administrative districts during the weekdays, where each of the 77 administrative districts forms a nodal point in the commuting network, and the traffic volume becomes the link. In this context, the nodes in the commuter network structure represent residential and workplace areas, while the links represent the flow of the labor force through the connections established between these nodes [31].
3.2.2. POI Big Data
POI big data are web-based points of interest and include point data that contain spatial information about various urban facilities. POI data provide a much larger volume of data compared to conventional land use data and are highly accurate as they reflect real-time user demand and activity. Moreover, while traditional building data can only express the main purpose of each facility, POI data have a great advantage as they represent numerous subdivisions and amenities within each facility [46]. Thus, POI data enable a more accurate depiction of people’s daily activities, serving as a valuable indicator of various urban facilities.
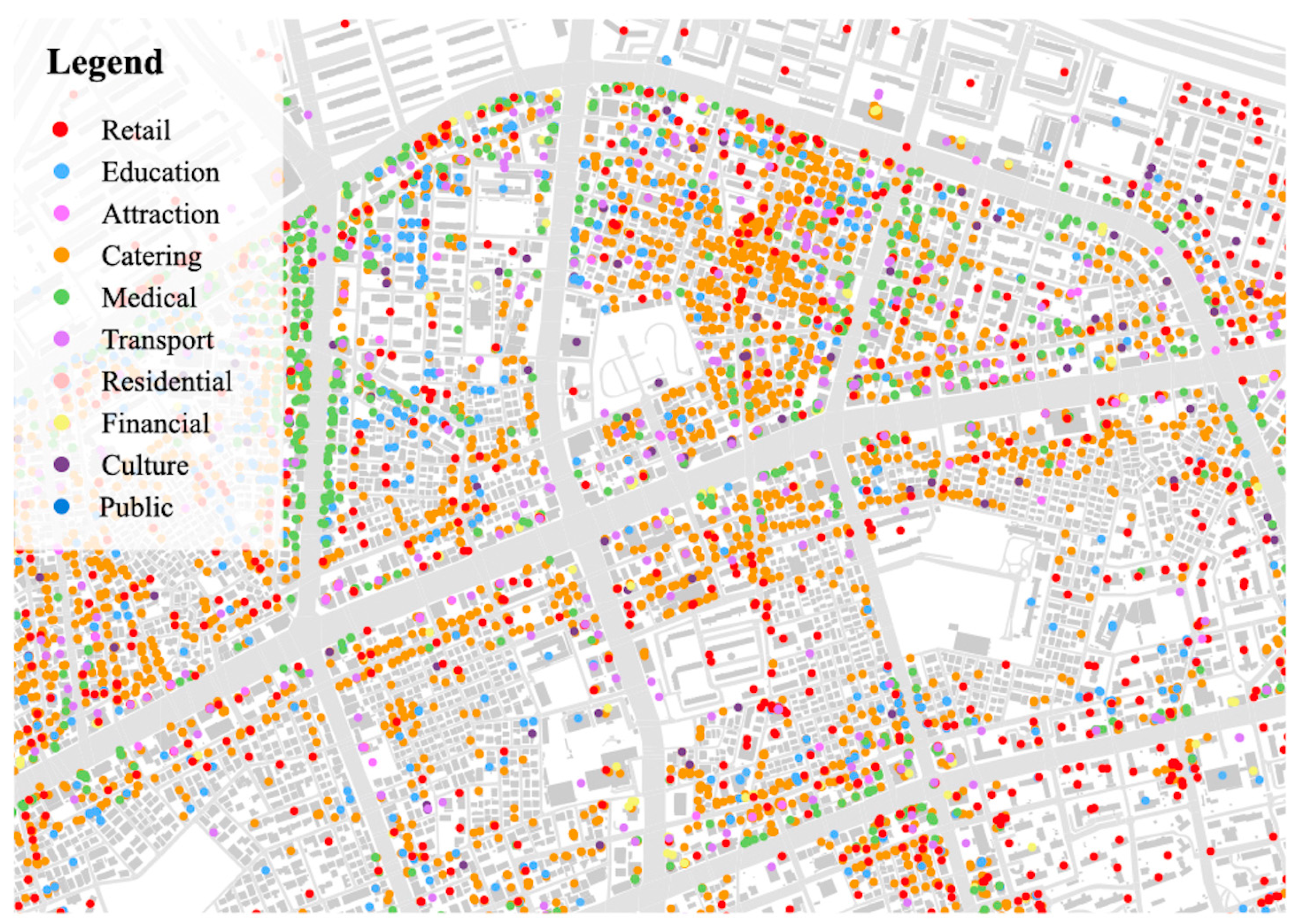
With the recent expansion of the open API service, the acquisition of POI data has become more convenient. Through the open API service, the user can request certain information by specifying the search parameters, and the web service returns the requested information. The POI data used in this study were accumulated based on Kakao Map’s navigation service (KakaoMap 5.2.1), which is one of the most widely used map services in South Korea, with more than 10 million users. A total of 761,456 POIs were collected in the metropolitan area, including Seoul, Incheon, and Gyeonggi Province. Based on the initial 18 categories of POI provided by Kakao Map, the data used in the analysis were simplified to 10 different categories to address the redundancy and crossovers between them. This process was guided by the previous studies conducted in a similar urban context [43,47], and the final classification of POI is shown in Table 1. Figure 2 provides an example of the type and distribution of POI in Gangnam, a highly concentrated district in Seoul Metropolitan City.

Table 1.
POI categories and characteristics of Seoul metropolitan area.
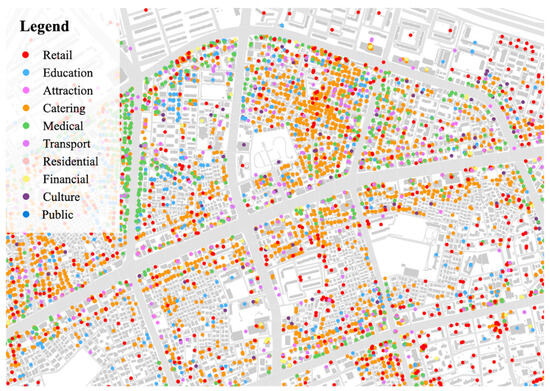
Figure 2.
Distribution and types of POI (example of Gangnam, Seoul).
3.3. Analysis Flow and Methods
3.3.1. Analysis Flow
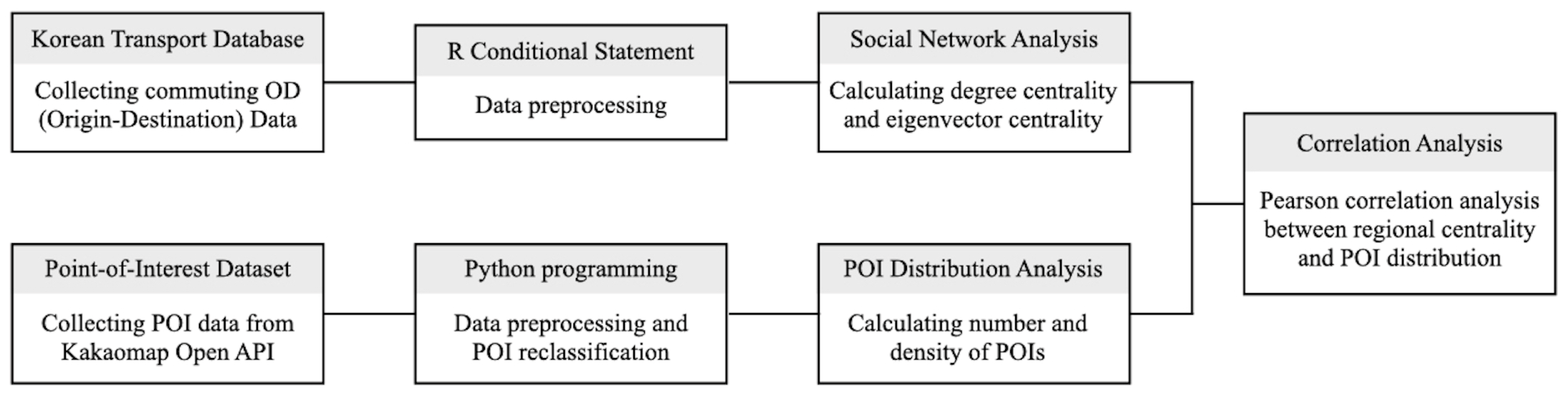
Essentially, the general framework of the study was designed to conduct a feasible correlation analysis between regional centrality and spatial distribution of POI facilities. To this end, we have calculated the degree and eigenvector centrality score for each administrative district through social network analysis and derived the number and density of POI facilities for the corresponding region. This process provides a simple yet effective framework that identifies the relationship between two distinct bodies of urban representation based on easily accessible datasets, applicable across various urban settings with relatively few contextual barriers. The specifics of each methodology are laid out in the following sections.
In the data collection stage, commuting OD data and POI big data were each obtained from National Transportation DB and Kakao Map open APIs. Subsequently, the collected data went through preprocessing to eliminate redundancy and unnecessary information. Based on the refined datasets, degree and eigenvector centrality scores were calculated through social network analysis for each administrative district, and the number and density of POI facilities were derived likewise. Finally, the relationships between degree centrality, eigenvector centrality, number of POIs, and POI density were observed using 77 administrative districts as a unit of analysis through Pearson correlation analysis. The analysis process of this study is summarized in Figure 3.
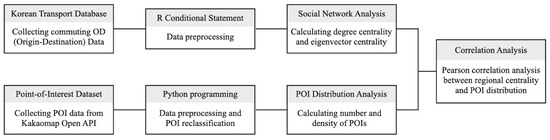
Figure 3.
Study process.
This study used Python 3.10.5 for data collection, UCINET 6 and ‘igraph’ package in RStudio 4.1.2 for social network analysis, and ArcGIS 10.7 for the visualization of the result.
3.3.2. Social Network Analysis
In this study, degree centrality and eigenvector centrality were derived through social network analysis to identify the centrality of the administrative districts in the Seoul metropolitan area. Among many centrality measures, degree centrality was deemed suitable as it captures the direct activities between nodes, making it appropriate for estimating the direct commute flow between workplaces and homes. Eigenvector centrality serves as a complementary measure to the degree centrality by considering not only the importance of directly connected nodes but also the relative influence of indirectly connected nodes. While other centrality measures like closeness and betweenness centrality are useful for capturing control or mediating roles within the network, they are not as relevant for identifying the direct relationship between nodes. Hence, degree and eigenvector centrality were considered as applicable centrality measures for the study.
Degree centrality measures centrality based on the number of nodes directly connected to the nodal point. That is, the centrality of a specific node is determined by the number of connected nodes, and the influence of the node increases when connected to more nodes [31]. In the case of commuting flow data, it can be interpreted as inflow and outflow traffic from other regions, and the area with a high total traffic volume is considered to have a high degree of degree centrality. As such, degree centrality is used as the most basic measure of identifying the spatial structure of a city [7].
The calculation formula for connection degree centrality is as follows:
where is the degree centrality of node , is the number of nodes, and is the number of links between nodes and (traffic volume).
Eigenvector centrality measures centrality by considering not only direct and indirect connections but also the influence of other connected nodes [1]. In other words, when connected to a node with high influence or importance, the centrality of the actor also increases. This reflects the influence of the commuting form in a more realistic way, implemented as a measure to understand the spatial structure along with the centrality of connection [48].
The calculation formula for eigenvector centrality is as follows:
where is the eigenvector centrality of node , is a constant used to compute standardized centrality index, is the level of interactions, and is the number of links between nodes and (traffic volume).
3.3.3. POI Distribution Analysis
To examine the spatial distribution of POI data, this study identifies the number and density of POI facilities in each of the 77 administrative districts. In this case, the number of POI facilities represents the sheer volume of urban facilities in each region, while density represents the relative concentration of facilities with respect to the population. Considering that urban facilities are primarily associated with human activities rather than land area characteristics, this study calculates POI density based on the population of each administrative district instead of the land area, i.e., the number of POI divided by the number of populations.
The number and density of POI facilities were measured for each district based on the address information attached to the geospatial points, further distinguished into detail by POI categories. This POI distribution analysis thus identifies the number and density of POI by categories in each administrative district in correspondence to regional centrality results, which provides ground for the succeeding correlation analysis.
Based on the previous analysis results, Pearson correlation analysis was executed between regional centrality and POI distribution, represented through four different variables: degree centrality, eigenvector centrality, number of POI, and density of POI. The findings from the correlation analysis were then used to draw implications for the study.
4. Results
4.1. Regional Centrality Result
Gangnam ranked first in the list of degree centrality measures in the metropolitan area, followed by Seocho; Jung; Yeongdeungpo; Songpa; and Bundang, Seongnam (see Table 2). This indicates that these districts have the highest level of direct connection in terms of commuter traffic. Notably, the districts in Seoul dominate the top positions in the list, highlighting the significant role of Seoul in commuting patterns. The high degree centrality values in these districts can be attributed to the concentration of workplaces within Seoul Metropolitan City.

Table 2.
Top 10 rankings of centrality result in Seoul metropolitan area.
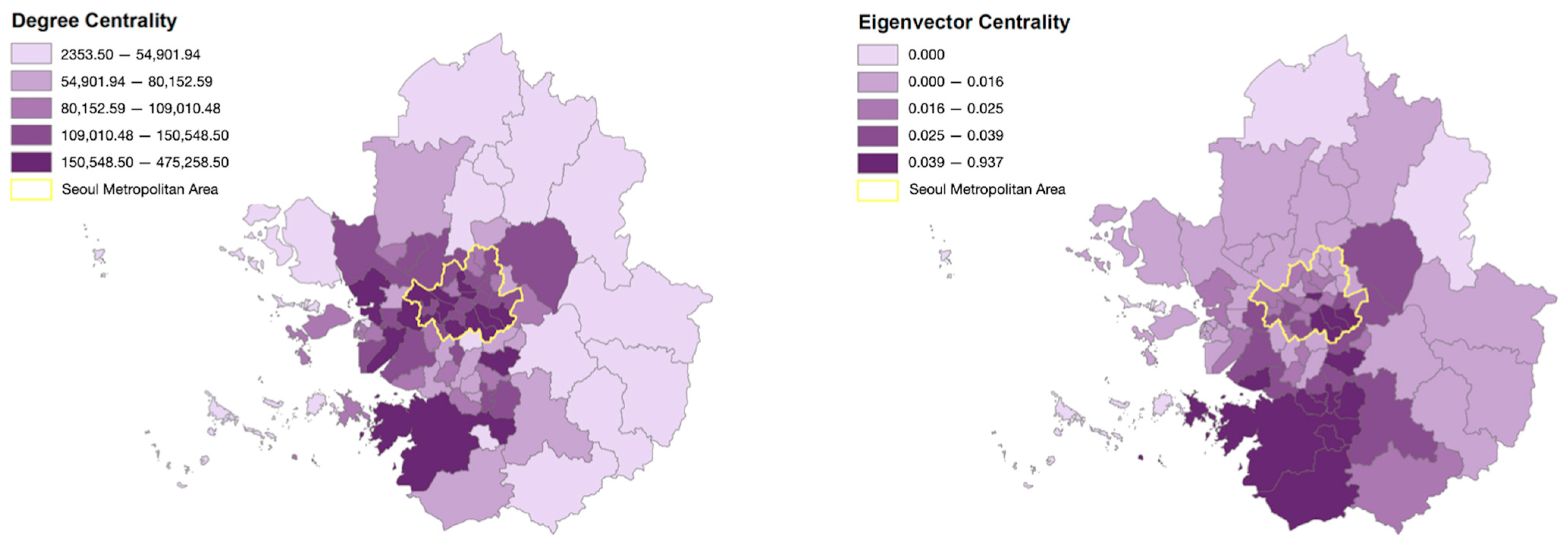
On the other hand, Hwaseong in Gyeonggi province ranked first in the case of eigenvector centrality, which reflects not only the actual traffic volume but also the influence of the connected region. Following Hwaseong, Gangnam, Pyeongtaek, Yeongtong, and Bundang were among the top-ranked districts. This suggests that the commuting center has shifted to the southwestern part of Gyeonggi province compared to the degree centrality result (see Figure 4).
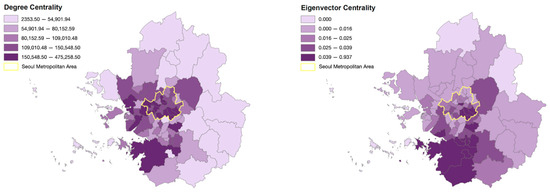
Figure 4.
Degree and eigenvector centrality result in Seoul metropolitan area.
4.2. POI Distribution Result
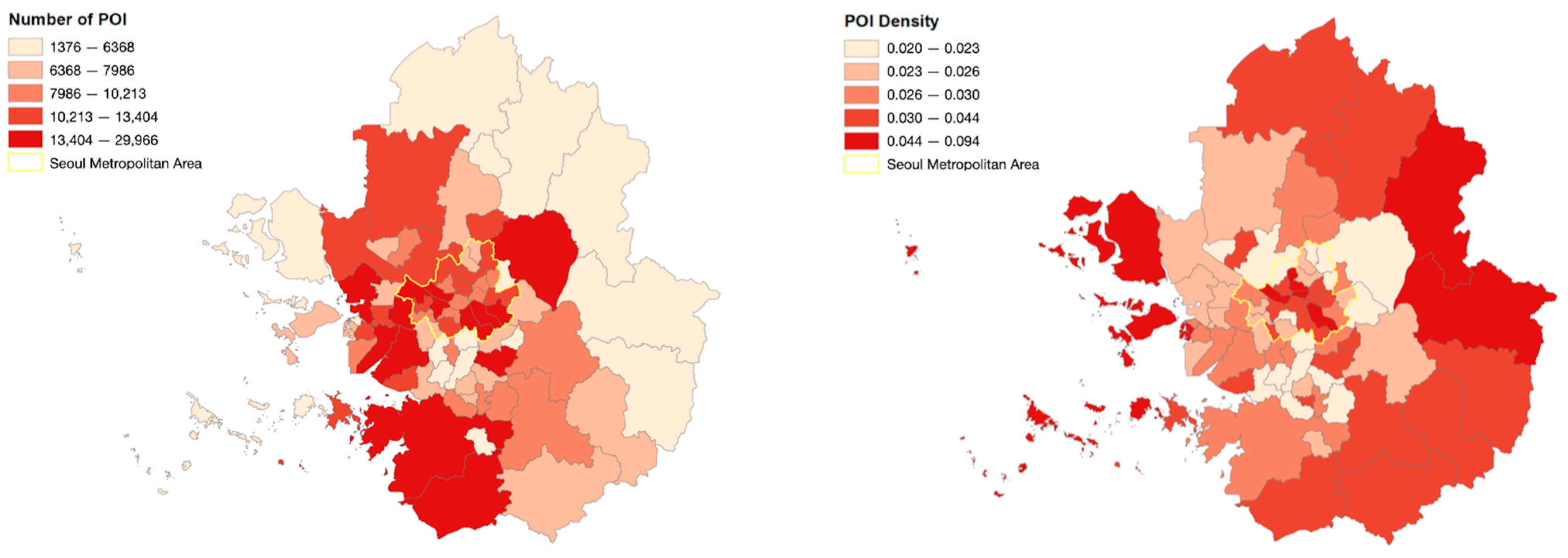
In terms of the number of POIs in the metropolitan area, Gangnam, Seoul, topped the list with 29,966 out of a total of 77 cities and counties, followed by Hwaseong, Bucheon, Songpa, and Mapo. The result reveals that POI facilities are distributed in large volumes, specifically in Seoul city, as six administrative districts in Seoul occupy the top 10 rankings (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Top 10 rankings of POI distribution result in Seoul metropolitan area.
However, in terms of the density of POI facilities based on the population, Gyeonggi and Incheon areas ranked high on the list. Jung, Seoul, ranked first, followed by areas such as Gapyeong, Jongno, Ongjin, and Gangnam. Contrary to the number of POIs, the administrative districts in Gyeonggi province ranked relatively high on the list in terms of POI density (see Figure 5).
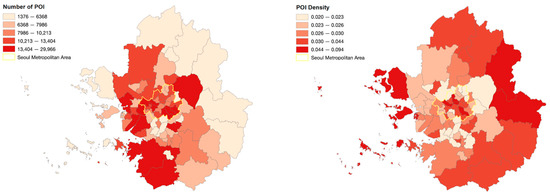
Figure 5.
POI distribution result in Seoul metropolitan area.
4.3. Correlation Analysis Result
Table 4 presents the results of the correlation analysis between regional centrality and the distribution of POI facilities. The analysis reveals a significant correlation between the number of POIs and regional centrality. Across different types of facilities, there is a significant positive correlation between the number of POIs and regional centrality, except for tourist facilities (−0.281). While there is no significant correlation between the number of POIs for tourism and cultural facilities, all other facility types show a significant correlation. The correlation analysis indicates that the higher the regional centrality, the greater the number of POI facilities, suggesting a strong relationship between the two variables.

Table 4.
Pearson correlation analysis result.
In contrast to the number of POI facilities, the correlation between the density of POI facilities and regional centrality was found to be limited. Degree centrality exhibited a significant correlation with POI density for specific facility types, including education (0.650), tourism (−0.329), restaurant (0.304), medical (0.767), housing (0.645), and finance (0.373). However, no significant relationship was observed between degree centrality and the density of commercial, transportation, culture, and public facilities. On the other hand, eigenvector centrality did not show a significant correlation with POI density across all facility types, as indicated by p-values higher than 0.05.
Among the analyzed facilities, several types showed a strong correlation coefficient of 0.8 or higher. The facility type with the highest correlation was medical facilities, with a coefficient of 0.892, followed by transportation (0.871), finance (0.850), and restaurant (0.808) facilities. Additionally, several facilities exhibited relatively strong correlations of 0.6 or higher. Specifically, the correlation between degree centrality and POI density was notable for medical facilities (0.767), education facilities (0.650), and housing facilities (0.645). Moreover, the correlation between eigenvector centrality and the number of POIs indicated a strong relationship with commercial facilities (0.611).
5. Discussion
5.1. Identification of Growing Urban Centers
The regional centrality results in Table 2 and Figure 4 reveal noticeable differences between degree and eigenvector centrality in detecting urban centers. While degree centrality identifies the central regions of Seoul as the prominent commuting centers, eigenvector centrality indicates the outer districts of Hwaseong, Pyeongtaek, and Seongnam as the centers of commute. Considering that traditional urban centers in South Korea have long been associated with the central districts in Seoul, the unusual result detected by eigenvector centrality is noteworthy. As discussed above, degree centrality is measured based on the number of directly connected nodes—in this case, the volume of traffic between districts—while eigenvector centrality takes into account the prominence and weight of other nodes. Under this context, the high degree centrality in the central districts of Seoul can be attributed to the large volume of traffic commuting to the area, and high eigenvector centrality in the outskirts of the metropolitan area can be understood through their close ties with such central nodes in Seoul.
In support of this argument, the areas that exhibit high eigenvector centrality have experienced rapid growth in recent years, with active development centered around the high-tech industry. The sites emerged as the central hubs for large corporate investment and development, including Samsung Electronics’ large semiconductor manufacturing hub in Pyeongtaek and Hyundai Motors’ Electronic Vehicle (EV) plants in Hwaseong [49,50]. Numerous industries followed suit with growing national attention surrounding the new wave of development, leading to significant expansion of employment opportunities and shifting geography of industry in South Korea. In retrospect, these areas were never considered traditional urban centers, yet they have been growing rapidly in population and influence by establishing strong ties with traditional commuting centers and their resources. The analysis results thus underscore the importance of eigenvector centrality in understanding the urban network, as it provides a more accurate depiction of reality by detecting growing urban centers unnoticed by alternative centrality measures.
5.2. Spatial Patterns of POI Distribution
The POI distribution analysis results illustrated in Table 3 and Figure 5 also reveal distinctive outcomes in the number and density of POI across the metropolitan area. While a greater number of POI facilities are present in Seoul and its surrounding regions, the density of POI indicates a higher concentration of facilities in the outer regions on the east periphery, notably Gapyeong, Yangpyeong, and Pocheon. Considering that facility density is measured with respect to population in each district, such results suggest that POI facilities are more densely distributed in these suburban areas than the central districts, considering their users. In the urban context of South Korea, the eastern sectors of the metropolitan area have established themselves as popular leisure and travel destinations, setting them apart from congested urban centers proximate to the capital [51]. Despite the comparatively low populations in these regions, there has been continual development in attraction and leisure-related facilities to foster the growth of local economies through the leisure and travel industry. However, the spatial pattern detected through the POI distribution analysis highlights the necessity for more facility development in the central regions in correspondence with the concentration of users. The analysis would yield an entirely different conclusion when density is measured by land area, and central districts in Seoul that are comparatively smaller in size would exhibit extremely high concentrations than their counterparts. In this sense, measuring facility density by population is a more sensible approach that reflects the realistic demands of the city, as opposed to a land area that solely focuses on the geographical concentration of urban facilities without consideration for its actual users.
5.3. Disparities in Provision of Urban Facilities
Taken together, the correlation analysis result shows a relationship between regional centrality and the distribution of facilities, represented in Table 4. From the analysis result, one distinguished finding arises between the two focal points of discussion highlighted above: eigenvector centrality and density of POI. According to the result, eigenvector centrality exhibits a positive correlation with the number of POI facilities across different categories, implying that there tend to be more urban facilities in areas with higher eigenvector centrality. However, no statistically significant relationships are to be found between eigenvector centrality and density of POI. Considering the significance of the two variables—eigenvector centrality detecting growing urban centers of influence and POI density representing a user-sensitive distribution of urban facilities—the absence of correlation necessitates further inspection between the two.
The follow-up dissection of individual regional entities reveals that Hwaseong, Pyeongtaek, and Yeongtong, which each placed 1, 3, and 4 in the rank of eigenvector centrality, experienced a significant drop to 38, 29, and 40 in POI density, respectively. In the specific urban context of South Korea, the relatively low rankings of such influential regions can be attributed to the dramatic rise in population. Hwaseong experienced explosive growth after the semiconductor, automobile, and R&D industries started to establish ground in the region, its population growing nearly five-fold within the last two decades from 190,000 in 2000 to nearly one million in 2023 [52]. Not as dramatic, but Pyeongtaek has also experienced significant growth within the same time frame, from 356,000 to 590,100 [53]. In this context, the analysis results indicate that the growing commuting centers are experiencing significant deficiencies in the provision of urban facilities, failing to provide adequate service to the users. In other words, the overall number of facilities is increasing, but the rate of provision is simply not enough to keep pace with the explosive growth of the urban population. Taken together, with an accurate depiction of commuting centers and real-time data that represent urban facilities, the correlation analysis provides valuable insight into the disparities in the provision of urban facilities, i.e., whether adequate facility development is achieved in correspondence to the pace of growing commuting centers.
We expect such a method to provide numerous applications in planning practices. First, by identifying the provision and deficiency of urban facilities in urban centers, the analysis would help planners make informed decisions about the prioritization of development and allocation of limited capital and resources. Second, from the economic development perspective, detecting the disparity between rising commuting centers and the shortage of facilities hints at the potential for future economic growth in particular regions.
5.4. High Demand for Particular Facility Types
The correlation analysis of regional centrality and POI distribution reveals a strong demand for specific types of facilities. Degree centrality showed a strong correlation of 0.8 or more with the number of medical, transportation, finance, and restaurant facilities, reflecting the high demand for these facilities in the center of workflow. This observation suggests that certain facility types exhibit a closer association with work centers compared to others. The strong correlation with medical and financial facilities can be attributed to their typical weekday operation schedules, in alignment with the commuting patterns of individuals who seek the services during their work hours. Similarly, the high correlation with restaurant facilities can be explained by the presence of numerous dining establishments and cafes strategically located near business facilities targeting the work population. The high correlation between centrality and transportation POIs can be attributed to the unique urban settings of South Korea; the convenient accessibility to public transit in the metropolitan area encourages the extensive use of public transportation for daily commuting. In support of this pattern, statistical data from July 2022 indicate a substantial commuting rate of 57.9% by buses or subways in the Seoul metropolitan area [52].
The analysis result holds significance as it not only confirms the centrality theory, which posits that urban centers hold spatial privileges in urban amenities and facilities [10], but also uncovers the specifics of such ‘spatial privileges’ by identifying high demands in specific categories of urban facilities. In this regard, such findings provide valuable implications from the real estate perspective, hinting at particular facilities as the focus of development and investment in commuting centers. Further, considering that OD data and POI data are updated every so often, the analysis establishes a responsive framework that captures the changing demands of the cities more accurately. Overall, by analyzing the correlation between regional centrality and POI distribution, this study provides valuable insights into the specific facilities that exhibit a strong association with commuting centers, thus expanding our understanding of the interplay between commuting patterns and urban functionality.
6. Conclusions
While understanding the urban network through regional centrality has provided various implications regarding the structure and hierarchy of cities, a large number of studies have focused on macro-scale analysis over a wide geographic distance, overlooking its relation and interaction with smaller urban entities like physical urban facilities. Meanwhile, the wide availability and easy accessibility of POI data opened up a new horizon for urban research, replacing much of traditional urban facility data with its quantity, access, and accuracy. This study conducts a correlation analysis between regional centrality and POI distribution in the Seoul metropolitan area, thereby examining unique relationships and interactions between the centers of workforce and urban facilities that have been overlooked in the past.
The result of the analysis opens up unique discussions regarding working centers and the distribution of urban facilities. First, the social network analysis reveals different commuting centers detected by degree centrality and eigenvector centrality. While both centrality measures have been applied in previous studies as a feasible method of identifying centers in the urban network, the analysis result highlights the significance of eigenvector centrality as an accurate centrality measure in detecting growing urban centers. Second, the POI distribution analysis result identifies the spatial patterns of urban facilities throughout the metropolitan area. In particular, measuring the density of POI through the lens of population captures the unbalanced facility development with respect to the actual users, suggesting user-sensitive facility density as a more favorable measure over density based on land area. Third, the absence of correlation between eigenvector centrality and POI density indicates a shortage of facility provision with respect to rapidly growing commuting centers. With eigenvector centrality providing an accurate depiction of influential urban centers and POI density representing a concentration of urban facilities with respect to population, identifying the relationship between the two reveals whether sufficient urban facilities are provided at the rate of urban growth. In the case of the Seoul metropolitan area, the provision of urban facilities failed to keep up with the pace of population growth in the commuting centers of Hwaseong, Pyeongtaek, and Yeongtong, resulting in the absence of correlation. This framework can thus provide an empirical ground for identifying the provision of urban facilities with respect to urban growth. Fourth, the strong correlation identified between the number of POIs and centrality scores signifies high demands for specific types of facilities in the commuting centers. The positive correlation with medical, transportation, finance, and catering facilities reflects the strong demands of the workforce, which can contribute as a guide for future facility development.
The findings of the study provide notable implications in both academic and practical terms. First, the study fills the knowledge gap between regional centrality and urban facilities that have not been addressed in the past by identifying the direct relationship through correlation analysis. Second, the research framework designed to conduct feasible correlation analysis can be easily replicated and applied to different urban settings, with widely accessible OD data and POI data as its building blocks. Third, the findings of the study provide pragmatic implications over various sectors of urban planning, from facility development to urban economy, as well as real estate perspective. Since the data utilized for the study are up-to-date and real-time data renewed frequently, the study provides empirical evidence for such facility management and decision-making processes that are responsive and sensitive to urban growth and transformations.
One limitation of the study arises concerning the modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP), as the centrality measures and POI results are sensitive to the definition of the spatial unit and can be interpreted differently according to the arbitrary delineation of geographic boundaries. Future studies should recognize its presence and address the concern by applying the method in multiscale and multizonal systems analysis. In alignment with the same discussion, understanding the distribution of individual POI as an interconnected whole or topology could also provide unique insights [54]. While this study particularly focuses on drawing direct correlation through statistical analysis, comparative studies between two different approaches—understanding POI as aggregated entities and as a topological dimension—with respect to regional centrality could further bolster the methodological ground by identifying potential differences or advantages. As another limitation of the study, the uncertainty and incompleteness of the POI data should be noted. Although the POI data provide a significant advantage over the conventional facility data, they do not consider the size or influence of the entity. In other words, all POIs are considered equally despite their unique size or popularity. Future research endeavors should address these limitations by incorporating attributes such as area or popularity and assigning appropriate weights to the data, thereby capturing the spatial features of the POIs in a more accurate and precise manner.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Yose Lee and Ducksu Seo; methodology, Yose Lee and Ducksu Seo; formal analysis, Yose Lee and Ducksu Seo; investigation, Yose Lee and Ducksu Seo; resources, Yose Lee and Ducksu Seo; data curation, Yose Lee; writing—original draft preparation, Yose Lee; writing—review and editing, Yose Lee and Ducksu Seo; visualization, Yose Lee and Ducksu Seo; supervision, Ducksu Seo; funding acquisition, Ducksu Seo. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korea Ministry of Science and ICT (No. 2022R1G1A1006825).
Data Availability Statement
Data underlying the results presented in this paper are not publicly available at this time but may be obtained from the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kim, Y. Social Network Analysis, 1st ed.; Parkyoungsa: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2003; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Koo, D. The Change of Spatial Structure of Urban Networks in Korea. J. Korean Geogr. Soc. 2019, 54, 621–636. [Google Scholar]
- Beaverstock, J.; Smith, R.; Taylor, P. World-City Network: A New Metageography? Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2000, 90, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Seo, D. Accuracy of Regional Centrality Using Social Network Analysis: Evidence from Commuter Flow in South Korea. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgatti, S.P.; Everett, M.G. A Graph-Theoretic Perspective on Centrality. Soc Netw. 2006, 28, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Seo, Y.; Kim, S. Network Centrality Analysis Based on Regional Size: Focusing on Transformation of Commuting Data. J. Korean Reg. Dev. Assoc. 2018, 30, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Seo, D. Analysis of Regional Centrality by Investigating Direct and Indirect Flows of Commuters. J. Agric. Ext. Community Dev. 2020, 27, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Seo, D.; Kwon, Y. Impact of Innovation City Projects on National Balanced Development in South Korea: Identifying Regional Network and Centrality. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hyeon, S.; Park, M.; Lee, J.; Seo, D. Identifying Regional Centrality of Seoul Metropolitan Area in the Context of Relocating Public Agencies to Regional Areas: Social Network Analysis Using O-D Data. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2022, 57, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucitti, P.; Latora, V.; Porta, S. Centrality in Networks of Urban Streets. Chaos 2006, 16, 015113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Harrison, J.; Miguelez, E. Connecting Cities, Revitalizing Regions: The Centrality of Cities to Regional Development. Reg. Stud. 2018, 52, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Pang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, C.; Tang, X.; Cheng, W. Mapping Urban Spatial Structure Based on POI (Point of Interest) Data: A Case Study of the Central City of Lanzhou, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Luo, A. Detecting Urban Polycentric Structure from POI Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Song, W. Identification and Geographic Distribution of Accommodation and Catering Centers. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S. Regional Development; Kritiki Publications: Athens, Greece, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nystuen, J.D.; Dacey, M.F. A Graph Theory Interpretation of Nodal Regions. Pap. Reg. Sci. Assoc. 1961, 7, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harary, F.; Norman, R.; Cartwright, D. Structural Models: An Introduction to the Theory of Directed Graphs; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S. Network Analysis Methodology; Nonhyeong: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, L. Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification. Soc. Netw. 1978, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacich, P. Factoring and Weighting Approaches to Status Scores and Clique Identification. J. Math. Sociol. 1972, 2, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacich, P. Power and Centrality: A Family of Measures. Am. J. Sociol. 1987, 92, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.D.; Hughes, H.L. Centrality and the Structure of Urban Interaction: Measures, Concepts, and Applications. Soc. Forces 1992, 71, 17–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.; Ban, Y. Exploring the Relationship between Street Centrality and Land Use in Stockholm. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wen, P. The Relationship between Centrality and Land Use Patterns: Empirical Evidence from Five Chinese Metropolises. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 78, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmolejo-Duarte, C. Does Urban Centrality Influence Residential Prices? An Analysis for the Barcelona Metropolitan Area. Rev. De La Construcción. J. Constr. 2017, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bergé, L.R.; Wanzenböck, I.; Scherngell, T. Centrality of Regions in R&D Networks: A New Measurement Approach Using the Concept of Bridging Paths. Reg. Stud. 2017, 51, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodor, K.; Staniewska, A.; Dudzic-Gyurkovich, K. Study of Centrality Measures in the Network of Green Spaces in the City of Krakow. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Seo, Y.; Kim, S. Measurement of Regional Centrality Using Network Analysis: Focused on the Competitive Relationship among Regions. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2018, 53, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. A Study on Commuting Patterns Using Social Network Analysis in the Seoul Metropolitan Area. J. Geogr. Educ. 2008, 52, 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. The Establishment of Spatial Structure and Its Change in the Capital Region by Using Interaction Analysis: 1995–2005. J. Korean Urban Geogr. Soc. 2008, 11, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H. The Transformation of the Spatial Structure by Commuting Flows in the Capital Region Using Network Analysis, 1980–2000. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2006, 41, 133–151. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Ha, C. Analysis on Migration and Regional Structural Change in Jeju Region. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2014, 49, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ahn, K. The Relation of Population, Jobs, Social Capitals and Centrality in Seoul Metropolitan Area, Using Social Network Theory. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2012, 47, 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lee, W.; Joh, C. A Study for Seoul Traffic Network Based on the Metropolitan Household Travel Survey. Geogr. J. Korea 2012, 46, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Zhu, X. Exploring the Relationship between Urban Vitality and Street Centrality Based on Social Network Review Data in Wuhan, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saaidy, H.J.E.; Alobaydi, D. Studying Street Centrality and Human Density in Different Urban Forms in Baghdad, Iraq. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agryzkov, T.; Tortosa, L.; Vicent, J.F.; Wilson, R. A Centrality Measure for Urban Networks Based on the Eigenvector Centrality Concept. Environ. Plan B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2019, 46, 668–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz Amen, M. The Effects of Buildings’ Physical Characteristics on Urban Network Centrality. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Han, Y. Identification of Urban Functional Areas Based on POI Data: A Case Study of the Guangzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Analyzing Urban Spatial Patterns and Functional Zones Using Sina Weibo POI Data: A Case Study of Beijing. Sustainability 2021, 13, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, D.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J. Identification and Analysis of Urban Functional Area in Hangzhou Based on OSM and POI Data. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Korea. Available online: https://kostat.go.kr (accessed on 9 August 2023).
- Kim, S.; Lee, S. Identifying Urban Activity Centers and Their Functions Using POI Big Data: The Case of Seoul Metropolitan Area. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2021, 56, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Transport Database. Available online: https://www.ktdb.go.kr (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Plane, D. The Geography of Urban Commuting Fields: Some Empirical Evidence from New England. Prof. Geogr. 1981, 33, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Yeh, A.; Xie, J.; Ma, C.; Li, Q. Measurements of POI-Based Mixed Use and Their Relationships with Neighbourhood Vibrancy. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 658–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lee, S. Analysis of Urban Vitality and Its Determinant Factors Using POI Bigdata in Seoul, Korea. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2021, 56, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. A Study on the Change of Spatial Structure in the Seoul Metropolitan Area between 1995 and 2010. Geogr. J. Korea 2014, 48, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J. Samsung Starts Operation of Mega Chip Manufacturing Line in S. Korea. Available online: https://en.yna.co.kr/view/AEN20220907009400320 (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Shin, H. Kia Breaks Ground on Hwaseong EV Plant, Plans Huge Investments. Available online: https://koreajoongangdaily.joins.com/2023/04/11/business/industry/Korea-Kia-Hyundai-Motor/20230411174204834.html (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Lee, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, T. Changes in the Population Structure and Policy of Gyeonggi-Do. Gyeonggi Res. Inst. Issue Diagn. 2011, 11, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Korean Statistical Information Service. Available online: https://kosis.kr/index/index.do (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- PYEONGTAEK CITY. Available online: https://www.pyeongtaek.go.kr/en/main.do (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Jiang, B. A Topological Representation for Taking Cities as a Coherent Whole. Geogr. Anal. 2018, 50, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).