De Novo Synthesis of Resveratrol from Sucrose by Metabolically Engineered Yarrowia lipolytica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.3. Genes, Plasmid, and Strain Construction
2.4. Small-Scale Fermentation
2.5. Fed-Batch Fermentation
2.6. Analytical Methods
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
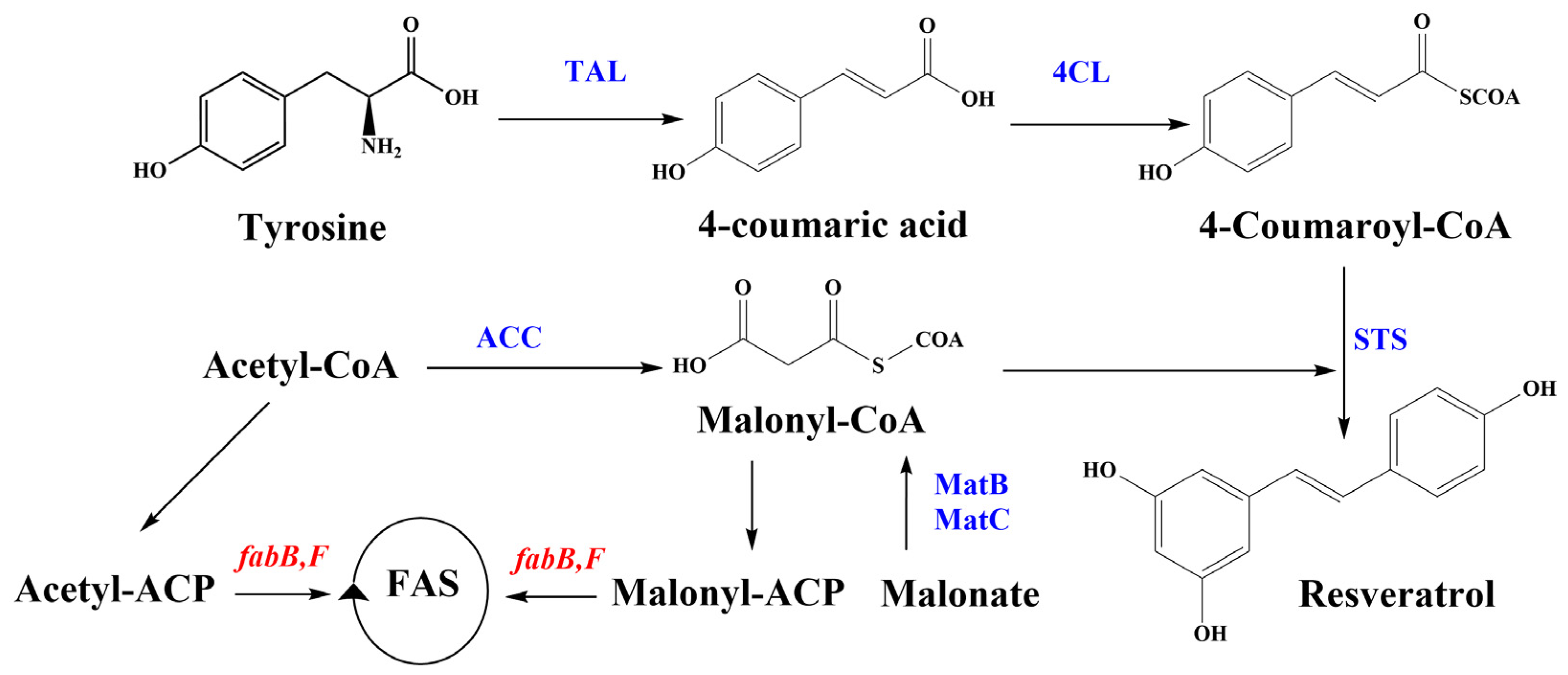
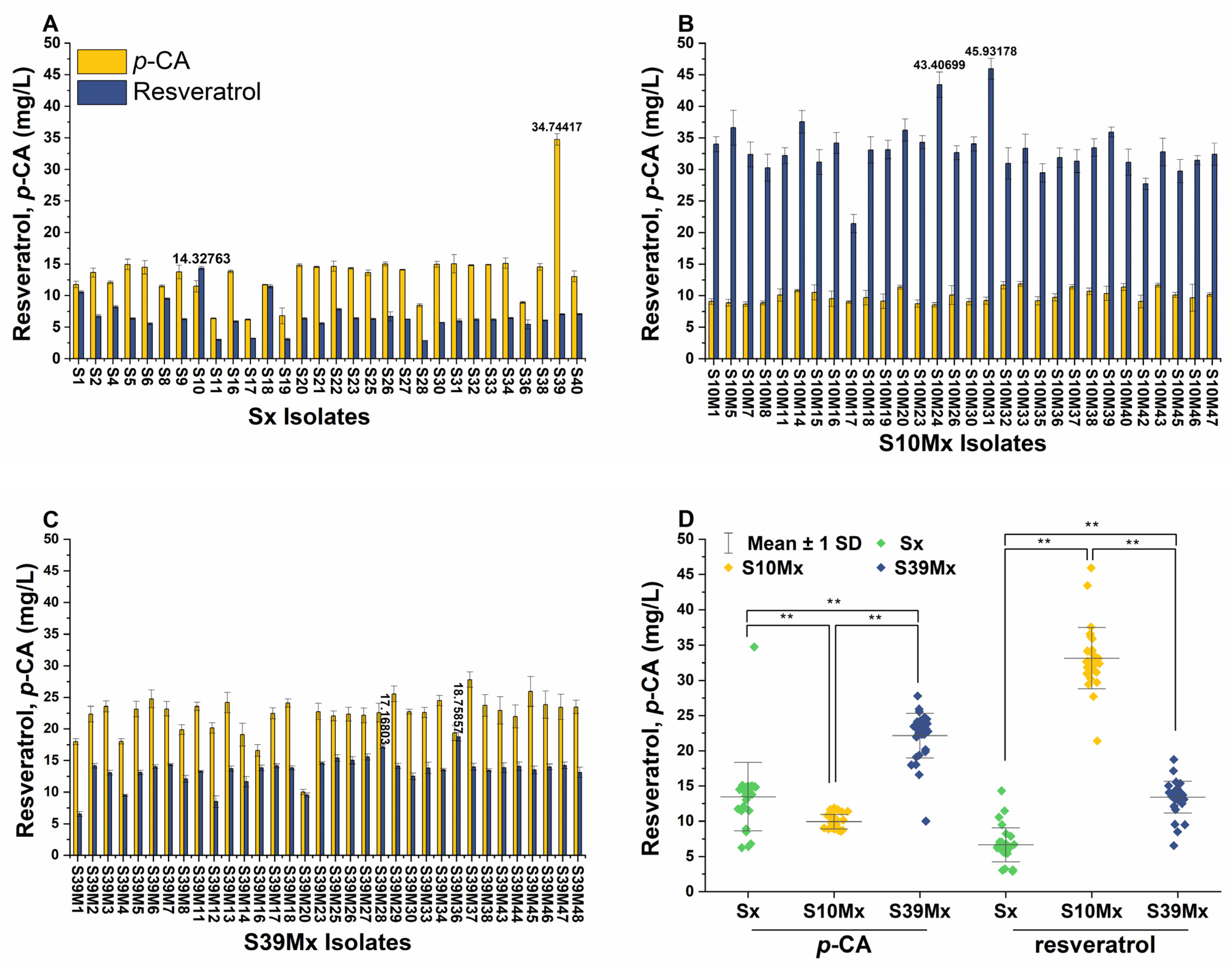
3.1. De Novo Production of Resveratrol
3.2. Enhancing Malonyl-CoA Availability
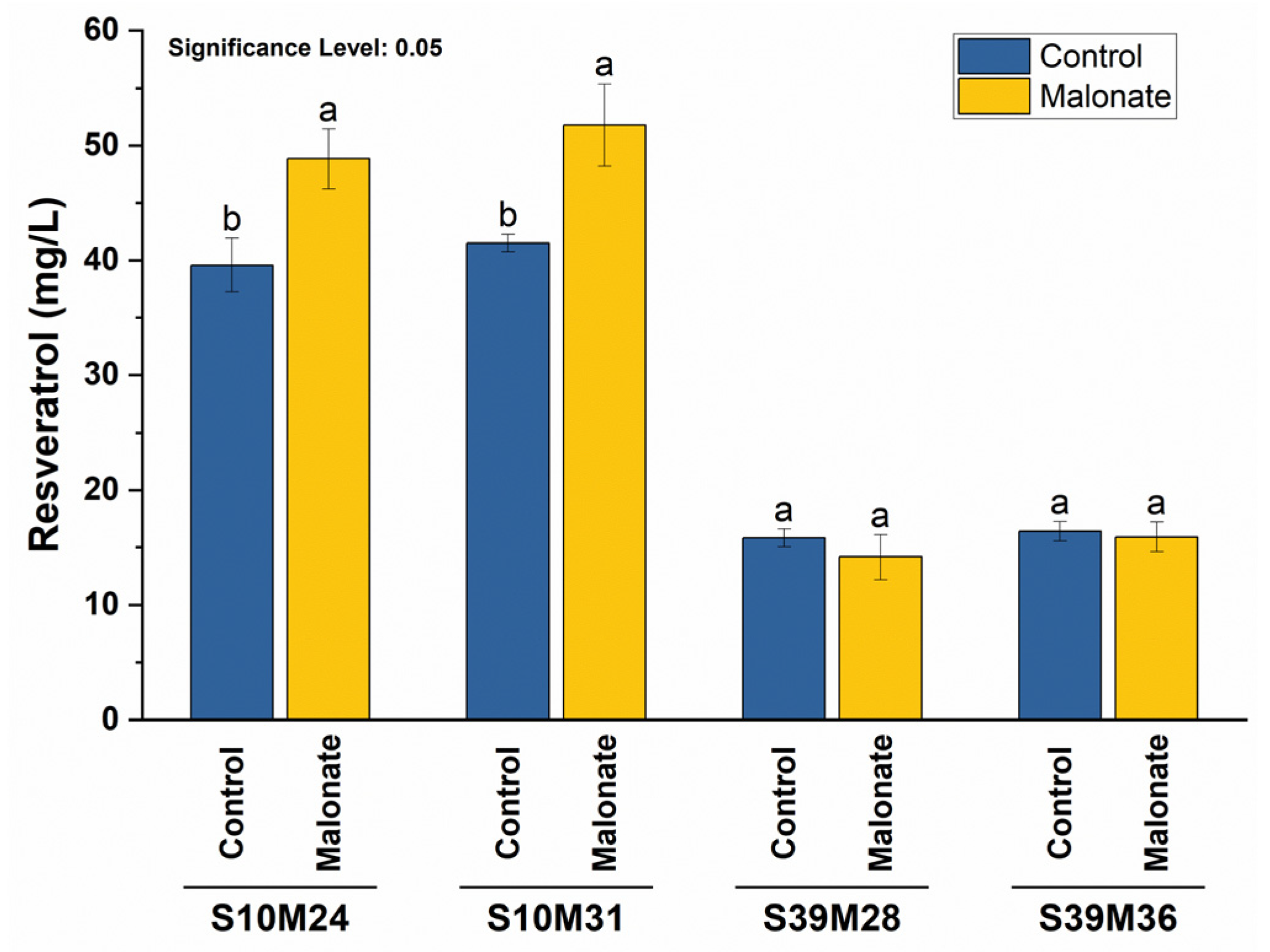
3.3. Expression of matB and matC Genes
3.4. The Effects of Cerulenin on Resveratrol Production
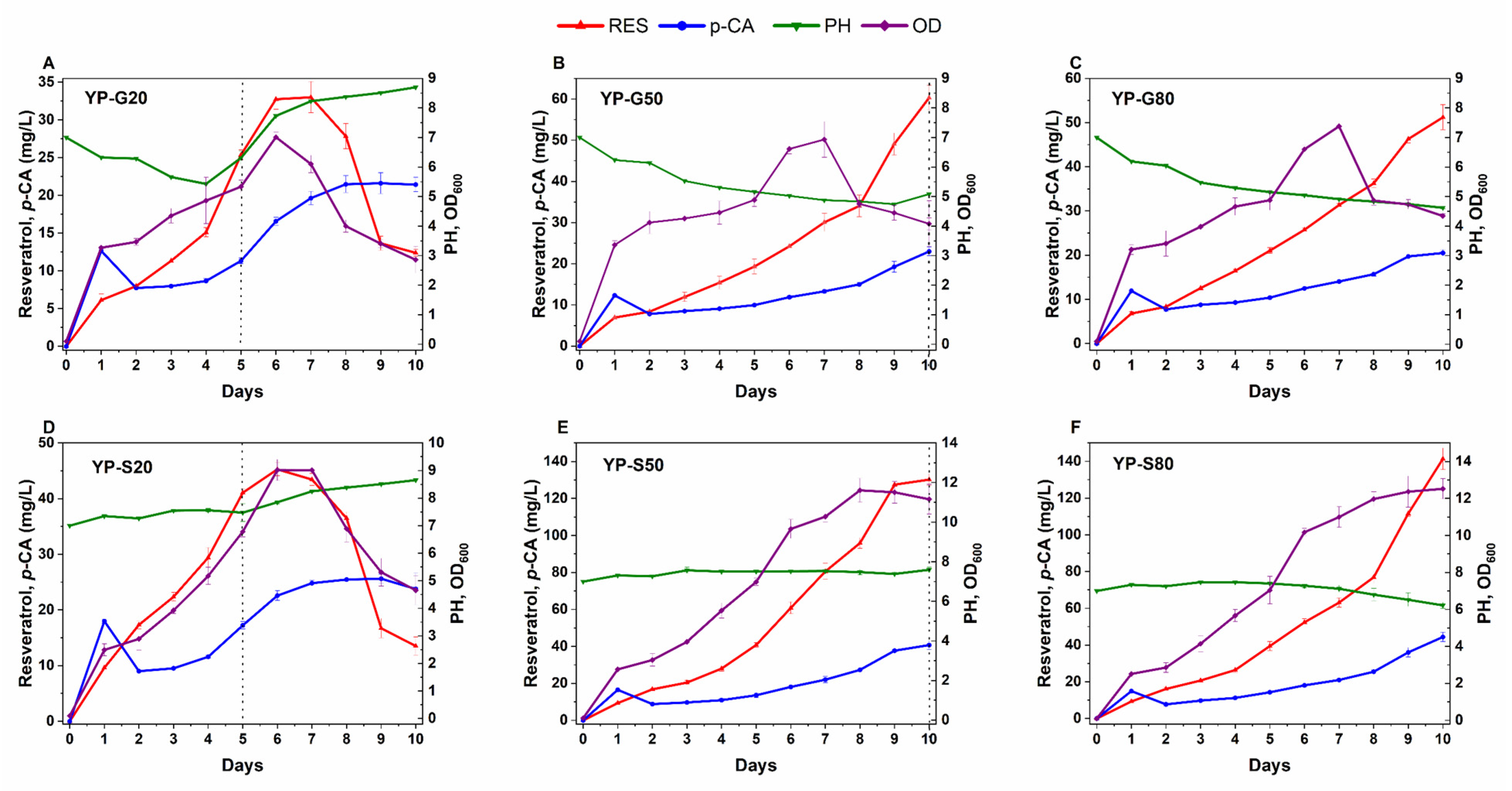
3.5. Media Optimization for Resveratrol Production
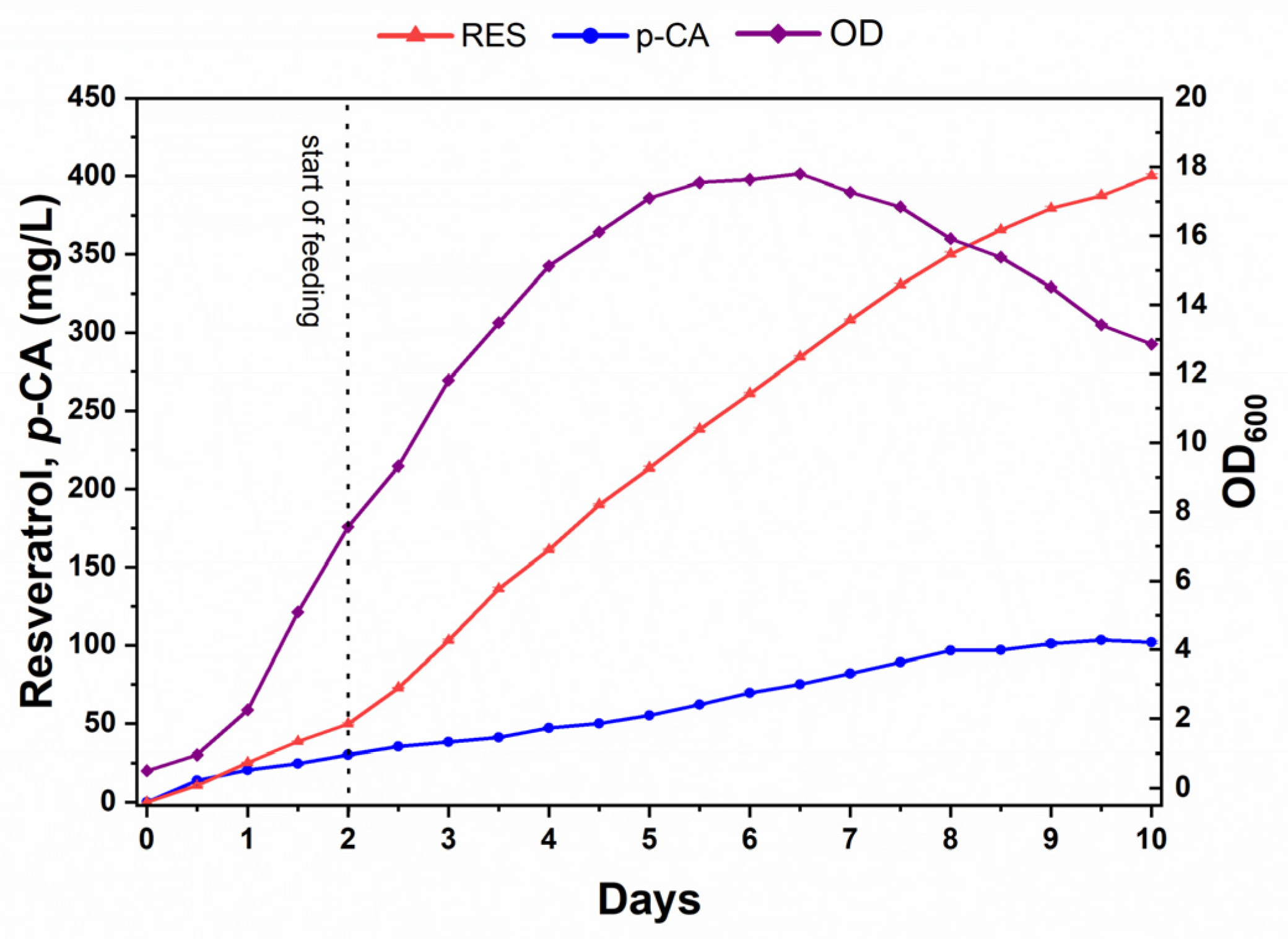
3.6. Fed-Batch Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, B.; Liu, J. Resveratrol: A review of plant sources, synthesis, stability, modification and food application. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2020, 100, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, G.G.; Yan, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, M.; Yan, Y. Resveratrol production in yeast hosts: Current status and perspectives. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, R.G.; Kovoor, C.; Brown, K. Direct molecular targets of resveratrol: Identifying key interactions to unlock complex mechanisms. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1348, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Martínez, B.I.; Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Mendoza-Núñez, V.M. Hypoglycemic effect of resveratrol: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koushki, M.; Amiri-Dashatan, N.; Ahmadi, N.; Abbaszadeh, H.-A.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M. Resveratrol: A miraculous natural compound for diseases treatment. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2473–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richer, S.; Stiles, W.; Ulanski, L.; Carroll, D.; Podella, C. Observation of human retinal remodeling in octogenarians with a resveratrol based nutritional supplement. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1989–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-L.; von Bergen, V.; Chyu, M.-C.; Jenkins, M.R.; Mo, H.; Chen, C.-H.; Kwun, I.-S. Fruits and dietary phytochemicals in bone protection. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zordoky, B.N.M.; Robertson, I.M.; Dyck, J.R.B. Preclinical and clinical evidence for the role of resveratrol in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 1155–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prysyazhna, O.; Wolhuter, K.; Switzer, C.; Santos, C.; Yang, X.; Lynham, S.; Shah, A.M.; Eaton, P.; Burgoyne, J.R. Blood Pressure–Lowering by the antioxidant resveratrol is counterintuitively mediated by oxidation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Circulation 2019, 140, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Clément, C.; Tisserant, L.-P.; Crouzet, J.; Courot, É. Use of grapevine cell cultures for the production of phytostilbenes of cosmetic interest. C. R. Chim. 2016, 19, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Silva, A.S.; Clément, C.; Nabavi, S.F.; Battino, M.; Rasekhian, M.; Belwal, T.; Habtemariam, S.; Koffas, M. Whole-cell biocatalytic, enzymatic and green chemistry methods for the production of resveratrol and its derivatives. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 39, 107461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-J.; Lu, I.J.; Fu, Y.-S.; Fang, Y.-P.; Huang, Y.-B.; Wu, P.-C. Nanocarriers enhance the transdermal bioavailability of resveratrol: In vitro and in vivo study. Colloid Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ruan, Q.; Ye, Z.; Chu, Z.; Xi, M.; Li, M.; Hu, W.; Guo, X.; Yao, P.; Xie, W. Resveratrol accelerates wound healing by attenuating oxidative stress-induced impairment of cell proliferation and migration. Burns 2021, 47, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, M.; Pawliczak, R. Resveratrol and its derivatives in inflammatory skin disorders—Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: A review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreary, M.R.; Schnell, P.M.; Rhoda, D.A. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled proof-of-concept trial of resveratrol for outpatient treatment of mild coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resveratrol Market by Product Type (Natural Resveratrol and Synthetic Resveratrol), Form (Powder and Liquid), Application (Nutraceuticals, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics and Others): Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2021–2030. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/resveratrol-market-A14242 (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Jeandet, P.; Delaunois, B.; Aziz, A.; Donnez, D.; Vasserot, Y.; Cordelier, S.; Courot, E. Metabolic engineering of yeast and plants for the production of the biologically active hydroxystilbene, resveratrol. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 579089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, G.G.; Yan, Y. Microbial production of resveratrol. In Microbial Production of Food Bioactive Compounds; Jafari, S.M., Harzevili, F.D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–34. ISBN 978-3-030-81403-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Shen, X.; Jain, R.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Yuan, Q. Synthesis of chemicals by metabolic engineering of microbes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3760–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madzak, C. Yarrowia lipolytica: Recent achievements in heterologous protein expression and pathway engineering. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4559–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Wei, Y.; Ji, B.; Ji, X.-J. Metabolic engineering for increased lipid accumulation in Yarrowia lipolytica—A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasylenko, T.M.; Ahn, W.S.; Stephanopoulos, G. The oxidative pentose phosphate pathway is the primary source of NADPH for lipid overproduction from glucose in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab. Eng. 2015, 30, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Y. Bioproduction of resveratrol. In Biotechnology of Natural Products; Schwab, W., Lange, B.M., Wüst, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 61–79. ISBN 978-3-319-67903-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, X.; Dong, M. Efficient de novo synthesis of resveratrol by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, P.; Fan, Y.; Bao, H.; Du, G.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Multivariate modular metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to produce resveratrol from L-tyrosine. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madzak, C.; Tréton, B.; Blanchin-Roland, S. Strong hybrid promoters and integrative expression/secretion vectors for quasi-constitutive expression of heterologous proteins in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 2, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicaud, J.-M.; Madzak, C.; van den Broek, P.; Gysler, C.; Duboc, P.; Niederberger, P.; Gaillardin, C. Protein expression and secretion in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. FEMS Yeast Res. 2002, 2, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.C.; Beckerich, J.M.; Gaillardin, C. One-step transformation of the dimorphic yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 48, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak-Workman, A.L.; Vignali, K.M.; Vignali, D.A. Design and construction of 2A peptide-linked multicistronic vectors. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2012, 2012, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourrain, L.; Boissonneault, G. DNA repair in haploid context. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Ren, X.; Gao, S.; Yu, S.; Zhou, J. Remodelling metabolism for high-level resveratrol production in Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 365, 128178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Su, T.; Lu, X.; Hou, J.; Qi, Q. Identification of genome integration sites for developing a CRISPR-based gene expression toolkit in Yarrowia lipolytica. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Sáez, J.; Wang, G.; Marella, E.R.; Sudarsan, S.; Cernuda Pastor, M.; Borodina, I. Engineering the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for high-level resveratrol production. Metab. Eng. 2020, 62, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, X.; Xu, P. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica as a chassis for de novo synthesis of five aromatic-derived natural products and chemicals. ACS Synth. Biol. 2020, 9, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.O.; Gonzalez-Villanueva, M.; Wong, L.; Steinbüchel, A.; Tee, K.L.; Xu, P.; Wong, T.S. Design and application of genetically-encoded malonyl-CoA biosensors for metabolic engineering of microbial cell factories. Metab. Eng. 2017, 44, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decoene, T. Expanding the Portfolio of Synthetic Biology Tools in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae for the Optimization of Heterologous Production Pathways at the Transcriptional and Translational Level. Ph.D Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schuetze, T.; Meyer, V. Polycistronic gene expression in Aspergillus niger. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2017, 16, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.M.; Miller, K.K.; Nguyen, A.; Alper, H.S. Engineering 4-coumaroyl-CoA derived polyketide production in Yarrowia lipolytica through a β-oxidation mediated strategy. Metab. Eng. 2020, 57, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Kildegaard, K.R.; Chen, Y.; Rodriguez, A.; Borodina, I.; Nielsen, J. De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 2015, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.-F.; Yi, X.; Johnston, T.G.; Alper, H.S. De novo resveratrol production through modular engineering of an Escherichia coli–Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-culture. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2020, 19, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moteallehi-Ardakani, M.H.; Asad, S.; Marashi, S.-A.; Moghaddasi, A.; Zarparvar, P. Engineering a novel metabolic pathway for improving cellular malonyl-CoA levels in Escherichia coli. Mol. Biotechnol. 2023, 65, 1508–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Du, G.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for (2S)-pinocembrin production from glucose by a modular metabolic strategy. Metab. Eng. 2013, 16, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, Z.K.; Yang, X. Metabolic engineering of Rhodotorula toruloides for resveratrol production. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2022, 21, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.G.; Fowler, Z.L.; Hueller, T.; Schaffer, S.; Koffas, M.A. High-yield resveratrol production in engineered Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3451–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.; Oliveira, J.; Silva, R.; Ferreira, P.; Rocha, I.; Kallscheuer, N.; Marienhagen, J.; Faria, N. Impact of the cultivation strategy on resveratrol production from glucose in engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 265, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, I.H.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Martinez, J.L. Recombinant β-carotene production by Yarrowia lipolytica—Assessing the potential of micro-scale fermentation analysis in cell factory design and bioreaction optimization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Dulermo, R.; Niehus, X.; Nicaud, J.-M. Combining metabolic engineering and process optimization to improve production and secretion of fatty acids. Metab. Eng. 2016, 38, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madzak, C. Yarrowia lipolytica strains and their biotechnological applications: How natural biodiversity and metabolic engineering could contribute to cell factories improvement. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubiak, M.; Borkowska, M.; Białas, W.; Korpys, P.; Celińska, E. Feeding strategy impacts heterologous protein production in Yarrowia lipolytica fed-batch cultures—Insight into the role of osmolarity. Yeast 2019, 36, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, Š.; Lavrič, Z.; Kristl, J. Stability and solubility of trans-resveratrol are strongly influenced by pH and temperature. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Inokuma, K.; Matsuda, M.; Kondo, A.; Hasunuma, T. Resveratrol production from several types of saccharide sources by a recombinant Scheffersomyces stipitis strain. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2021, 13, e00188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Szczepańska, P.; Yuzbashev, T.; Lazar, Z.; Ledesma-Amaro, R. De novo production of resveratrol from glycerol by engineering different metabolic pathways in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2020, 11, e00146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.L.; Xue, Z.; Zhu, Q.Q. Method for the Production of Resveratrol in a Recombinant Oleaginous Microorganism; United States E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company: Wilmington, DE, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, G.G.; Perera, M.; Abdulmalek, S.A.; Yan, J.; Yan, Y. De Novo Synthesis of Resveratrol from Sucrose by Metabolically Engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060712
Ibrahim GG, Perera M, Abdulmalek SA, Yan J, Yan Y. De Novo Synthesis of Resveratrol from Sucrose by Metabolically Engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(6):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060712
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Gehad G., Madhavi Perera, Saadiah A. Abdulmalek, Jinyong Yan, and Yunjun Yan. 2024. "De Novo Synthesis of Resveratrol from Sucrose by Metabolically Engineered Yarrowia lipolytica" Biomolecules 14, no. 6: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060712
APA StyleIbrahim, G. G., Perera, M., Abdulmalek, S. A., Yan, J., & Yan, Y. (2024). De Novo Synthesis of Resveratrol from Sucrose by Metabolically Engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Biomolecules, 14(6), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060712





