Nethotrons: Exploring the Possibility of Measuring Relativistic Spin Precessions, from Earth’s Satellites to the Galactic Centre
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analytical Expressions of the Newtonian and Post-Newtonian Spin Precessions
2.1. The Gravitoelectric de Sitter Spin Precession
2.2. The Gravitomagnetic Pugh–Schiff Spin Precession
2.3. The Newtonian Spin Precession Due to the Gyroscope’s Own Oblateness
3. The Case of the SLR Satellites
4. The Pulsar–Supermassive Black Hole Scenario
5. The Double Pulsar
6. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Such papers contain expressions which are also valid in the case of a two-body system whose members both have comparable masses, angular momenta, and quadrupole moments; see also [7]. |
| 2 | |
| 3 | It is the intersection of the orbital plane with the fundamental one. |
| 4 | The Schwarzschild radius is defined as . |
| 5 | In fact, it is of the order of , as per Equation (42). |
References
- Barker, B.M.; O’Connell, R.F. Gravitational two–body problem with arbitrary masses, spins, and quadrupole moments. Phys. Rev. D 1975, 12, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.C.M.; Laskar, J.; Farago, F.; Boué, G. Tidal evolution of hierarchical and inclined systems. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 2011, 111, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sitter, W. On Einstein’s theory of gravitation and its astronomical consequences. Second paper. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1916, 77, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokker, A.D. The geodesic precession: A consequence of Einsteins’s theory of graviation. Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. 1921, 23, 729–738. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, G.E. Proposal for a Satellite Test of the Coriolis Prediction of General Relativity; Research memorandum; Weapons Systems Evaluation Group, The Pentagon: Washington, DC, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Schiff, L. Possible new experimental test of general relativity theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1960, 4, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damour, T.; Ruffini, R. Sur certaines vérifications nouvelles de la Relativité générale rendues possibles par la découverte d’un pulsar membre d’un système binaire. C. R. Acad. Sc. Paris Sér. 1974, 279, 971–973. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, B.M.; O’Connell, R.F. The gravitational interaction: Spin, rotation, and quantum effects–a review. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1979, 11, 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, C.W.F.; Muhlfelder, B.; Debra, D.B.; Parkinson, B.W.; Turneaure, J.P.; Silbergleit, A.S.; Acworth, E.B.; Adams, M.; Adler, R.; Bencze, W.J.; et al. The Gravity Probe B test of general relativity. Class. Quantum Gravit. 2015, 32, 224001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, C.W.F.; Debra, D.B.; Parkinson, B.W.; Turneaure, J.P.; Conklin, J.W.; Heifetz, M.I.; Keiser, G.M.; Silbergleit, A.S.; Holmes, T.; Kolodziejczak, J.; et al. Gravity Probe B: Final Results of a Space Experiment to Test General Relativity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 221101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, C.W.F. The Gyroscope experiment-I: General description and analysis of gyroscope performance. In Proceedings of the International School of Physics “Enrico Fermi”. Course LVI. Experimental Gravitation; Bertotti, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974; pp. 331–360. [Google Scholar]
- Everitt, C.W.F.; Buchman, S.; Debra, D.B.; Keiser, G.M.; Lockhart, J.M.; Muhlfelder, B.; Parkinson, B.W.; Turneaure, J.P.; Gravity Probe B Team. Gravity Probe B: Countdown to Launch. In Gyros, Clocks, Interferometers …: Testing Relativistic Gravity in Space; Lämmerzahl, C., Everitt, C.W.F., Hehl, F.W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 52–82, Volume 562 of Lecture Notes in Physics. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, C.M. Finally, results from Gravity Probe B. Phys. Mag. 2011, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskupek, L.; Müller, J.; Torre, J.-M. Benefit of New High-Precision LLR Data for the Determination of Relativistic Parameters. Universe 2021, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.G.; Folkner, W.M. Lunar Laser Ranging: Relativistic Model and Tests of Gravitational Physics. Bullettin Am. Astron. Soc. 2009, 41, 882. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, F.; Müller, J. Relativistic tests with lunar laser ranging. Class. Quantum Gravit. 2018, 35, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, R.P.; Kaspi, V.M.; Kramer, M.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Lyutikov, M.; Ransom, S.M.; Stairs, I.H.; Ferdman, R.D.; Camilo, F.; Possenti, A. Relativistic Spin Precession in the Double Pulsar. Science 2008, 321, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lower, M.E.; Kramer, M.; Shannon, R.M.; Breton, R.P.; Wex, N.; Johnston, S.; Bailes, M.; Buchner, S.; Hu, H.; Venkatraman Krishnan, V.; et al. A MeerKAT view of the double pulsar eclipses. Geodetic precession of pulsar B and system geometry. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 682, A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgay, M.; D’Amico, N.; Possenti, A.; Manchester, R.N.; Lyne, A.G.; Joshi, B.C.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Kramer, M.; Sarkissian, J.M.; Camilo, F.; et al. An increased estimate of the merger rate of double neutron stars from observations of a highly relativistic system. Nature 2003, 426, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyne, A.G.; Burgay, M.; Kramer, M.; Possenti, A.; Manchester, R.N.; Camilo, F.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Lorimer, D.R.; D’Amico, N.; Joshi, B.C.; et al. A Double–Pulsar System: A Rare Laboratory for Relativistic Gravity and Plasma Physics. Science 2004, 303, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, P.C.C.; Wex, N. Gravity experiments with radio pulsars. Living Rev. Relativ. 2024, 27, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, M.; Arnold, D.; Davis, M.; Barlier, F.; Biancale, R.; Vasiliev, V.; Ciufolini, I.; Paolozzi, A.; Pavlis, E.C.; Sośnica, K.; et al. Laser geodetic satellites: A high-accuracy scientific tool. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulot, D.; Deleflie, F.; Bonnefond, P.; Exertier, P.; Laurain, O.; de Saint-Jean, B. Satellite laser ranging. In Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics; Gupta, H.K., Ed.; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, T.; Amagai, J.; Kunimori, H.; Elphick, M. Spin motion of the AJISAI satellite derived from spectral analysis of laser ranging data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovchyk, Y.; Blahodyr, Y.; Lohvynenko, O.; Bilinskyy, A.; Virun, N.; Klym, B.; Pochapskyy, Y. Electrophotometric observations of artificial objects. Adv. Space Res. 2001, 28, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, J.I.; Noomen, R.; Bianco, G.; Currie, D.G.; Otsubo, T. Spin axis behavior of the LAGEOS satellites. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, B06403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, T.; Sherwood, R.A.; Gibbs, P.; Wood, R. Spin Motion and Orientation of LAGEOS-2 From Photometric Observation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, G.; Hausleitner, W.; Cristea, E. Ajisai Spin Parameter Determination Using Graz Kilohertz Satellite Laser Ranging Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Kirchner, G.; Otsubo, T.; Koidl, F. 22 Years of AJISAI spin period determination from standard SLR and kHz SLR data. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 44, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Otsubo, T.; Kirchner, G.; Koidl, F. Spin axis orientation of Ajisai determined from Graz 2 kHz SLR data. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Kirchner, G.; Koidl, F. Spin parameters of nanosatellite BLITS determined from Graz 2 kHz SLR data. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 48, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Otsubo, T.; Kirchner, G.; Bianco, G. Spin rate and spin axis orientation of LARES spectrally determined from Satellite Laser Ranging data. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Lim, H.-C.; Kirchner, G.; Hwang, J.Y. Spin parameters of LAGEOS-1 and LAGEOS-2 spectrally determined from Satellite Laser Ranging data. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 52, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Otsubo, T.; Kirchner, G.; Lim, H.-C. Spectral response of Experimental Geodetic Satellite determined from high repetition rate SLR data. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Kirchner, G.; Lim, H.-C.; Koidl, F. Spin parameters of High Earth Orbiting satellites Etalon-1 and Etalon-2 determined from kHz Satellite Laser Ranging data. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Kirchner, G.; Otsubo, T.; Lim, H.-C.; Bennett, J.; Koidl, F.; Kim, Y.-R.; Hwang, J.-Y. Confirmation of gravitationally induced attitude drift of spinning satellite Ajisai with Graz high repetition rate SLR data. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 57, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshkin, N.; Shakun, L.; Burlak, N.; Korobeynikova, E.; Strakhova, S.; Melikyants, S.; Terpan, S.; Ryabov, A. Ajisai spin-axis precession and rotation-period variations from photometric observations. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshkin, N.; Shakun, L.; Korobeynikova, E.; Melikyants, S.; Strakhova, S.; Dragomiretsky, V.; Ryabov, A.; Terpan, S.; Golubovskaya, T. Determination of the spacecraft’s spin axis orientation. Photometric patterns method. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 5725–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q. On the Existence of Pulsars in the Vicinity of the Massive Black Hole in the Galactic Center. Astrophys. J. 2014, 784, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Desvignes, G.; Eatough, R.P.; Karuppusamy, R.; Kramer, M.; Torne, P.; Wharton, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Cordes, J.M.; Crew, G.B.; et al. An 86 GHz Search for Pulsars in the Galactic Center with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array. Astrophys. J. 2021, 914, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleo, A.; Ben-Salem, B. Effect of environment in the timing of a pulsar orbiting SgrA*. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 124027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torne, P.; Liu, K.; Eatough, R.P.; Wongphechauxsorn, J.; Cordes, J.M.; Desvignes, G.; De Laurentis, M.; Kramer, M.; Ransom, S.M.; Chatterjee, S.; et al. A Search for Pulsars around Sgr A* in the First Event Horizon Telescope Data Set. Astrophys. J. 2023, 959, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Shao, L.; Hu, Z.; Miao, X.; Wang, Z. Prospects for constraining the Yukawa gravity with pulsars around Sagittarius A*. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 2022, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Shao, L.; Xu, R.; Liang, D.; Mai, Z.-F. Probing the vector charge of Sagittarius A* with pulsar timing. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 2024, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Shao, L.; Zhang, F. Prospects for probing small-scale dark matter models with pulsars around Sagittarius A*. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 123034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wex, N.; Kopeikin, S.M. Frame Dragging and Other Precessional Effects in Black Hole Pulsar Binaries. Astrophys. J. 1999, 514, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfahl, E.; Loeb, A. Probing the Spacetime around Sagittarius A* with Radio Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2004, 615, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wex, N.; Kramer, M.; Cordes, J.M.; Lazio, T.J.W. Prospects for Probing the Spacetime of Sgr A* with Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2012, 747, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltis, D.; Wex, N.; Kramer, M. A Quantitative Test of the No-hair Theorem with Sgr A* Using Stars, Pulsars, and the Event Horizon Telescope. Astrophys. J. 2016, 818, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Saha, P. Probing the Spinning of the Massive Black Hole in the Galactic Center via Pulsar Timing: A Full Relativistic Treatment. Astrophys. J. 2017, 849, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Shao, L. Measuring the Spin of the Galactic Center Supermassive Black Hole with Two Pulsars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 231402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M. Kerr Metric Black Holes. Nature 1970, 226, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, R.P. Gravitational Field of a Spinning Mass as an Example of Algebraically Special Metrics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1963, 11, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teukolsky, S.A. The Kerr metric. Class. Quantum Gravit. 2015, 32, 124006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhoon, B.; Singh, D. Dynamics of extended spinning masses in a gravitational field. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 124006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackmann, E.; Lämmerzahl, C.; Obukhov, Y.N.; Puetzfeld, D.; Schaffer, I. Motion of spinning test bodies in Kerr spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 064035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangsri, U.; Vigeland, S.J.; Hughes, S.A. Gyroscopes orbiting black holes: A frequency-domain approach to precession and spin-curvature coupling for spinning bodies on generic Kerr orbits. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 044008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, L. General Post-Newtonian Orbital Effects from Earth’s Satellites to the Galactic Center; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, M.; Lucchesi, D.M. Comprehensive model for the spin evolution of the LAGEOS and LARES satellites. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 044034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capderou, M. Satellites: Orbits and Missions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, R. Gravity Probe B-Post Flight Analysis·Final Report; Technical Report; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bertotti, B.; Iess, L. The rotation of LAGEOS. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinella, P.; Vokrouhlicky, D.; Barlier, F. The rotation of LAGEOS and its long-term semimajor axis decay: A self-consistent solution. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 17861–17872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokrouhlický, D. Non-gravitational effects and LAGEOS’ rotation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 3079–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, D.; Kissell, K.; Avizonis, P.; Wellnitz, D. On the Dynamics of the LAGEOS Spin Vector High-Precision and Comparisons to Theoretical Modeling. In IAU Colloq. 165: Dynamics and Astrometry of Natural and Artificial Celestial Bodies; Wytrzyszczak, I.M., Lieske, J.H., Feldman, R.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, G.; Chersich, M.; Devoti, R.; Luceri, V.; Selden, M. Measurement of LAGEOS-2 rotation by satellite laser ranging observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2113–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Hashimoto, H. Launch and Observation Program of the Experimental Geodetic Satellite of Japan. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1987, 25, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, W. Event Horizons in Static Vacuum Space–Times. Phys. Rev. 1967, 164, 1776–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B. Axisymmetric Black Hole Has Only Two Degrees of Freedom. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1971, 26, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.C. Uniqueness of the Kerr Black Hole. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1975, 34, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geroch, R. Multipole Moments. II. Curved Space. J. Math. Phys. 1970, 11, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.O. Multipole moments of stationary space–times. J. Math. Phys. 1974, 15, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.L.; Teukolsky, S.A. Black Holes, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars: The Physics of Compact Objects; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Yodzis, P.; Seifert, H.-J.; Müller Zum Hagen, H. On the occurrence of naked singularities in general relativity. Commun. Math. Phys. 1973, 34, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.L.; Teukolsky, S.A. Formation of naked singularities: The violation of cosmic censorship. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. The Question of Cosmic Censorship. J. Astrophys. Astron. 1999, 20, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. “Golden Oldie”: Gravitational Collapse: The Role of General Relativity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2002, 7, 1141–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peißker, F.; Eckart, A.; Zajaček, M.; Britzen, S. Observation of S4716-a Star with a 4 yr Orbit around Sgr A*. Astrophys. J. 2022, 933, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuchaev, V.I. Spins of Supermassive Black Holes M87* and SgrA* Revealed from the Size of Dark Spots in Event Horizon Telescope Images. Astronomy 2023, 2, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianov, A.S.; Chernov, S.V. Estimation of the Spin of a Supermassive Black Hole in Sagittarius A*. Astron. Rep. 2024, 68, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, R.A.; Donahue, M.; O’Dea, C.P.; Sebastian, B.; Haggard, D.; Lu, A. New black hole spin values for Sagittarius A* obtained with the outflow method. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laarakkers, W.G.; Poisson, E. Quadrupole Moments of Rotating Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 1999, 512, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, M.; Melia, F.; Tagger, M.; Goldwurm, A.; Bélanger, G. General Relativistic Flux Modulations from Disk Instabilities in Sagittarius A*. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2007, 662, L15–L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meyer, L.; Schödel, R.; Eckart, A.; Duschl, W.J.; Karas, V.; Dovčiak, M. On the orientation of the Sagittarius A* system. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 473, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Broderick, A.E.; Fish, V.L.; Doeleman, S.S.; Loeb, A. Estimating the Parameters of Sagittarius A*’s Accretion Flow Via Millimeter VLBI. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, A.E.; Fish, V.L.; Doeleman, S.S.; Loeb, A. Evidence for Low Black Hole Spin and Physically Motivated Accretion Models from Millimeter-VLBI Observations of Sagittarius A*. Astrophys. J. 2011, 735, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbakov, R.V.; Penna, R.F.; McKinney, J.C. Sagittarius A* Accretion Flow and Black Hole Parameters from General Relativistic Dynamical and Polarized Radiative Modeling. Astrophys. J. 2012, 755, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.H.; Bjælde, O.E.; Hannestad, S. Probing the spin of the central black hole in the Galactic Centre with secondary images. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 3614–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Lu, Y. Prospects for Constraining the Spin of the Massive Black Hole at the Galactic Center via the Relativistic Motion of a Surrounding Star. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saida, H. How to measure a black hole’s mass, spin, and direction of spin axis in the Kerr lens effect 1: Test case with simple source emission near a black hole. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2017, 2017, 053E02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R. Shapes and Positions of Black Hole Shadows in Accretion Disks and Spin Parameters of Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration. First Sagittarius A* Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole in the Center of the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 930, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, V.; Umirbayeva, A.; Aimuratov, Y. Estimates of the Surface Magnetic Field Strength of Radio Pulsars. Universe 2023, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatough, R.P.; Falcke, H.; Karuppusamy, R.; Lee, K.J.; Champion, D.J.; Keane, E.F.; Desvignes, G.; Schnitzeler, D.H.F.M.; Spitler, L.G.; Kramer, M.; et al. A strong magnetic field around the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Galaxy. Nature 2013, 501, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, K. et al. [Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration] First Sagittarius A* Event Horizon Telescope Results. VII. Polarization of the Ring. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 964, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanazzi, J.J.; Lai, D. Electromagnetic torques, precession and evolution of magnetic inclination of pulsars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 451, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.; Goldstein, M. Magnetic-Dipole Alignment in Pulsars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1970, 159, L81–L86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.; Stairs, I.H. The double pulsar. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astr. 2008, 46, 541–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.; Stairs, I.H.; Manchester, R.N.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Lyne, A.G.; Ferdman, R.D.; Burgay, M.; Lorimer, D.R.; Possenti, A.; D’Amico, N.; et al. Tests of General Relativity from Timing the Double Pulsar. Science 2006, 314, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.; Wex, N. TOPICAL REVIEW: The double pulsar system: A unique laboratory for gravity. Class. Quantum Gravit. 2009, 26, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.O.; Holgado, A.M.; Cárdenas-Avendaño, A.; Yunes, N. Astrophysical and Theoretical Physics Implications from Multimessenger Neutron Star Observations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 181101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, L. The impact of the spin–orbit misalignment and of the spin of B on the Lense–Thirring orbital precessions of the double pulsar PSR J0737-3039A/B. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 507, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
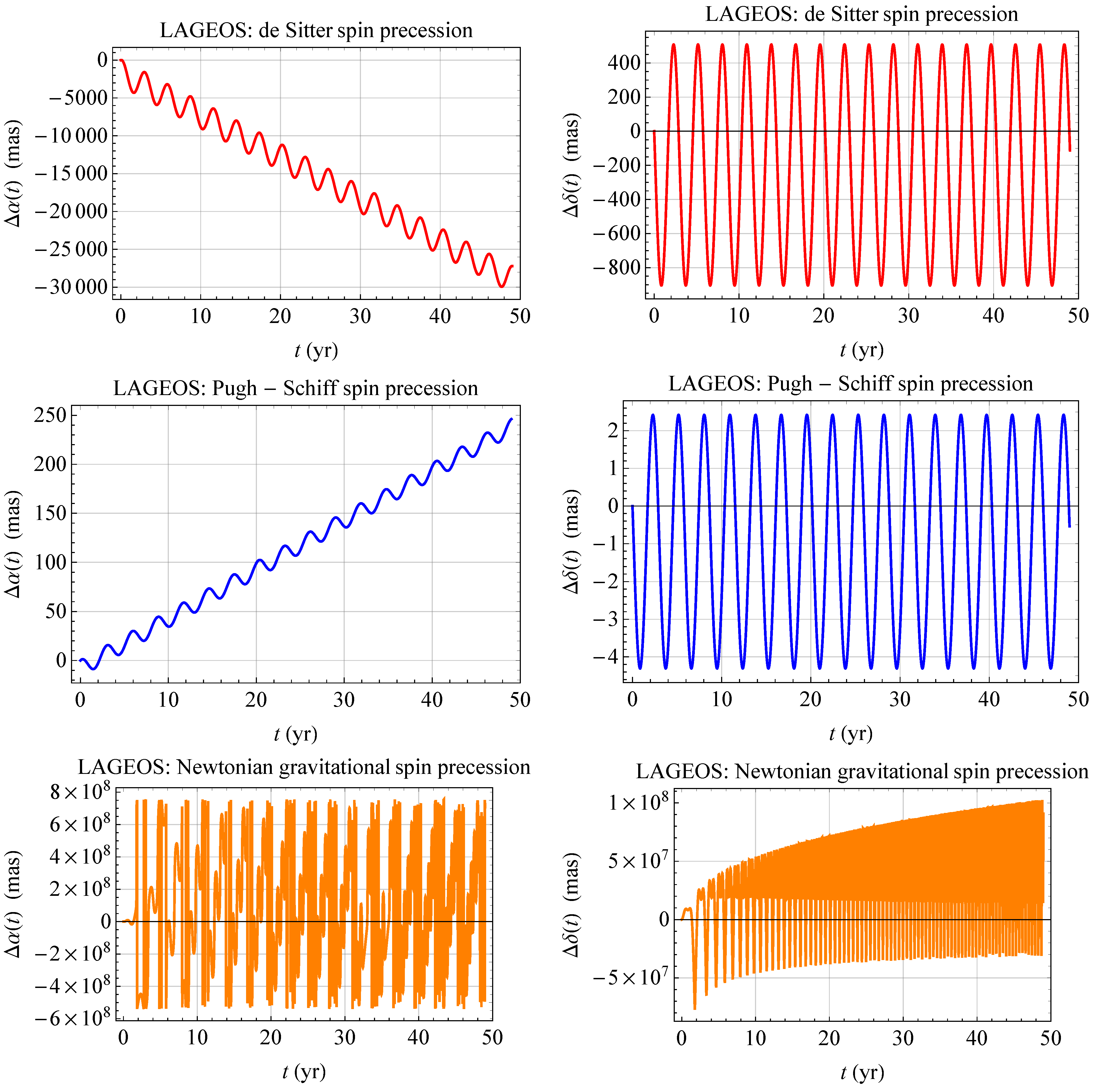
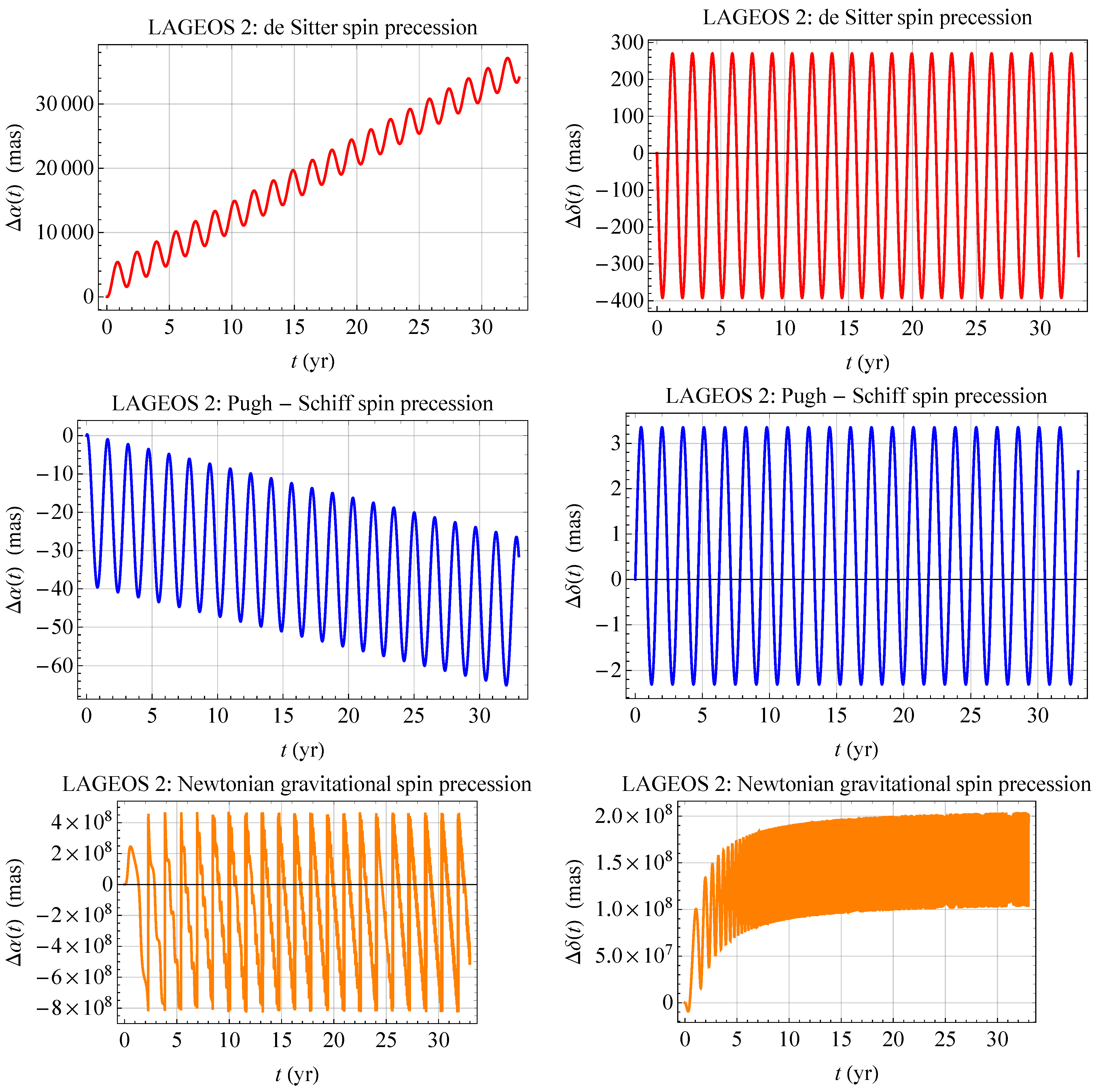
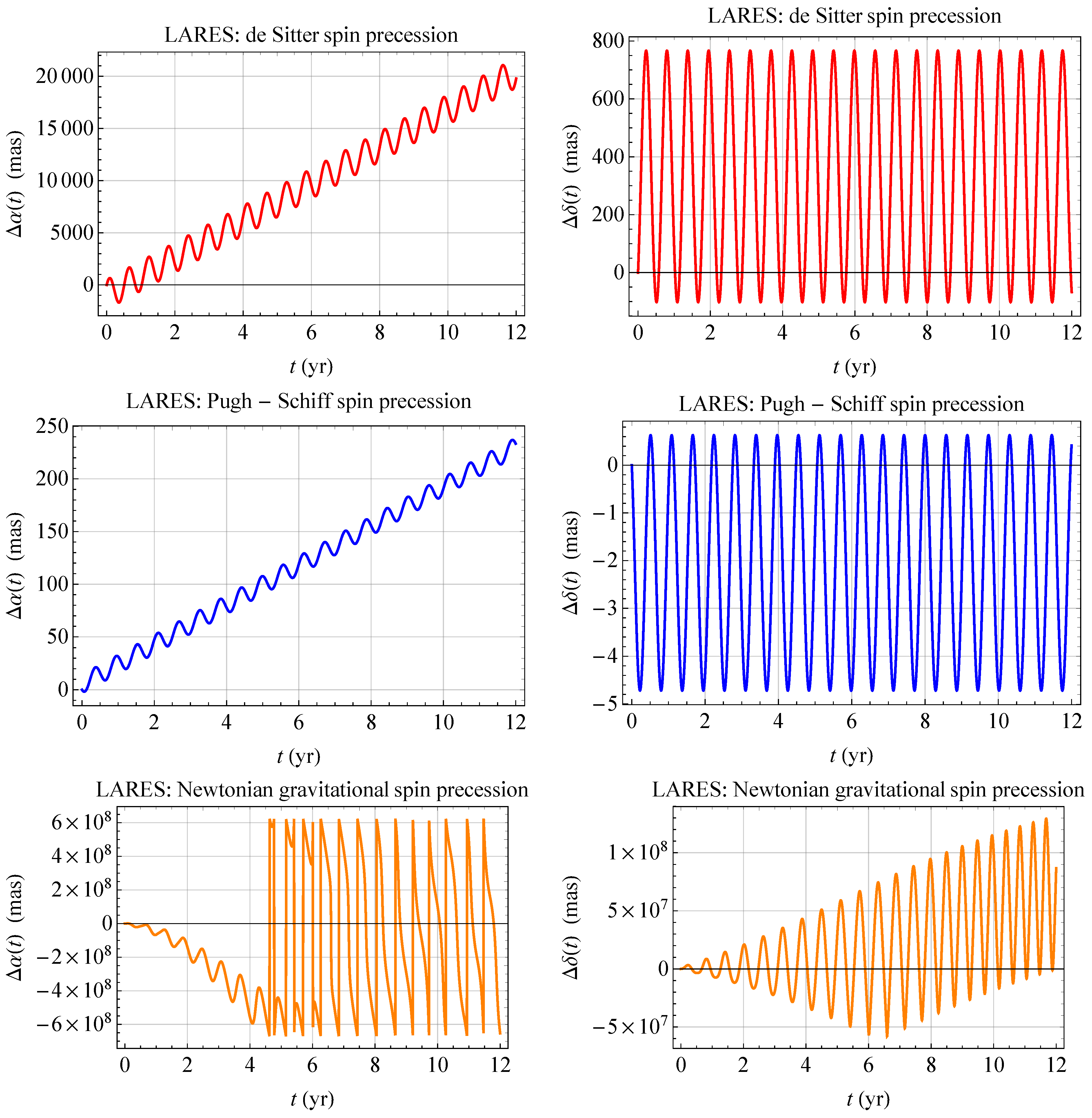
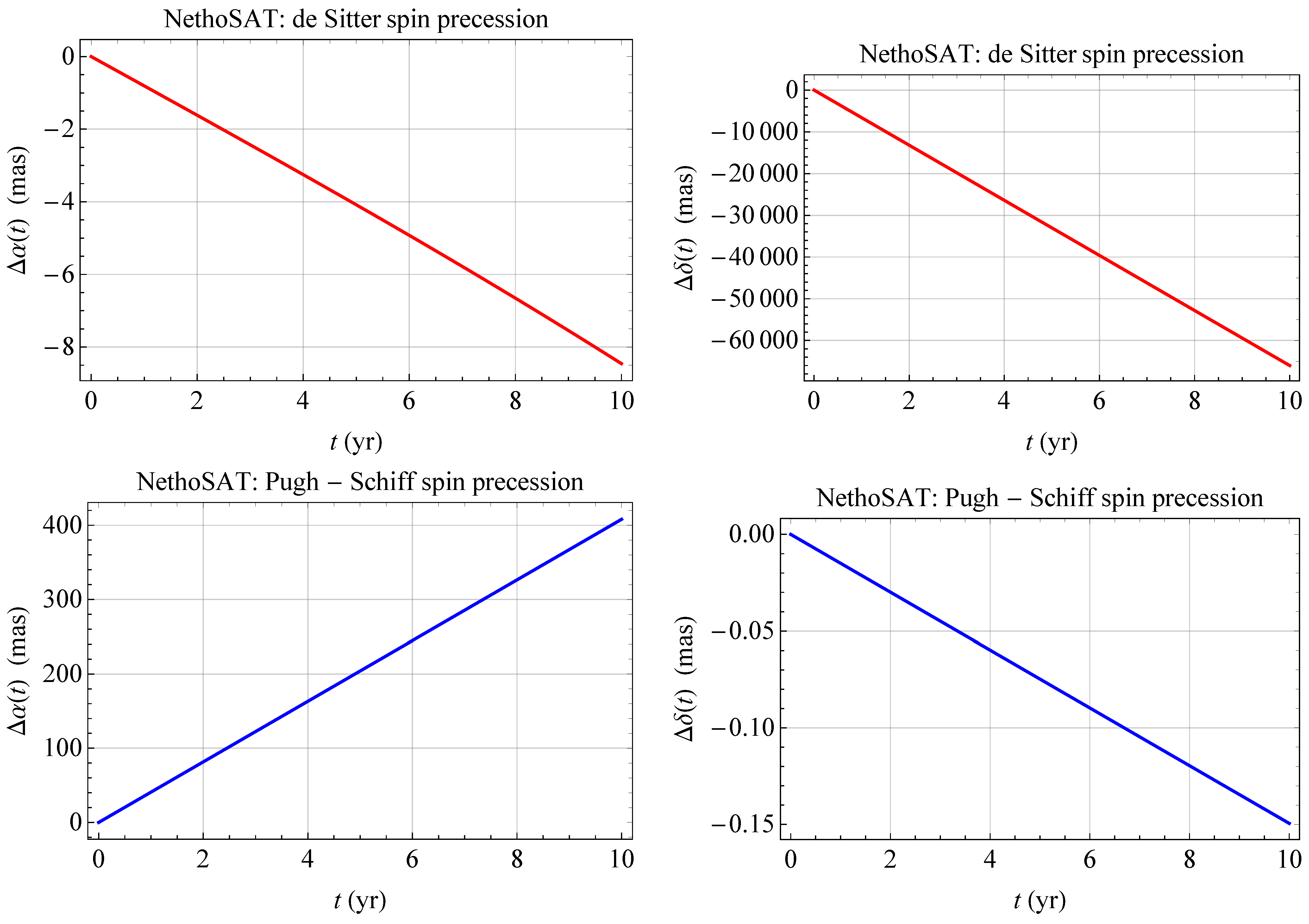

| Satellite | Semimajor Axis a | Eccentricity e | Inclination I | Node | RA | decl. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAGEOS | 12,270 km | s | m | |||||||
| LAGEOS 2 | 12,162 km | s | m | |||||||
| LARES | km | s | m | |||||||
| GP-B | km | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iorio, L. Nethotrons: Exploring the Possibility of Measuring Relativistic Spin Precessions, from Earth’s Satellites to the Galactic Centre. Universe 2025, 11, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11060189
Iorio L. Nethotrons: Exploring the Possibility of Measuring Relativistic Spin Precessions, from Earth’s Satellites to the Galactic Centre. Universe. 2025; 11(6):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11060189
Chicago/Turabian StyleIorio, Lorenzo. 2025. "Nethotrons: Exploring the Possibility of Measuring Relativistic Spin Precessions, from Earth’s Satellites to the Galactic Centre" Universe 11, no. 6: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11060189
APA StyleIorio, L. (2025). Nethotrons: Exploring the Possibility of Measuring Relativistic Spin Precessions, from Earth’s Satellites to the Galactic Centre. Universe, 11(6), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11060189






