Circulating MicroRNAs Associated with Changes in the Placenta and Their Possible Role in the Fetus During Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
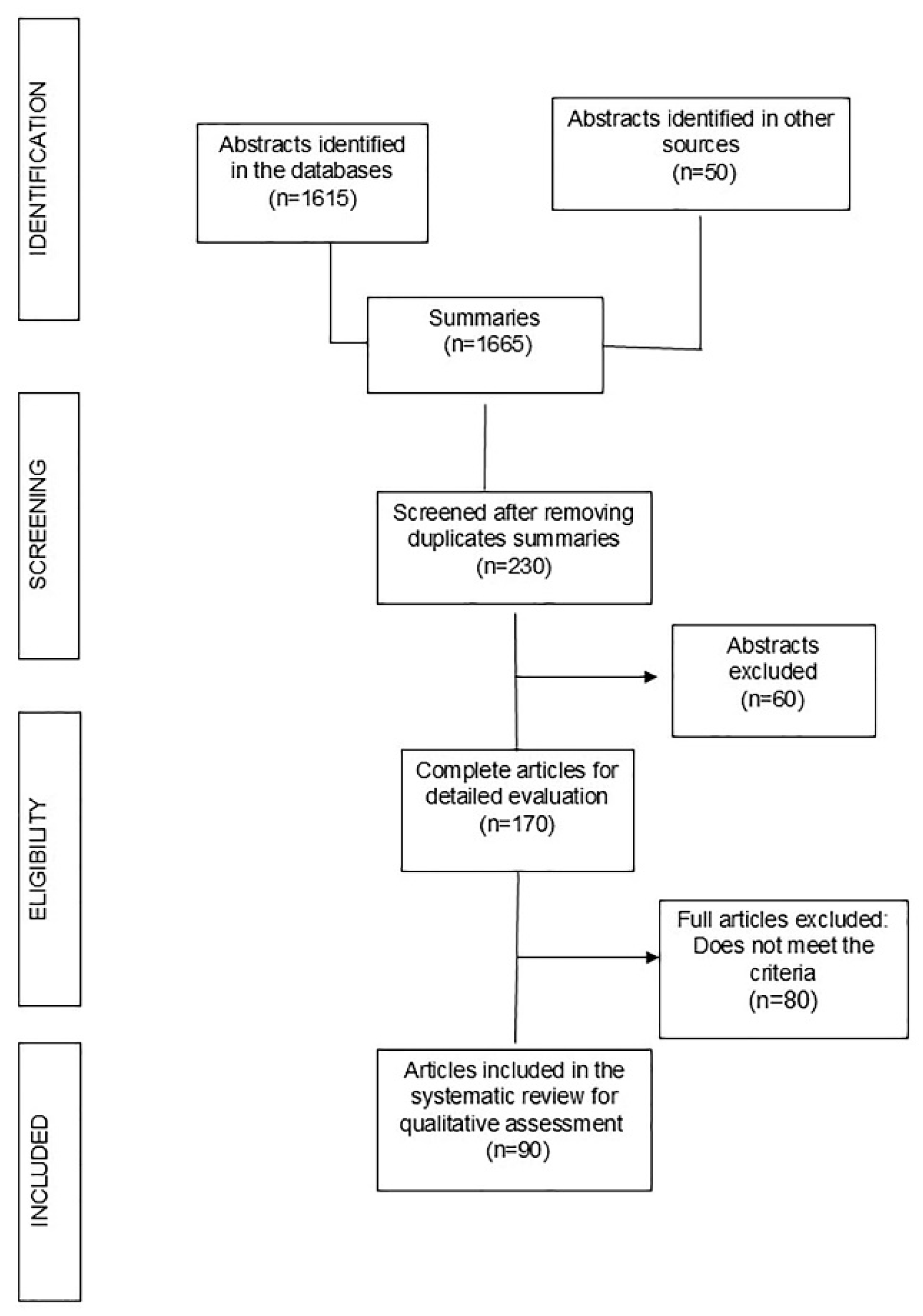
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Literature
3.2. Characteristics of the Studies
- A total of 70% of the studies examined blood, serum, or plasma.
- A total of 94.59% reported the number of patients included. Among these, a total of 3782 women were diagnosed with GDM, and 3817 served as controls (CTR).
- The minimum number of women with GDM or controls included in the studies was 5, while the maximum was 236 women with GDM and 204 controls.
- A total of 30% of the articles reported participant age, with a minimum range of 21–27 years and a maximum of 35 years.
- A total of 41% of the articles referenced the body mass index (BMI), with values ranging from 21 to 34.
- Data on glucose tolerance tests were included in 40% of the reports. Additionally, some articles described neonatal weight.
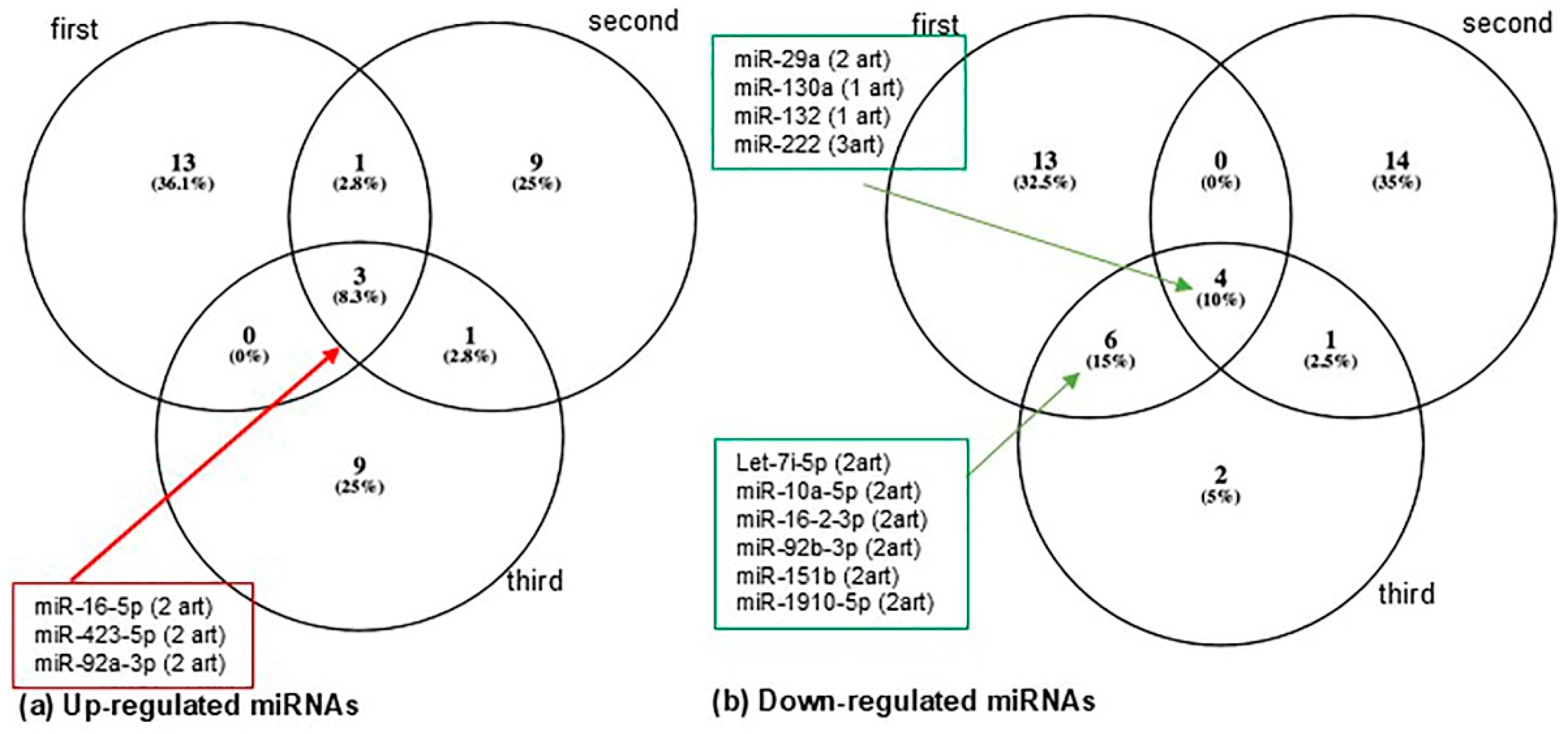
3.3. Circulating MiRNA Profiles in Women with Gestational Diabetes
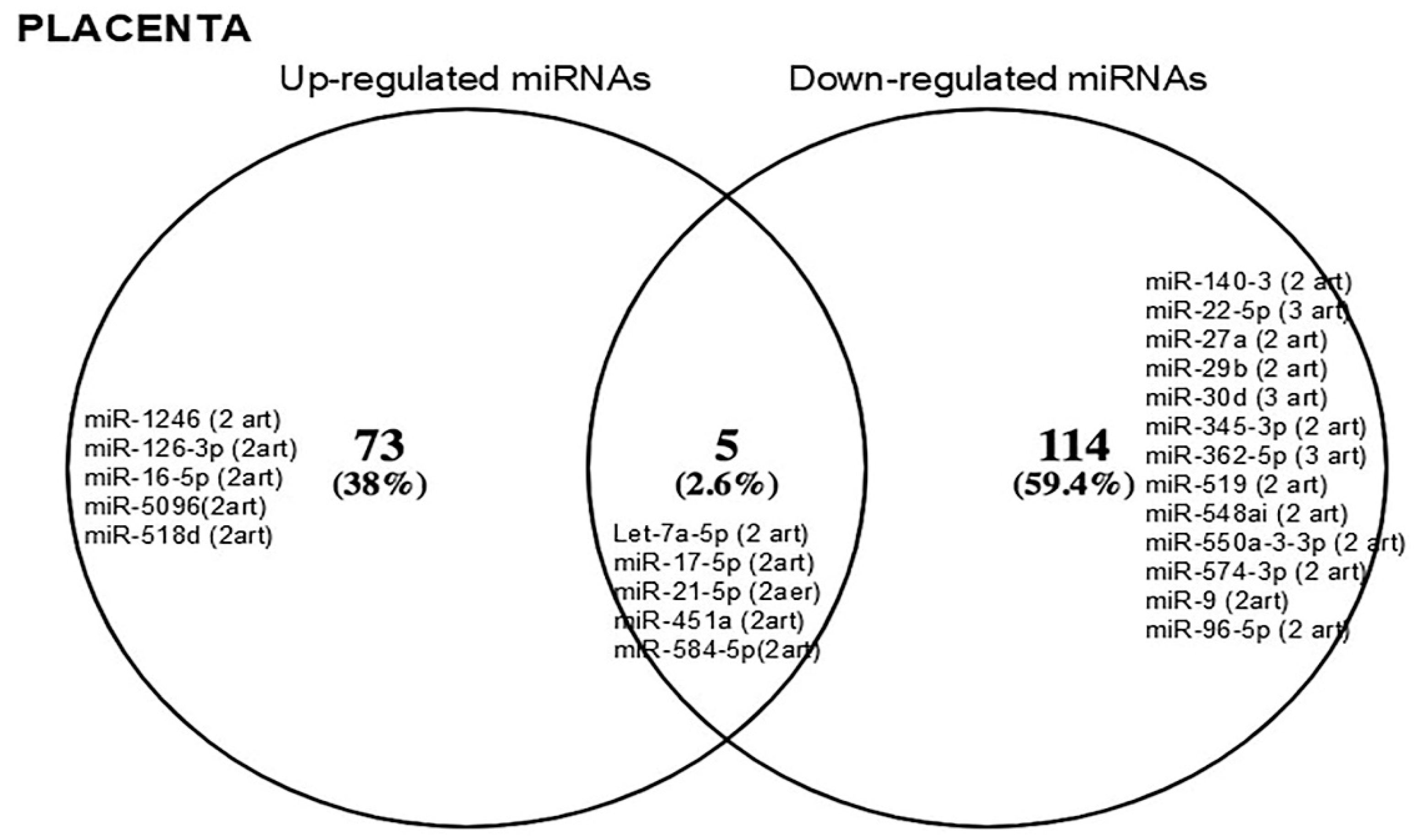
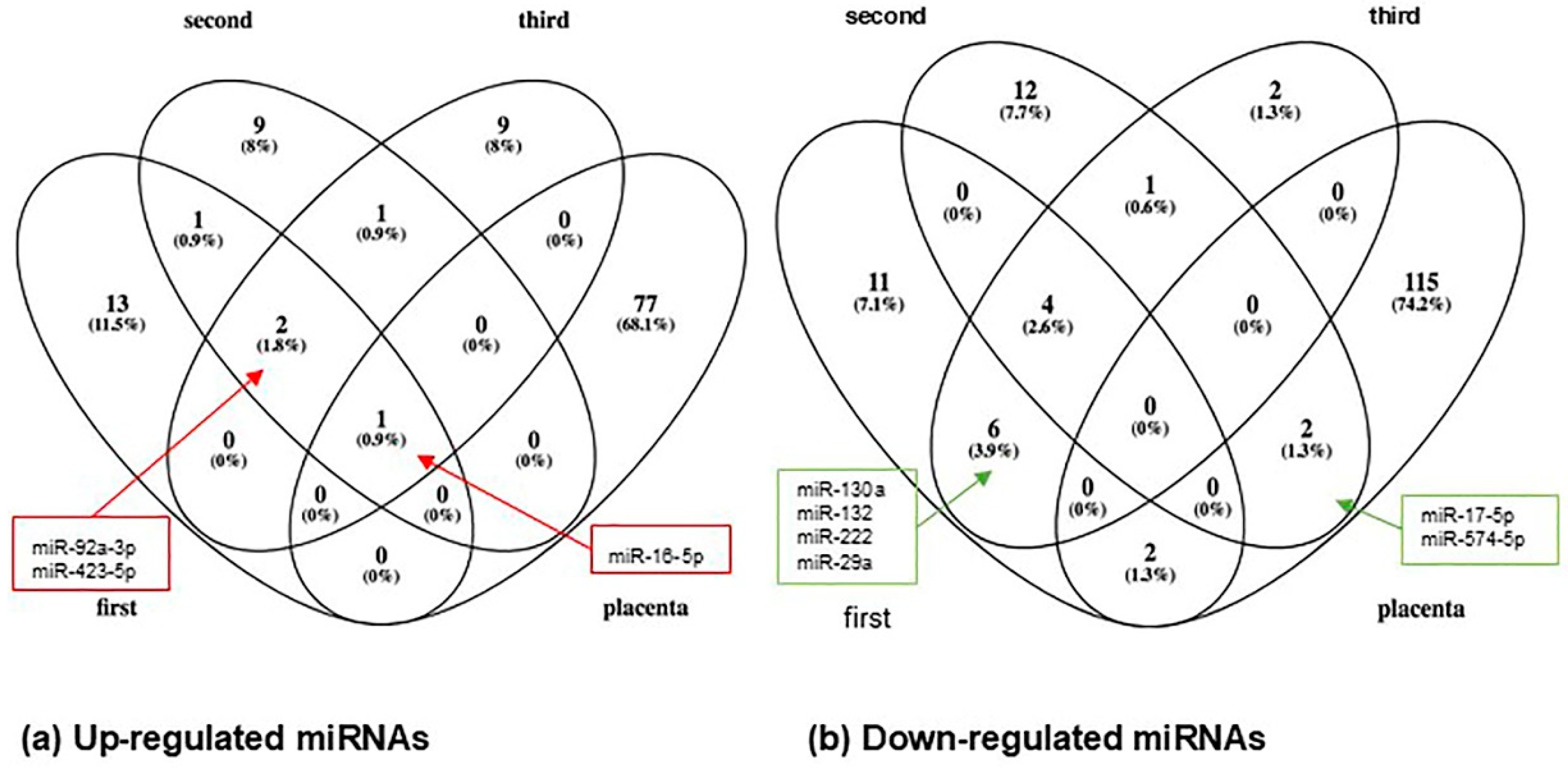
3.4. MiRNAs Identified in Maternal Circulation vs. Placenta
3.5. Functional Studies
3.6. MiRNAs in Umbilical Cord Blood and Amniotic Fluid vs. Placenta and Circulation in Gestational Diabetes
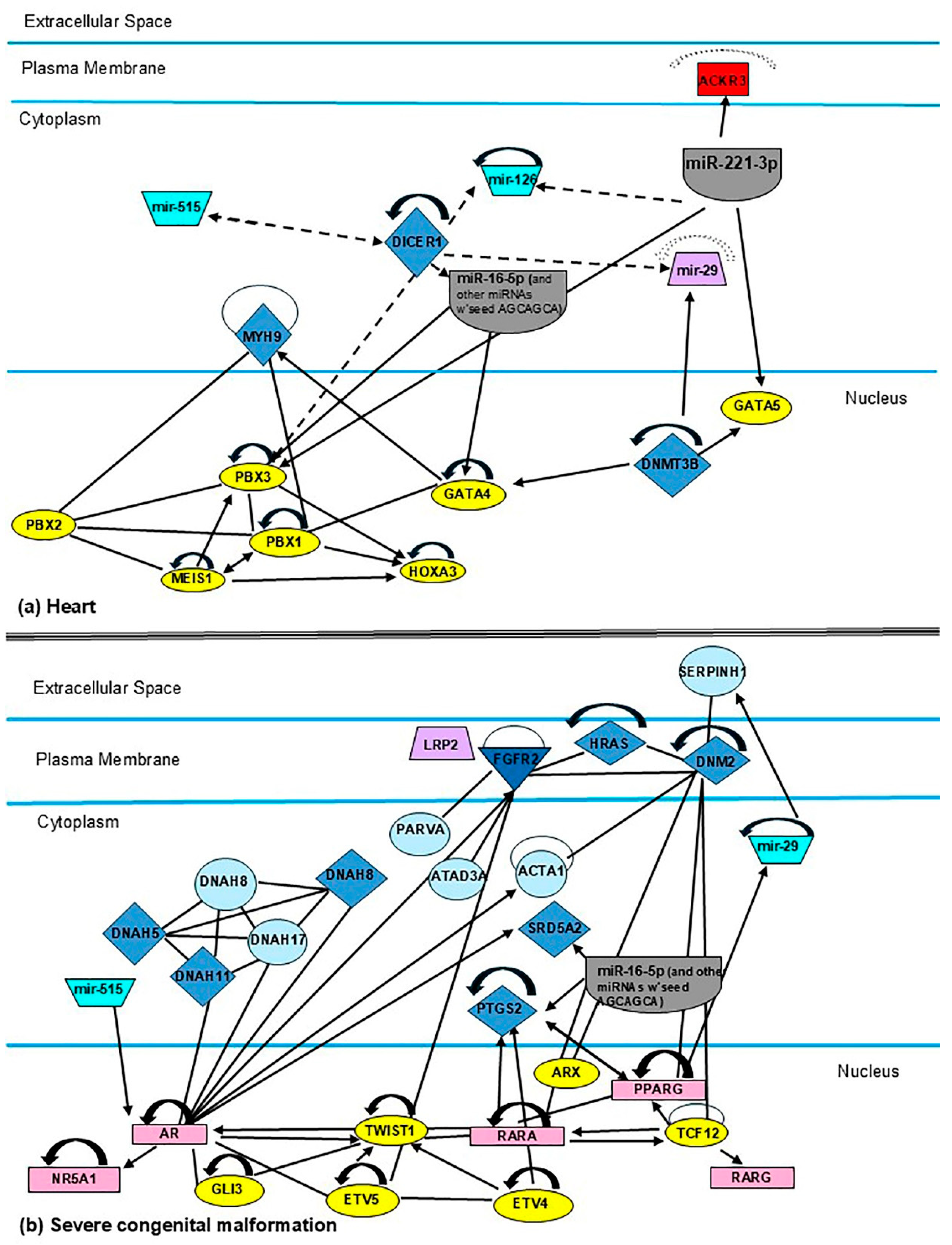
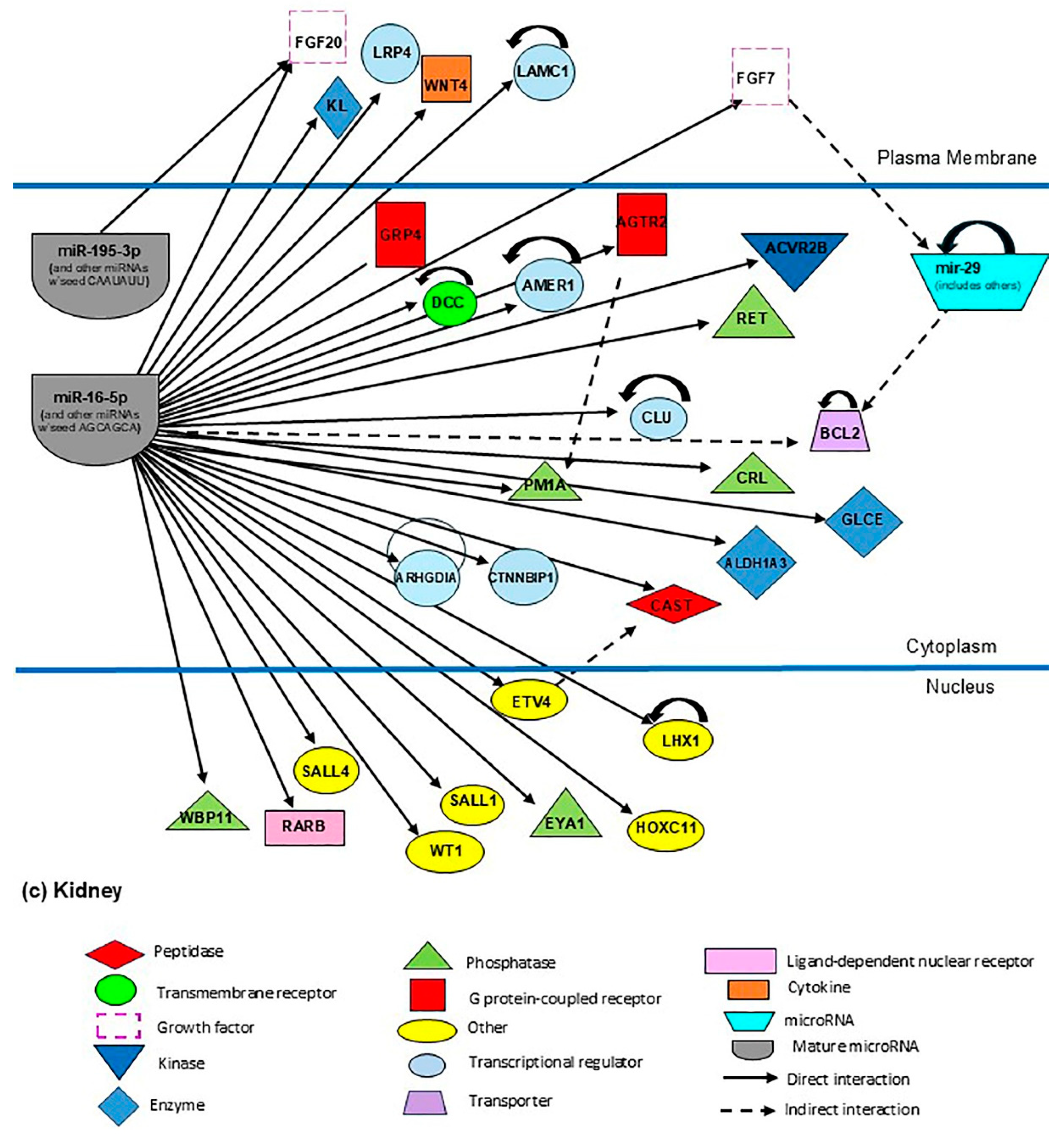
3.7. Identification of Candidate MiRNAs and Their Target Genes (miR-16-5p, -126-3p, -185-5p, -195-5p, -222-3p, -518b, and the miR-29 Family) Related to Neonatal Development
4. Discussion
4.1. Scope of Case Records
4.2. Biological Implications of the MiR-29 Family, MiR-16-5p, -126-3p, -195-5p, and -518b in the Mother–Child Binomial Affected by Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
4.2.1. MiR-16-5p
4.2.2. MiR-126-3p
4.2.3. MiR-195
4.2.4. MiR-518d
4.2.5. MiR-29 Family
5. Conclusions
6. Strengths, Limitations, and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation. Magliano DJ, Boyko EJ. 10th edition scientific committee ed. 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S20–S42. [CrossRef]
- Cartín, A.C. Diabetes mellitus gestacional: Generalidades. Rev. Médica De Costa Rica Y Centroamérica 2011, 68, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.R.; Su, G.D.; Chi, Y.L.; Wu, T.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.C. Dysregulated miRNAs contribute to altered placental glucose metabolism in patients with gestational diabetes via targeting GLUT1 and HK2. Placenta 2021, 105, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampetaki, A.; Kiechl, S.; Drozdov, I.; Willeit, P.; Mayr, U.; Prokopi, M.; Mayr, A.; Weger, S.; Oberhollenzer, F.; Bonora, E.; et al. Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Ding, J.; Shi, Y.; Lin, L.; Huang, W.; Shen, D.; Wang, W. MiR-330-3p contributes to INS-1 cell dysfunction by targeting glucokinase in gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2020, 46, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.L.; Jia, Y.J.; Xing, B.H.; Shi, D.D.; Dong, X.J. Plasma microRNA-16-5p, -17-5p and -20a-5p: Novel diagnostic biomarkers for gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2017, 43, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.-L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Tian, S.; Lv, X.-D.; Wang, X.-Q.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ma, X. Up-regulation of miR-98 and unraveling regulatory mechanisms in gestational diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Azuma, R.; Akumuo, R.; Goetzl, L.; Pinney, S.E. Gestational diabetes and maternal obesity are associated with sex-specific changes in miRNA and target gene expression in the fetus. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.-M.; Xiang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.-W.; Sheng, J.-Z.; Huang, H.-F.; Zhang, J.-Y. Integrated transcriptome sequencing analysis reveals role of miR-138-5p/TBL1X in placenta from gestational diabetes mellitus. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J.; Sheng, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Huang, W. A microRNA signature in gestational diabetes mellitus associated with risk of macrosomia. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Sun, D.; Cheng, G.; Ren, H.; Hong, H.; Chen, L.; Jing, X.-J.; Du, Y.; Zou, Y. Diagnostic Value of Dysregulated miRNAs in the Placenta and Circulating Exosomes for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. EBioMedicine 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, A.E.; van Poppel, M.N.; Desoye, G.; Damm, P.; Simmons, D.; Jensen, D.M.; Dalgaard, L.T.; The DALI Core Investigator Group. The predictive value of miR-16,-29a and-134 for early identification of gestational diabetes: A nested analysis of the DALI cohort. Cells 2021, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromadnikova, I.; Kotlabova, K.; Krofta, L. Cardiovascular Disease-Associated MicroRNAs as Novel Biomarkers of First-Trimester Screening for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in the Absence of Other Pregnancy-Related Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, L.; Gu, M.; He, B.; Qu, Q.; Lao, Y.; Gu, K.; Zheng, B.; et al. Serum miR-195-5p Exhibits Clinical Significance in the Diagnosis of Essential Hypertension with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Targeting DRD1. Clinics 2021, 76, e2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.; Li, D.; Wu, A.; Cao, T.; Luo, S. miR-377 inhibition enhances the survival of trophoblast cells via upregulation of FNDC5 in gestational diabetes mellitus. Open Med. 2021, 16, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalpour, S.; Zain, S.M.; Vazifehmand, R.; Mohamed, Z.; Pung, Y.F.; Kamyab, H.; Omar, S.Z. Analysis of serum circulating MicroRNAs level in Malaysian patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, E.; Gabr Youssef, H. Evaluation of MicroRNA-16 and MicroRNA-221 in Serum and Placenta in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Correlation with Macrosomia. Egypt. J. Radiat. Sci. Appl. 2020, 33, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeltawab, A.; Zaki, M.; Abdeldayem, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Zaied, S. Circulating micro RNA-223 and angiopoietin-like protein 8 as biomarkers of gestational diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 78, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, M.N.; Kasap, B.; Pirincci, F.; Sezgin, B.; Ozdemir, C.; Bilgic, A.D.; Aftabi, Y.; Edgunlu, T.G. Changes of miR-139-5p, TGFB1, and COL1A1 in the placental tissue of cases with gestational diabetes mellitus. Gene 2024, 897, 148061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yan, J. A preliminary integrated analysis of miRNA-mRNA expression profiles reveals a role of miR-146a-3p/TRAF6 in plasma from gestational diabetes mellitus patients. Ginekol. Pol. 2024, 95, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Q.; Zhong, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y. miR-942-5p Regulates Proliferation, Invasion and EMT of Trophoblast Cells in Gestational Diabetes by Targeting the CEBPA. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2024, 30, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Zhu, X.; Xia, H. MiR-2467 is a Potential Marker for Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnancy. Clin. Lab. 2020, 66, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Su, J. Serum miR-29a/b expression in gestational diabetes mellitus and its influence on prognosis evaluation. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 0300060520954763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Qu, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, X. MicroRNA-33a-5p sponges to inhibit pancreatic β-cell function in gestational diabetes mellitus LncRNA DANCR. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2020, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filardi, T.; Catanzaro, G.; Grieco, G.E.; Splendiani, E.; Trocchianesi, S.; Santangelo, C.; Brunelli, R.; Guarino, E.; Sebastiani, G.; Dotta, F.; et al. Identification and Validation of miR-222-3p and miR-409-3p as Plasma Biomarkers in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Sharing Validated Target Genes Involved in Metabolic Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaneialvar, H.; Mohseni, M.M.; Kenarkoohi, A.; Kakaee, S. Are miR-26a and miR-26b microRNAs potent prognostic markers of gestational diabetes? Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, V.; Ouellet, A.; Stepanov, Y.; Rodosthenous, R.S.; Croft, E.K.; Brennan, K.; Abdelouahab, N.; Baccarelli, A.; Takser, L. miRNA profiles in extracellular vesicles from serum early in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 5157–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Ribot, D.; Diaz, E.; Fazio, M.V.; Gómez, H.L.; Fornes, D.; Macchi, S.B.; Gresta, C.A.; Capobianco, E.; Jawerbaum, A. An extra virgin olive oil-enriched diet improves maternal, placental, and cord blood parameters in GDM pregnancies. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.-Y.; Tian, S.; Cao, J.-L.; Wang, X.-Q.; Ma, X.; Xia, H.-F. Down-regulated miR-21 in gestational diabetes mellitus placenta induces PPAR-α to inhibit cell proliferation and infiltration. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.Y.; Cao, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.Q.; Ma, X.; Xia, H.F. miR-199a Is Upregulated in GDM Targeting the MeCP2-Trpc3 Pathway. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 917386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, P. Correlation between serum microRNA-122 and VEGF expression and pregnancy outcome in gestational diabetes mellitus patients. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 40, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Bai, J.; Liu, P.; Dong, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Han, P.; Xing, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X. miR-494 protects pancreatic β-cell function by targeting PTEN in gestational diabetes mellitus. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Li, C. MiR-193b inhibits autophagy and apoptosis by targeting IGFBP5 in high glucose-induced trophoblasts. Placenta 2020, 101, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Gao, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, S.; Du, Y.; Fang, C.; et al. miR-17-5p Promotes Glucose Uptake of HTR8/SVneo Trophoblast Cells by Inhibiting TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 3361–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juchnicka, I.; Kuźmicki, M.; Niemira, M.; Bielska, A.; Sidorkiewicz, I.; Zbucka-Krętowska, M.; Krętowski, A.J.; Szamatowicz, J. miRNAs as Predictive Factors in Early Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 839344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunysz, M.; Cieśla, M.; Darmochwał-Kolarz, D. Evaluation of miRNA Expression in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Investigating Diagnostic Potential and Clinical Implications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamadrid-Romero, M.; Solís, K.; Cruz-Reséndiz, M.; Pérez, J.; Díaz, N.; Flores-Herrera, H.; García-López, G.; Perichart, O.; Reyes-Muñoz, E.; Arenas-Huertero, F. Central nervous system development-related microRNAs levels increase in the serum of gestational diabetic women during the first trimester of pregnancy. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 130, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Légaré, C.; Desgagné, V.; Thibeault, K.; White, F.; Clément, A.A.; Poirier, C.; Luo, Z.C.; Scott, M.S.; Jacques, P.; Perron, P.; et al. First Trimester Plasma MicroRNA Levels Predict Risk of Developing Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 928508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Légaré, C.; Desgagné, V.; Thibeault, K.; White, F.; Clément, A.A.; Poirier, C.; Luo, Z.C.; Scott, M.S.; Jacques, P.; Perron, P.; et al. First-Trimester Plasmatic microRNAs Are Associated with Fasting Glucose Levels in Late Second Trimester of Pregnancy. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Wan, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C. microRNA-96 protects pancreatic β-cell function by targeting PAK1 in gestational diabetes mellitus. Biofactors 2018, 44, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Monazzam, A.; Razmara, M.; Chu, X.; Stålberg, P.; Skogseid, B. MiR-486-3p was downregulated at microRNA profiling of adrenals of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 mice, and inhibited human adrenocortical carcinoma cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhuang, J. miR-345-3p serves a protective role during gestational diabetes mellitus by targeting BAK1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, X. Effects of miR-195-5p on cell proliferation and apoptosis in gestational diabetes mellitus via targeting EZH2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, T.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Pan, S. Unraveling the role of microRNAs: Potential biomarkers for gestational diabetes mellitus revealed through RNA sequencing analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2024, 310, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Feng, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Ma, J.; Yang, L. MicroRNA-143-3p levels are reduced in the peripheral blood of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and influences pancreatic β-cell function and viability. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. MicroRNA-1323 serves as a biomarker in gestational diabetes mellitus and aggravates high glucose-induced inhibition of trophoblast cell viability by suppressing TP53INP1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralimanoharan, S.; Maloyan, A.; Myatt, L. Mitochondrial function and glucose metabolism in the placenta with gestational diabetes mellitus: Role of miR-143. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Guanzon, D.; Jayabalan, N.; Lai, A.; Scholz-Romero, K.; de Croft, P.K.; Ormazabal, V.; Palma, C.; Diaz, E.; McCarthy, E.A.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-associated miRNAs are an adaptive response to gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Jayabalan, N.; Guanzon, D.; Palma, C.; Scholz-Romero, K.; Elfeky, O.; Zuñiga, F.; Ormazabal, V.; Diaz, E.; Rice, G.E.; et al. Human placental exosomes in gestational diabetes mellitus carry a specific set of miRNAs associated with skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 2451–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Yu, K.; Wang, W.; Tan, X.; Xin, H.; The, M.W. Expression and Clinical Value of miR-221 and miR-320 in the Plasma of Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Lab. 2022, 68, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.Y.; Li, M.Q.; Li, H.P. High glucose suppresses the viability and proliferation of HTR-8/SVneo cells through regulation of the miR-137/PRKAA1/IL-6 axis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Li, M.Q.; Li, H.P. MiR-137 Restricts the Viability and Migration of HTR-8/SVneo Cells by Downregulating FNDC5 in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Mol. Med. 2019, 19, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, S.; Sánchez-Lechuga, B.; Donovan, P.; Halang, L.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Campos-Caro, A.; Byrne, M.M.; López-Tinoco, C. Circulating miR-330-3p in Late Pregnancy is Associated with Pregnancy Outcomes Among Lean Women with GDM. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pheiffer, C.; Dias, S.; Rheeder, P.; Adam, S. Decreased expression of circulating miR-20a-5p in South African women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 22, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Wang, X. Decreased Expression of miR-185 in Serum and Placenta of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Liu, X.; Yao, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Du, J. Regulation and mechanism of miR-518d through the PPARα-mediated NF-κB pathway in the development of gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 7019597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Shangguan, Z.; Zhang, H. Downregulation of miR-451a in plasma may promote prothrombin expression and contribute to high blood coagulation state in gestational diabetes mellitus. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, G.; Guarino, E.; Grieco, G.E.; Formichi, C.; Poggi, C.D.; Ceccarelli, E.; Dotta, F. Circulating microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling in plasma of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus reveals upregulation of miRNA miR-330-3p. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serati, A.; Novielli, C.; Anelli, G.M.; Mandalari, M.; Parisi, F.; Cetin, I.; Paleari, R.; Mandò, C. Characterization of Maternal Circulating MicroRNAs in Obese Pregnancies and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.B.; Chernausek, S.D.; Teague, A.M.; Bard, D.E.; Tryggestad, J.B. Maternal diabetes alters microRNA expression in fetal exosomes, human umbilical vein endothelial cells and placenta. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Cai, A.; Ye, Q.; Chen, X.; Lin, L.; Hao, X. MiR-34b-3p impaired HUVECs viability and migration via targeting PDK1 in an in vitro model of gestational diabetes mellitus. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, A.E.; van Poppel, M.N.M.; Desoye, G.; Simmons, D.; Damm, P.; Jensen, D.M.; Dalgaard, L.T.; The DALI Core Investigator Group. The Temporal Profile of Circulating miRNAs during Gestation in Overweight and Obese Women with or without Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirm, L.; Huypens, P.; Sass, S.; Batra, R.; Fritsche, L.; Brucker, S.; Abele, H.; Hennige, A.M.; Theis, F.; Beckers, J. Maternal whole blood cell miRNA-340 is elevated in gestational diabetes and inversely regulated by glucose and insulin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.-G.; Tian, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Guan, C.-Y.; Ma, X.; Xia, H.-F. The miRNA-29b Is Downregulated in Placenta During Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and May Alter Placenta Development by Regulating Trophoblast Migration and Invasion Through a HIF3A-Dependent Mechanism. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagoma, A.; Alnek, K.; Kirss, A.; Uibo, R.; Haller-Kikkatalo, K. MicroRNA profiling of second trimester maternal plasma shows upregulation of miR-195-5p in patients with gestational diabetes. Gene 2018, 672, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toljic, M.; Nikolic, N.; Joksic, I.; Carkic, J.; Munjas, J.; Orlic, N.K.; Milasin, J. Expression of miRNAs and proinflammatory cytokines in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 162, 104211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryggestad, J.B.; Vishwanath, A.; Jiang, S.; Mallappa, A.; Teague, A.M.; Takahashi, Y.; Thompson, D.M.; Chernausek, S.D. Influence of gestational diabetes mellitus on human umbilical vein endothelial cell miRNA. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Wang, L.; Tao, H.; Gu, L.; Zhu, S.; Chen, X. Expression of miR-409-5p in gestational diabetes mellitus and its relationship with insulin resistance. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3324–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, J.; Barabash, A.; de la Torre, N.G.; De Miguel, P.; Melero, V.; Del Valle, L.; Moraga, I.; Familiar, C.; Durán, A.; Torrejón, M.J.; et al. The Relationship between Serum Adipokines, miR-222-3p, miR-103a-3p and Glucose Regulation in Pregnancy and Two to Three Years Post-Delivery in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Adhering to Mediterranean Diet Recommendations. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villota, S.D.; Toledo-Rodriguez, M.; Leach, L. Compromised barrier integrity of human feto-placental vessels from gestational diabetic pregnancies is related to downregulation of occludin expression. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wander, P.L.; Boyko, E.J.; Hevner, K.; Parikh, V.J.; Tadesse, M.G.; Sorensen, T.K.; Williams, M.A.; Enquobahrie, D.A. Circulating early-and mid-pregnancy microRNAs and risk of gestational diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 132, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M.; Ye, W.; Wu, H.; Liao, Q.; Bu, S.; Zhang, Y. Circulating miRNAs miR-574-5p and miR-3135b are potential metabolic regulators for serum lipids and blood glucose in gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2021, 37, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Xie, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y.; Di, C.; Gan, L.; Si, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. MicroRNA-16-5p regulates cell survival, cell cycle and apoptosis by targeting AKT3 in prostate cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Dai, F.; Wang, F.; Qiu, H.; Huang, X. Serum miR-195-5p is upregulated in gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Z. MiR-6869-5p induces M2 polarization by regulating PTPRO in gestational diabetes mellitus. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 6696636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiu, X.; Teng, P.; Wang, Z. Dysregulation of microRNA-657 influences inflammatory response via targeting interleukin-37 in gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7141–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Jin, C.; Zhang, Q.; Man, S.; Wang, Z. miR-657 promotes macrophage polarization toward M1 by targeting FAM46C in gestational diabetes mellitus. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 485121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wei, D.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, B. MiR-190b impedes pancreatic β cell proliferation and insulin secretion by targeting NKX6-1 and may associate to gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2021, 41, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Cao, C.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, P. Elevated Serum and Urine MiR-429 Contributes to the Progression of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Bai, X. miR-520h Inhibits cell survival by targeting mTOR in gestational diabetes mellitus. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2021, 68, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Bian, D.; Hao, L.; Huang, F.; Xu, M.; Qin, J.; Liu, Y. microRNA-503 contribute to pancreatic beta cell dysfunction by targeting the mTOR pathway in gestational diabetes mellitus. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 1177. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Chen, P.; Deng, L.; Li, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B. Plasma Exosomal miRNAs Associated With Metabolism as Early Predictor of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 2022, 71, 2272–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoffe, L.; Polsky, A.; Gilam, A.; Raff, C.; Mecacci, F.; Ognibene, A.; Crispi, F.; Gratacós, E.; Kanety, H.; Mazaki-Tovi, S. Early diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus using circulating microRNAs. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Fang, J.; Qi, H. miR-96-5p: A potential diagnostic marker for gestational diabetes mellitus. Medicine 2021, 100, e25808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Tian, S.; Wang, X.-Q.; Li, J.-H.; Dong, Y.-C.; Xia, H.-F.; Ma, X. Down-regulation of microRNA-30d-5p is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus by targeting RAB8A. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2021, 35, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Song, F.; Guo, Y. Differential expression of miR-136 in gestational diabetes mellitus mediates the high-glucose-induced trophoblast cell injury through targeting E2F1. Int. J. Genom. 2020, 2020, 3645371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Liang, Z. Chemerin-Induced Down-Regulation of Placenta-Derived Exosomal miR-140-3p and miR-574-3p Promotes Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Proliferation, Migration, and Tube Formation in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Cells 2022, 11, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Xu, X.; Yan, J. Placenta-derived exosomal miR-135a-5p promotes gestational diabetes mellitus pathogenesis by activating PI3K/AKT signalling pathway via SIRT1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 3729–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Dong, J.; Jiang, T.; Shi, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; Huo, R.; Dai, J. Early second-trimester serum miRNA profiling predicts gestational diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, T.; Shi, Z.; Ding, H.; Ling, X. MicroRNA-518d regulates PPARα protein expression in the placentas of females with gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 2085–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, H. Defective insulin receptor signaling in patients with gestational diabetes is related to dysregulated miR-140 which can be improved by naringenin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 128, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xiang, C.; Zheng, X. miR-132 serves as a diagnostic biomarker in gestational diabetes mellitus and its regulatory effect on trophoblast cell viability. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Rigolet, M.; Bourc’his, D.; Nigon, F.; Bokesoy, I.; Fryns, J.; Hulten, M.; Jonveaux, P.; Maraschio, P.; Megarbane, A. DNMT3B mutations and DNA methylation defect defines two types of ICF syndrome. Human. Mutat. 2005, 25, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elballal, M.S.; Sallam, A.-A.M.; Elesawy, A.E.; Shahin, R.K.; Midan, H.M.; Elrebehy, M.A.; Elazazy, O.; El-Boghdady, R.M.; Blasy, S.H.; Amer, N.M.; et al. miRNAs as potential game-changers in renal cell carcinoma: Future clinical and medicinal uses. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 245, 154439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Y. Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulate miR-126 to Ameliorate Hyperglycemia-Induced Retinal Inflammation Via Targeting HMGB1. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.N.; Chang, B.S.; Kim, J.H. MicroRNA dysregulation in liver and pancreas of CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase null mice disrupts insulin/PI3K-AKT signaling. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 236385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.S.; Tang, C.H.; Chie, M.J.; Tsai, C.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Chen, W.C.; Lai, C.T.; Wei, C.Y.; Tai, H.C.; et al. Resistin facilitates VEGF-A-dependent angiogenesis by inhibiting miR-16-5p in human chondrosarcoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A. Role of MIR-126 in Placental Development and Glucose Metabolism. Ph.D. Thesis, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. The role of miR-126 in embryonic angiogenesis, adult vascular homeostasis, and vascular repair and its alterations in atherosclerotic disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 97, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Martinez, M.; Cidad, P.; Moreno-Estar, S.; Fernández, M.; Albinsson, S.; Cózar-Castellano, I.; López-López, J.R.; Pérez-Garcia, M.T. miR-126 contributes to the epigenetic signature of diabetic vascular smooth muscle and enhances antirestenosis effects of Kv1.3 blockers. Mol. Metab. 2021, 53, 101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Liu, L.; Cui, Y.; Liu, H.; Yi, J.; Bing, W.; Liu, C.; Jiang, D.; Bi, Y. miR-126-3p containing exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis and attenuate ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis in a preclinical rat model of premature ovarian failure. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.-M.; Min, K.-H.; Park, S.-W.; Lee, W. Data on the expression of PEPCK in HepG2 hepatocytes transfected with miR-195. Data Brief 2017, 15, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolina, D.S.; Tavintharan, S.; Armugam, A.; Sepramaniam, S.; Pek, S.L.T.; Wong, M.T.K.; Lim, S.C.; Sum, C.F.; Jeyaseelan, K. Circulating miRNA Profiles in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E2271–E2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Brkić, J.; Hayder, H.; Peng, C. MicroRNAs in Human Placental Development and Pregnancy Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5519–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlabova, K.; Doucha, J.; Hromadnikova, I. Placental-specific microRNA in maternal circulation--identification of appropriate pregnancy-associated microRNAs with diagnostic potential. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 89, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Flores, M.; Baiza-Gutman, L.A.; Ibáñez-Hernández, M.Á.; Pascoe-Lira, D.; Guzmán-Greenfel, A.M.; Kumate-Rodríguez, J. Aspectos moleculares del daño tisular inducido por la hiperglucemia crónica. Gac. Médica De México 2004, 140, 437–448. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Bezerra, D.P.; Santos, A.S.; Guimarães, G.C.; Admoni, S.N.; Perez, R.V.; Machado, C.G.; Pelaes, T.S.; Passarelli, M.; Machado, U.F.; Queiroz, M.S. Micro-RNAs 518d-3p and 618 are upregulated in individuals with type 1 diabetes with multiple microvascular complications. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ding, X.; Liang, M. The miR-29 family: Genomics, cell biology, and relevance to renal and cardiovascular injury. Physiol. Genom. 2012, 44, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgaard, L.T.; Sørensen, A.E.; Hardikar, A.A.; Joglekar, M.V. The microRNA-29 family: Role in metabolism and metabolic disease. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C367–C377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Zhong, X.; Huang, X.R.; Meng, X.-M.; You, Y.; Chung, A.C.; Lan, H.Y. MicroRNA-29b inhibits diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, A.; Lu, C.; Gu, X.; Jiang, L. Construction of a novel miRNA regulatory network and identification of target genes in gestational diabetes mellitus by integrated analysis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 966296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X. Dysregulation of microRNA-770-5p influences pancreatic-β-cell function by targeting TP53 regulated inhibitor of apoptosis 1 in gestational diabetes mellitus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Author Year (Cita) | Cellular Line | Expression | Biological Process | Target Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tryggestad, Vishwanath et al., 2016 [69] | HUVEC/BeWo | miR-130b | Insuline regulation/IGF1 | AMPKα1 |
| Zhang, Wang et al., 2020 [88] | HRT-8/Svneo/BeWo | miR-136 | Pro-apoptosis | E2F1 |
| Ding, Guo et al., 2018 [11] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-138-5p | Migration Proliferation | TBL1X |
| Zhao, Zhao et al., 2020 [93] | HTR-8/SVneo/HEK293/HUVEC | miR-140 | Insulin resistance | IR-α, IRS-1, and IGF1R |
| Zhang, Wu et al., 2022 [89] | HUVEC | miR-140-3p | Antiproliferation, anti-migration, tube formation | IL-18 and IL-1β |
| Muralimanoharan, Maloyan et al., 2016 [49] | Villous cytotrophoblasts | miR-143 | Mitochondrial function Glucose metabolism | PPARγ and PGC1α |
| Tryggestad, Vishwanath et al., 2016 [69] | HUVEC/BeWo | miR-148a | Insulin signaling pathway/IGF2 | AMPKα2 |
| Jiang, Wei et al., 2022 [36] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-17-5p | Glucose captation | TXNIP NLRP3 |
| Villota, Toledo-Rodriguez et al., 2021 [72] | HUVEC | miR-181a-5p | Compromised barrier integrity | OCCLUDIN |
| Wang, Wei et al., 2021 [80] | Min6 | miR-190b | Antiproliferation Anti-insulin secretion | NKX6-1 |
| Liao, Zhou et al., 2020 [45] | HUVEC | miR-195-5p | Cell viability and proliferation Apoptosis | EZH2 |
| Guan, Cao et al., 2022 [32] | JEG-3 | miR-199a-5p | Glucose metabolism | MeCP2 and TRPC3 |
| Guan, Tian et al., 2020 [31] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-21-5p | Anti-proliferation Infiltration | PPAR-α |
| Song, Su et al., 2021 [5] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-22 | Glucose metabolism | GLUT1 and HK2 |
| Sun, Tian et al., 2020 [66] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-29b | Anti-migration Invasion | ING2, ING3, and HIF3A |
| Zhang, Li et al., 2021 [87] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-30d-5p | Regulation of glycolysis | RAB8A |
| Li and Zhuang 2021 [44] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-345-3p | Anti-apoptosis | BAK1 |
| Song, Cai et al., 2021 [63] | HUVEC | miR-34b-3p | Anti-viability Anti-migration | PDK1 |
| Zhang and Zhao 2021 [13] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-362-5p | Inhibition proliferation Pro-apoptosis | GSR |
| Wei, L., et al., 2021 [81] | HRT8/SVneo | miR-373 | Insulin pathway, including IRS, PI3K, AKT, and GLUT5 | SLC2A5 |
| Li et al., 2015 [12] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-508-3p | Regulator of EGFR | PIKfyve |
| Zhao et al., 2014 [92] | HEK-293 | miR-518d | Antiproliferation | PPAR-α |
| Qiu, Liu et al., 2020 [59] | HTR8/SVneo | miR-518d | PPARα-mediated NF-κB pathway | PPARα- |
| Zhang et al., 2020 [89] | HUVEC | miR-574-3p | Antiproliferation | IL-18 and IL-1β |
| Wang, Wang et al., 2019 [78] | THP-1 | miR-657 | Anti-inflammatory | IL-37 |
| Wang, Ma et al., 2021 [77] | THP-1 | miR-6869-5p | Induces M2 polarization | Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptor type O (PTPRO) |
| Song, Su et al., 2021 [5] | HTR-8/Svneo | miR-9 | Glucose metabolism | GLUT1 and HK3 |
| Chu, Zhong et al., 2024 [23] | HTR-8/SVneo | miR-942-5p | Regulation of trophoblast cells’ biological function | CEBPA |
| Li, Wang et al., 2018 [42] | INS-1 | miR-96 | Regulating PAK1 expression, insulin secretion, and β-cell function | PAK1 |
| Yu, Liu et al., 2021 [86] | HRT-8/SVneo | miR-96-5p | Viability | |
| Cao, Zhang et al., 2016 [9] | HEK-293T/JEG-3 | miR-98 | Glucose metabolism | Mecp2 |
| Author/Year | Tissue | Up-RT-PCR | Down-RT-PCR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gomez Ribot, Diaz et al., 2020 [30] | Cord blood umbilical blood/placenta | miR-518d | |
| Shah, Chernausek et al., 2021 [62] | Cord blood, umbilical blood/placenta | miR-126–3p | miR-148a-3p and miR-29a-3p |
| Liao, Zhou et al., 2020 [45] | Cord blood Umbilical blood | miR-195-5p | |
| Yu, Liu et al., 2021 [86] | Serum/placenta | miR-96-5p | |
| Li and Zhuang 2021 [44] | Serum/placenta | miR-345-3p | |
| Peng, Li et al., 2019 [53] | Umbilical vein plasma/CEV | miR-137 | |
| Joshi, Azuma et al., 2020 [10] | Amniotic fluid (second trimester) | mR-7-1-3pa, miR-126-3p, miR-185-5p, miR-302a-3p, miR-1268a, miR-146a-5p, miR-15b-5p, miR-197-3p, miR-199a-3pa, miR-378a-3pa, miR-486-3p, and miR-885-5pa | miR-210-3p, miR-99a-5p, and miR-138-5p |
| MiRNA | Cord Blood Umbilical | Amniotic Fluid (Second Trimester) | Maternal Plasma | Placenta | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-126-3p | 1↑ | 1↑ | 1↑ | 2↑ | [6,10,62,69] |
| miR-518d | 1↑ | 1↑ | 2↑ | [30,58,89] | |
| miR-195-5p | 1↑ | 2↑ | 1↓ | [16,67] | |
| miR-345-3p | 1↓ | 1↓ | [44] | ||
| miR-96-5p | 1↓ | 1↓ | [86] | ||
| miR-29a-3p | 1↓ | 1↑/4↓ | 2↓ | [14,25,61,66,68] | |
| miR-137 | 1↑ | 1↓ | [53,54] | ||
| miR-148a-3p | 1↓ | 1↑/1↓ | [62,69] | ||
| miR-185-5p | 1↑ | 1↑ | 1↑ | [10,57] | |
| miR-197-3p | 1↑ | 1↑ | [10,51] | ||
| miR-199a-3p | 1↑ | 1↑ | [10,31] | ||
| miR-138-5p | 1↓ | 1↓ | [10,11] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trejo-Gonzalez, N.L.; Palomar-Morales, M.; Baiza-Gutman, L.A.; Diaz-Rosas, G.; Ortega-Camarillo, C.; Contreras-Ramos, A. Circulating MicroRNAs Associated with Changes in the Placenta and Their Possible Role in the Fetus During Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Metabolites 2025, 15, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060367
Trejo-Gonzalez NL, Palomar-Morales M, Baiza-Gutman LA, Diaz-Rosas G, Ortega-Camarillo C, Contreras-Ramos A. Circulating MicroRNAs Associated with Changes in the Placenta and Their Possible Role in the Fetus During Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Metabolites. 2025; 15(6):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060367
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrejo-Gonzalez, Ninna Leslie, Martin Palomar-Morales, Luis Arturo Baiza-Gutman, Guadalupe Diaz-Rosas, Clara Ortega-Camarillo, and Alejandra Contreras-Ramos. 2025. "Circulating MicroRNAs Associated with Changes in the Placenta and Their Possible Role in the Fetus During Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Review" Metabolites 15, no. 6: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060367
APA StyleTrejo-Gonzalez, N. L., Palomar-Morales, M., Baiza-Gutman, L. A., Diaz-Rosas, G., Ortega-Camarillo, C., & Contreras-Ramos, A. (2025). Circulating MicroRNAs Associated with Changes in the Placenta and Their Possible Role in the Fetus During Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Metabolites, 15(6), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060367






