Improved Solubility and Dissolution Rates in Novel Multicomponent Crystals of Piperine with Succinic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Cocrystals of Piperine–Succinic Acid
2.2.2. Characterization of Cocrystal Piperine–Succinic Acid
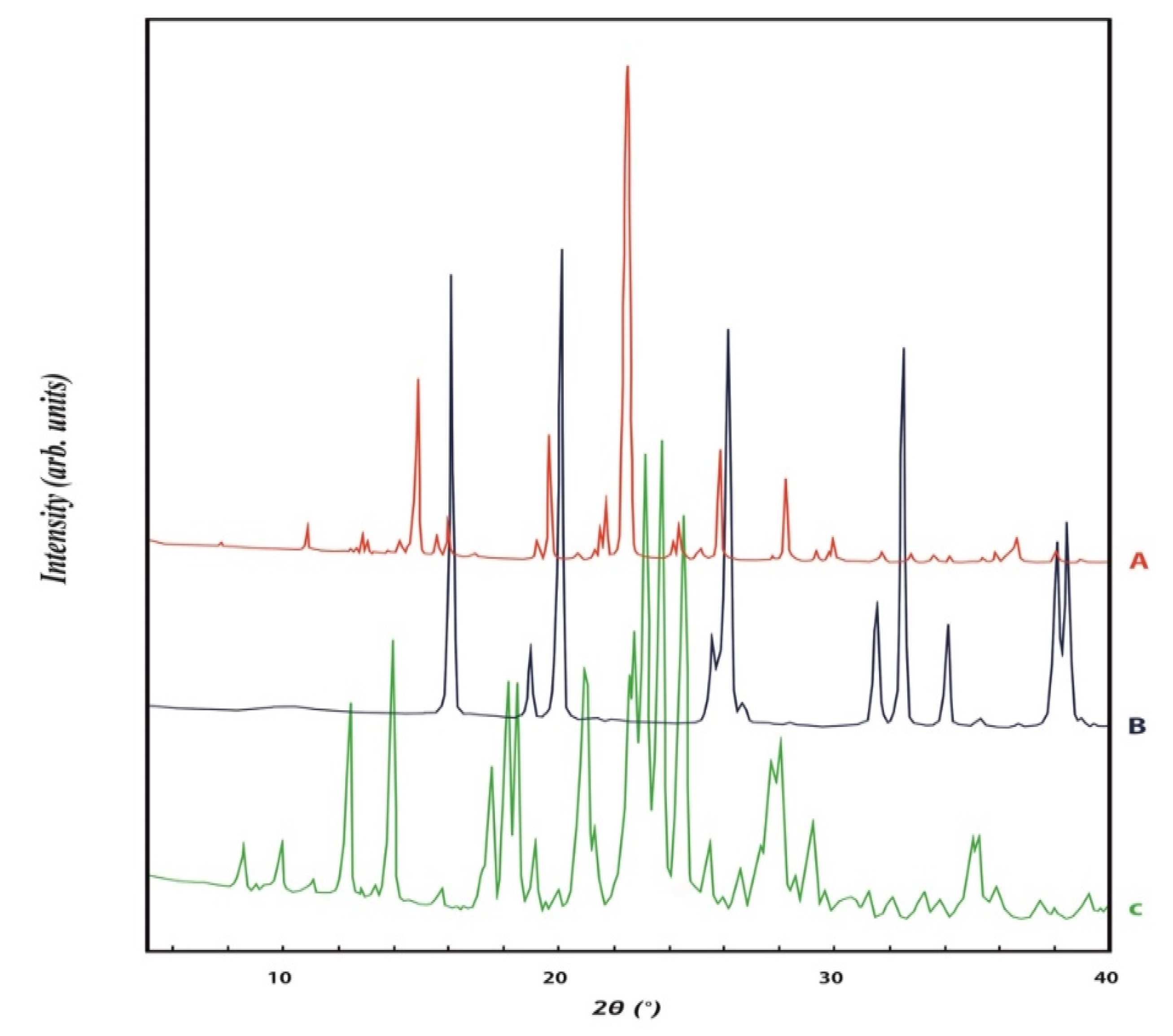
Powder X-ray diffraction analysis
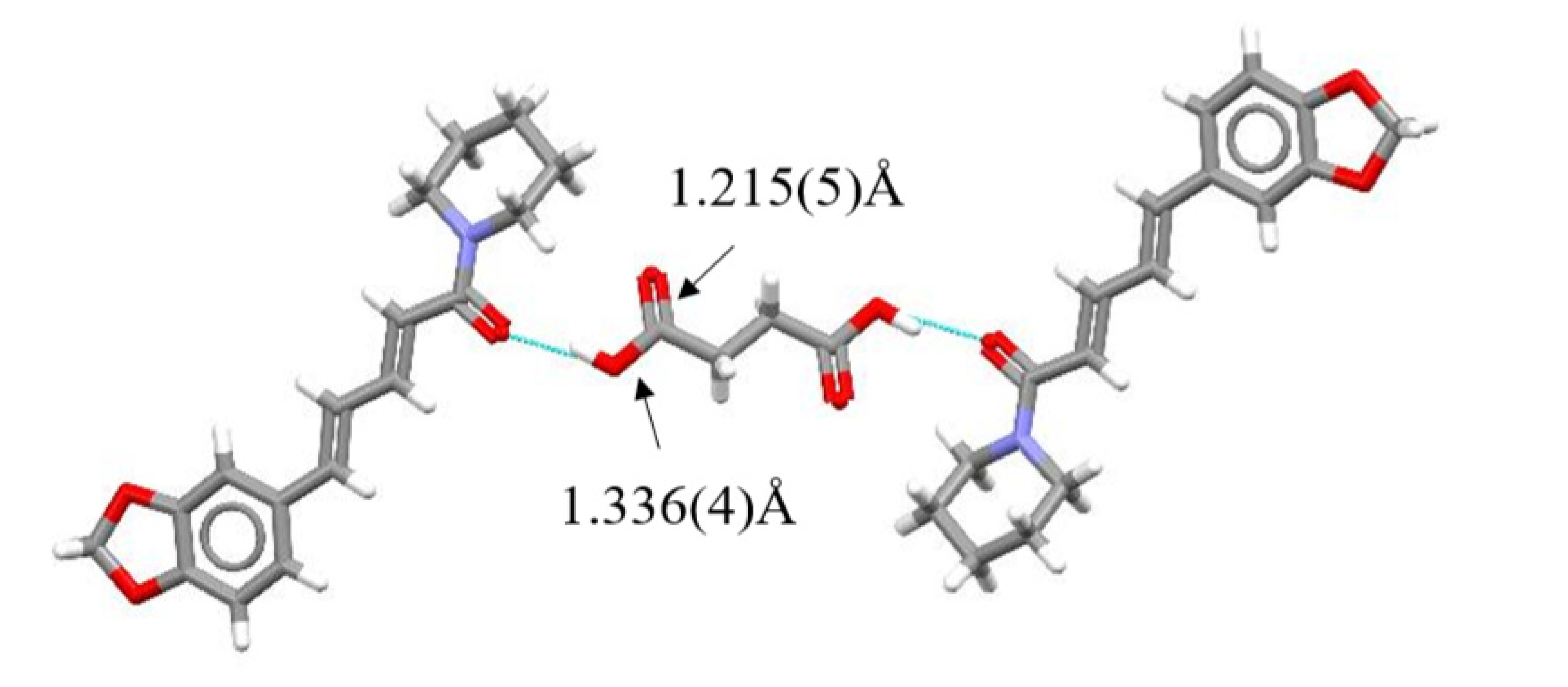
Single Crystal X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
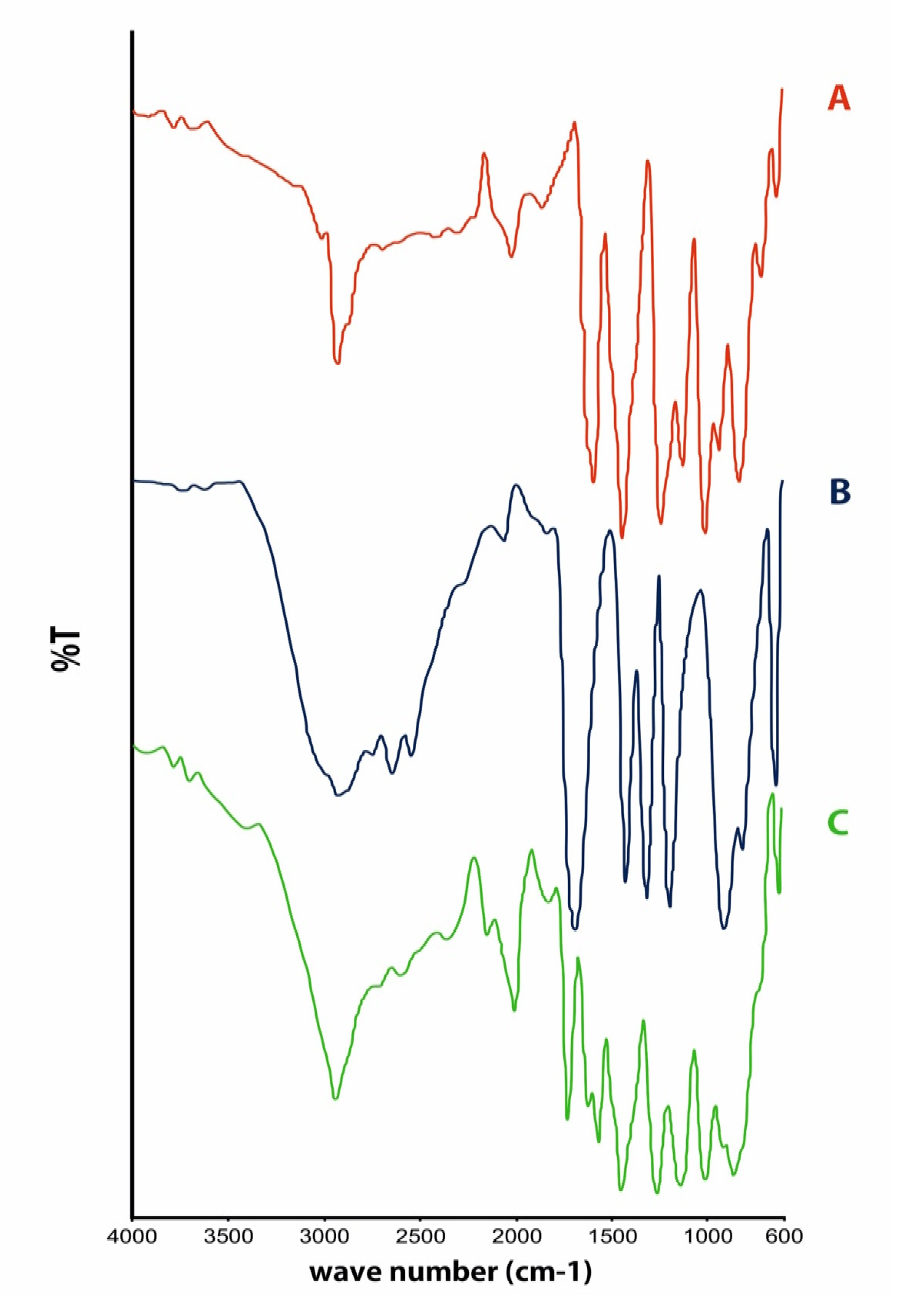
Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
Solubility Test
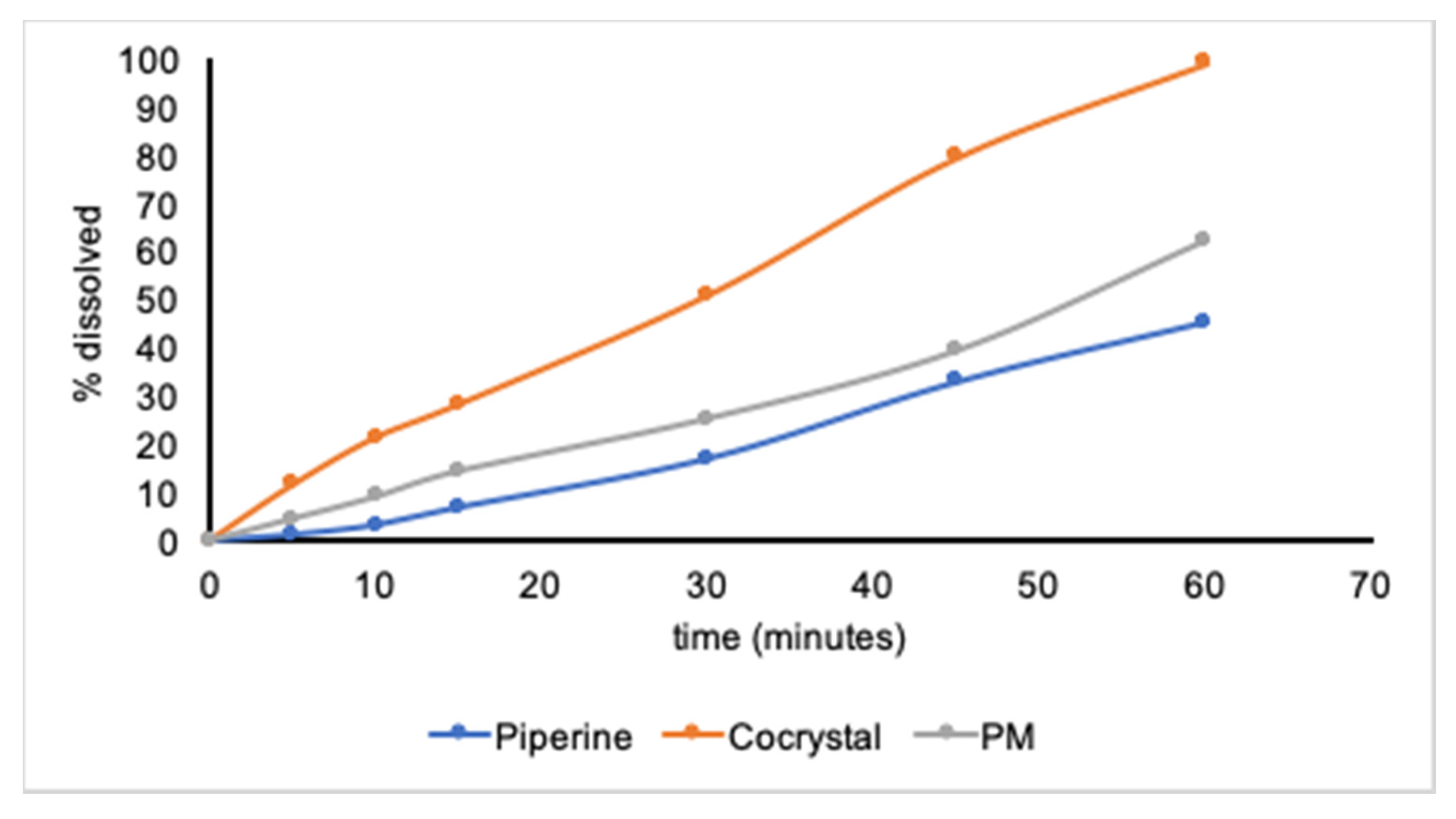
In Vitro Dissolution Rate Profiles
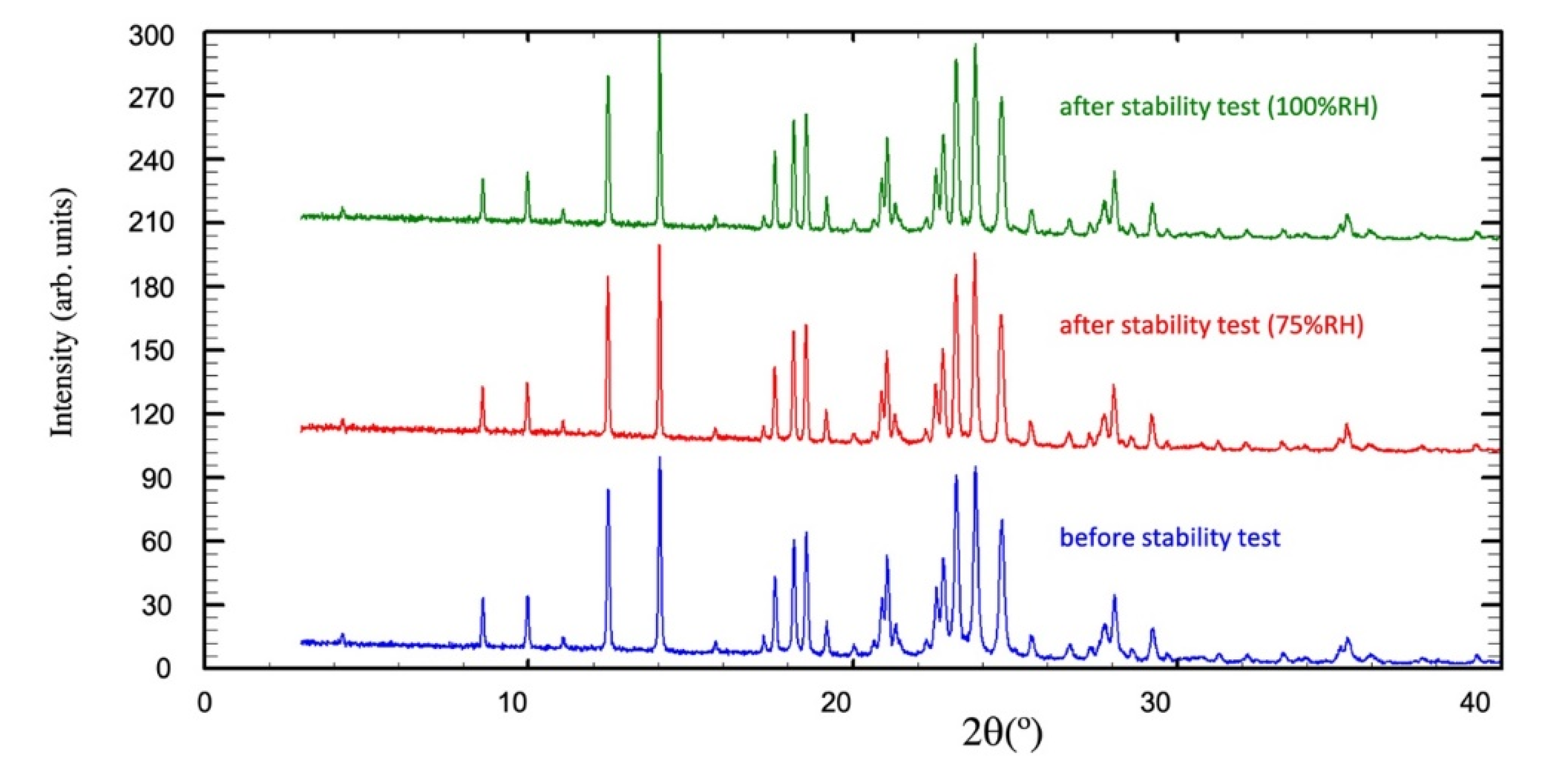
Stability Test
Hydration Energy Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorgani, L.; Mohammadi, M.; Najafpour, G.D.; Nikzad, M. Piperine—The Bioactive Compound of Black Pepper: From Isolation to Medicinal Formulations. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanhouri, Z.A. A Review on Therapeutic Potential of Piper nigrum L. (Black Pepper): The King of Spices. Med. Aromat. Plants 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johri, R.K.; Zutshi, U. An Ayurvedic formulation “Trikatu” and its constituents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1992, 37, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasleem, F.; Azhar, I.; Ali, S.N.; Perveen, S.; Mahmood, Z.A. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of Piper nigrum L. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, S461–S468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwal, M.; Goswami, T.K. Piper nigrum and piperine: An update. Phyther. Res. 2013, 27, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.S.; Pasha, I.; Sultan, M.T.; Randhawa, M.A.; Saeed, F.; Ahmed, W. Black Pepper and Health Claims: A Comprehensive Treatise. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbanda, C.; Alam, M.S.; Hamid, H.; Javed, K.; Bano, S.; Ali, Y.; Dhulap, A.; Alam, P.; Pasha, M.A.Q. Novel Piperine Derivatives with Antidiabetic Effect as PPAR-γ Agonists. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 88, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, T.; Shi, L.; Takasu, S.; Cho, Y.-M.; Kiriyama, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Ogawa, K.; Tatematsu, M.; Tsukamoto, T. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Capsaicin and Piperine on Helicobacter pylori-Induced Chronic Gastritis in Mongolian Gerbils. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarai, Z.; Boujelbene, E.; Ben Salem, N.; Gargouri, Y.; Sayari, A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of various solvent extracts, piperine and piperic acid from Piper nigrum. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, I.A.; Alhumayyd, M.S.; Mahesar, A.L.; Gilani, A.H. The analgesic and anticonvulsant effects of piperine in mice. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 64, 789. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, R.S.; Surya, D.; Nalini, N. Antioxidant efficacy of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) and piperine in rats with high fat diet induced oxidative stress. Redox Rep. 2004, 9, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattanathorn, J.; Chonpathompikunlert, P.; Muchimapura, S.; Priprem, A.; Tankamnerdthai, O. Piperine, the potential functional food for mood and cognitive disorders. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3106–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, S.S.; Muntimadugu, E.; Rafeeqi, T.A.; Domb, A.J.; Khan, W. Co-delivery of rapamycin- and piperine-loaded polymeric nanoparticles for breast cancer treatment. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2608–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, P. Neuroprotective potential of curcumin in combination with piperine against 6-hydroxy dopamine induced motor deficit and neurochemical alterations in rats. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athukuri, B.L.; Neerati, P. Enhanced oral bioavailability of domperidone with piperine in male wistar rats: Involvement of CYP3A1 and P-gp inhibition. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 20, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegeto, L.A.; Caleffi-Ferracioli, K.R.; Nakamura-Vasconcelos, S.S.; de Almeida, A.L.; Baldin, V.P.; Nakamura, C.V.; Siqueira, V.L.D.; Scodro, R.B.L.; Cardoso, R.F. In vitro combinatory activity of piperine and anti-tuberculosis drugs in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2018, 111, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakatani, M.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagden, N.; de Matas, M.; Gavan, P.T.; York, P. Crystal engineering of active pharmaceutical ingredients to improve solubility and dissolution rates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, K.; Yoo, Y.J. Enhanced solubility of piperine using hydrophilic carrier-based potent solid dispersion systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, E.A.; Majumdar, S.; Alsheteli, A.; Alshehri, S.; Alsulays, B.; Feng, X.; Gryczke, A.; Kolter, K.; Langley, N.; Repka, M.A. Hot melt extrusion as an approach to improve solubility, permeability and oral absorption of a psychoactive natural product, piperine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilaqueo, M.; Millao, S.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; Campos-Vega, R.; Acevedo, F.; Shene, C.; Rubilar, M. Inclusion of piperine in β-cyclodextrin complexes improves their bioaccessibility and in vitro antioxidant capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Kanamoto, I.; Ezawa, T.; Tunvichien, S.; Inoue, Y. Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Piperine/β-Cyclodextrin due to the Formation of Inclusion Complexes. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ezawa, T.; Inoue, Y.; Murata, I.; Takao, K.; Sugita, Y.; Kanamoto, I. Characterization of the Dissolution Behavior of Piperine/Cyclodextrins Inclusion Complexes. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, M.; Khan, M.; Khan, R.A.; Ahmed, B. Preparation, characterization, in vivo and biochemical evaluation of brain targeted Piperine solid lipid nanoparticles in an experimentally induced Alzheimer’s disease model. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, F.; Jahan, N.; Rahman, K.-U.; Bhatti, H.N. Increased Oral Bioavailability of Piperine from an Optimized Piper nigrum Nanosuspension. Planta Med. 2019, 85, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedeky, A.S.; Khalil, I.A.; Hefnawy, A.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Development of core-shell nanocarrier system for augmenting piperine cytotoxic activity against human brain cancer cell line. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 118, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumondor, A.C.F.; Taylor, L.S. Effect of polymer hygroscopicity on the phase behavior of amorphous solid dispersions in the presence of moisture. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, J.R.; Arias-Blanco, M.J.; Gines, J.M.; Rabasco, A.M.; Pérez-Martínez, J.I.; Mor, M.; Giordano, F. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Investigations of the Inclusion Complexation of Gliclazide with β-Cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Taylor, L.S. Ability of different polymers to inhibit the crystallization of amorphous felodipine in the presence of moisture. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriani, L.; Haqi, A.; Zaini, E. Preparation and characterization of solid dispersion freeze-dried efavirenz—Polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2016, 7, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vioglio, P.C.; Chierotti, M.R.; Gobetto, R. Pharmaceutical aspects of salt and cocrystal forms of APIs and characterization challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 117, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, C.C.; Guimarães, F.F.; Ribeiro, L.; Martins, F.T. Salt or cocrystal of salt? Probing the nature of multicomponent crystal forms with infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 167, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaini, E.; Fitriani, L.; Sari, R.Y.; Rosaini, H.; Horikawa, A.; Uekusa, H. Multicomponent Crystal of Mefenamic Acid and N-Methyl-d-Glucamine: Crystal Structures and Dissolution Study. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Umeda, D.; Nugraha, Y.P.; Nango, K.; Yonemochi, E.; Uekusa, H. Simultaneous Improvement of Epalrestat Photostability and Solubility via Cocrystallization: A Case Study. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.C.; Gelain, A.B.; Rosa, J.; Cardoso, S.G.; Caon, T. Cocrystallization as a novel approach to enhance the transdermal administration of meloxicam. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainurofiq, A.; Mauludin, R.; Mudhakir, D.; Umeda, D.; Soewandhi, S.N.; Putra, O.D.; Yonemochi, E. Improving mechanical properties of desloratadine via multicomponent crystal formation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliandra, Y.; Zaini, E.; Syofyan, S.; Pratiwi, W.; Putri, L.N.; Pratiwi, Y.S.; Arifin, H. Cocrystal of ibuprofen–nicotinamide: Solid-state characterization and in vivo analgesic activity evaluation. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, D.R.; Walsh, D.; O’Connell, P.; Mugheirbi, N.A.; Worku, Z.A.; Bolas-Fernandez, F.; Galiana, C.; Dea-Ayuela, M.A.; Healy, A.M. Optimising the in vitro and in vivo performance of oral cocrystal formulations via spray coating. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 124, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.R.; King, N.L.C.; Oswald, I.D.H.; Rollo, D.G.; Spiteri, R.; Walls, A. Structural study of salt forms of amides; paracetamol, benzamide and piperine. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1154, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.R.; Mei, X. Structure, physicochemical properties and pharmacokinetics of resveratrol and piperine cocrystals. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 6154–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfund, L.Y.; Chamberlin, B.L.; Matzger, A.J. The bioenhancer piperine is at least trimorphic. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2047–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Molnar, L.F.; Jung, Y.; Kussmann, J.; Ochsenfeld, C.; Brown, S.T.; Gilbert, A.T.B.; Slipchenko, L.V.; Levchenko, S.V.; O’Neill, D.P.; et al. Advances in methods and algorithms in a modern quantum chemistry program package. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 3172–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothe, E.; Meekes, H.; Vlieg, E.; Ter Horst, J.H.; De Gelder, R. Solvates, Salts, and Cocrystals: A Proposal for a Feasible Classification System. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3237–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Hirakura, Y.; Yuda, M.; Teramura, T.; Terada, K. Detection of cocrystal formation based on binary phase diagrams using thermal analysis. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, E.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N.; Suryanarayanan, R. A rapid thermal method for cocrystal screening. CrystEngComm 2008, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Yonemochi, E.; Uekusa, H. Isostructural Multicomponent Gliclazide Crystals with Improved Solubility. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 6568–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Desiraju, G.R. Acid⋯Amide Supramolecular Synthon in Cocrystals: From Spectroscopic Detection to Property Engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 6361–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Raj, C.J.; Priya, S.M.N.; Robert, R.; Dinakaran, S.; Das, S.J. Optical and dielectric studies on succinic acid single crystals. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2008, 43, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, S.; Rani, R.; Dhingra, D.; Kumar, S.; Dilbaghi, N. Conjugation of epigallocatechin gallate and piperine into a zein nanocarrier: Implication on antioxidant and anticancer potential. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuliaş, A.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Şuta, L.-M.; Şoica, C.; Ledeţi, I. Screening and characterization of cocrystal formation between carbamazepine and succinic acid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 121, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, C.A.; Montgomery, S.E.; Gupta, R.B. Formation of itraconazole/L-malic acid cocrystals by gas antisolvent cocrystallization. Powder Technol. 2013, 236, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokoumetzidis, A.; Macheras, P. A century of dissolution research: From Noyes and Whitney to the Biopharmaceutics Classification System. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 321, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, W.L.; Niazi, S. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems: Dissolution of griseofulvin–succinic acid eutectic mixture. J. Pharm. Sci. 1976, 65, 1212–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.T.; Pervez, H.; Shehzad, M.T.; Saeed-Ul-Hassan, S.; Mehmood, Z.; Shah, S.N.H.; Razi, M.T.; Murtaza, G. Improved physicochemical characteristics of artemisinin using succinic acid. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2014, 71, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Furuta, H.; Mori, S.; Yoshihashi, Y.; Yonemochi, E.; Uekusa, H.; Sugano, K.; Terada, K. Physicochemical and crystal structure analysis of pranlukast pseudo-polymorphs II: Solvate and cocrystal. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 111, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Furuishi, T.; Yonemochi, E.; Terada, K.; Uekusa, H. Drug-Drug Multicomponent Crystals as an Effective Technique to Overcome Weaknesses in Parent Drugs. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Umeda, D.; Nugraha, Y.P.; Furuishi, T.; Nagase, H.; Fukuzawa, K.; Uekusa, H.; Yonemochi, E. Solubility improvement of epalrestat by layered structure formation: Via cocrystallization. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

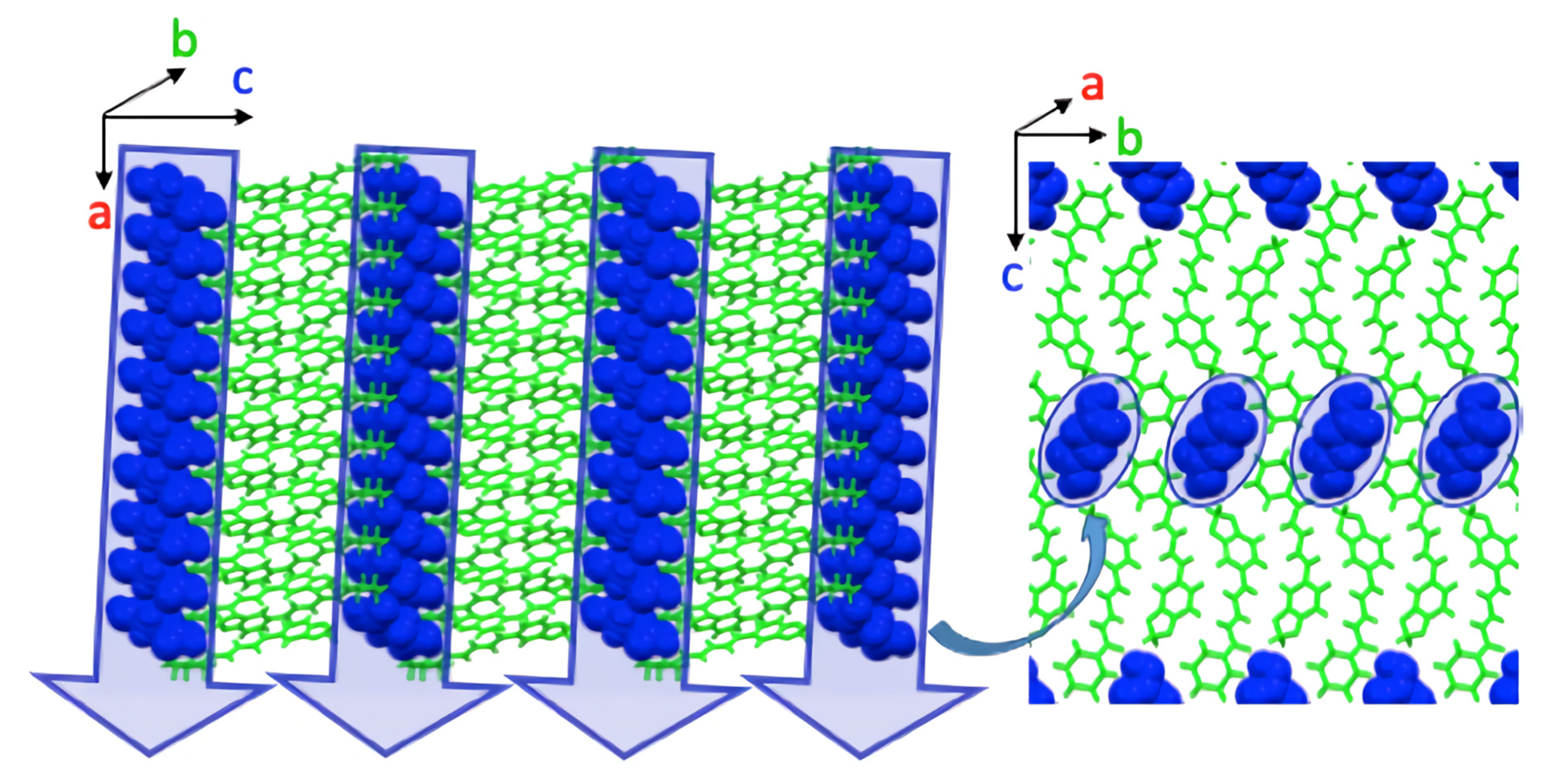
| Parameter | Piperine–Succinic Acid |
|---|---|
| Moiety formula | C17H19NO3, 0.5(C4H6O4) |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c |
| a (Å) | 4.1459(1) |
| b (Å) | 9.6960(3) |
| c (Å) | 41.1214(10) |
| ß(°) | 92.703(2) |
| V (Å3) | 1651.19(8) |
| Z/Z′ | 4/1 |
| T (K) | 93 |
| R-factor (%) | 8.64 |
| Compound | Solubility (μg/mL) | ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Piperine | 2.93 | ± 0.04 |
| Piperine–succinic acid | 11.71 | ± 0.26 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaini, E.; Afriyani; Fitriani, L.; Ismed, F.; Horikawa, A.; Uekusa, H. Improved Solubility and Dissolution Rates in Novel Multicomponent Crystals of Piperine with Succinic Acid. Sci. Pharm. 2020, 88, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020021
Zaini E, Afriyani, Fitriani L, Ismed F, Horikawa A, Uekusa H. Improved Solubility and Dissolution Rates in Novel Multicomponent Crystals of Piperine with Succinic Acid. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2020; 88(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaini, Erizal, Afriyani, Lili Fitriani, Friardi Ismed, Ayano Horikawa, and Hidehiro Uekusa. 2020. "Improved Solubility and Dissolution Rates in Novel Multicomponent Crystals of Piperine with Succinic Acid" Scientia Pharmaceutica 88, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020021
APA StyleZaini, E., Afriyani, Fitriani, L., Ismed, F., Horikawa, A., & Uekusa, H. (2020). Improved Solubility and Dissolution Rates in Novel Multicomponent Crystals of Piperine with Succinic Acid. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 88(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020021






