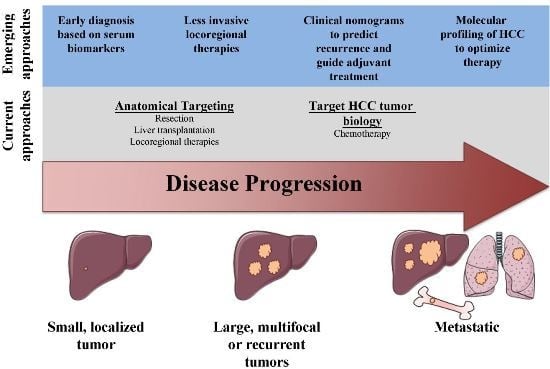
A Surgical Perspective on Targeted Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Article Selection
2. Targeting HCC Anatomically: Resection, Liver Transplantation, and Locoregional Therapies
2.1. Resection
| Intervention | Indication & Patient Tumor Characteristics | Patient Liver Function | Clinical Outcomes | Disadvantages | Emerging Treatment Advancements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resection | -Localized -Single tumor -Resection should preserve >50% TLV [9] -Bridging tx to transplant 1 [1] | No portal hypertension [8,14] | -Recurrence: 80% within five years [22] -Five-year survival: 53% [21] | High surgical morbidity in patients with cirrhosis [12] | -Biomarkers to predict recurrence [34,35,36] -Postoperative adjuvant sorafenib [33] -Laparoscopic resection [19,20] |
| Liver transplantation | -Localized -Single tumor <5 cm or 2–3 tumors ≤3 cm (Milan criteria) [37] | Decompensated cirrhosis ok (Child-Pugh C) | -Recurrence: ~18% at one year [38] -Five-year survival: 70%–80% if within Milan criteria [37,39] | -Shortage of donor organs -Long waiting time [40] | -Nomograms and biomarkers to predict recurrence [41,42,43,44,45,46] -Post-transplant adjuvant sorafenib [47] -Expansion of Milan criteria [48,49] LDLT, and use of ECD livers [7,8,50] |
| Percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI) | Localized Tumors <3 cm [8] | Preserved liver function (Child-Pugh A) [8] | -Recurrence: 43% for tumors >3 cm at 2 years [51] -Five-year survival: 28%–40% (single tumor <3 cm) [52] | Multiple treatment sessions required | Use decreasing in US, as RCTs have shown RFA is superior to PEI for tumors >2 cm [53,54,55] |
| Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)/Microwave ablation (MWA) | -Localized, unresectable -Tumors <4 cm [7] -Bridging tx to transplant [56] | Preserved liver function (Child-Pugh A) | -Recurrence: 50% within three years [54,57] -Five-year survival: 33%–40% (≤3.5 cm) [57] | -More adverse events vs. PEI [58,59] -RFA is less effective for highly vascular tumors [60] | Emerging ablation methods have potential to treat pts with advanced liver disease and tumors near vital structures [61,62,63,64] |
| Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE)/Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) | -Localized, multifocal, unresectable [65] -Tumors >4 cm [7] TARE for pts w/ portal vein thrombosis [66,67,68] -Bridging tx to transplant [56] | Preserved liver function (Child-Pugh A) [65] | Two-year survival: 63% (Child-Pugh A) [69,70] | -Low CR rate (6%) [71] -Post-embolization syndrome in 60%–80% of pts [72] | -TACE w/ drug eluting beads [73] -TACE + sorafenib [74,75] |
| Sorafenib | -Metastatic, unresectable -Any size -Vascular invasion ok [76] | Preserved liver function (Child-Pugh A) [77] | -Radiological progression: 75% of pts within six months [77] -One-year survival: 44% [77] | -No CR or PR [77] -Unclear efficacy in pts with poor liver function (Child-Pugh B or C) [77] | -Combination therapies (sorafenib + RFA, TACE, liver transplant) [75,78,79] -Molecular analysis of tumors to predict tx response [80,81] |
2.2. Liver Transplantation
2.3. Non-Surgical Targeting: Locoregional Therapies
2.3.1. Percutaneous Ethanol Injection
2.3.2. Radiofrequency Ablation
2.3.3. Microwave Ablation
2.3.4. Transarterial Chemoembolization
2.3.5. Transarterial Radioembolization
2.4. Emerging Ablation Methods
2.4.1. Cryoablation
| Method | Advantages | Status of Clinical Studies | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cryoablation | Less painful and may be optimal ablation method for medium-sized tumors [61] | One RCT and multiple prospective studies [141,142] | Similar to RFA/MWA for tumors <2 cm, superior efficacy for tumors >2 cm [141,142] |
| Irreversible electroporation (IRE) | Suitable for tumors adjacent to blood vessels [143,144] | Prospective studies only [62] | No studies yet comparing IRE to other methods |
| Laser ablation | Low cost (70% < RFA) and technical ease [145] | RCTs [63,145] | Equivalent to RFA for tumors <4 cm [63,145] |
| High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) | Option for patients with decompensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh C), completely extracorporeal, effective even if tumor is near major hepatic vessels [64,146,147] | Prospective studies only [146,148] | Effective as a bridging therapy to transplantation [146] |
2.4.2. Irreversible Electroporation
2.4.3. Laser Ablation
2.4.4. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
| Patient Tumor Characteristics | PEI | RFA | MWA | TACE | TARE | CRYO | IRE | Laser | HIFU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small tumor <2 cm | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | ± | + |
| Medium tumor <4 cm | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Large tumor >4 cm | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| Multifocal | − | ± | ± | + | + | ± | ± | ± | ± |
| Near vascular structures | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | − | + |
| Decompensated cirrhosis | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| Portal vein thrombosis | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
3. Targeting HCC Tumor Biology
Chemotherapy
4. Future Directions: Improving the Targeting of HCC
4.1. Diagnostic Biomarkers
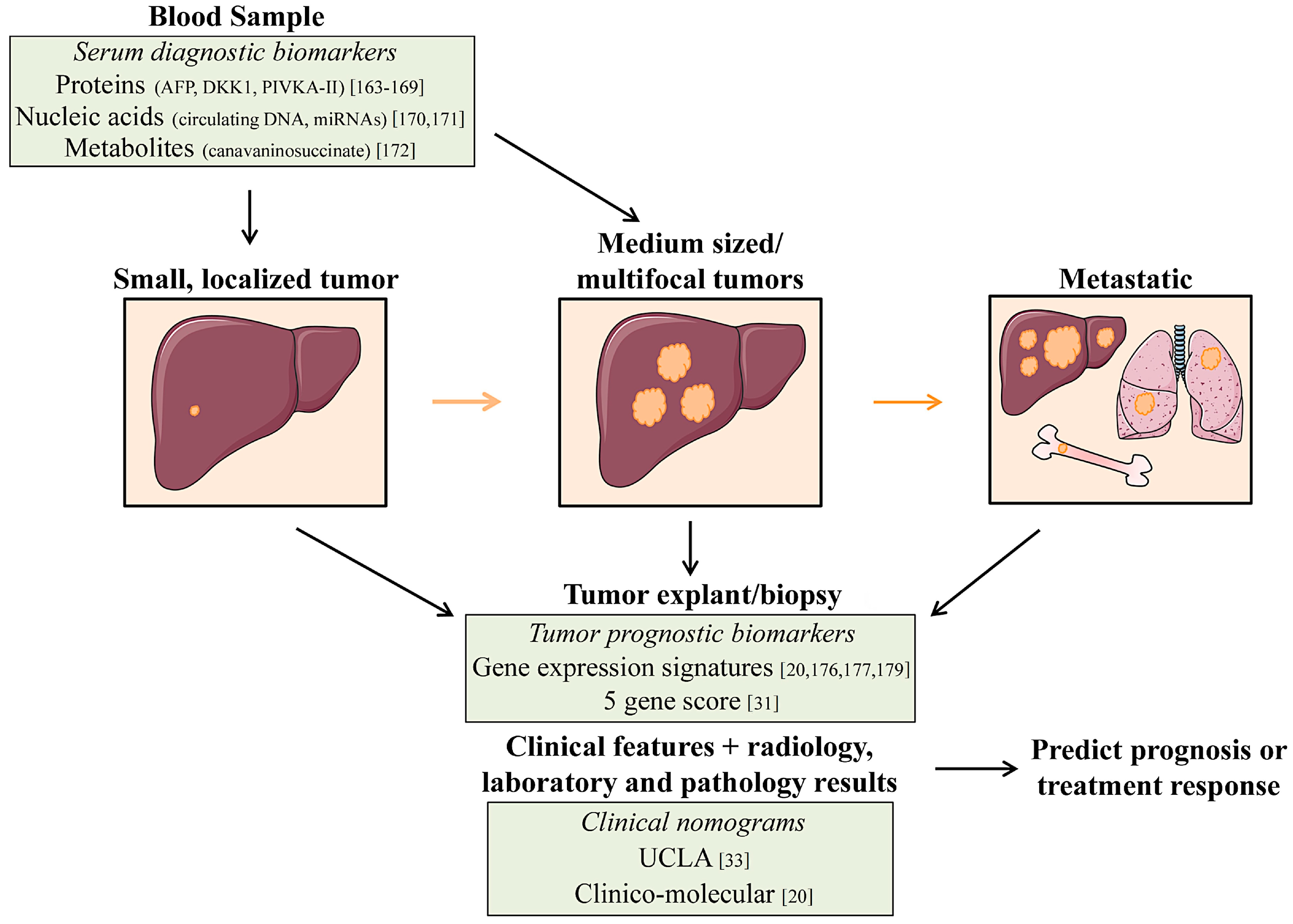
4.2. Prognostic Biomarkers
4.3. New Therapeutic Strategies for HCC
| Targeting Approach | Molecular Alteration/Gene Signature (% Alteration Frequency) | Status of Therapeutic Targeting |
|---|---|---|
| Direct targeting of genetically altered genes in tumors (mutations or DNA amplifications) | KRAS/NRAS mutations (<5% [6,196,197]) | Phase I RCT for HCC: refametinib (RAS-RAF-MEK pathway inhibitor) NTC01915589 [80] |
| c-MET amplification (<5% [185,198]) | Phase II RCT for HCC: tivantinib (c-Met inhibitor) [80] | |
| Targeting of altered cellular pathways in tumors (based on genomic alterations and gene expression) | Wnt/B-catenin (B-catenin 18% [198,199], APC < 5% [6], AXIN < 15% [6]) | LGK974 (Porcupine inhibitor ) in preclinical testing [200] |
| Telomere maintenance (TERT 40% [184]) | Antisense nucleotides targeting telomerase in preclinical testing [201] | |
| Targeting of altered cellular pathways in tumors (based on genomic alterations and gene expression) | Chromatin remodeling (ARID1A < 20% [6,181,182], ARID2 < 10% [196,202], MLL complex < 15% [181,182]) | Resminostat, vorinostat, belinostat (HDAC inhibitors) in CTs [203] |
| PIK3-AKT-mTOR (PTEN < 5% [182], PIK3CA < 5% [6,196], RPS6KA3 ~10% [6,189]) | Everolimus, sirolimus (mTOR) [174] in CTs for HCC, MK-2206 (AKT1) [204] in CTs for solid cancers | |
| IGF-signaling (phosphorylation of IGF-1R 20% [188]) | Multiple CTs for HCC: Cixutumumab (IGF-1R ab) ± sorafenib, OSI-906 (IGF-1R inhibitor) [205] | |
| JAK-STAT signaling (JAK1 9%,Il-6R [181]) | Ruxolitinib (JAK1/2) used for hematological malignancies [206] | |
| TP53 pathway/Cell cycle (TP [66] ~30% [6,174,183], RB < 10% [189]) | Preclinical development | |
| Oxidative stress (NFE2L2 < 10% [6]) | ||
| Targeting tumor subtypes based on gene expression signatures | Hepatoblast/hepatocyte signature [176] Metastasis gene signature [36] Survival gene signature [179] | Preclinical testing. HCC cell lines with hepatoblast signature respond to dasatinib (Src/Abl inhibitor) [194] |
| Targeting tumors with immunotherapy | High expression of glypican-3 [207,208,209] Immune checkpoint blockade [210] | Some Glypican-3 antibodies in CTs [211]; JX-594 (oncolytic virus) targeting HCC cells in CT [212,213], anti-CTLA-4/PD-1 (immune checkpoint inhibitors ) in CTs [210] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGlynn, K.A.; London, W.T. The global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Present and future. Clin. Liver Dis. 2011, 15, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Boix, L.; Sala, M.; Llovet, J.M. Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Burroughs, A.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2003, 362, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, C.; Amaddeo, G.; Imbeaud, S.; Ladeiro, Y.; Pelletier, L.; Maad, I.B.; Calderaro, J.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Letexier, M.; Degos, F.; et al. Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.; Roayaie, S.; Konstadoulakis, M. Strategies for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2007, 4, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1208–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morise, Z.; Kawabe, N.; Tomishige, H.; Nagata, H.; Kawase, J.; Arakawa, S.; Yoshida, R.; Isetani, M. Recent advances in liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Surg. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Marrero, J.A.; Rudolph, L.; Reddy, R.K. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghiti, J.; Kianmanesh, R. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB Oxf. 2005, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziser, A.; Plevak, D.J.; Wiesner, R.H.; Rakela, J.; Offord, K.P.; Brown, D.L. Morbidity and mortality in cirrhotic patients undergoing anesthesia and surgery. Anesthesiology 1999, 90, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadon, M.; Costa, G.; Cimino, M.; Procopio, F.; del Fabbro, D.; Palmisano, A.; Torzilli, G. Safe hepatectomy selection criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A validation of 336 consecutive hepatectomies. The BILCHE score. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Castells, A.; Bosch, J.; Feu, F.; Fuster, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Visa, J.; Bru, C.; Rodés, J. Surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: Prognostic value of preoperative portal pressure. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuuchi, M.; Thai, B.L.; Takayasu, K.; Takayama, T.; Kosuge, T.; Gunvén, P.; Yamazaki, S.; Hasegawa, H.; Ozaki, H. Preoperative portal embolization to increase safety of major hepatectomy for hilar bile duct carcinoma: A preliminary report. Surgery 1990, 107, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makuuchi, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Yamazaki, S. Ultrasonically guided subsegmentectomy. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1985, 161, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, K.; Kokudo, N.; Imamura, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Aoki, T.; Minagawa, M.; Sano, K.; Sugawara, Y.; Takayama, T.; Makuuchi, M. Prognostic impact of anatomic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakai, T.; Shirai, Y.; Sakata, J.; Kaneko, K.; Cruz, P.V.; Akazawa, K.; Hatakeyama, K. Anatomic resection independently improves long-term survival in patients with T1-T2 hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirnezami, R.; Mirnezami, A.H.; Chandrakumaran, K.; Abu Hilal, M.; Pearce, N.W.; Primrose, J.N.; Sutcliffe, R.P. Short- and long-term outcomes after laparoscopic and open hepatic resection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. HPB Oxf. 2011, 13, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigano, L.; Laurent, A.; Tayar, C.; Tomatis, M.; Ponti, A.; Cherqui, D. The learning curve in laparoscopic liver resection: improved feasibility and reproducibility. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikai, I.; Arii, S.; Okazaki, M.; Okita, K.; Omata, M.; Kojiro, M.; Takayasu, K.; Nakanuma, Y.; Makuuchi, M.; Matsuyama, Y.; et al. Report of the 17th Nationwide Follow-up Survey of Primary Liver Cancer in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, 676–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belghiti, J.; Panis, Y.; Farges, O.; Benhamou, J.P.; Fekete, F. Intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma complicating cirrhosis. Ann. Surg. 1991, 214, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.D.; Schwartz, M.; Mandeli, J.; Sung, M. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Review of the randomised clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, E.C.; Lo, C.M.; Fan, S.T.; Liu, C.L.; Wong, J. Postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Surg. 1998, 133, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Arii, S.; Sugahara, K.; Tobe, T. Adjuvant oral chemotherapy to prevent recurrence after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 1996, 83, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.P.; Lai, E.C.; Li, A.J.; Fu, S.Y.; Zhou, J.P.; Pan, Z.Y.; Lau, W.Y.; Wu, M.C. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of preoperative transarterial chemoembolization for resectable large hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2009, 249, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, T.; Yamanoi, A.; el Assal, O.N.; Kohno, H.; Nagasue, N. Adjuvant chemotherapy after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma causes deterioration of long-term prognosis in cirrhotic patients: metaanalysis of three randomized controlled trials. Cancer 2001, 91, 2378–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.Y.; Lai, E.C.; Leung, T.W.; Yu, S.C. Adjuvant intra-arterial iodine-131-labeled lipiodol for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial-update on 5-year and 10-year survival. Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.Y.; Lai, E.C.; Leung, T.W.; Yu, S.C. Adjuvant intra-arterial iodine-131-labelled lipiodol for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomised trial. Lancet 1999, 353, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, T.; Sekine, T.; Makuuchi, M.; Yamasaki, S.; Kosuge, T.; Yamamoto, J.; Shimada, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S.; Ohashi, Y.; et al. Adoptive immunotherapy to lower postsurgical recurrence rates of hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised trial. Lancet 2000, 356, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, Y.; Moriwaki, H.; Saito, A. Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1046–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Arase, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, F.; Tsubota, A.; Chayama, K.; Murashima, N.; Kumada, H. Interferon beta prevents recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after complete resection or ablation of the primary tumor-A prospective randomized study of hepatitis C virus-related liver cancer. Hepatology 2000, 32, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.B.; Jaffe, D.; Choti, M.M.; Belghiti, J.; Curley, S.; Fong, Y.; Gores, G.; Kerlan, R.; Merle, P.; O’Neil, B.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Consensus recommendations of the National Cancer Institute Clinical Trials Planning Meeting. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3994–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2012, 379, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A.; Hoshida, Y.; Battiston, C.; Tovar, V.; Sia, D.; Alsinet, C.; Cornella, H.; Liberzon, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Kumada, H.; et al. Combining clinical, pathology, and gene expression data to predict recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roessler, S.; Jia, H.L.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Ye, Q.H.; Lee, J.S.; Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Sun, Z.; Tang, Z.Y.; Qin, L.X.; et al. A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10202–10212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Montalto, F.; Ammatuna, M.; Morabito, A.; Gennari, L. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roayaie, S.; Schwartz, J.D.; Sung, M.W.; Emre, S.H.; Miller, C.M.; Gondolesi, G.E.; Krieger, N.R.; Schwartz, M.E. Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplant: Patterns and prognosis. Liver Transpl. 2004, 10, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Bhoori, S.; Sposito, C.; Bongini, M.; Langer, M.; Miceli, R.; Mariani, L. Milan criteria in liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an evidence-based analysis of 15 years of experience. Liver Transpl. 2011, 17 (Suppl. S2), S44–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.Y.; Bass, N.M.; Nikolai, B.; Davern, T.J.; Kerlan, R.; Wu, V.; Ascher, N.L.; Roberts, J.P. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of survival according to the intention-to-treat principle and dropout from the waiting list. Liver Transpl. 2002, 8, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, M.; Altimari, A.; Ravaioli, M.; Gruppioni, E.; Gabusi, E.; Corti, B.; Vivarelli, M.; Bringuier, P.P.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Grigioni, W.F.; et al. Predictive value of biological markers for hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with orthotopic liver transplantation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhu, A.; Jia, H.L.; Forgues, M.; Liu, C.G.; Goldstein, D.; Lam, A.; Zanetti, K.A.; Ye, Q.H.; Qin, L.X.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Identification of metastasis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, F.; Hatano, E.; Kitamura, K.; Myomoto, A.; Fujiwara, T.; Takizawa, S.; Tsuchiya, S.; Tsujimoto, G.; Uemoto, S.; Shimizu, K.; et al. MicroRNA profile predicts recurrence after resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan Criteria. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nault, J.C.; de Reyniès, A.; Villanueva, A.; Calderaro, J.; Rebouissou, S.; Couchy, G.; Decaens, T.; Franco, D.; Imbeaud, S.; Rousseau, F.; et al. A hepatocellular carcinoma 5-gene score associated with survival of patients after liver resection. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiki, M.; Takada, Y.; Ogura, Y.; Oike, F.; Kaido, T.; Teramukai, S.; Uemoto, S. Significance of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin in selection criteria for living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 2362–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agopian, V.G.; Harlander-Locke, M.; Zarrinpar, A.; Kaldas, F.M.; Farmer, D.G.; Yersiz, H.; Finn, R.S.; Tong, M.; Hiatt, J.R.; Busuttil, R.W. A novel prognostic nomogram accurately predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation: Analysis of 865 consecutive liver transplant recipients. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2015, 220, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, S.; McTigue, M.; Finn, R.S.; Busuttil, W.R. Sorafenib as adjuvant therapy for high-risk hepatocellular carcinoma in liver transplant recipients: Feasibility and efficacy. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2010, 8, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.Y.; Ferrell, L.; Bass1, N.M.; Atson, J.J.; Bacchetti, P.; Venook, A.; Ascher, N.L.; Roberts, J.P. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Expansion of the tumor size limits does not adversely impact survival. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, J.P.; Vardanian, A.; Benjamin, E.; Watson, M.; Farmer, D.G.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Lipshutz, G.; Yersiz, H.; Lu, D.S.; Lassman, C.; et al. Liver transplantation criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma should be expanded: A 22-year experience with 467 patients at UCLA. Ann. Surg. 2007, 246, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todo, S.; Furukawa, H. Living donor liver transplantation for adult patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Experience in Japan. Ann Surg 2004, 240, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livraghi, T.; Giorgio, A.; Marin, G.; Salmi, A.; de Sio, I.; Bolondi, L.; Pompili, M.; Brunello, F.; Lazzaroni, S.; Torzilli, G.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis in 746 patients: Long-term results of percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 1995, 197, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, M.; Llovet, J.M.; Vilana, R.; Bianchi, L.; Solé, M.; Ayuso, C.; Brú, C.; Bruix, J.; Barcelona Clínic Liver Cancer Group. Initial response to percutaneous ablation predicts survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.A.; Allgaier, H.P.; Cioni, D.; Olschewski, M.; Deibert, P.; Crocetti, L.; Frings, H.; Laubenberger, J.; Zuber, I.; Blum, H.E.; et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation vs. percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 2003, 228, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.M.; Lin, C.J.; Lin, C.C.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.C. Radiofrequency ablation improves prognosis compared with ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma < or =4 cm. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brunello, F.; Veltri, A.; Carucci, P.; Pagano, E.; Ciccone, G.; Moretto, P.; Sacchetto, P.; Gandini, G.; Rizzetto, M. Radiofrequency ablation vs. ethanol injection for early hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized controlled trial. Scand J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padma, S.; Martinie, J.B.; Iannitti, A.D. Liver tumor ablation: Percutaneous and open approaches. J. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 100, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Iimuro, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Maetani, Y.; Ametani, F.; Itoh, K.; Konishi, J. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy. Radiology 2002, 223, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teratani, T.; Yoshida, H.; Shiina, S.; Obi, S.; Sato, S.; Tateishi, R.; Mine, N.; Kondo, Y.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in so-called high-risk locations. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livraghi, T.; Solbiati, L.; Meloni, M.F.; Gazelle, G.S.; Halpern, E.F.; Goldberg, S.N. Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology 2003, 226, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, R.T.; Fan, S.T.; Tsang, F.H.; Wong, J. Locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: A critical review from the surgeon’s perspective. Ann. Surg. 2002, 235, 466–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.Q. Advances in clinical application of cryoablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic liver tumor. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpentier, K.P. Irreversible electroporation for the ablation of liver tumors: are we there yet? Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacella, C.M.; Francica, G.; di Costanzo, G.G. Laser ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mearini, L. High intensity focused ultrasound, liver disease and bridging therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7494–7499. [Google Scholar]
- European Association for the Study of The Liver; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar]
- Sangro, B.; Inarrairaegui, M.; Bilbao, J.I. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangro, B.; Carpanese, L.; Cianni, R.; Golfieri, R.; Gasparini, D.; Ezziddin, S.; Paprottka, P.M.; Fiore, F.; van Buskirk, M.; Bilbao, J.I.; et al. Survival after yttrium-90 resin microsphere radioembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma across Barcelona clinic liver cancer stages: A European evaluation. Hepatology 2011, 54, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, C.; Cappelli, A.; Pettinato, C.; Golfieri, R. Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 microspheres in hepatocellular carcinoma: Role and perspectives. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, G.; Ducreux, M.; Gay, F.; Luboinski, M.; Hagège, H.; Dao, T.; van Steenbergen, W.; Buffet, C.; Rougier, P.; Adler, M.; et al. Treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with lipiodol chemoembolization: A multicenter randomized trial. Groupe CHC. J. Hepatol. 1998, 29, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Montaña, X.; Planas, R.; Coll, S.; Aponte, J.; Ayuso, C.; Sala, M.; Muchart, J.; Solà, R.; et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation vs. symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammà, C.; Schepis, F.; Orlando, A.; Albanese, M.; Shahied, L.; Trevisani, F.; Andreone, P.; Craxì, A.; Cottone, M. Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Radiology 2002, 224, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Sala, M.; Llovet, J.M. Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S179–S188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammer, J.; Malagari, K.; Vogl, T.; Pilleul, F.; Denys, A.; Watkinson, A.; Pitton, M.; Sergent, G.; Pfammatter, T.; Terraz SLlovet, J.M.; et al. Prospective randomized study of doxorubicin-eluting-bead embolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of the PRECISION V study. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 33, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik, T.M.; Reyes, D.K.; Cosgrove, D.; Kamel, I.R.; Bhagat, N.; Geschwind, J.F. Phase II trial of sorafenib combined with concurrent transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3960–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K. TACE and sorafenib: a good marriage? J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3949–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Printz, C. Clinical trials of note. Sorafenib as adjuvant treatment in the prevention of disease recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (STORM). Cancer 2009, 115, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, A.I.; Waked, I. Recent advances in multidisciplinary management of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worns, M.A.; Galle, P.R. HCC therapies—Lessons learned. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Hernandez-Gea, V. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Reasons for phase III failure and novel perspectives on trial design. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M. Focal gains of VEGFA: Candidate predictors of sorafenib response in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki, S.; Starzl, T.E.; Sheahan, D.G.; Yokoyama, I.; Demetris, A.J.; Todo, S.; Tzakis, A.G.; van Thiel, D.H.; Carr, B.; Selby, R. Hepatic resection vs. transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 1991, 214, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringe, B.; Pichlmayr, R.; Wittekind, C.; Tusch, G. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Experience with liver resection and transplantation in 198 patients. World J. Surg. 1991, 15, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roayaie, K.; Feng, S. Allocation policy for hepatocellular carcinoma in the MELD era: Room for improvement? Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, S36–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roayaie, S.; Frischer, J.S.; Emre, S.H.; Fishbein, T.M.; Sheiner, P.A.; Sung, M.; Miller, C.M.; Schwartz, M.E. Long-term results with multimodal adjuvant therapy and liver transplantation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas larger than 5 centimeters. Ann. Surg. 2002, 235, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaca, N.; Davis, G.L.; Goldstein, R.M.; Jennings, L.W.; Klintmalm, B.G. Expanded criteria for liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A report from the International Registry of Hepatic Tumors in Liver Transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Perkins, J.D.; Carithers, R.L., Jr. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Impact of the MELD allocation system and predictors of survival. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.Y. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Beyond the Milan criteria. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Fuster, J.; Llovet, J.M. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Foucault pendulum vs. evidence-based decision. Liver Transpl. 2003, 9, 700–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, M.L.; Vijan, S.; Marrero, J.A. A novel model measuring the harm of transplanting hepatocellular carcinoma exceeding Milan criteria. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavien, P.A.; Lesurtel, M.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Gores, G.J.; Langer, B.; Perrier, A.; OLT for HCC Consensus Group. Recommendations for liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: An international consensus conference report. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Mas, X.; Aponte, J.J.; Fuster, J.; Navasa, M.; Christensen, E.; Rodés, J.; Bruix, J. Cost effectiveness of adjuvant therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma during the waiting list for liver transplantation. Gut 2002, 50, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halazun, K.J.; Patzer, R.E.; Rana, A.A.; Verna, E.C.; Griesemer, A.D.; Parsons, R.F.; Samstein, B.; Guarrera, J.V.; Kato, T.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; et al. Standing the test of time: Outcomes of a decade of prioritizing patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, results of the UNOS natural geographic experiment. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belghiti, J.; Cortes, A.; Abdalla, E.K.; Régimbeau, J.M.; Prakash, K.; Durand, F.; Sommacale, D.; Dondero, F.; Lesurtel, M.; Sauvanet, A.; et al. Resection prior to liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2003, 238, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, S.G.; Joh, J.W.; Suh, K.S.; Kim, D.G. Liver transplantation for adult patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea: Comparison between cadaveric donor and living donor liver transplantations. Liver Transpl. 2005, 11, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broering, D.C.; Wilms, C.; Bok, P.; Fischer, L.; Mueller, L.; Hillert, C.; Lenk, C.; Kim, J.S.; Sterneck, M.; Schulz, K.H.; et al. Evolution of donor morbidity in living related liver transplantation: a single-center analysis of 165 cases. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiropoulos, G.C.; Molmenti, E.P.; Lösch, C.; Beckebaum, S.; Broelsch, C.E.; Lang, H. Meta-analysis of tumor recurrence after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma based on 1,198 cases. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2007, 12, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pokorny, H.; Gnant, M.; Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S.; Gollackner, B.; Steiner, B.; Steger, G.; Steininger, R.; Mühlbacher, F. Does additional doxorubicin chemotherapy improve outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by liver transplantation? Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderdahl, G.; Bäckman, L.; Isoniemi, H.; Cahlin, C.; Höckerstedt, K.; Broomé, U.; Mäkisalo, H.; Friman, S.; Ericzon, B.G. A prospective, randomized, multi-centre trial of systemic adjuvant chemotherapy vs. no additional treatment in liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Transpl. Int. 2006, 19, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, M.J.; Klintmalm, G.B.; Polter, D.; Husberg, B.S.; Mennel, R.G.; Ramsay, M.A.; Flemens, E.R.; Goldstein, R.M. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A pilot study in 20 patients. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujiki, M.; Aucejo, F.; Kim, R. Adjuvant treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma after orthotopic liver transplantation: Do we really need this? Clin. Transplant. 2013, 27, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guba, M.; Graeb, C.; Jauch, K.W.; Geissler, E.K. Pro- and anti-cancer effects of immunosuppressive agents used in organ transplantation. Transplantation 2004, 77, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guba, M.; von Breitenbuch, P.; Steinbauer, M.; Koehl, G.; Flegel, S.; Hornung, M.; Bruns, C.J.; Zuelke, C.; Farkas, S.; Anthuber, M.; et al. Rapamycin inhibits primary and metastatic tumor growth by antiangiogenesis: Involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, F.L.; Hojo, M.; Maluccio, M.; Yamaji, K.; Suthanthiran, M. Rapamycin blocks tumor progression: Unlinking immunosuppression from antitumor efficacy. Transplantation 2002, 73, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneteman, N.M.; Oberholzer, J.; Al Saghier, M.; Meeberg, G.A.; Blitz, M.; Ma, M.M.; Wong, W.W.; Gutfreund, K.; Mason, A.L.; Jewell, L.D.; et al. Sirolimus-based immunosuppression for liver transplantation in the presence of extended criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl. 2004, 10, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toso, C.; Meeberg, G.A.; Bigam, D.L.; Oberholzer, J.; Shapiro, A.M.; Gutfreund, K.; Ma, M.M.; Mason, A.L.; Wong, W.W.; Bain, V.G.; et al. De novo sirolimus-based immunosuppression after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Long-term outcomes and side effects. Transplantation 2007, 83, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, M.A.; Trotter, J.F.; Wachs, M.; Bak, T.; Campsen, J.; Skibba, A.; Kam, I. Sirolimus-based immunosuppression following liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl. 2008, 14, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toso, C.; Merani, S.; Bigam, D.L.; Shapiro, A.M.; Kneteman, N.M. Sirolimus-based immunosuppression is associated with increased survival after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanik, E.; Chinnakotla, S.; Israni, A.; Snyder, J.; Gustafson, S.; Engels, E. Associations between sirolimus use and outcomes after liver transplant for hepatocellular carcinoma. In Proceedings of 2015 American Transplant Congress, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2–6, May, 2015.
- Cheng, A.L.; Kang, Y.K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salizzoni, M.; Romagnoli, R.; Lupo, F.; David, E.; Mirabella, S.; Cerutti, E.; Ottobrelli, A. Microscopic vascular invasion detected by anti-CD34 immunohistochemistry as a predictor of recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Transplantation 2003, 76, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Llovet, J.M.; Miceli, R.; Bhoori, S.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L.; Camerini, T.; Roayaie, S.; Schwartz, M.E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Predicting survival after liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: A retrospective, exploratory analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadaa, M.; Yonemurab, Y.; Ijichib, H.; Haradab, N.; Shiotanib, S.; Ninomiyab, M.; Terashib, T.; Yoshizumib, T.; Soejimab, Y.; Maeharab, Y. Living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A special reference to a preoperative des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin value. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parfitt, J.R.; Marotta, P.; Alghamdi, M.; Wall, W.; Khakhar, A.; Suskin, N.G.; Quan, D.; McAllister, V.; Ghent, C.; Levstik, M.; et al. Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after transplantation: Use of a pathological score on explanted livers to predict recurrence. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R. Loco-regional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 52, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, K.; Yoshioka, H.; Ito, S.; Fujiwara, K. Prospective randomized controlled trial comparing percutaneous acetic acid injection and percutaneous ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1998, 27, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoppmeyer, K.; Weis, S.; Mössner, J.; Fleig, W.E. Percutaneous ethanol injection or percutaneous acetic acid injection for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Bartolozzi, C.; Caramella, D.; Paolicchi, A.; Carrai, M.; Maltinti, G.; Capria, A.; Tafi, A.; Conte, P.F.; Bevilacqua, G. Treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma with percutaneous ethanol injection. Analysis of prognostic factors in 105 Western patients. Cancer 1995, 76, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilana, R.; Bruix, J.; Bru, C.; Ayuso, C.; Solé, M.; Rodés, J. Tumor size determines the efficacy of percutaneous ethanol injection for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1992, 16, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.M.; Lin, C.J.; Lin, C.C.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.C. Randomised controlled trial comparing percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and percutaneous acetic acid injection to treat hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Gut 2005, 54, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiina, S.; Teratani, T.; Obi, S.; Sato, S.; Tateishi, R.; Fujishima, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Koike, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kawabe, T.; et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouza, C.; Lopez-Cuadrado, T.; Alcazar, R.; Saz-Parkinson, Z.; Amate, J.M. Meta-analysis of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation vs. ethanol injection in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.S.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Mahvi, D.M. Hepatic microwave ablation with multiple antennae results in synergistically larger zones of coagulation necrosis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 10, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Shen, Q.; Cheng, W.; Qian, G.J. Therapeutic efficacy of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation vs. microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.J.; Farshid, P.; Naguib, N.N.; Zangos, S.; Bodelle, B.; Paul, J.; Mbalisike, E.C.; Beeres, M.; Nour-Eldin, N.E. Ablation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: A comparative study between radiofrequency and microwave ablation. Abdom. Imaging. 2015, 40, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.X.; Cheng, Z.L.; Wu, P.P.; Sheng, Y.H.; Qu, X.J.; Lu, W.; Zhao, C.G.; Qian, G.J. Clinical outcome of medium-sized hepatocellular carcinoma treated with microwave ablation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2997–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medhat, E.; Abdel Aziz, A.; Nabeel, M.; Elbaz, T.; Zakaria, Z.; Shousha, H.; Amer, A.; Fouad Fathalah, W.; Maher, R.; Musa, S. Value of Microwave Ablation in Treatment of large lesions of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 16, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.C.; Lai, H.S.; Shih, T.T.; Wu, C.H.; Huang, K.W. Initial institutional experience of uncooled single-antenna microwave ablation for large hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Radiol. 2015, 70, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Percutaneous microwave ablation of larger hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groupe d’Etude et de Traitement du Carcinome Hépatocellulaire. A comparison of lipiodol chemoembolization and conservative treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.M.; Ngan, H.; Tso, W.K.; Liu, C.L.; Lam, C.M.; Poon, R.T.; Fan, S.T.; Wong, J. Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003, 37, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, D.; Wenger, J.J.; Bergier, J.M.; Doffoel, M.; Bockel, R. Transcatheter oily chemoembolization in the management of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Results of a Western comparative study in 60 patients. Hepatology 1991, 13, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; Petruzzi, P.; Crocetti, L. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 30, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xu, H.; Gao, Z.Q.; Ning, H.F.; Sun, Y.Q.; Cao, G.W. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Acta Radiol. 2008, 49, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.; Wu, J.K.; Huang, C.M.; Huang, D.Y.; Cheng, S.H.; Lin, Y.M.; Jian, J.J.; Yang, P.S.; Chuang, V.P.; Huang, A.T. Radiation-induced liver disease after radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical manifestation and dosimetric description. Radiother. Oncol. 2002, 63, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, R.J.; Kulik, L.M.; Riaz, A.; Senthilnathan, S.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Ryu, R.K.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Sato, K.T.; Baker, T.; Miller, F.H.; et al. A comparative analysis of transarterial downstaging for hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization vs. radioembolization. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, B.I.; Kondragunta, V.; Buch, S.C.; Branch, R.A. Therapeutic equivalence in survival for hepatic arterial chemoembolization and yttrium 90 microsphere treatments in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A two-cohort study. Cancer 2010, 116, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, R.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Kulik, L.; Wang, E.; Riaz, A.; Ryu, R.K.; Sato, K.T.; Gupta, R.; Nikolaidis, P.; Miller, F.H.; et al. Radioembolization results in longer time-to-progression and reduced toxicity compared with chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ei, S.; Hibi, T.; Tanabe, M.; Itano, O.; Shinoda, M.; Kitago, M.; Abe, Y.; Yagi, H.; Okabayashi, K.; Sugiyama, D.; et al. Cryoablation provides superior local control of primary hepatocellular carcinomas of >2 cm compared with radiofrequency ablation and microwave coagulation therapy: An underestimated tool in the toolbox. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Hu, K.; Xie, H.; Hu, K.Q.; Bai, W.; Dong, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Multicenter randomized controlled trial of percutaneous cryoablation vs. radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.W.; Loh, C.T.; Kee, S.T. Imaging guided percutaneous irreversible electroporation: Ultrasound and immunohistological correlation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 6, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpentier, K.P.; Wolf, F.; Noble, L.; Winn, B.; Resnick, M.; Dupuy, D.E. Irreversible electroporation of the liver and liver hilum in swine. HPB Oxf. 2011, 13, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Costanzo, G.G.; Tortora, R.; D’Adamo, G.; de Luca, M.; Lampasi, F.; Addario, L.; Galeota Lanza, A.; Picciotto, F.P.; Tartaglione, M.T.; Cordone, G.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation vs. laser ablation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: A randomized trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chok, K.S.; Cheung, T.T.; Lo, R.C.; Chu, F.S.; Tsang, S.H.; Chan, A.C.; Sharr, W.W.; Fung, J.Y.; Dai, W.C.; Chan, S.C.; et al. Pilot study of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation as a bridging therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma patients wait-listed for liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2014, 20, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavaglia, C.; Mancuso, A.; Foschi, A.; Rampoldi, A. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Is it time to abandon standard ablative percutaneous treatments? Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2013, 2, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.K.; Poon, R.T.; Chan, S.C.; Chok, K.S.; Cheung, T.T.; Tung, H.; Chu, F.; Tso, W.K.; Yu, W.C.; Lo, C.M.; et al. High-intensity focused ultrasound for hepatocellular carcinoma: A single-center experience. Ann. Surg. 2011, 253, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, R.; Ellis, S.; Hayes, D.; Narayanan, G.; Martin, C.R., 2nd. Safety and early efficacy of irreversible electroporation for hepatic tumors in proximity to vital structures. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacella, C.M.; Bizzarri, G.; Magnolfi, F.; Cecconi, P.; Caspani, B.; Anelli, V.; Bianchini, A.; Valle, D.; Pacella, S.; Manenti, G.; et al. Laser thermal ablation in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma: Results in 74 patients. Radiology 2001, 221, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, P.; Chen, X.; Bie, P. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) plus sorafenib versus TACE for intermediate or advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.L.; Kang, Y.K.; Lin, D.Y.; Park, J.W.; Kudo, M.; Qin, S.; Chung, H.C.; Song, X.; Xu, J.; Poggi, G.; et al. Sunitinib vs. sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular cancer: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4067–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cainap, C.; Qin, S.; Huang, W.T.; Chung, I.J.; Pan, H.; Cheng, Y.; Kudo, M.; Kang, Y.K.; Chen, P.J.; Toh, H.C.; et al. Linifanib versus Sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Qin, S.; Park, J.W.; Poon, R.T.P.; Raoul, J.L.; Phillip, P.A.; Hsu, C.H.; Hu, T.H.; Heo, J.; Xu, J.; Lu, L.; et al. Brivanib vs. sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with unresectable, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from the randomized phase III BRISK-FL study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Rosmorduc, O.; Evans, T.R.J.; Ross, P.J.; Santoro, A.; Carrilho, F.J.; Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Thuluvath, P.J.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. SEARCH: A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of sorafenib plus erlotinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Decaens, T.; Raoul, J.; Boucher, E.; Kudo, M.; Chang, C.; Kang, Y.K.; Assenat, E.; Lim, H.Y.; Boige, V.; et al. Brivanib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who were intolerant to sorafenib or for whom sorafenib failed: Results from the randomized phase III BRISK-PS study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kudo, M.; Assenat, E.; Cattan, S.; Kang, Y.K.; Lim, H.Y.; Poon, R.T.; Blanc, J.F.; Vogel, A.; Chen, C.L.; et al. Effect of everolimus on survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after failure of sorafenib: The EVOLVE-1 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 312, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Rimassa, L.; Borbath, I.; Daniele, B.; Salvagni, S.; van Laethem, J.L.; van Vlierberghe, H.; Trojan, J.; Kolligs, F.T.; Weiss, A.; et al. Tivantinib for second-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.J.; Cleary, S.P.; Dawson, L.A. Localized and systemic approaches to treating hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arao, T.; Ueshima, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Nagai, T.; Kimura, H.; Hagiwara, S.; Sakurai, T.; Haji, S.; Kanazawa, A.; Hidaka, H.; et al. FGF3/FGF4 amplification and multiple lung metastases in responders to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ho, D.W.; Lee, N.P.; Sun, S.; Lam, B.; Wong, K.F.; Yi, X.; Lau, G.K.; Ng, E.W.; Poon, T.C.; et al. Enhanced detection of early hepatocellular carcinoma by serum SELDI-TOF proteomic signature combined with alpha-fetoprotein marker. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 2518–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colli, A.; Fraquelli, M.; Casazza, G.; Massironi, S.; Colucci, A.; Conte, D.; Duca, P. Accuracy of ultrasonography, spiral CT, magnetic resonance, and alpha-fetoprotein in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Dai, W.; Wang, F.; Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, K.; Cheng, P.; et al. Diagnostic performance of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangkijvanich, P.; Chanmee, T.; Komtong, S.; Mahachai, V.; Wisedopas, N.; Pothacharoen, P.; Kongtawelert, P. Diagnostic role of serum glypican-3 in differentiating hepatocellular carcinoma from non-malignant chronic liver disease and other liver cancers. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Mallory, T.; Satomura, S. AFP-L3: A new generation of tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 313, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardina, M.G.; Matarazzo, M.; Varriale, A.; Morante, R.; Napoli, A.; Martino, R. Serum alpha-l-fucosidase. A useful marker in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 1992, 70, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.R.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, N.; Niu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Serum DKK1 as a protein biomarker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A large-scale, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Plymoth, A.; Ge, S.; Feng, Z.; Rosen, H.R.; Sangrajrang, S.; Hainaut, P.; Marrero, J.A.; Beretta, L. Identification of osteopontin as a novel marker for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012, 55, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, T.; Shen, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Z.; Chu, W.; Lv, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Fan, J.; Qin, W. Diagnostic values of alpha-fetoprotein, dickkopf-1, and osteopontin for hepatocellular carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramantieri, L.; Fornari, F.; Callegari, E.; Sabbioni, S.; Lanza, G.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Negrini, M. MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2189–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Cao, M.; Xie, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Zheng, S.; Li, L. Metabonomic profiles discriminate hepatocellular carcinoma from liver cirrhosis by ultraperformance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimhofer, T.; Fye, H.; Taylor-Robinson, S.; Thursz, M.; Holmes, E. Proteomic and metabonomic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive review. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1141–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinyol, R.; Nault, J.C.; Quetglas, I.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Llovet, J.M. Molecular profiling of liver tumors: Classification and clinical translation for decision making. Semin. Liver Dis. 2014, 34, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, N.; Ye, Q.H.; Qin, L.X.; Zhang, B.H.; Liu, Y.K.; Tang, Z.Y. Circulating DNA level is negatively associated with the long-term survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 3911–3914. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Chu, I.S.; Heo, J.; Calvisi, D.F.; Sun, Z.; Roskams, T.; Durnez, A.; Demetris, A.J.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology 2004, 40, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, S.; Takemasa, I.; Nagano, H.; Kittaka, N.; Noda, T.; Wada, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Marubashi, S.; Takeda, Y.; Umeshita, K.; et al. Molecular prediction of early recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Ohkubo, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Miyagawa, S.; Sugawara, Y.; Minagawa, M.; Takayama, T.; Kawasaki, S.; et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Peix, J.; Chiang, D.Y.; Camargo, A.; Gupta, S.; Moore, J.; Wrobel, M.J.; Lerner, J.; et al. Gene expression in fixed tissues and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Ye, Q.H.; Jia, H.L.; He, P.; Zanetti, K.A.; Kammula, U.S.; Chen, Y.; Qin, L.X.; Tang, Z.Y.; et al. Prediction of venous metastases, recurrence, and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma based on a unique immune response signature of the liver microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, K.; Imbeaud, S.; Letouzé, E.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Calderaro, J.; Rebouissou, S.; Couchy, G.; Meiller, C.; Shinde, J.; Soysouvanh, F.; et al. Exome sequencing of hepatocellular carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, A.; Totoki, Y.; Abe, T.; Boroevich, K.A.; Hosoda, F.; Nguyen, H.H.; Aoki, M.; Hosono, N.; Kubo, M.; Miya, F.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of liver cancers identifies etiological influences on mutation patterns and recurrent mutations in chromatin regulators. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleary, S.P.; Jeck, W.R.; Zhao, X.; Chen, K.; Selitsky, S.R.; Savich, G.L.; Tan, T.X.; Wu, M.C.; Getz, G.; Lawrence, M.S.; et al. Identification of driver genes in hepatocellular carcinoma by exome sequencing. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nault, J.C.; Mallet, M.; Pilati, C.; Calderaro, J.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Laurent, C.; Laurent, A.; Cherqui, D.; Balabaud, C.; Zucman-Rossi, J. High frequency of telomerase reverse-transcriptase promoter somatic mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma and preneoplastic lesions. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawey, E.T.; Chanrion, M.; Cai, C.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zender, L.; Zhao, A.; Busuttil, R.W.; Yee, H.; Stein, L.; et al. Identification of a therapeutic strategy targeting amplified FGF19 in liver cancer by Oncogenomic screening. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Hoshida, Y.; Peix, J.; Newell, P.; Minguez, B.; LeBlanc, A.C.; Donovan, D.J.; Thung, S.N.; Solé, M.; et al. Focal gains of VEGFA and molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6779–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Elella, A.; Gramlich, T.; Fritsch, C.; Gansler, T. c-myc amplification in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts unfavorable prognosis. Mod. Pathol. 1996, 9, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tovar, V.; Alsinet, C.; Villanueva, A.; Hoshida, Y.; Chiang, D.Y.; Solé, M.; Thung, S.; Moyano, S.; Toffanin, S.; Mínguez, B.; et al. IGF activation in a molecular subclass of hepatocellular carcinoma and pre-clinical efficacy of IGF-1R blockage. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.M.; Jang, S.J.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, D.; Hong, S.M.; Sung, C.O.; Baek, D.; Haq, F.; Ansari, A.A.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Genomic portrait of resectable hepatocellular carcinomas: Implications of RB1 and FGF19 aberrations for patient stratification. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, H.; Sanderson, N.D.; Nagy, P.; Marino, P.A.; Merlino, G.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Transgenic mouse model for synergistic effects of nuclear oncogenes and growth factors in tumorigenesis: Interaction of c-myc and transforming growth factor alpha in hepatic oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harada, N.; Oshima, H.; Katoh, M.; Tamai, Y.; Oshima, M.; Taketo, M.M. Hepatocarcinogenesis in mice with beta-catenin and Ha-ras gene mutations. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ferrell, L.D.; Faouzi, S.; Maher, J.J.; Bishop, J.M. Activation of the Met receptor by cell attachment induces and sustains hepatocellular carcinomas in transgenic mice. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deane, N.G.; Parker, M.A.; Aramandla, R.; Diehl, L.; Lee, W.J.; Washington, M.K.; Nanney, L.B.; Shyr, Y.; Beauchamp, R.D. Hepatocellular carcinoma results from chronic cyclin D1 overexpression in transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5389–5395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Aleshin, A.; Dering, J.; Yang, P.; Ginther, C.; Desai, A.; Zhao, D.; von Euw, E.; Busuttil, R.W.; Slamon, D.J. Molecular subtype and response to dasatinib, an Src/Abl small molecule kinase inhibitor, in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines in vitro. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Heo, J.; Libbrecht, L.; Chu, I.S.; Kaposi-Novak, P.; Calvisi, D.F.; Mikaelyan, A.; Roberts, L.R.; Demetris, A.J.; Sun, Z.; et al. A novel prognostic subtype of human hepatocellular carcinoma derived from hepatic progenitor cells. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A.; Llovet, J.M. Liver cancer in 2013: Mutational landscape of HCC—The end of the beginning. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyault, S.; Rickman, D.S.; de Reyniès, A.; Balabaud, C.; Rebouissou, S.; Jeannot, E.; Hérault, A.; Saric, J.; Belghiti, J.; Franco, D.; et al. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology 2007, 45, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Aburatani, H. Exploration of liver cancer genomes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Coste, A.; Romagnolo, B.; Billuart, P.; Renard, C.A.; Buendia, M.A.; Soubrane, O.; Fabre, M.; Chelly, J.; Beldjord, C.; Kahn, A.; et al. Somatic mutations of the beta-catenin gene are frequent in mouse and human hepatocellular carcinomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8847–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liua, J.; Pana, S.; Hsieha, M.H.; Nga, N.; Suna, F.; Wangb, T.; Kasibhatlaa, S.; Schullerc, A.G.; Lia, A.G.; Chenga, D.; et al. Targeting Wnt-driven cancer through the inhibition of Porcupine by LGK974. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20224–20229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folini, M.; Zaffaroni, N. Targeting telomerase by antisense-based approaches: Perspectives for new anti-cancer therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Wood, L.D.; Anders, R.A.; Choti, M.A.; Pawlik, T.M.; Daniel, H.D.; Kannangai, R.; Offerhaus, G.J.; et al. Inactivating mutations of the chromatin remodeling gene ARID2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2001, 43, 828–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassadonia, A.; Cioffi, P.; Simiele, F.; Iezzi, L.; Zilli, M.; Natoli, C. Role of hydroxamate-based histone deacetylase inhibitors (Hb-HDACIs) in the treatment of solid malignancies. Cancers 2013, 5, 919–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Sootome, H.; Nakatsuru, Y.; Miyama, K.; Taguchi, S.; Tsujioka, K.; Ueno, Y.; Hatch, H.; Majumder, P.K.; Pan, B.S.; et al. MK-2206, an allosteric Akt inhibitor, enhances antitumor efficacy by standard chemotherapeutic agents or molecular targeted drugs in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1956–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.C.; Lin, Z.Z.; Hsu, C.H.; Hsu, C.; Shao, Y.Y.; Cheng, A.L. Clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Liver Cancer 2013, 2, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Vaddi, K.; Liu, P.; Manshouri, T.; Li, J.; Scherle, P.A.; Caulder, E.; Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Waeltz, P.; et al. Preclinical characterization of the selective JAK1/2 inhibitor INCB018424: Therapeutic implications for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2010, 115, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurro, M.; Wanless, I.R.; Sherman, M.; Deboer, G.; Shi, W.; Miyoshi, E.; Filmus, J. Glypican-3: A novel serum and histochemical marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Gao, W.; Wang, R.; Chen, W.; Man, Y.G.; Figg, W.D.; Wang, X.W.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Ho, M. Therapeutically targeting glypican-3 via a conformation-specific single-domain antibody in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurro, M.I.; Xiang, Y.Y.; Lobe, C.; Filmus, J. Glypican-3 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by stimulating canonical Wnt signaling. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6245–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangro, B.; Gomez-Martin, C.; de la Mata, M.; Iñarrairaegui, M.; Garralda, E.; Barrera, P.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Larrea, E.; Alfaro, C.; Sarobe, P.; et al. A clinical trial of CTLA-4 blockade with tremelimumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Gold, P.J.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Abrams, T.A.; Morikawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Ohtomo, T.; Philip, P.A. First-in-man phase I study of GC33, a novel recombinant humanized antibody against glypican-3, in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, T.F.; Duffy, A.G.; Korangy, F. Hepatocellular carcinoma from an immunologic perspective. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6678–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.; Reid, T.; Ruo, L.; Breitbach, C.J.; Rose, S.; Bloomston, M.; Cho, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Chung, H.C.; Kim, C.W.; et al. Randomized dose-finding clinical trial of oncolytic immunotherapeutic vaccinia JX-594 in liver cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faltermeier, C.; Busuttil, R.W.; Zarrinpar, A. A Surgical Perspective on Targeted Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diseases 2015, 3, 221-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3040221
Faltermeier C, Busuttil RW, Zarrinpar A. A Surgical Perspective on Targeted Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diseases. 2015; 3(4):221-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3040221
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaltermeier, Claire, Ronald W. Busuttil, and Ali Zarrinpar. 2015. "A Surgical Perspective on Targeted Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Diseases 3, no. 4: 221-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3040221
APA StyleFaltermeier, C., Busuttil, R. W., & Zarrinpar, A. (2015). A Surgical Perspective on Targeted Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diseases, 3(4), 221-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3040221