Safety and Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Advanced and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
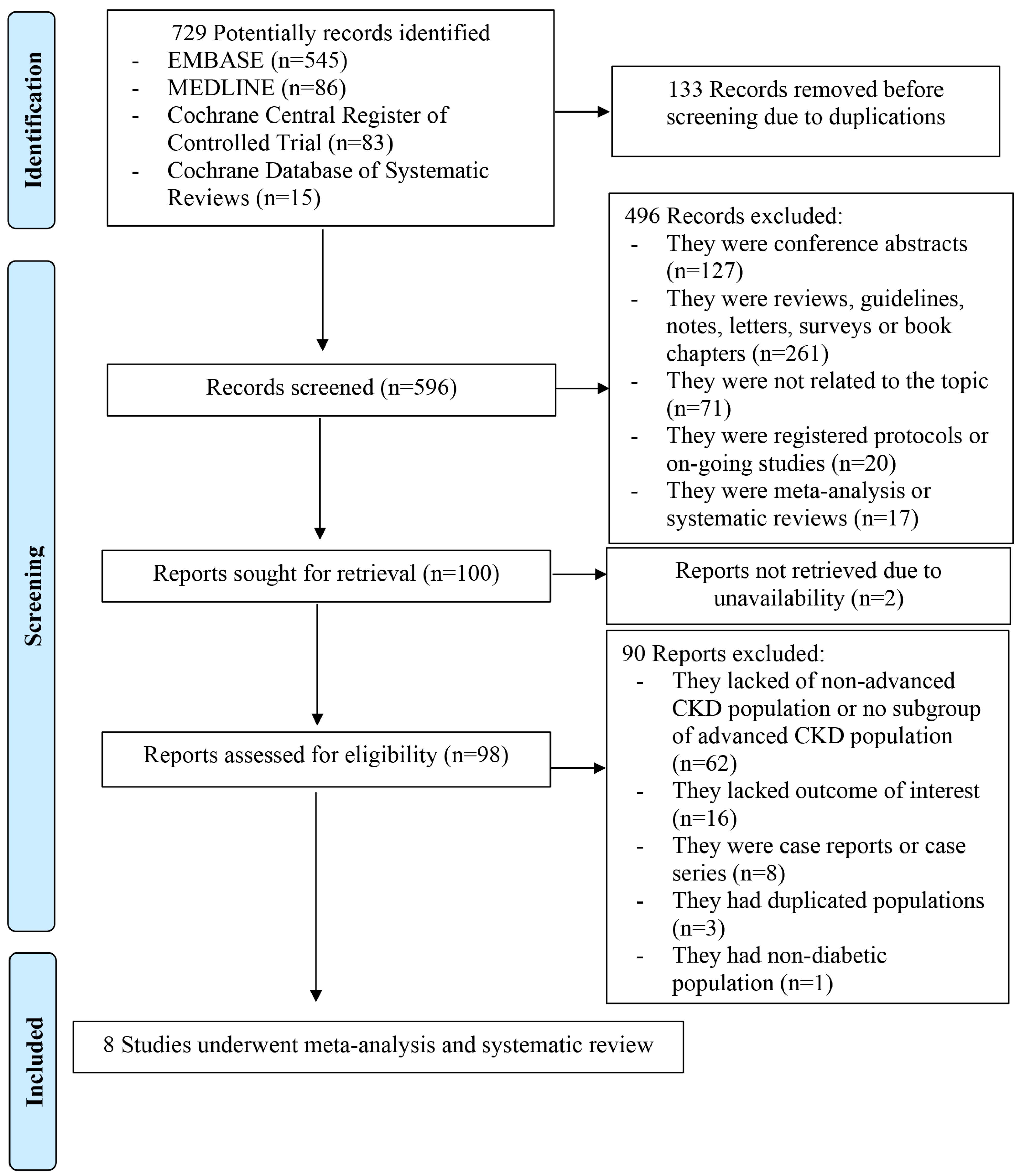
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and StudyEligilbility
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. Statisical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Efficacy of GLP-1RAs on Mortality
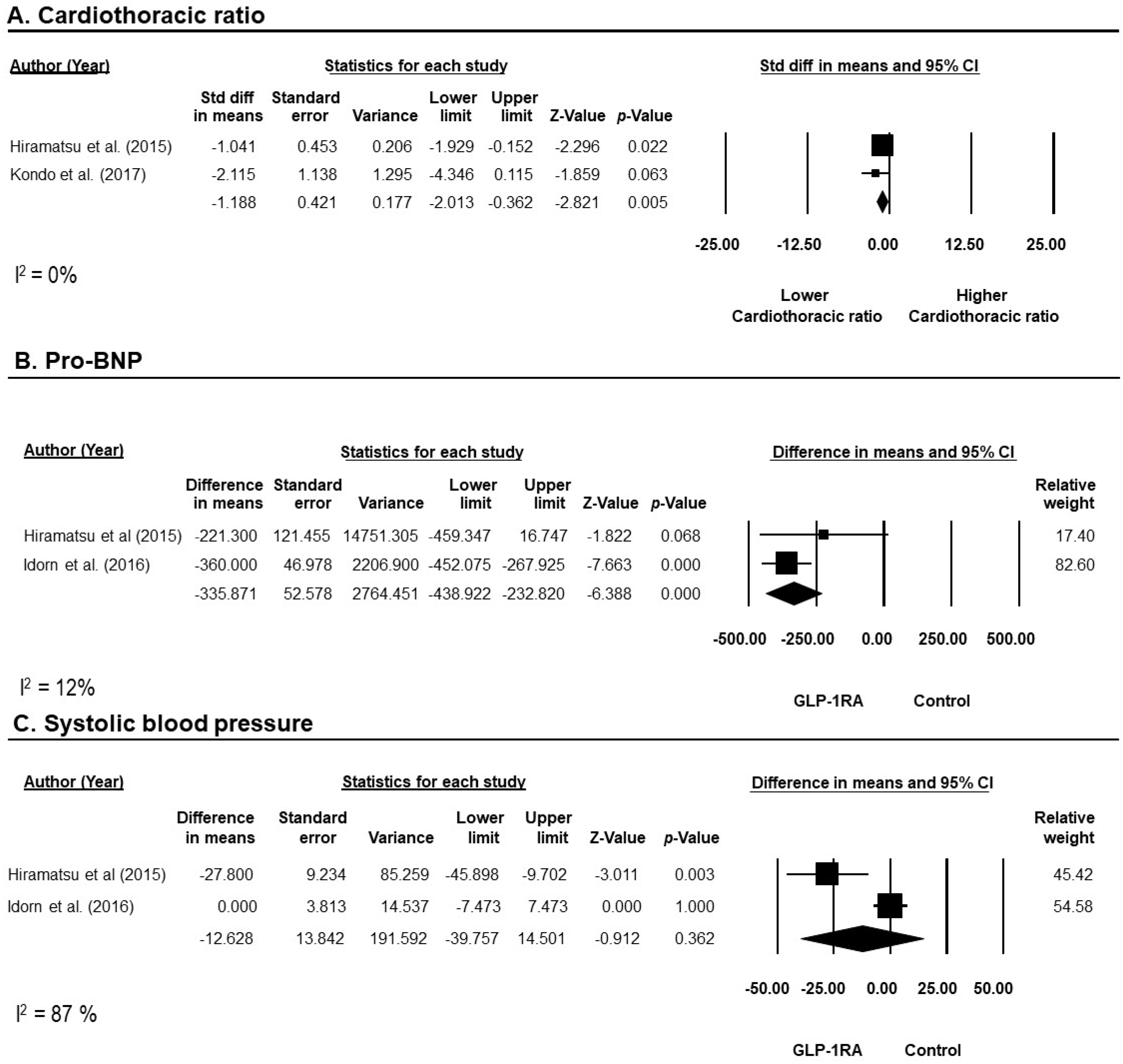
3.3. Efficacy of GLP-1RAs on Cardiovascular Outcomes
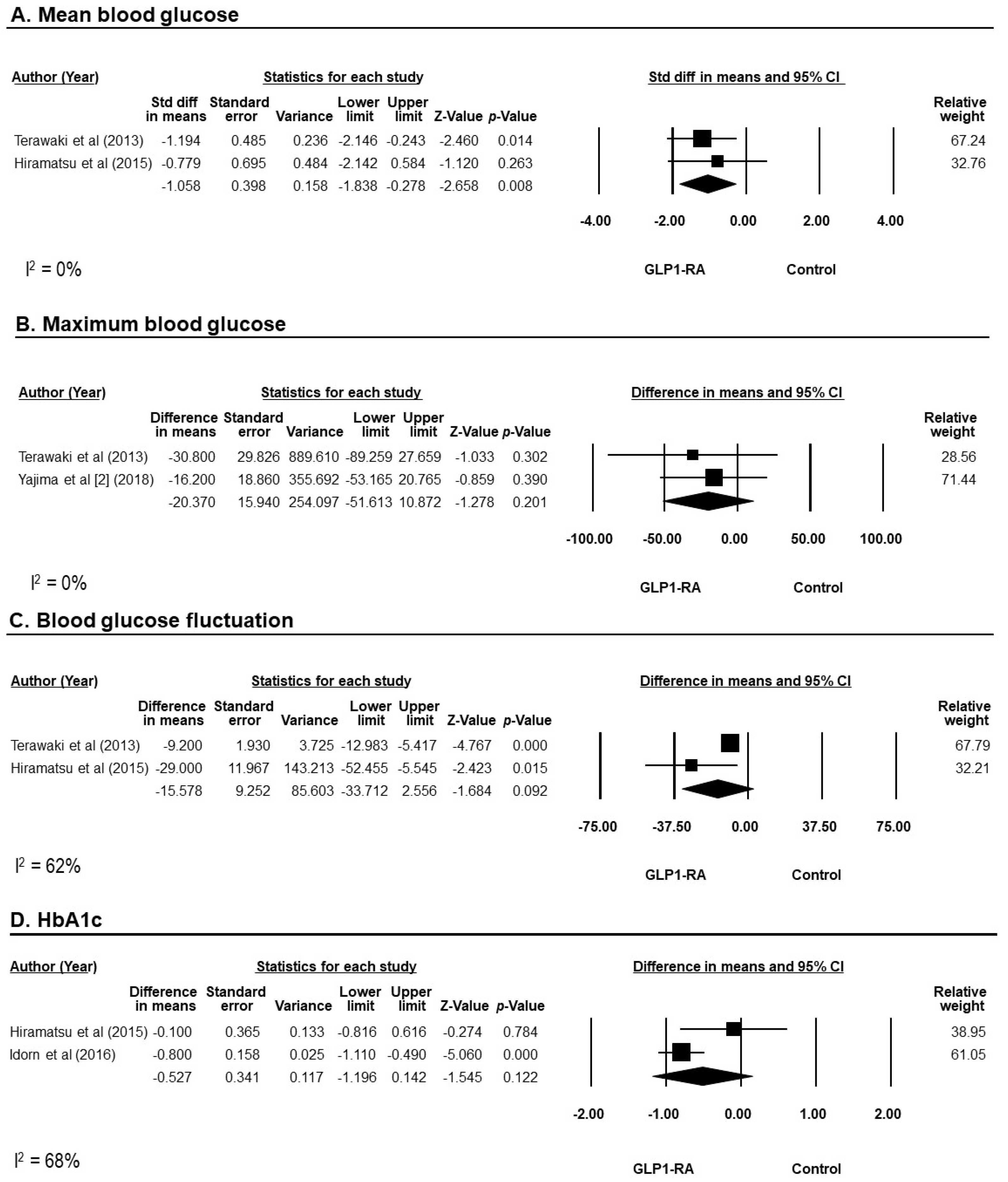
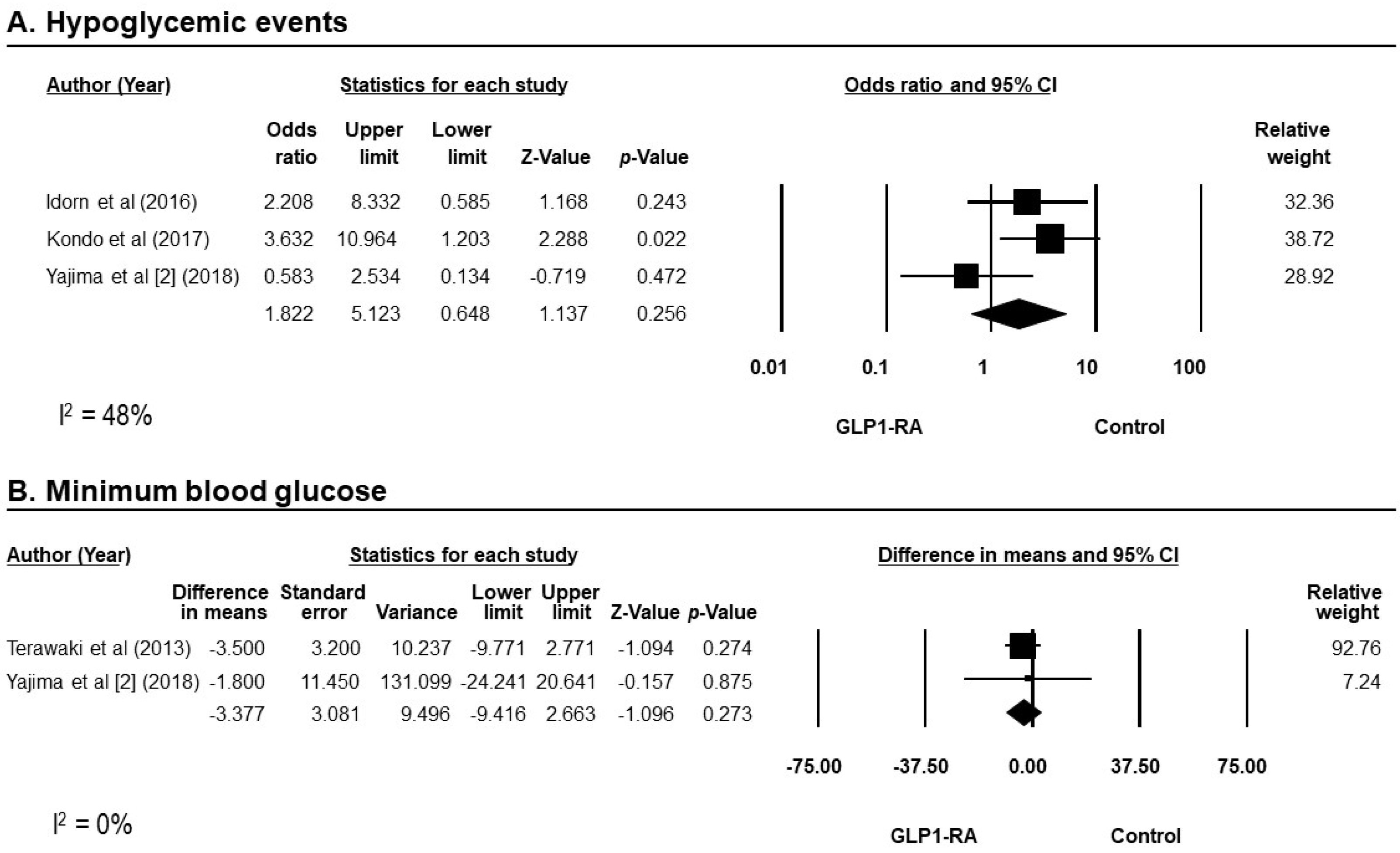
3.4. Efficacy of GLP-1RAs on Blood Glucose
3.5. Efficacy of GLP-1RAs on Weight Reduction
3.6. Efficacy of GLP-1RAs on Renal Outcomes
3.7. Safety of GLP-1RAs
4. Evaluation of Publication Bias
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Bowe, B.; Mokdad, A.H.; Xian, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, T.; Maddukuri, G.; Tsai, C.Y.; Floyd, T.; Al-Aly, Z. Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.T.; Xu, X.; Lim, P.S.; Hung, K.Y. Worldwide Epidemiology of Diabetes-Related End-Stage Renal Disease, 2000–2015. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Benjamin, I.J.; Burke, G.L.; Chait, A.; Eckel, R.H.; Howard, B.V.; Mitch, W.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 1999, 100, 1134–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Renal Data System. 2022 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States; National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2022.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Diabetes Work, G. KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, S1–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S125–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grespan, E.; Guolo, A.; Muscelli, E.; Ferrannini, E.; Mari, A. Loss of the Incretin Effect in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Ryden, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Green, J.B.; Janmohamed, S.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; Granger, C.B.; Jones, N.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Sigmon, K.N.; Somerville, M.C.; et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jodar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; van Baar, M.J.B.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Hoorn, E.J.; Joles, J.A.; van Raalte, D.H. GLP-1 and the kidney: From physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Sattar, N.; Rosenstock, J.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Pratley, R.; Lopes, R.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; Khurmi, N.S.; Heenan, L.; Del Prato, S.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Efpeglenatide in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of Once-Weekly Exenatide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Diaz, R.; Dickstein, K.; Gerstein, H.C.; Kober, L.V.; Lawson, F.C.; Ping, L.; Wei, X.; Lewis, E.F.; et al. Lixisenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Flor, J.C.; Lorenzo, J.D.; Marschall, A.; Valga, F.; Vazquez, T.M.; Cicero, E.R. Efficacy and Safety of Semaglutide, a Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist in Real-Life: A Case Series of Patients in Maintenance Incremental Hemodialysis. Case Rep. Nephrol. Dial. 2022, 12, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, T.; Ozeki, A.; Asai, K.; Saka, M.; Hobo, A.; Furuta, S. Liraglutide Improves Glycemic and Blood Pressure Control and Ameliorates Progression of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Peritoneal Dialysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2015, 19, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idorn, T.; Knop, F.K.; Jorgensen, M.B.; Jensen, T.; Resuli, M.; Hansen, P.M.; Christensen, K.B.; Holst, J.J.; Hornum, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B. Safety and Efficacy of Liraglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and End-Stage Renal Disease: An Investigator-Initiated, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terawaki, Y.; Nomiyama, T.; Akehi, Y.; Takenoshita, H.; Nagaishi, R.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Murase, K.; Nagasako, H.; Hamanoue, N.; Sugimoto, K.; et al. The efficacy of incretin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing hemodialysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touzot, M.; Urena-Torres, P.; Dupuy, O. Semaglutide for treatment of obesity in hemodialysis patients waiting for a kidney transplant: New hope? Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1782–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, T.; Yajima, K.; Hayashi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Yasuda, K. Improved glycemic control with once-weekly dulaglutide in addition to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients on hemodialysis evaluated by continuous glucose monitoring. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, T.; Yajima, K.; Takahashi, H.; Yasuda, K. The effect of dulaglutide on body composition in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients on hemodialysis. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.A.; Wald, J.A.; Matthews, J.E.; Yang, F.; Reinhardt, R.R. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety of albiglutide. Postgrad. Med. 2014, 126, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernan, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savovic, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savovic, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterbrook, P.J.; Gopalan, R.; Berlin, J.; Matthews, D.R. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 1991, 337, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Jenq, C.C.; Lee, T.H.; Tsai, C.Y.; Tu, H.T.; Huang, Y.T.; Yen, C.L.; Yen, T.H.; Chen, Y.C.; et al. Association of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist vs Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Use With Mortality Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e221169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, N.; Tsujimoto, N.; Katayose, T.; Chin, R. Utilization of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and changes in clinical characteristics in patients with type 2 diabetes by chronic kidney disease stage in Japan: A descriptive observational study using a nationwide electronic medical records database. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, M.; Toyoda, M.; Kimura, M.; Ishida, N.; Fukagawa, M. Favorable Effect on Blood Volume Control in Hemodialysis Patients with Type 2 Diabetes after Switching from Insulin Therapy to Liraglutide, a Human Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Analog--Results from a Pilot Study in Japan. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2017, 42, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Rossing, P.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Bakris, G.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Gislum, M.; Gough, S.C.L.; Idorn, T.; Lawson, J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; et al. The rationale, design and baseline data of FLOW, a kidney outcomes trial with once-weekly semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Botros, F.T.; Riddle, M.C.; Ryden, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: An exploratory analysis of the REWIND randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Orsted, D.D.; Buse, J.B. Liraglutide and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2197–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Nakao, T. Semaglutide, a newly available glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist, shows remarkable favorable effects in hemodialysis patients with obesity and Type 2 diabetes. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2022, 26, 242–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Chai, S.; Yu, K.; Quan, X.; Yang, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Wang, J.; Shi, L. Gastrointestinal adverse events of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, L.M.; Gorter, K.J.; Hak, E.; Goudzwaard, W.L.; Schellevis, F.G.; Hoepelman, A.I.; Rutten, G.E. Increased risk of common infections in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Castro, P.; Shapiro, N.I. Diabetes and sepsis: Preclinical findings and clinical relevance. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, F.A.; Mahmud, H.; Gallego-Martin, T.; Jurczak, M.J.; O’Donnell, C.P.; McVerry, B.J. Therapeutic Effects of Endogenous Incretin Hormones and Exogenous Incretin-Based Medications in Sepsis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 5274–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, S.; Jurk, K.; Kopp, M.; Kroller-Schon, S.; Mikhed, Y.; Schwierczek, K.; Roohani, S.; Kashani, F.; Oelze, M.; Klein, T.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signalling reduces microvascular thrombosis, nitro-oxidative stress and platelet activation in endotoxaemic mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1620–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khunti, K.; Knighton, P.; Zaccardi, F.; Bakhai, C.; Barron, E.; Holman, N.; Kar, P.; Meace, C.; Sattar, N.; Sharp, S.; et al. Prescription of glucose-lowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide observational study in England. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, L.A.; Mankad, S.; Sokos, G.G.; Miske, G.; Shah, A.; Elahi, D.; Shannon, R.P. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with acute myocardial infarction and left ventricular dysfunction after successful reperfusion. Circulation 2004, 109, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Fonarow, G.C.; McGuire, D.K.; Hernandez, A.F.; Vaduganathan, M.; Rosenstock, J.; Handelsman, Y.; Verma, S.; Anker, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Heart Failure: The Need for Further Evidence Generation and Practice Guidelines Optimization. Circulation 2020, 142, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ussher, J.R.; Drucker, D.J. Cardiovascular biology of the incretin system. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 1. Improving Care and Promoting Health in Populations: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnen, D. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Wu, H.X.; Hu, N.; Zhou, Y.H.; Li, L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.L.; Xu, S.N.; Huang, B.L.; et al. Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight in adults with obesity without diabetes mellitus-a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author (Year) | Terawaki et al. [23] (2013) | Hiramatsu et al. [21] (2015) | Idorn et al. [22] (2016) | Kondo et al. [34] (2017) | Yajima et al. [1] (2018) | Yajima et al. [2] (2018) | Hirose et al. [33] (2021) | Chen et al. [32] (2022) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study type | Crossover controlled trial | Non-randomized controlled study | Randomized controlled trial | Retrospective cohort | Non-randomized controlled study | Non-randomized controlled study | Retrospective cohort | Retrospective cohort |
| Site | Japan, single center | Japan, single center | Denmark, multicenter | Japan, single center | Japan, single center | Japan, single center | Japan, national database | Taiwan, national database |
| GLP-1RA name | Liraglutide | Liraglutide | Liraglutide | Liraglutide | Dulaglutide | Dulaglutide | 61.5% Dulaglutide, 36.5% Liraglutide, 2% Lixisenatide | N/A |
| GLP-1RA dosage | 0.3 mg daily | 0.6–0.9 mg daily | Titrate to a maximum dose of 1.8 mg daily | 0.3–0.9 mg daily | 0.75 mg weekly | 0.75 mg weekly | N/A | N/A |
| Use of GLP-1RA | Single therapy | Single therapy | Add on therapy | Single therapy | Add on therapy | Add on therapy | Both single and add on therapy | Both single and add on therapy |
| Concomitant insulin used with GLP-1RA, % | 0 | 0 | 80 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 34.1 | 16.3 |
| Control | Vildaglipin, alogliptin, and insulin | Standard therapy | Placebo | None | Teneligliptin | Insulin | None | DPP-4i |
| Total N GLP1-RA Control | 10 10 10 | 30 15 15 | 24 a (20 b) 14 a (10 b) 10 | 5 5 0 | 21 11 10 | 15 15 15 | 255 255 0 | 27,279 701 26,578 |
| Male, n (%) | 7 (70.0) | 22 (73.3) | 17 (85.0) | 4 (80.0) | 16 (76.2) | 13 (86.7) | 167 (65.5) | 14,789 (54.2) |
| Age, year | 62.9B ± 4.3 | 67.6 ± 7.0 | 67.1 ± 3.8 | 67.8 ± 4.3 | 68 (61, 72) c | 72 (66, 79) c | 66.5 ± 11.6 | 64.8 ± 13.0 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 23.0 ± 1.5 | 24.8 ± 3.9 | 31.6 ± 2.4 | 23.2 ±1.2 | 23.1 (21.6, 26.3) c | 23.6 (22.9, 25.3) c | 24.5 ± 5.1 | N/A |
| Stage of advanced CKD | ESKD undergoing HD | ESKD undergoing PD | ESKD | ESKD undergoing HD | ESKD undergoing HD | ESKD undergoing HD | Stage 5 ND and ESKD | Stage 5 ND and ESKD |
| Duration of RRT | 4.1 ± 1.1 years | 10 ± 9.3 months | N/A | N/A | 13.5 (3.7, 30.8) months c | 12 (2, 82) months c | N/A | N/A |
| Duration of DM, years | 25.4 ± 2.3 | 17.6 ± 12 | 14.2 ± 2.4 | N/A | N/A | 22 (18, 32) c | 6.9 ± 6.9 | N/A |
| Baseline HbA1c, % | N/A | 5.9 ± 0.8 | 6.7 ± 0.4 | 6.0 ± 1.0 | N/A | 6.2 (5.3, 6.8) c | 7.4 ± 1.6 | N/A |
| Baseline glycated albumin, % | 24.1 ± 1.5 | 16.9 ± 0.4 | N/A | N/A | 22.3 (17.6, 25.1) c | 21.8 (17.9, 25.1) c | 24.9 ± 8.3 | N/A |
| Baseline Hemoglobin, mg/dL | N/A | N/A | N/A | 10.1± 0.5 | 10.4 (9.3, 11.6) c | 10.6 (9.5, 12.5) c | N/A | N/A |
| Comorbidities CAD, n (%) Stroke, n (%) HF, n (%) DR, n (%) | N/A N/A N/A 0 (0) | N/A | 7 (35) N/A N/A 9 (45) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 87 (34.1) 29 (11.4) 124 (48.6) 51 (20) | 5722 (21.0) 3387 (12.4) 4751 (17.4) N/A |
| Follow-up time | 3 months | 12 months | 3 months | 3 months | 6 months | 5 weeks | N/A | 4 years d |
| Source of funding | Ministry of health, labor and welfare, Japan | None | Drug company (Novo Nordisk) | None | N/A | N/A | Drug company (Eli Lilly) | Chang Gung memorial hospital and ministry of science and technology, Taiwan |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krisanapan, P.; Sanpawithayakul, K.; Pattharanitima, P.; Thongprayoon, C.; Miao, J.; Mao, M.A.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Craici, I.M.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Safety and Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Advanced and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diseases 2024, 12, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12010014
Krisanapan P, Sanpawithayakul K, Pattharanitima P, Thongprayoon C, Miao J, Mao MA, Suppadungsuk S, Tangpanithandee S, Craici IM, Cheungpasitporn W. Safety and Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Advanced and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diseases. 2024; 12(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrisanapan, Pajaree, Kanokporn Sanpawithayakul, Pattharawin Pattharanitima, Charat Thongprayoon, Jing Miao, Michael A. Mao, Supawadee Suppadungsuk, Supawit Tangpanithandee, Iasmina M. Craici, and Wisit Cheungpasitporn. 2024. "Safety and Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Advanced and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diseases 12, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12010014
APA StyleKrisanapan, P., Sanpawithayakul, K., Pattharanitima, P., Thongprayoon, C., Miao, J., Mao, M. A., Suppadungsuk, S., Tangpanithandee, S., Craici, I. M., & Cheungpasitporn, W. (2024). Safety and Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Advanced and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diseases, 12(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12010014








