Abstract
Electromigration (EM) presents a major reliability challenge in advanced electronic packaging as device scaling and rising power demands lead to higher current densities in solder joints. While eutectic Sn-58Bi solder is widely adopted as a low-temperature alternative for its energy efficiency and compatibility with heat-sensitive substrates, its heterogeneous microstructure renders it vulnerable to EM-induced degradation. This review summarizes recent progress in understanding the EM behavior of Sn-Bi solder joints. We first introduce lifetime prediction models based on Black’s law, emphasizing the influences of current density, Joule heating, and thermomigration. Subsequently, the microstructural mechanisms accelerating degradation, including phase segregation and the coarsening of intermetallic compounds (IMCs), are examined. Various alloying strategies are evaluated for their effectiveness in strengthening the solder matrix and suppressing atomic diffusion to improve EM resistance. The critical role of substrate metallization is also discussed, comparing how different surface finishes affect interfacial reactions and joint lifetimes. Additionally, operational methods such as current polarity reversal are explored as potential pathways to mitigate degradation. Finally, we conclude that the EM reliability of Sn-Bi solder joints depends on the combined effects of alloy chemistry, interfacial reactions, and operating conditions, and we suggest future research directions in advanced modeling and material design for next-generation electronic applications.
1. Introduction
The electronic packaging industry has continuously pursued both the miniaturization and performance enhancement of semiconductor devices. This trend inevitably leads to a reduction in the interconnect line width and an increase in power consumption [1,2,3]. As the integration density increases, the current density per unit area also increases sharply [4,5,6], significantly accelerating electromigration (EM) and posing a critical challenge to the long-term reliability of electronic packaging [7,8,9,10,11]. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms of EM and developing methods to suppress its effects have become major research topics in the fields of semiconductor packaging and electronic materials.
Electromigration is defined as the gradual transport of metal atoms within a conductor caused by momentum transfer from conducting electrons [12,13]. At high current densities, atomic migration results in the formation of voids at the cathode and hillocks at the anode. The formation of voids decreases the effective cross-sectional area of the interconnects, leading to an increased electrical resistance, localized Joule heating, and eventually open-circuit failure. By contrast, the accumulation of atoms at the anode forms hillocks, which may cause short-circuit failures by bridging adjacent lines or contacting the upper layers. These processes collectively degrade the reliability of fine-pitch interconnects and solder joints, thereby threatening the overall stability of electronic devices.
The progression of EM is strongly dependent on the metallurgical properties of the interconnected material and the thermally activated nature of atomic diffusion [14,15]. The grain boundaries act as preferential diffusion paths, thereby accelerating the atomic flux. Moreover, once voids are formed, a reduction in the cross-sectional area increases the local current density. This results in additional Joule heating, which in turn enhances diffusion and forms a self-accelerating feedback mechanism. Thus, EM should not be regarded as a simple diffusion process, but rather as a coupled electrothermal degradation phenomenon.
Early EM research focused primarily on metallic interconnects, particularly aluminum (Al) and copper (Cu) [16,17]. Although aluminum was widely adopted in the early stages of integrated circuit fabrication, its relatively low melting point and limited electrical properties have led to its gradual replacement with copper. Copper, which has a high melting point, low resistivity, and superior electrical conductivity, has become a dominant interconnect material. Studies on copper interconnects have investigated the influence of the grain size, crystal orientation, line thickness, and metal/dielectric interfacial interactions. These studies established reliability prediction models, such as Black’s equation, which is widely used to estimate EM lifetime.
More recently, the focus has shifted toward electromigration in solder joints rather than in interconnected lines. With the widespread adoption of lead-free solders driven by environmental regulations, the reliability of solder joints has become a critical issue [18,19,20,21]. Among these alloys, the Sn-58Bi eutectic solder has attracted particular attention as a low-temperature alternative to conventional SAC305 (Sn-Ag-Cu) alloys. Its melting point of approximately 139 °C allows for significantly lower reflow temperatures compared to SAC305 (~217 °C), thereby reducing thermal damage to substrates and components, improving process compatibility with heat-sensitive materials, and lowering overall manufacturing energy consumption.
However, the presence of a high fraction of Bi-rich phases introduces intrinsic brittleness and limited ductility, which compromise the thermomechanical durability under current stress and thermal cycling. During EM, phase segregation and coarsening further accentuate the heterogeneous microstructure, making crack initiation and propagation more likely in Bi-rich regions [22,23]. In contrast, Sn-rich phases generally exhibit ductility and provide greater resistance to crack growth. This mechanical anisotropy of the segregated phases renders Sn-Bi solder joints more vulnerable to EM-induced degradation, thereby accelerating failure compared with SAC305.
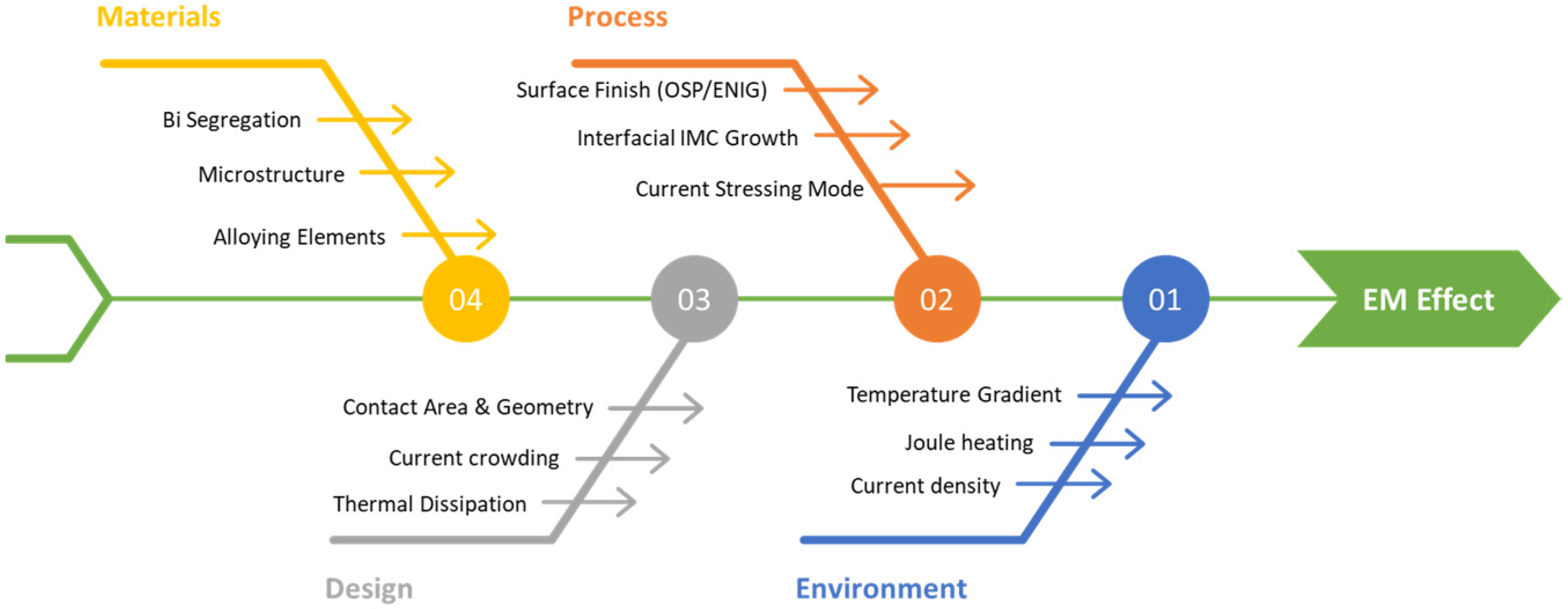
Therefore, to ensure the reliability of next-generation electronic packaging, a comprehensive understanding of EM behavior in solder joints, particularly in low-temperature Sn-Bi systems, is essential [24]. Recent studies have focused on the diffusion pathways of metallic species, the microstructural evolution caused by phase segregation, and the monitoring of electrical property degradation during EM. To provide a holistic view, the major factors governing the EM reliability in Sn-Bi solder joints are categorized into four aspects: Materials, Process, Design, and Environment, as summarized in Figure 1. This fishbone diagram highlights that EM degradation is not driven by a single factor but rather by the coupled effects of alloy chemistry, interfacial reactions, current stressing, and operating conditions.
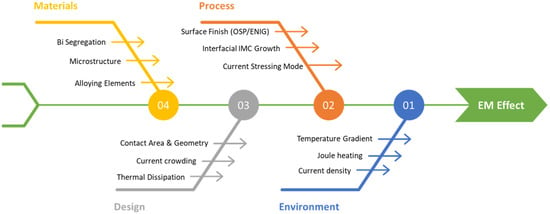
Figure 1.
Fishbone diagram summarizing the key factors influencing the EM reliability of Sn-Bi solder joints. The diagram categorizes the governing factors into Materials [e.g., Bi segregation, microstructure], Process [e.g., Organic Solderability Preservative (OSP)/Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) surface finish, IMC growth], Design [e.g., contact geometry, thermal dissipation], and Environment [e.g., Joule heating, temperature gradient], illustrating their combined effects on joint failure.
To provide a comprehensive overview of the field, a literature search was conducted using databases such as Web of Science and Scopus. The search focused on peer-reviewed articles published up to 2025, using keywords including ‘electromigration reliability’, ‘Sn-Bi solder’, ‘anode segregation’, and ‘interfacial reaction’. While this paper follows the format of a narrative review to delve into specific microstructural mechanisms rather than a systematic meta-analysis, the selected references represent the key experimental and theoretical advancements in the field. To ensure a rigorous and comprehensive coverage of these factors, a literature search strategy was implemented using databases including Web of Science and Scopus. The selection process prioritized peer-reviewed articles published up to 2025, utilizing keywords such as ‘electromigration reliability’, ‘Sn-Bi solder’, ‘anode segregation’, and ‘interfacial reaction’. While this study adopts a narrative review structure to focus on microstructural mechanisms rather than a quantitative meta-analysis, the selected references were systematically chosen to represent the key experimental and theoretical advancements in the field
2. The Failure Mechanisms of Interconnections Undergoing Electromigration
2.1. Current Density Driven Scaling: Lifetime by Black’s Law
The EM lifetime in packaging-scale interconnects is most effectively captured by Black’s empirical relation [25,26,27]
where is an empirical pre-factor determined by the test vehicle and failure criterion, is the current density ( is the applied current, is the cross-sectional area of the stressed segment), is the current exponent (typically 1–2 for solder/IMC interfaces), is the activation energy (eV), is the Boltzmann constant, and is the absolute temperature. At a fixed temperature, doubling j reduces MTTF by a factor of , which makes the geometric control of the primary lever: enlarging the cross-section (width and thickness), adding parallel paths to share current, and avoiding necks or abrupt corners that concentrate current. Because the contact regions (pads, vias, and intermetallic interfaces) often possess a higher local resistance, ensuring symmetric, low-resistance connections is equally important for suppressing local current crowding and its consequential lifetime penalty.
2.2. Thermal Coupling: Average Temperature, Joule Heating, and Temperature Gradients
The exponential term in Black’s law makes EM acutely sensitive to temperature [28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. In practice, the solder joint temperature can be decomposed as:
where is the ambient temperature, is the Joule-heating rise, is the electrical resistance of the stressed segment, and is the corresponding thermal resistance () along the heat-removal path. Recasting with j using and (resistivity , length ) shows that, for a fixed geometry, scales with . Consequently, lowering j improves lifetime twice: through the factor and by reducing self-heating in the exponential term.
Quantitative evidence from recent literature underscores the criticality of this Joule heating effect, particularly in Bi-containing solder systems where thermal diffusion plays a significant role. For instance, Deo et al. employed a four-point resistance measurement technique to monitor the in situ temperature of Bi-doped SAC solder joints [35]. They reported that under a current density of 0.61 × 104 A/cm2, the solder joint temperature rose by approximately 24.6 °C solely due to Joule heating, reaching an absolute temperature of 144.6 °C from an ambient condition of 120 °C. This temperature elevation is significant as it correlates directly with the observed microstructural degradation; specifically, the accumulation of Bi atoms and the migration of (Cu,Ni)Sn intermetallic compounds towards the anode side were found to be accelerated at these elevated temperatures. This confirms that Joule heating acts as a primary driving force for phase segregation in these alloys.
A convenient sensitivity measure follows directly from Black’s law:
Even modest temperature errors can result in large lifetime-prediction errors, particularly at high operating temperatures. In addition to the average solder joint temperature, spatial temperature gradients across solder joints can drive thermomigration. The strength of this effect is proportional to the product of the local temperature gradient ∣∇T∣ and a material-dependent parameter known as the heat of transport (Q*). If Q* is positive, atoms are biased to move toward the cooler region; if negative, toward the hotter region. Thus, thermomigration can either reinforce or counteract electron-wind-driven mass transport. From a design perspective, increasing copper thickness, adding thermal vias, or using heat spreaders lowers the effective thermal resistance and thereby reduces Joule-heating-induced temperature rise. Symmetric routing and uniform, low-resistance interfaces limit temperature non-uniformity and suppress thermomigration-related asymmetry. For accurate lifetime prediction based on temperature-corrected parameters, it is insufficient to rely solely on ambient temperature. Therefore, experimental studies typically employ Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) monitoring or specific test structures (e.g., Kelvin structures) to calibrate the in situ solder joint temperature. This approach ensures that the effective thermal resistance is accurately determined, allowing for the decoupling of Joule heating effects from electromigration kinetics.
2.3. Coarsening Under Electrical Thermal Stress
In an environment where electrical stress (Electromigration, EM) and Joule heating are applied simultaneously, the microstructure of the Sn-Bi solder gradually changes. The core of this change can be summarized by two main processes: the coarsening phenomenon, where the Bi-rich phase becomes thicker and rougher, and the growth of intermetallic compounds (IMCs) such as Cu6Sn5. Analysis of protrusions from solder joints often shows a mixture of Sn and Bi, indicating that the two phases are redistributed and agglomerated because of internal stress. Specifically, the process of Cu6Sn5 IMC layer formation and thickening at the interface generates strong compressive stress in the surroundings. This stress acts as an out-of-plane extrusion force, pushing the solder material outward, and becoming a direct cause of protrusion and whisker growth. During this process, coarsened Bi particles tend to accumulate near the IMC interface, becoming a factor which further deteriorates the reliability by concentrating the local stress, current, and heat. From a morphological perspective, whiskers primarily nucleate on surfaces with micro-voids and grow from their roots. The coarsening process roughens the interface and connects these micro-voids, thereby forming and reinforcing stable growth paths for whiskers. If a very high current density is applied, protrusions may undergo a cycle of temporary melting, rearrangement, and re-solidification (softening-rearrangement-reprecipitation), through which the IMC and Bi particles merge into even larger clusters, and internal damage paths become more continuous. To mitigate this degradation phenomenon, a comprehensive set of countermeasures is necessary, including materials and process controls to maintain a fine, discontinuous initial dispersion of Bi and IMC phases by optimizing the alloy composition and precisely controlling the soldering and annealing processes; interface engineering to improve the surface treatment or finish of circuit boards to lower contact resistance and slow down IMC formation at the interface; and enhanced thermal management to secure effective heat dissipation paths from the joint to limit the temperature rise that accelerates coarsening. Ultimately, by quantitatively tracking the changes in Bi agglomeration, Cu6Sn5 particle size and area fraction, and micro-void connectivity against the applied electrical/thermal stress, it is possible to obtain data that can more precisely calibrate the variables (A, n, Ea) of reliability prediction models, such as Black’s framework.
3. Reliability of Sn-Bi Based Solder Joints
The reliability of Sn-Bi-based solder joints is dictated by multiple degradation mechanisms arising from their intrinsic microstructural and thermomechanical characteristics. Unlike SAC-type alloys, the Sn-58Bi eutectic system exhibits a heterogeneous two-phase structure, in which ductile Sn-rich regions coexist with brittle Bi-rich phases. This inherent microstructural anisotropy, together with the low reflow temperature of the Sn-Bi solder, renders joints particularly vulnerable to damage under thermal and electrical stress conditions. Cracks are frequently initiated along the Bi-rich regions owing to the localized stress concentration, whereas the ductile Sn matrix tends to accommodate plastic deformation.
In addition to microstructural instability, interfacial reactions strongly influence the long-term performance of Sn-Bi solder joints. The surface finish of the substrate modifies the wetting behavior and controls the nucleation and growth kinetics of intermetallic compounds (IMCs), which act as diffusion pathways and potential crack initiation sites. Excessive IMC growth or uneven phase segregation can accelerate the electromigration-induced void formation and interfacial fracture, thereby reducing the mechanical robustness and electrical reliability of the joint. As summarized in Table 1, the failure mode is heavily dependent on the metallurgical reaction at the interface. For instance, on Ni/Au finishes, the formation of brittle Au-Ni-Bi-Sn IMCs [23] dominates the failure, whereas on Cu pads, the stress-induced growth of Bi-rich whiskers [36] is more prevalent. Investigating electromigration behaviors under current densities ranging from 3.0 × 103 to 7.3 × 104 A/cm2 and temperatures between 70 and 125 °C. The data indicates that varying the surface finish (e.g., OSP vs. ENIG) significantly influences the electromigration reliability. This disparity arises from their distinct fabrication processes: OSP involves coating a thin organic film on Cu that allows direct solder-to-Cu contact, whereas ENIG is manufactured by plating a Ni barrier layer capped with Au. Consequently, the direct interaction in OSP versus the barrier effect in ENIG leads to distinct intermetallic growth behaviors and failure modes. On the other hand, the addition of alloying elements such as Ag, Sb, or reinforcements like MWCNT (Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube) can effectively retard Bi-segregation and enhance the overall joint stability. Consequently, the failure of Sn-Bi-based solder joints typically results from the combined effects of thermomechanical stresses, surface-finish-dependent interfacial reactions, and IMC-driven degradation, reflecting the coupled electrothermal-mechanical nature of electromigration damage.

Table 1.
Summary of electromigration test conditions and results for Sn-Bi based solder joints reported in previous studies.
3.1. Alloying and Particle Reinforcement Effects on Electromigration Reliability
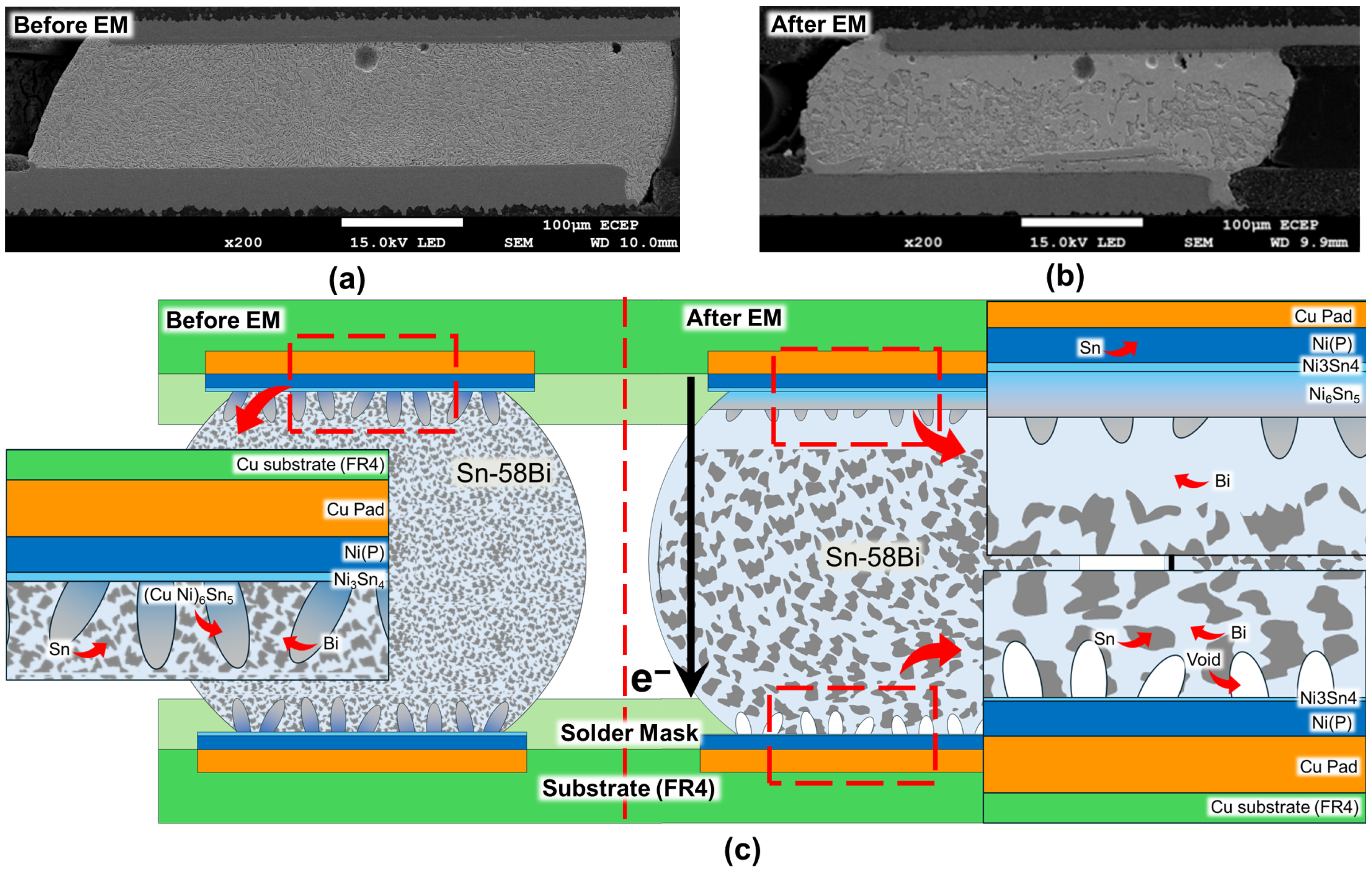
Electromigration (EM) is a primary degradation mechanism that impairs the reliability of Sn-58Bi solders and is characterized by the formation of a brittle Bi-rich layer at the anode and the corresponding extrusion of Sn hillocks. To investigate this, Zhao et al. conducted a comparative study of several solder alloys, namely eutectic Sn-58Bi (SB), silver-doped Sn-58Bi-0.5Ag (SBA), and a multicomponent Sn-58Bi-0.5Ag-0.1Cu-0.07Ni-0.01Ge (SBACNG) alloy, under accelerated testing conditions [40]. The degradation process is schematically illustrated in the provided figure; Figure 2 illustrates the microstructural evolution of a Sn-58Bi solder joint on an ENIG surface finish before and after an electromigration (EM) test. To visualize the failure mechanism, a preliminary EM test was conducted under a current stress of 1.07 A at an ambient temperature of 90 °C. In its initial state before EM as shown in Figure 2a, the solder joint consists of a uniform dispersion of Sn and Bi phases on the Cu pad. Figure 2b presents the microstructure after failure, which was defined as a 20% increase in electrical resistance. The failure occurred after approximately 570 h of stressing. Compared to the initial state, the post-EM microstructure reveals significant phase coarsening and segregation, confirming the migration of Bi atoms toward the anode and Sn atoms toward the cathode, as depicted in the schematic in Figure 2c. A planar Ni3Sn4 layer and a scallop-type (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 intermetallic compound (IMC) layer are formed at the interface from the reaction between the Ni(P) layer and the Sn-58Bi solder. The bulk solder itself exhibits a fine and homogeneous microstructure with finely dispersed Sn and Bi phases. During the EM test, however, the electron flow from the cathode (top) to the anode (bottom) induces significant microstructural changes. At the cathode interface, the electron wind drives the migration of Ni atoms toward the anode, consuming the Ni(P) layer and completely dissolving the (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 IMC, which in turn leads to the formation of large voids. The formation and growth of these voids are a primary reliability concern, as they increase electrical resistance and can ultimately cause an open-circuit failure. Conversely, at the anode interface, the (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 IMC layer grows abnormally thick due to the accumulation of Ni atoms from the cathode, while Bi atoms, having a high effective charge number, migrate with the electron flow to form a thick Bi-rich layer. Furthermore, the EM phenomenon causes significant coarsening of the entire bulk solder microstructure, where the Bi phase segregates from the Sn matrix and agglomerates not only at the anode but also within the bulk, resulting in a much coarser and more heterogeneous structure compared to the initial state. This accumulation generated significant compressive stress, which was subsequently relieved through plastic deformation and extrusion of more mobile Sn atoms, leading to the formation of surface hillocks. The experimental results supported this mechanism, showing distinct differences in the degree of degradation observed at the anode of each solder after 30 h of current stress. In the basic SB solder, the thickest Bi-rich layer was observed with severe Sn hillock formation, whereas the Ag-added SBA solder showed reduced degradation. The SBACNG solder exhibited the most stable surface morphology with the thinnest Bi-rich layer. This systematic improvement in resistance is explained by the role of each alloying element: Ag enhanced the resistance by forming Ag3Sn intermetallic compounds (IMCs) within the Sn matrix, which increased its mechanical strength and inhibited hillock extrusion. The superior resistance of the SBACNG alloy is attributed to the synergistic effects of Ni and Ge, which are proposed to chemically stabilize Bi atoms by forming Ni-Bi compounds and act as physical barriers at phase boundaries to impede Bi migration.
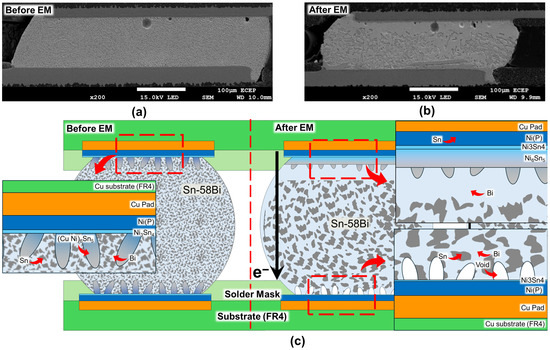
Figure 2.
Microstructural evolution at the anode side of Sn-58Bi based solder joints. (a) Cross-sectional SEM image of the initial microstructure before current stressing. (b) Cross-sectional SEM image after electromigration (EM) failure, showing significant phase coarsening and segregation. (c) Schematic illustration of the EM mechanism, depicting the formation of Bi-rich and Sn-rich regions due to atomic migration [22,23,40,43,44,45]. The black arrow indicates the direction of electron flow (). The red dashed markings and arrows denote the specific regions corresponding to the magnified schematic views.
The average Bi-rich layer thickness after 30 h was 6.4 µm for SB, 4.2 µm for SBA, and only 3.3 µm for SBACNG. Correspondingly, the Bi accumulation rate decreased from 5.9 × 10−5 μm/s in SB to 3.9 × 10−5 μm/s in SBA and 3.1 × 10−5 μm/s in SBACNG. These results confirmed that alloying systematically retarded Bi transport under current stress, thereby reducing the formation of brittle interfacial layers and delaying catastrophic failure. In particular, the reduction in hillock density and stabilization of the anode morphology in the SBACNG solder provide strong evidence that multicomponent alloying is an effective strategy for enhancing the electromigration resistance of low-temperature Sn-Bi systems [41].
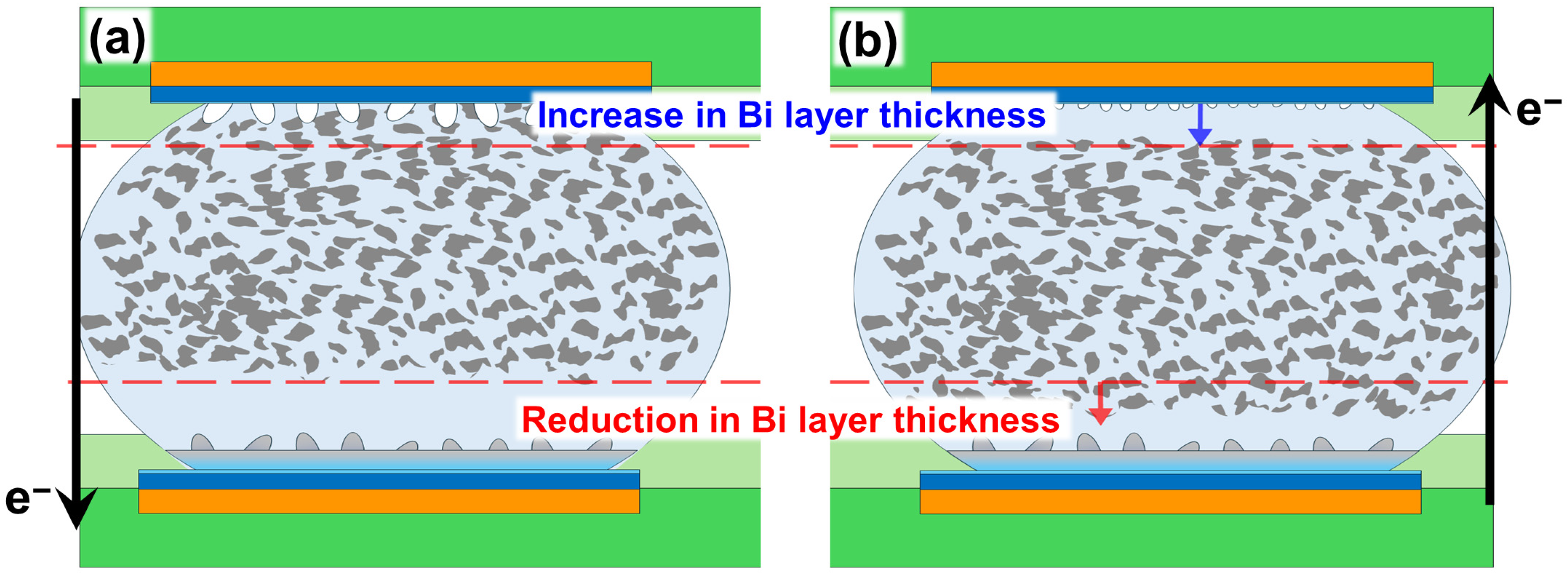
The electrical resistance changes observed in the SBA solder illustrate the electromigration mechanism. During the initial 30 h of current stressing, the resistance steadily increased, which was directly correlated with the progressive thickening of the Bi-rich layer at the anode. This behavior contrasts with that of high-Sn solders, where the resistance growth is primarily linked to void nucleation at the cathode. The higher intrinsic resistivity of Bi compared to that of Sn explains why even a thin Bi-rich layer can induce a measurable voltage increase. Figure 3a conceptually depicts the typical microstructure of the initial anode after 30 h of stress, showing the formation of a Bi-rich layer at the interface and the growth of hillocks. Subsequently, upon current reversal at the 30 h mark, the previously formed Bi-rich layer at the former anode began to partially dissipate, and new hillocks started to nucleate at the opposite side (the new anode). During this period, the resistance initially experienced an immediate drop, as the dissolution of the high-resistivity Bi layer outweighed any early Bi accumulation at the new anode. However, with continued stress, Bi migration rebuilt a new Bi-rich layer at the reversed anode, and the resistance increased again. Figure 3b shows the final state after current reversal, illustrating the reformation of the Bi-rich layer and the growth of hillocks at the new anode. This distinctive ‘rise-fall-rise’ sequence in resistance provides direct evidence that Bi migration, rather than cathodic voiding, dominates electromigration-induced electrical degradation in Sn-Bi joints. Furthermore, the microstructural evidence, as conceptually presented in Figure 3, indicates that the Bi-rich layer not only acts as a high-resistivity path, but also introduces local stress that drives the extrusion of Sn, leading to hillock formation. Thus, the electrical signature integrates the resistive effect of Bi enrichment and the mechanical response of Sn extrusion, highlighting the coupled electromechanical nature of degradation in low-temperature Sn-Bi systems.
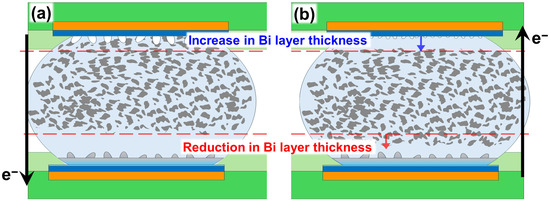
Figure 3.
(a) Before reversal, Bi migrates toward the electron flow exit (anode) to form a continuous Bi-rich layer, leading to hillock growth. (b) After reversing the current direction, Bi atoms migrate to the new anode, where a new Bi-rich layer and corresponding hillocks are reformed [40,45]. The black arrows indicate the direction of electron flow (). The red dashed lines represent the reference lines used to observe the changes in layer thickness.
In summary, Zhao et al. demonstrated that the EM reliability of Sn-Bi solder joints is governed by the growth of a brittle Bi-rich layer at the anode, accompanied by Sn hillock extrusion driven by compressive stress. Quantitative measurements confirmed that the Bi-rich layer thickened to 6.4 μm in SB, 4.2 μm in SBA, and 3.3 μm in SBACNG after 30 h, with corresponding Bi accumulation rates of 5.9, 3.9, and 3.1 × 10−9 cm/s. Electrical resistance measurements under current reversal provided direct evidence that Bi migration, rather than cathodic voiding, dominates electrical degradation: the resistance increased with Bi accumulation, dropped upon bi-layer dissolution, and increased again with renewed accumulation. Alloying additions mitigated this degradation through distinct mechanisms: Ag strengthened the Sn matrix and reduced hillock formation, whereas Ni and Ge more effectively suppressed Bi migration at the source. The comparative results from SB, SBA, and SBACNG clearly establish that multicomponent alloying strategies are more effective than single-element additions, providing valuable design guidelines for enhancing the long-term reliability of low-temperature Sn-Bi solders.
3.2. Surface Finish and Interfacial Reliability Under Electromigration
The quantifies the electromigration lifetime of Sn58Bi solder joints as functions of current density (3.0–4.5 × 103 A/cm2), temperature (80–110 °C), and substrate metallizations (ENIG, ENEPIG, OSP-Cu) [41]. The test vehicle was a daisy-chain PCB with identical finishes on both sides; the pad opening was 200 µm, the FR-4 thickness was 1 mm, and the underlying Cu pad was approximately 38 µm. Reported finish thicknesses were ~5/0.1 µm for ENIG (Ni(P)/Au), ~5/0.1/0.1 µm for ENEPIG (Ni(P)/Pd/Au), and ~0.3 µm for OSP on Cu; the reflow peak was 180 °C. Current densities were calculated from the pad opening area, and failure was defined as a 10% increase over the initial resistance. To decouple the EM kinetics from self-heating, this study used TCR-based temperature correction for Arrhenius analysis and extracted the current-density exponent n from log-log MTTF-j plots. The unusually high n values (ENIG 5.1 ± 0.4, ENEPIG 4.65 ± 0.38, OSP-Cu 4.06 ± 0.58) indicate significant Joule heating during stressing, while the TCR-corrected activation energies rank OSP-Cu highest (0.434 ± 0.008 eV), followed by ENIG (0.361 ± 0.002 eV) and ENEPIG (0.338 ± 0.003 eV), consistent with improved EM resistance for OSP-Cu [46]. Under these conditions, the MTTF decreased monotonically with increasing current density, whereas the temperature effect remained comparatively small. Building on the alloying results that primarily suppress Bi-driven anode degradation [43], we next examined how substrate metallization governs the localization of EM damage. Under identical Sn-58Bi solder and test conditions, finish selection dictates whether failure is trapped at the interfaces (ENIG/ENEPIG) or diverted into bulk solder deformation (OSP-Cu), thereby acting as a complementary lever to alloy chemistry. At a representative condition of 80 °C and 3.0 × 103 A/cm2, the measured MTTFs were 213,315 s for ENIG, 261,371 s for ENEPIG, and 396,989 s for OSP-Cu. The metallization-dependent lifetime separation was pronounced at milder stresses (lower current densities and temperatures) and diminished as the stress became severe.
The observed time-to-failure (MTTF) trends offer critical insights from a reliability engineering perspective, with a consistent lifetime ranking of OSP-Cu > ENEPIG > ENIG, demonstrating the direct impact of substrate metallization choice on joint durability. This performance gap between metallization types varies distinctly with the stress conditions, indicating a shift in the dominant failure mechanism. For example, under milder stress at 80 °C (3.0 × 103 A/cm2), the influence of interface properties was maximized, with OSP-Cu achieving a lifetime approximately 1.9 times longer than ENIG and 1.5 times longer than ENEPIG. This gap progressively narrowed as the temperature increased to 90 °C (~1.6× that of ENIG) and 100 °C (~1.2× that of ENIG). Ultimately, under the harshest conditions of 110 °C and 4.5 × 103 A/cm2, the distinction became marginal, with OSP-Cu’s lifetime being only 1.3 times longer than ENIG’s and nearly indistinguishable from ENEPIG’s (~1.03×). These results confirm that while substrate metallization governs the electromigration lifetime at lower stresses, its relative influence is suppressed at higher current densities and temperatures. Under these aggressive conditions, intense Joule heating accelerates diffusion, causing the thermomechanical behavior in the bulk solder to dominate failure rather than the specific properties of the interface. Mechanistically, this divergence in lifetime is attributed to fundamentally different failure modes. The Sn-58Bi/ENIG and Sn-58Bi/ENEPIG joints failed because of brittle fracture resulting from the complete depletion of the Ni(P) layer and subsequent interfacial cracking. In contrast, the Sn-58Bi/OSP-Cu joints failed more gradually owing to the ductile bulk solder deformation. Therefore, OSP-Cu exhibits an extended MTTF, particularly under moderate conditions, where interfacial reactions are the primary reliability bottleneck, because of their ability to divert damage away from the fragile interface and into the solder itself.
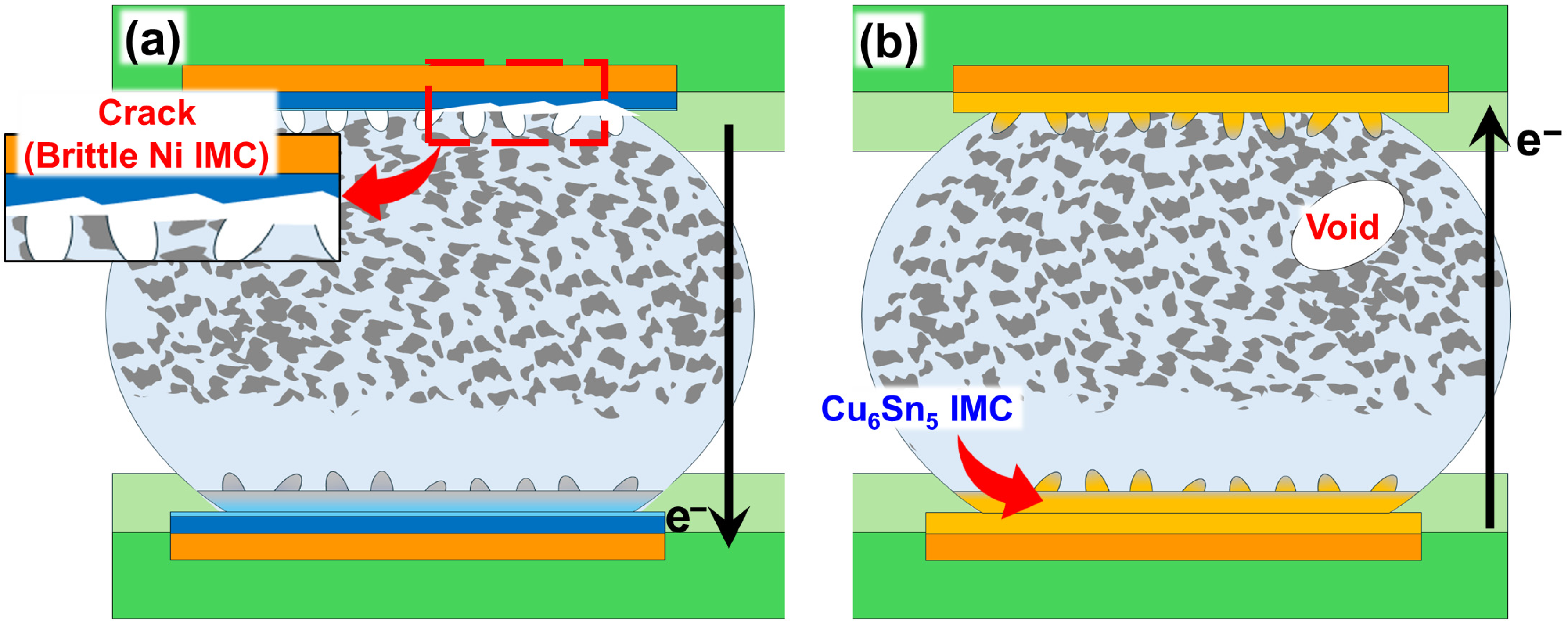
The Sn-58Bi solder joints exhibited two fundamentally different electromigration-induced failure mechanisms that were critically dependent on the PCB surface finish. Electromigration originates from the “electron wind” effect, where momentum transfer from flowing electrons displaces metal atoms, leading to distinct and asymmetric damage at the cathode (top) and anode (bottom). For Ni-based finishes, such as ENIG and ENEPIG (Figure 4a), the failure is predominantly an interfacial failure occurring at the cathode. Here, the electron flow consumes the Ni layer to form a Ni3Sn4 intermetallic compound (IMC), and the phosphorus from the electroless plating process contributes to a highly brittle Ni3P phase, ultimately leading to catastrophic cracking along this interface. In contrast, the OSP-Cu finish underwent bulk failure (Figure 4b). In this case, the electron wind pushes the Bi atoms, which have a positive effective charge, toward the anode, causing massive segregation of a low-melting-point Bi-rich phase. This accumulation, coupled with localized Joule heating from current crowding, severely weakens the solder matrix, leading to significant plastic deformation, Cu-Sn IMC formation, and eventual partial melting within the solder bulk. These contrasting microstructural evolutions, one driven by brittle IMC formation at the interface and the other by elemental segregation and softening in the bulk, underscore how the surface finish dictates the physical failure pathway, and consequently, the overall reliability of electronic interconnects under high current stress.
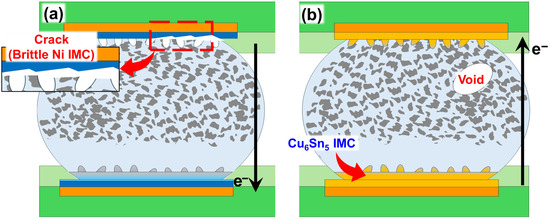
Figure 4.
Schematic illustrations of electromigration failure mechanisms in Sn-58Bi solder joints with different PCB surface finishes: (a) Failure mode for Ni-based finishes (e.g., ENIG/ENEPIG), showing Ni-Sn intermetallic compound (IMC) layer degradation. (b) Failure mode for an OSP-Cu finish, characterized by the formation of Cu-Sn IMCs and significant migration of a Bi-rich phase to the anode [37,41,43,44,45,46,47]. The black arrows indicate the direction of electron flow (). The red arrows and dashed markings highlight specific failure features, including cracks and IMC layers, as well as the magnified regions.
Under electromigration stress, the failure of a Sn-58Bi solder joint on an OSP-Cu finish is governed by a bulk degradation mechanism rather than interfacial cracking. The high current density and temperature accelerate the reaction between copper from the substrate and tin from the solder, resulting in the continuous growth of a mechanically robust Cu6Sn5-Cu3Sn intermetallic compound (IMC) stack at the interface. This strong IMC adhesion effectively suppresses the cathodic opening often observed in other surface finishes. Simultaneously, the electron wind drives the Bi, which is not incorporated into the growing IMCs, to migrate extensively and segregate at the anode. This accumulation forms large, low-melting-point, Bi-rich regions that severely compromise the structural integrity of the bulk solder. Consequently, joint failure manifests not at the strong interface but through plastic deformation and rupture within the weakened bulk material, a process exacerbated by localized Joule heating [46].
The distinctive reliability pathway of OSP-Cu (Organic Solderability Preservative on Copper) joints becomes particularly evident under harsh electromigration stressing conditions (4.0 × 103 A/cm2, 110 °C). Even under this severe stress, the joint maintains its interfacial integrity, showing no signs of cathodic cracking, which typically plagues Ni-based finishes. The strong adhesion between the continuously growing Cu-Sn (copper-tin) intermetallic compounds (IMCs) and the Cu substrate ensures electrical continuity despite the significant consumption of the cathodic copper pad. Instead of failure at the interface, the degradation mechanism shifts within the bulk solder. The pronounced electromigration-driven migration of Bi toward the anode results in the formation of large segregated Bi-rich regions. This accumulation creates mechanically weak low-melting-point zones that, when combined with localized Joule heating, lead to severe internal voiding, chaotic phase segregation, and gross deformation of the entire solder joint. This failure mode highlights a key kinetic disparity: the rapid growth of Cu-Sn IMCs stabilizes the OSP-Cu interface against cracking, but shifts the dominant failure mode to bulk degradation. This destructive pathway ultimately provides a longer lifetime than the abrupt interfacial failure characteristic of thin Ni(P) barrier systems such as ENIG and ENEPIG.
For quantitative kinetics, the current exponent n and activation energy Ea were extracted from Black’s law. The authors reported n = 5.1 ± 0.4 (ENIG), 4.65 ± 0.38 (ENEPIG), and 4.06 ± 0.58 (OSP-Cu), notably higher than 1–2, and interpreted this as evidence of substantial Joule heating during stressing. To account for this, the temperature axis was corrected using the temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR ≈ 0.00215 °C−1), and Ea is calculated with the corrected temperature. The activation energies rank with OSP-Cu highest at ~0.434 ± 0.008 eV, followed by ENIG (~0.361 ± 0.002 eV) and ENEPIG (~0.338 ± 0.003 eV). The authors, therefore, concluded that OSP-Cu exhibits superior electromigration reliability compared to ENIG and ENEPIG, consistent with the observed sustained Cu supply to form Cu-Sn IMCs and prominent Bi migration on the anode side. They further rationalized the modest advantage of ENEPIG over ENIG by the Pd barrier effect—retarding Ni(P) depletion via PdSn4 formation and Pd solutes in Ni3Sn4.
This study confirmed that MTTF decreases with increasing current density and temperature. Substrate metallization has a significant effect on the lifetime; under the same conditions, OSP-Cu shows the longest MTTF, ENEPIG follows, and ENIG is the shortest. The separation was clearer under milder stresses and diminished under harsher conditions. The ENEPIG MTTF is slightly longer than that of the ENIG. Mechanistically, polarity accelerated IMC growth at the anode. In ENIG/ENEPIG, cathodic Ni(P) is fully consumed and cracks form at the Ni3Sn4 + Ni3P/Cu interfaces. For OSP-Cu, no cathodic interfacial openings were observed; failure proceeded via bulk-solder deformation, which was attributed to the remaining cathodic Cu layer and good Cu-Sn/Cu adhesion. During the electrical monitoring, the current remained stable until failure, followed by an abrupt decrease, indicating a sudden open circuit induced by electromigration. Black’s analysis yielded a current density exponent (n) in the range of 4–5, implying significant Joule heating effects. After correcting for the temperature rise using a temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) of approximately 0.00215/℃, the activation energy was determined to be highest for the OSP-Cu finish (0.434 ± 0.008 eV). In contrast, the activation energies for ENIG (0.361 ± 0.002 eV) and ENEPIG (0.338 ± 0.003 eV) were found to be comparable. Therefore, we conclude that Sn-58Bi/OSP-Cu is more reliable against EM than ENIG or ENEPIG. This aligns with prior studies: in Sn-Pb, OSP-Cu lifetimes were approximately four times those of ENEPIG; in SAC, lifetimes on Cu were at least twice those on ENIG/ENEPIG, supporting OSP-Cu superiority and ENEPIG’s Pd-barrier benefit over ENIG.
A subsequent study further corroborates these findings, investigating the electromigration (EM) reliability of Sn-58Bi solder joints under a higher current density (1.3 × 104 A/cm2) through detailed microstructural analysis [38]. This study also compared OSP, ENIG, and ENEPIG surface finishes, reaffirming the fundamental differences in their failure mechanisms with consistent results. The MTTF was the longest for OSP at 6372 min, followed by ENEPIG (5284 min) and ENIG (4568 min), confirming the reliability ranking of OSP > ENEPIG > ENIG. Notably, this study reinforces the mechanistic interpretations of previous research by identifying the physical locations of failures. In the OSP-finished joints, the electron wind caused Bi to segregate at the anode, forming a brittle Bi-rich layer where the final fracture occurred. Conversely, for the ENIG and ENEPIG joints, the depletion of the Ni layer at the cathode and the corresponding growth of brittle IMCs acted as direct causes of failure, and cracking was observed at the cathode interface. This result demonstrates that, even under more severe current stressing, the surface finish remains the critical variable that dictates the failure mode (bulk vs. interfacial) and location.
Synthesizing the results of both studies, the electromigration reliability of the Sn-58Bi solder joints can be attributed to two distinct failure pathways, which are governed by the interaction between the solder and surface finish. The first pathway is the “Bulk Degradation Model,” characteristic of the OSP-Cu finish. In this system, the Cu-Sn IMC interface was sufficiently robust and did not serve as a failure initiation site. Instead, the electrical stress was transferred to the more vulnerable bulk solder. Consequently, the intrinsic property of the solder alloy, that is, the segregation of Bi at the anode, became the dominant failure mechanism. The stability of the interface effectively diverted failure to a slower bulk-driven process, thereby securing a longer overall lifetime. The second pathway is the “Interfacial Failure Model,” observed in ENIG/ENEPIG finishes. This system introduced a Ni diffusion barrier layer, which was the most vulnerable point for electromigration. The continuous consumption of Ni and the growth of brittle IMCs fundamentally compromised the structural integrity of the interface, leading to a more rapid and catastrophic interfacial failure that preceded the severe degradation of the solder bulk. Therefore, the reliability design of Sn-58Bi solder systems requires moving beyond the selection of individual alloys or finishes. This necessitates a system-level approach that predicts and controls the failure pathway activated by a specific combination of solder and surface finish.
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Ag Addition and Surface Finish Effects on Joint Reliability
The preceding sections individually examined the effects of the solder joint composition (Section 3.1) and pad surface finish (Section 3.2) on the microstructure and reliability of the joint. However, in a real-world electronic packaging environment, these two factors do not act independently; rather, they determine interfacial reactions and final mechanical properties through complex interactions. A specific solder alloy may promote or suppress unexpected IMC growth when paired with a particular surface finish, which directly affects the long-term lifetime of the product. Therefore, this section aims to provide an in-depth investigation of the unique failure mechanisms and reliability changes that occur in each combination by comparatively analyzing four systems that simultaneously consider solder composition (with and without Ag) and surface finish (ENIG and Cu-OSP).
Fan et al. conducted displacement-controlled shear fatigue tests under isothermal conditions at 30 °C to precisely simulate the real-world operating environment of electronic components [48]. Using a custom-built, nanometer-precision tester, a cyclic load profile—including a ramp to 39 µm (15% strain) displacement and a 200 s dwell time—was repeatedly applied. Under these stringent test conditions, Sn-Bi-based solder joints with an ENIG surface finish exhibited severe reliability issues. During thermal annealing at 125 °C, the 50 nm thick gold (Au) layer in the ENIG finish acted as a catalyst, inducing the rapid growth of a thick and porous (Ni,Au)Sn4 IMC at the interface. The porous nature of this IMC layer, as confirmed by 3D X-ray microscopy, rendered it mechanically fragile, leading to a catastrophic brittle failure within the IMC before the completion of the first fatigue cycle. Meanwhile, the addition of 1 wt% Ag to the solder (creating Sn-57Bi-1Ag) showed some positive effects, significantly suppressing the growth rate of the problematic (Ni,Au)Sn4 IMC on the ENIG finish. As a result, the IMC layer formed after annealing was much thinner (approx. 2.5 µm) compared to the solder without Ag (approx. 50 µm). However, despite this suppressed growth, the inherent brittleness of the thin IMC layer remained unchanged. Consequently, the solder with Ag exhibited the same brittle failure mechanism, failing within the first cycle and did not overcome the low reliability. This indicates that while Ag addition can control the reaction kinetics of ENIG, it cannot resolve the fundamental failure mode induced by the presence of gold. In contrast, the Copper-Organic Solderability Preservative (Cu-OSP) surface finish demonstrated far more stable behavior when used with Sn-Bi-based solders. On the Cu-OSP interface, instead of a detrimental IMC like (Ni,Au)Sn4, a dense and stable Cu6Sn5 IMC was formed. Consequently, the failure mechanism shifted from brittle interfacial fracture to a more desirable ductile failure occurring within the solder bulk. This allowed the joint to achieve a measurable fatigue life of approximately 8–10 cycles (N50 for Sn-58Bi), proving its superior mechanical reliability compared to ENIG. In conclusion, this study, through precise mechanical testing and in-depth analysis, including SEM-EDS, 3D X-ray, and thermodynamic calculations, identified the gold layer in ENIG as the key factor undermining the reliability of Sn-Bi solders. This demonstrates that Cu-OSP is a more suitable surface finish for implementing a stable low-temperature soldering system.
4. Conclusions
This review confirms that the electromigration (EM) reliability of Sn-Bi solder joints is governed by the coupled effects of polarity-driven Bi segregation and interfacial reactions. To mitigate these failures, a multi-tiered strategy is required. First, multicomponent alloying (e.g., Ag + Ni + Ge) should be employed to create fine dispersions that suppress Bi diffusion and stabilize the microstructure [Point 3]. Second, interface engineering is critical; prioritizing OSP-Cu finishes promotes robust Cu-Sn IMCs, whereas Pd interlayers in ENEPIG can mitigate Ni depletion relative to ENIG [Point 2]. These material controls must be paired with optimized interconnect geometry to minimize current crowding and reduce thermal resistance through heat spreaders and thermal vias [Point 1]. However, practical deployment faces distinct limitations. While dynamic stress protocols such as polarity reversal or pulsed currents offer a potential pathway to dissolve Bi-rich layers and mitigate migration, their application is often constrained by trade-offs in signal integrity, IR drop, and thermal cycling reliability [Point 4]. Additionally, the economic cost of noble metal alloying remains a barrier to widespread adoption in cost-sensitive applications. Looking forward, future research should prioritize advanced reliability modeling. This involves moving beyond simple Black’s law extrapolations by integrating in situ resistance monitoring with TCR-based temperature correction to decouple thermal effects from electrical acceleration [Point 1]. Furthermore, applying these optimized material systems to flexible and wearable electronics where Sn-Bi’s low-temperature advantage is paramount requires new investigations into electromechanical reliability under simultaneous bending and current stressing. In summary, IMC-mediated interfacial reactions and Bi diffusion are the two fulcrums that determine whether the low-temperature processability of Sn-Bi can be translated into robust EM reliability. The most reliable paths combine multicomponent alloying strategies with substrate-level interface engineering, supported by optimized current-density management and, where viable, dynamic stressing schemes that suppress anode-side Bi accumulation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and J.B.K.; investigation, J.L.; data curation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L. and J.B.K.; visualization, J.L.; supervision, J.B.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government (Ministry of Science and ICT) [grant number NRF 2021R1A2C1007016] and the Regional Innovation System & Education (RISE) program through the Gwangju RISE Center, funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE) and the Gwangju Metropolitan City, Republic of Korea [grant number 2025-RISE-05-013].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bourjot, E.; Putero, M.; Perrin-Pellegrino, C.; Gergaud, P.; Gregoire, M.; Nemouchi, F.; Mangelinck, D. Kinetics study of NiPt(10 at.%)/Si0.7Ge0.3 solid state reactions. Microelectron. Eng. 2014, 120, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z. Recent progress on the development of Sn–Bi based low-temperature Pb-free solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 3222–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cai, C.; Pham, V.L.; Pan, K.; Wang, H.; Park, S. A Comprehensive Study of Electromigration in Lead-free Solder Joint. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 70th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Orlando, FL, USA, 3–30 June 2020; pp. 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, T.-C.; Lin, K.-L. Electromigration behavior of the Cu/Au/SnAgCu/Cu solder combination. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.M.; Roy, A. Electromigration in ULSI interconnects. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2007, 58, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.N. Recent advances on electromigration in very-large-scale-integration of interconnects. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 5451–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tong, H.M.; Tu, K.N. Electromigration and Thermomigration in Pb-Free Flip-Chip Solder Joints. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2010, 40, 531–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najm, F.; Hajj, I.N.; Yang, P. Electromigration median time-to-failure based on a stochastic current waveform. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 1989 IEEE International Conference on Computer Design: VLSI in Computers and Processors, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2–4 October 1989; pp. 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Sigal, L.; Hu, C.K.; Xu, C.; Smith, H.; Wanock, J.; Nassif, S. Uniting to overcome a mounting BEOL electromigration reliability challenge. In Proceedings of the ICCAD ′12: The International Conference on Computer-Aided Design 2011, San Jose, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pak, J.; Pathak, M.; Lim, S.K.; Pan, D.Z. Modeling of electromigration in through-silicon-via based 3D IC. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 61st Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 31 May–3 June 2011; pp. 1420–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J.; Liang, L.; Meng, G. Electromigration Simulation for Metal Lines. J. Electron. Packag. 2010, 132, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, J.; Lim, S.K.; Pan, D.Z. Electromigration-aware routing for 3D ICs with stress-aware EM modeling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2012; pp. 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Jang-Hee, L.; Gi-Tae, L.; Park, Y.B.; Seung-Taek, Y.; Min-Suk, S.; Qwan-Ho, C.; Kwang-Yoo, B. Size effect on electromigration reliability of pb-free flip chip solder bump. In Proceedings of the 2008 58th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2008; pp. 2030–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Basaran, C.; Hopkins, D.C. Damage mechanics of microelectronics solder joints under high current densities. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 4021–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Papanikolaou, A.; Stucchi, M.; Croes, K.; TÖkei, Z.; Catthoor, F. The Analysis of System-Level Timing Failures Due to Interconnect Reliability Degradation. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2008, 8, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Kim, G.; Kim, K. Electromigration for advanced Cu interconnect and the challenges with reduced pitch bumps. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 64th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Orlando, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2014; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Huang, W.; Stan, M.R.; Skadron, K.; Lach, J. Interconnect Lifetime Prediction for Reliability-Aware Systems. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2007, 15, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Mansoor, M.A.; Basirun, W.J.; Sookhakian, M.; Huang, N.M.; Mun, L.K.; Söhnel, T.; Arifin, Z.; Mazhar, M. The synthesis and characterization of a hexanuclear copper–yttrium complex for deposition of semiconducting CuYO2–0.5Cu2O composite thin films. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraz, U.; Ansari, T.; Arain, S.; Mansoor, M.A.; Mazhar, M. Study of solvent effect on structural and photoconductive behavior of ternary chalcogenides InBiS3-In2S3-Bi2S3 composite thin films deposited via AACVD. Main Group Met. Chem. 2019, 42, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir Bashir, M.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A. Grain size stability of interfacial intermetallic compound in Ni and Co nanoparticle-doped SAC305 solder joints under electromigration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 14240–14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.N.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Wakeel, S.; Khan, M.A.; Quazi, M.M.; Khan, N.B.; Ahmed, A.; Soudagar, M.E.M. Effect of Ni and Co nanoparticle-doped flux on microstructure of SAC305 solder matrix. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 20106–20120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhao, H.; Guo, F.; Xu, G. Bi Layer Formation at the Anode Interface in Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu Solder Joints with High Current Density. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-t.; Chen, C.-m. Electromigration study in the eutectic SnBi solder joint on the Ni/Au metallization. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.N.; Butt, S.U.; Mansoor, M.A.; Khan, N.B.; Bashir, S.; Wong, Y.H.; Alamro, T.; Eldin, S.M.; Jameel, M. Role of Crystallographic Orientation of β-Sn Grain on Electromigration Failures in Lead-Free Solder Joint: An Overview. Coatings 2022, 12, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, S.; Nishio, N.; Suzuki, T.; Murakami, Y.; Ohashi, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Okumura, H. Electromigration Reliability of the Contact Hole in SiC Power Devices Operated at Higher Junction Temperatures. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 645–648, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieu, N.; Salm, C.; Krabbenborg, B.; Weide-Zaage, K.; Bisschop, J.; Mouthaan, A.J.; Kuper, F.G. Effect of thermal gradients on the electromigration life-time in power electronics. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium. Proceedings, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–29 April 2004; Volume 2004, pp. 619–620. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, G.; Haslett, J.W.; Dew, S.K.; Brett, M.J. Simulation of temperature cycling effects on electromigration behavior under pulsed current stress [VLSI metallization]. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1998, 45, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, Y.H.; Hu, Y.C.; Tsai, C.M.; Kao, C.R.; Tu, K.N. In situ observation of the void formation-and-propagation mechanism in solder joints under current-stressing. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.R.; Tsai, C.M.; Lin, Y.W.; Kao, C.R. Pronounced electromigration of Cu in molten Sn-based solders. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Kao, C.R.; Tu, K.N. Electromigration failure in flip chip solder joints due to rapid dissolution of copper. J. Mater. Res. 2003, 18, 2544–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Chang, C.W.; Tsai, C.M.; Lee, C.W.; Kao, C.R. Electromigration-induced UBM consumption and the resulting failure mechanisms in flip-chip solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 2006, 35, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.-W. Recent Progress in Physics-Based Modeling of Electromigration in Integrated Circuit Interconnects. Micromachines 2022, 13, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.N.; Khan, N.B.; Bashir, S.; Khan, A.F.; Quazi, M.M.; Gul, M.; Wakeel, S.; Saad, H.M. Effect of Zn nanoparticle-doped flux on mechanical properties of SAC305 solder joint after electromigration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, K.; Kurihara, T.; Sakai, T.; Imaizumi, N.; Shimizu, K.; Sakuyama, S.; Higashi, M. Electro-migration Behavior in Eutectic Sn-Bi Flip Chip Solder Joints with Cu-Pillar Electrodes. J. Smart Process. 2013, 2, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun Deo, K.; Yang, J.; Lai, Y.; Yang, D.; Park, S. Influence of Doping on the Electromigration Performance of SAC Solder Alloys on BGA Components. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 75th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Dallas, TX, US, 27–30 May 2025; pp. 1405–1411. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Xu, G.; Guo, F. Electromigration-induced Bi-rich whisker growth in Cu/Sn–58Bi/Cu solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Xu, G.; Sun, J.; Xia, Z.; Lei, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, X. Resistance Changes in Eutectic Sn-Bi Solder Joints During Electromigration. J. Electron. Mater. 2009, 38, 2756–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-M.; Jung, S.-B. Effect of surface finishes on electromigration reliability in eutectic Sn–58Bi solder joints. Microelectron. Eng. 2014, 120, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadian, F.; Flores, J.; Cotts, E. The Variation of the Electrical Resistance and Microstructure of SnBi based Solder Joints with Current Stressing. JOM 2022, 74, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Saka, M.; Muraoka, M.; Yamashita, M.; Hokazono, H. Electromigration Behaviors and Effects of Addition Elements on the Formation of a Bi-rich Layer in Sn58Bi-Based Solders. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 4179–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, K.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, C.-J.; Jung, S.-B. Electromigration behaviors of Sn58%Bi solder containing Ag-coated MWCNTs with OSP surface finished PCB. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-m.; Huang, C.-c. Effects of silver doping on electromigration of eutectic SnBi solder. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 461, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Ye, S. Effect of surface finish (OSP and ENEPIG) on failure mechanism induced by electromigration in Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu flip chip solder interconnect. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Advanced Packaging Materials (APM), Xiamen, China, 25–28 October 2011; pp. 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.K.J.; Lee, M.J.; Pai, S.Y.; Chen, S.; Kuo, F. Evaluation of electromigration (EM) life of ENEPIG and CuSOP surface finishes with various solder bump materials. In Proceedings of the 2010 Proceedings 60th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1–4 June 2010; pp. 1841–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Guo, F.; Wang, X.; Xia, Z.; Lei, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, X. Retarding the electromigration effects to the eutectic SnBi solder joints by micro-sized Ni-particles reinforcement approach. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Yoon, J.-W.; Jung, S.-B. Electromigration effect on Sn-58 % Bi solder joints with various substrate metallizations under current stress. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, K.P.L.; Islam, M.N.; Rotanson, J.; Cheung, C.-w.; Chan, A.H.S. Enhancement of Sn-Bi-Ag Solder Joints with ENEPIG Surface Finish for Low-Temperature Interconnection. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 5191–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dale, T.F.; Lakshminarayana, S.A.P.; Greene, C.V.; Badwe, N.U.; Aspandiar, R.F.; Blendell, J.E.; Subbarayan, G.; Handwerker, C.A. Influence of Pad Surface Finish on the Microstructure Evolution and Intermetallic Compound Growth in Homogeneous Sn-Bi and Sn-Bi-Ag Solder Interconnects. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 6615–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).