A Comprehensive Review of AI Methods in Agri-Food Engineering: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Firstly, unlike previous reviews that focus on single AI subfields such as examining only deep learning for disease detection [16], this work systematically maps several core AI pillars to key agricultural processes across the entire value chain of pre-production (crop variety selection, land preparation), in-production (sowing, precision irrigation/fertilization, pest management), and post-production (storage, supply chain traceability). This taxonomy clarifies how different AI techniques address specific agricultural tasks, providing a unified framework for understanding technical pathways.
- Secondly, beyond technical challenges, this review identifies and addresses the fundamental barriers that have hindered widespread AI adoption in agriculture. The primary challenges stem from the inherent complexities of agricultural environments, including high data variability due to diverse climatic conditions, soil types, and crop varieties, which make it difficult to develop generalizable models. Small sample problems persist due to the cost and time-intensive nature of collecting high-quality agricultural datasets, while the lack of standardized data formats across different farming systems creates integration difficulties. Additionally, the economic constraints faced by smallholder farmers limit access to expensive AI-powered technologies, and the digital divide in rural areas poses significant deployment challenges.
- Thirdly, looking toward the future, this review establishes the directions for AI-driven agricultural transformation by linking current applications to specific bottlenecks in traditional farming practices. The identified directions include the establishment of robust dataset construction and standardization systems, the development and deployment of emerging AI technologies that can democratize access, and the enhancement of AI security and explainability. This comprehensive analysis bridges the gap between academic research and practical implementation, serving as a reference for researchers, policymakers, and agricultural technology developers in advancing sustainable and intelligent agriculture.
| Reference | Remote Sensing | IoT Hardware | ML/DL Algorithm | Soil/Crop Monitor | Irrigation Optimization | Pest/Disease Detect | IoT Security | Dataset Build |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| [11] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| [12] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| [13] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| [14] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| [17] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| [18] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| This work | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
2. Overview of AI
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Literature Search Strategy
3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
3.3. Screening and Selection Process
- Clarity of objectives: Are the aims and research questions of the study explicitly stated and well motivated?
- Appropriateness of design: Does the research design comprehensively address the relevant aspects of AI applications in agriculture (e.g., data sources, sensing modalities, algorithms, deployment contexts) and enabling technologies (e.g., IoT, connectivity, security protocols)?
- Methodological transparency: Are the methods, models, and experimental setups described in sufficient detail to enable reproducibility?
- Evidence and benchmarks: Are the datasets, benchmarks, and evaluation metrics credible, representative, and aligned with the stated objectives?
- Validity of conclusions: Are the findings supported by adequate data analysis, and do the conclusions logically follow from the presented evidence?
4. The Application of AI in Agri-Food Engineering
4.1. Agricultural Product Quality Monitoring
4.1.1. Ingredients and Condition Inspection
4.1.2. Classification Identification
4.2. Agricultural Product Safety Analysis
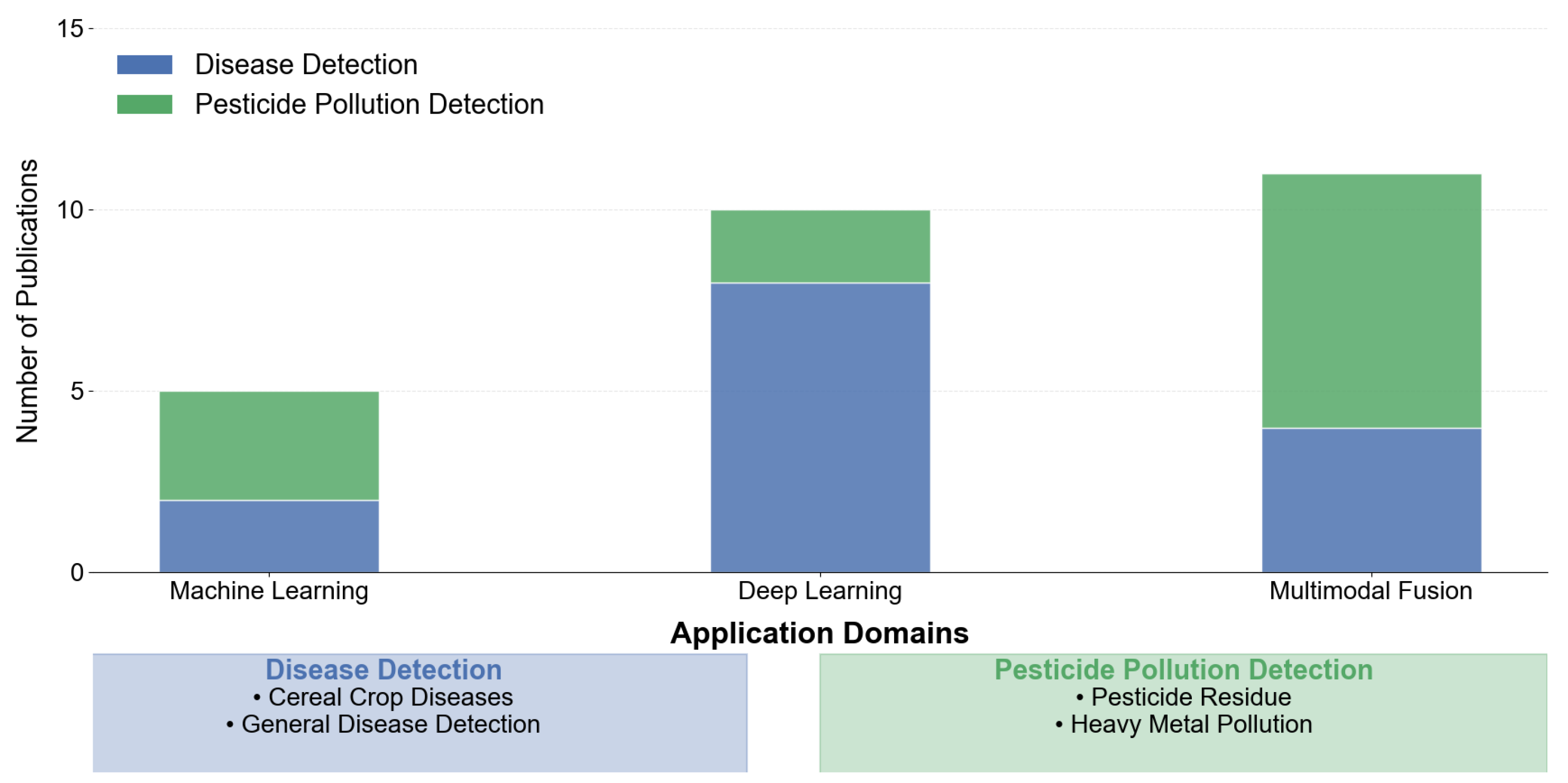
4.2.1. Disease Detection
4.2.2. Pesticide Pollution Detection
4.3. Agricultural Production Process Management
4.3.1. Environmental Monitoring
4.3.2. Optimization of Production Decision Making
4.3.3. Supply Chain Management and Control
5. Existing Challenges
5.1. Dataset Construction Challenges
5.1.1. Technical and Cost Barriers in Data Collection
5.1.2. Professional Knowledge Requirements and Annotation Challenges
5.1.3. Lack of Standardization and Interoperability
5.1.4. Privacy Protection and Sharing Mechanisms
5.2. Algorithm Performance and Deployment Challenges
5.2.1. Computational Complexity and Real-Time Requirements
5.2.2. Technology Acceptance Barriers for Smallholder Farmers
5.2.3. Few-Shot Learning Limitations
5.2.4. Insufficient Explainability
5.3. Environmental Sustainability and Regulatory Framework
5.3.1. Environmental Impact Duality
5.3.2. Regulatory Landscape Complexity
5.3.3. Policy Implementation Gaps
6. Future Directions
6.1. Dataset Construction and Standardization Systems
6.1.1. Multi-Source Data Integration and Standardization
6.1.2. Crowdsourcing Annotation and Expert Knowledge Integration
6.1.3. Data Sharing Incentive Mechanisms
6.1.4. Synthetic Data Generation Technologies
6.2. Emerging AI Technologies in Agricultural Applications
6.2.1. Low-Cost Deployment Solutions
6.2.2. Large Models Empowering Agricultural Knowledge Services
6.2.3. Meta-Learning for Adaptability Solutions
6.3. AI Security and Explainability Enhancement
6.3.1. Explainable AI Model Development
6.3.2. Agricultural AI Security Assurance Technologies
6.3.3. Ethical and Regulatory Frameworks
7. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Artificial Bee Colony | LS | Least Squares |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence | LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network | MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers | NIRS | Near-infrared Spectroscopy |
| CARS | Competitive Adaptive Reweighted Sampling | NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network | PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| CV | Computer Vision | PLS | Partial Least Squares |
| ELM | Extreme Learning Machine | PLSR | Partial Least Squares Regression |
| FCM | Fuzzy C-means | RF | Random Forest |
| FDCM | Fuzzy Discriminant C-means | RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm | RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Networks | SPA | Successive Projections Algorithm |
| GIS | Geographic Information System | SSC | Sparse Subspace Clustering |
| GPT | Generative Pretrained Transformer | SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| HSI | Hyperspectral Imaging | SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbor | SWIR | Short Wave InfraRed |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis | VIP | Variable Importance in Projection |
References
- Nakase, T.; Giovanetti, M.; Obolski, U.; Lourenço, J. Population at risk of dengue virus transmission has increased due to coupled climate factors and population growth. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, M.; Rastogi, M.; Rajesh, C.; Saikanth, D.; Rout, S.; Kumar, S.; Patel, A.K. Exploring traditional agricultural techniques integrated with modern farming for a sustainable future: A review. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 2024, 30, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymeni, S.; Plastras, S.; Skoutas, D.N.; Kormentzas, G.; Skianis, C. The impact of 6G-IoT technologies on the development of agriculture 5.0: A review. Electronics 2023, 12, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Z.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Yi, S.Y.; Moon, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J. Path-tracking simulation and field tests for an auto-guidance tillage tractor for a paddy field. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 112, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Noguchi, N.; Yang, L. Leader–follower system using two robot tractors to improve work efficiency. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 121, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Noguchi, N. Development of a multi-robot tractor system for agriculture field work. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 142, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfani, P.; Thuraga, V.; Banerjee, B.; Chawade, A. Integrative approaches in modern agriculture: IoT, ML and AI for disease forecasting amidst climate change. Precis. Agric. 2024, 25, 2589–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talero-Sarmiento, L.H.; Parra-Sanchez, D.T.; Lamos-Diaz, H. A bibliometric analysis of computational and mathematical techniques in the cocoa sustainable food value chain. Heliyon 2025, 11, e43015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Islam, M.R.; Mamun, Q.; Mahboubi, A.; Walsh, P.; Islam, M.Z. A comprehensive survey on AI-enabled secure social industrial internet of things in the Agri-food supply chain. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 11, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniyan, S.; Varma, V.A.; Naidu, C.T. Crop yield prediction using machine learning techniques. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2023, 175, 103326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhajharia, K.; Mathur, P.; Jain, S.; Nijhawan, S. Crop yield prediction using machine learning and deep learning techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.C.; Ribeiro, J.; Morais, R.; Sousa, J.J.; Cunha, A. A systematic review on automatic insect detection using deep learning. Agriculture 2023, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithambarathanu, M.; Jeyakumar, M. Survey on crop pest detection using deep learning and machine learning approaches. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 42277–42310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EG, A.; Bala, G.J. IoT and ML-based automatic irrigation system for smart agriculture system. Agron. J. 2024, 116, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Gebresenbet, G.; Bosona, T.; Patterson, D.; Persson, H.; Fischer, B.; Mandaluniz, N.; Chirici, G.; Zacepins, A.; Komasilovs, V.; Pitulac, T.; et al. A concept for application of integrated digital technologies to enhance future smart agricultural systems. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Shah, B.; Ei-Sappagh, S.; Ali, A.; Ullah, A.; Alenezi, F.; Gechev, T.; Hussain, T.; Ali, F. An advanced deep learning models-based plant disease detection: A review of recent research. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1158933. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, Y. Satellite-and drone-based remote sensing of crops and soils for smart farming–a review. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 66, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Alsmadi, I. Machine learning approaches to IoT security: A systematic literature review. Internet Things 2021, 14, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeschi, R. AI turns fifty: Revisiting its origins. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2007, 21, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, H.; Yin, S.; Kaynak, O. Quo vadis artificial intelligence? Discov. Artif. Intell. 2022, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestino, A.; De Mauro, A. Leveraging artificial intelligence in business: Implications, applications and methods. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2022, 34, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazemi, T.; Darwish, M.; Radi, M. Renewable energy sources integration via machine learning modelling: A systematic literature review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benos, L.; Tagarakis, A.C.; Dolias, G.; Berruto, R.; Kateris, D.; Bochtis, D. Machine learning in agriculture: A comprehensive updated review. Sensors 2021, 21, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binson, V.; Thomas, S.; Subramoniam, M.; Arun, J.; Naveen, S.; Madhu, S. A review of machine learning algorithms for biomedical applications. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 52, 1159–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolón-Canedo, V.; Morán-Fernández, L.; Cancela, B.; Alonso-Betanzos, A. A review of green artificial intelligence: Towards a more sustainable future. Neurocomputing 2024, 599, 128096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.D.; Islam, M.; Sobuz, M.H.R.; Ahmed, S.; Kar, M. Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications in the project lifecycle of the construction industry: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forootan, M.M.; Larki, I.; Zahedi, R.; Ahmadi, A. Machine learning and deep learning in energy systems: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadi, Y.Y.; Mazhar, T.; Al Shloul, T.; Shahzad, T.; Salaria, U.A.; Ahmed, A.; Hamam, H. Machine learning solutions for the security of wireless sensor networks: A review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 12699–12719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyortsuun, N.K.; Kim, S.H.; Jhon, M.; Yang, H.J.; Pant, S. A review of machine learning and deep learning approaches on mental health diagnosis. Healthcare 2023, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Pan, W.; Chen, Q. Real-time monitoring of process parameters in rice wine fermentation by a portable spectral analytical system combined with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.E.; Xiaobo, Z.; Jiyong, S.; Mariod, A.A.; Wiliam, T. Rapid determination of antioxidant compounds and antioxidant activity of Sudanese Karkade (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) using near infrared spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.E.; Xiaobo, Z.; Tinting, S.; Jiyong, S.; Mariod, A.A. Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy for rapid measurement of antioxidant properties and discrimination of Sudanese honeys from different botanical origin. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.E.; Xiaobo, Z.; Zhihua, L.; Jiyong, S.; Zhai, X.; Wang, S.; Mariod, A.A. Rapid prediction of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of Sudanese honey using Raman and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareef, M.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Arslan, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Ahmad, W.; Viswadevarayalu, A.; Wang, P.; Ancheng, W. Rapid screening of phenolic compounds in congou black tea (Camellia sinensis) during in vitro fermentation process using portable spectral analytical system coupled chemometrics. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e13996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zareef, M.; He, P.; Sun, H.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, D. Evaluation of matcha tea quality index using portable NIR spectroscopy coupled with chemometric algorithms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5019–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Man, Z.x.; Kang, W.c.; Guan, B.b.; Chen, Q.s.; Xue, Z.l. A novel colorimetric sensor array based on boron-dipyrromethene dyes for monitoring the storage time of rice. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, S.; Ning, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z. Evaluating green tea quality based on multisensor data fusion combining hyperspectral imaging and olfactory visualization systems. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Chen, Q. Monitoring black tea fermentation using a colorimetric sensor array-based artificial olfaction system. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, Z.; Xuan, L.; Lu, M.; Shi, B.; Shi, J.; He, F.; Battino, M.; Zhao, L.; Zou, X. Rapid determination of geographical authenticity and pungency intensity of the red Sichuan pepper (Zanthoxylum bungeanum) using differential pulse voltammetry and machine learning algorithms. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 137978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinger, D.; Longin, L.; Grbeš, F.; Benković, M.; Jurina, T.; Kljusurić, J.G.; Tušek, A.J. Detection of honey adulteration–The potential of UV-VIS and NIR spectroscopy coupled with multivariate analysis. LWT 2021, 145, 111316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q. Prediction and visualization of moisture content in Tencha drying processes by computer vision and deep learning. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5486–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, M.A.; Balmaki, B.; Dyer, L.A.; Allen, J.M.; Sallam, M.F.; Frontalini, F. Efficient pollen grain classification using pre-trained Convolutional Neural Networks: A comprehensive study. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Liang, X.; Fan, C. Nondestructive detecting maturity of pineapples based on visible and near-infrared transmittance spectroscopy coupled with machine learning methodologies. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Carneiro, L.; Coradi, P.C.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Lima, R.E.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; Santos de Moraes, R.; Teodoro, P.E.; Nunes, M.T.; Leal, M.M.; Lopes, L.R.; et al. Characterizing and predicting the quality of milled rice grains using machine learning models. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 1196–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lv, R.; Wang, S.; Aheto, J.H.; Dai, C. Integration of computer vision and colorimetric sensor array for nondestructive detection of mango quality. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Huang, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J. A novel hyperspectral microscopic imaging system for evaluating fresh degree of pork. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 362. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, S.; Yating, L.; Xiaohong, W.; Chunxia, D.; Yong, C. SSC prediction of cherry tomatoes based on IRIV-CS-SVR model and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, B.; Sun, J.; Dai, C. Identification of tea varieties by mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy coupled with a possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering with a fuzzy covariance matrix. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Xu, H.; Aheto, J.H.; Bonah, E.; Ma, M.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X. Rapid and nondestructive detection of freshness quality of postharvest spinaches based on machine vision and electronic nose. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Lu, B.; Wu, M.; Dai, C. Grade identification of tieguanyin tea using fluorescence hyperspectra and different statistical algorithms. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q. Determination of tea polyphenols in green tea by homemade color sensitive sensor combined with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongyang, T.; Daming, H.; Xingyi, H.; Aheto, J.H.; Yi, R.; Yu, W.; Ji, L.; Shuai, N.; Mengqi, X. Detection of browning of fresh-cut potato chips based on machine vision and electronic nose. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, F.; Yang, X.; Li, J. Application of long-wave near infrared hyperspectral imaging for determination of moisture content of single maize seed. Spectrochim. Acta Part Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 254, 119666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wu, P.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Ji, X.; Shen, Q.; Yu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Combining computer vision score and conventional meat quality traits to estimate the intramuscular fat content using machine learning in pigs. Meat Sci. 2022, 185, 108727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, A.; Singh, V.; Kamruzzaman, M. Identification of informative spectral ranges for predicting major chemical constituents in corn using NIR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Kalita, D.; Ahmed, M.T.; ElMasry, G.; Makino, Y. Effect of variable selection algorithms on model performance for predicting moisture content in biological materials using spectral data. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1202, 339390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yang, C.; Hu, B.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Dong, C. Research on moisture content detection method during green tea processing based on machine vision and near-infrared spectroscopy technology. Spectrochim. Acta Part Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 271, 120921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lin, H.; Kang, W.; Shao, X.; Cai, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Application of colorimetric sensor array coupled with machine-learning approaches for the discrimination of grains based on freshness. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 6790–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Sui, Y. Prediction of anthocyanin content in purple-leaf lettuce based on spectral features and optimized extreme learning machine algorithm. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Niu, Y. Estimating leaf chlorophyll content of winter wheat from UAV multispectral images using machine learning algorithms under different species, growth stages, and nitrogen stress conditions. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.y.; Pan, S.h.; Sun, Z.y.; Ye, W.t.; Aheto, J.H. Evaluating quality of tomato during storage using fusion information of computer vision and electronic nose. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, S.; Mao, H.; Wu, X.; Li, Q. Classification of black beans using visible and near infrared hyperspectral imaging. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, B.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Du, H. Discrimination of apples using near infrared spectroscopy and sorting discriminant analysis. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, B.; Sun, J.; Yang, N. Classification of apple varieties using near infrared reflectance spectroscopy and fuzzy discriminant c-means clustering model. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, P.; Zheng, Y.; An, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, P.; Pan, X. Spatial-spectral feature extraction of hyperspectral images for wheat seed identification. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 101, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Nirere, A.; Dusabe, K.D.; Yuhao, Z.; Adrien, G. Rapid and nondestructive watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) seed viability detection based on visible near-infrared hyperspectral imaging technology and machine learning algorithms. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 4403–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putri, L.A.; Rahman, I.; Puspita, M.; Hidayat, S.N.; Dharmawan, A.B.; Rianjanu, A.; Wibirama, S.; Roto, R.; Triyana, K.; Wasisto, H.S. Rapid analysis of meat floss origin using a supervised machine learning-based electronic nose towards food authentication. NPJ Sci. Food 2023, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Infante, M.; Castro-Valdecantos, P.; Delgado-Pertiñez, M.; Teixeira, A.; Guzmán, J.; Horcada, A. Machine learning strategy for light lamb carcass classification using meat biomarkers. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Geng, J.; Wu, Y.; Fan, R.; Kang, Z. Identification of pesticide residues on black tea by fluorescence hyperspectral technology combined with machine learning. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e55822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fan, S.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, Q.; Kong, J. Discrimination of new and aged seeds based on on-line near-infrared spectroscopy technology combined with machine learning. Foods 2024, 13, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Hughes, D.P.; Salathé, M. Using deep learning for image-based plant disease detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 215232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Sun, J.; Mao, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X. Non-destructive detection for mold colonies in rice based on hyperspectra and GWO-SVR. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Yuan, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J.; Mao, H. Tea diseases detection based on fast infrared thermal image processing technology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3459–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Jun, S.; Ning, Y.; Xiaohong, W.; Xin, Z. Identification of tea white star disease and anthrax based on hyperspectral image information. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cai, J.R.; Zhang, W.; Bai, J.W.; Li, Z.Q.; Tan, B.; Sun, L. Detection of citrus Huanglongbing (HLB) based on the HLB-induced leaf starch accumulation using a home-made computer vision system. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 218, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, Q.; Guo, Z.; Wu, J. Rapid Pseudomonas species identification from chicken by integrating colorimetric sensors with near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addissouky, T.A.; El Sayed, I.E.T.; Ali, M.M.; Alubiady, M.H.S. Optical insights into fibrotic livers: Applications of near-infrared spectroscopy and machine learning. Arch. Gastroenterol. Res. 2024, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, J.A.; Kumar, V.D.; Geman, O.; Hnatiuc, M.; Arif, M.; Kanchanadevi, K. Plant disease detection using deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, M.; Chawla, P. Deep Learning-Based Maize Crop Disease Classification Model in Telangana Region of South India. IEEE Trans. Agrifood Electron. 2024, 2, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, H.R.; Mumtaz, R.; Inayat, S.; Shafi, U.; Haq, I.U.; Zaidi, S.M.H.; Hafeez, M. Assessing the impact of segmentation on wheat stripe rust disease classification using computer vision and deep learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 164986–165004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Hartley, M.; Morris, R.J.; Brown, J.K. Classification of wheat diseases using deep learning networks with field and glasshouse images. Plant Pathol. 2023, 72, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyi, E.O.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sukumaran, A.T.; Thames, H.T.; Pokhrel, D. Non-destructive assessment of microbial spoilage of broiler breast meat using structured illumination reflectance imaging with machine learning. Food Anal. Methods 2024, 17, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, H.T.; Shahabi, S.M.; Sharma, A.; Tande, L.Q.; Husarik, K.; Qin, J.; Chan, D.E.; Baek, I.; Kim, M.S.; MacKinnon, N.; et al. Combining deep learning and fluorescence imaging to automatically identify fecal contamination on meat carcasses. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Weng, S.; Xiao, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y. Rapid and accurate identification of bakanae pathogens carried by rice seeds based on hyperspectral imaging and deep transfer learning. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 311, 123889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yoon, S.; Jeong, Y.; Park, D.S. Transfer learning for versatile plant disease recognition with limited data. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1010981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Mao, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q. D iscrimination of pesticide residues in lettuce based on chemical molecular structure coupled with wavelet transform and near infrared hyperspectra. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ge, X.; Wu, X.; Dai, C.; Yang, N. Identification of pesticide residues in lettuce leaves based on near infrared transmission spectroscopy. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Jun, S.; Bing, L.; Xiaohong, W.; Chunxia, D.; Ning, Y. Study on pesticide residues classification of lettuce leaves based on polarization spectroscopy. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Xu, Q.; Qiu, X.; Jin, Y.; Ji, J.; Lin, Y.; Le, S.; She, J.; Lu, D.; Wang, G. Evaluation and application of machine learning-based retention time prediction for suspect screening of pesticides and pesticide transformation products in LC-HRMS. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, G. Detecting different pesticide residues on Hami melon surface using hyperspectral imaging combined with 1D-CNN and information fusion. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapcharoensuk, R.; Fhaykamta, C.; Anurak, W.; Chadwut, W.; Sitorus, A. Nondestructive detection of pesticide residue (Chlorpyrifos) on bok choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis) using a portable NIR spectrometer coupled with a machine learning approach. Foods 2023, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Quan, X.; Zhang, T.; Kong, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Y. Integrated surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and convolutional neural network for quantitative and qualitative analysis of pesticide residues on pericarp. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajikhani, M.; Hegde, A.; Snyder, J.; Cheng, J.; Lin, M. Integrating transformer-based machine learning with SERS technology for the analysis of hazardous pesticides in spinach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Hasi, W.; Lin, X.; Han, S. Automated identification of pesticide mixtures via machine learning analysis of TLC-SERS spectra. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, X.; Dai, C.; Li, B. Spectral classification of lettuce cadmium stress based on information fusion and VISSA-GOA-SVM algorithm. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Tian, Y.; Lu, B.; Hang, Y.; Chen, Q. Hyperspectral technique combined with deep learning algorithm for detection of compound heavy metals in lettuce. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, S.M.; Mansoor, S.; Wani, O.A.; Kumar, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, A.; Arya, V.M.; Kirkham, M.; Hou, D.; Bolan, N.; et al. Artificial intelligence and IoT driven technologies for environmental pollution monitoring and management. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1336088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.A.; El-Habib, M.F.; Sababa, R.Z.; Al-Hanjor, M.M.; Abunasser, B.S.; Abu-Naser, S.S. Artificial intelligence in agriculture: Enhancing productivity and sustainability. Int. J. Eng. Inf. Syst. (IJEAIS) 2024, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Rhee, J. AMSR2 soil moisture downscaling using multisensor products through machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1984–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Heddam, S.; Wu, S.; Dai, J.; Jia, B. Extreme learning machine-based prediction of daily water temperature for rivers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizamir, M.; Kisi, O.; Ahmed, A.N.; Mert, C.; Fai, C.M.; Kim, S.; Kim, N.W.; El-Shafie, A. Advanced machine learning model for better prediction accuracy of soil temperature at different depths. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaydukova, M.; Kirsanov, D.; Sarkar, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Ashina, J.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Chanda, S.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Legin, A. One shot evaluation of NPK in soils by “electronic tongue”. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 186, 106208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Y. Improving carbon flux estimation in tea plantation ecosystems: A machine learning ensemble approach. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 160, 127297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.J.; Lucas, D.D. Machine learning predictions of a multiresolution climate model ensemble. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4273–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Razzaq, A.; Tariq, W.; Hameed, A.; Rehman, A.; Razzaq, K.; Sarfraz, S.; Rajput, N.A.; Zaki, H.E.; Shahid, M.S.; et al. Spectral intelligence: AI-driven hyperspectral imaging for agricultural and ecosystem applications. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, G.; Rani, C.; GaneshKumar, P. An automated low cost IoT based Fertilizer Intimation System for smart agriculture. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2020, 28, 100300. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.; Oliullah, K.; Kabir, M.M.; Alom, M.; Mridha, M. Machine learning enabled IoT system for soil nutrients monitoring and crop recommendation. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, C. Rapid prediction of the re-watering time point of Orychophragmus violaceus L. based on the online monitoring of electrophysiological indexes. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lian, Y.; Zou, R.; Zhang, S.; Ning, X.; Han, M. Real-time grain breakage sensing for rice combine harvesters using machine vision technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jin, M.; Tian, C.; Yang, S.X. Prediction of seed distribution in rectangular vibrating tray using grey model and artificial neural network. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 175, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, B.; Sun, J.; Mujumdar, A.S. Artificial intelligence assisted technologies for controlling the drying of fruits and vegetables using physical fields: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Hewitt, A.J.; Wang, P.; Luo, X.; Zang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lan, Y.; O’Donnell, C. Development of droplet characteristics prediction models for air induction nozzles based on wind tunnel tests. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmansyah, E.; Pardamean, B.; Ginting, C.; Mawandha, H.G.; Putra, D.P.; Suparyanto, T. Development of artificial intelligence for variable rate application based oil palm fertilization recommendation system. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information Management and Technology (ICIMTech), Jakarta, Indonesia, 19–20 August 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Durai, S.K.S.; Shamili, M.D. Smart farming using machine learning and deep learning techniques. Decis. Anal. J. 2022, 3, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Hussain, I.; Huang, N.F. Soil suitability classification for crop selection in precision agriculture using GBRT-based hybrid DNN surrogate models. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, T.; Patle, B.; Kashyap, S.K. Intelligent insecticide and fertilizer recommendation system based on TPF-CNN for smart farming. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 3, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Hao, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Xu, J.; Guo, S.; Huo, J.; Wang, W. An Efficient Computer Vision-Based Dual-Face Target Precision Variable Spraying Robotic System for Foliar Fertilisers. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeltagi, A.; Srivastava, A.; Deng, J.; Li, Z.; Raza, A.; Khadke, L.; Yu, Z.; El-Rawy, M. Forecasting vapor pressure deficit for agricultural water management using machine learning in semi-arid environments. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, B.; Jignasa, G.; Madhubabu, K.; Gopi, A. AI-Driven Smart Irrigation: Enhancing Agricultural Water Efficiency Through Intelligent Valve Regulation in Piped and Micro Irrigation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 First International Conference on Pioneering Developments in Computer Science & Digital Technologies (IC2SDT), Delhi, India, 2–4 August 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Manikantan, M.; Parameswari, P.; Dhivakar, R. An IoT-Based Smart System for Crop Management by Dynamic Irrigation System Using Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2025 3rd International Conference on Advancements in Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computing and Automation (ICAECA), Coimbatore, India, 4–5 April 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ashfaq, T.; Khalid, R.; Yahaya, A.S.; Aslam, S.; Azar, A.T.; Alsafari, S.; Hameed, I.A. A machine learning and blockchain based efficient fraud detection mechanism. Sensors 2022, 22, 7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amponsah, A.A.; Adekoya, A.F.; Weyori, B.A. A novel fraud detection and prevention method for healthcare claim processing using machine learning and blockchain technology. Decis. Anal. J. 2022, 4, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jin, X.; Yang, H.; Tu, L.; Ye, Y.; Li, S. Blockchain-Based Internet of Things: Machine Learning Tea Sensing Trusted Traceability System. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 8618230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavai, A.; Bouzembrak, Y.; Mu, W.; Martin, F.; Kaliyaperumal, R.; Van Soest, J.; Choudhury, A.; Heringa, J.; Dekker, A.; Marvin, H.J. Applying federated learning to combat food fraud in food supply chains. NPJ Sci. Food 2023, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Albarrak, A.S. A blockchain-driven food supply chain management using QR code and XAI-faster RCNN architecture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyuktepe, O.; Catal, C.; Kar, G.; Bouzembrak, Y.; Marvin, H.; Gavai, A. Food fraud detection using explainable artificial intelligence. Expert Syst. 2025, 42, e13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukas, V.; Gkogkidis, A.; Kampa, A.; Spathoulas, G.; Kakarountas, A. Enhancing food supply chain security through the use of blockchain and TinyML. Information 2022, 13, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, I.M.M.; Aravindhar, D.J. Integrated blockchain-based agri-food traceability and deep learning for profit-optimized supply chain management in agri-food supply chains. In Proceedings of the 2024 Fourth International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Computing, Communication and Sustainable Technologies (ICAECT), Bhilai, India, 11–12 January 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, M.; Xu, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, S.; Sun, C. Integration of privacy protection and blockchain-based food safety traceability: Potential and challenges. Foods 2022, 11, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gu, J.; Wang, M. A review on the application of computer vision and machine learning in the tea industry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1172543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabhan, B.; Obaidat, M.A. Privacy-preserving blockchain framework for supply chain management: Perceptive Craving Game Search Optimization (PCGSO). Sustainability 2023, 15, 6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, S.B.; Rana, M.M.; Sohag, H.J.; Shikder, F.; Faraji, M.R.; Hasan, M.M. Understanding the financial transaction security through blockchain and machine learning for fraud detection in data privacy and security. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2024, 22, 17782–17803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondaveeti, H.K.; Sai, G.B.; Athar, S.A.; Vatsavayi, V.K.; Mitra, A.; Ananthachari, P. Federated learning for smart agriculture: Challenges and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2024 Third International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics (ICDCECE), Ballari, India, 26–27 April 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Freyhof, M.; Grispos, G.; Pitla, S.K.; Mahoney, W. Investigating The Implications of Cyberattacks Against Precision Agricultural Equipment. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security (ICCWS 2025), Williamsburg, VA, USA, 28–29 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Li, J.; Bai, Y. Federated learning-based intrusion detection system for iot environments with locally adapted model. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 10th International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing (CSCloud)/2023 IEEE 9th International Conference on Edge Computing and Scalable Cloud (EdgeCom), Hunan, China, 1–3 July 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Alsulaimawi, Z. Securing Federated Learning with Control-Flow Attestation: A Novel Framework for Enhanced Integrity and Resilience against Adversarial Attacks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavlas, N.C.; Porre, R.; Meng, L.; Elhakeem, A.; van Egmond, F.; Kooistra, L.; De Deyn, G.B. Cover crop impacts on soil organic matter dynamics and its quantification using UAV and proximal sensing. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 9, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. Deep learning in agriculture: A survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Young, S. A survey of public datasets for computer vision tasks in precision agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameski, P.; Zdravevski, E.; Trajkovik, V.; Kulakov, A. Weed detection dataset with RGB images taken under variable light conditions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on ICT Innovations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Giselsson, T.M.; Jørgensen, R.N.; Jensen, P.K.; Dyrmann, M.; Midtiby, H.S. A public image database for benchmark of plant seedling classification algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cicco, M.; Potena, C.; Grisetti, G.; Pretto, A. Automatic model based dataset generation for fast and accurate crop and weeds detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 5188–5195. [Google Scholar]
- Teimouri, N.; Dyrmann, M.; Nielsen, P.R.; Mathiassen, S.K.; Somerville, G.J.; Jørgensen, R.N. Weed growth stage estimator using deep convolutional neural networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.; Konovalov, D.A.; Philippa, B.; Ridd, P.; Wood, J.C.; Johns, J.; Banks, W.; Girgenti, B.; Kenny, O.; Whinney, J.; et al. DeepWeeds: A multiclass weed species image dataset for deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espejo-Garcia, B.; Mylonas, N.; Athanasakos, L.; Fountas, S.; Vasilakoglou, I. Towards weeds identification assistance through transfer learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 171, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.; Whelan, B.; Sukkarieh, S. A high-resolution, multimodal data set for agricultural robotics: A Ladybird’s-eye view of Brassica. J. Field Robot. 2020, 37, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestur, R.; Meduri, A.; Narasipura, O. MangoNet: A deep semantic segmentation architecture for a method to detect and count mangoes in an open orchard. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 77, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumam, K.; Krajník, T.; Pearson, S.; Cielniak, G.; Duckett, T. Can you pick a broccoli? 3D-vision based detection and localisation of broccoli heads in the field. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 646–651. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, S.A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Elfiky, N.M.; Kak, A. A novel benchmark RGBD dataset for dormant apple trees and its application to automatic pruning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Alencastre-Miranda, M.; Davidson, J.R.; Johnson, R.M.; Waguespack, H.; Krebs, H.I. Robotics for sugarcane cultivation: Analysis of billet quality using computer vision. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3828–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.K.; Skovsen, S.; Karstoft, H.; Gislum, R. The oil radish growth dataset for semantic segmentation and yield estimation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 2703–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfert, S.; Ge, L.; Verdouw, C.; Bogaardt, M.J. Big data in smart farming—A review. Agric. Syst. 2017, 153, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, K.G.; Busato, P.; Moshou, D.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Machine learning in agriculture: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraforos, D.S.; Sharipov, G.M.; Griepentrog, H.W. ISO 11783-compatible industrial sensor and control systems and related research: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 163, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhiary, M.; Kumar, R.; Sethi, L.N. Navigating the future of agriculture: A comprehensive review of automatic all-terrain vehicles in precision farming. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. A 2024, 105, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Tong, Y. Federated machine learning: Concept and applications. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2019, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlZubi, A.A.; Galyna, K. Artificial intelligence and internet of things for sustainable farming and smart agriculture. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 78686–78692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The Future of Food and Agriculture: Trends and Challenges; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ferentinos, K.P. Deep learning models for plant disease detection and diagnosis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 145, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R. Artificial intelligence in agriculture: A review. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 6–8 May 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 937–942. [Google Scholar]
- Getahun, S.; Kefale, H.; Gelaye, Y. Application of precision agriculture technologies for sustainable crop production and environmental sustainability: A systematic review. Sci. World J. 2024, 2024, 2126734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delort, E.; Riou, L.; Srivastava, A. Environmental Impact of Artificial Intelligence. Ph.D. Thesis, INRIA, CEA Leti, Grenoble, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chiappetta, A. Navigating the AI frontier: European parliamentary insights on bias and regulation, preceding the AI Act. Internet Policy Rev. 2023, 12, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The FDA Moves into Third Phase of Artificial Intelligence Imported Seafood Pilot Program. 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/hfp-constituent-updates/fda-moves-third-phase-artificial-intelligence-imported-seafood-pilot-program (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Srinatha, T.; Abhishek, G.; Kumar, P.; Aravinda, B.; Baruah, D.; Gireesh, S.; Thakur, N.; Perumal, A. Agricultural policy reforms and their effects on smallholder farmers: A comprehensive review. Arch. Curr. Res. Int. 2024, 24, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibbern, T.; Romani, L.A.S.; Massruhá, S.M.F.S. Main drivers and barriers to the adoption of Digital Agriculture technologies. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, N.; Othman, M.F.; Abdoulghafor, R.; Belhaouari, S.B.; Mamat, N.; Mohd Hussein, S.F. Advanced technology in agriculture industry by implementing image annotation technique and deep learning approach: A review. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, F. Agricultural data sharing and sustainable development of ecosystem based on block chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 127869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylianidis, C.; Osinga, S.; Athanasiadis, I.N. Introducing digital twins to agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 184, 105942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakuri, J.P.; Nkundineza, C.; Gatera, O.; Nkurikiyeyezu, K.; Mwitende, G. AI and IoT-powered edge device optimized for crop pest and disease detection. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoumas, I.; Sitokonstantinou, V.; Giannarakis, G.; Lampiri, E.; Athanassiou, C.; Camps-Valls, G.; Kontoes, C.; Athanasiadis, I.N. Leveraging causality and explainability in digital agriculture. Environ. Data Sci. 2025, 4, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S. Few-shot crop disease recognition using sequence-weighted ensemble model-agnostic meta-learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1615873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade Porto, J.V.; Dorsa, A.C.; de Moraes Weber, V.A.; de Andrade Porto, K.R.; Pistori, H. Usage of few-shot learning and meta-learning in agriculture: A literature review. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Marinello, F.; Ercisli, S.; Zhang, Z. A survey of few-shot learning in smart agriculture: Developments, applications, and challenges. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouni, M.; Hssina, B.; Douzi, K.; Douzi, S. Interpretable machine learning techniques for an advanced crop recommendation model. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2024, 2024, 7405217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
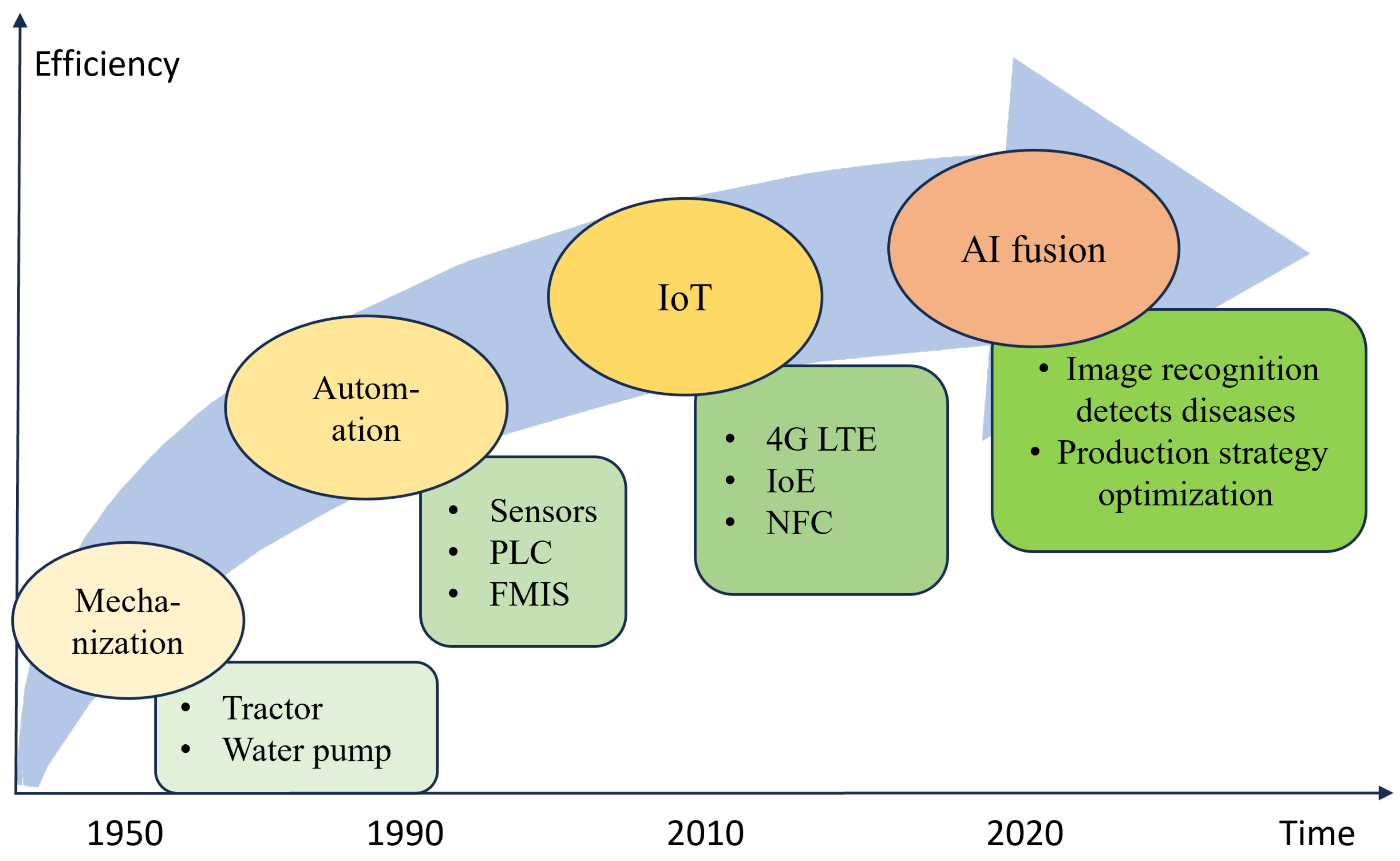
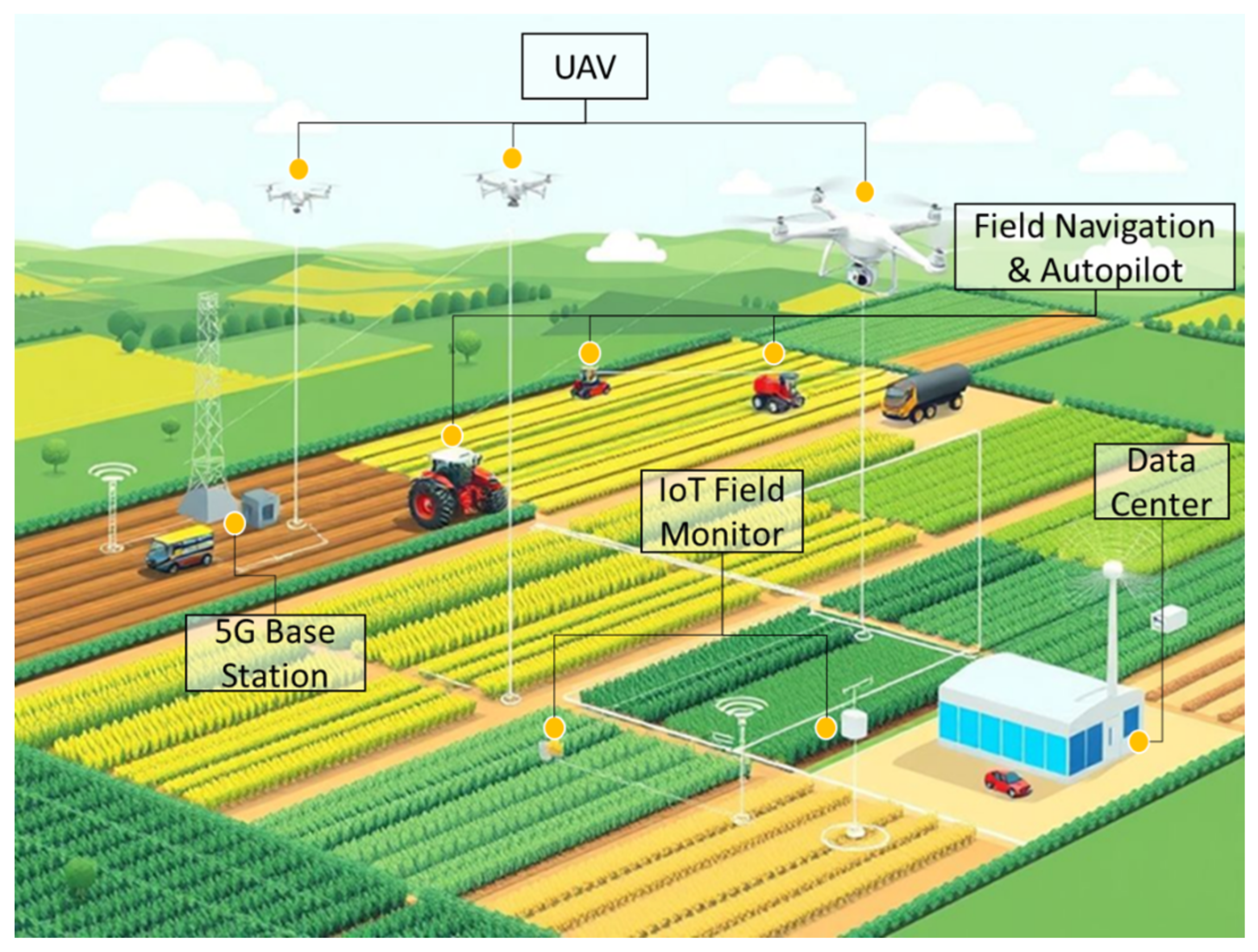

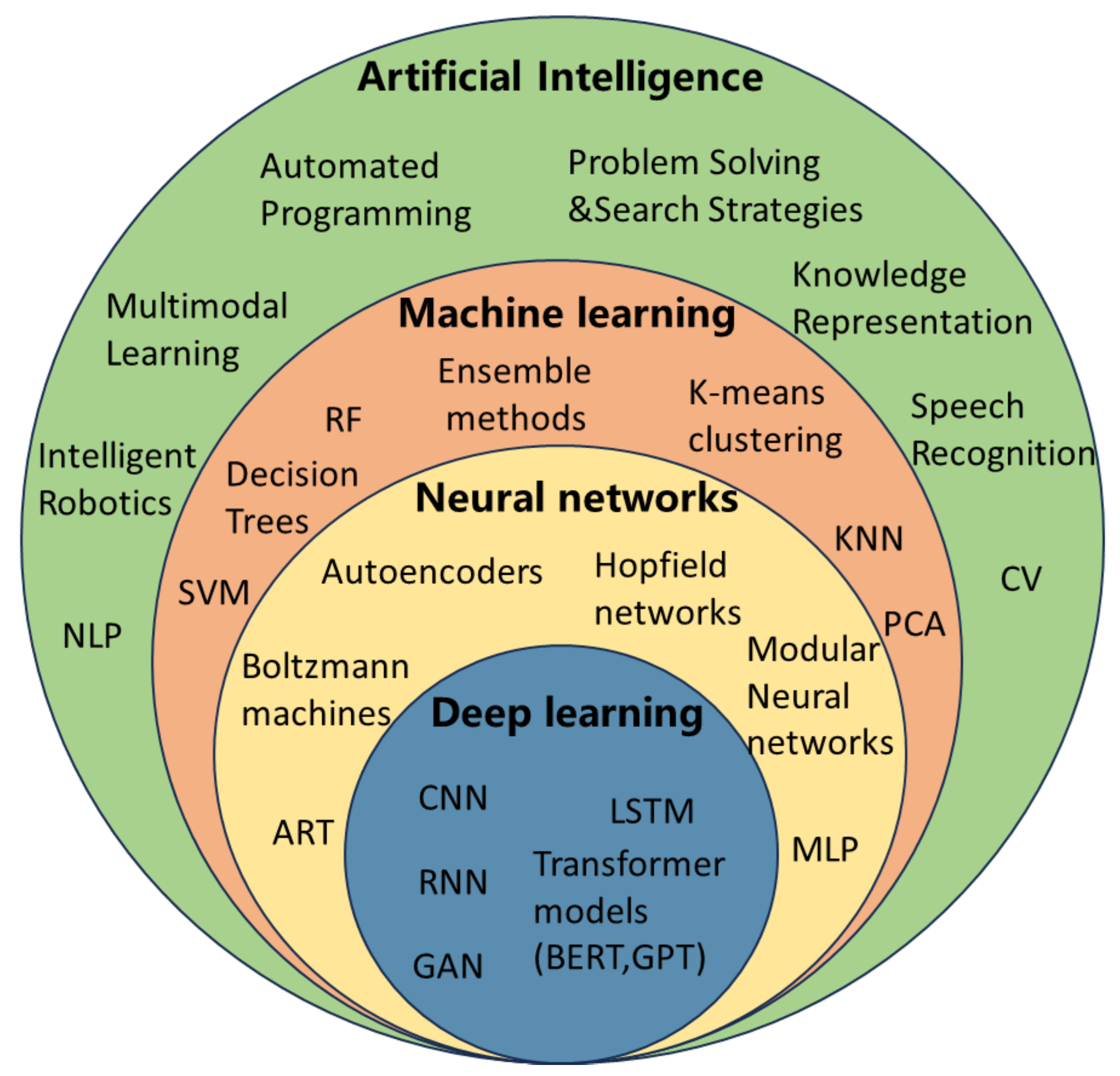

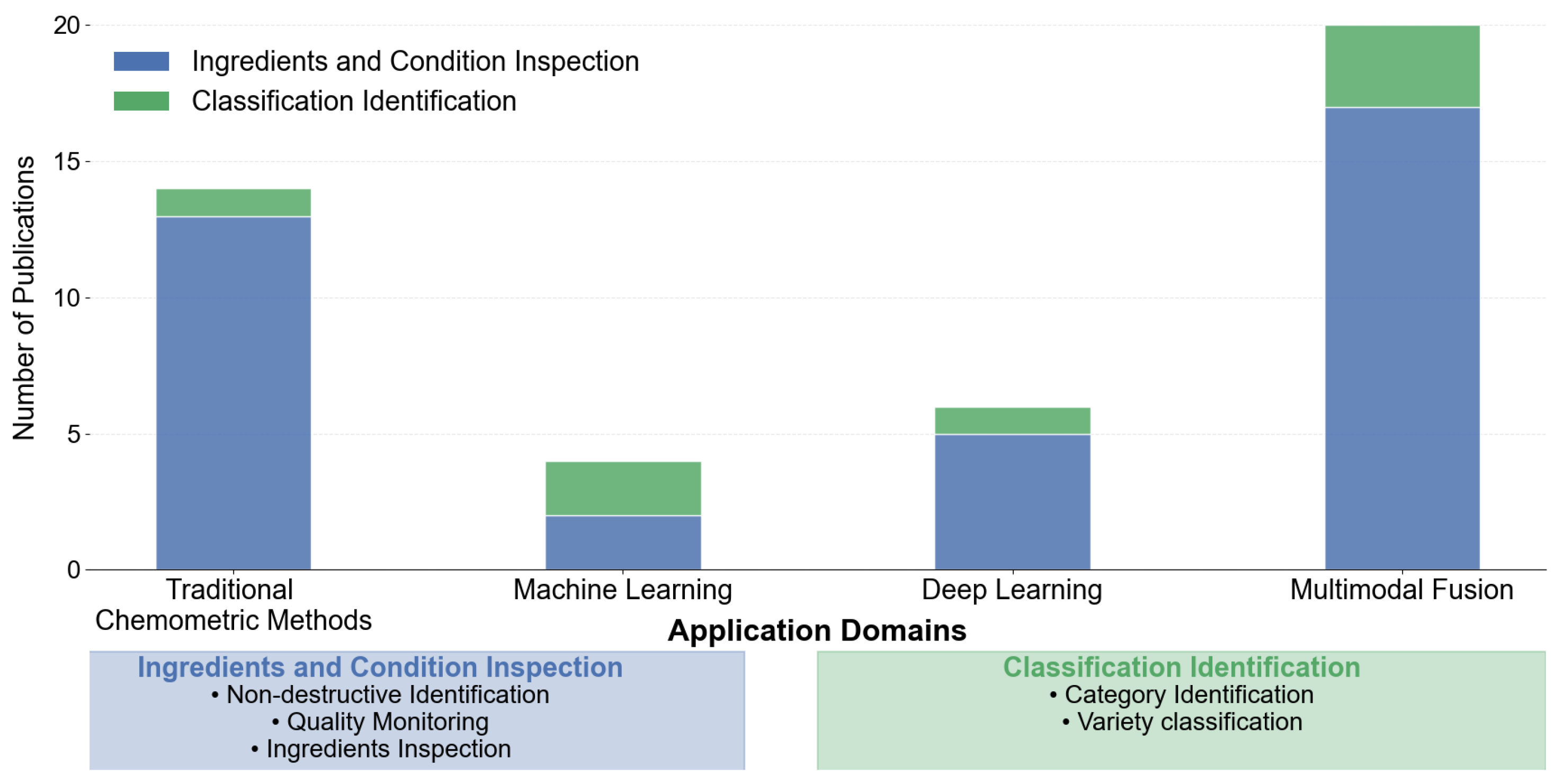

| Product | Parameter | Best Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Honey | Antioxidation | LDA | [33] |
| Antioxidation | PLSR | [34] | |
| Adulteration Detection | ANN | [41] | |
| Apple | Classification | PCA-LDA | [64] |
| Classification | FDCM | [65] | |
| Black Tea | Fermentation Parameters | CARS-PLS | [35] |
| Fermentation Parameters | KNN-AdaBoost | [39] | |
| Pesticide Residue | 1D-CNN-RF | [70] | |
| Green Tea | Tea Polyphenol | ACO-ELM | [52] |
| Approbation | PFCM | [49] | |
| Quality Rating | PCA-LDA | [38] | |
| Quality Rating | VISSA-SVM | [51] | |
| Moisture Content | CARS-SVR | [58] | |
| Maize | Moisture Content | CARS-SPA-LS-SVM | [54] |
| Moisture Content | CARS-PLSR | [57] | |
| Moisture Content | VIP-GA | [56] | |
| Non-Destructive Inspection | PLS-DA | [71] |
| Reference | Modeling Algorithm | Accuracy on the Prediction Set |
|---|---|---|
| Sun2017 [87] | CMS-WT-SVM | 100% |
| Sun2018 [88] | CARS-IRIV-GSA-SVM | 98.33% |
| Xin2018 [89] | CARS-SVM | 97.78% |
| Lapcharoensuk2023 [92] | SVM-PC-ANN | 100% |
| Zhou2019 [96] | VISSA-GOA-SVM | 98.57% |
| Parameter | Best Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cyanidin | DBO-ELM | [60] |
| Pesticide Residue | CMS-WT | [87] |
| Pesticide Residue | CARS-IRIV-GSA-SVM | [88] |
| Pesticide Residue | CARS - SVM | [89] |
| Pesticide Residue | PC-ANN-SVM | [92] |
| Heavy Metal Residue | VISSA-GOA-SVM | [96] |
| Heavy Metal Residue | WT-SCAE-SVR | [97] |
| Dataset Name | Main Deficiency |
|---|---|
| Carrot-Weed [141] | Small scale (only 39 images) |
| Plant Seedlings [142] | Only image-level annotation (no target location information) |
| Synthetic SugarBeet Weeds [143] | Algorithm generation (non-real scene) |
| Leaf Counting [144] | Only leaf number classification is supported |
| DeepWeeds [145] | Only image-level labels (no pixel/target labeling) |
| Early Crop Weed [146] | Each graph contains only a single species. |
| Ladybird Cobbitry Brassica [147] | Without any label, the amount of data is very large (>2.8 TB) |
| MangoNet [148] | The user needs to cut the high-resolution image (4000 × 3000 → 200 × 200) by himself |
| 3D Broccoli [149] | No annotation; only original point cloud and video data are provided |
| Apple Trees [150] | Only raw depth and color images are available |
| Sugarcane Billets [151] | Only image-level labels (no target location/segmentation labeling) |
| Oil Radish Growth [152] | The test set is unannotated (34 images) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.; Ji, Z.; Wang, H.; Shao, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Kong, W.; Xia, J.; Bao, X. A Comprehensive Review of AI Methods in Agri-Food Engineering: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions. Electronics 2025, 14, 3994. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14203994
Wu K, Ji Z, Wang H, Shao X, Li H, Zhang W, Kong W, Xia J, Bao X. A Comprehensive Review of AI Methods in Agri-Food Engineering: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions. Electronics. 2025; 14(20):3994. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14203994
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kaichen, Zhenyang Ji, Hanyue Wang, Xiaoyan Shao, Haohan Li, Wence Zhang, Wa Kong, Jing Xia, and Xu Bao. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of AI Methods in Agri-Food Engineering: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions" Electronics 14, no. 20: 3994. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14203994
APA StyleWu, K., Ji, Z., Wang, H., Shao, X., Li, H., Zhang, W., Kong, W., Xia, J., & Bao, X. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of AI Methods in Agri-Food Engineering: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions. Electronics, 14(20), 3994. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14203994






