Abstract
The synthesis of two series of poly(lactic acid) (PLA)-based polymer nanocomposites (PNCs) filled with small amounts (0.5 and 1%) of Ag and Cu nanoparticles (NPs) was performed. Moreover, two methods for the PNC synthesis were performed, namely, ‘conventional mixing techniques’ and ‘in situ ring opening polymerization (ROP)’. The latter method was employed for the first time; moreover, it was found to be more effective in achieving very good NP dispersion in the polymer matrix as well as the formation of interfacial polymer–NP interactions. The in situ ROP for PLA/Cu was not productive due to the oxidation of Cu NPs being faster than the initiation of ROP. The presence of NPs resulted in suppression of the glass transition temperature, Tg (23–60 °C), with the effects being by far stronger in the case of ROP-based PNCs, e.g., exhibiting Tg decrease by tens of K. Due to that surprising result, the ROP-based PLA/Ag PNCs exhibited elevated ionic conductivity phenomena (at room temperature). This can be exploited in specific applications, e.g., mimicking the facilitated small molecules permeation. The effects of NPs on crystallinity (2–39%) were found opposite between the two series. Crystallinity was facilitated/suppressed in the mixing/ROP -based PNCs, respectively. The local and segmental molecular mobility map was constructed for these systems for the first time. Combining the overall data, a concluding scenario was employed, that involved the densification of the polymer close to the NPs’ surface and the free volume increase away from them. Finally, an exceptional effect was observed in PLA + 0.5% Ag (ROP). The crystallization involvement resulted in a severe suppression of Tg (−25 °C).
1. Introduction
Polymer nanocomposites (PNCs) [1,2] have attracted significant attention during the past decades, as they combine the excellent performance of polymers with the further properties improvement imposed by the addition of nanoparticles (NPs) [3]. The benefit of NPs as fillers against conventional micro- or macro- additives arises from the fact that due to the nanoscale dimensions of NPs, the surface-to-volume ratio is severely larger [3,4]. Thus, the specific surface area being offered for ‘interactions’ with the polymer is significantly larger in the NPs [5,6]. Therefore, the NPs may introduce tremendous effects on the polymer at very small loadings. From a similar point of view, it has been proposed that the aspect ratio of the NPs, i.e., the ratio of the larger to smaller dimension, plays the critical role [7,8]. The said role lies in the modifications of the polymer characteristics (structure [9,10], chain topology [10,11], and molecular dynamics [12,13,14]) some nanometers from the filler surface. This is actually the case for amorphous polymers. In the case of semicrystalline polymers, the impact of NP is indirect, namely, via the impact on crystalline fraction, nucleation, crystal formation and semicrystalline morphology [15,16]. For moderate and high crystallinity degrees, the presence of polymer crystals is the dominant factor over the macroscopic performance, namely, mechanical strength [17,18], glass transition temperature [19,20], heat transport [8,16,21], and permeation of small molecules [22,23], even in physical polymer decomposition [24]. In this sense, the role of NPs size, dispersion, and surface characteristics, as well as the interfacial adhesion of the polymer, are indeed indirect via the corresponding effects on crystallinity.
Obviously, crucial is the quality of the NP dispersion throughout the polymer matrix [25,26]. This aspect is controlled by a variety of parameters, among them, for example, being the method of polymer–particle mixing and the NPs’ surface modifications that can potentially affect the polymer chains’ adhesion and the NPs’ size [11,27]. We have recently prepared and studied a series of PNCs based on renewable polyesters via ‘in situ polymerization’ methods [15,28,29]. This synthetic route involves the polymerization of monomers in the presence of NPs. The NPs offer active-polar groups (--COOH and -OH, etc.) onto which the initial monomers are attached and, thus, the polymerization initiates from these sites. This method has been proved, at least so far for the published studies in polyesters, to offer practically a high possibility for excellent NPs dispersion in PNCs. However, a relative disadvantage is being implemented, i.e., the drop of the polymer molecular weight (Mn, Mw). This is expected to have a first negative impact on the mechanical performance [30]. However, it may lead to advantages in the processing or other properties and other aspects (e.g., minimization of NPs content).
Since the main focus is on polymer-based materials, we should consider the environmental concerns (e.g., impacts on the plastic waste accumulation [31,32]) and the modern green and circular economic frame [33,34]. During the last two decades, the scientific community has made a serious turn towards this direction. In particular for polymers, much effort has been paid to developing and applying biobased polymers derived from renewable resources. Among them are the following well-known polyesters: poly(lactic acid), PLA [32,35], and poly(ε-caprolactone), PCL [36,37]. More recently, an additional class of sustainable polyesters has been developed, namely, based on acids produced via metabolic processes of plants, in particular, from succinic acid, vanillic acid, and 2.5 furandicarboxyl acid.
The polymer of interest here is PLA, an aliphatic semicrystalline polyester [35,38]. Despite the extensive work on PLA-based PNCs already published, this polymer still offers space for more studies. PLA combines a range of characteristics that makes it still a quite interesting candidate to use in nanotechnology. Thus, this polymer is involved in a variety of applications, from academia, biochemistry, and industry to our everyday life [39,40,41,42,43]. Next to the green and sustainable character of PLA, arising from its favorable synthesis from renewable resources (e.g., from cornstarch, beets or sugarcane, and potatoes) [44,45], it can be prepared employing relatively mild processes, both chemically and thermally. These are connected with its relatively low glass transition temperatures, Tg, ~50–60 °C, as well as its melting points, Tm ~160–190 °C [46,47,48]. Furthermore, these thermal properties can be easily tuned to large extents compared with the known fossil-based industrial polymers (PS, PE, and PMMA).
PLA has been studied in bulk form as well as in the form of PNCs, within which a variety of nanosized (spherical, sheet, and tube) fillers have been added and dispersed by mixing routes [49,50]. In the present study, we attempt to synthesize PLA-based PNCs, with the fillers being the Ag and Cu metal NPs. Such PNCs have been studied in the past [51,52,53,54]; however, they were prepared by trivial mixing and solution casting methods. The main project herein is to assess the NPs’ effects on a PLA matrix with the simultaneous comparison between PNCs synthesized via mixing(s) and in situ ring opening polymerization (ROP) of PLA in the presence of the NPs. The latter in situ method has been applied to other renewable polyesters [15,28] and proved quite successful, producing good PNC properties with very low NP loadings. This is also necessary in the present work, as the prepared PLA/Ag-Cu PNCs are envisaged for use as substrates for electronic applications [54,55,56]. Next to the PNCs preparation, here, the materials are studied employing a sum of complementary techniques for the structure, thermal transitions, crystallinity, electrical conductivity, and molecular dynamics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
1-dodecanol and tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate Sn(Oct)2 were supplied by Aldrich Co. (London, UK). L-lactide (LA) (99.9%) was purchased from PURAC Biochem BV (Gorinchem, The Netherlands) under the brand name PURASORB® L, and the Luminy® PLA L175, with a melt flow index (MFI) at 8 g/10 min (Flow, 210 °C/2.16 kg) and 3 g/10 min (Flow, 190 °C/2.16 kg), was purchased from Corbion N.V. (Amsterdam, The Netherlands). Ag nanopowder, APS 20–40 nm (99.9%), and Cu nanopowder, APS 20–50 nm (99.9%), nanoparticles were supplied from ThermoFisher Scientific (Berlin, Germany). All other materials and solvents used were of analytical grade.
2.2. Nanocomposite Preparation
2.2.1. Solution Casting and Melt-Mixing
PLA-based PNCs incorporated with Ag and Cu masterbatches were initially prepared by solution casting. In brief, 2 g of PLA were dissolved in 20 mL of chloroform (10% w/v). Subsequently, the quantity of the NPs required for the final concentration of 0.5 and 1.0 wt%, in 10 g, which corresponds to the total amount of the PLA PNCs, was dispersed in chloroform (1 mg/mL) via ultrasonication bath for 1 h. Then, the prepared solution was added into a PLA solution under magnetic stirring for an additional 1 h. Each of the mixtures were placed in Petri dishes and was left overnight in a vacuum at 80 °C for the solvents to evaporate.
The PLA and PLA PNC masterbatches were dried again overnight in a vacuum at 80 °C. To prepare the PNCs by melt mixing, the appropriate amount of each dried masterbatch and dried PLA was added to a melt mixer, a Haake–Buchler twin-screw co-rotating extruder, with a mixing head with a volumetric capacity of 11 cm3, operating at 190 °C and 30 rpm for 5 min. In total, five materials were prepared via the melt-mixing method.
2.2.2. In Situ Ring Opening Polymerization (ROP)
ROP of L-lactide was conducted for the synthesis of PLA and PLA PNCs based on Ag nanoparticles. Concerning the synthesis of PLA, during the first step of the reaction, 400 ppm of Sn(Oct)2 and 1-dodecanol (dissolved in acetone) were added in a round-bottom flask at 160 °C for 1.5 h (350 rpm) under nitrogen flow (N2). The unreacted monomers were removed from the reaction mixture by slowly applying high vacuum distillation (5.0 Pa) for 15 min at 180 °C (400 rpm). The polymerization reaction was ended by rapidly cooling the flask at room temperature. In the case of PLA PNCs, the in situ ROP reactions were performed in the presence of Ag NPs at two different mass concentrations, 0.5 and 1.0 wt%. In total, three samples were prepared via the in situ polymerization approach.
We should note that when attempting to prepare similar PNCs with Cu NPs as filler, the in situ ROP was not productive. The problematic parameter was most probably the fast oxidation of Cu NPs, taking place already at room conditions [57]; moreover, upon the temperature elevation (involved within the ROP), the oxidation already occurred prior to the initiation of ROP and, thus, the ‘grafting’ of the lactide monomers on these NPs was precluded. Thus, the polymerization was developed independently from the NPs, resulting in neat PLA polymerization. The latter was checked by the final molecular weight.
In all cases, the samples were studied in the form of self-standing films of ~0.2–0.5 mm in thickness. This form was achieved by melt-pressing using homemade molds.
2.3. Characterization Methods
The technique of attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy was employed to assess the existence of physical bonds between the polymer and the filler NPs. The spectra were recorded for the samples in the amorphous state, namely, priorly melted and subsequently quenched. An IRTracer-100 spectrophotometer by Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan) equipped with a QATR™ 10 Single-Reflection ATR Accessory with a Diamond Crystal was employed, and the spectra were recorded in the absorbance mode, within the wavenumber range from 400 to 4000 cm−1 and at steps of 2 cm−1. The presented spectra correspond to a total of 32 co-added scans that were normalized and baseline-corrected.
The molecular weight of the materials was evaluated using Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) with a Waters 600 high-performance liquid chromatographic pump (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA), Waters Ultrastyragel columns HR-1, HR-2, HR-4E, HR-4, and HR-5, and a Shimadzu RID10A refractive index detector. Nine polystyrene (PS) standards of MW between 2.5 and 900 kg/mol were employed for the calibration. The prepared solutions had a 10 mg/mL concentration in chloroform; the injection volume was 150 µL, and the total elution time was 50 min. The oven temperature was 40 °C.
Intrinsic viscosity [η] measurements were also performed using an Ubbelohde viscometer (capillary 0c) at 25 °C, with chloroform as the solvent. The solutions were filtered through a disposable Teflon membrane to remove any solid residues. Intrinsic viscosity was calculated by applying the Solomon–Cuita equation as follows:
where c is the solution concentration, t is the flow time of the solution and t0 is the flow time of pure solvent.
To examine the quality of the Ag and Cu NPs distribution throughout the polymeric matrix, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) measurements were performed. The employed apparatus was an emission scanning electron microscope [JEOL (Tokyo, Japan) JSM 7610F] operating at 5 kV. Each specimen was positioned on the holder and coated with carbon to enhance the conductivity for the electron beam. The SEM micrographs were captured at the gold-sputtered cross-section of cryo-fractured samples.
Conventional differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was employed for thermal transitions’ investigation. To that aim, a TA Q200 calorimeter (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) was employed. The measurements were carried out on samples of 6–8 mg in mass in a nitrogen atmosphere (99.9995% purity) and within the temperature range from −90 to 205 °C. Prior to the main study, the samples were heated at T well above melting in order to erase the thermal history and maximize the pan-sample thermal contact. Then, two thermal scans were conducted beginning from the melt state, as follows: (scan 1) fast cooling in order to suppress melt-crystallization and subsequent heating at 10 K/min and (scan 2) cooling at 10 K/min, aiming at the facilitation of melt-crystallization and subsequent heating at 10 K/min. For selected samples, additional thermal treatments were employed, namely, slower cooling and/or isothermal annealing, aiming at the study of exception crystallization-induced phenomena on the glass transition.
Broadband dielectric spectroscopy (BDS) [58] was employed for the study of molecular mobility. The BDS measurements were conducted by means of a Novocontrol Alpha frequency response analyzer (Novocontrol GmbH, Montabaur, Germany) on the prepared films (0.2–0.5 mm in thickness), inserted between polished brass plates, i.e., in the form of a sandwich-like capacitor. The molecular mobility was assessed by following the various dipolar relaxation mechanisms, based on the alternation in the dielectric permittivity ε* = ε′ − i∙ε″, as a function of frequency (Df ~10−1–106 Hz) and temperature (T varying from −120 to 120 °C). BDS was also employed for the evaluation of conductivity, σAC, via ε* at room temperature (RT) [59], within the same frequency range from 10−1 up to 106 Hz.
The semi-crystalline structure was studied via X-ray diffraction (XRD) in the angle 2θ range from 5° to 45° by means of a MiniFlex II XRD system (Rigaku Co., Tokyo, Japan) with CuKα radiation (λ = 0.154 nm). The measurements were performed on samples previously subjected to melting and cooling at 10 K/min, similarly to scan 2 in DSC (i.e., melt-crystallized).
We also studied the semicrystalline morphology during melt crystallization optically, employing polarized light microscopy (PLM). The PLM images were taken during cooling from the melt state by means of a Nikon Optiphot-1 polarizing microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a Linkam THMS 600 heated stage (Linkam Scientific Instruments Ltd., Redhill, UK), a Linkam TP91 control unit, and a Jenoptic Gryphax Naos camera (Jenoptik, Jena, Germany), accompanied by the Jenoptic Gryphax software, version 2.1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure–Interactions–Filler Dispersion
The ATR-FTIR results are presented in Figure 1a for all PNC compositions. We recall that the data correspond to samples in the amorphous state. Due to the small NP amount, the signals are dominated by the bond vibrations originating from the polymer (e.g., C-H, C-O, -C=O), as expected. The recorded spectra herein are in accordance with those of previous materials based on PLA [60].
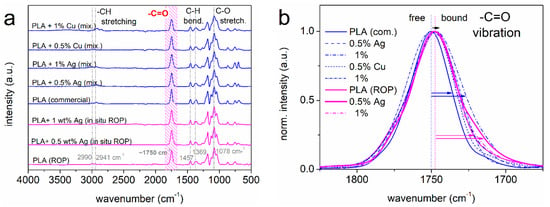
Figure 1.
(a) Comparative FTIR spectra for all samples. The data correspond to samples being priorly melted and quenched, i.e., with the polymers in the amorphous state. (b) Focus on the region of the ester bond vibration (FTIR peaks) for all samples upon normalization to the peak maxima. The added horizontal arrows mark either the migration or the widening of the said peaks to the lower wavenumber side for some PNCs, as compared to neat PLAs.
Our main interest is to seek documentation on the formation of polymer-NP interactions. In PLA it is expected that the ester site, belonging to the carbonyl group, should be involved in interfacial interactions, if any, as this is the most polar group of PLA [61].
The vibration of the ester bond (C=O) is recorded in FTIR within the wavenumber range from 1700 to 1800 cm−1. Figure 1b provides a focus on that range for all samples, wherein a normalization to the peak maximum has been performed [13]. In the case of strong or/and extended interfacial interactions via this group, the vibration becomes weaker (more rigid), and this can be followed in FTIR as either an overall migration of the peak towards lower wavenumbers or the recording of an additional contribution (secondary peak) at the lower wavenumbers [13,15].
In Figure 1b, both effects are recorded in the PNCs prepared by ‘mixing’, although to a low extent. This is manifested by both the weak migration of the peak maxima and the mild broadening at the low wavenumber side. On the other hand, there is no overall migration in the case of the ‘in situ ROP’ prepared PNCs. However, there is a clear recording of additional contribution on the ester group vibration at the lower wavenumber side, being recorded as a shoulder of the main peak in Figure 1b. Interestingly, the effect is stronger for the case of 0.5% Ag as compared to that of 1% Ag.
It can be, thus, concluded that there are interfacial interactions between the polymer and the NPs and are possibly stronger and much more extended in the case of the ROP-based PNCs, as compared to the ‘mixing-based’ ones. The latter is actually a strong indication for the successful in situ ROP, during which the scope was the initiation of the polymerization on the NPs’ surfaces (i.e., ab initio formed interactions/bonds).
In Table 1, we list the data for the number average molecular weights, Mn, the polydispersity indices, Đ, and the intrinsic viscosity [η]. For the commercial PLA and the corresponding PNCs Mn~140 kg/mol. The in-house synthesized PLA via ROP of L-lactide exhibits a relatively high Mn of ~90 kg/mol, being accompanied by a low Đ = 1.18. In the ROP-based PNCs, Mn is strongly decreased to 55 kg/mol for 0.5% Ag and mildly decreased to 85 kg/mol for 1% Ag. The effects in Mn are also reflected on those in [η] (Table 1), as expected. While the latter Mn values are not considered too low, for example, to affect the glass transition temperature [47] and the mechanical performance of the PNCs, the decrease is expected when the in situ polymerization over NPs is successful [15,28,29]. The stronger Mn decrease is observed at the lower Ag NP loadings and originates, most probably, from the better NP dispersion, in the sense that the NPs offer more sites for the initiation of ROP over the NPs’ surfaces. Thus, for given filler loadings and fixed ROP thermochemical conditions, the better dispersion should lead to the development of more PLA chains with shorter lengths (lower Mn) [15,28,29]. From another point of view, and upon correlations with previous findings in the literature [62,63,64], the strong Mn decrease could also be associated with ‘catalyst deactivation’. This can be caused by the oxidation on the Ag NPs’ surfaces, which, in the case of excellent NP dispersion, exhibit quite large specific surface areas as compared with the ones of filler loadings (i.e., 1% of Ag).

Table 1.
Number average molecular weight, Mn, and polydispersity index, Đ, and intrinsic viscosity [η] of neat PLAs and the PNCs prepared by in situ ROP.
The filler dispersion throughout the polymer matrix was examined by SEM. The representative images for all samples can be seen in Figure S1 of the Supplementary Materials. Figure 2 shows comparatively two PNCs filled with 0.5% Ag but prepared, on the one hand, by mixing (Figure 2a) and, on the other hand, by in situ ROP (Figure 2b).
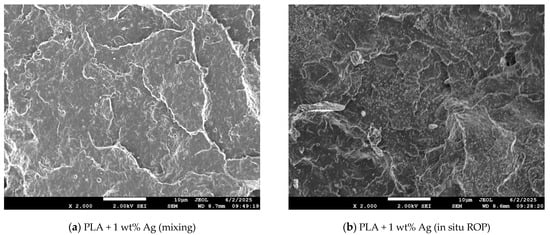
Figure 2.
Representative SEM micrographs of the PLA-based PNCs prepared by in situ ROP, filled with (a) 0.5% and (b) 1.0% Ag NPs. The images were captured at the cross-section, and the scale bars correspond to 10 μm.
In the mixing-based PNCs, the dispersion of NPs is moderate, while, as expected, the observed particles are mainly in the form of aggregates. Contrariwise, the NPs’ dispersion is almost excellent within the ROP-based PNCs, with some Ag aggregates also being observed. The view in Figure 2b for the latter case is wanted and expected due to the synthetic route. Practically, the excellent dispersion of NPs provides further indirect proof for the successful in situ ROP [28].
3.2. Glass Transition in the Amorphous’ State’
The attention is now turned on the thermal transitions, beginning with the DSC results by scan 1, which are presented in Figure 3. Scan 1 involves the melting and fast cooling (Figure 3a) of the samples. These aimed at the suppression of the crystallization and, subsequently, the study of the glass transition with the polymers preserved in the amorphous state. Consequently, any recorded effects on the glass transition and the cold crystallization (heating scan, Figure 3b) are considered to directly arise from the presence of the NPs.
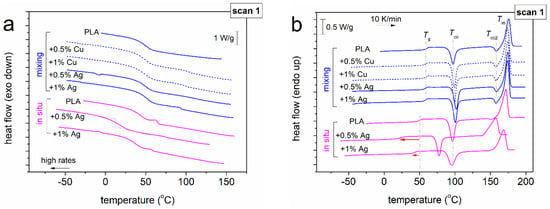
Figure 3.
Raw DSC results for scan 1, being shown for all samples, during (a) cooling and (b) the subsequent heating. The recorded heat flow is presented here upon normalization to the sample mass.
Indeed, the employed fast cooling in Figure 3a was fruitful in the elimination of crystallization, as the cooling rates [non-linear, T(t)] in the region of the expected crystallization (~70–120 °C) were estimated as 80–100 K/min. Then, from the subsequent heating, single and strong glass transition steps for all the amorphous samples were recorded, i.e., between about 20 to 60 °C. At the elevated temperatures of 60–110 °C, we recorded strong ‘cold crystallization’ exothermal peaks, and, finally, melting endothermal peaks at about 130–180 °C.
The main interest in this section is on the glass transition. Therefore, the characteristic temperature, Tg, was estimated via the half heat capacity change, Δcp, method. The estimated values are presented in the form of column diagrams as a function of composition in Figure 4a,b, with the results being quite interesting.
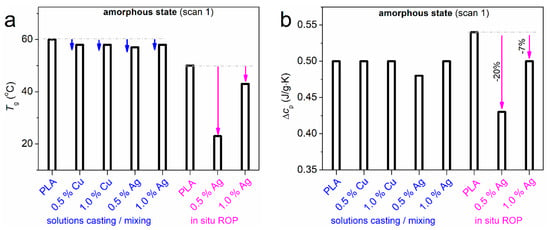
Figure 4.
The PNC composition dependence of the glass transition values, in the form of column diagrams, namely, the (a) glass transition temperature and (b) heat capacity change. The data correspond to initially amorphous samples. The added horizontal dashed lines correspond to the values for the neat amorphous PLA.
In the mixing-based PNCs, which were prepared employing the commercial PLA, the presence of NPs, although at very low loading, affects the Tg. More precisely, the Tg of PLA (60 °C) drops by 2–3 K (57–58 °C, Figure 4a). The strength of the glass transition, represented by Δcp, equals ~0.50 (±0.02) J/g∙K in commercial PLA and barely changes in the PNCs (Figure 4b).
Interestingly, the corresponding effects in the ROP-based PNCs are significantly stronger. Neat PLA exhibits a lower Tg of 50 °C which is strongly suppressed in the PNCs, i.e., down to the surprising values of 23 °C and 43 °C for 0.5% and 1% Ag, respectively (Figure 4a). The values were confirmed by additional measurements on the same as well as fresh samples. The effects on Δcp were found to be strong as well (Figure 4b). The Δcp of neat PLA-ROP [0.54 (±0.02) J/g∙K] was decreased to 0.23 and 0.50 for 0.5% and 1% Ag, respectively. Δcp is actually the measure of the mobile amorphous polymer fraction (MAF) that contributes to the glass transition process [14,20]. The reduction of Δcp indicates the partial immobilization of polymer [14], most probably of the polymer chains in the NPs-PLA interfacial layer/zone. This polymer zone is considered to be formed by amorphous rigid polymer chains, i.e., the so-called rigid amorphous fraction (RAF), and is estimated by the % reduction in MAF [14,20]. In our case this RAF is estimated as ~20 and ~7 wt% for 0.5% and 1% Ag, respectively. The results provide additional evidence for the existence of strong interfacial interactions in the case of the ROP-based PNCs; this provides support to the findings by FTIR (Figure 1b) as discussed in the previous.
Comparing our results with data for neat PLAs of various Mn [47], the impressive Tg drop here is not expected to originate directly from the recorded drop in Mn (Table 1). A hypothetical, although realistic, scenario to explain the parallel drop in the Tg and the existence of RAF in the ROP-based PNCs would be the significant densification of the polymer around the NPs and the density decrease in the bulk-like polymer fraction (i.e., away from the NPs). This will be further discussed later in the light of segmental dynamics results shed by BDS.
3.3. Crystallinity Aspects
The attention is now turned on the crystallinity-related effects. First, the raw data for DSC are presented in Figure 5a,b. To assess the direct filler effects on crystallization, melt crystallization is mainly studied, i.e., the exothermal peak developed during cooling directly upon the melt (hot) state. The corresponding data are presented in Figure 5a. Single crystallization peaks are recorded for all samples. It is worth noting that in neat commercial PLA, the crystallization is rather weak, which is expected, as the PLAs are known to lack nucleation in general [35].
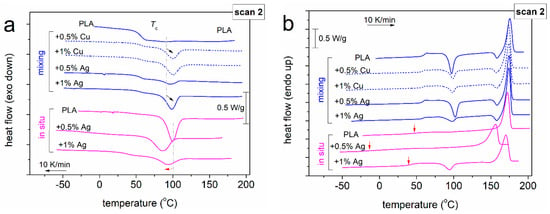
Figure 5.
Comparative DSC traces of scan 2 shown during (a) cooling and (b) heating. In (a), the added vertical lines and the arrows are used to mark the effects of NPs on the melt crystallization of PLA. In (b) the red vertical arrows were added to mark the glass transition region in the ROP-based systems.
In the PNCs, there are clear effects recorded, both in the temperature position (nucleation) and strength (crystalline fraction) towards various directions. In Figure 6, we have plotted in the form of column diagrams the composition dependences of the crystallization peak, Tc (Figure 6a), and the crystalline fraction, CF (Figure 6b). CF was estimated from melt crystallization (CFc) and, for comparison, from the melting peak (CFm) of Figure 5b. For the sake of methodological completeness, CFi was estimated following the trivial method of comparing the recorded enthalpy change (ΔHi), normalized to the polymer mass fraction, with the bibliographic value of the enthalpy change for the 100% crystalline PLA (taken here as 93 J/g [65]).
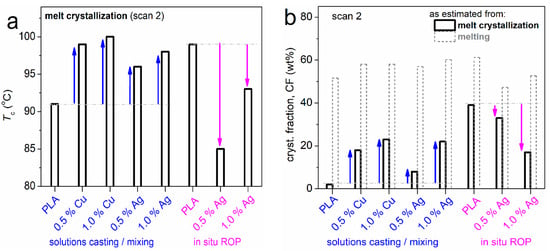
Figure 6.
The PNC composition effects on the melt-crystallization, namely, (a) crystallization temperature and (b) the corresponding crystalline fraction.
In Figure 6, one can follow two distinct behaviors regarding crystallization. For the mixing-based PNCs, the Tc of PLA (91 °C) increases in the PNCs by 5–9 K, whereas CFc increases significantly from 2 wt% (commercial PLA) to 8–23 wt%. The effects become stronger monotonically with the filler amount increase, while the effects of Cu NPs are slightly stronger than those of Ag NPs. It is quite clear from these data that the NPs favor nucleation and the crystalline fraction. Most probably, Cu and Ag play the additional role of nucleating agents [16,35,56,66]. This is quite expected for such nanofillers when there are no strong interfacial interactions involved [15].
On the other hand, in the ROP-based PNCs, opposite effects are revealed. Tc of neat PLA (99 °C) drops to 93 and 85 °C in the PNCs and, in parallel, CFc decreases from 39 wt% to 33 and 17 wt%. This suggests that Ag NPs here play the opposite role, namely, they reduce (steal) the number of active crystallization nuclei, despite the excellent distribution of the Ag NPs in the polymer matrix. The effect is familiar for our group(s) and can be explained in terms of the ‘ab initio’ formation of strong polymer-particles interaction, being formed from the initial stages of the in situ ROP synthesis. The strong and large number of interactions have been proven in the past to lead to the loss of nucleation sites [15,16] in PNCs.
Regarding crystallization in DSC, it is worth mentioning the last two points. First, the overall crystalline fraction that can be achieved in our systems can be relatively high. This is expressed by CFm ~50–60% in Figure 6b. This value includes the crystallization taking place both during cooling (melt crystallization) and the additional one taking place during the subsequent heating (cold crystallization). This overall CF is mildly suppressed only in the case of ROP-based PNCs. Finally, it is worth taking a last glance at Figure 5b, within which there is an interesting effect on the glass transition of the ROP-based PNCs. While crystallization is generally expected to elevate Tg, in the said materials, the presence of the crystals seems to impose a severe Tg decrease (even to sub-zero temperatures). The phenomenon is quite strong in PLA + 0.5% Ag.
For the more in-depth study of the polymer crystal structure, XRD was employed. All samples were melted and cooled at 10 K/min in order to melt and crystallize. The XRD spectra are shown in Figure 7a. Regarding the main diffraction peaks, mainly at 2θ positions between 10 and 25°, the number of the peaks is unchanged comparing the neat PLA and the PNCs. Comparing with previous findings on various PLAs from the literature [67,68] (and references therein), it can be concluded that the said peaks originate mainly from the so-called α-type crystals of PLA. In the case of ROP-based PLA and PNCs, additional peaks were recorded at the higher 2θ positions (Figure 7b), which are stronger in PLA + 1% Ag (ROP). The said peaks originate, most probably, from the formation of the α’ crystal form (see also Figure S2 in the Supplementary Materials), i.e., less ordered crystals, with sparser lamellae packing and possibly smaller spherulites. The latter is partly connected with the recorded drop in Mn for the said PNCs (Table 1).
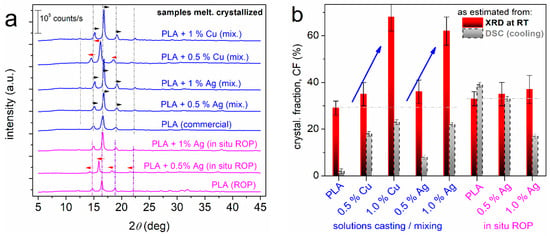
Figure 7.
(a) Comparative XRD spectra for all samples, previously subjected to melt-crystallization. The added vertical dash-dotted lines and horizontal arrows are used to mark the peak 2θ alternations recorded for the PNCs as compared to neat PLAs. (b) Crystalline fraction, CF, for all samples as estimated by XRD at DSC.
As far as the 2θ position of the crystalline peaks is concerned, they are quite similar for all samples, with a weak tendency to migrate toward higher 2θ in the mixing-based PNCs and toward lower 2θ in the ROP-based PNCs.
From the said XRD data and upon proper critical analysis (Figure S2 in the Supplementary Materials), the crystalline fraction, CFXRD, was estimated [15,69]. The results for CFXRD are shown in Figure 7b, comparatively with the CFc data by DSC (scan 2). The qualitative trends are similar for the two series of PNCs. In general, CF increases in the mixing-based PNCs and decreases in the ROP-based ones. However, the quantitative differences recorded in the absolute values of CF in the mixing-based systems and neat commercial PLA should be noted. The CFXRD are severely larger as compared to the corresponding CFc by DSC. The same is true for the estimated uncertainty in CFXRD. Conversely, in the ROP-synthesized neat PLA, CFXRD and CFc are values quite close in absolute terms, in general.
The PLM results are shown in Figure 8 for the mixing-based PNCs and in Figure 9 for the ROP-based PNCs. They partly confirm the previous findings by DSC and XRD. In particular, compared with the neat commercial PLA, for the PNCs, and especially in the cases of 0.5% Ag and Cu, the number of the formed crystallites is greater and the semicrystalline morphology is denser. Thus, both the facilitated nucleation and CF are confirmed. In the ROP-based PNCs, the semicrystalline morphology is quite similar between the polymer and the PNC with 0.5% Ag. On the other hand, fewer crystallites and sparser semicrystalline morphology are recorded for 1% Ag, again in qualitative agreement with the previous techniques.
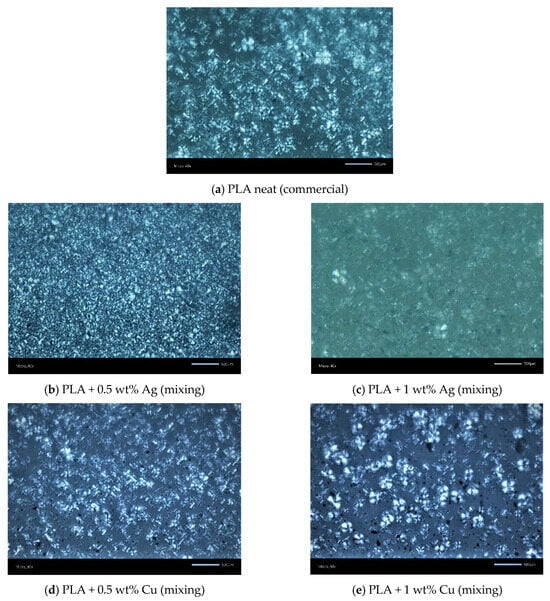
Figure 8.
Polarized light microscopy images for (a) commercial PLA and (b–e) the corresponding PNCs prepared by mixing. The scale bars correspond to 500 μm.
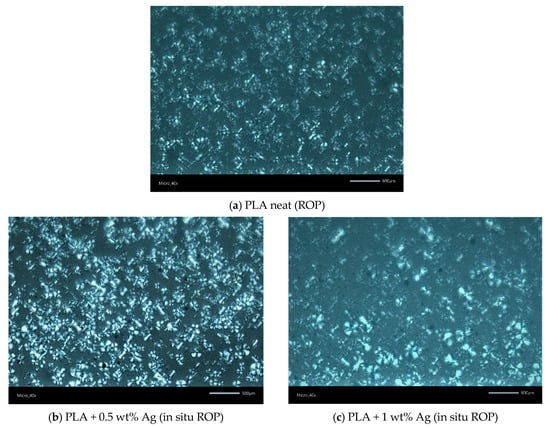
Figure 9.
PLM images for (a) neat PLA prepared by ROP and (b,c) the corresponding PNCs prepared in situ ROP. The scale bars correspond to 500 μm.
Please note that, from the material’s performance point of view, the variations in the degree of crystallinity, semicrystalline morphology, and inter-crystal distances (amorphous zone dimensions) are known to affect, in various manners, the final material’s properties (mechanical [17,18], permeation [22,23], and heat transport [8,16,21], etc.) as well as the physical degradation of our polyester [24].
3.4. Electrical Conductivity
Based on the BDS recordings at RT, the electrical AC conductivity, σAC, was estimated [58,59] and the data are presented in Figure 10a. Both neat PLAs and the majority of the PNCs exhibit, in general, low σAC and a certain frequency dependence of σAC, indicative of the electrically insulating character. Contrary to that, the PLA/Ag (ROP) systems exhibit an overall elevated conductivity, namely, by one to three orders of magnitude. The comparison between the various compositions can be clearly seen also on the basis of Figure 10b, wherein we present the σAC values at the lowest frequency of the recordings, i.e., ~0.1 Hz.
In the case of percolation [70] of conducting NPs or in PNCs filled with percolating conducting NPs, the electronic conductivity is recorded as a σAC(f) plateau at significantly high levels (i.e., about 10–6–103 S/cm, inset to Figure 10a). Although the employed NPs here are electron conductors, we neither record such a plateau nor extremely high σAC values.
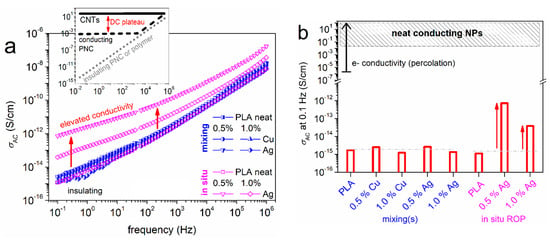
Figure 10.
(a) Comparative BDS spectra of the AC electrical conductivity, σAC, vs. frequency at room temperature. (b) Shows the PNC composition dependence of σAC values at the lowest frequency of the measurements. The expected σ ranges for the e-percolation (arrow) and percolating neat conducting NPs (upper area) [59,71] are marked in (b).
Therefore, in the mixing-based PNC, the insulating character of PLA is preserved, and, obviously, neither Ag nor Cu NPs percolate. In the case of the ROP-based PNCs, the elevated signal in the composites can be related to either an increased internal field [72]. The latter may exist due to the polarization of the finely dispersed Ag NPs or/and due to enhanced ‘ionic’ conductivity. The latter is quite more possible. The measurements have been conducted at RT~20–22 °C, i.e., below the glass transition temperature for most cases (50–60 °C). Compared to the DSC data of Figure 5, the ROP-based PNCs exhibit quite lower Tg. In particular, PLA + 0.5% Ag demonstrated a sub-zero Tg (Figure 5b) in the semicrystalline state, in addition to the expected decrease in the density of the bulky polymer in the PNCs. This enables the intense mobility of ions throughout the polymer matrix at RT >> Tg, i.e., in the rubbery state. This is quite compatible with the highest σAC values of the recordings (Figure 10b).
3.5. Local and Segmental Molecular Dynamics
In this section, the molecular dynamics of the polymers and the accompanying effects induced by the NPs presence are discussed. Moreover, we aim at the construction of the local-segmental dielectric relaxation map. The various types of polymer molecular mobility are studied in BDS via recording peaks of the dielectric losses ε”(f,T), as mainly performed in the literature [58]. Selected results are shown in Figure 11, whereas the overall data of all samples can be seen in Figures S3 and S4 in the Supplementary Materials.
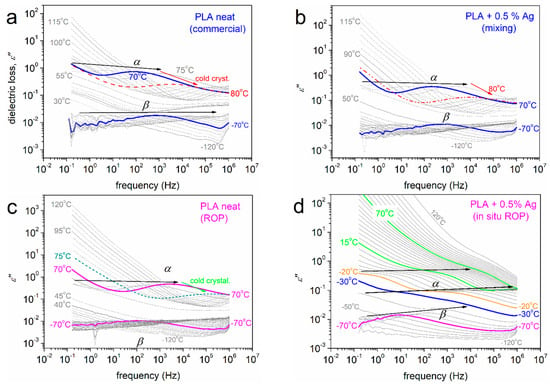
Figure 11.
Raw BDS data for (a) commercial PLA and (b) a corresponding PNC prepared by mixing and (c) neat PLA prepared by ROP and (d) a corresponding PNC prepared by in situ ROP. The data are shown in the form of isothermal ε”(f) curves. The marked isothermals at selected temperatures show the main relaxation processes (β, β’, and α).
At the lower temperatures and the glassy state of the polymer, i.e., Τ < Τg, the recorded peaks are weak and originate from the relaxations of dipole moments due to localized motions of the polymer side groups. Herein, this is the case of local β relaxation arising from the ester group (-C=O) at the chain backbone of PLA [73] and the local β΄ relaxation (not trivial). Whenever recorded in polyesters, β’ has been proposed to arise from the same group with attached water molecules [74,75], with its origins not being definite yet. When T increases and passes Tg, the dielectric response increases strongly as the mobilization of the overall polymer chains takes place (glass transition), and the so-called segmental α relaxation of PLA [73,76] dominates the signal. Actually, α is the dielectric and dynamical analog of the glass transition and is believed to arise from the relaxation of dipole moments located perpendicularly on the polymer chain axis [Kremer]. Obviously, α is the one exhibiting the main interest here.
Figure 12 presents at selected temperatures the local (Figure 12a,b) and segmental (Figure 12b–d) relaxations for all samples. A variety of effects is recorded on both local and segmental dynamics, introduced by the NPs addition. The stronger effects are recorded in the case of the ROP-based PNCs, wherein, for example, β relaxation is decelerated (Figure 12a, arrows), whereas α is severely accelerated (Figure 12b,c, arrows) in the PNCs.
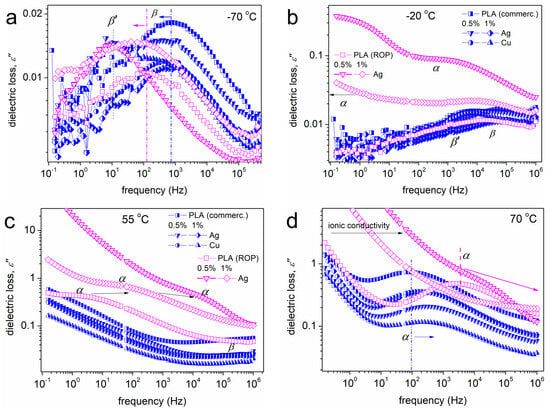
Figure 12.
Comparatives BDS ε”(f) curves for all samples, at the selected temperatures (a) −70 °C beta, (b) −20 °C, (c) 55 °C and (d) 70 °C to focus on the local (β, β’) and segmental (α) relaxations/peaks.
In order to draw a more in-depth view of dynamics and provide a full comparison of the relaxation time scale, a widely employed method of analysis of the BDS spectra was employed. This analysis involved the ‘critical’ fitting of model functions to each ε”(f,T) peak. These models are the known asymmetric Havriliak-Negami (HN) or symmetric Cole-Cole (CC) functions [58]. Examples of the fitting can be seen in Figure S5 (Supplementary Materials). From the results of the said fitting, the so-called ‘Arrhenius plots’, or else the ‘dielectric relaxation map’, were constructed. This map presents the reciprocal temperature (1000/T) dependence of the relaxations’ peak maxima, logfmax, for all samples. The map is shown in Figure 13a for all relaxations and in Figure 13b uniquely for the α relaxations.
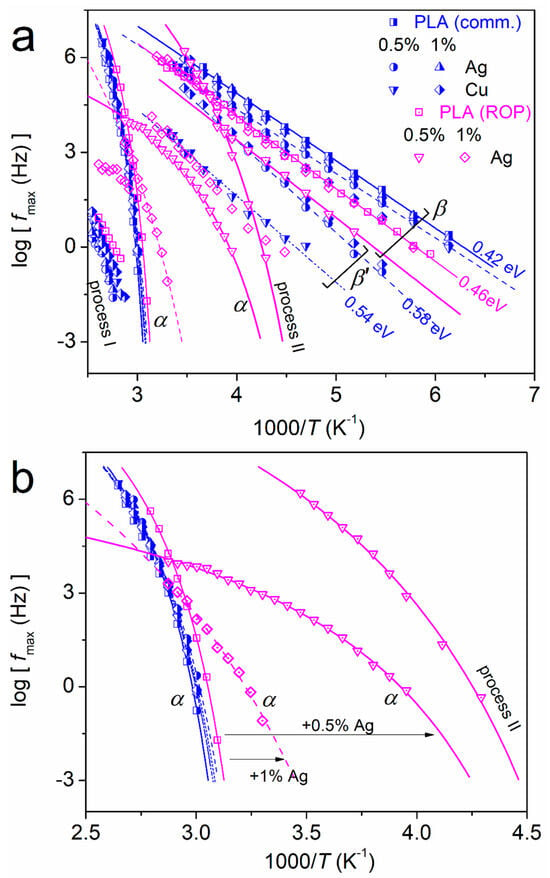
Figure 13.
(a) Dielectric relaxation map for all samples in terms of the reciprocal temperature dependences of the various peak maxima, fmax. The added straight and curved lines connecting the experimental points correspond to fitted model functions, i.e., Arrhenius and Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher-Hesse equations, respectively. (b) Shows a focus on the regions of segmental dynamics (α relaxations).
Beginning with the faster dynamics, β relaxation (ester group dipolar relaxation) is recorded at all cases. Due to its local character, its time scale in Figure 13a is linear, obeying the Arrhenius law [58]. The estimated activation energy equals 0.42–0.46 eV, being slightly higher in the ROP-based systems. For these systems, polymer and PNCs, β is located at higher temperatures/lower frequencies and, thus, ‘exhibits slower dynamics’, as compared to the mixing-based systems. For both systems, there seems to be a general tendency of β to become slower (decelerated) in the PNCs, with the effect being slightly stronger in the PLA + 0.5% Ag (ROP). These effects are compatible with the formation of interfacial interactions, within which a fraction of the ester groups is involved.
The case of β’ relaxation is not trivial, at least for PLA. Herein, the relaxation could be uniquely resolved in PNCs and mainly by fitting. The time scale of β’ is Arrhenius-like, as expected, and the activation energy is slightly larger (0.54–0.60 eV) as compared to that of β. Since its origins are not yet clear, more work is needed to evaluate its characteristics and correlation to the effects recorded here.
The focus is turned now on segmental dynamics. The α relaxation was recorded for all samples. Its time scale in Figure 13a,b is curved, or else, can be described by the Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher-Hesse (VFTH) equation [58,77]. This is characteristic of cooperative dynamics (non-local). In Figure 13b, it is clear that two sets of data for α are recorded, interestingly, corresponding to the two methods of preparation. The mixing-based systems and neat commercial PLA exhibit the slower α relaxation, whereas the effects of Ag and Cu NPs are extremely mild. On the other hand, the ROP-based systems exhibit faster dynamics and more intense effects induced by the addition of Ag.
In PLA + 0.5 Ag (ROP), an additional process could be resolved. This is the case of process II in Figure 13. The process was necessary for the sufficient fitting of the spectra. Judging from its time scale position (close to Tg) and its VFTH trend, one would propose that the process is another type of α relaxation. This option cannot be excluded totally, however, as there are opposite facts to this. For example, the extrapolation of its time scale to the very high temperatures results at extremely high frequencies, which is not expected for pure segmental relaxation. The relaxation is symmetric and quite narrow, whereas its dielectric strength is low. The relaxation was recorded in more than one sample of the same composition. The molecular origins of this relaxation can only be speculated. For example, it could be some kind of ‘precursor’ relaxation of segmental relaxation [78]. Yet, such relaxation has not been reported for PLA. Thus, this issue is open and needs further investigation.
For all samples and at the higher temperatures of recording, the relaxation addressed as process I is recorded and well resolved by fitting. The fitted term is symmetric and quite narrow, whereas its dielectric strength is high in general. The process is most probably related to ionic phenomena or interfacial polarization [58].
From the time-scale data of Figure 13 and upon proper fixing of the VFTH preexponential factor as 1013 Hz (phonon frequency) [79], two critical values were estimated. First, the dielectric glass transition temperature, Tg,diel, was estimated [8,11,12,15] and, second, the fragility of α relaxation, mα [79]. The composition dependence of Tg,diel is shown in Figure 14a alongside that of the calorimetric Tg. The results are qualitatively similar between the two techniques, despite any expected qualitative discrepancies [80]. In all cases, the presence of NPs leads to a drop of Tg, with the latter being severe in the in situ-ROP synthesized PNCs.
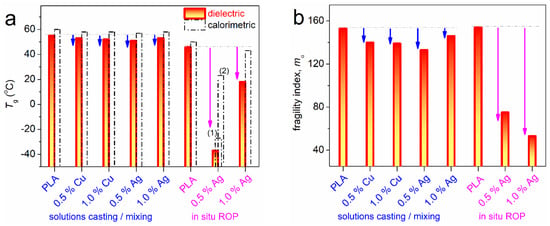
Figure 14.
Effects of the NPs addition in both PLA-based systems regarding (a) the dielectric/calorimetric glass transition temperatures and (b) the fragility index of the α relaxation, mα. For PLA + 0.5% Ag (ROP) in (a), the data marked as (1) and (2) correspond to the semicrystalline and amorphous cases, respectively.
Please observe the severe drop of Tg in PLA + 0.5% Ag (ROP).
Similar suppression is observed in the fragility of α relaxation. For neat PLAs, mα equals ~155. In Figure 14b, the NPs impose a drop in mα, namely, by 7–20 units in the mixing-based systems and by 80–100 units in the ROP-based ones. In simple polymeric systems [79], a drop in the fragility can be used as a measure of the chain–chain cooperative degree [47]. A drop in cooperativity suggests that either the cooperativity length, ξ, increases [81] or/and the interchain distances are increased and, respectively, fewer polymer chains are cooperative within a given volume unit.
Such situation is compatible with the scenario mentioned in the DSC section, suggesting that in our PNCs, there seems to be a condensation of the polymer around the NPs and a reduction in the polymer density away from the NPs [8,29,56]. Thus, increased free volume should exist in the bulk-like polymer fraction and, consequently, severely easier polymer chain diffusion. This can be understood better as follows: due to the supposed free volume increase, there is severe disentanglement between neighboring polymer chains and, in parallel, a facilitated degree of freedom of motion for the polymer chains. The latter are recorded here as the strong decrease in Tg. It should be noted that such alterations are of severe importance regarding the macroscopic performance and processing of polymeric materials.
3.6. Exceptional Crystallinity-Induced Effects on Mobility
The final point worth noting refers to an interesting effect recorded in the glass transition of PLA + 0.5% Ag (ROP). Usually in polymeric materials, when changing from the amorphous to the semicrystalline state, Tg elevates either slightly or intensely [11,16,19,20]. This is because the presence of the crystals (rigid structures) introduces significant constraints on the amorphous polymer chains’ diffusion/mobility. Within almost all samples here, the said relationship between crystallinity and glass transition is confirmed.
Nevertheless, this is not the case in PLA + 0.5% Ag (ROP), wherein Tg drops from 23 °C (amorphous) to −25 °C (semicrystalline, Figure 15a). The behavior is quite exceptional, and in order to further check this point, a series of additional measurements on the same as well as fresh samples for neat PLA (ROP) and the two PNCs PLA/Ag (ROP) were performed. Next to the scan involving melting and fast cooling to produce amorphous polymers, slower and faster cooling (5–20 K/min) as well as isothermal melt-crystallization annealing were performed.
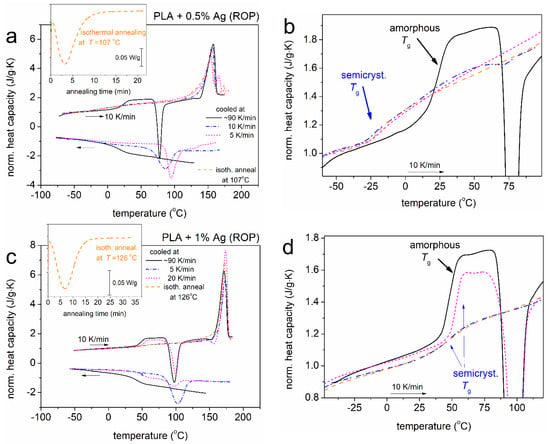
Figure 15.
Comparative DSC curves for (a,b) PLA + 0.5% Ag (in situ) and (c,d) PLA + 1% Ag (in situ) subjected to various thermal/crystallization treatments. The recorded signals are presented here upon normalization in heat capacity, cp, units. (b,c) show a focus on the glass transition steps during heating.
Figure 15a–d present such results (raw DSC data) for the two ROP-based PNCs. In PLA + 1% Ag and in neat PLA (ROP), the crystallization effects on Tg are toward the expected direction. Contrary to that, in PLA + 0.5% Ag, the introduction of crystalline fraction leads to severe suppression of Tg by ~50 K. This striking effect was further followed and confirmed by BDS. In Figure 16, we present the dielectric relaxation map for PLA + 0.5% Ag (ROP). The development of crystallinity imposes a systematic acceleration of the α relaxation as well as of process II. The respective effects on local β relaxation are minor. Usually, the involvement of crystallinity introduces constraints on the amorphous chains, and, subsequently, a deceleration of α relaxation is recorded [11,76].
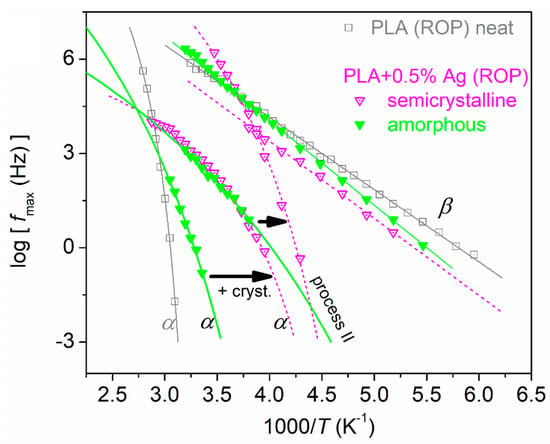
Figure 16.
Dielectric relaxation map for PLA + 0.5% Ag (in situ ROP), shown in the amorphous and semicrystalline state. For comparison, we have included the results for neat PLA (ROP).
The situation on this effect is not trivial; however, seeking similar cases in the literature, we recall two works from our groups on different homopolymers: PLA of low Mw~20 kg/mol and PCL of relatively high Mn~80 kg/mol [82]. Therein, the introduction of both high and low CF was found responsible for significant drops in the Tg. At the same time, the fragility indices of the corresponding segmental relaxation were minimized. Comparing these with the alternations in the semicrystalline morphology and crystal structure, we had concluded that the severe mobility acceleration was due to the involvement of strong spatial nanoconfinement. The said nanoconfinement occurred between the crystals, with the dimensions of intercrystallite zones being comparable to the cooperativity length of the polymers [82,83].
4. Conclusions
The synthesis of PLA-PNCs reinforced with 0.5 and 1% Ag and Cu NPs, employing mixing and in situ lactide-ROP, was performed. The latter method was attempted for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The incorporation of Ag was found successful for both synthetic routes, whereas that of Cu was achieved only by simple mixing, due to fast oxidation of these NPs during the time period of ROP. The mixing method was less productive in terms of filler dispersion in the polymer matrix. The latter was found to be almost excellent within the ROP-based PNCs. Despite that, the mixing-based PNCs exhibited an elevated crystallinity degree (from 2% in PLA to 23%) and facilitated nucleation (Tc elevation from 91 to 100 °C), when compared to the neat polymer. The ab initio stronger NPs-PLA interactions during the in situ ROP were found responsible for the suppression of crystallinity (from 39 to 17%), in agreement with recently proposed models [15]. The direct NPs effects on molecular mobility were assessed in the amorphous state and found to impose moderate and very strong lowering of Tg and of chains’ cooperativity in the mixing- (from 60 down to 58 °C) and ROP-based PNCs (from 50 down to 23 °C), respectively. Such effects are not trivial in the literature for polymer-based nanocomposites. To rationalize these effects, a realistic scenario that involves differences in the density (free volume) of the polymer away from and close to the NPs was proposed. Due to that, the ion transport through these PNCs’ volume was facilitated at RT, whereas this aspect can be exploited in future applications that involve small molecule permeation. Stronger impact on the segmental dynamics, as well as the local relaxation, was recorded in the ROP-based systems. This is most probably connected directly to the method of synthesis and the excellent filler dispersion. Last but not least, in the case of ROP-synthesized PLA at the presence of 0.5%, a surprising lowering of the amorphous Tg (i.e., from 25 down to −25 °C) was revealed with the involvement of crystallization. The said effect is obviously worthy of further study. Overall, the recordings suggest, once again, that PLA offers a wide range of properties’ tuning via synthetic routes and mild thermal treatments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/electronics14193826/s1. Supporting Information (SI) file including additional data and analysis results on SEM (Figure S1), XRD (Figure S2) and BDS (Figures S3–S5).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.N.B.; methodology, P.A.K.; validation, A.K. and D.N.B.; formal analysis, P.A.K. and R.O.I.; investigation, P.A.K., R.O.I. and K.L.; resources, A.K. and D.N.B.; writing—original draft preparation, P.A.K.; writing—review and editing, R.O.I., K.L., A.K., and D.N.B.; supervision, A.K. and D.N.B.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union under the GA no 101070556 (Sustain-a-Print, https://www.sustainaprint.eu/). Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or RIA. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Data Availability Statement
The DSC, FTIR, XRD, and BDS raw data are available on Zenodo (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17182719, accessed on 19 September 2025). The rest of the data supporting this article have been included as part of the Supplementary Materials file. The rest of the data supporting this article will be available upon request to the corresponding authors, uniquely in the frame of private communication.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Maria Nikopoulou and Eleni Pavlidou, from the Physics department of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (Greece), for the SEM observations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kumar, S.K.; Krishnamoorti, R. Nanocomposites: Structure, phase behavior, and properties. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2010, 1, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N. Some basic aspects of polymer nanocomposites: A critical review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokobza, L.; Chauvin, J.P. Reinforcement of natural rubber: Use of in situ generated silicas and nanofibres of sepiolite. Polymer 2005, 46, 4144–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, M.; Dutta, S.J.; Kuntze, M.; Bading, J.; Rüßbült, J.S.; Fabig, C.; Langfeldt, M.; Schulz, F.; Horcajada, P.; Parak, W.J. Visualization of the high surface-to-volume ratio of nanomaterials and its consequences. J. Chem. Educ. 2024, 101, 3146–3155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, Z.; Aliannezhadi, M.; Chominejad, M.; Tehrani, F.S. High specific surface area γ--Al2O3 nanoparticles synthesized by facile and low--cost co--precipitation method. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klonos, P.; Kyritsis, A.; Pissis, P. Interfacial dynamics of polydimethylsiloxane adsorbed on fumed metal oxide particles of a wide range of specific surface area. Polymer 2015, 77, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadiello, L.; D’Arienzo, M.; Di Credico, B.; Hanel, T.; Matejka, L.; Mauri, M.; Morazzoni, F.; Simonutti, R.; Spirkova, M.; Scotti, R. The filler–rubber interface in styrene butadiene nanocomposites with anisotropic silica particles: Morphology and dynamic properties. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4022–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klonos, P.A.; Bikiaris, R.D.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Mouchlianiti, K.; Tsachouridis, K.; Anastasiou, A.D.; Kyritsis, A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Structure-properties relationships in new polymer nanocomposites based on the renewable poly(butylene succinate) filled with low amounts of nanoparticles of 1-3D geometries. Polymer 2024, 296, 126841. [Google Scholar]
- Vogiatzis, G.G.; Theodorou, D.N. Structure of polymer layers grafted to nanoparticles in silica-polystyrene nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 4670–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gin, P.; Jiang, N.; Liang, C.; Taniguchi, T.; Akgun, B.; Satija, S.K.; Endoh, M.K.; Koga, T. Revealed architectures of adsorbed polymer chains at solid-polymer melt interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 265501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.; Kulyk, K.; Borysenko, M.V.; Gun’ko, V.M.; Kyritsis, A.; Pissis, P. Effects of molecular weight below the entanglement threshold on interfacial nanoparticles/polymer dynamics. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 9457–9473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiadakis, D.; Pissis, P.; Bokobza, L. Glass transition and molecular dynamics in poly(dimethylsiloxane)/silica nanocomposites. Polymer 2005, 46, 6001–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füllbrandt, M.; Purohit, P.J.; Schönhals, A. Combined FTIR and dielectric investigation of poly(vinyl acetate) adsorbed on silica particles. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 4626–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargsyan, A.; Tonoyan, A.; Davtyan, S.; Schick, C. The amount of immobilized polymer in PMMA SiO2 nanocomposites determined from calorimetric data. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3113–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.A.; Papadopoulos, L.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Kyritsis, A.; Pissis, P.; Bikiaris, D.N. Interfacial interactions, crystallization, and molecular dynamics of renewable poly(propylene furanoate) in situ filled with initial and surface modified carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 10220–10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.A.; Peoglos, V.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kyritsis, A. Rigid amorphous fraction and thermal diffusivity in nanocomposites based on poly(L-lactic acid) filled with carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 123, 5469–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, U.K.; Adhikari, J.; Naskar, A.; Dey, D.; Roy, A.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, M. Mechanical properties of crystalline and semicrystalline polymer systems. Encycl. Mater. Plast. Polym. 2022, 2, 917–927. [Google Scholar]
- Galeski, A. Strength and toughness of crystalline polymer systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1643–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, S.M. Increased glass transition temperature in motionally constrained semicrystalline polymers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1998, 9, 169–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, A.; Ismail, M.; Kretzschmar, B.; Pospiech, D.; Schick, C. Retarded crystallization in polyamide/layered silicates nanocomposites caused by an immobilized interphase. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, R.; Pourot, G.; Delaunay, D.; Fulchiron, R.; Koscher, E. Study and modeling of heat transfer during the solidification of semi-crystalline polymers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 5417–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedenqvist, M.; Gedde, U.W. Diffusion of small-molecule penetrants in semicrystalline polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1996, 21, 299–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, T.; De Almeida, O. Influence of semi-crystalline microstructure on gas permeability of poly(ether-ketone-ketone). Polymer 2024, 308, 127349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Harsi, S.; Thierry, A.; Schweyer, F.; Guenet, J.M. Physical corrosion of semi-crystalline polymers. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 166, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Jouault, N.; Benicewicz, B.; Neely, T. Nanocomposites with polymer grafted nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiadakis, D.; Bokobza, L.; Pissis, P. Dynamics near the filler surface in natural rubber-silica nanocomposites. Polymer 2011, 52, 3175–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Chen, Q.; Moll, J.F.; Kumar, S.K.; Colby, R.H. Segmental dynamics of polymer melts with spherical nanoparticles. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.A.; Papadopoulos, L.; Tzetzis, D.; Kyritsis, A.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Thermal, nanoindentation and dielectric study of nanocomposites based on poly(propylene furanoate) and various inclusions. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 20, 100585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, S.P.; Xanthopoulou, E.; Klonos, P.A.; Grigoropoulos, A.; Kyritsis, A.; Deligkiozi, I.; Zoikis Karathanasis, A.; Nikolaidis, N.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Terzopoulou, Z. Lignin particle size affects the properties of PLA composites prepared by in situ ring-opening polymerization. Polymers 2024, 16, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, H.E.H.; Govaert, L.E. Mechanical performance of polymer systems: The relation between structure and properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 915–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayanathara Thathsarani Pilapitiya, P.G.C.; Ratnayake, A.S. The world of plastic waste: A review. Clean. Mater. 2024, 11, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainali, N.M.; Kalaronis, D.; Evgenidou, E.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Bobori, D.C.; Kaloyianni, M.; Yang, X.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Do poly(lactic acid) microplastics instigate a threat? A perception for their dynamic towards environmental pollution and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladapo, B.I.; Olawumi, M.A.; Olugbade, T.O.; Tin, T.T. Advancing sustainable materials in a circular economy for decarbonisation. J. Env. Manag. 2024, 360, 121116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, J.; Sequerth, O.; Pilla, S. Green chemistry design in polymers derived from lignin: Review and perspective. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 113, 101344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidlou, S.; Huneault, M.A.; Li, H.; Park, C.B. Poly(lactic acid) crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntrivala, M.A.; Pitsavas, A.C.; Lazaridou, K.; Baziakou, Z.; Karavasili, D.; Papadimitriou, M.; Ntagkopoulou, C.; Balla, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. Polycaprolactone (PCL): The biodegradable polyester shaping the future of materials—A review on synthesis, properties, biodegradation, applications and future perspectives. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 234, 114033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipitria, A.; Skwlton, A.; Dargaville, T.R.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Design, fabrication and characterization of PCL electrospun scaffolds—A review. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9419–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, E.; Daniilidis, V.; Karlioti, G.; Kalamas, T.; Stefanidou, M.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Vlachopoulos, A.; Koumentakou, I.; Bikiaris, D.N. Poly(lactic acid) a versatile biobased polymer of next decades with multifunctional properties. From monomer synthesis, polymerization techniques and molecular weight increase to PLA applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.Z.; Deiab, I.; Darras, B.M. Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum-based plastics: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17151–17196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Varshney, S.K. Polylactides-chemistry, properties and green packaging technology: A review. Int. J. Food. Prop. 2011, 14, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constanzo, A.; Spotorno, R.; Candal, M.V.; Fernández, M.M.; Müller, A.J.; Graham, R.S.; Cavallo, D.; McIlroy, C. Residual alignment and its effect on weld strength in material-extrusion 3D-printing of polylactic acid. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101415. [Google Scholar]
- Casalini, T.; Rossi, F.; Castrovinci, A.; Perale, G. A perspective on polylactic acid-based polymers use for nanoparticles synthesis and applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Z. Polylactic acid based nanocomposites: Promising safe and biodegradable materials in biomedical field. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 6869154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A literature review of poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P.; Arora, M.; Kumar, M.N.V.R. Poly(lactic acid) blends in biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Du, F.; Jariyavidyanont, K.; Zhuravlev, E.; Schick, C.; Androsch, R. Glass transition temperature of poly(d,l-lactic acid) of different molar mass. Thermochim. Acta 2022, 718, 179387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.A.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Barmpalexis, P.; Kyritsis, A. Segmental mobility in linear polylactides of various molecular weights. Polymer 2024, 305, 127177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Guo, Y.T.; Yang, C.; Meng, X.B.; Du, F.S.; Li, Z.C. High-Tg PLA copolymers via base-catalyzed transesterification of PLA with 2,5,7-trioxabicyclo [2.2.2]octan-6-one. Polym. Chem. 2024, 15, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaifel, M.H.; Shahdan, S.; Mhareb, M.H.A.; Ahmad, S.H.; Alghamdi, A.A.A.; Alajerami, Y.S.; Sayyed, M.I. Unveiling enhanced properties of sustainable hybrid multifunctional graphene nanoplatelets incorporated polylactide/liquid natural rubber/polyaniline bio-nanocomposites for advanced radiation and particle shielding applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 13824–13842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailan, F.D.; Chen, R.S.; Flaifel, M.H.; Shahdan, D.; Makhtar, N.; Yu, L.J.; Mhareb, M.H.A.; Makhtar, N.; Yu, L.J.; Mhareb, M.H.A.; et al. Improved mechanical, magnetic and radiation shielding performance of rubbery polymer magnetic nanocomposites through incorporation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Compos. Part B Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 186, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, Y.J.; Ahn, K.H. Interconnected network of Ag and Cu in bioplastics for ultrahigh electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency with high thermal conductivity. Compos. Commun. 2022, 30, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruel, A.; Kim, H.; Russo, R.; Grugeon, S.; Armand, M.; Panier, S.; Dupont, L. Ag-Coated Cu/polylactic acid composite filam56ent for lithium and sodium-ion battery current collector three-dimensional printing via thermoplastic material extrusion. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 651041. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, J.; Arfat, Y.A.; Castro-Aquirre, E.; Auras, R. Mechanical, structural and thermal properties of Ag–Cu and ZnO reinforced polylactide nanocomposite films. Int. J. Biol. Macrom. 2016, 86, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stano, G.; D’Orazio, M.; Pavone, A.; Percoco, G. Next generation of 3D-printed electronics: Electroplating inside channels to embed 3D copper features within polymeric structures fabricated through material extrusion. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2025, 10, 2401923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.; Carniello, S.; Beni, V.; Sudheshwar, A.; Malinverno, N.; Alesanco, Y. Defining and achieving next-generation green electronics: A perspective on best practices through the lens of hybrid printed electronics. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 117135–117161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.A.; Ioannidis, R.O.; Pitsavas, A.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Makri, S.P.; Koutsourea, S.; Grigoropoulos, A.; Deligkiozi, I.; Zoikis-Karathanasis, A.; Kyritsis, A.; et al. Segmental mobility, interfacial polymer, crystallization and conductivity study in polylactides filled with hybrid lignin-CNT particles. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardón-Maximino, N.; Pérez-Alvarez, M.; Sierra-Ávila, R.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Jiménez-Regalado, E.; Bello, A.M.; González-Morones, P.; Cadenas-Pliego, G. Oxidation of copper nanoparticles protected with different coatings and stored under ambient conditions. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 9512768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, F.; Schönhals, A. (Eds.) Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Logakis, E.; Pollatos, E.; Pandis, C.; Peoglos, V.; Zuburtikudis, I.; Delidis, C.G.; Vatalis, A.; Gjoka, M.; Syskakis, E.; Viras, K.; et al. Structure-property relationships in isotactic polypropylene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmandi, R.; Hassan, A.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Mohamad Haafiz, M.K.; Zakaria, Z.; Tanjung, F.A. Enhanced ductility and tensile properties of hybrid montmorillonite/cellulose nanowhiskers reinforced polylactic acid nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 3118–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuniarto, K.; Purwanto, Y.A.; Purwanto, S.; Welt, B.A.; Purwadaria, H.K.; Sunarti, T.C. Infrared and Raman studies on polylactide acid and polyethylene glycol-400 blend. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1725, 020101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechy-Cabaret, O.; Martin-Vaca, B.; Bourissou, D. Controlled ring-opening polymerization of lactide and glycolide. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6147–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzeiwa, W.A.; Omondi, B.O.; Nyamori, V.O. A perspective into ring--opening polymerization of ε--caprolactone and lactides: Effect of, ligand, catalyst structure and system dynamics, on catalytic activity and polymer properties. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 9419–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun-Ur-Rashid, M.; Foyez, T.; Krishna, S.B.N.; Poda, S.; Imran, A.B. Recent advances of silver nanoparticle-based polymer nanocomposites for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 8480–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Kolloid-Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Szymoniak, P.; Kang, N.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Wurm, A.; Schick, C.; Schönhals, A. Influence of interfaces on the crystallization behavior and the rigid amorphous phase of poly(L-lactide)-based nanocomposites with different layered double hydroxides as nanofiller. Polymer 2019, 184, 121929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, M.C.; Gazzano, M.; Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Androsch, R. Enthalpy of melting of α′- and α-crystals of poly(L-lactic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 70, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, M.C.; Gazzano, M.; Delpouve, N.; Saiter, A. Contribution of the rigid amorphous fraction to physical ageing of semi-crystalline PLLA. Polymer 2017, 125, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, F.; Shinohara, K.; Nagasawa, N.; Takeshita, H.; Takenaka, K.; Miya, M.; Shiomi, T. Crystallization behavior and higher-order structure in miscible crystalline/crystalline polymer blends. Polym. J. 2013, 45, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Chanda, A.; Sinha, S.K.; Dalta, N.V. Electrical conductivity of random and aligned nanocomposites: Theoretical models and experimental validation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 149, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, K.A.; Adachi, K. Dielectric relaxation in montmorillonite/polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 2006, 47, 6406–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Urakawa, O.; Adachi, K. Dielectric study on dynamics and conformations of poly(D,L-lactic acid) in dilute and semi-dilute solutions. Polymer 2003, 44, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibos, L.; Bernes, A.; Teyssedre, G.; Lacabanne, C.; Wu, S.L.; Scheinbeim, J.I. Study of dielectric relaxations in polyamide 11 by thermostimulated currents and broadband dielectric spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Electrets (ISE 10), Athens, Greece, 22–24 September 1999; pp. 623–626. [Google Scholar]
- Franzon, C.H.; Roggero, A.R.; Pruvost, S.; Gérard, J.F. Ambient moisture influence on the secondary relaxations of epoxy-amine networks with different crosslink densities. Polymer 2024, 315, 127750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, A.R.; Viciosa, M.T.; Wang, Y.; Dionisio, M.; Mano, J.F. Crystallization of poly(L–lactic acid) probed with dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6513–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G.; Hesse, W. Die Abhängigkeit der Viscosität von der Temperatur bie unterkühlten Flüssigkeiten. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1926, 156, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, G.P.; Goldstein, M. Viscous liquids and the glass transition. II. Secondary relaxations in glasses of rigid molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 53, 2372–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhmer, R.; Ngai, K.; Angell, C.A.; Plazek, D.J. Nonexponential relaxations in strong and fragile glass formers. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 4201–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, S.; Yin, H.; Füllbrandt, M.; Schönhals, A. Calorimetric evidence for a mobile surface layer in ultrathin polymeric films: Poly(2-vinyl pyridine). Soft Matter 2015, 11, 7942–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpouve, N.; Saiter, A.; Dargent, E. Cooperativity length evolution during crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.A.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Christodoulou, E.; Zamboulis, A.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Kyritsis, A. Molecular mobility, crystallization and melt-memory investigation of molar mass effects on linear and hydroxyl-terminated poly(ε-caprolactone). Polymer 2022, 242, 124603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Guan, Y.; Liu, G.; Müller, A.J.; Wang, D. Segmental dynamics govern the cold crystallization of poly(lactic acid) in nanoporous alumina. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 6904–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).