Abstract
Due to its portability, non-invasiveness, and real-time capabilities, ultrasound imaging has been widely adopted for liver disease detection. However, conventional ultrasound examinations heavily rely on operator expertise, leading to high workload and inconsistent imaging quality. To address these challenges, we propose a Robotic Ultrasound Scanning System (RUSS) based on reinforcement learning to automate the localization of standard liver planes. It can help reduce physician burden while improving scanning efficiency and accuracy. The reinforcement learning agent employs a Deep Q-Network (DQN) integrated with LSTM to control probe movements within a discrete action space, utilizing the cross-sectional area of the abdominal aorta region as the criterion for standard plane determination. System performance was comprehensively evaluated against a target standard plane, achieving an average Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) of 24.51 dB and a Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) of 0.70, indicating high fidelity in the acquired images. Furthermore, a mean Dice coefficient of 0.80 for the abdominal aorta segmentation confirmed high anatomical localization accuracy. These preliminary results demonstrate the potential of our method for achieving consistent and autonomous ultrasound scanning.
1. Introduction
Liver diseases persistently threaten human health, rendering their diagnosis and treatment a perennial focus of medical research. In recent years, the incidence of hepatic pathologies such as fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma has shown a marked increase worldwide. Medical imaging plays a pivotal role in the diagnostic workflow, with modalities including ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Since its inaugural diagnostic application in the 1940s, ultrasound (US) imaging has emerged as one of the most ubiquitous diagnostic modalities globally [1,2]. Owing to its portability, non-invasiveness, cost-effectiveness, and real-time capabilities compared to alternative imaging techniques, ultrasonography has been extensively adopted across medical disciplines including cardiology [3], urology [4], neurology [5], and obstetrics/gynecology [6], demonstrating substantial clinical utility in disease diagnosis and treatment.
In standardized US examinations, standard planes refer to anatomically defined imaging planes established through expert consensus, which encapsulate essential structural information for diagnostic interpretation, biometric measurement, or interventional guidance [7,8]. The localization of these standardized planes facilitates clinicians’ identification of hepatic anatomical landmarks for diagnostic or surgical purposes [9]. However, current standard plane localization necessitates manual probe navigation based on real-time US image interpretation and anatomical knowledge, demanding sonographers’ extensive training and experience. Consequently, practitioners endure significant physical and cognitive burdens due to excessive workloads [10], while imaging quality remains highly operator-dependent [11]. These challenges underscore the potential of autonomous robotic US scanning systems to mitigate user fatigue and enhance imaging consistency [12].
2. Related Work
Robotic Ultrasound Scanning Systems (RUSS) represent sensor-integrated platforms capable of performing optimized US scanning with minimal human intervention. Such systems exhibit adaptive control capabilities through sensor feedback. Nakadate et al. [13,14] developed a hybrid robotic system combining a 6-DoF parallel manipulator with a passive serial arm, integrated with real-time image processing algorithms for automated localization of optimal carotid artery longitudinal views. Mustafa et al. [15,16] employed a commercial 6-DoF robotic manipulator with RGB camera guidance to autonomously screen liver regions, utilizing surface topography derived from abdominal RGB images. Conventional robotic US systems typically employ stereovision sensors for depth perception, implementing point cloud processing algorithms for 3D scene reconstruction and kinematics-based path optimization [17,18,19,20,21]. However, such scene reconstruction approaches face inherent occlusion challenges, particularly in marker-dependent methods, while their accuracy and efficiency remain constrained by 3D imaging hardware limitations. The complex hepatic anatomy, multiplicity of standard scanning planes, and probe-position-dependent image quality render surface-topography-based planning inadequate for comprehensive US path planning. In addition, some cross-disciplinary works can also be helpful in constructing a robotic ultrasound scanning system [22,23].
When performing autonomous ultrasound scanning tasks, it is often necessary to segment and identify scanned targets in standard sections for clinical evaluation. This paper focuses on widely used medical image segmentation models such as SAM, MedSAM, and Unet. SAM has a revolutionary zero-shot segmentation capability and performs strongly on natural images [24], but recent studies have also shown that it performs poorly on medical image segmentation [25]. If directly applied to ultrasound images, it may output a large number of segmentation masks that are not of interest. For medical images such as ultrasound, which have special textures and artifacts, its zero-shot accuracy may not be sufficient to meet clinical localization requirements. Therefore, MedSAM [26], trained on medical data, was proposed. However, due to its core Transformer structure, it requires a lot of computing power. Standard SAM typically takes hundreds of milliseconds or even seconds to perform inference on a single GPU, which is far from meeting the requirements of real-time control. Therefore, in future work, with the development of model compression technology and the emergence of more powerful hardware, lightweight and fine-tuned SAM variants may become a better choice. The U-Net we chose to use is a lightweight convolutional network with an efficient structure [27]. After optimization, it can easily achieve real-time inference speeds on mid-range GPUs.
Reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising paradigm for autonomous US probe navigation. Given RL’s inherent strengths in sequential decision-making and exploratory tasks, increasing research efforts have focused on RL-based probe navigation. Dou et al. [28] adopted this methodology to fetal brain US standard plane detection. However, these approaches remain limited to pre-acquired 3D volume analysis rather than realtime probe control. Jarosik et al. [29] implemented RL agents for virtual probe manipulation in simplified static phantom environments. Similarly, Milletari’s work [30] demonstrated RL-based cardiac US navigation in a simulation environment constructed from spatially tracked US frames. Hase et al. [31] employed 2D image grids for RL training in sacrum localization, while it is restricted to 2-DoF translational movements requiring precise initialization. Li et al. [32] proposed a Deep Q-Learning framework accommodating 6-DoF movements while constraining probe contact, validated in a virtual spine US environment. Bi et al. [33] introduced VesNet-RL, a simulation-based RL framework for vascular standard view localization. However, these studies have not applied RL algorithms on robotic US scanning systems in an actual test environment. While our study employs a model-free reinforcement learning approach for probe navigation, the broader field of robotics has seen significant advancements in other intelligent control paradigms. For instance, sophisticated methods like self-triggered approximate optimal neuro-control and adaptive critic designs have been developed for robust control of complex nonlinear systems [34,35]. In addition, novel deep learning frameworks are continuously emerging for related challenges in perception and control, such as unsupervised image stitching using GANs [36]. These advanced frameworks represent important directions in intelligent robotics and could inspire future enhancements to our system’s underlying control and perception modules.
The main contributions of this article are listed as follows. (1) A novel robotic system is developed for liver US scanning, which can autonomously localize the standard liver plane using reinforcement learning algorithm. (2) A Unet-Liver model is proposed to segment the liver and abdominal aorta, serving as the reward for the reinforcement learning agent. (3) A novel Sim-to-Real transfer strategy is proposed together with the construction of a high-fidelity simulation environment, which improves the generalization of reinforcement learning algorithm for physical deployment.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Robotic Ultrasound Scanning System Construction
The robotic ultrasound scanning system comprises the following components: a 7 DOF robotic arm (Diania7 Med, Agile Robots, Beijing, China), an ATI force sensor (Mini 40, ATI Industrial Automation, Apex, NC, USA), and an ultrasound system (Affiniti 30, Philips, Inc., Amsterdam, The Netherlands) with convex array probe (C6-2), a control computer and a liver phantom (057A, CIRS, Arlington, VA, USA). The configuration of the robotic system is illustrated in Figure 1.
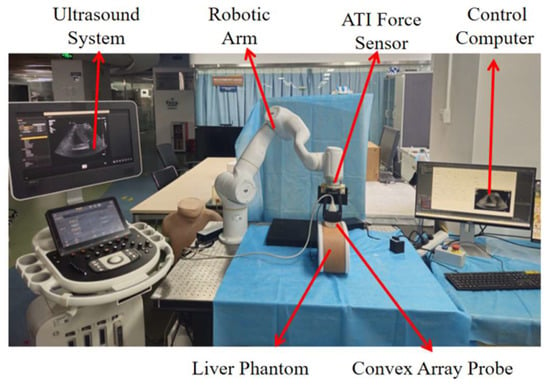
Figure 1.
Configuration of the robotic ultrasound scanning system (Robotic arm: Diania7 Med, ATI force sensor: Mini 40, Ultrasound system: Philips, Affiniti 30, Ultrasound probe: Philips C6-2, liver phantom: CIRS, 057A).
The system utilizes the official C++ based API interfaces provided for the robotic arm. The upper computer application was developed using Qt framework (5.9.5). This integrated system incorporates multiple functionalities including force feedback, pose information, and real-time image display. For the reinforcement learning based liver ultrasound standard plane localization algorithm, the computational hardware configuration consists of an NVIDIA RTX 3070Ti GPU, an Intel i7-12700K CPU, 32GB RAM, running on Windows 10 operating system. The center point of the ultrasound probe’s scanning array was designated as the origin of the tool coordinate system. The six-axis force sensor and ultrasound probe were integrated at the robotic arm’s flange end and constituted the end-effector tool assembly, as shown in Figure 2a.
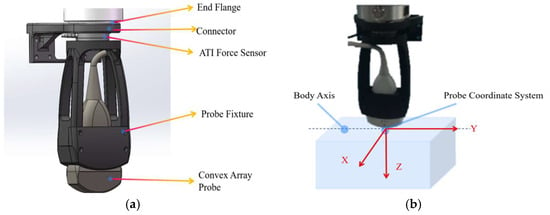
Figure 2.
(a) End-effector tool assembly model, (b) Probe coordinate system.
3.2. Liver Standard Plane Localization
To start the liver standard plane localization, the probe is initially perpendicularly in contact with the abdominal surface, with its long axis aligned parallel to the body’s longitudinal axis, as illustrated in Figure 2b. Then the robot, guided by a reinforcement learning agent, incrementally adjusts the position and orientation of the probe in order to acquire a clear and accurate image of the subcostal longitudinal section of the aorta. During this process, the contact force is set as 7N to keep stable ultrasound image quality, and the ultrasound images provide interactive information that serves as state feedback to the reinforcement learning agent. Based on the current state, the agent generates a sequence of action commands to drive the robot in executing precise movements. The sensor also functions as a safety monitor; any force exceeding a predefined threshold will trigger an immediate emergency stop. At the software level, the agent’s action space is constrained within a safe, predefined workspace, and the robot’s maximum velocity and acceleration are limited to ensure all movements are gentle and predictable.
3.3. Construction and Training of the Reinforcement Learning Agent
The training of the reinforcement learning agent requires continuous interaction with the environment and involves lengthy training cycles. Considering safety concerns associated with training directly in a physical environment, the training is conducted within a simulated environment. Upon completion of training, the agent is then deployed onto the robot. Since the standard liver imaging planes are typically located within a fixed acoustic window, and given the occlusion caused by the ribs which makes full three-dimensional reconstruction of the liver challenging and unnecessary, a local 3D reconstruction is performed solely within the acoustic window containing the standard plane. This reconstructed volume serves as the simulation environment for the reinforcement learning agent’s training.
The local 3D ultrasound reconstruction of the liver is implemented using the open-source medical software 3D Slicer (https://www.slicer.org/), which can autonomously perform 3D reconstruction and rendering based on DICOM slices acquired in parallel at fixed intervals. In this study, the task of acquiring parallel images at fixed intervals is controlled by a robot through an auxiliary localization system developed with Qt.
This study takes the identification of the standard plane of subcostal longitudinal section of the aorta as an example. In the ultrasound image shown in Figure 3, the completeness and clarity of the abdominal aorta (highlighted by the red rectangular box) serve as critical criteria for identifying the standard plane of subcostal longitudinal section of the aorta. Hence, these key features must be distinctly annotated.
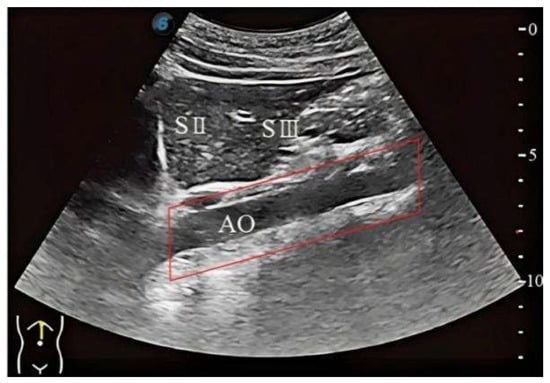
Figure 3.
The standard plane of subcostal longitudinal section of the aorta.
To simplify the training environment and enable the reinforcement learning agent to focus on scanning the liver and key anatomical structures, a deep learning model, Unet-Liver, was trained to segment the liver and abdominal aorta from complex ultrasound images. This model is based on the U-Net architecture [37], and the training workflow is illustrated in Figure 4. To ensure the network focuses on relevant information and meets the input requirements of Unet-Liver, the ultrasound images undergo cropping and padding processing. The original image size is 1024 × 768 pixels and the processed image size is 560 × 560 pixels. The trained Unet-Liver network outputs a three-class segmentation map, with red indicating the liver, green representing the abdominal aorta, and black representing cavity.
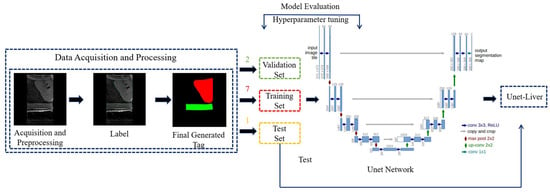
Figure 4.
Training workflow of the Unet-Liver model.
After completing the local 3D liver reconstruction and the training of the segmentation network, the reinforcement learning simulation environment can be constructed. This environment facilitates interaction with the agent during training and consists of two main functions: state acquisition and action execution. The state acquisition function performs the following operations: first, within the local 3D liver reconstruction volume, a probe pose is randomly initialized within a given range. The intersection plane between the ultrasound probe at this pose and the 3D reconstructed liver volume is computed to generate the corresponding ultrasound image. Next, this ultrasound image is processed and fed into the Unet-Liver network to produce a three-class segmentation map. Finally, the current state is returned. The action execution function includes the following steps: first, the decision for the next probe movement is obtained by inputting the current state into the DQN network. Then, the chosen movement is executed, resulting in an updated probe pose and a new ultrasound image acquired at this pose. Subsequently, the reward feedback for the current movement is computed based on the data from the current and previous time steps. Finally, relevant data including the updated state are returned, concluding the current action step. This simulation environment provides an interactive platform for training the reinforcement learning agent and lays the foundation for subsequent agent training.
The Markov Decision Process (MDP) constitutes the standard framework for reinforcement learning, encompassing the state space, action space, state transition function, reward function, and discount factor. In the task of localizing standard ultrasound planes, the true state of the ultrasound probe is not directly observable, resulting in a partially observable Markov decision process (POMDP).
Within the reinforcement learning framework, the agent’s behavior is determined by the actions it executes, and the set of all possible actions is referred to as the action space. The action space is designed as a discrete set. All translational and rotational movements are performed within the end-effector coordinate. Specifically, translational movements occur along the end-effector’s X and Y axes with 1 mm increments, and rotational movements are executed around the end-effector’s Z axis in 1° increments. This action space corresponds to the probe’s three degrees of freedom (translational motion along the X/Y axes and rotational motion around the Z-axis).
The state represents a comprehensive description of the environment during the agent’s interaction, encompassing all information necessary for decision-making. The area of the abdominal aorta region within the ultrasound image are utilized as observations to estimate the actual state.
Reward is the immediate feedback provided by the environment following the agent’s action execution, serving to quantify the quality of that action. The reward constitutes the core driving force for the agent’s learning, with the ultimate goal of maximizing the cumulative reward, i.e., the long-term return. The design of the reward function directly impacts the agent’s learning effectiveness and policy optimization. The reward is designed to motivate the agent to locate the maximal transverse cross-section of the abdominal aorta, which corresponds to the standard plane of subcostal longitudinal section of the aorta. The reward design incorporates the area of the segmented abdominal aorta region together with the distance to the target. In the local 3D liver reconstruction volume, the position of the probe corresponding to the standard imaging plane is known. The distance to the standard plane posture can be defined as
where denotes the position of the ultrasound probe corresponding to the standard imaging plane, represents the current position of the ultrasound probe, and is the Euclidean distance between the two positions. A distance-related reward can be defined for the current state as
where denotes probe-to-target distance at the last time step, denotes probe-to-target distance at current time step and denotes the maximum distance from any position within the defined acoustic window to the target position. In addition to the distance-based reward, the score of the current state is also influenced by the reward associated with the segmented abdominal aorta region in the current ultrasound frame, which is defined as
where denotes pixel number of the abdominal aorta in the standard plane, denotes the number of pixels corresponding to the abdominal aorta in the ultrasound image at the last time step, and represents the number of pixels in the abdominal aorta at the current time step. The reward function settings are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Reward Function.
Our reward function design aims to balance two core objectives: navigation efficiency and image quality. Rewarding only for distance may lead the agent to reach the target point as quickly as possible, but neglect the clarity and diagnosability of the final image. For example, if tissue deforms, the scanning at the original position may lead to a poor image. Conversely, rewarding only for segmentation area may lead to slow convergence. By combining these two, namely (), we provide the agent with a smoother and denser reward signal, effectively guiding it towards the target with both accurate location and clear image quality. Furthermore, our reward function design considers the common sparse reward problem in reinforcement learning, introducing a distance constant for fine-tuning under different conditions. This dense reward mechanism significantly improves learning efficiency and helps the agent establish a correct sense of direction during early exploration. The stable convergence of the training curve in Figure 5 largely validates the rationale of this composite reward design.
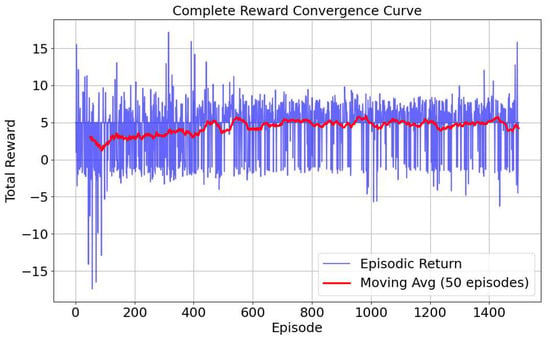
Figure 5.
Reward curve.
Since the reinforcement learning problem in this work involves a continuous state space and a discrete action space, the DQN algorithm [38] is selected for the reinforcement learning agent. As previously described, the process in this study is modeled as a Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP). To handle the uncertainties introduced by partial observability, LSTM units [39] are incorporated to fully exploit sequential information and to help the agent better understand its environment. The network architecture is illustrated in Figure 6.
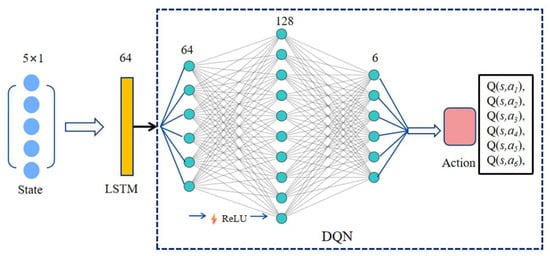
Figure 6.
LSTM-DQN network. The network processes a sequence of 5 states, each with a 1-dimensional value. The input tensor [Batch, 5, 1] is fed into an LSTM layer (hidden size = 64). The output from the LSTM’s final time step [Batch, 64] is then passed through a two-layer MLP (64 × 128 with ReLU, followed by 128 × 6) to produce the final Q-values for the 6 discrete actions.
3.4. Sim-to-Real Transfer Strategy
Bridging the simulation-to-reality gap is a critical challenge in robotic reinforcement learning. As we have discussed above, our approach addresses this through three primary strategies to ensure successful policy transfer.
First, we developed a high-fidelity, data-driven simulation. The environment was built from a 3D model reconstructed from a sequence of real DICOM images acquired from the physical phantom. This method ensures that the simulated ultrasound images share highly consistent visual characteristics—such as texture, artifacts, and noise—with the real-world domain. Second, our system uses a decoupled perception and control architecture. The agent’s state is not based on raw pixels but on low-dimensional semantic features (i.e., aorta area) extracted by a U-Net. This makes the policy robust to minor visual discrepancies between domains, as the U-Net acts as a domain adapter by providing a consistent state representation. Finally, the U-Net itself was trained using mixed-domain data, composed of both reconstructed slices from the simulation and real images from the physical phantom. This exposed the network to the target domain’s data distribution during training, directly improving its generalization for physical deployment. Collectively, these strategies proved effective for bridging the Sim-to-Real gap in our experiments, as validated by the system’s performance in the physical trials.
4. Results
4.1. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction Results of Local Liver Ultrasound
To enable the training interaction of the reinforcement learning agent, a 3D liver reconstruction model was required to simulate the training environment. A Qt-based auxiliary localization system was developed and used in conjunction with the PHILIPS Affiniti 30 ultrasound system to collect ultrasound data that met the reconstruction requirements. In this study, the fixed movement distance was set to 0.26 mm, corresponding to the pixel spacing of the DICOM images. A total of 538 ultrasound images were acquired, as shown in Figure 7a. These images were imported into 3D Slicer and reconstructed along the X-axis, resulting in a local 3D liver reconstruction volume, as shown in Figure 7b. A slice along the Y-axis at the center of the reconstructed volume is shown in Figure 7c, which clearly presents the anatomical structure of the organ.
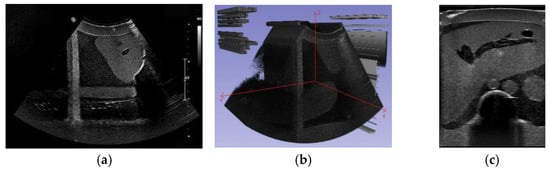
Figure 7.
(a) Sample of the acquired ultrasound images, (b) local 3D reconstruction volume of the liver, (c) reconstructed slice along the Y-Axis at the center of the reconstructed volume.
4.2. Image Segmentation and Recognition Results
To ensure data diversity and enhance the model’s generalization capability, the training dataset for the network was composed of both reconstructed ultrasound slices and real ultrasound slices obtained by scanning the phantom. This approach facilitates the later transfer of the reinforcement learning agent from the virtual environment to the real environment. A total of 310 ultrasound images were collected, including 280 images from the 3D reconstructed volume and 30 images from the real phantom scanning. Among the 3D reconstructed volume images, 136 were obtained by translational movement of the probe collected at different positions, and 144 were obtained by rotational movement of the probe around Z-axis with varying angles. The images in the dataset were annotated using LabelMe [40] and converted into final three-class label maps, where red indicates the liver, green indicates the abdominal aorta, and black indicates cavity. The 310 image-label pairs were split into training, validation, and test sets in a ratio of 7:2:1, resulting in 217 pairs for training, 62 for validation, and 31 for testing. Standard data augmentation techniques such as random rotations and flips were employed during training to artificially increase the diversity of the training data and mitigate overfitting.
The Unet-Liver model was trained on the PyCharm2020 platform with a learning rate set to 0.0001, using the Adam optimizer and cross-entropy loss function. The model was trained for 100 epochs. The performance of Unet-Liver was evaluated using the Intersection over Union (IoU) and Dice metrics. On the test set, it achieved an average IoU of 0.9717 and an average Dice of 0.9838. The predicted segmentation maps generated by the model exhibit high similarity to the ground truth labels, as shown in Figure 8, demonstrating that the model meets the requirements of this study.
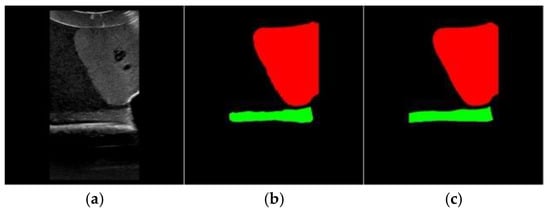
Figure 8.
Example of segmentation Results. (a) Original image, (b) segmentation result of Unet-Liver, (c) ground truth label.
4.3. Experiment Results of the Reinforcement Learning Agent
The designed network model described above was implemented and trained based on the open-source deep learning framework PyTorch 2.2.1. The training was conducted in the simulated environment with the following parameters: initial learning rate set to 1 × 10−3, which was decreased by 0.5% after each episode, with a minimum learning rate of 0.00001; initial exploration rate set to 0.9, which was also decreased by 0.5% after each episode, with a minimum exploration rate of 0.02. The total number of training episodes was 1500. Other hyperparameters included a hidden layer dimension of 128, discount factor of 0.98, target network update interval of 10 episodes, LSTM hidden unit dimension of 64, experience replay buffer size of 10,000, minimum buffer size for sampling of 500, batch size of 64, historical sequence length of 5, state dimension of 1, and action space dimension of 6. During training, we found that both the reward and loss curves converged well, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 9a, demonstrating the effectiveness of our reward function. Due to the randomness of the probe’s initial position, it is possible for the probe to initially be located at the standard section position. This led to significant fluctuations in the success rate during the initial stages of training. However, overall, the success rate gradually increased as training progressed, ultimately stabilizing at around 77%, as shown in Figure 9b.
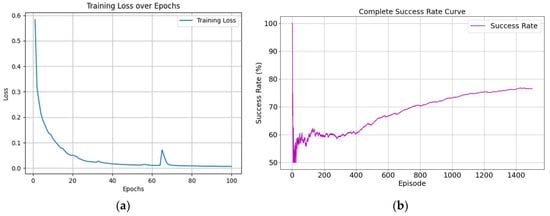
Figure 9.
Training process curves. (a) is training loss curve and (b) is success rate curve.
To validate the effectiveness of the reinforcement learning agent, experiments were conducted to acquire the standard plane of subcostal longitudinal section of the aorta. The experimental procedure is as follows: First, the ultrasound probe starts from a random posture within the target acoustic window. Then, the system begins using the trained RL agent to make decisions based on real-time ultrasound image inputs, autonomously controlling the robotic arm’s next movement. When the termination condition is met, the scanning ends and the final ultrasound image is saved.
The experimental procedure is as follows: First, the ultrasound probe starts from a random posture within the target acoustic window. The black dots and lines in Figure 10 represent the starting postures (positions and orientations) for each of the five experiments, while the red dot and line indicate the probe posture (position and orientation) corresponding to the standard plane. Then, the system begins using the trained RL agent to make decisions based on real-time ultrasound image inputs, autonomously controlling the robotic arm’s next movement. When the termination condition is met, the scanning ends and the final ultrasound image is saved.
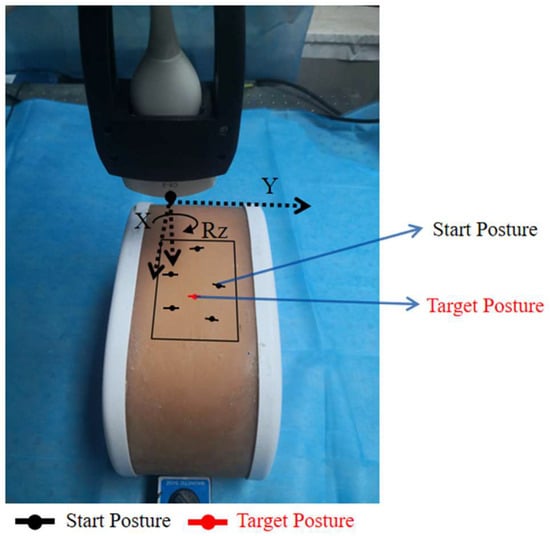
Figure 10.
Experimental setup.
Three typical images in the searching process are shown in Figure 11. The target ultrasound image is shown in Figure 12. The similarity between the obtained images and the target ultrasound image was evaluated. In this study, the Mean Squared Error (MSE) was used to calculate the difference between each of images and the target ultrasound image. Then, the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) was computed using Equation (4) to intuitively quantify the image similarity. The Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) was also used, as it better correlates with human visual perception of image quality. SSIM is defined as Equation (5). To quantitatively evaluate the anatomical localization accuracy of our system, we computed the Dice coefficient. The Dice coefficient measures the spatial overlap between the predicted segmentation mask (A) and the ground truth mask (B) and is defined in Equation (6). The experimental results are shown in Table 2.
where , , and are the local mean, variance, and cross-covariance for images x and y, respectively.
where TP (True Positives) represents the correctly identified target pixels, FP (False Positives) represents the incorrectly identified pixels (over-segmentation), and FN (False Negatives) represents the missed target pixels (under-segmentation).
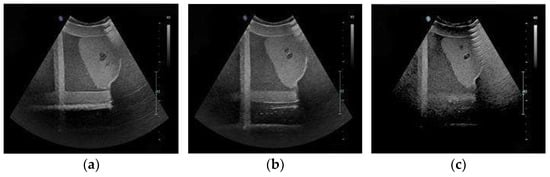
Figure 11.
The ultrasound image of standard plane obtained in three experiments. (a) is the best acquired image. (b) is the medium acquired image. (c) is the worst acquired image.
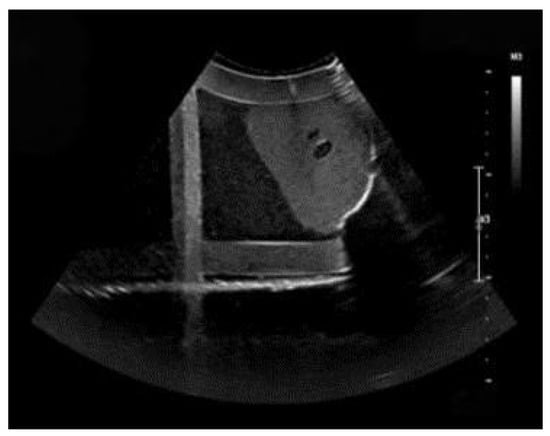
Figure 12.
The target ultrasound image of standard plane.

Table 2.
Experiment results summary.
To evaluate the system’s performance, ten independent trials were conducted from randomized initial positions. On our current hardware (NVIDIA RTX 3070Ti), the entire perception-to-action loop has an average latency of approximately 85 ms, which can meet the control frequency of 10 Hz. The quantitative results are summarized in Table 2. The system achieved an average Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) of 24.51 dB, a Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) of 0.70, and a Dice coefficient of 0.80. The PSNR value indicates pixel-level differences between the acquired and target images, which is an expected outcome in a physical robotic task. The SSIM score of 0.70 suggests that the structural components of the image were largely preserved. The primary metric for clinical relevance, the Dice coefficient, reached an average of 0.80, indicating a high degree of overlap for the target anatomical structure. Analysis of the trial-by-trial data shows that while image quality metrics such as PSNR and SSIM exhibited variance, the Dice coefficient remained relatively stable, with nine out of ten trials scoring above 0.74. These results demonstrate the system’s capability to repeatedly localize the specified anatomical plane. The data confirms the functionality of the reinforcement learning-based approach for the autonomous liver ultrasound scanning task.
5. Discussion
5.1. Evaluation of System Performance
In this study, we developed and validated a Robotic Ultrasound Scanning System (RUSS) capable of autonomously localizing a standard liver plane using a reinforcement learning-based approach. The experimental results conducted in the real world confirm the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed system.
The quantitative analysis provides a multi-faceted view of the system’s performance. The average PSNR of 24.51 dB and MSE of 280.11 indicate that, as expected in a physical robotic task, there are discernible pixel-level differences between the acquired images and the target image. These variations can be attributed to minor, unavoidable discrepancies in the final robotic pose and the inherent stochasticity of ultrasound imaging.
However, the average SSIM of 0.70 demonstrates that the structural integrity and key features of the target plane were well-preserved in the autonomously acquired images. The system achieved an average Dice coefficient of 0.80 for the abdominal aorta, the primary anatomical landmark for this task. This high degree of spatial overlap provides strong quantitative evidence that the agent successfully and consistently navigates the probe to the anatomically correct location. The stability of the Dice score across trials, even when pixel-level metrics fluctuated, underscores the robustness of our semantic-guided RL policy.
5.2. Limitations and Future Work
Despite the promising results, this study has several limitations that must be acknowledged and will guide our future research.
First, the experimental validation was conducted exclusively on a phantom model. While phantoms are essential for initial system development and validation, they do not capture the complexities of in vivo scanning, such as patient breathing motion, tissue deformation under probe pressure, and anatomical variability across different individuals. Future work will involve pilot studies on human volunteers to assess the system’s performance and adaptability in a clinical setting. Second, the current RL agent has not been trained to actively avoid obstacles like ribs, which can create acoustic shadows and obscure the target. Integrating a penalty into the reward function for images with significant shadowing, or developing a more sophisticated exploration strategy, will be a key focus for improving the system’s practical utility. We will prioritize a comparative analysis of our DQN agent against at least two key baselines: behavioral imitation from expert demonstrations and a visual servo on segmented features. Finally, this study focused on a single, relatively simple standard plane. Our future roadmap includes expanding the system’s capabilities to locate multiple, more complex standard planes of the liver and other organs, which will require a more advanced state representation and hierarchical reinforcement learning strategies.
5.3. Potential Clinical Integration and Practical Significance
Beyond the technical implementation, the practical significance of this work lies in its potential to be integrated into various clinical workflows, addressing key challenges in medical ultrasound.
We envision three primary application scenarios. First, in Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) and initial screening, our system could empower non-specialist professionals to acquire high-quality, standardized images. This would enable faster triage and extend expert-level diagnostics in remote or underserved areas. Second, for the longitudinal monitoring of chronic diseases, the system’s high reproducibility is a distinct advantage. By recording and returning to the exact robotic coordinates, it can acquire highly comparable images over time, minimizing the inter-operator variability that currently complicates the assessment of disease progression. Third, within specialized radiology departments, the RUSS could serve as an intelligent assistant to reduce sonographer workload and ergonomic strain. By automating the repetitive task of standard plane searching, it allows clinicians to focus their expertise on complex diagnostic interpretation and patient interaction, ultimately improving both efficiency and occupational health.
In summary, the practical impact of this technology is threefold: it enhances consistency by minimizing operator variability, optimizes healthcare resources through automation, and improves the well-being of sonographers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.Z.; methodology, C.L.; software, Z.Z.; formal analysis, B.Z.; resources, X.Q.; data curation, P.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, T.Z.; writing—review and editing, B.Z.; visualization, Z.Z.; project administration, B.Z.; funding acquisition, X.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shenzhen Key Technology Research and Development Project (Grant No. JSGG20220831100202004), Shenzhen Fundamental Research Funds (Grant No. JCYJ20241202152803005, KJZD20240903100200002), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62403450, U23A20391).
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used Google Translate for the purposes of translating Chinese into English. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Newman, P.G.; Rozycki, G.S. The history of ultrasound. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1998, 78, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shung, K.K. Diagnostic ultrasound: Past, present, and future. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2011, 31, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmailzl, K.J.; Ormerod, O. Ultrasound in Cardiology; Blackwell Sci.: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Peeling, W.B.; Griffiths, G.J. Imaging of the prostate by ultrasound. J. Urol. 1984, 132, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinenga, G.; Langton, C.; Nisbet, R.; Götz, J. Ultrasound treatment of neurological diseases—Current and emerging applications. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callen, P.W. Ultrasonography in Obstetrics and Gynecology; Elsevier Health Sciences: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, C.F.; Kamnitsas, K.; Matthew, J.; Fletcher, T.P.; Smith, S.; Koch, L.M.; Kainz, B.; Rueckert, D. SonoNet: Real-time detection and localisation of fetal standard scan planes in freehand ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.V.; Kara, M.; Su, D.C.J.; Gürçay, E.; Kaymak, B.; Wu, W.T.; Özçakar, L. Sonoanatomy of the spine: A comprehensive scanning protocol from cervical to sacral region. Med. Ultrason. 2019, 21, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, M.K.; Chin, K.J. Spinal Sonography and Applications of Ultrasound for Central Neuraxial Blocks. 2017. Available online: http://www.nysora.com/techniques/neuraxialand-perineuraxial-techniques/ultrasoundguided/3276-spinal-and-epidural-block.html,1 (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Muir, M.; Hrynkow, P.; Chase, R.; Boyce, D.; Mclean, D. The nature, cause, and extent of occupational musculoskeletal injuries among sonographers: Recommendations for treatment and prevention. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2004, 20, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A.; Blume, J.D.; Cormack, J.B.; Mendelson, E.B. Operator dependence of physician-performed whole-breast US: Lesion detection and characterization. Radiology 2006, 241, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Z.; Nelson, B.J.; Murphy, R.R.; Choset, H.; Christensen, H.; Collins, S.H.; Dario, P.; Goldberg, K.; Ikuta, K.; Jacobstein, N.; et al. Combating COVID-19—The role of robotics in managing public health and infectious diseases. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eabb5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakadate, R.; Solis, J.; Takanishi, A.; Minagawa, E.; Sugawara, M.; Niki, K. Implementation of an automatic scanning and detection algorithm for the carotid artery by an assisted-robotic measurement system. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Nakadate, R.; Uda, H.; Hirano, H.; Solis, J.; Takanishi, A.; Minagawa, E.; Sugawara, M.; Niki, K. Development of assisted-robotic system designed to measure the wave intensity with an ultrasonic diagnostic device. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 11–15 October 2009; pp. 510–515. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Mustafa, A.S.; Ishii, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Nakadate, R.; Ishii, H.; Ogawa, K.; Saito, A.; Sugawara, M.; Niki, K.; Takanishi, A. Development of robotic system for autonomous liver screening using ultrasound scanning device. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Shenzhen, China, 12–14 December 2013; pp. 804–809. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Mustafa, A.S.; Ishii, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Nakadate, R.; Ishii, H.; Ogawa, K.; Saito, A.; Sugawara, M.; Niki, K.; Takanishi, A. Human abdomen recognition using camera and force sensor in medical robot system for automatic ultrasound scan. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 4855–4858. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, J. Surgical robotics. In Medical Devices: Surgical and Image-Guided Technologies; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 63–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Tian, S.; Guo, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, N.; Xin, Y. Comparison of medical image 3D reconstruction rendering methods for robot-assisted surgery. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), Hefei and Tai’an, China, 27–31 August 2017; pp. 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, G.T.; Gill, I.S. Robotic laparoscopic surgery: A comparison of the da Vinci and Zeus systems. Urology 2001, 58, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Lan, J.; Li, X. Robotic arm based automatic ultrasound scanning for three-dimensional imaging. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merouche, S.; Allard, L.; Montagnon, E.; Soulez, G.; Bigras, P.; Cloutier, G. A robotic ultrasound scanner for automatic vessel tracking and three-dimensional reconstruction of b-mode images. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2015, 63, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Z.; Bai, X.; Mao, Z. Predicting flow status of a flexible rectifier using cognitive computing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 264, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Suzuki, S.; Wiranata, A.; Zheng, Y.; Miyagawa, S. Bio-inspired circular soft actuators for simulating defecation process of human rectum. J. Artif. Organs 2025, 28, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Hong, M.; Ji, W.; Fu, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, M.; Jin, Y. Medical sam adapter: Adapting segment anything model for medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 102, 103547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Cui, C.; Liu, Q.; Yao, T.; Remedios, L.W.; Bao, S.; Landman, B.A.; Wheless, L.E.; Coburn, L.A.; Wilson, K.T.; et al. Segment anything model (sam) for digital pathology: Assess zero-shot segmentation on whole slide imaging. In Proceedings of the IS&T International Symposium on Electronic Imaging, Burlingame, CA, USA, 2–6 February 2025; Volume 37, p. COIMG-132. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Law, H.; Poon, C.; Yen, S.; Lall, K.; Jamshidi, A.; Malis, V.; Hwang, D.; Bae, W.C. Segment Anything Model (SAM) and Medical SAM (MedSAM) for Lumbar Spine MRI. Sensors 2025, 25, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Lin, L.; Tong, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.-W.; Wu, J. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–9 May 2020; pp. 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, H.; Yang, X.; Qian, J.; Xue, W.; Qin, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Heng, P.-A.; et al. Agent with warm start and active termination for plane localization in 3D ultrasound. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 290–298. [Google Scholar]
- Jarosik, P.; Lewandowski, M. Automatic ultrasound guidance based on deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Glasgow, Scotland, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 475–478. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Liu, D. Self-triggered approximate optimal neuro-control for nonlinear systems through adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 4713–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; Yan, J.; Qin, C. Adaptive critic design for safety-optimal FTC of unknown nonlinear systems with asymmetric constrained-input. ISA Trans. 2024, 155, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Ran, X.; Zhang, D. Unsupervised image stitching based on Generative Adversarial Networks and feature frequency awareness algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 183, 113466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milletari, F.; Birodkar, V.; Sofka, M. Straight to the point: Reinforcement learning for user guidance in ultrasound. In Proceedings of the Smart Ultrasound Imaging and Perinatal, Preterm and Paediatric Image Analysis: First International Workshop, SUSI 2019, and 4th International Workshop, PIPPI 2019, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2019, Shenzhen, China, 13 and 17 October 2019, Proceedings; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hase, H.; Azampour, M.F.; Tirindelli, M.; Paschali, M.; Simson, W.; Fatemizadeh, E.; Navab, N. Ultrasound-guided robotic navigation with deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 5534–5541. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Qin, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, L.; Meng, M.Q.H. Autonomous navigation of an ultrasound probe towards standard scan planes with deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 8302–8308. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wendler, T.; Karlas, A.; Navab, N. VesNet-RL: Simulation-based reinforcement learning for real-world US probe navigation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 6638–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Qurri, A.; Almekkawy, M. Improved UNet with attention for medical image segmentation. Sensors 2023, 23, 8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, G.; Kumar, A.; Bhat, S.A. Recent developments of game theory and reinforcement learning approaches: A systematic review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 9999–10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Li, W. Time series prediction based on LSTM-attention-LSTM model. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 48322–48331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.C.; Torralba, A.; Murphy, K.P.; Freeman, W.T. LabelMe: A database and web-based tool for image annotation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).