Denoising the ECG from the EMG Using Stationary Wavelet Transform and Template Matching
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. Simulations
2.1.2. Experimental Conditions
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Wavelet Transforms
2.2.2. Wavelet Thresholding
2.2.3. Template Masking
2.3. Performance Evaluation
2.3.1. Performance Indexes
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
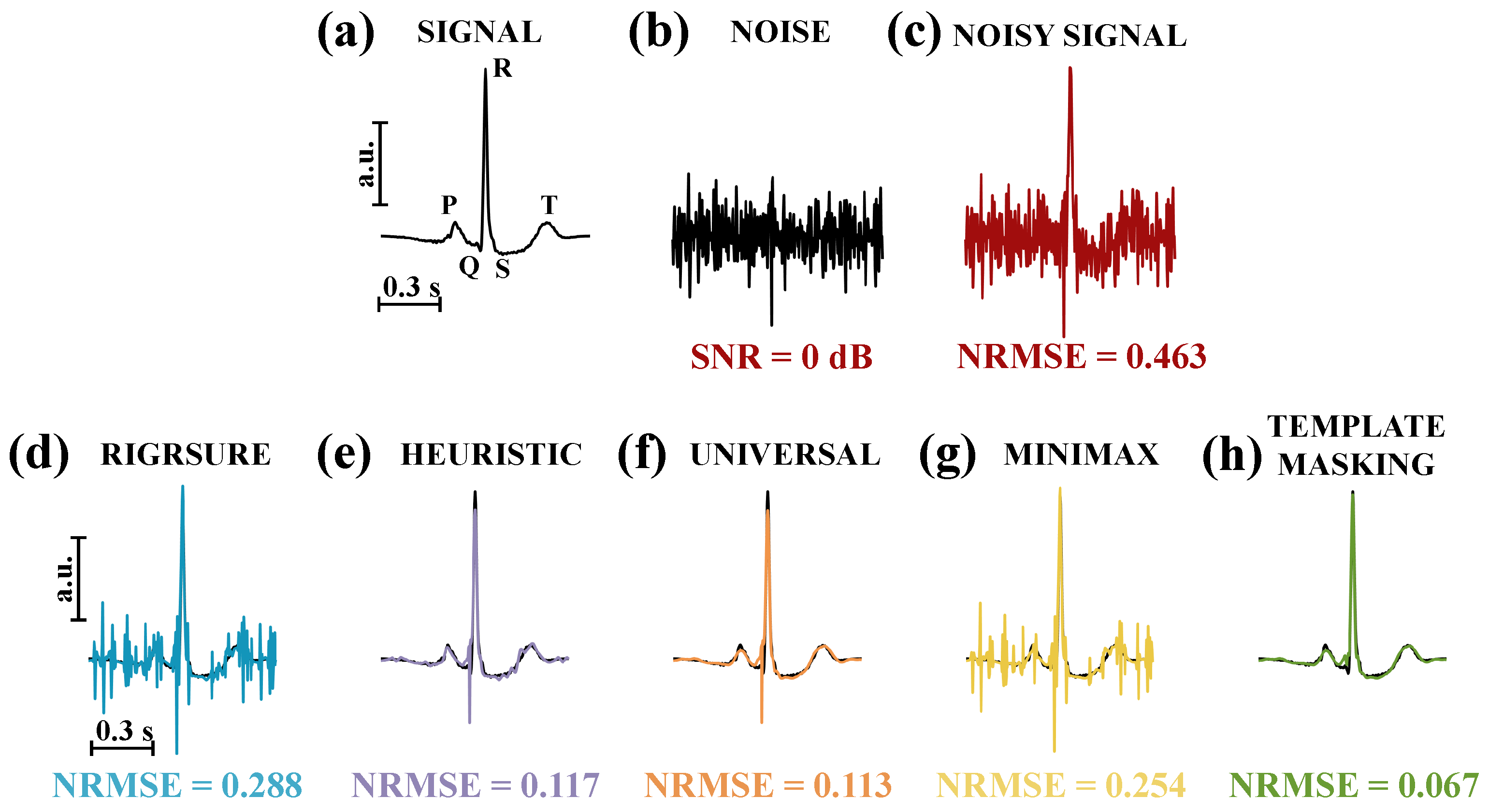
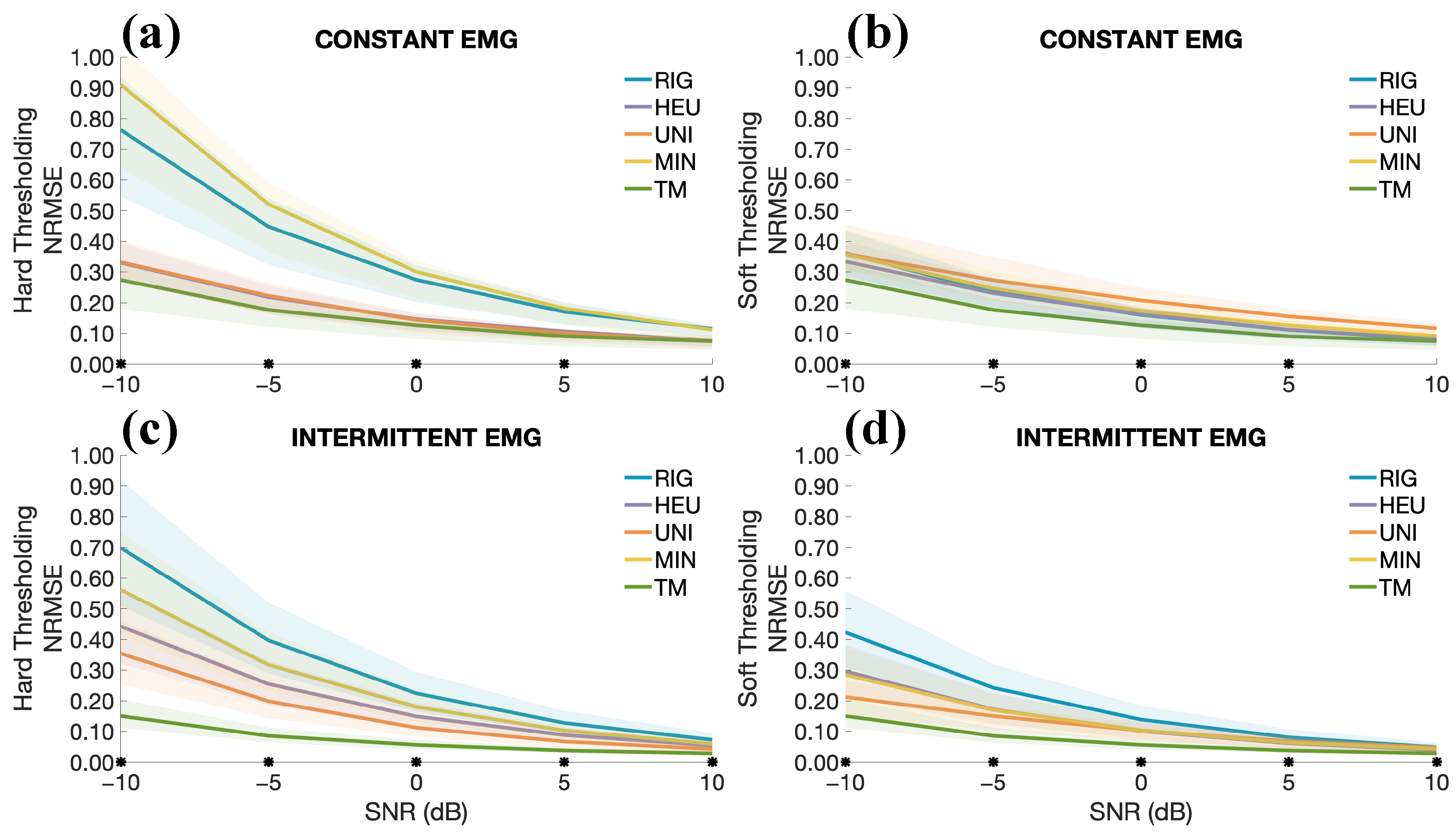
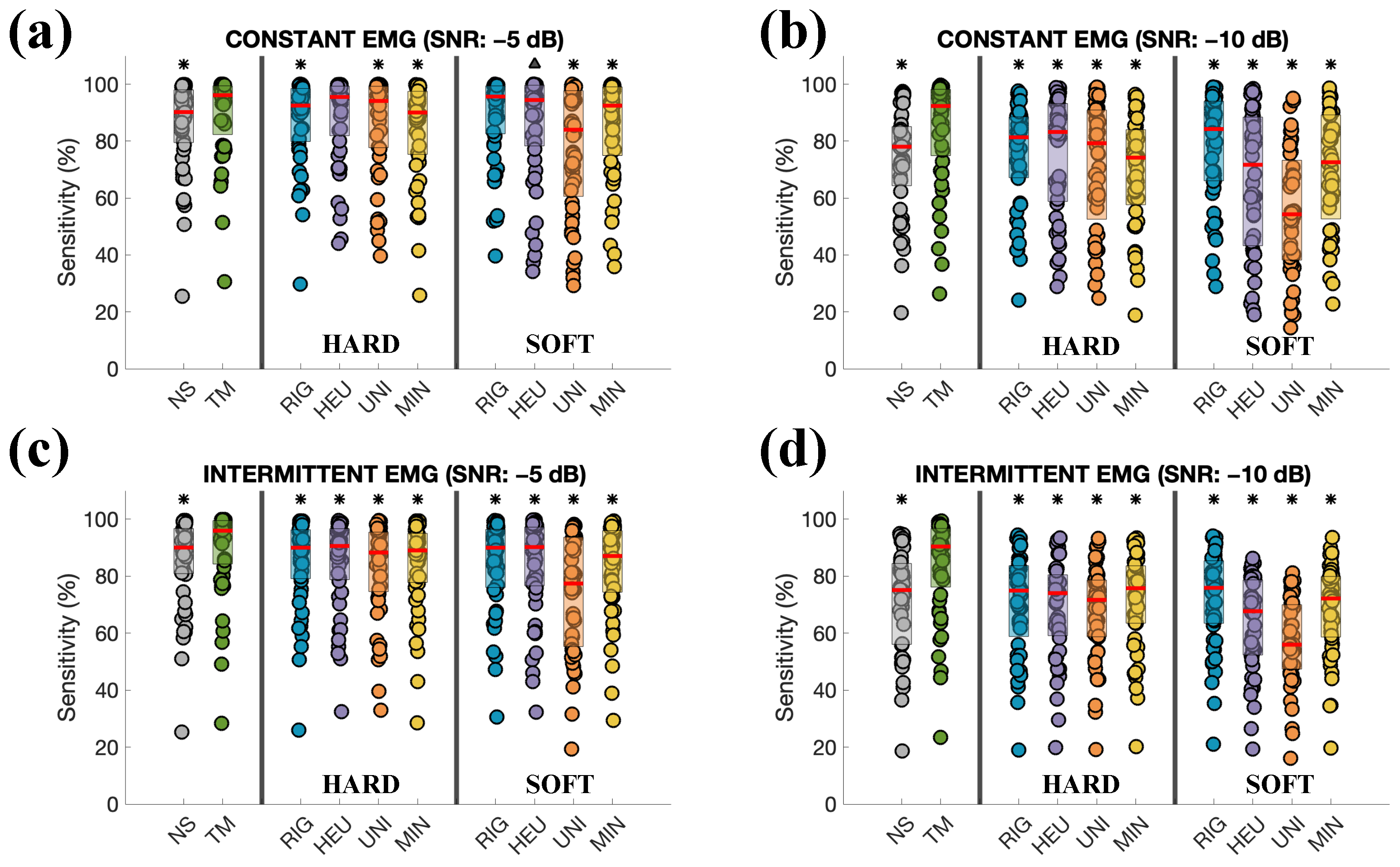
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Mc Namara, K.; Alzubaidi, H.; Jackson, J.K. Cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death: How are pharmacists getting involved. Integr. Pharm. Res. Pract. 2019, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.E.; Sarrafzadeh, M. A survey of smartwatches in remote health monitoring. J. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2018, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, S. Wristband-type wearable health devices to measure construction workers’ physical demands. Autom. Constr. 2017, 83, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiong, W.; Li, Y. Wearable measurement of ECG signals based on smart clothing. Int. J. Telemed. Appl. 2020, 2020, 6329360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Towards the Internet of smart clothing: A review on IoT wearables and garments for creating intelligent connected e-textiles. Electronics 2018, 7, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroudi, A.; Hernández, N.; Berglin, L.; Nierstrasz, V. Electrode placement in electrocardiography smart garments: A review. J. Electrocardiol. 2019, 57, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Kan, C.; Yang, H. Sensitivity analysis of wearable textiles for ECG sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical & Health Informatics (BHI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–7 March 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Brittain, J.S.; Holland, P.; Yianni, J.; Green, A.L.; Stein, J.F.; Aziz, T.Z.; Wang, S. Removing ECG noise from surface EMG signals using adaptive filtering. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 462, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakor, N.V.; Zhu, Y.S. Applications of adaptive filtering to ECG analysis: Noise cancellation and arrhythmia detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 38, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahankova, R.; Mikolasova, M.; Martinek, R. Optimization of adaptive filter control parameters for non-invasive fetal electrocardiogram extraction. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesen, G.M.; Jannett, T.C.; Jadallah, M.A.; Yates, S.L.; Quint, S.R.; Nagle, H.T. A comparison of the noise sensitivity of nine QRS detection algorithms. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1990, 37, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beni, N.H.; Jiang, N. Heartbeat detection from single-lead ECG contaminated with simulated EMG at different intensity levels: A comparative study. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 83, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.A.; Shahnaz, C. Denoising of ECG signals based on noise reduction algorithms in EMD and wavelet domains. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2012, 7, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 4144–4147. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Wavelets for electrocardiogram: Overview and taxonomy. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 25627–25649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, M.; Abdelmalik, T.; Larbi, B. R-peaks detection based on stationary wavelet transform. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2015, 121, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalidas, V.; Tamil, L. Real-time QRS detector using stationary wavelet transform for automated ECG analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Washington, DC, USA, 23–25 October 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 457–461. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Tomar, H.; Mehla, V.K.; Komaragiri, R.; Kumar, M. Stationary wavelet transform based ECG signal denoising method. ISA Trans. 2021, 114, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Bouny, L.; Khalil, M.; Adib, A. ECG noise reduction based on stationary wavelet transform and zero-crossings interval thresholding. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies (ICEIT), Rabat, Morocco, 15–18 November 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, D.; Xie, F. Electrocardiogram Signal Denoising Based on Multi-Threshold Stationary Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Messina, Italy, 22–24 June 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Lin, J. The optimal de-noising algorithm for ECG using stationary wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the 2009 WRI World Congress on Computer Science and Information Engineering, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 31 March–2 April 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 6, pp. 469–473. [Google Scholar]
- Baldazzi, G.; Solinas, G.; Del Valle, J.; Barbaro, M.; Micera, S.; Raffo, L.; Pani, D. Systematic analysis of wavelet denoising methods for neural signal processing. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 066016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsene, C.T.; Hankins, R.; Yin, H. Deep Learning Models for Denoising ECG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), A Coruña, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. A novel deep wavelet convolutional neural network for actual ECG signal denoising. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 87, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chang, X.; Yao, Z.; Shi, D.; Chen, Y. A deep learning framework for ECG denoising and classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 94, 106441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G. The MIT-BIH arrhythmia database on CD-ROM and software for use with it. In Proceedings of the [1990] Proceedings Computers in Cardiology, Chicago, IL, USA, 23–26 September 1990; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, D.; Mesin, L.; Martina, S.; Merletti, R. A surface EMG generation model with multilayer cylindrical description of the volume conductor. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesin, L. Separation of interference surface electromyogram into propagating and non-propagating components. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 52, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglevand, A.J.; Winter, D.A.; Patla, A.E. Models of recruitment and rate coding organization in motor-unit pools. J. Neurophysiol. 1993, 70, 2470–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasoski, V.; Petrovic, J.; Maneski, L.P.; Miletić, M.; Babić, M.; Nikolić, A.; Panescu, D.; Ivanović, M.D. A database of simultaneously recorded ECG signals with and without EMG noise. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2023, 4, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasoski, V.; Popovic Maneski, L.; Miletic, M.; Babic, M.; Ivanovic, M.; Nikolic, A.; Petrovic, J.; Bojovic, B.; Hadzievski, L. SimEMG Database- Simultaneous Recordings of Noise-Free and Noise-Contaminated ECG Signals. Mendeley Data. 2022. Available online: https://doi.org/10.17632/yx5pb66hwz.1 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Jaffery, Z.A.; Ahmad, K.; Sharma, P. Selection of optimal decomposition level based on entropy for speech denoising using wavelet packet. J. Bioinform. Intell. Control 2012, 1, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, S.K.; Swarnakar, B.; Kansabanik, S.; Ray, S. A novel signal denoising method using stationary wavelet transform and particle swarm optimization with application to rolling element bearing fault diagnosis. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 66, 3935–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, D.; Orejuela, D.; Salazar, J.; Valencia, J. Comparison analysis between rigrsure, sqtwolog, heursure and minimaxi techniques using hard and soft thresholding methods. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXI Symposium on Signal Processing, Images and Artificial Vision (STSIVA), Bucaramanga, Colombia, 31 August–2 September 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abi-Abdallah, D.; Chauvet, E.; Bouchet-Fakri, L.; Bataillard, A.; Briguet, A.; Fokapu, O. Reference signal extraction from corrupted ECG using wavelet decomposition for MRI sequence triggering: Application to small animals. Biomed. Eng. Online 2006, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W.J. A Real-Time QRS Detection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1985, BME-32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, D. MATLAB—Pan-Tompkins QRS Detector. 2025. Available online: https://github.com/danielwedekind/qrsdetector (accessed on 26 July 2025).
- Scheirer, C.J.; Ray, W.S.; Hare, N. The analysis of ranked data derived from completely randomized factorial designs. Biometrics 1976, 32, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamga, P.; Mostafa, R.; Zafar, S. The use of wearable ECG devices in the clinical setting: A review. Curr. Emerg. Hosp. Med. Rep. 2022, 10, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, Z.; Al-Zaiti, S.S.; Bond, R.; Sejdić, E. Remote and wearable ECG devices with diagnostic abilities in adults: A state-of-the-science scoping review. Heart Rhythm 2022, 19, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldo, R.; Xu, W.; Melillo, P.; Pecchia, L.; Santamaria, L.; James, C. Detection of mental stress due to oral academic examination via ultra-short-term HRV analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3805–3808. [Google Scholar]
- Mesin, L. Heartbeat monitoring from adaptively down-sampled electrocardiogram. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 84, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raggi, M.; Chiri, S.; Roatta, S.; Rabbito, R.; Mesin, L. A Novel Approach for Acute Mental Stress Mitigation Through Adapted Binaural Beats: A Pilot Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satija, U.; Ramkumar, B.; Manikandan, M.S. A review of signal processing techniques for electrocardiogram signal quality assessment. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 11, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, M.; Sarmento, A.; Gugliandolo, P.; Leonardi, A.; Longinotti-Buitoni, G.; Minella, C.; Vignati, C.; Mapelli, M.; Aliverti, A.; Agostoni, P. Validation of a new wearable device for type 3 sleep test without flowmeter. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoons, M.; Hugenholtz, P. Gradual changes of ECG waveform during and after exercise in normal subjects. Circulation 1975, 52, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligfield, P.; Gettes, L.S.; Bailey, J.J.; Childers, R.; Deal, B.J.; Hancock, E.W.; Van Herpen, G.; Kors, J.A.; Macfarlane, P.; Mirvis, D.M.; et al. Recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: Part I: The electrocardiogram and its technology: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; The American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. Circulation 2007, 115, 1306–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Mesin, L.; Cipriani, G.E.; Amanzio, M. Electroencephalography-based brain–machine interfaces in older adults: A literature review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Jeong, J.; Kim, H.B.; Kwon, I.H.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, Y. Electrocardiogram sampling frequency range acceptable for heart rate variability analysis. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2018, 24, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesin, L. A neural algorithm for the non-uniform and adaptive sampling of biomedical data. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 71, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raggi, M.; Mesin, L. Denoising the ECG from the EMG Using Stationary Wavelet Transform and Template Matching. Electronics 2025, 14, 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173474
Raggi M, Mesin L. Denoising the ECG from the EMG Using Stationary Wavelet Transform and Template Matching. Electronics. 2025; 14(17):3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173474
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaggi, Matteo, and Luca Mesin. 2025. "Denoising the ECG from the EMG Using Stationary Wavelet Transform and Template Matching" Electronics 14, no. 17: 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173474
APA StyleRaggi, M., & Mesin, L. (2025). Denoising the ECG from the EMG Using Stationary Wavelet Transform and Template Matching. Electronics, 14(17), 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173474






