An Ensemble Learning Approach for Facial Emotion Recognition Based on Deep Learning Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. FER
2.2. ML and DL Techniques
2.2.1. Traditional Approaches
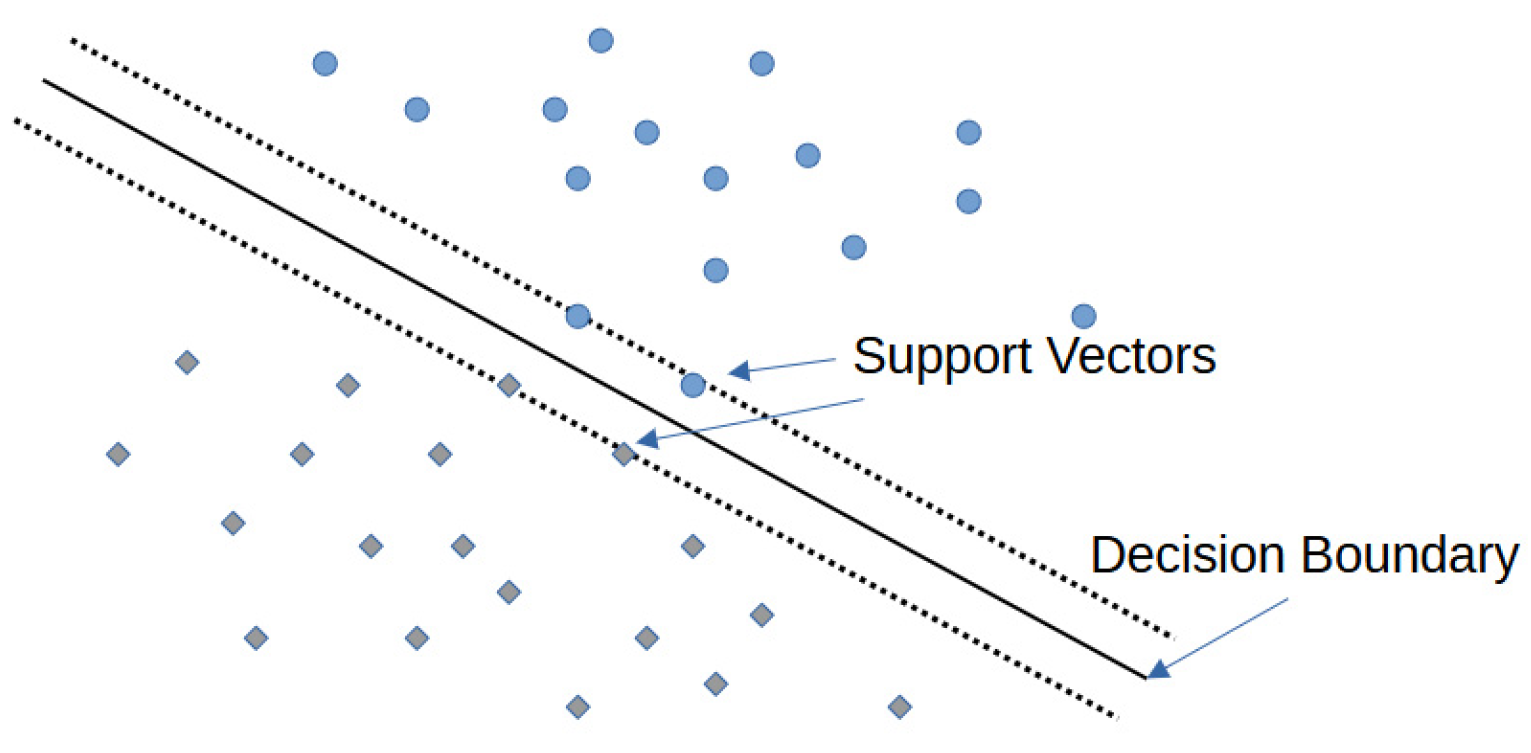
2.2.2. ML Paradigms
- One-to-one approach, where a binary SVM classifier is trained for each pair of classes. If there are m classes, this results in the following [35]:
- One-to-rest approach, where a binary SVM classifier is trained for each class. If there are m classes, one class is selected and designated as the positive class, while all other classes are treated as the negative class. By iteratively considering each of the m classes as the positive class, the original multiclass classification problem is transformed into m separate binary classification problems. Each classifier then determines whether a given instance belongs to its respective positive class or not [35].
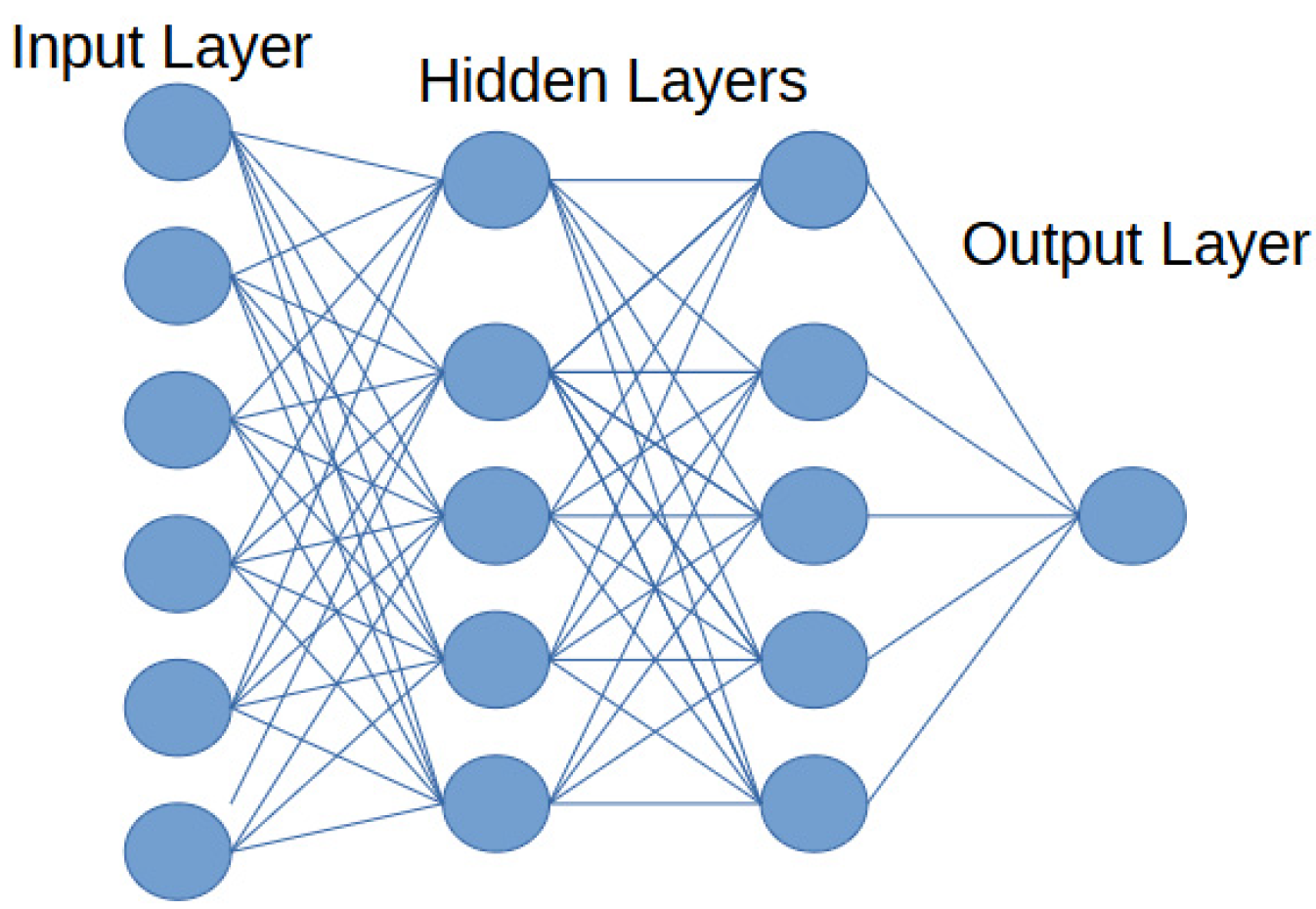
2.2.3. Rise of DL
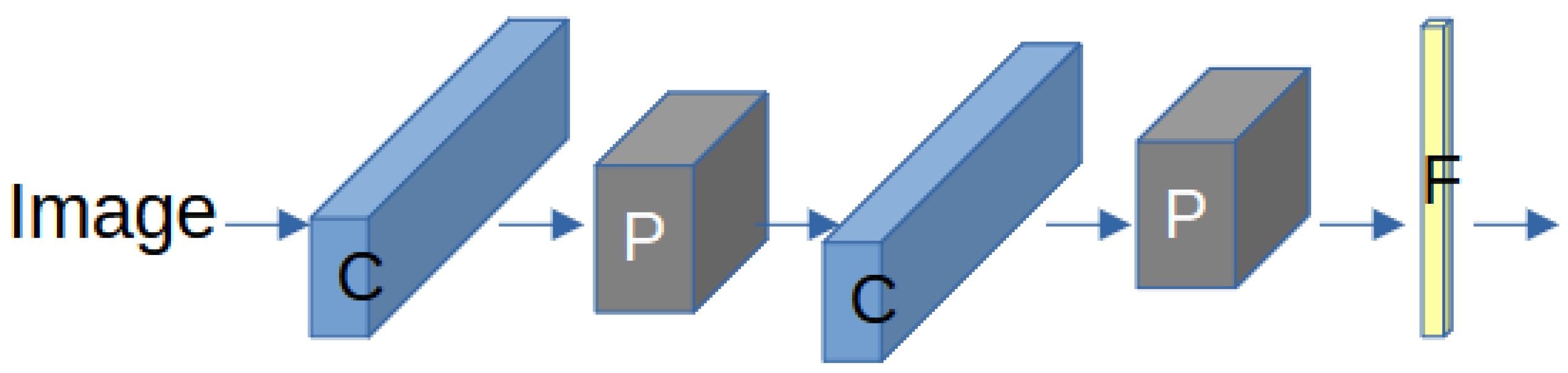
- Convolution layers: These perform convolution operations on the input data using a collection of filters to produce feature maps that reflect and represent the spatial characteristics of the facial image.
- Max pooling layers: In these layers, a form of dimensionality reduction is performed by reducing the spatial resolution of the feature maps. This operation helps to focus on the most relevant features while discarding less significant details.
- Fully connected layers: These layers are typically found at the end of a CNN and are often followed by activation functions. Fully connected layers utilize the high-level features extracted by the preceding layers to perform predictions or classifications. Figure 4 shows a CNN architecture that consists of convolution layers, pooling layers, and fully connected layer.
2.3. EfficientNet
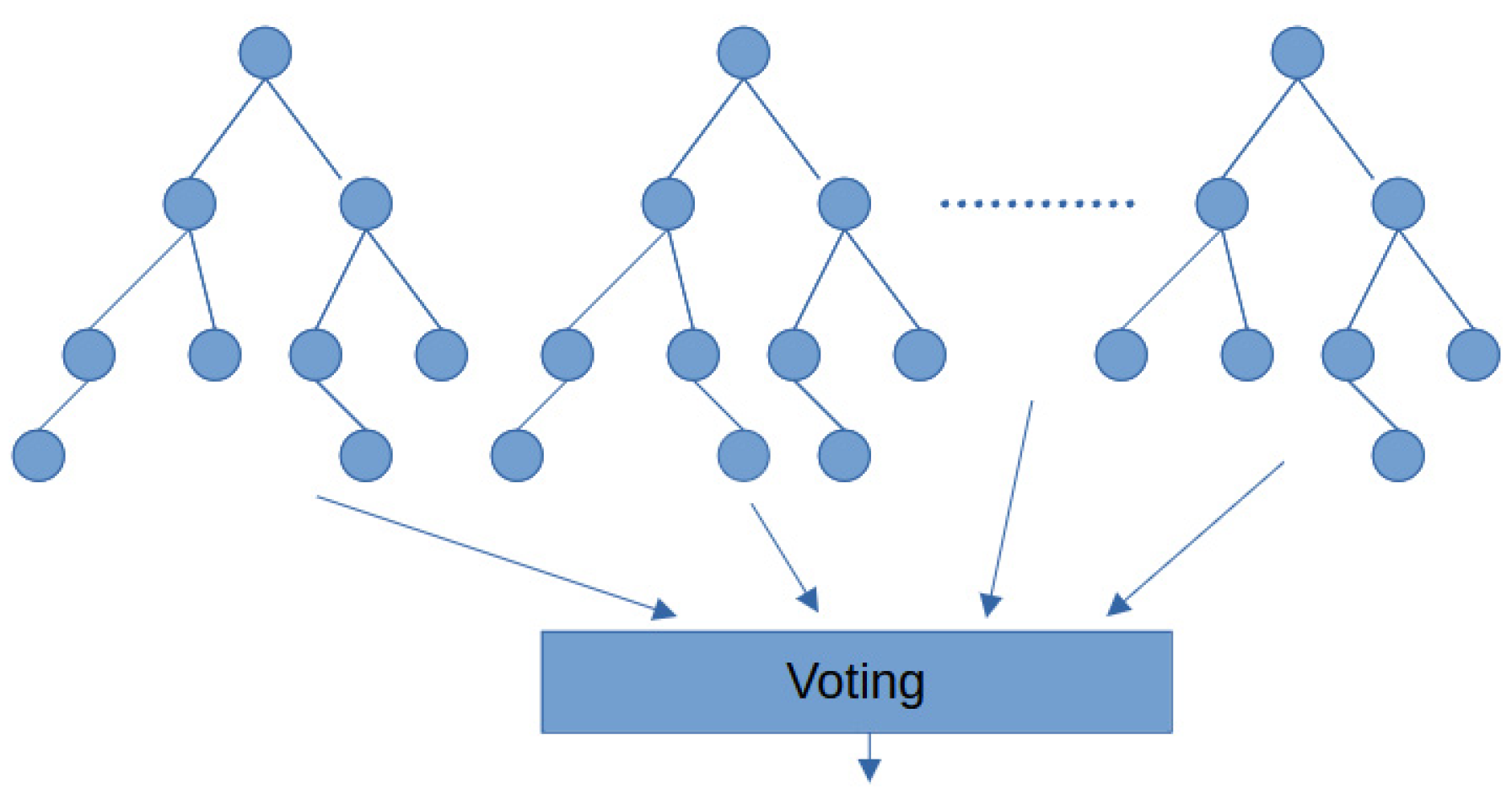
2.4. Ensemble Learning
3. Literature Review
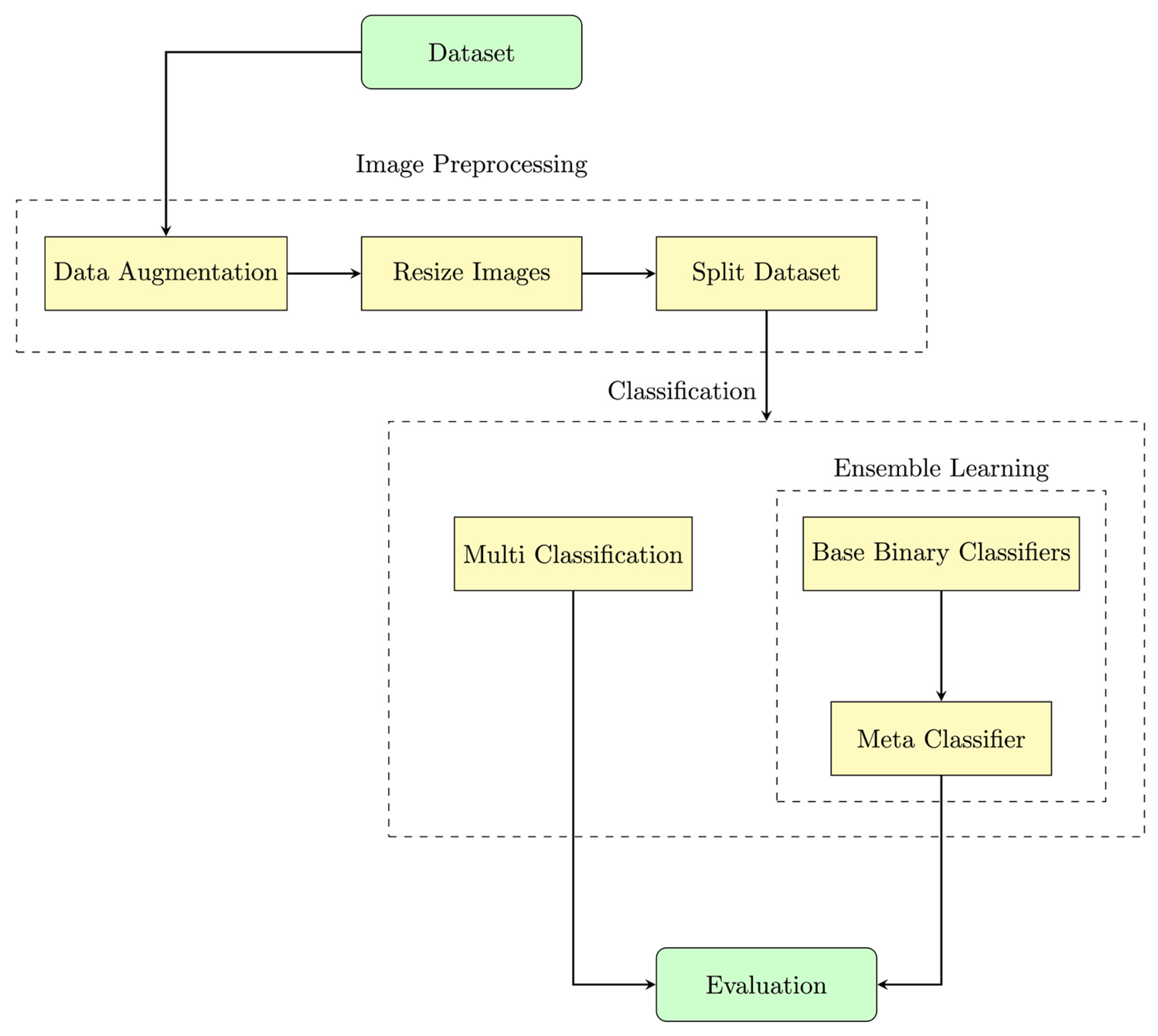
4. Methodology
- Improved Predictive Performance: This is achieved by combining the strengths of multiple models.
- Model Diversity: This is achieved by using various base models at the same time and then combining their predictions.
- Reduced Overfitting: It generalizes better to unseen data.
- Flexibility: It can accommodate various types of models and algorithms.
- Ensemble Learning: Ensemble methods often outperform individual models.
- Adaptability: It can be adapted to different types of ML tasks, including classification, regression, and clustering. It can also be extended to handle more complex scenarios, such as multiclass classification.
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Data Preprocessing
4.2.1. Image Resizing
4.2.2. Data Augmentation
4.2.3. Balancing the Dataset
4.2.4. Splitting the Dataset
4.3. Model Architecture
4.4. Model Training
4.5. Model Evaluation
5. Experiment
5.1. Tools
5.2. Performance Measures
5.3. Experimental Settings
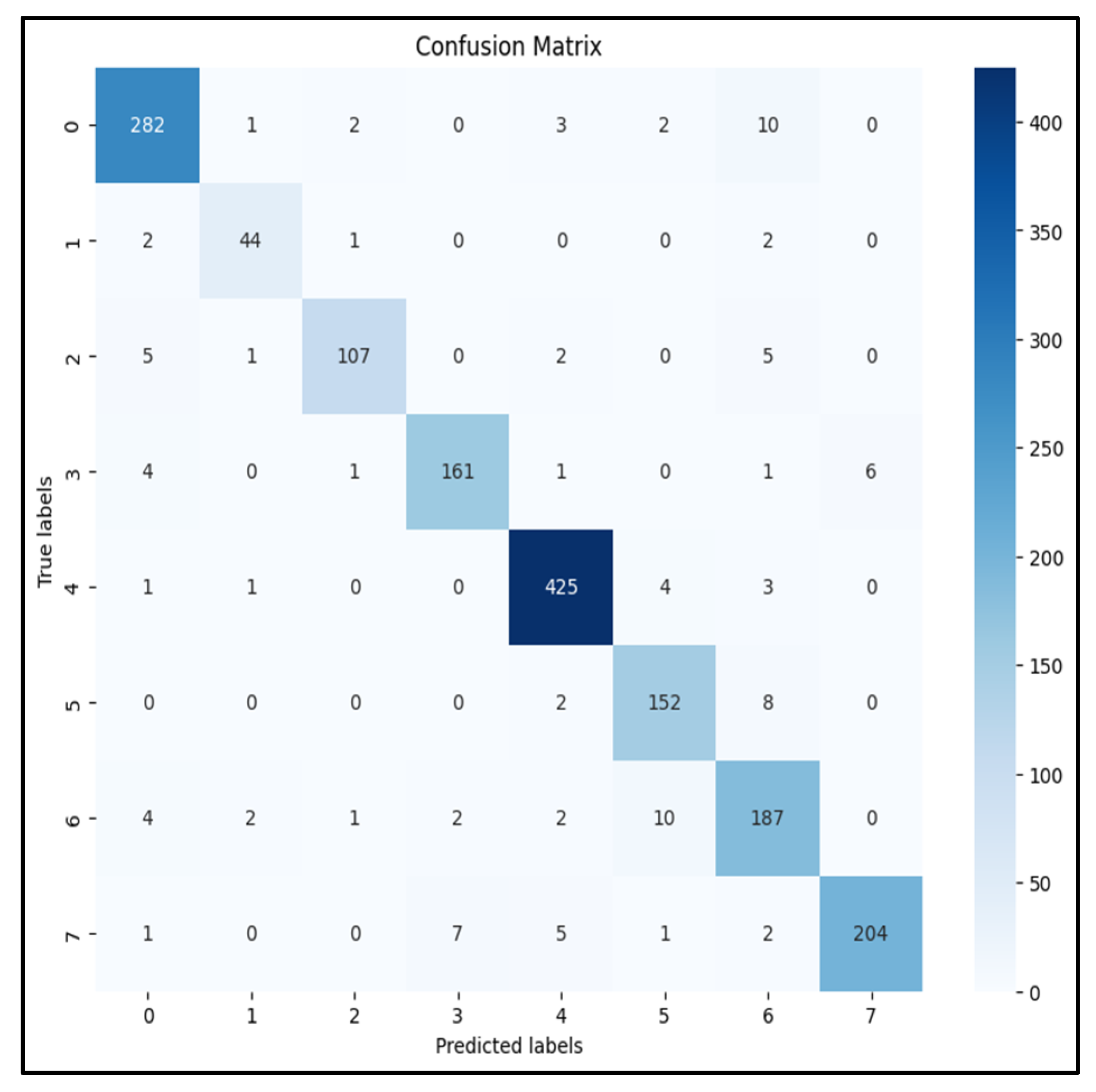
5.3.1. Multiclass Classification Experiment
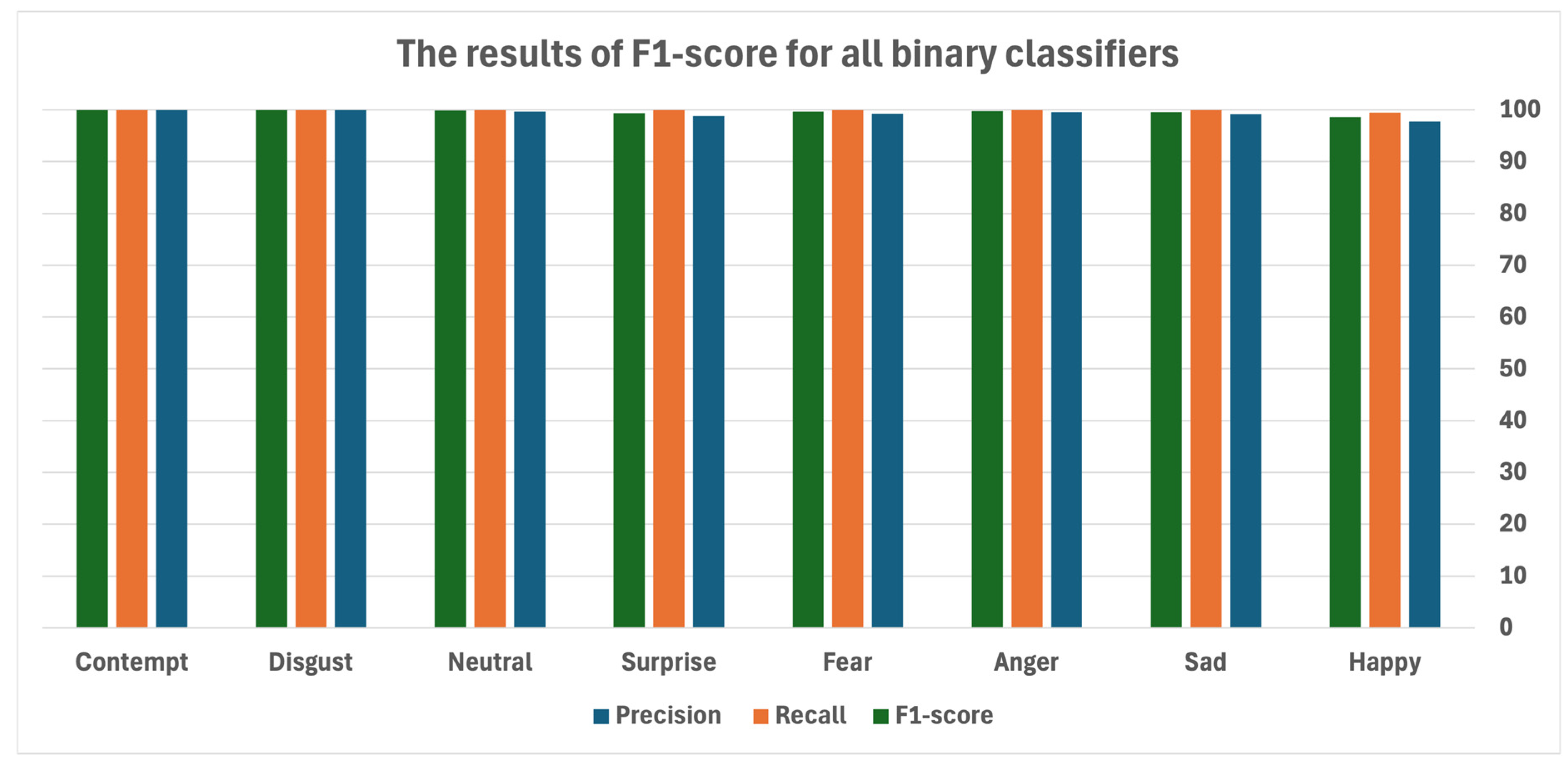
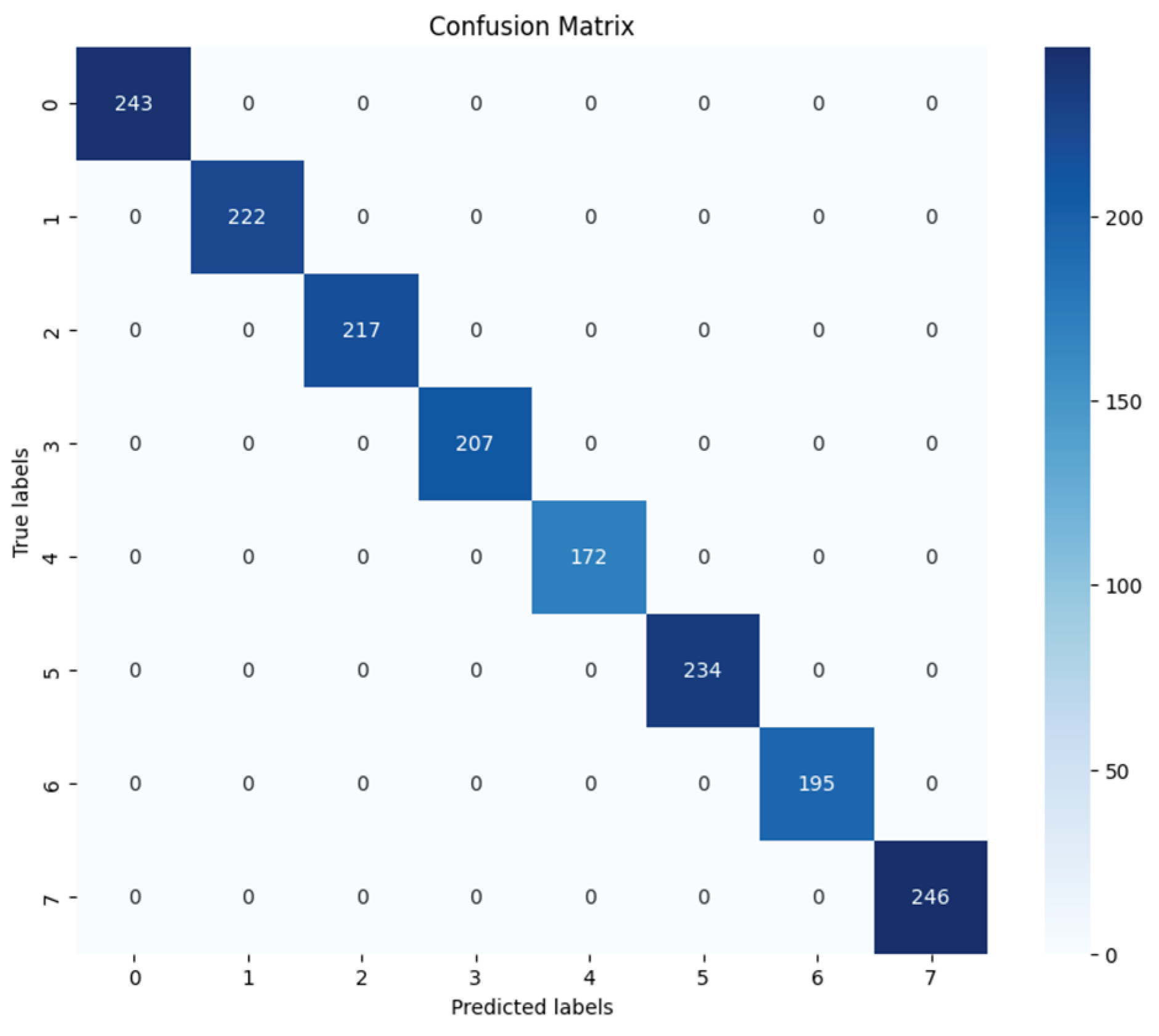
5.3.2. Ensemble Learning Approach
5.3.3. Implementation of the Meta-Classifier
6. Results and Analysis
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FER | Facial Emotion Recognition |
| NHFIER | Natural Human Face Images for Emotion Recognition |
| CK+ | Cohn–Kanade |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| k-NN | k-Nearest Neighbors |
| CNNs | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| RNNs | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| FACS | Facial Action Coding System |
| AUs | Action Units |
| LBP | Local Binary Pattern |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| RF | Random Forest |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| d | Depth |
| w | Width |
| r | Resolution |
| AdaBoost | Adaptive Boosting |
| SGB | Stochastic Gradient Boosting |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| FAC | Facial Action Unit |
| LDP | Local Directional Pattern |
| HoG | Histogram of Oriented Gradients |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| AAM | Active Appearance Model |
| SDM | Supervised Descent Method |
| DISFA | Denver Intensity of Spontaneous Facial Actions |
| FERC | Facial Emotion Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| VGG-16 | Visual Geometry Group-16 |
| GAP | Global Average Pooling |
| RAF-DB | Real-World Affective Faces |
| AR-TE-CATFFNet | Attention-Rectified and Texture-Enhanced Cross-Attention Transformer Feature Fusion Network |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| OvR | One-versus-Rest |
| TP | True Positive |
| TN | True Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| FN | False Negative |
References
- Mehrabian, A. Nonverbal Communication; Aldine Transaction: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liliana, D.Y. Emotion recognition from facial expression using deep convolutional neural network. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1193, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Chan, D.; Mahoor, M.H. Going deeper in facial expression recognition using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paweł, T.; Marcin, K.; Andrzej, M.; Remigiusz, R. Emotion recognition using facial expressions. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 108, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehendale, N. Facial emotion recognition using convolutional neural networks (FERC). SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Mittal, N. Using CNN for facial expression recognition: A study of the effects of kernel size and number of filters on accuracy. Vis. Comput. 2020, 36, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.U.; Hossain, S.; Hossain, M.S.; ul islam, R.; Andersson, K. Facial Expression Recognition using Convolutional Neural Network with Data Augmentation. In Proceedings of the Joint 8th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV) and 2019 3rd International Conference on Imaging, Vision & Pattern Recognition (icIVPR), Spokane, WA, USA, 30 May–2 June 2019; pp. 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, G.P.; Jonathan, J.; Andreas, L. Emotion Recognition on FER-2013 Face Images Using Fine-Tuned VGG-16. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2020, 5, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Sharma, H.; Mehta, N.K.; Vohra, A.; Singh, S. EfficientNet For Human Fer Using Transfer Learning. ICTACT J. Soft Comput. 2022, 13, 2792–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawpanom, R.; Songpan, W.; Kaewyotha, J. Advancing Facial Expression Recognition in Online Learning Education Using a Homogeneous Ensemble CNN Approach. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talele, M.; Jain, R. A Comparative Analysis of CNNs and ResNet50 for Facial Emotion Recognition. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2025, 15, 20693–20701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Cui, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Liao, X.; Hu, B.; Li, Y. Attention-Rectified and Texture-Enhanced Cross-Attention Transformer Feature Fusion Network for Facial Expression Recognition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 11823–11832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasi, A.T.; Šerbetar, K.; Islam, R.; Rafi, T.; Chae, D.-K. ARBEx: Attentive feature extraction with reliability balancing for robust facial expression learning. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aroussi, M.; El Hassouni, M.; Ghouzali, S.; Rziza, M.; Aboutajdine, D. Local appearance-based face recognition method using block-based steerable pyramid transform. Signal Process. 2011, 91, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhar, K.; El Aroussi, M.; Saadane, R.; Wahbi, M.; Aboutajdine, D. Fusion of face and iris features extraction based on steerable pyramid representation for multimodal biometrics. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Multimedia Computing and Systems, Ouarzazate, Morocco, 7–9 April 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar]
- “Google Colaboratory”, Google. Available online: https://colab.google/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Safonova, A.; Ghazaryan, G.; Stiller, S.; Main-Knorn, M.; Nendel, C.; Ryo, M. Ten deep learning techniques to address small data problems with remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 125, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Constants across cultures in the face and emotion. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1971, 17, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helkar, Y.; Sayyad, A.; Patil, P.G. Facial Emotion Recognition System (FERS) Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 12, 7781–7786. [Google Scholar]
- Mellouk, W.; Wahida, H. Facial emotion recognition using deep learning: Review and insights. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 175, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA Group. Facial Action Coding System (FACS). 2022. Available online: https://www.eiagroup.com/resources/facial-expressions/facial-action-coding-system-facs/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Ming, Z.; Bugeau, A.; Rouas, J.; Shochi, T. Facial Action Units intensity estimation by the fusion of features with multi-kernel Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the 2015 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015; Volume 6, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gudi, A.; Tasli, H.E.; Den Uyl, T.M.; Maroulis, A. Deep Learning based FACS Action Unit Occurrence and Intensity Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2015 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.S.; Windeatt, T. Facial action unit recognition using multi-class classification. Neurocomputing 2015, 150, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Qiu, Q.; Chellappa, R. Structure-preserving sparse decomposition for facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Publ. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 2014, 23, 3590–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valstar, M.F.; Almaev, T.; Girard, J.M.; McKeown, G.; Mehu, M.; Yin, L.; Pantic, M.; Cohn, J.F. FERA 2015—Second Facial Expression Recognition and Analysis Challenge. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015; Volume 6, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, W.S.; De la Torre, F.; Cohn, J.F. Learning Facial Action Units with Spatiotemporal Cues and Multi-label Sampling. Image Vis. Comput. 2019, 81, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bařina, D. Gabor Wavelets in Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 17th Conference STUDENT EEICT 2011, Brno, Czech Republic, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.P.; Tse, S.H.; Wong, K.W.; Lam, K.M. Simplified Gabor wavelets for human face recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 41, 1186–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Gong, S.; Mcowan, P.W. Facial expression recognition based on Local Binary Patterns: A comprehensive study. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Gao, Z.; Guo, B. Facial Expression Recognition with LBP and ORB Features. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 8828245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sisquella Andrés, J. Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Emotion Recognition. Available online: https://upcommons.upc.edu/bitstream/handle/2117/184076/tfm-joan-sisquella.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Jain, V.; Aggarwal, P.; Kumar, T.; Taneja, V. Emotion Detection from Facial Expression using Support Vector Machine. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 167, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeldung. Multiclass Classification Using Support Vector Machines. Baeldung on Computer Science. 2024. Available online: https://www.baeldung.com/cs/svm-multiclass-classification (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Decision Tree. GeeksforGeeks. 2023. Available online: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/decision-tree/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- What Is Random Forest? IBM. 2024. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/topics/random-forest (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Ko, B.C. A Brief Review of Facial Emotion Recognition Based on Visual Information. Sensors 2018, 18, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D. Skip Connections & Resnet50. Medium. 2024. Available online: https://medium.com/@danushidk507/skip-connections-ab515d634e6d (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Chen, B.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Le, Q.V. MnasNet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.; Kora, R. A comprehensive review on ensemble deep learning: Opportunities and challenges. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegua, R. An Empirical Study of Ensemble Techniques (Bagging, Boosting and Stacking). 2019. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338681876_An_Empirical_Study_of_Ensemble_Techniques_Bagging_Boosting_and_Stacking (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Mehrabian, A.; Ferris, S.R. Inference of attitudes from nonverbal communication in two channels. J. Consult. Psychol. 1967, 31, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadiani, N.; Huang, G.; Cai, B.; Luo, W.; Chi, C.-H.; Xiang, Y.; He, J. A Review on Automatic Facial Expression Recognition Systems Assisted by Multimodal Sensor Data. Sensors 2019, 19, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luma, A. Artificial Intelligence Tools for Facial Expression Analysis. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354172772_Artificial_Intelligence_Tools_for_Facial_Expression_Analysis (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Bhushan, S.C.; Babu, S.; Pushpendra, Y. Facial Expression Recognition. 2021. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3852666 (accessed on 7 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pedraza, A.; Gallego, J.; Lopez, S.; Gonzalez, L.; Laurinavicius, A.; Bueno, G. Glomerulus Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Medical Image Understanding and Analysis. MIUA 2017. Communications in Computer and Information Science; Valdés Hernández, M., González-Castro, V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, R.; Matthews, I.; Cohn, J.; Kanade, T.; Baker, S. Multi-pie. Image Vis. Comput. 2010, 28, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantic, M.; Valstar, M.; Rademaker, R.; Maat, L. Web-based database for facial expression analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 6 July 2005; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mavadati, S.M.; Mahoor, M.H.; Bartlett, K.; Trinh, P.; Cohn, J.F. Disfa: A spontaneous facial action intensity database. Affect. Comput. IEEE Trans. 2013, 4, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Kanade, T.; Saragih, J.; Ambadar, Z.; Matthews, I. The extended cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): A complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bänziger, T.; Scherer, K.R. Introducing the geneva multimodal emotion portrayal (gemep) corpus. In Blueprint for Affective Computing: A Sourcebook; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 271–294. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Goecke, R.; Lucey, S.; Gedeon, T. Static facial expression analysis in tough conditions: Data, evaluation protocol and benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2106–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitru; Goodfellow, I.; Cukierski, W.; Bengio, Y. Challenges in Representation Learning: Facial Expression Recognition Challenge. 2013. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/c/challenges-in-representation-learning-facial-expression-recognition-challenge (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Li, B.Y.L.; Mian, A.S.; Liu, W.; Krishna, A. Using Kinect for face recognition under varying poses, expressions, illumination, and disguise. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Clearwater Beach, FL, USA, 15–17 January 2013; pp. 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Lundqvist, D.; Flykt, A.; Öhman, A. The Karolinska Directed Emotional Faces—KDEF. CD ROM from Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Psychology section, Karolinska Institutet, No. 1998. 1998. Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037%2Ft27732-000 (accessed on 24 August 2024).
- Ogiela, M.R.; Tadeusiewicz, R. Pattern recognition, clustering and classification applied to selected medical images. Stud. Comput. Intell. 2008, 84, 117–151. [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos, P.; Perikos, I.; Hatzilygeroudis, I. Deep learning approaches for facial emotion recognition: A case study on fer-2013. In Advances in Hybridization of Intelligent Methods; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Aifanti, N.; Papachristou, C.; Delopoulos, A. The mug facial expression database. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Image Analysis for Multimedia Interactive Services WIAMIS 10, Desenzano del Garda, Italy, 12–14 April 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, M.G.; Lundqvist, D. Facial expressions of emotion (kdef): Identification under different display-duration conditions. Behav. Res. Methods 2008, 40, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Xia, S.; Fu, Y. Genealogical face recognition based on ub kinface database. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011 WORKSHOPS, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In Proceedings of COMPSTAT 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S. Network in network. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations—ICLR 2014, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Deng, W. Reliable Crowdsourcing and Deep Locality-Preserving Learning for Unconstrained Facial Expression Recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.C.; Yuen, P.C.; Dai, D.Q. Human face recognition using PCA on wavelet subband. J. Electron. Imaging 2000, 9, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Deng, W.; Du, J. Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for expression recognition in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2584–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Hasani, B.; Mahoor, M.H. AffectNet: A database for facial expression, valence, and arousal computing in the wild. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 10, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, D.; Tzirakis, P.; Baird, A.; Cowen, A.; Zafeiriou, S. ABAW: Valence-arousal estimation, expression recognition, action unit detection, and emotional reaction intensity estimation challenges. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5889–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.J. Excavating AI re-excavated: Debunking a fallacious account of the Jaffe dataset. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.13998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneja, D.; Colburn, A.; Faigin, G.; Shapiro, L.; Mones, B. Modeling stylized character expressions via deep learning. In The Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 136–153. [Google Scholar]
- Barsoum, E.; Zhang, C.; Canton Ferrer, C.; Zhang, Z. Training deep networks for facial expression recognition with crowd-sourced label distribution. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI’16), Tokyo, Japan, 12–16 November 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Chiew, T.K.; Xu, Z. Image recognition based on lightweight convolutional neural network: Recent advances. Image Vis. Comput. 2024, 146, 105037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, K.; Chandra, T.B.; Singh, A. ResNet-50 vs. EfficientNet-B0: Multi-centric classification of various lung abnormalities using deep learning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 235, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.P.P.; Megat Mohamed Noor, M.N.; Darwis, H.; Hayati, L.N.; Irawati; As’ad, I. A comparative study on efficacy of CNN VGG-16, DenseNet121, ResNet50V2, and EfficientNetB0 in Toraja carving classification. Indones. J. Data Sci. 2025, 6, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunidar, R.; Yusni, N.; Nasaruddin; FitriArnia. CNN performances for stunting face image classification. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (ICECOS), Palembang, Indonesia, 25–26 September 2024; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, M.; Bo, J.; Liu, H.; Ren, L.; Li, X.; Deen, M.J. A comparative analysis of eleven neural network architectures for small datasets of lung images of COVID-19 patients toward improved clinical decisions. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 139, 104887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.-L.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, T.-W.; She, F.-R.; Xiong, X.; He, J.-F. Diabetic retinopathy diagnosis based on RA-EfficientNet. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S. Multiclass Classification: OneVsRest and OneVsOne Classification Strategy. Medium. 2023. Available online: https://medium.com/@agrawalsam1997/multiclass-classification-onevsrest-and-onevsone-classification-strategy-2c293a91571a (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Soni, B. Stacking to Improve Model Performance: A Comprehensive Guide on Ensemble Learning in Python. Medium. 2023. Available online: https://medium.com/@brijesh_soni/stacking-to-improve-model-performance-a-comprehensive-guide-on-ensemble-learning-in-python-9ed53c93ce28 (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Brownlee, J. What Is Meta-Learning in Machine Learning? MachineLearningMastery.Com. 2021. Available online: https://machinelearningmastery.com/meta-learning-in-machine-learning/ (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Wolpert, D.H. Stacked Generalization. Neural Networks; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; Volume 5, pp. 241–259. [Google Scholar]
- Chanamarn, N.; Tamee, K.; Sittidech, P. Stacking Technique for Academic Achievement Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Workshop on Smart Info-Media Systems in Asia, Ayutthaya, Thailand, 14–17 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Your Machine Learning and Data Science Community. Kaggle. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/ (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Vaidya, S. Natural Human Face Images for Emotion Recognition. Kaggle. 2020. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sudarshanvaidya/random-images-for-face-emotion-recognition (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Vaidya, S. Detecting Human Facial Emotions—Multistage Transfer Learning Approach. Medium. 2020. Available online: https://sudarshanvaidya.medium.com/detecting-human-emotions-facial-expression-recognition-ebf98fdf87a1 (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- lys620. EfficientNet with Keras. Kaggle. 2021. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/code/lys620/efficientnet-with-keras (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Ray, S. What Is Data Augmentation? Medium. 2021. Available online: https://medium.com/lansaar/what-is-data-augmentation-3da1373e3fa1 (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Dwyer, B.; Nelson, J.; Hansen, T.; et al. Roboflow, Version 1.0. 2024. Available online: https://roboflow.com (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Wizards. A Guide to Data Splitting in Machine Learning. Medium. 2022. Available online: https://medium.com/@datasciencewizards/a-guide-to-data-splitting-in-machine-learning-49a959c95fa1 (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Python Software Foundation. Python, Version 3.11.0. 2022. Available online: https://www.python.org (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. 2015. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Team, K. Keras Documentation: About Keras. Keras. Available online: https://keras.io/about/ (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Keras: The High-Level API for Tensorflow: Tensorflow Core. TensorFlow. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M.L. seaborn: Statistical data visualization. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.C.; Guido, S. Introduction to Machine Learning with Python: A Guide for Data Scientists; O’Reilly: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, D.M. Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness & Correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Logunova, I. A Guide to F1 Score. F1 Score in Machine Learning. Serokell. 2023. Available online: https://serokell.io/blog/a-guide-to-f1-score (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Modelcheckpoint. Keras. 2024. Available online: https://keras.io/api/callbacks/model_checkpoint/ (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Earlystopping. Keras. 2024. Available online: https://keras.io/api/callbacks/early_stopping/ (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Reducelronplateau. Keras. 2024. Available online: https://keras.io/api/callbacks/reduce_lr_on_plateau/ (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Cohn, J.F.; Kanade, T. CK+ Dataset. Kaggle. 2023. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/shuvoalok/ck-dataset/data (accessed on 7 July 2024).

| Dataset | Subject-Independent | Cross-Database |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-PIE | 94.7 | 45.7 |
| MMI | 77.6 | 55.6 |
| DISFA | 55.0 | 37.7 |
| FERA | 76.7 | 39.4 |
| SFEW | 47.7 | 39.8 |
| CK+ | 93.2 | 64.2 |
| FER2013 | 66.4 | 34.0 |
| Authors | Datasets | Architecture | Recognition Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liliana, Dewi Yanti [2] | CK+ [2] | CNN | 92.81% (two sets: training and test) |
| Mollahosseini et al. [3] | Multi-PIE [53], MMI [54], DISFA [55], FERA [57], SFEW [58], CK+ [56], FER2013 [59] | CNN | 94.7%, 77.6%, 55.0%, 76.7%, 47.7%, 93.2%, and 66.4% |
| Paweł et al. [4] | KDEF [61] | 3-NN classifier and MLP neural network classifier | 95.5% for 3-NN classifier (two sets: training and test) and 75.9% for MLP classifier (three sets: training, validation, and test) |
| Mehendale [5] | Caltech faces, CMU, and NIST [5] | CNN | 96% (two sets: training and test) |
| Agrawal and Mittal [6] | FER2013 [6] | CNN | 65% |
| T.U. Ahmed et al. [7] | CK and CK+ [56], FER2013 [63], MUG [64], KDEF and AKDEF [65], KinFaceW-I and -II [66] | CNN | 96.24% validation accuracy |
| Kusuma Negara et al. [8] | FER2013 [8] | VGG-16 | 69.40% |
| Rajesh Singh et al. [9] | RAF-DB [69], FER2013 [9], and Cohn–Kanade [56] | EfficientNet-B0 | 81.68% for RAF-DB 71.02% for FER2013 Cross-data on RAF-DB and CK+: 78.59% Cross-data on RAF-DB and on FER2013: 56.10% |
| Rit Lawpanom et al. [10] | FER2013 [10] | HoE-CNN | Achieved accuracy of 75.51% |
| Milind Talele et al. [11] | FER2013 [11] | Custom CNN and ResNet-50 | 74% for custom CNN and 85.75% for ResNet-50 model |
| Sun et al. [12] | RAF-DB [71], AffectNet [72], and FER2013 [12] | AR-TE-CATFFNet | 89.50%, 65.66%, and 74.84% |
| Wasi [13] | AffWild2 [73], RAF-DB [71], JAFFE [74], FERG-DB [75], and FER+ [76] | W-BCSA-Vit and reliability balancing | 72.48%, 92.47%, 96.67%, 93.09%, and 98.18% |
| Experiment No. | Experiment Type | Training Split | Validation Split | Test Split |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Multiclass Classification | 70% | 15% | 15% |
| 2 | Eight Binary Classifiers | 70% | 15% | 15% |
| Meta-Classifier | 70% | 15% | 15% |
| Parameter | Multiclass Model | Binary Model |
|---|---|---|
| Input Shape | (224, 224, 3) | (224, 224, 3) |
| Include Top | False | False |
| Weights | ImageNet | ImageNet |
| Global Average Pooling | Applied | Applied |
| Dropout Rate (1st) | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Output Dense Units | 8 | 1 |
| Activation Function (Output) | SoftMax | Sigmoid |
| Intermediate Dense Layer | 16 neurons, ReLU | 16 neurons, ReLU |
| Batch Normalization | Applied | Applied |
| Dropout Rate (2nd) | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Binary Classifier | Positive Class | Negative Class |
|---|---|---|
| Happy | 8346 | 8346 |
| Sad | 9607 | 9607 |
| Anger | 9248 | 9248 |
| Fear | 9994 | 9994 |
| Surprise | 9660 | 9660 |
| Neutral | 10,034 | 10,034 |
| Disgust | 10,212 | 10,212 |
| Contempt | 10,701 | 10,701 |
| Binary Classifier | Training Accuracy | Validation Accuracy | Testing Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Happy | 99.86 | 99.12 | 98.68 |
| 2 | Sad | 99.99 | 99.90 | 99.61 |
| 3 | Anger | 99.99 | 99.50 | 99.74 |
| 4 | Fear | 99.97 | 99.83 | 99.69 |
| 5 | Surprise | 99.99 | 99.62 | 99.41 |
| 6 | Neutral | 99.99 | 99.83 | 99.90 |
| 7 | Disgust | 99.99 | 99.97 | 99.96 |
| 8 | Contempt | 100 | 100 | 99.90 |
| Binary Classifier | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Happy | 97.79 | 99.43 | 98.60 |
| 2 | Sad | 99.21 | 99.92 | 99.57 |
| 3 | Anger | 99.57 | 100 | 99.78 |
| 4 | Fear | 99.32 | 100 | 99.65 |
| 5 | Surprise | 98.82 | 100 | 99.40 |
| 6 | Neutral | 99.66 | 100 | 99.83 |
| 7 | Disgust | 99.93 | 100 | 99.96 |
| 8 | Contempt | 99.93 | 100 | 99.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almubarak, M.; Alsulaiman, F.A. An Ensemble Learning Approach for Facial Emotion Recognition Based on Deep Learning Techniques. Electronics 2025, 14, 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173415
Almubarak M, Alsulaiman FA. An Ensemble Learning Approach for Facial Emotion Recognition Based on Deep Learning Techniques. Electronics. 2025; 14(17):3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173415
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmubarak, Manal, and Fawaz A. Alsulaiman. 2025. "An Ensemble Learning Approach for Facial Emotion Recognition Based on Deep Learning Techniques" Electronics 14, no. 17: 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173415
APA StyleAlmubarak, M., & Alsulaiman, F. A. (2025). An Ensemble Learning Approach for Facial Emotion Recognition Based on Deep Learning Techniques. Electronics, 14(17), 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173415





