Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to review the specialized literature to highlight the effects produced by energy drinks in terms of skin health. To carry out this review, we consulted previous articles with descriptive cross-sectional designs, case series, and individual case reports published between 2000 and 2023. Therefore, while caffeine acute consumption among adults can have beneficial effects, in children, it can cause health problems like overnight breaks, headaches, and dulled cognition since their organs are still developing and their endocrine system is not yet stable. Despite the antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of caffeine from energy drinks, their excessive consumption among adolescents can cause disorders like high systolic blood pressure, agitation, nausea, anxiety, osteoporosis, heart palpitations, poor sleep quality, and stomach ulcers. Among athletes, taurine supplementation has been proven to improve exercise capacity in cold weather conditions. Also, vigilance, attention, and reaction time were all improved by caffeine consumption. Caffeine administration in low doses caused a risk of cardiovascular disease. It was effective in treating migraines in children, but raised systolic blood pressure, and contributed to skin healing in adolescents. On the other side, taurine prevents obesity among children, causes positive effects on oxidative stress and inflammation in adolescents, helps shield the skin from damaging oxidative stress among students, and impacts exercise capacity in athletes. Significant increases in serum levels of uric acid, creatinine, BUN, ALT, and ALP caused by chronic intake of EDs indicated different degrees of injury to the kidneys and liver. Furthermore, the effects on the cardiovascular system could be worse if taurine and caffeine are combined. Caffeine alone does not significantly decrease sleep as much as a taurine/high caffeine ratio. On the other hand, a low ratio does.
1. Introduction
Energy drinks (EDs) are known to be beverages which firstly debuted in Austria, in 1987, and then in North America during 1997. Their composition mainly contains carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and most importantly, caffeine and taurine [1]. They have gained popularity, especially among the youth and people who have stressful jobs and need energy to achieve their tasks. In this context, it is important to mention that skin cells are susceptible to senescence brought on by oxidative stress, which can result in aberrant aging or illnesses associated with aging. Consequently, methods that might reduce the senescence brought on by oxidative stress should protect the skin from injury and have the potential to treat skin problems in medical situations.
Caffeine is one of the most often taken drugs by professional athletes, since it is believed that it has the ability to improve mental activity and focus. Another important ingredient is taurine, which, even though it is produced by the liver and kidneys, is known to modulate calcium release and, during exercise, can contribute to calcium homeostasis, fat metabolism, and exercise performance [2]. Some studies have shown that caffeine can reduce levels of anxiety and depression, and taurine could enhance voluntary alcohol intake and preference in rats and, long-term, can lead to substantial decreases in rats’ brain weight and an increase in body weight [3,4].
Also, caffeine is utilized as an active ingredient in anticellulite cosmetic treatments because it inhibits the excessive accumulation of fat within cells. This alkaloid inhibits phosphodiesterase activity, which promotes the degradation of fats during lipolysis. Thus, high antioxidant capacities are present in caffeine. It slows down the skin’s photoaging process and aids in protecting cells from UV light [5]. Based on the activation of A2AR/SIRT3/AMPK-mediated autophagy, caffeine protects the skin from oxidative stress-induced senescence. The results suggest that caffeine may have a protective effect against skin problems [6].
Also, high concentrations of taurine can be observed in the skin and are thought to be crucial for regulating moisture homeostasis. The development of wrinkles caused by ultraviolet B radiation diminished after administering taurine orally for eight weeks. Additionally, pre-established wrinkles lowered in a dose-dependent manner after four weeks of oral taurine supplementation. Regarding the decrease in epidermal taurine levels caused by UVB exposure, dietary taurine supplementation somewhat increased the epidermal content. Taurine may provide antiaging benefits to the skin because of its osmoregulatory function [7]. Even so, consuming taurine can decrease platelet aggregation by 30–70%, suggesting a potential cardioprotective action [8].
It is shown that the natural β-glucuronidase (βG) inhibitor D-glucaro-1,4-lactone (1,4-GL) and its synthetic precursors, such as 2,5-di-O-acetyl-D-1,4-glucaro-6,3-dilactone (DADGL), detoxify chemical carcinogens that require glucuronidation and block chemically induced experimental tumorigenesis, partly through the suppression of cell proliferation and inhibition of the enzyme βG [9,10].
Other studies showed that EDs promote faster healing of soft tissue wounds. This benefit might be caused by enhanced collagen deposition, re-epithelialization, and the development of new blood vessels in the wound. The hypothesis that the high-nutrient contents in EDs could aid in wound healing served as the driving force for these investigations [11].
As for ED intake in humans, their consumption became popular in the last decade amongst young adults, students, sportsmen, and even children. Up to 28% of 12- to 14-year-olds, 31% of 12- to 17-year-olds, and 34% of 18- to 24-year-olds have been reported to consume EDs, a study has shown. Among college students, a survey stated that 51% used to ingest more than one ED among 496 participants [12]. The lack of pharmacological tolerance in adolescents results in caffeine intoxication susceptibility and, in high doses, causes harmful effects on the developing brain and cardiovascular system [13]. Overall, ED effectiveness in the case of sports depends on different factors, such as the sport type or the body’s response, and long-lasting sport activities benefit the most [14].
Short-term consumption has beneficial impacts. The long-term administration of EDs has generated a series of debates in the scientific world, with invisible repercussions in the political world. These debates stem from the fact that there is still no correct labeling of these drinks due to controversial data from the studies so far [15]. Behavioral changes, such as addiction are eventually developed, due to the fact that caffeine is considered a drug [16]. Some consequences of its acute or chronic use may lead to acute organ inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and even dermatitis [17].
Combining taurine with caffeine may exacerbate the effects on the cardiovascular system. This is concerning because caffeine alone can raise blood pressure and heart rate. At the same time, it is beneficial that numerous animal studies have looked at the effects of this compound mixture on various behavioral parameters, as people also consume taurine and caffeine together. Kimura et al. [18] used male ddY mice (age not specified) to investigate the combined effects of taurine and caffeine on locomotor activity. In comparison to control and caffeine-only treated mice, animals administered 400 mg/kg taurine and 2 mg/kg caffeine exhibited markedly increased activity. Two distinct effects that differ based on the taurine-to-caffeine ratio can be observed in flies that are treated with both caffeine and taurine. A high taurine/caffeine ratio stimulates sleep, but a low ratio more strongly suppresses sleep than a comparable dose of caffeine alone [19]. According to available research, neuroprotection may be provided by caffeine and/or taurine when taken at the proper dosage and under the right conditions. Rodent animal models are useful in elucidating the differences in effects related to the ingestion of taurine, caffeine, and alcohol, both separately and in combination, as human lifestyles vary considerably and study results may become compromised [20]. However, ED consumption mixed with alcohol is quite common among the college population, which can provide a route to many cardiovascular affections, such as coronary vasospasm and even sudden cardiac death [8].
Furthermore, there are very few studies on the effects of these drinks on the skin. Recently, more and more young people have problems with their skin, especially as a result of the lifestyle that they have adopted, but also due to the stress that they are constantly subjected to. Among them, there is a close connection between self-esteem and physical appearance, in particular the health of the skin [21]. The purpose of this paper is to review the specialized literature to highlight the effects produced by EDs in terms of skin health.
2. Materials and Methods
We consider case reports/studies and case series involving human subjects with medical reports that can provide useful knowledge for systematic reviews in the context associated with particular events, including acute intoxication or preliminary reports of legal substances. As a result, studies with descriptive cross-sectional designs, case series, and individual case reports were among the types of observational study designs that were taken into consideration for this review. We acquired the research and critically evaluated it after performing a thorough search of the literature. Studies that need ethical permission, including interventional research involving humans or animals, must specify the ethical approval code and the body that granted it. To find peer-reviewed articles published between 2000 and 2023, a web search was carried out using PubMed, Google Scholar, Science Direct, and ProQuest search platforms. The search terms used in the title, abstract, and keywords of the articles included ED, Red Bull, caffeine, niacin, taurine, skin effects, arrhythmia, brain failure, kidney damage, death, and digestive problems. To locate objective information, online search platforms like Google were also utilized. To find additional appropriate studies, the reference lists of all of the papers that were collected were also examined.
Original research articles in humans, original research articles in animals, and case reports/series were among the eligibility criteria. These papers underwent a thorough evaluation that considered the primary goals of the review. Also, reviews and mini-reviews were utilized to identify any omitted articles. The current paper only included papers written in English. For each case, the age and gender of the participants, the ED brand (some brands were unknown), the primary pathology, the type of incident, and when it started were all collected. The chosen studies were divided into short-term and long-term studies, which in turn were divided into children, adolescents, students, athletes, and animals.
3. Short-Term Studies on Children
As aforementioned, short-term studies have proven to have beneficial effects, but in adults. The effects may not be as good in children, whose bodies and organs are in growth. Also, their endocrine system is not stable/constant at this age. According to Ellison et al. [22], children aged 6 to 10 consumed caffeine, on average, for eight days out of ten. Additionally, individuals aged 7 to 8 reported consuming up to 16 mg of caffeine per day, while those aged 9 to 10 reported consuming 24 mg, and those aged 5 to 18 reported consuming 37.4 mg. Caffeine withdrawal symptoms closely resemble intoxication symptoms. Conversely, the data suggest that caffeine may be advised for young people with specific conditions (ADHD and apnea of prematurity), but it is not advised for children in good health, particularly when taken in high or moderate amounts that may alter physiological processes [23].
Also, caffeine consumption was linked to a potentially lower risk of cardiovascular disease, mortality, and cancers of the breast, colon, endometrial, and prostate. Studies conducted in the short term have demonstrated a correlation between increased coffee consumption and improved cognitive test scores [24]. In a study involving 9- to 11-year-olds who consumed low amounts of caffeine (12 mg/day) and chronic amounts (109 mg/day), habitual caffeine users reported a reversal of withdrawal symptoms at 50 mg of caffeine after an overnight break (e.g., headaches and dulled cognition) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Recommended intake doses of caffeine and taurine per day.
There were no reported differences in the cognitive performance, alertness, or incidence of headaches in children who did not regularly consume caffeine [32]. Caffeine intake may be rising among consumers, based on the recent boom of innovative goods containing the stimulant. Furthermore, there seems to be a push toward marketing consumable caffeine goods to younger demographics, maybe to encourage product usage and get children “hooked” on the drug at a younger age [33]. Because of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, caffeine may be beneficial for eczema patients [34].
Additionally, dietary supplements containing taurine can help prevent and treat obesity, cardiovascular disease, and disorders associated with aging. They can also inhibit the growth of tumors, enhance the health of bones and the skin, prevent and treat neurological disorders, and increase wellbeing in children, adults, and newborns [35]. It is important to know that numerous biological actions are mediated by taurine, including antioxidation, ion transport modulation, membrane stabilization, osmoregulation, neurotransmission modulation, bile acid conjugation, hypolipidemia, antiplatelet activity, and fetal development modification. Consistent with this, taurine produces endothelium-dependent and -independent relaxant effects in isolated vascular tissue preparations [36] (Table 2).

Table 2.
Short-term effects of caffeine and taurine.
4. Short-Term Studies on Adolescents
The effects produced by EDs in adolescents can be even more serious compared to adults because their endocrine system is not yet fully stable. In a study that involved questioning teenagers about the amount and time of ED consumption, out of the 375 teenagers that completed the survey, 206 (55%), including 91 males (44.4%) and females (55.6%), wrote that they drank EDs. During the trial phase of this research, it was discovered that the majority of participants’ systolic blood pressure (SBP) raised noticeably in the short time after consuming EDs [26].
Healthy individuals without diseases or metabolic disorders typically do not experience adverse reactions from a single dosage of caffeine (200 mg or less) [43]. Caffeine intoxication, on the other hand, can result from a dose greater than 300 mg taken all at once in adults (Table 1). This condition’s symptoms are mostly linked to caffeine’s stimulating effects [44]. The negative effects of caffeine use in teenagers are not well understood [45].
According to factors including gender, age, weight, and individual susceptibilities, various doses of caffeine can have different negative effects on individuals [46]. Concern over the rising intake of caffeinated foods and beverages, such as coffee, EDs, tea, and chocolate products, has been increasing, especially among teenagers [47]. Sweetened beverages such as EDs and coffee are the main sources of caffeine consumption for teenagers, with a daily intake of the stimulant dropping under the currently recommended maximum tolerable levels for adolescents (2.5 mg/kg body weight/day or 100–175 mg/day with bodyweight 40–70 kg) [48]. However, other researchers have found that teenagers who consume excessive amounts of caffeine have been linked to a multitude of negative health effects, including anxiety, agitation, nausea, heart palpitations, poor sleep, osteoporosis, and stomach ulcers [49].
On the one hand, caffeine, being an antioxidant, counteracts the damaging effects of oxidative stress and oxidative–antioxidant imbalances on adolescents, just as it does on adults. In addition to protecting against oxidative stress and damage to neuronal cells, caffeine also has a neuroprotective effect on neurodegenerative processes by reducing free radical production. Caffeine can also reduce UV-induced harm to the skin and improve the body’s natural process of reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS), preserving skin cells from the damaging effects of solar radiation [38].
On the other hand, caffeine and taurine can both cause natriuresis and diuresis in rats and humans. Their diuretic effects may complement one another even though they operate through distinct cellular pathways. Given that both compounds are included in several commercially accessible EDs, this is of great importance [40]. Research indicates that caffeine affects the kidneys by preventing the proximal and distal tubules from reabsorbing sodium, which increases the excretion of solutes and, in turn, the excretion of free water [50]. Skin that is too dry is obviously dehydrated since it has lost a lot of moisture. Dryness, increased visibility of small wrinkles, and itching are indicators of dehydrated skin. Very dry skin has cracks in its epidermis. This makes it possible for bacteria to enter and cause an infection on the skin [51]. According to results from an important German study, individuals with dry skin may experience allergic skin reactions or irritated skin [52] (Table 2).
5. Short-Term Studies on Students
In most studies, ED effects are attributed to the main components. Thus, it was observed that caffeine acute ingestion can have beneficial effects on short-term maximal performance by promoting muscle fat oxidation and better glycogen sparing capacity [53]. A meta-analysis research also supported the notion that caffeine intake can increase both peak and mean power output during the Wingate test [54]. In a comprehensive review of 21 published meta-analyses, it was shown that caffeine ingestion improves various aspects of exercise performance, including muscle strength, endurance, anaerobic power, and aerobic endurance [55]. These effects may be attributed to increased Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and alterations in neuromuscular transmission caused by caffeine [56]. Additionally, caffeine has been shown to enhance Ca2+ release and improve motor unit recruitment by inhibiting the action of adenosine on the central nervous system in animal studies [57]. The increase in blood glucose levels before and after exercise may also contribute to the improvement in short-term maximal performance [58] (Table 2).
There was a study that investigated the effects of Fearless and Predator EDs on various health markers in male volunteers, aged between 18 and 30 years old. Alcohol consumers and smokers were excluded from this study. The findings revealed that there were no significant differences in mean SBP and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) among the groups. The mean pulse rate showed a significant decrease in Fearless ED consumers after one month of consumption. In terms of body mass index (BMI), there was a significant decrease in the mean BMI among Predator ED consumers after two weeks of intake, compared to their initial value. Similarly, Fearless ED consumers showed a significant decrease in mean BMI after one month of consumption. Regarding plasma glucose levels, both groups showed a significant increase after two weeks of consumption compared to their baseline values. Predator ED consumers had a further increase in plasma glucose levels after one month of consumption. There were no significant differences in mean serum triglyceride and apolipoprotein A-I levels among the groups. However, both Fearless and Predator ED consumers exhibited a significant decrease in mean serum apolipoprotein B (ApoB) levels after two weeks of consumption. Fearless ED consumers had a significantly lower mean ApoB compared to Predator ED consumers after one month of consumption. The study suggests that short-term consumption of Fearless and Predator EDs may lead to decreased pulse rate, BMI, and ApoB levels. However, it also indicates an increase in plasma glucose levels [41].
To control vascular resistance and blood flow in tissues and vital organs, microcirculation is essential. The skin’s microvascular network has gained popularity as a model for researching microvascular function because it is readily accessible. Through the use of physiological and pharmacological threats, including caffeine, that selectively target vascular signaling pathways, cutaneous microcirculation can be studied non-invasively [59]. For example, iontophoresis of acetylcholine (Ach) can be used to study endothelium-dependent microvascular responses. The release of acetylcholine can be stimulated by caffeine. It is commonly used in conjunction with iontophoresis of sodium nitroprusside (SNP) as an endothelium-independent control. The skin condition known as post-occlusive reactive hyperemia (PORH) can be utilized to investigate the role of sensory nerves and hyperpolarizing processes. Significantly, the reproducibility of microvascular assessment in the skin has been further enhanced by the recent development of image-based blood flow measurement techniques [60].
6. Short-Term Studies on Athletes
EDs can boost energy, improve alertness, and promote wakefulness when performing high-intensity physical exercise, and for this reason, they have become one of the substances most commonly consumed by athletes and other practitioners of physical activity. According to Froiland et al. [61], some 72.9% of U.S. college athletes are ED consumers. Hahn et al. [62] also described a significant reduction in perceived fatigue during repeated sprinting, and Wesnes et al. [63] demonstrated significant improvements in the attentional capacity, vigilance, and numeric and spatial working memory of healthy young adults after ingesting caffeine-containing EDs. It was hypothesized that the ergogenic effects of caffeine-containing EDs on short-term maximal performance and reaction times would be related to positive changes in both psychological factors (mood state, RPE, and affective load) and physiological parameters (blood pressure and blood glucose) [53]. A study by Alford et al. [37] investigated the cognitive effects of EDs and found that caffeine can improve alertness and cognitive performance [37]. As we mentioned previously, caffeine is a psychoactive compound and it can increase resistance and reduce effort during physical activities. Another study found that caffeine intake improved cycling performance [64]. Different EDs may have diuretic effects due to increased caffeine content, potentially leading to increased urine production and dehydration. Also, ED consumption can cause an increase in diuresis and electrolyte imbalance [40].
Caffeine is well-known for its acute stimulant effects. A study by McLellan et al. [65] demonstrated that a moderate dose of caffeine can enhance alertness and cognitive performance. Alertness, vigilance, attention, and reaction time all improve after low (about 40 mg or 0.5 mg kg−1) to moderate (approximately 300 mg or 4 mg kg−1) caffeine dosages. However, effects on memory and higher order executive functions, such as judgment and decision making, are less consistent. After dosages greater than around 200 mg (~3 mg kg−1), effects on physical performance are observed on a wide range of physical performance metrics, including time to exhaustion, time trials, muscle strength and endurance, and high-intensity sprints typical of team sports [65] (Table 2). It has been demonstrated that caffeine improves physical performance by lowering perceived effort and raising endurance. An overview of the acute effects of caffeine on exercise performance has shown that ingestion of caffeine should be made before the competition. Powerlifters should think about consuming caffeine only before their most intense training sessions as this would help maximize the benefits of acute caffeine ingestion during competition and likely eliminate the attenuation of the effects associated with chronic caffeine ingestion [39].
Acute taurine supplementation has been shown to impact exercise capacity in cold weather conditions. Taurine impacts were observed through vascular and metabolic pathways, but in the end, exercise performance remained unaltered [42]. When given one dose of taurine before physical activity, healthy, well-trained men’s running times and cycling performances were barely affected [66,67].
7. Short-Term Studies on Animals
ED administration can lead to a significantly increased glycemia level, tripled glycogen content in the liver, and even a significant rise in serum AST, ALT, and LDH activities [68]. In another study conducted on trained and untrained animals, a decrease in glucose concentration was noted. Moreover, both in trained and untrained animal subjects, a massive increase in glycogen concentration in the heart was noticed [69]. Additional research has demonstrated that acute taurine therapy decreases voluntarily consumed alcohol, inhibits anxiogenic-like behaviors associated with alcohol withdrawal in rats, and increases the positive reinforcement effect of dopamine on the reward pathway [4]. Research has shown that rats treated with EDs experienced no changes in locomotion but had improved attention, memory, and increased oxidative imbalance. During recognition memory tests, the combination of taurine and caffeine found in EDs had an improving effect on short-term memory. The brain’s antioxidant system is modulated by increasing the concentration of glutathione, reducing lipid peroxidation, and increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes [70].
According to Sudakov et al. [71], the impact of caffeine use depends on the genetic susceptibility to the drug as well as environmental elements, such as social isolation. Anxiety only rose in low-anxious rats kept in comfortable environments following chronic caffeine use, while short-term caffeine consumption had a more noticeable effect on high-anxious rats, especially those placed individually [71].
Further, a short-term study conducted on mice under alcohol only or alcohol mixed with ED treatments has shown increased microglial recruitment. Also, consistent with earlier research, the group treated only with alcohol showed significantly higher levels of cerebral capillary dysfunction and astroglial cell activation, as expected. However, the effects were significantly reduced in the group treated with alcohol in combination with EDs. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines did not significantly differ in mice given only EDs or alcohol mixed with EDs. Thus, the acute negative effects of alcohol on cerebral capillary integrity and astrogliosis may be paradoxically diminished by taking an ED that is high in taurine and caffeine and contains B vitamins [72]. Adolescent mice that were given EDs in addition to alcohol saw a substantially slower rate of loss of their righting reflex compared to mice that were simply given alcohol. Teenage mice’s motor impairment and ataxia were prolonged when they were exposed to alcohol and EDs together [73].
8. Long-Term Studies on Children
Long-term research, however, revealed that coffee has long been associated with migraines, both as a trigger and a treatment. Patients with headaches frequently use caffeine-containing headache medications, either on their own or in conjunction with other therapies [74]. Combinations of caffeine and analgesic medications, such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and acetylsalicylic acid, demonstrated significantly better efficacy in treating patients with TTH or migraines when compared to analgesic medication alone. Excessive caffeine intake is known to cause tachycardia, tremors, elevated blood pressure, and in the worst situations, abrupt death [75]. Caffeine consumption has been shown to have detrimental effects on the neurological and cardiovascular systems in children and adolescents, which can lead to physical dependence and addiction. Although many of them acknowledge unpleasant side effects like weakness, shivering, headache, tachycardia, insomnia, tremors, or depression, EDs are widely used among the youth, adolescents, and even children [14] (Table 3).
Another long-term effect of caffeine on children is related to skin. An innovative non-invasive biomarker of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and other fluorophores in the skin is the measurement of skin intrinsic fluorescence (SIF). Skin fluorescence has been demonstrated to be strongly correlated with cardiovascular disease mortality and/or subclinical atherosclerosis in the general population, in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, in individuals with renal failure, and in individuals [76]. All biological membranes are easily crossed by caffeine, which is why it has been linked in epidemiological and animal studies to the prevention of UVB-induced skin cancer. Ingested caffeine also acts as a sunscreen on the skin. Both SIF1LED 375 nm [0.6, 0.2] and SIF14LED 456 nm [0.4, 0.8], which detect unique compounds at each end of the spectrum as well as common fluorophores like AGEs, were linked to caffeine [77]. Caffeine did in fact demonstrate fluorescent qualities with excitation/emission wavelengths in the UV range 311/363 nm14; however, SIF1LED 375 nm [0.6, 0.2], the lowest excitation LED investigated in the DCCT/EDIC and the EDC investigation, could not reach this level [77]. The impairment of vascular reactivity, intimal thickening, arteriosclerosis, endothelial apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation, which are primarily associated with diabetes and, to a lesser extent, with obesity, hypertension, and nicotine-induced vascular adverse events, were also ameliorated by oral taurine administration [36]. On the other hand, some authors considered that one important negative long-term effect of excessive taurine intake might be its potential involvement in the pathophysiology of acute renal failure by inducing tubular necrosis [78]. Different data indicated that continuous taurine supplementation significantly reduces the severity of delayed onset muscle soreness induced by elbow eccentric exercise in healthy young men [79] (Table 3).

Table 3.
Long-term beneficial effects of caffeine and taurine.
Table 3.
Long-term beneficial effects of caffeine and taurine.
| Compound | Children | Adolescents | Students | Athletes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | Effective in treating patients with TTH or migraines | Barrier healing | Higher corrected QT interval | Improves alertness and cognitive performance | [37,75,80,81] |
| Prevents UVB-induced skin cancer | Promotes wound healing | Therapeutic impact on renal cancer | Enhancesendurance | [77,82,83,84] | |
| Taurine | Decreases blood pressure and ise antiarrhythmic | Positive effects on oxidative stress and inflammation | Helps shield the skin from damaging oxidative stress | May reduce tissue damage | [85,86,87] |
9. Long-Term Studies on Adolescents
Adolescence is the time when being attractive becomes important. While a good part of the desire for a distinct personal identity is represented by heightened narcissism in teens, developing a positive self-image is not an easy task. The media’s unrealistic expectations and internal conflicts intensify the problems faced by teenagers. Adolescents look to dermatologists as reliable information sources, believing that these professionals can improve their skin through good hygiene and skin care products [88]. EDs’ high caffeine content may cause sleep disturbances. Adequate sleep is crucial for skin health, and disruptions in sleep can contribute to issues like dark circles, puffiness, and a tired complexion [89]. Growth hormones are among the several hormones and neurotransmitters whose release peaks during sleep. Anger, as well as issues with memory and thinking, are brought on by sleep deprivation. Additionally, it negatively affects our skin and other bodily functions [90]. There was a considerable increase in TEWL (trans-epidermal water loss) among those who slept poorly. Compared to bad sleepers, good sleepers noticed 30% better barrier healing. Those who slept well recovered from erythema considerably better 24 h after being exposed to UV radiation. When compared to bad sleepers, good sleepers also reported feeling far better about their physical appearance and attractiveness [80] (Table 4).
According to Nawrot et al. [91], caffeine consumption is one of the dietary habits that is formed in childhood and typically carries over into adulthood [91]. Dietary behaviors have been associated with the risk of numerous non-communicable diseases [92]. Teenagers can, however, gain a healthy status if they have sufficient knowledge and comprehension of dietary guidelines and nutrient intake [93]. According to Grosso et al., children and young adolescents who have better nutritional knowing may change their eating patterns. Consuming caffeine has implications on behavior, physiology, and self-perception, when part of a dietary routine. Few studies have examined the effects of caffeine on children’s and teenagers’ health, despite the drug’s use everywhere [94].

Table 4.
Long-term adverse effects of caffeine and taurine.
Table 4.
Long-term adverse effects of caffeine and taurine.
| Compound | Children | Adolescents | Students | Athletes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | Detrimental effects on the neurological and cardiovascular systems | Affects the skin and other bodily functions | Increases systolic blood pressure | Increases the risk of heart problems | [14,90,95,96] |
| Migraines | Obesity and dental enamel degradation | - | Weakened bone health | [74,96,97] | |
| Taurine | Acute renal failure | Can induce coronary vasospasm | Gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea or diarrhea | - | [78,98,99] |
| Tubular necrosis | Slows down cellular senescence | Liver and renal dysfunctions | - | [78,99,100] |
Obesity and dental enamel degradation brought on by EDs’ acidity are two additional health risks associated with their chronic use (Table 3). According to a previous study’s findings, teenagers who routinely drink EDs run a higher risk of developing mental health issues, especially if they also consume junk food. Additionally, there was a substantial difference in the likelihood of mental health issues between users who used the product moderately and often. As a result, it is important to closely monitor how many EDs are consumed, and teenagers who routinely drink EDs should receive teaching materials about their harmful consequences [97]. Adolescent ED users’ increased risk-taking behaviors, impaired driving, and increased use of other illicit substances have all been linked to the co-ingestion of caffeine and ethanol. Compared to drinking alcohol alone, several studies have shown that combining alcohol with EDs results in different subjective states, such as reduced reported intoxication, increased excitation, and a stronger impulse to drink [101] (Table 4).
Among its many functions in humans, taurine is a natural metabolite that helps control neuronal excitability, stabilize membranes, produce bile salts, and detoxify some xenobiotics. Humans are thought to consume an average of 40–400 mg of taurine daily. Certain EDs have more than ten times the suggested daily amount of taurine for a normal individual [102]. Like caffeine, taurine can induce coronary vasospasm by altering the intracellular calcium concentration in smooth muscles [98]. The majority of hazardous incidents induced by the consumption of EDs are associated with taurine, guarana, and caffeine. It is unknown how excessive and long-term consumption of additional compounds, both alone and together with caffeine, will affect a person’s body immediately and over time [103]. Reduced DNA damage, attenuated inflammation, inhibited mitochondrial dysfunction, protection against telomerase insufficiency, and slowed down cellular senescence are all effects of taurine [100]. In addition to promoting collagen production in osteoblast-like UMR-106 cells, taurine has also been shown to promote wound healing in mice by upregulating skin collagen synthesis. The observations aforementioned indicate that taurine can affect the extracellular matrix (ECM), which includes collagen, in the skin. The underlying mechanisms of taurine’s numerous stated benefits for skin function remain unclear [104]. Furthermore, the activities of caspase-1 and NF-κB were significantly inhibited by taurine [105]. Since taurine’s anti-inflammatory properties have gained considerable interest, collagen sponges and taurine are being combined as a biopharmaceutical to promote tissue growth and wound healing [82]. Moreover, data from clinical trials demonstrate that taurine has positive effects on oxidative stress and inflammation 56 days after supplementation by significantly reducing malondialdehyde and protein C reactive levels [85].
ED addiction has lately been associated with fatality in Canada and the US in the youth [106]. The amount of caffeine ingested varies based on the population categories and the most popular drink types [107]. Regulations and prospective prohibitions on the sale and use of these beverages may alter people’s habits of ED intake and foster favorable views in their thoughts. This analysis provides a thorough overview of the many factors surrounding the use of EDs, cardiovascular concerns, danger in the younger population, and the regulations that need to be put in place [108]. There have been reports that externally supplied artificial taurine may aggravate cardiac conditions and raise blood pressure [12].
10. Long-Term Studies on Students
It turned out that individuals who consumed EDs had a significantly higher corrected QT interval and SBP two hours after consumption compared to those who consumed caffeine from other sources, such as coffee [81]. In terms of safety, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandates comprehensive investigation for all new drugs that affect the QT/QT c interval. However, since the primary ingredient in EDs is caffeine, further investigation is required. Although there is no evidence of significant short-term consequences from the daily consumption of EDs over a few weeks, long-term daily use may potentially be associated with cardiovascular issues like arrhythmias [81]. Caffeine can also cause apoptosis via a variety of pathways, including those that are dependent on and independent of p-53, phosphatase and tensin homolog, PI3K/protein kinase B (AKT), and the mTOR pathway [95]. It is believed to have a therapeutic impact on renal cancer due to its ability to bind to glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH), considered a biomarker and possible therapeutic target for this kind of cancer, as shown in [83]. Research indicates that the use of coffee lowers biomarkers associated with inflammation, hence postponing weariness and enhancing endurance abilities. In the vastus lateralis muscle of mice given lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation, this study investigated the effects of caffeine administration on the expression of genes associated with oxidative metabolism, inflammatory processes, and adenosine receptors [109].
Because of caffeine’s strong biological activity and capacity to pass through the skin barrier, its application in cosmetics is growing. Caffeine is utilized as an active ingredient in anticellulite cosmetic treatments because it inhibits the excessive buildup of fat within cells (Figure 1). This alkaloid inhibits phosphodiesterase activity, which promotes the breakdown of fats during lipolysis. Caffeine slows down the skin’s photoaging process and aids in shielding cells from UV light. Additionally, caffeine included in cosmetics promotes blood flow to the skin and inhibits 5-α-reductase activity, which in turn promotes hair growth [5] (Figure 1). Another beneficial effect was highlighted by Li et al. [6], whose experiments showed that caffeine protects the skin from senescence induced by oxidative stress [6].
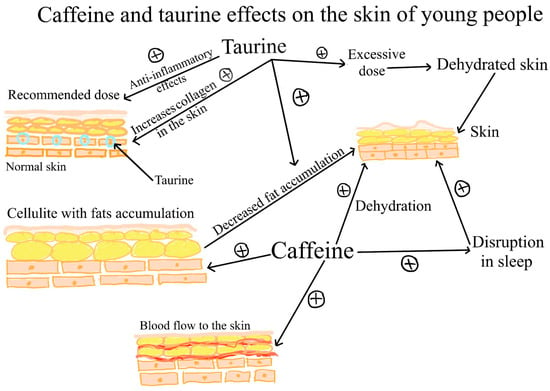
Figure 1.
Caffeine and taurine effects on the skin of young people. Taurine, in normal doses, has anti-inflammatory effects and increases the amount of skin collagen. Also, both caffeine and taurine can reduce fat accumulation in adipose tissue. In large doses, caffeine, as well as taurine, provokes dehydration. Caffeine stimulates blood circulation in the skin. It causes sleep disturbances that are associated with unhealthy skin.
Similar to caffeine, taurine is an antioxidant, and this compound helps shield the skin from damaging oxidative stress. This may offer antiaging benefits and improve the health of the skin [86]. From a more comprehensive macro perspective, taurine supports the immune system by acting as an antioxidant and an anti-inflammatory agent. At the microscopic level, it controls the balance of electrolytes and minerals in cells [110]. Neutrophil taurine concentrations in psoriasis patients were shown to be lower than in normal participants, indicating that taurine plays a part in the body’s defense against skin inflammation [104] (Figure 1). However, taurine has shown promise in mitigating obesity-related inflammation. Research involving obese women who were administered taurine for eight weeks demonstrated increased levels of adiponectin (a hormone involved in regulating glucose levels and fatty acid breakdown) and a reduction in inflammatory biomarkers and lipid peroxidation. These findings highlight the potential role of taurine supplementation in reducing obesity-related inflammation, thereby potentially reducing the development of coronary artery disease [111]. High doses of taurine may cause gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea or diarrhea. Long-term supplementation has been associated with liver and renal dysfunction [99].
11. Long-Term Studies on Athletes
Prolonged consumption may increase the risk of heart problems. Some EDs contain phosphoric acid, which may leach calcium from bones, potentially leading to weakened bone health [96]. EDs may have diuretic effects, potentially leading to dehydration when consumed in excess. Dehydration can have a negative impact on athletic performance and overall health. EDs might cause sleep disturbances due to their high caffeine content. Athletes require adequate and high-quality sleep for recovery and performance, so long-term sleep disturbances can be detrimental [112]. Regular consumption of EDs can lead to caffeine addiction. Over time, individuals may develop a tolerance, requiring increasing amounts of caffeine to achieve the same stimulating effects. This can lead to a cycle of increasing consumption and potential withdrawal symptoms [113]. Caffeine has also been applied therapeutically and is currently a part of many over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medication products [2]. A study by Alford et al. [37] investigated the cognitive effects of EDs and found that caffeine, a common ingredient, can improve alertness and cognitive performance [37]. For physical performance, it has been shown to enhance endurance and reduce perceived effort during physical activities. A study by Astorino et al. [84] found that caffeine intake improved cycling performance [84]. Additionally, caffeine mobilizes intracellular calcium stores and changes the way in which the body metabolizes fat and carbohydrates by stimulating lipolysis, which is caused by the inhibition of phosphodiesterase enzymes. It can also inhibit several of the key factors that contribute to the development of cancer, including cellular senescence and resistance to cell death [114] (Table 3).
Taurine, a sulfur-containing non-proteinogenic β-amino acid, is one of the body’s numerous antioxidants and has been demonstrated to have a unique role as a crucial natural regulator of the antioxidant defense networks. According to the examination of current data, only a small number of mammals with rather high (>15–20 mM) taurine concentrations may be predicted to benefit directly from taurine’s antioxidant impact, which is caused by the protein’s ability to scavenge free radicals [115].
Because of its capacity to preserve the normal electron transport chain, upregulate antioxidant responses, maintain glutathione reserves, promote membrane integrity, reduce inflammation, and prevent calcium buildup, taurine is also considered a cytoprotective chemical [116] (Figure 1). Nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, IL-12, macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2), and monocyte chemo-attractant protein (MCP)-1 and -2 are examples of inflammatory mediators that are inhibited by Tau Cl (taurine chloramine) [117]. Therefore, it can be utilized as a physiologically non-toxic biomolecule to prevent cellular damage brought on by chronic inflammatory illness circumstances, given its capacity to control the overproduction of NO and TNF-α [118]. Taurine’s anti-inflammatory qualities may reduce tissue damage, but pathogen removal would be hampered by a potential lack of antimicrobial action coupled with an increase in macrophage and polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) pro-inflammatory activity [87]. While there is not any proof that using taurine alongside other drugs can have negative consequences, there might be a connection between taurine supplementation and different cytochrome P450 systems that are in charge of hepatic drug metabolism. In particular, taurine blocks the activity of cytochrome P450 2E1, a highly conserved xenobiotic-metabolizing P450 that breaks down over 70 substrates, including some widely used anesthetics, analgesics, antidepressants, antibacterials, and antiepileptics [119].
12. Long-Term Studies on Animals
Long-term consumption can cause biochemical and ultrastructural alterations in the heart muscles, such as increased glucose and glycogen concentrations in the myocardium and significantly decreased cholesterol concentration [120]. Also, it may lead even to respiratory acidosis in rats due to damaged fibers in the striated muscles [121]. Other changes that were observed in animal models were relative to similar weights of organs, and even weight gain, after an exposure of three months to EDs. Also, regarding water consumption, irritability, piloerection, and behavior, there were no signs of change. Also, a decrease in the concentration of sperm was remarked [122]. Unfortunately, other findings revealed the fact that long-term intake of EDs can produce the opposite effects regarding brain weight, probably due to the neurotoxic effects of EDs on brain cells [123]. Various kidney and liver damage was demonstrated by the substantial increases in serum levels of uric acid, creatinine, BUN, ALT, and ALP that were brought on by EDs. Raised hepatic enzyme levels in the blood are a good way to observe if toxic substances have damaged the liver. Rats treated with caffeinated EDs have shown significant elevations in serum AST, ALT, and ALP, according to reports. Rats given an ED either by itself or in conjunction with alcohol were shown to have greater serum levels of AST, ALT, ALP, and total bilirubin than the untreated controls [124].
Surprisingly, according to the study by Qasim L. [125], there were no significant differences in the index of body and organ weight for mice, but histopathological study of the liver showed the infiltration and accumulation of inflammatory cells in the liver parenchyma with hepatocyte necrosis, where some of the necrosis was replaced by red blood cells and inflammatory cells. The kidneys were restricted only to red blood cells and inflammatory cell aggregation within renal tubules, which indicated vacuolar degeneration. Also, taurine’s reaction with other active ingredients of EDs could have led to the infiltration of leucocytes through the hepatocytes and ischemia of the myocardial by inducing coronary vasospasm. An elevation in sera levels of the GOT, ALP, and GPT enzymes was also observed in the mice that consumed EDs [125]. Another study involving mice compared different control groups, including control mice that were given water; the animals kept on EDs for 13 weeks displayed a declining trend in their SBP. In the ED-administered mice, diastolic and mean arterial pressures were significantly reduced. Systolic pressure in the sugar-free ED-treated mice was significantly lower than in the control group. Comparing the diastolic and mean arterial pressures to the control group, similar substantial reductions were seen [126].
The effect of caffeine on animal subjects, such as rats, showed abnormal microscopic findings: increased keratinization and disorganization of the epidermal cells, and epidermal and dermal atrophy, which leads to a reduction in skin thickness and may be a risk factor for inducing skin atrophy [127]. Increased collagen synthesis was observed in subjects who received caffeine and its daily consumption affects full-thickness skin graft healing [128]. Also, it was demonstrated that taurine reduces oxygen radicals, promotes angiogenesis and collagen synthesis, and inhibits neutrophil infiltration in the muscle flaps during ischemia and reperfusion. The main outcome is that taurine significantly improves muscle survival [129].
13. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
EDs, as was previously indicated, are beneficial in the short term, but this varies greatly depending on the age range. Children’s and teenagers’ ED consumption effects were not the same compared to adults. After short-term caffeine consumption, it was observed that the systolic pressure increased in these age groups. Also, the youth who drink too much coffee have been connected to a host of detrimental health outcomes, such as poor sleep, anxiety, agitation, nausea, and stomach ulcers. We only paid attention to the two primary compounds, taurine and caffeine, as is clear from the preceding subsections. The effects that they may have on skin health were observed, which is crucial for the groups that they target. Long-term use and large doses of EDs have been shown to have the opposite effects. This was demonstrated by the positive effects of the two components when taken independently over an extended time and in tiny dosages, which makes it intriguing. Chronic taurine intake (daily recommended doses) in adolescents was associated with reduced DNA damage, attenuated inflammation, prevented mitochondrial dysfunction, protection against telomerase deficiency, and slowed down cellular senescence. Due to its ability to prevent excessive fat accumulation within cells, caffeine is an active ingredient in cosmetic treatments aimed to reduce the appearance of cellulite in students. The combination of both does not have the same effect; however, they probably do individually. Significant increases in serum levels of uric acid, creatinine, BUN, ALT, and ALP caused by chronic intake of EDs indicated different degrees of injury to the kidneys and liver. Elevated circulatory levels of the liver’s enzymes can be an excellent indicator of liver damage caused by the two main compounds. There have been substantial increases in blood AST, ALT, and ALP in rats treated with caffeinated EDs. It has been demonstrated that rats administered EDs alone or in combination with alcohol had higher serum levels of AST, ALT, ALP, and total bilirubin than the untreated controls. It was observed that there has been minimal research on the impact of EDs on the skin.
Therefore, more studies are needed regarding the short- and long-term effects of EDs on skin physiology. Also, there is a need to examine the separate effects of the main compounds, caffeine and taurine, on human skin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M., S.M.M., I.P. and S.T.; methodology, L.A. and E.P.; software, S.T.; validation, M.S. and R.M.; formal analysis, M.S.; investigation, R.M. and L.A.; resources, E.P. and M.S.; data curation, R.M.; writing—original draft preparation, S.T.; writing—review and editing, C.M. and T.M.; visualization, S.M.M.; supervision, I.P. and T.M.; project administration, T.M.; funding acquisition, S.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Richards, G.; Smith, A.P. A review of energy drinks and mental health, with a focus on stress, anxiety, and depression. J. Caffeine Res. 2016, 6, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, S.L.; Díaz-Lara, J.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Del Coso, J. Caffeinated drinks and physical performance in sport: A systematic review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, M.S.; Soares, A.C.; Sousa, D.N.; Eudes-Filho, J.; Faro, L.R.F.; Carneiro, F.P.; Carneiro, F.P.; Silva, M.V.; Motoyama, A.B.; Souza, G.M.R.; et al. Effects of caffeine on behavioural and cognitive deficits in rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 123, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulcinelli, R.R.; de Paula, L.F.; Nietiedt, N.A.; Bandiera, S.; Hansen, A.W.; dos Reis Izolan, L.; Almeida, R.I.; Gomez, R. Taurine enhances voluntary alcohol intake and promotes anxiolytic-like behaviors in rats. Alcohol 2020, 88, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.; Herman, A. Caffeine’s mechanisms of action and its cosmetic use. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2012, 26, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Ouyang, S.H.; Tu, L.F.; Wang, X.; Yuan, W.L.; Wang, G.E.; Wu, Y.P.; Duan, W.J.; Yu, H.M.; Fang, Z.Z.; et al. Caffeine protects skin from oxidative stress-induced senescence through the activation of autophagy. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Manabe, C.; Inokuchi, Y.; Mutou, C.; Nagahama, T.; Murakami, S. Protective effect of taurine on UVB-induced skin aging in hairless mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, K.T.; Peterson, M.B.; Smith, M.B.; Bunch, T.J. An Overview of the Risks of Contemporary Energy Drink Consumption and Their Active Ingredients on Cardiovascular Events. Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep. 2023, 17, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walaszek, Z. Potential use of D-glucaric acid derivatives in cancer prevention. Cancer Lett. 1990, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, N.; Walaszek, Z.; Kinjo, T.; Nishimaki, T.; Hanausek, M.; Slaga, T.J.; Mori, H.; Yoshimi, N. Effects of synthetic and natural in vivo inhibitors of β-glucuronidase on azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008, 1, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tek, M.; Toptas, O.; Akkas, I.; Kazancioglu, H.O.; Firat, T.; Ezirganli, S.; Ozan, F. Effects of energy drinks on soft tissue healing. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, 2084–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, S.M.; Schaechter, J.L.; Hershorin, E.R.; Lipshultz, S.E. Health effects of energy drinks on children, adolescents, and young adults. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadoni, C.; Peana, A.T. Energy drinks at adolescence: Awareness or unawareness? Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1080963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soós, R.; Gyebrovszki, Á.; Tóth, Á.; Jeges, S.; Wilhelm, M. Effects of caffeine and caffeinated beverages in children, adolescents and young adults: Short review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, N.; Miskulin, I.; Jokic, S.; Kovacevic, J.; Miskulin, M. Consumption of Energy Drinks among University Students in Eastern Croatia. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholewa, K.; Czarnek, K.; Grzywacz, A.; Masiak, J. Energy Drink Use Disorder–a Review of the Literature. Teka Komisji Prawniczej PAN Oddział w Lublinie 2023, 16, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, A.; Maiese, A.; Lazzari, J.; Casula, C.; Turillazzi, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. The dark side of energy drinks: A comprehensive review of their impact on the human body. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Ushijima, I.; Hiraki, M.; Ono, N. Enhancement of caffeine-induced locomotor hyperactivity produced by the combination with L-arginine or taurine in mice: Possible involvement of nitric oxide. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 31, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.J.; Pierce, M.M.; Sehgal, A.; Wu, T.; Skipper, D.C.; Chabba, R. Effect of taurine and caffeine on sleep–wake activity in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2010, 2, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, C.P.; Marczinski, C.A. Taurine, caffeine, and energy drinks: Reviewing the risks to the adolescent brain. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaziga, R.; Muchunguzi, C.; Achen, D.; Kools, S. Beauty is skin deep; the self-perception of adolescents and young women in construction of body image within the Ankole society. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, R.C.; Singer, M.R.; Moore, L.L.; Nguyen, U.S.D.; Garrahie, E.J.; Marmor, J.K. Current caffeine intake of young children: Amount and sources. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1995, 95, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atik, A.; Harding, R.; De Matteo, R.; Kondos-Devcic, D.; Cheong, J.; Doyle, L.W.; Tolcos, M. Caffeine for apnea of prematurity: Effects on the developing brain. Neurotoxicology 2017, 58, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, R.; Kennedy, O.J.; Roderick, P.; Fallowfield, J.A.; Hayes, P.C.; Parkes, J. Coffee consumption and health: Umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple health outcomes. BMJ 2017, 359, j5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruxton, C. The suitability of caffeinated drinks for children: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials, observational studies and expert panel guidelines. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 27, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, B.; Amarah, W.; Nasralla, E.; Elias, N. Energy drinks in children and adolescents: Demographic data and immediate effects. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera-Sampol, A.; Rodas, L.; Martínez, S.; Moir, H.J.; Tauler, P. Caffeine intake among undergraduate students: Sex differences, sources, motivations, and associations with smoking status and self-reported sleep quality. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, A.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Willems, M.T. Timing, optimal dose and intake duration of dietary supplements with evidence-based use in sports nutrition. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Villalona, Y.; Weimer, J.; Ludwig, C.P.; Hays, B.T.; Massie, L.; Marczinski, C.A.; Curran, C.P. Supplemental taurine during adolescence and early adulthood has sex-specific effects on cognition, behavior and neurotransmitter levels in C57BL/6J mice dependent on exposure window. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2020, 79, 106883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, S.; Peeyush Kumar, T.; Mathew, J.; Anju, T.R.; Paulose, C.S. Hypoglycemia induced changes in cholinergic receptor expression in the cerebellum of diabetic rats. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J.A.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Doyle, J.A.; Otis, J.S. Taurine in sports and exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heatherley, S.V.; Hancock, K.M.; Rogers, P.J. Psychostimulant and other effects of caffeine in 9-to 11-year-old children. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2006, 47, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temple, J.L. Caffeine use in children: What we know, what we have left to learn, and why we should worry. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alashqar, M.B. Caffeine in the treatment of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: A review. SKIN J. Cutan. Med. 2019, 3, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Important roles of dietary taurine, creatine, carnosine, anserine and 4-hydroxyproline in human nutrition and health. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, W.; Mozaffari, M.S. Role of taurine in the vasculature: An overview of experimental and human studies. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 1, 293–311. [Google Scholar]
- Alford, C.; Cox, H.; Wescott, R. The effects of red bull energy drink on human performance and mood. Amino Acids 2001, 21, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gan, C.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J. Caffeine targets SIRT3 to enhance SOD2 activity in mitochondria. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.L.; Guilherme, J.P.L.F.; Ferreira, L.H.B.; de Souza-Junior, T.P.; Lancha, A.H., Jr. Caffeine and exercise performance: Possible directions for definitive findings. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesenhuber, A.; Boehm, M.; Posch, M.; Aufricht, C. Diuretic potential of energy drinks. Amino Acids 2006, 31, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iheanacho, M.M.; Analike, R.A.; Meludu, S.C.; Ogbodo, E.C.; Onah, C.E. Short-term energy drink consumption influences plasma glucose, apolipoprotein B, body mass index and pulse rate among students. Discoveries 2022, 10, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, R.; Cole, J.; Tallent, J.; Jeffries, O.; Theis, N.; Waldron, M. Physiological and thermoregulatory effects of oral taurine supplementation on exercise tolerance during forced convective cooling. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2022, 22, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies. Scientific opinion on the safety of caffeine. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4102. [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave, I.F.; Farrington, R.L.; Hoban, C.; Byard, R.W. Caffeine toxicity in forensic practice: Possible effects and under-appreciated sources. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2016, 12, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordt, S.P.; Vilke, G.M.; Clark, R.F.; Lee Cantrell, F.; Chan, T.C.; Galinato, M.; Nguyen, V.; Castillo, E.M. Energy drink use and adverse effects among emergency department patients. J. Community Health 2012, 37, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keefe, J.H.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Bhatti, S.K.; Patil, H.R.; DiNicolantonio, J.J.; Lucan, S.C.; Lavie, C.J. Effects of habitual coffee consumption on cardiometabolic disease, cardiovascular health, and all-cause mortality. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, N.; Johnson, M.; Delaney, E.; Blankenship, M.B. Energy drinks: A new health hazard for adolescents. J. Sch. Nurs. 2010, 26, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.C.; Knight, C.A.; Hockenberry, J.; Teplansky, R.; Hartman, T.J. Beverage caffeine intakes in the US. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 63, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbeta, R.L.; Overpeck, M.D.; Ramcharran, D.; Kogan, M.D.; Ledsky, R. High caffeine intake in adolescents: Associations with difficulty sleeping and feeling tired in the morning. J. Adolesc. Health 2006, 38, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Coca, A.; Casa, D.J.; Antonio, J.; Green, J.M.; Bishop, P.A. Caffeine and diuresis during rest and exercise: A meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriessen, A. Prevention, recognition and treatment of dry skin conditions. Br. J. Nurs. 2013, 22, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, M.; Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Körber, A.; Kerscher, M.; Itschert, G.; Dippel, M.; Staubach, P. Diagnosis and treatment of xerosis cutis–a position paper. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chtourou, H.; Trabelsi, K.; Ammar, A.; Shephard, R.J.; Bragazzi, N.L. Acute effects of an “Energy drink” on short-term maximal performance, reaction times, psychological and physiological parameters: Insights from a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, counterbalanced crossover trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J.; Trexler, E.T.; Lazinica, B.; Pedisic, Z. Effects of caffeine intake on muscle strength and power: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J.; Grgic, I.; Pickering, C.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Bishop, D.J.; Pedisic, Z. Wake up and smell the coffee: Caffeine supplementation and exercise performance—An umbrella review of 21 published meta-analyses. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.K.; Green, J.M. Caffeine and anaerobic performance: Ergogenic value and mechanisms of action. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.M.; Zhao, Z.; Stock, H.S.; Mehl, K.A.; Buggy, J.; Hand, G.A. Central nervous system effects of caffeine and adenosine on fatigue. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R399–R404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, B.; Gonzalez-Millán, C.; Salinero, J.J.; Abian-Vicen, J.; Areces, F.; Barbero-Alvarez, J.C.; Muñoz, V.; Portillo, L.J.; Gonzalez-Rave, J.M.; Del Coso, J. Caffeine-containing energy drink improves physical performance in female soccer players. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustit, M.; Millet, C.; Blaise, S.; Dufournet, B.; Cracowski, J.L. Excellent reproducibility of laser speckle contrast imaging to assess skin microvascular reactivity. Microvasc. Res. 2010, 80, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iredahl, F.; Löfberg, A.; Sjöberg, F.; Farnebo, S.; Tesselaar, E. Non-invasive measurement of skin microvascular response during pharmacological and physiological provocations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froiland, K.; Koszewski, W.; Hingst, J.; Kopecky, L. Nutritional supplement use among college athletes and their sources of information. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2004, 14, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, C.J.; Jagim, A.R.; Camic, C.L.; Andre, M.J. Acute effects of a caffeine-containing supplement on anaerobic power and subjective measurements of fatigue in recreationally active men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesnes, K.A.; Brooker, H.; Watson, A.W.; Bal, W.; Okello, E. Effects of the Red Bull energy drink on cognitive function and mood in healthy young volunteers. J. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 31, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, S.C.; Candow, D.G.; Little, J.P.; Magnus, C.; Chilibeck, P.D. Effect of Red Bull energy drink on repeated Wingate cycle performance and bench-press muscle endurance. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2007, 17, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, T.M.; Caldwell, J.A.; Lieberman, H.R. A review of caffeine’s effects on cognitive, physical and occupational performance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.; Bridge, C.A.; McNaughton, L.R.; Sparks, S.A. The effect of acute taurine ingestion on 4-km time trial performance in trained cyclists. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2581–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rutherford, J.A.; Spriet, L.L.; Stellingwerff, T. The effect of acute taurine ingestion on endurance performance and metabolism in well-trained cyclists. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2010, 20, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crișan, M.; Munteanu, C.; Roșoriu, C.; Lang, C. Red bull induces biochemical changes in Wistar rat liver. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2013, 18, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Crișan, M.; Munteanu, C.; Jula, C.; Lang, C.; Rosioru, C. Effects of Red Bull on cardiac muscle in physically trained and untrained Wistar rat. Ann. RSCB 2014, 19, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Valle, M.C.; Couto-Pereira, N.S.; Lampert, C.; Arcego, D.M.; Toniazzo, A.P.; Limberger, R.P.; Dallegrave, E.; Dalmaz, C.; Arbo, M.D.; Leal, M.B. Energy drinks and their component modulate attention, memory, and antioxidant defences in rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudakov, S.; Medvedeva, O.F.; Rusakova, I.V.; Figurina, I.B. Effect of short-term and chronic caffeine intake on rats with various anxiety level. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2001, 132, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takechi, R.; Mamo, J.; Das, S.; Graneri, L.; D’Alonzo, Z.; Nesbit, M.; Junaldi, E.; Lam, V. Short-term consumption of alcohol (vodka) mixed with energy drink (AMED) attenuated alcohol-induced cerebral capillary disturbances and neuroinflammation in adult wild-type mice. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 2398–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahe, T.E.; Filgueiras, C.C.; Quaresma, S.R.; Schibuola, H.G.; Abreu-Villaça, Y.; Manhães, A.C.; Ribeiro-Carvalho, A. Energy drink enhances the behavioral effects of alcohol in adolescent mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 651, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowaczewska, M.; Wiciński, M.; Kaźmierczak, W. The ambiguous role of caffeine in migraine headache: From trigger to treatment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Diener, C.; Robbins, M.S.; Garas, S.Y.; Patel, K. Caffeine in the management of patients with headache. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Betriu, À.; Arroyo, D.; López, C.; Hernández, M.; Rius, F.; Fernández, E.; Lecube, A. Skin autofluorescence and subclinical atherosclerosis in mild to moderate chronic kidney disease: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eny, K.M.; Orchard, T.J.; Miller, R.G.; Maynard, J.; Grant, D.M.; Costacou, T.; Cleary, P.A.; Braffett, B.H.; The DCCT/EDIC Research Group; Paterson, A.D. Caffeine consumption contributes to skin intrinsic fluorescence in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Haas, N.A.; Dalla-Pozza, R.; Jakob, A.; Oberhoffer, F.S.; Mandilaras, G. Energy Drinks and Adverse Health Events in Children and Adolescents: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, S.G.; Akazawa, N.; Choi, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Oikawa, S.; Kumagai, H.; Tanahashi, K.; Ohmori, H.; Maeda, S. Taurine supplementation reduces eccentric exercise-induced delayed onset muscle soreness in young men. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 803, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyetakin-White, P.; Suggs, A.; Koo, B.; Matsui, M.S.; Yarosh, D.; Cooper, K.D.; Baron, E.D. Does poor sleep quality affect skin ageing? Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 40, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, E.A.; Lacey, C.S.; Aaron, M.; Kolasa, M.; Occiano, A.; Shah, S.A. Randomized controlled trial of high-volume energy drink versus caffeine consumption on ECG and hemodynamic parameters. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, W.; Chen, A.; Liu, J.; Xuan, X. Collagen sponge prolongs taurine release for improved wound healing through inflammation inhibition and proliferation stimulation. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hu, L.; Liu, T.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J. Caffeine targets G6PDH to disrupt redox homeostasis and inhibit renal cell carcinoma proliferation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 556162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astorino, T.A.; Matera, A.J.; Basinger, J.; Evans, M.; Schurman, T.; Marquez, R. Effects of red bull energy drink on repeated sprint performance in women athletes. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghfouri, A.H.; Seyyed Shoura, S.M.; Fathollahi, P.; Shadbad, M.A.; Papi, S.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Faghfuri, E. Profiling inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers following taurine supplementation: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkiewicz, J.; Kontny, E. Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrosian, I.; Sofia, R.D.; Wolff, S.M.; Dinarello, C.A. Taurolidine, an analogue of the amino acid taurine, suppresses interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor synthesis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cytokine 1991, 3, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcoux, D. Appearance, cosmetics, and body art in adolescents. Dermatol. Clin. 2000, 18, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanic, M.; Paunovic, K.; Lackovic, M.; Djurdjevic, K.; Nestorovic, M.; Jakovljevic, A.; Markovic, M. Energy Drinks and Sleep among Adolescents. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Grover, L.M.; Bertolotti, D.; Green, T.L. Growth hormone rescues hippocampal synaptic function after sleep deprivation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R1588–R1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, P.; Jordan, S.; Eastwood, J.; Rotstein, J.; Hugenholtz, A.; Feeley, M. Effects of caffeine on human health. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkilä, V.; Räsänen, L.; Raitakari, O.T.; Pietinen, P.; Viikari, J. Consistent dietary patterns identified from childhood to adulthood: The cardiovascular risk in Young Finns Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carraway-Stage, V.; Hovland, J.; Showers, C.; Díaz, S.; Duffrin, M.W. Food-based science curriculum yields gains in nutrition knowledge. J. Sch. Health 2015, 85, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, G.; Mistretta, A.; Turconi, G.; Cena, H.; Roggi, C.; Galvano, F. Nutrition knowledge and other determinants of food intake and lifestyle habits in children and young adolescents living in a rural area of Sicily, South Italy. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, L. Caffeine induces sustained apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells by activating the caspase-9/caspase-3 signalling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Jones, G. Soft drink and milk consumption, physical activity, bone mass, and upper limb fractures in children: A population-based case-control study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2004, 75, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.H. Association between energy drink intake, sleep, stress, and suicidality in Korean adolescents: Energy drink use in isolation or in combination with junk food consumption. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, M.; Weiss, M. The influence of a taurine containing drink on cardiac parameters before and after exercise measured by echocardiography. Amino Acids 2001, 20, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidot, H.; Cvejic, E.; Carey, S.; Strasser, S.I.; McCaughan, G.W.; Allman-Farinelli, M.; Shackel, N.A. Randomised clinical trial: Oral taurine supplementation versus placebo reduces muscle cramps in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Gollapalli, K.; Mangiola, S.; Schranner, D.; Yusuf, M.A.; Chamoli, M.; Shi, S.L.; Bastos, B.L.; Nair, T.; Riermeier, A.; et al. Taurine deficiency as a driver of aging. Science 2023, 380, eabn9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, V.; Soliman, N.; Soliman, A.T.; Elsedfy, H.; Di Maio, S.; El Kholy, M.; Fiscina, B. Caffeinated energy drink consumption among adolescents and potential health consequences associated with their use: A significant public health hazard. Acta Biomed. Atenei Parm. 2017, 88, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchan, E.; Patel, N.D.; Feucht, C. Energy drinks: A review of use and safety for athletes. Physician Sportsmed. 2010, 38, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Batenburg-Eddes, T.; Lee, N.C.; Weeda, W.D.; Krabbendam, L.; Huizinga, M. The potential adverse effect of energy drinks on executive functions in early adolescence. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Değim, Z.; Celebi, N.; Sayan, H.; Babül, A.; Erdoğan, D.; Take, G.Ü. An investigation on skin wound healing in mice with a taurine-chitosan gel formulation. Amino Acids 2002, 22, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.Y.; Kim, H.M.; Jeong, H.J. The potential protective role of taurine against experimental allergic inflammation. Life Sci. 2017, 184, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruser, D. Energy Drinks Suspected to Have Caused Deaths of 3 Canadians; Toronto Star: Toronto, ON, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, C.A.; Knight, I.; Mitchell, D.C. Beverage caffeine intakes in young children in Canada and the US. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2006, 67, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jacson, J. Potential effects of excessive Energy drinks consumption in young people on long-term cardiovascular risks: Energy Drinks and Long-term Cardiovascular risks. Indian J. Pharm. Drugs Stud. 2022, 1, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Eichwald, T.; Solano, A.F.; Souza, J.; de Miranda, T.B.; Carvalho, L.B.; dos Santos Sanna, P.L.; da Silva, R.A.F.; Latini, A. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Caffeine on Muscle under Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guta, R. Is taurine a pharmaconutrient. J. Pharmacol. Ther. Res 2018, 2, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Qaradakhi, T.; Gadanec, L.K.; McSweeney, K.R.; Abraham, J.R.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Zulli, A. The anti-inflammatory effect of taurine on cardiovascular disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsunni, A.A. Energy drink consumption: Beneficial and adverse health effects. Int. J. Health Sci. 2015, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, S.E.; Juliano, L.M.; Hughes, J.R.; Griffiths, R.R. Caffeine use disorder: A comprehensive review and research agenda. J. Caffeine Res. 2013, 3, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcelos, R.P.; Lima, F.D.; Carvalho, N.R.; Bresciani, G.; Royes, L.F. Caffeine effects on systemic metabolism, oxidative-inflammatory pathways, and exercise performance. Nutr. Res. 2020, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surai, P.F.; Earle-Payne, K.; Kidd, M.T. Taurine as a natural antioxidant: From direct antioxidant effects to protective action in various toxicological models. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliou, S.; Adamaki, M.; Ioannou, P.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Spandidos, D.A.; Christodoulou, I.; Kyriakopoulos, A.M.; Zoumpourlis, V. Protective role of taurine against oxidative stress. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignarro, L.J. Physiology and pathophysiology of nitric oxide. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1996, 55, S2–S5. [Google Scholar]
- William, R.; Watson, R.W.; Redmond, H.P.; Mc Carthy, J.; Bouchier-Hayes, D. Taurolidine, an antilipopolysaccharide agent, has immunoregulatory properties that are mediated by the amino acid taurine. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1995, 58, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caine, J.J.; Geracioti, T.D. Taurine, energy drinks, and neuroendocrine effects. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2016, 83, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Rosioru, C.; Tarba, C.; Lang, C. Long-term consumption of energy drinks induces biochemical and ultrastructural alterations in the heart muscle. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2018, 19, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, A.; Başgöze, S.; Çakıllı, K.; Aydın, Ü.; Şentürk, G.E.; Diker, V.Ö.; Ertürk, M. Histopathological changes in the myocardium caused by energy drinks and alcohol in the mid-term and their effects on skeletal muscle following ischemia-reperfusion in a rat model. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2023, 27, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxiddinovna, I.M. Effects of Energy Drinks on Biochemical and Sperm Parameters in Albino Rats. Cent. Asian J. Med. Nat. Sci. 2022, 3, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Adjene, J.; Emojevwe, V.; Idiapho, D. Effects of long-term consumption of energy drinks on the body and brain weights of adult Wistar rats. J. Exp. Clin. Anat. 2014, 13, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancy, W.; Alogaiel, D.; Hanafi, M.; Zakaria, E. Effects of chronic consumption of energy drinks on liver and kidney of experimental rats. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.Q. Histological and Physiological Studies on the Long-term Effect of Different Concentrations of Energy Drink (Tiger) on the Renal and Hepatic Systems of Young Mice. Baghdad Sci. J. 2019, 16, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graneri, L.; Lam, V.; D’Alonzo, Z.; Nesbit, M.; Mamo, J.C.L.; Takechi, R. The consumption of energy drinks induces blood-brain barrier dysfunction in wild-type mice. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 668514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasehirli, B.; Inaloz, H.S.; Inaloz, S.S.; Unal, B.; Eralp, A.; Can, I. The Effects of Caffeine on Rat Skin. Int. Med. J. 2001, 8, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Supit, T.; Susilaningsih, N.; Prasetyo, A. Effects of Caffeine Consumption on Autologous Full-Thickness Skin Graft Healing in an Animal Model. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2021, 54, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdemir, O.; Hede, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lineaweaver, W.C.; Arslan, Z.; Songur, E. Effects of taurine on reperfusion injury. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2011, 64, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).