Abstract
Paper can be reused to efficiently manage biomass consumption, meaning that it has potential as an environmentally friendly material. On the other hand, because of high energy usage during the recycling process and transportation inefficiencies, there is a call for the development of technologies that can mitigate this environmental burden. This study evaluated, from a lifecycle perspective, a new technology that can collect and recycle paper within the office. This technology can reduce by over 90% the amount of water used compared with the conventional recycled paper that is pulped and bleached once by the dry process. It also eliminates transportation from paper collection facilities to recycling factories, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This new technology is already in use in Japan, and analyses by user data indicate that evaluation results differ greatly depending on the utilization rate of the machine. In the future, environmental information should be shared by both users and manufacturers, so that users could increase their utilization rate, and manufacturers could develop alternative bonding agents in order to further reduce the total environmental burden.
1. Introduction
Forests mitigate climate change, conserve biodiversity, lessen the risk of natural disasters, and conserve soil, thus providing diverse functionality and value. These roles that forests play are essential assets and services to living things, and thus international efforts are underway to promote sustainable forest management as well as to prevent global warming. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) [1], forests covered a total of 4 billion hectares worldwide in 2015, approximately 31% of the world’s land area. In the five years from 2010 to 2015, the area of forested land has increased significantly through planting in China, Australia, and other countries; however, countries, such as Brazil and Indonesia, have seen a decrease in areas covered by tropical forests—this has given a net annual reduction of 3.31 million hectares [2]. This decrease is attributable to problems, such as felling of forests to make farmland, illegal logging, and forest fires. Focusing on forest fires in particular, a total of approximately 19,900 forest fires were confirmed in Brazil’s tropical rainforest along the Amazon River basin as of September 2019 with serious damage, including the loss of 43,500 km2 of forest between January and August [3]. Despite the situation of global deforestation, issues with marine plastic pollution in recent years mean we have seen a focus on using paper as a replacement, with an attendant increase in demand. Many companies in Japan are using slogans that urge reductions in the usage of plastics, thus promoting the development and usage of paper-based products. However, from the perspective of ever-decreasing forested areas, the effective usage, reuse, and recycling of paper are also important points of consideration.
Paper has a long history as a medium for transmitting information, and with printers becoming widespread, offices are using increasingly large quantities of paper. At present, Japan produces around 7.87 million tons of paper for printing and for communication paper, and around 800,000 tons of PPC (plain paper copier) paper [4]. A characteristic of paper is that as a medium, it is easier to read, understand, and find errors in information than with electronic media. Even in recent years, these characteristics have resulted in a minimal change in the amount of PPC paper production in spite of the prevalence of electronic media and the move towards a paperless society [5]. Paper used in the marketplace is actively recycled so that it can be used more effectively. The paper collection rate in Japan is around 81.6% [6], which is high when compared to other countries, but this high collection rate is primarily due to the recycling of cardboard, magazines, and newspaper, and the collection rate for shredded paper and office paper is low, at under 60% [6]. The reason for this is that office paper often has confidential information printed on it, which needs to be securely disposed of. Additionally, shredding paper reduces its transportation efficiency, and if it is shredded too finely, reuse of the paper itself becomes difficult. Recent years have seen an increase in the use of processing of paper by dissolving, after which this material is mainly reused as cardboard, with only a low proportion of it reused as paper for printing. However, in terms of energy usage, the pulp and paper industry is focusing on energy reductions, and is investing in the development of manufacturing processes that are efficient over the long term, triggered by increasing energy prices, as well as to maintain competitiveness [7,8]. In addition to the above, achieving efficiencies in energy usage is also considered to be the most cost-effective way to reduce CO2 emissions [9]. However, it is important that we recognize not only the impact of the paper manufacturing process but also that of the overall lifecycle, from the procurement of materials through to their disposal. In view of this, up until now, we have actively been using an LCA (lifecycle assessment) for paper [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21].
LCA is a methodological tool for assessing the environmental impact associated with a process, product, or services by identifying and quantifying the energy and materials used, as well as the waste products released into the environment. Many academic papers in the early 2000s discussed energy usage during the production stage while many recent studies tend to focus on waste processes and technical innovations. Furthermore, China had not formerly carried out proper LCA until this point, but given the increased paper consumption there, we are seeing an increase in paper-related academic papers [17]. When focusing on evaluation targets, there are a range of types of evaluations, not just for paper products but also for printing paper, newsprint, and for the paper industry as a whole. Similarly, some evaluation scopes cover only the paper production stage, but there are also articles covering everything from raw materials, production, and transport, through to sales and disposal [10,11,12,14,17,18]. While the majority of these academic papers used the literature to determine activity data, there are some [10] that also conducted interviews with multiple factories, and have highly reliable data. Most of the annual activity data comes from the late 1990s to early 2000s. There is some variance in the results from these academic papers, but this is due to differences in the evaluation scope and selections of energy source at the manufacturing stage, as well as in the disposal methods. In addition, there are academic papers that focus not only on greenhouse gas substances but also on water consumption [22], indicating that there is a large increase in paper-related water consumption. However, simply utilizing recycled paper will not in itself necessarily reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This is because the production stage of recycled paper uses large amounts of water, and other main causes include the energy required during drying processing, the high energy consumption of air blowing during the de-inking process, and greenhouse gas emissions during the collection process.
As mentioned above, research has been underway worldwide into the environmental burden of paper, and research and development is underway into reducing this environmental burden. However, the issue of the trade-off between greenhouse gas emissions and water consumption has not yet been resolved. Given this, Seiko Epson Corporation has developed a new dry-type paper recycling technology. This technology consists of three technologies, “defibration technology” for decomposing used paper into each one pulp fiber, “sheet forming technology” for forming fibers again into a uniform sheet, and “pressing and binding technology” for increasing the fiber density and bonding pulp fibers to each other to create new paper. As a specific aspect, it is possible to reduce CO2 emission and water consumption by this technology. Using this technology not only eliminates the need for both water disposal and drying processing, but because the machine using this technology can produce paper within the office, it also reduces the environmental burden from thte transport required during collection. The aim of this study was to use an LCA to analyze the environmental performance of this paper recycling technology.
1.1. Innovative Paper Recycling Technology (Development of the Dry Paper Recycling Technology that Realizes a New Office Papermaking System)
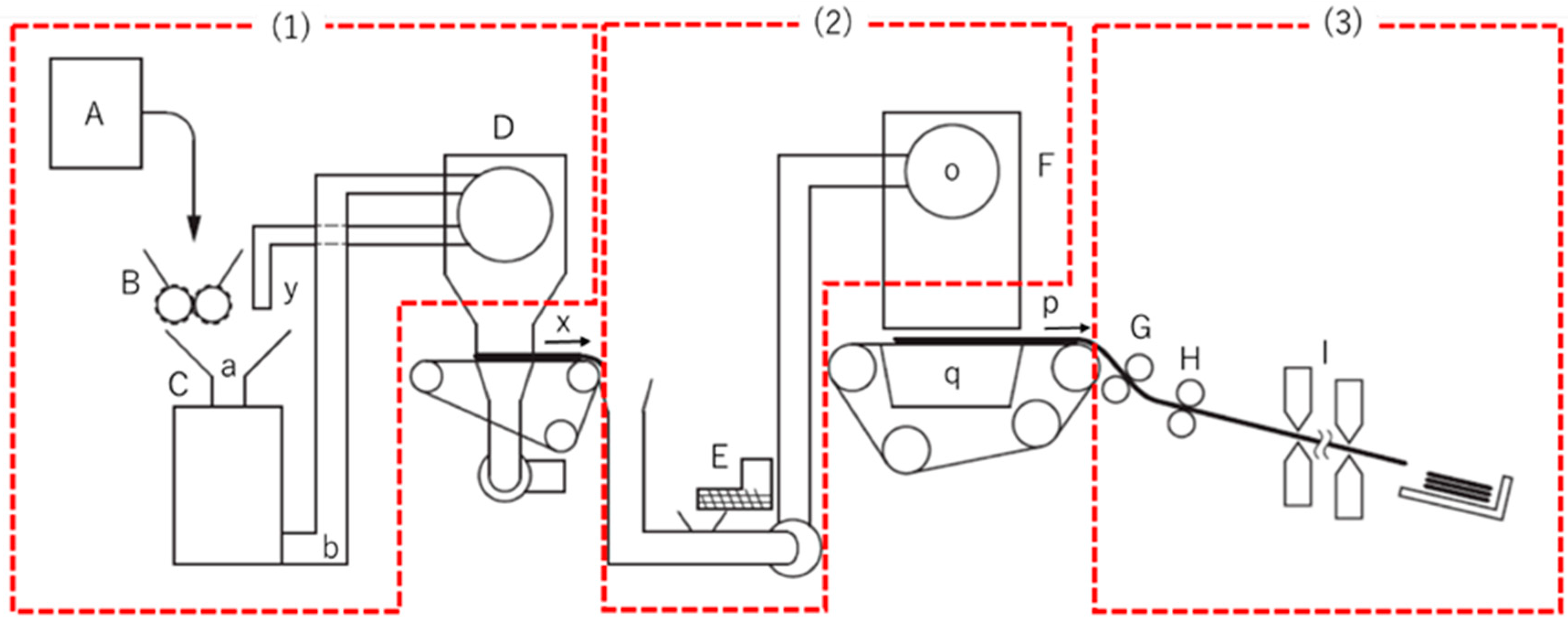
This chapter describes this newly developed dry-type used paper recycling technology. Figure 1 shows a schematic of this technology. This technology can be broadly categorized into three processes.
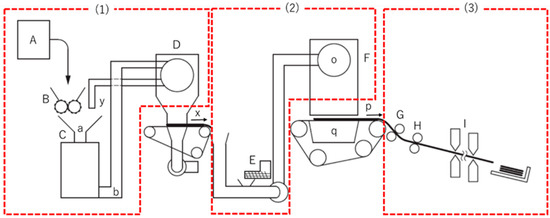
Figure 1.
Dry-type used paper recycling technology process diagram ((1) Defibration process, (2) Binding process, (3) Forming process); (A) Paper feeding section, (B) Shredding section, (C) Defibration section, (D) Selection section, (E) Mixing section, (F) Binding section, (G) Pressurization section, (H) Heating section, (I) Cutting section, (a) Insertion section, (b) Discharge section, (o) Rotating sieve, (p) Mesh belt, (q) Suction mechanism, (x) Following process path, (y) Return path.
(1) “Defibration processing” that degrades used paper into pulp fiber.
(Figure 1 (A) Paper feeding section, (B) shredding section, (C) defibration section, and (D) selection section)
(2) “Binding processing” that mixes a bonding agent to increase strength, and then forms sheets.
(Figure 1 (E) Mixing section, (F) binding section)
(3) “Forming processing” that uses pressure and heat to form sheets of paper.
(Figure 1 (G) Pressurization section, (H) heating section, (I) cutting section)
Furthermore, processes other than those detailed above are classified as “others.”
1.1.1. Defibration Processing
First, the used paper raw material is fed from the paper feeding section (A) to the shredding section (B). Next, in the shredding section (B), this is cut to a size of several millimeters to several centimeters, and then carried to the defibration section (C). In the defibration section, the cut paper is mechanically impacted to weaken the links between the fibers without shredding them. The aim of this procedure is to ensure the strength of the final paper product, and ensure it is uniform and free from unevenness. The defibration section (C) ensures that most of the fiber is evenly flocculated, but some remains uneven. Accordingly, there is a selection section (D) after the defibration section, and the fibers are selected by passing these through a sieve. The uneven fiber is returned to the defibration section (C) using the return path (y), and then is reprocessed to make it even. This minimizes fiber degradation, enabling continuous defibration and feeding to the binding processes.
1.1.2. Binding Processing
In the mixing section (E), material degraded into fiber in Section 1.1.1 is combined with fiber, and pneumatically fed to the binding section (F). In the binding section (F), the material is dispersed using a rotating sieve (o) comprising a cylindrical mesh, and the fiber is discharged at a constant speed and then deposited on a moving mesh belt (p), thus allowing the continuous formation of sheets. In order to continuously form sheets, it is important to ensure good dispersion of the fiber discharged from the rotating sieve (o) so that there is no difference in the density of the fibers on the belt. Additionally, reducing the size of the mesh in the rotating sieve (o) will make it is possible to prevent the discharge of fiber that is still clumped. However, a mesh size that is too small will make it difficult for the material to pass through the sieve, resulting in the sieve becoming clogged by the fiber. The machine was designed to set the selection section (D) sieve mesh size smaller than the rotating sieve (o) mesh size, enabling the continuous production of quality sheets of paper.
1.1.3. Forming Processing
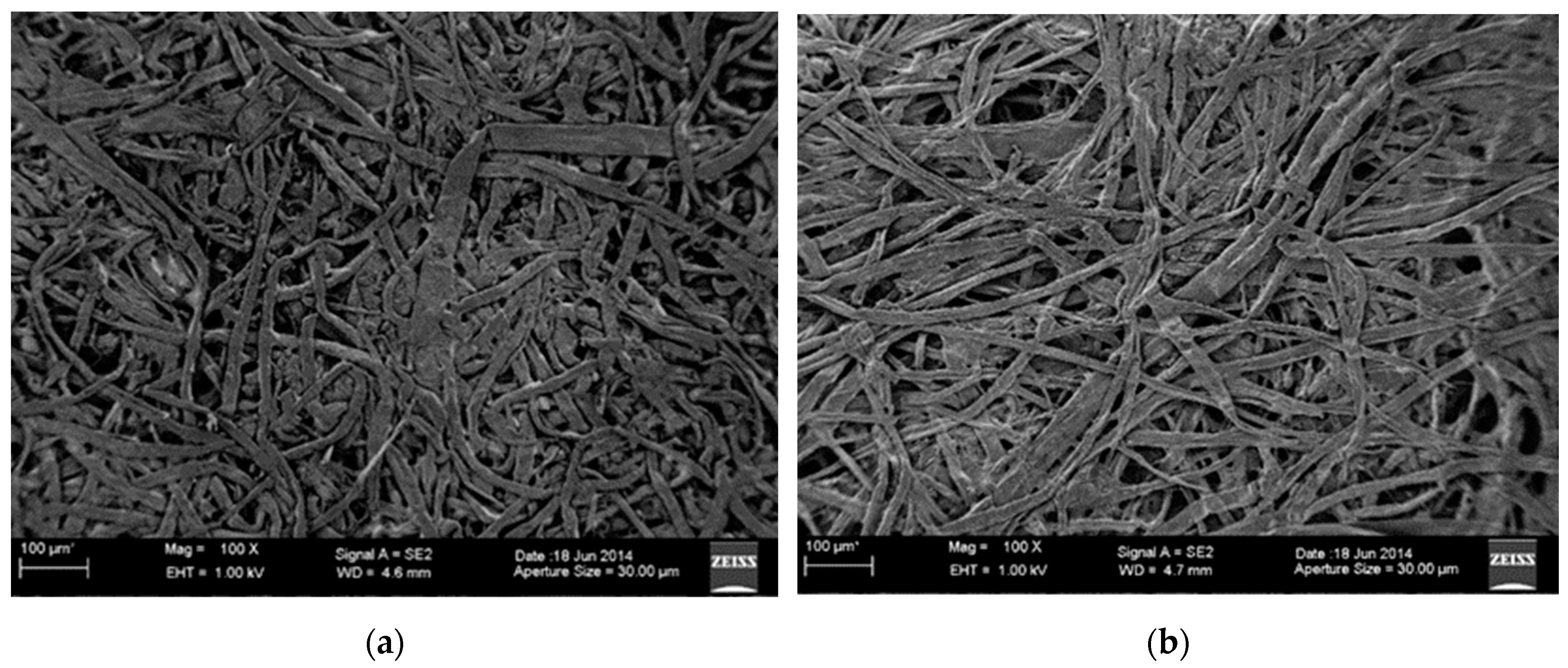
Forming processing increases the density of materials formed into sheets in Section 1.1.2, forming sheets of paper with the fibers bound together. In wet process paper manufacturing, hydroxyls in the cellulose form hydrogen bonds in the process that squeezes out water and dries the paper, thus binding together the fibers in the paper. For this dry-type technology, a powdered bonding agent was developed. Before binding processing, the bonding agent is mixed with the fiber through the mixing section (E), with the fibers in the sheet formed in the binding process having bonding agent applied. This has 1 to 3 tons of pressure applied in the pressurization section (G), increasing its density. After this, the heating section (H) as a whole applies approximately 3600 J of heat, fusing the bonding agent, and bonding the fibers together. We can see that this pressure means that paper manufactured with this method (Figure 2a) has a higher density with the pulp fibers bonded together when compared with conventional wet-type paper (Figure 2b). This technology that uses the dry-type process is recognized as providing the functionality required of PPC paper. Furthermore, the strength of the paper differs depending on the amount of pressure applied. Tensile testing of paper produced using this method showed results of 12 to 15 MN/m2 (density of 0.7 to 0.8/cm3), which has been confirmed as a sufficient strength performance required for PPC paper.
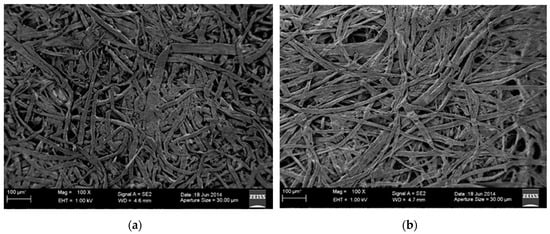
Figure 2.
Comparison image from scanning microscope. (a) Dry fiber paper (DFP) produced with this method (SEM), (b) Commercial plain paper copier (PPC) paper (SEM).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scope of Evaluation and Functional Units
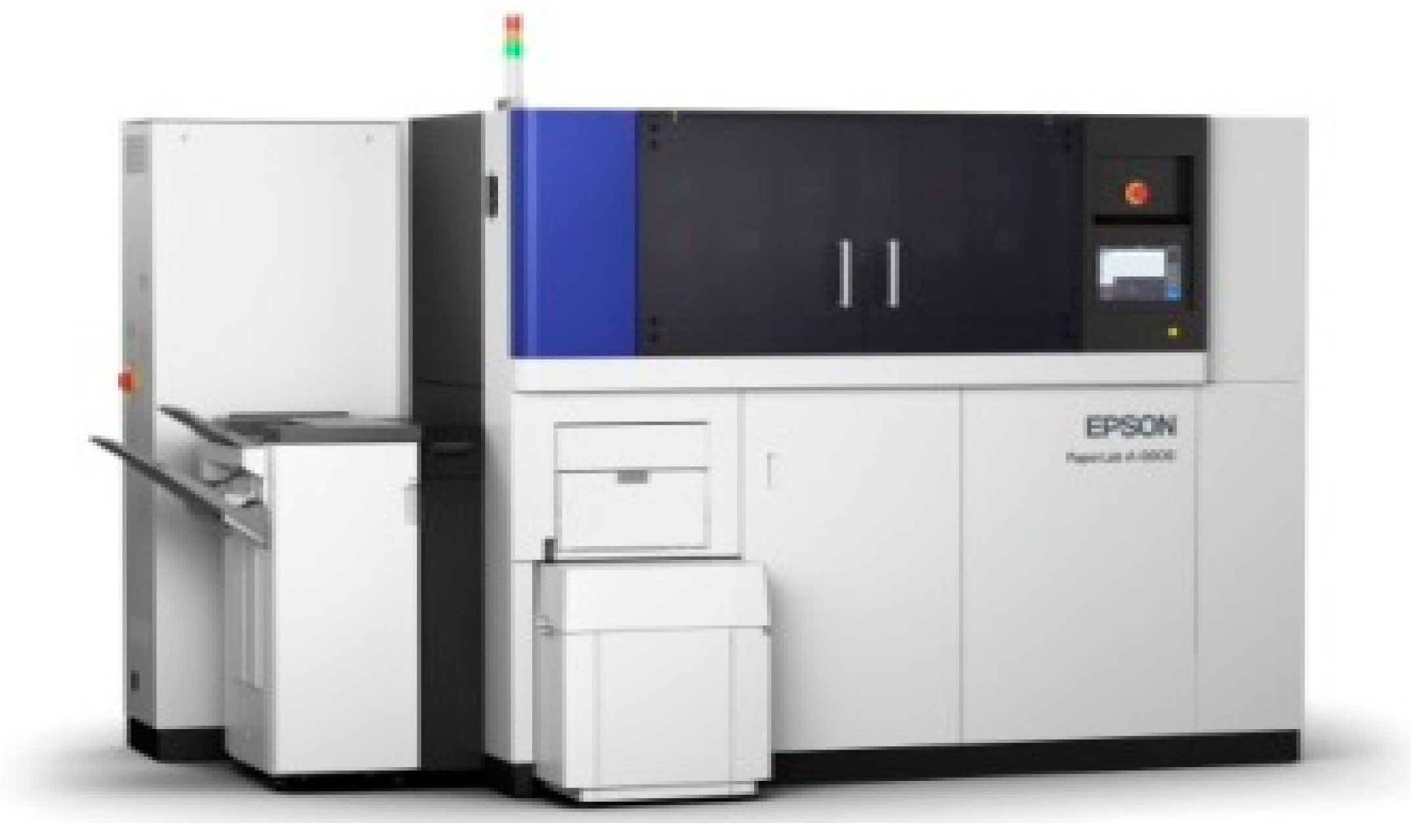
This study applied the fundamentals of the LCA methodology to evaluate the environmental impact of dry fiber paper (DFP) made by a dry-type office paper-making machine (Figure 3 and Table 1) in Japan. LCA can handle hundreds of inputs and outputs at different stages, “cradle-to-grave”, and provides for a means of comparing the impact of different products. In LCA, it is important to define the system being studied, and to determine the system boundaries to aid in narrowing down the elements of the lifecycle inventory. The lifecycle inventory consists of flows into and out of the system boundary. This section describes the functional unit, system boundaries, and data collection method used in this project.

Figure 3.
Dry-type office paper-making machine’s external view.

Table 1.
Dry-type office paper-making machine’s main specifications.
This study covers paper produced using this newly developed dry-type used paper recycling technology. Substances evaluated were CO2 emissions and water consumption. The main reasons for this are that CO2 has been well covered by research up until now, and large quantities of water are used as raw materials and in the production of paper. The functional unit in this study was 1 ton of DFP, and raw materials, energy, manufacture, transportation, and waste treatment were based on this functional unit. Although the ISO 14040 and ISO 14044 standards define the LCA methodology, some necessary flexibility is left to practitioners during implementation, especially regarding the allocation methods and definition of the system boundary.
2.2. System Boundary
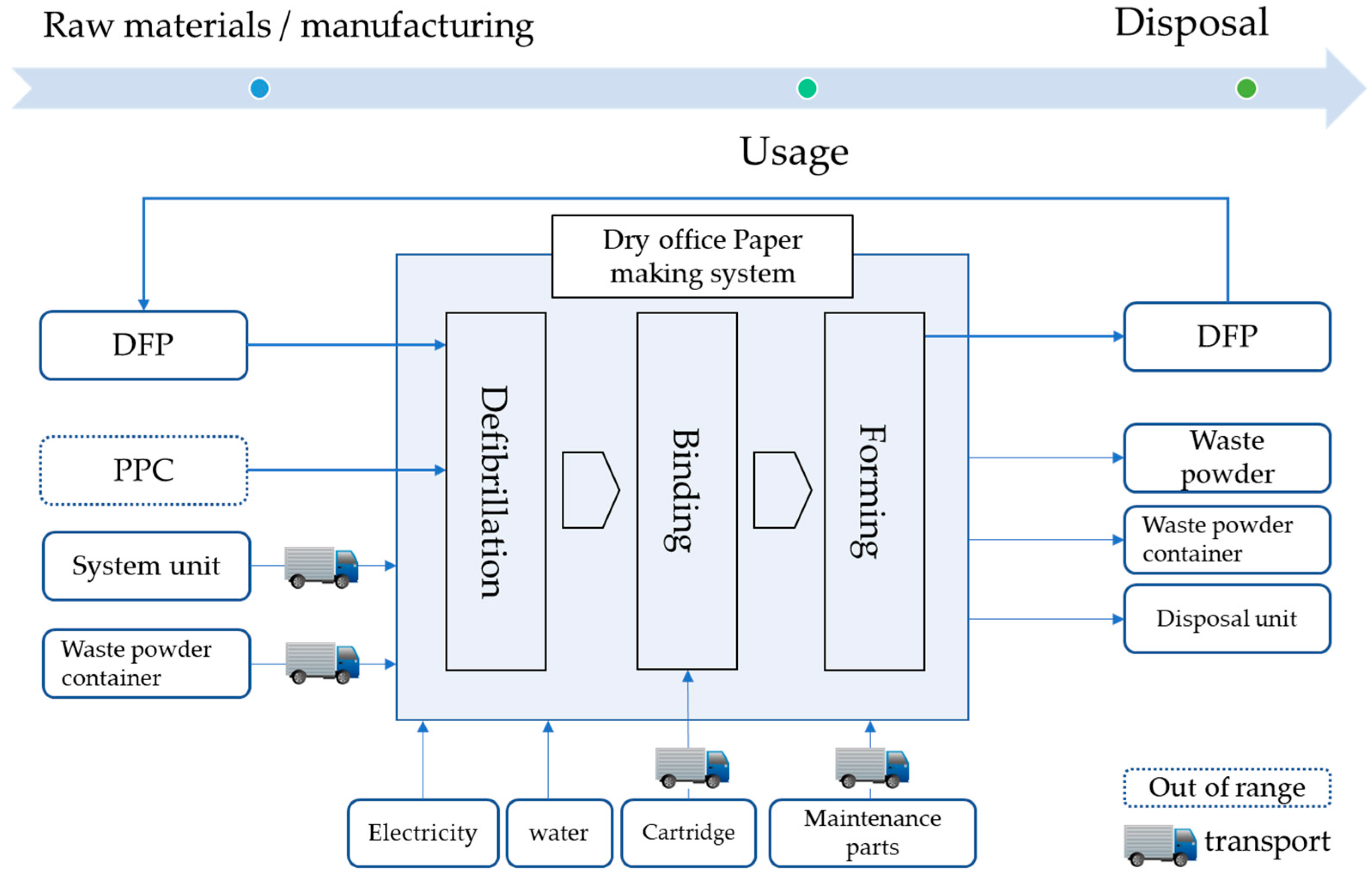
Figure 4 shows the system boundary. This study includes in its evaluation scope the flow from raw materials’ procurement and manufacturing through to disposal. Details for each flow are as follows. Raw materials’ procurement and manufacturing includes parts, unit replacement parts, and cartridge parts required in order to manufacture the main unit. Transport includes transport of the main unit, cartridges, and replacement parts, and usage includes consumption of electricity and water during the paper-making process. Disposal includes the environmental burden incurred from disposal of the main unit, and of the waste generated during the paper production process. However, it does not include the environmental burden from transportation for sales locations and transportation to disposal units, PPC paper being used to feed into the unit, or DFP manufactured by this product being re-fed into the unit.
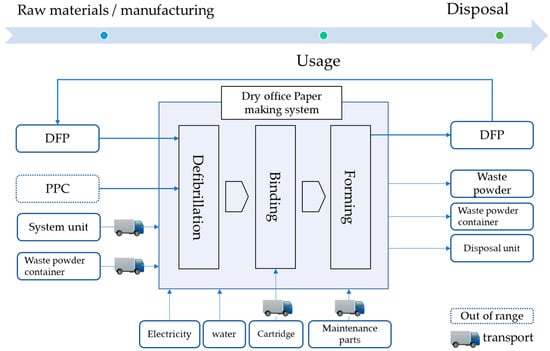
Figure 4.
System boundary of the dry office paper making system. This system includes defibrillation, binding, and forming. Making the producing system, usage, and disposal of this system were considered in LCA.
The system boundary considers the upstream processes associated with DFP production, transportation, and disposal. Figure 5 shows a schematic representation of the system boundary used in this analysis. DFP production requires chemicals, including polypropylene (PP), calcium carbonate, adhesion bond, liquefied, electricity, and water, at various stages in its production.
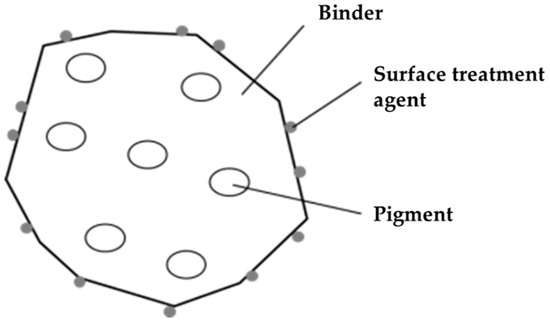
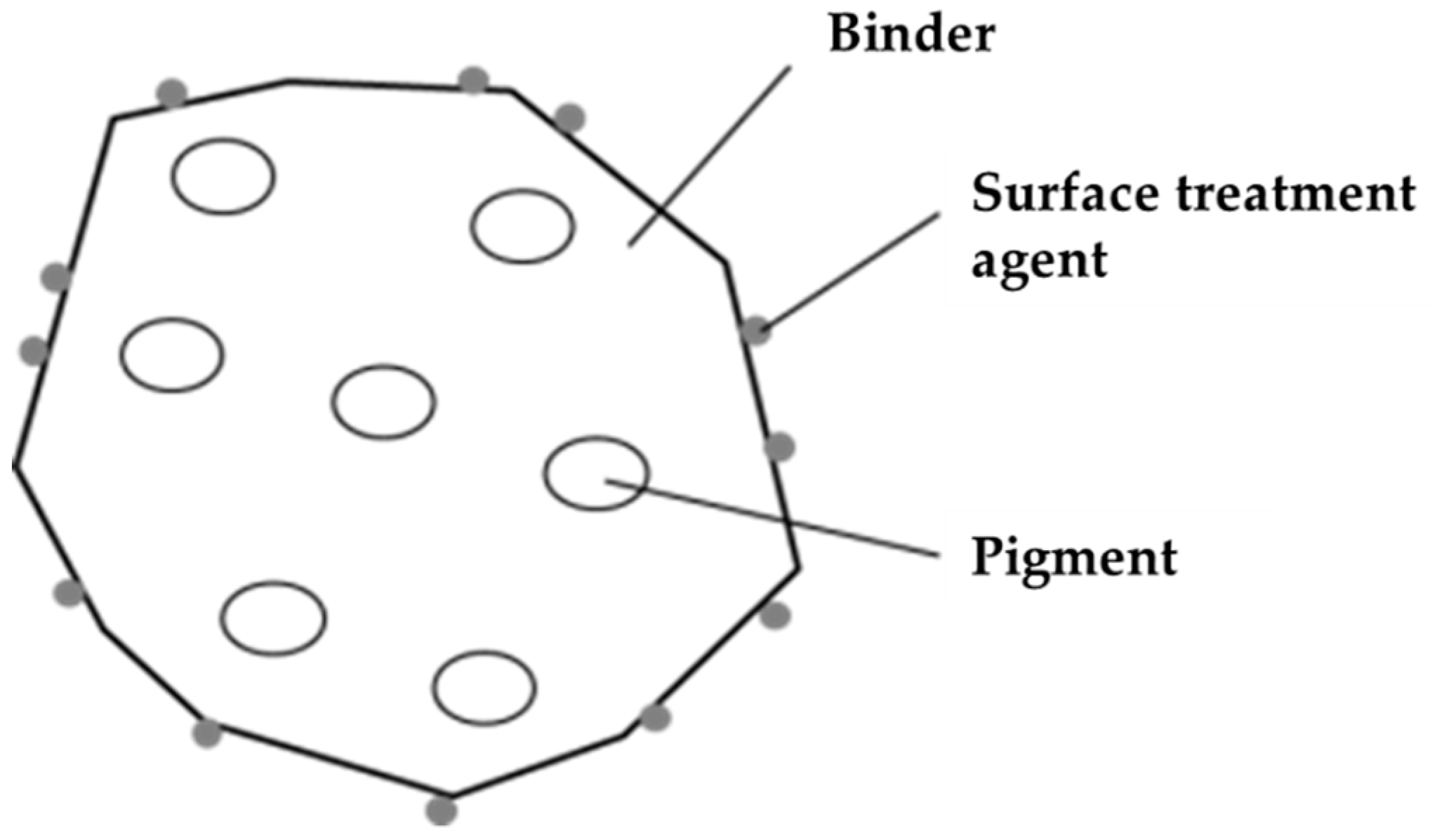
Figure 5.
Bonding agent structure.
2.3. Database and Activity Data
CO2 and water consumption were calculated using the following formula:
where “i” refers to articles, and “s” to substances that impact the environment (CO2, water consumption).
In order to obtain the CO2 emissions and water consumption results, we obtained basic units for the activity data and for the environmental burden.
The inventory analysis sums the emissions and calculates the consumption of energy, raw materials, water, chemicals, transport, wastewater, and solid waste treatment.
The inventory database used as the environmental burden basic units is as follows. CO2 emissions by sectors were obtained from Embodied Energy and Emission Intensity Data for Japan Using Input-Output Tables (3EID) developed by National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES) [23], CO2 emissions by processes from Inventory Database for Environmental Analysis (IDEA) developed by the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology [24], and finally the power generation inventory from the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy [25]. In the power generation results [25], the power company basic units and the amount of power generation are disclosed. This study used a weighted average of actual values from major power companies, creating and using power consumption basic units. Water consumption used the water consumption basic unit database developed by Ono et al. [26].
These databases were used to simulate the environmental burden. A generic database based on an input-output table was used to estimate the contributions of unavailable data. These databases were applied to the Japanese input-output table. 3EID covers the greenhouse gas emission intensity (CO2, CH4, N2O, etc.) and the water footprint inventory database covers the water consumption intensity (total water consumption, rain, surface and ground water). Both databases have about 400 sectors. As the databases applied in input-output analysis are generally based on monetary data, we used the unit price list released by the Japanese government to convert these data into quantitative data for 3571 sectors.
The activity data for this study were provided by Seiko Epson Corporation, which is the largest DFP producer in Japan. The data year was 2018. Including components in the product body would increase the number of activity data items to several thousand, therefore these individual components are not listed individually. However, important items (power consumption for office paper-making machines, for the production of bonding agent, and for paper making) are listed below.
2.3.1. Office Paper-Making Machine
Information regarding the office paper-making machine main unit is categorized by the process (defibration, binding, forming), exterior, and common parts (Table 2). Furthermore, parts information for each unit is based upon that from the manufacturer of the office paper-making machine, with activity data obtained per part.

Table 2.
Unit names and numbers of parts by process, exterior, and common parts.
2.3.2. Bonding Agent
As detailed above, a bonding agent is used to bind paper fibers together, thus creating the paper. The bonding agent is a powder mainly consisting of a thermoplastic resin. For its structure, the binder contains pigments, with a surface treatment agent applied to the exterior surface of the powder (Figure 5). Its composition is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Bonding agent composition.
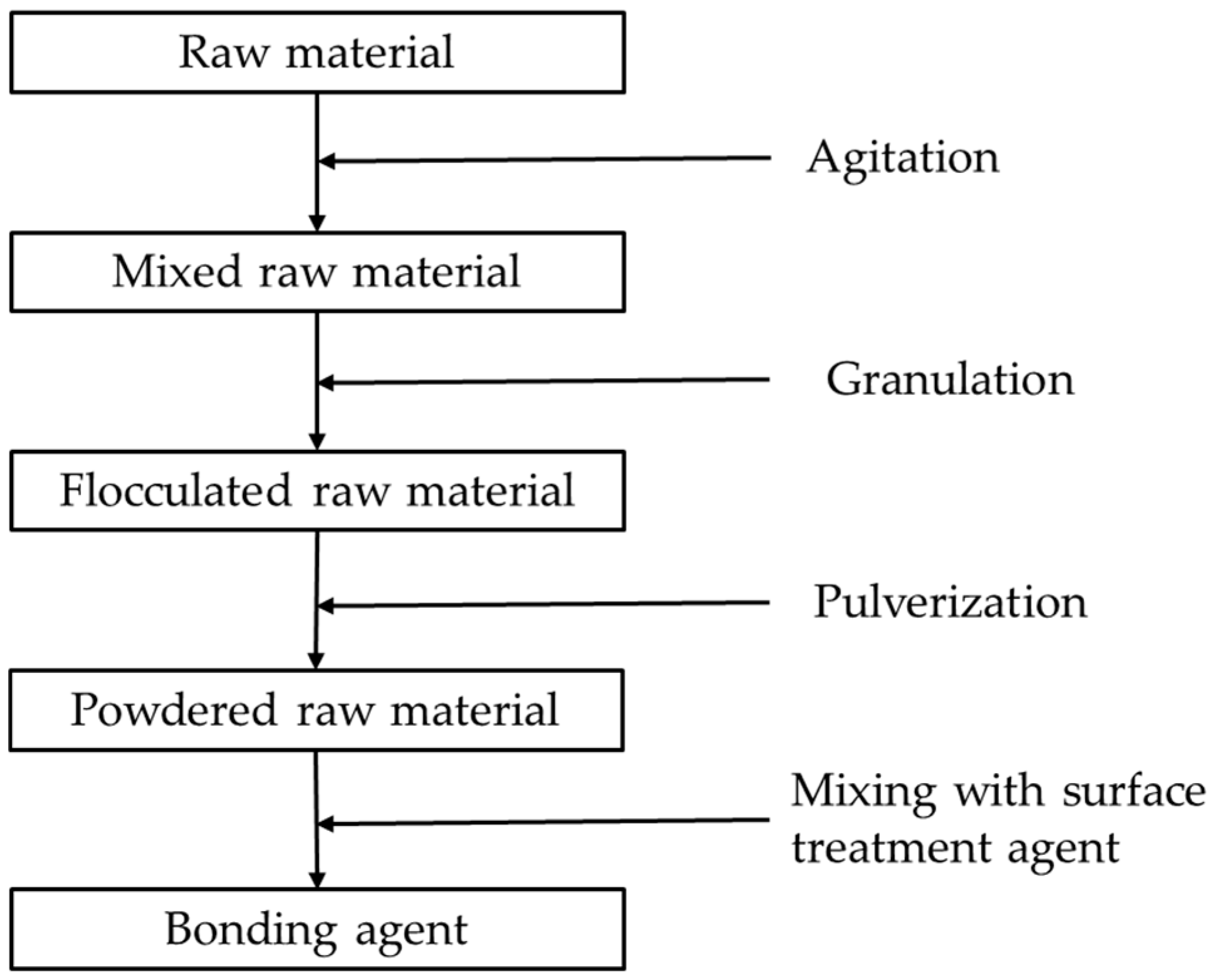
The manufacturing process for the bonding agent fully agitates and mixes together its raw materials, and then temporarily forms these into a mass. This mass is again pulverized, and then a functional surface treatment agent (for fluidity) as well as pigments (as necessary) are applied to the exterior surface. Figure 6 shows the bonding agent manufacturing process. Energy consumption and input/output data for all substances in all processes shown in Figure 6 were obtained from the primary supplier.
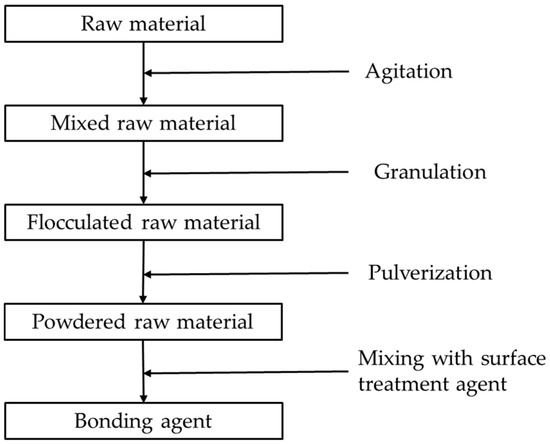
Figure 6.
Bonding agent manufacturing flow.
2.3.3. Power Consumption at the Paper-Making Stage
This study measured the amount of power consumed as the basic unit for processes in the paper-making operation, from start-up and paper production through to shut-down, and applied these units for evaluation. As mentioned before, the electrical power consumption basic unit was calculated based upon data disclosed by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy.
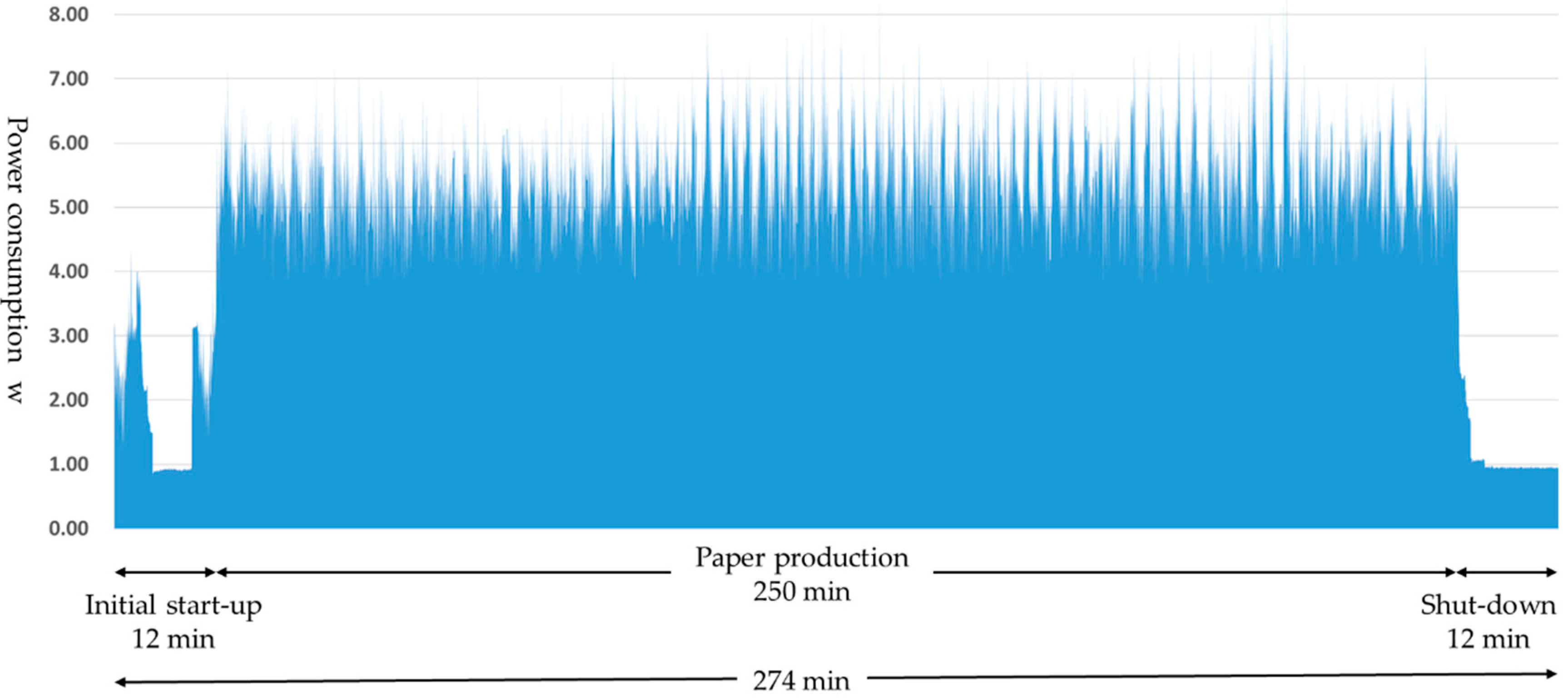
Figure 7 shows an example of the power consumption at the paper-making stage. Both start-up and shut-down take approximately 12 min, consuming a total of 0.74 kWh electricity. In total, 250 min of paper production produces 3040 sheets, consuming 21.75 kWh of electricity. As shown in Figure 7, variances in the power consumption in paper production are because of differences in the quantities of paper fed into the defibration section as well as in the quantities of materials returned from the selection section (separator drum unit) to the defibration section. From this, we can see that this series of processes consume a total of 22.49 kWh of electricity. Power consumption per sheet of paper is 7.40 Wh. Furthermore, these measurements were repeated three times, confirming their reproducibility (1st time: 22.50 kWh, 2nd time: 21.97 kWh, 3rd time: 22.62 kWh). The weight of DFP manufactured using this technology is 5.7 g per sheet, giving a power consumption of 1298.25 kWh (7.40 Wh/5.70 g × 1,000,000.00 g) per ton as the functional unit.
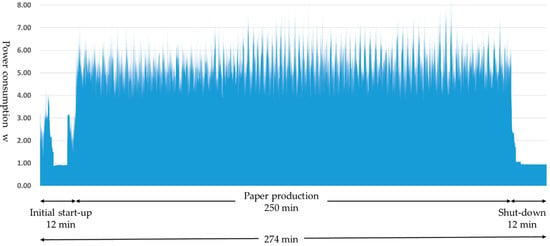
Figure 7.
Example measurement results for power consumption.
3. Results
3.1. CO2 Emissions
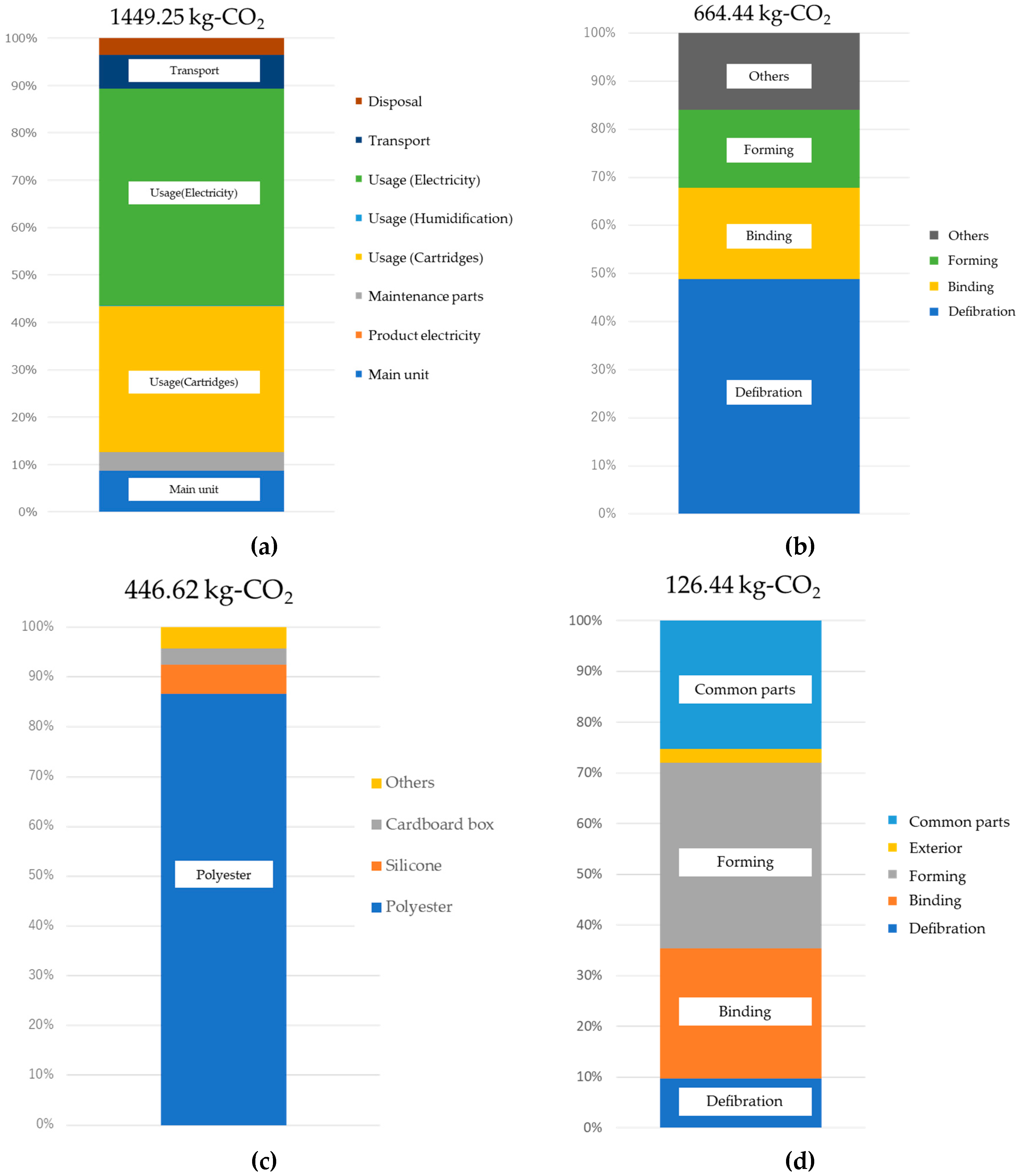
Figure 8a shows CO2 emissions throughout the whole lifecycle. These results show 1449 kg-CO2 per ton of paper. Looking at these emissions through each stage of the lifecycle, the discharge quantity in the usage stage had the largest influence on the results, comprising approximately 80% of the total. The next largest was the manufacturing of office paper-making machines, comprising approximately 10% of the total. In comparison to these, there was a low environmental burden for assembly and disposal, with each of these at below 5% of the total. CO2 emissions for transportation were also relatively low, because the implementation of this technology means used paper within the office can be used to produce DFP, without the need to transport it to an external facility from the office. Focusing on the usage stage, there was a high environmental burden from the power consumption and the production of cartridges including adhesives, comprising 50% and 30% of the total, respectively.
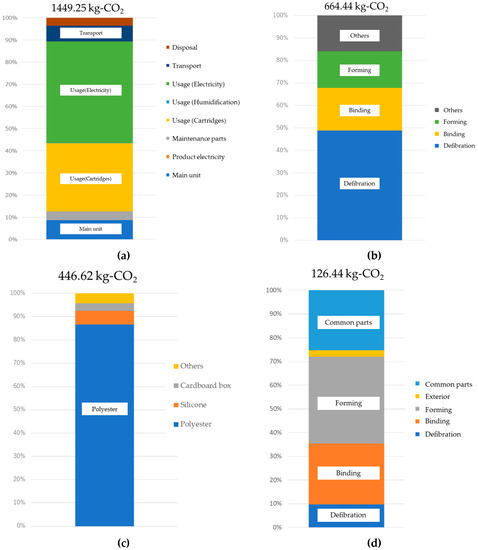
Figure 8.
Office paper-making machine’s CO2 emissions calculation results: (a) Whole lifecycle CO2 emissions and breakdown, (b) Power consumption breakdown at the usage stage, (c) CO2 emissions breakdown with a focus on cartridges, (d) CO2 emissions breakdown during the production stage.
Accordingly, Figure 8b shows a breakdown of the CO2 emissions in the usage stage. Among the defibration, binding, and forming processes, the defibration process had the highest emissions, taking up approximately half of the total, because this process requires time to break down paper into fiber, and thus takes longer than the other processes. Additionally, binding processing and forming processing each comprise under 20% of the total, with a large impact from the binding section heater and from the heater used during forming. This study assumes usage within Japan, and therefore uses CO2 emissions basic units corresponding to Japanese power generation. Accordingly, power structures and generation efficiency differ between countries and regions in which the product is used, meaning that CO2 emissions will also differ widely depending on these parameters.
Next, Figure 8c shows a breakdown of the CO2 emissions from the bonding agent cartridge. These results show a large proportion of CO2 emissions from the production of polyester, a major component in the bonding agent. Accordingly, when looking towards further future reductions in the environmental burden, the important parameters are the efficiency of the defibration section and the reduction of the bonding agent quantity used.
Finally, Figure 8d shows a breakdown of the CO2 emissions in the production stage. By process, this is defibration (9.7%), binding (25.7%), and forming (36.7%), with forming comprising the largest proportion. The reason that the forming process has the highest ratio is the large sizes of the pressurization and heating units used during manufacturing, with a corresponding large environmental burden from the procurement of these materials.
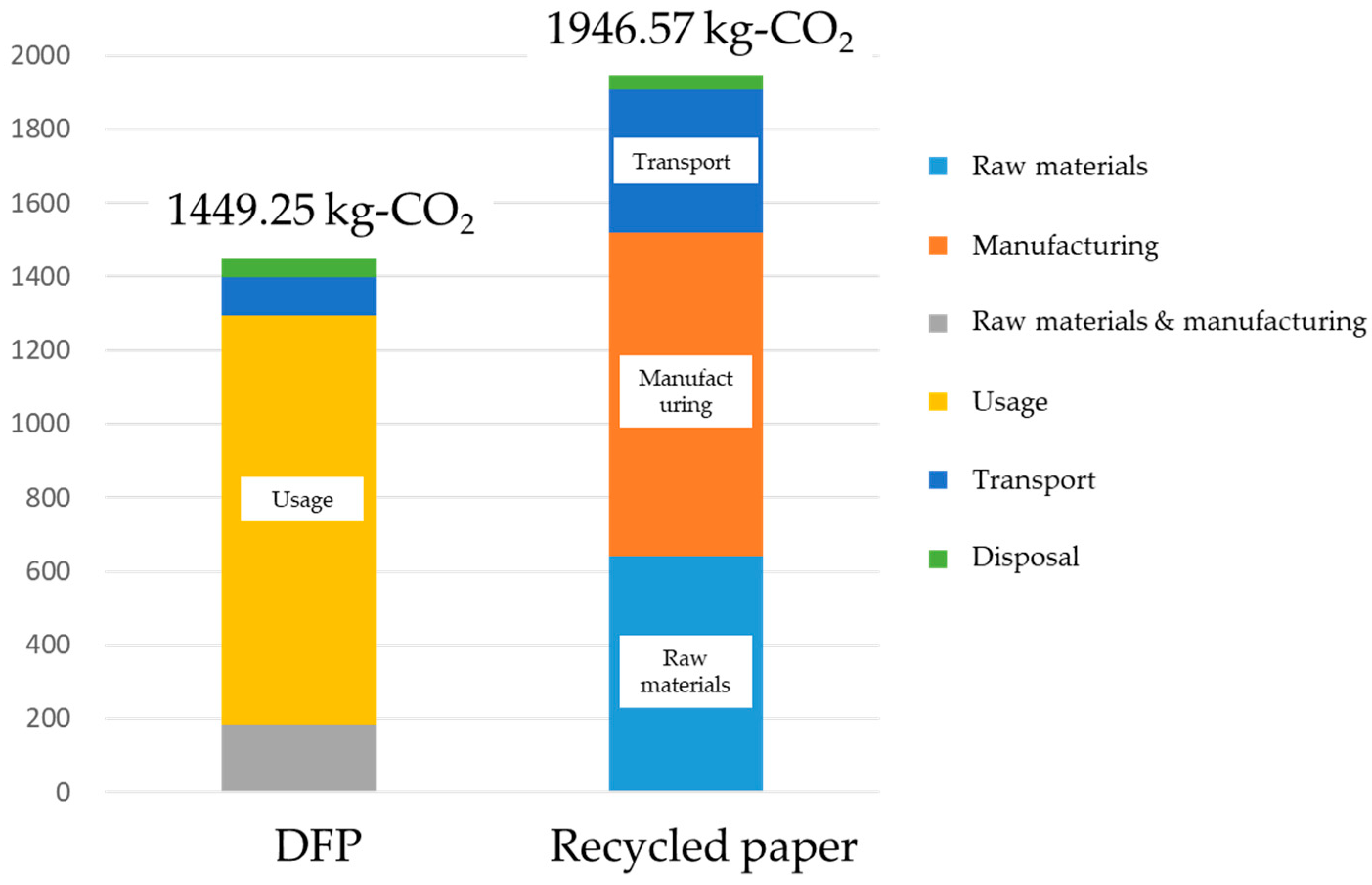
Next, the results from this study were compared with the case of recycled paper (Figure 9). To calculate the CO2 emissions for recycled paper, CO2 emissions until production used data from the Japan Paper Association [27], and emissions from transport and sales used data from Environmental Hotspot Analysis (EHSA) [28]. It was shown that utilization of the dry-type paper recycling technology enabled a total reduction of 500 kg, or 26% in CO2 emissions. In particular, this technology produced reductions in the environmental burden up until the procurement of pulp, and in the delivery and sales of the product. However, CO2 emissions through the use of this technology in the production stage of DFP were comparatively high. Therefore, as shown previously, further study is required in how to reduce the environmental burden by reducing power consumption and the amount of bonding agent used.
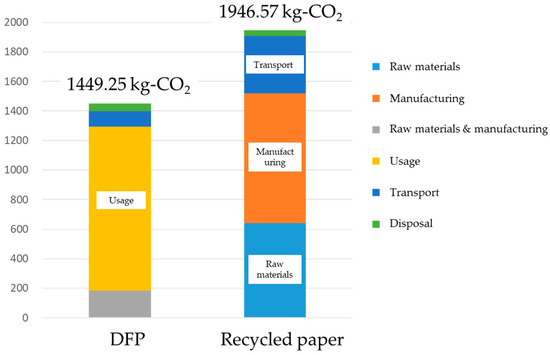
Figure 9.
Comparative results in CO2 emissions between the office paper-making machine (left) and recycled paper (right).
3.2. Water Consumption
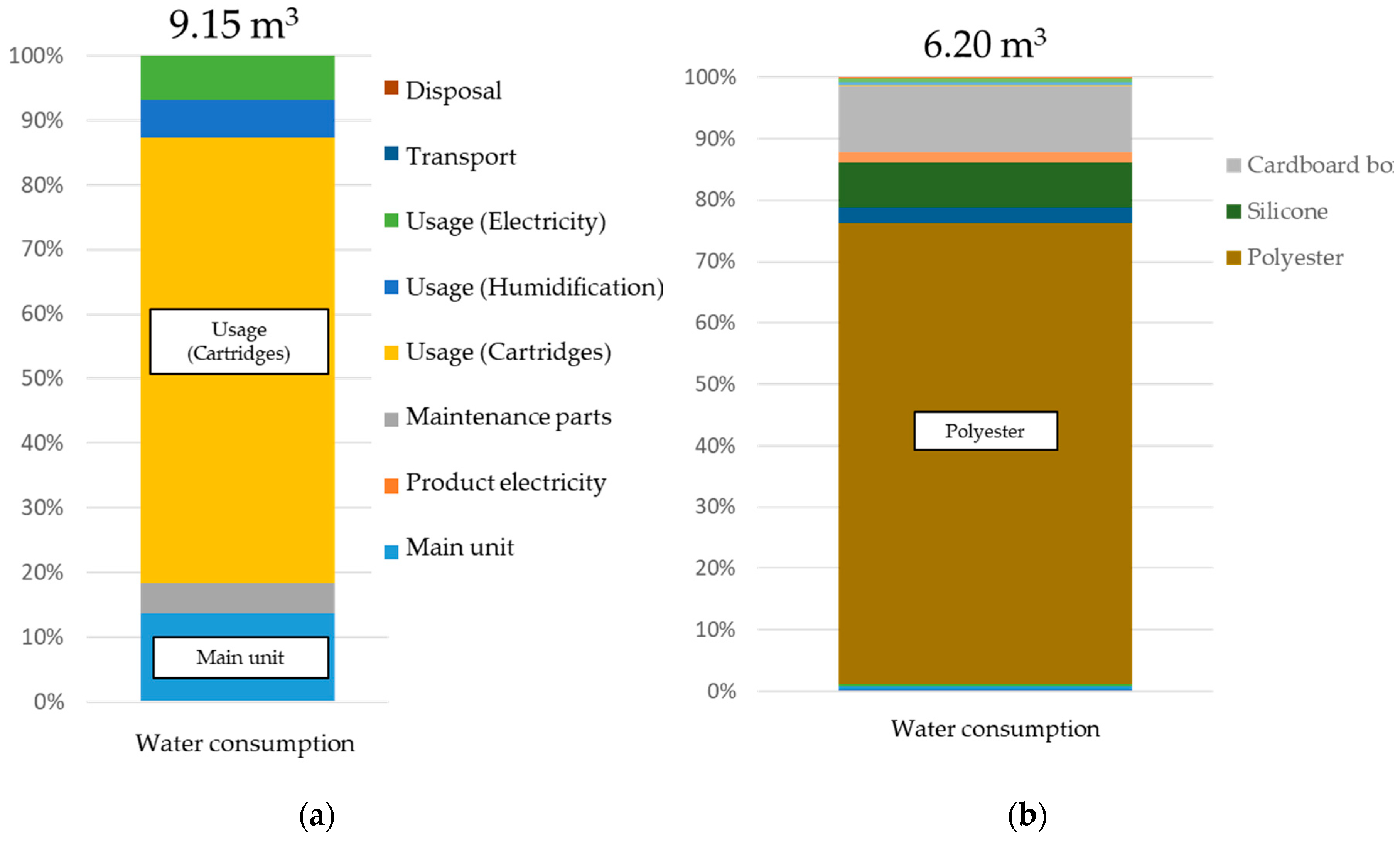
In addition to CO2 emissions, this study also focused on water consumption. Figure 10a shows the water consumption results when using this technology. Water consumption per ton of product is approximately 9 m3, and as with CO2 emissions, the usage stage was responsible for more than half of the total. However, the production of cartridges had high water consumption, rather than power consumption. Figure 10b shows a breakdown of the water consumption focusing on cartridges. As with CO2 emissions, there was high water consumption (approximately 75%) until the production of materials with polyester as a main ingredient, with packaging and external additives around 10% each.
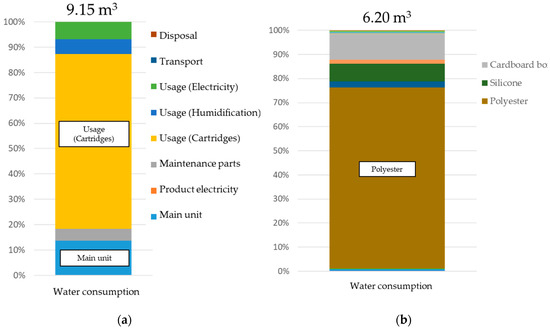
Figure 10.
Water consumption for office paper-making machines (a) and with a focus on cartridges (b).
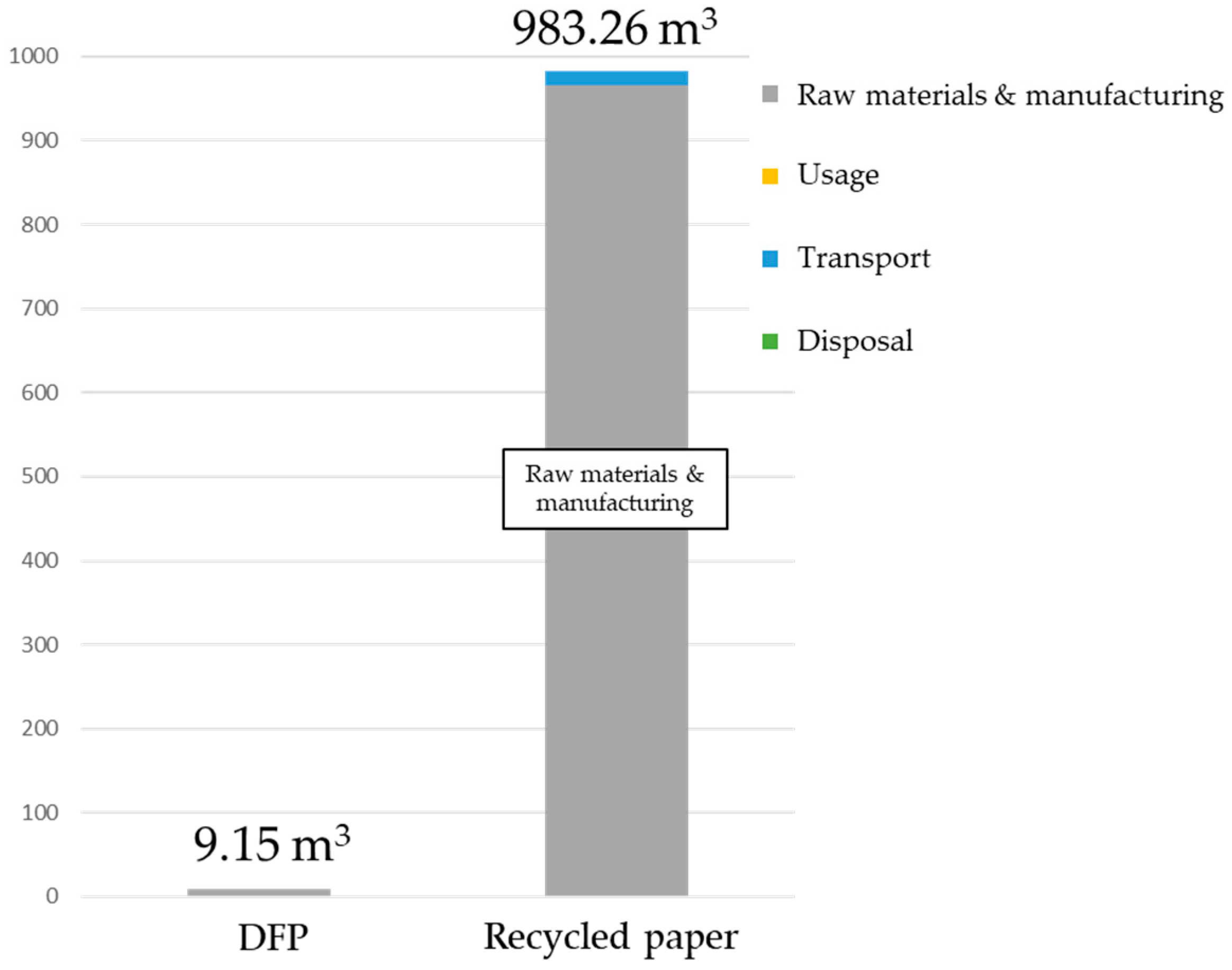
We compared the results above with existing studies (Figure 11). This comparison used data from the Japan Paper Association [27] and the Water Footprint Network (WFN) [22]. The WFN [22] has results for three types of printing paper (broadleaf, softwood, and eucalyptus), but as Japan mainly uses domestic and imported broadleaf, this study used the figures for broadleaf. Water consumption for the production of 1 ton of paper comes to 965 m3. The water consumption from the distribution of PPC paper from Ono et al. [24] was added to this, giving a total of 983 m3. Compared to the water consumption for PPC paper, that for producing 1 ton of DFP was approximately 9.15 m3, roughly 1% of that for PPC paper. The reason for this is that printing paper requires large amounts of rainwater in order to grow wood and to produce pulp, whereas DFP reduces the consumption of virgin pulp. Furthermore, because it uses a dry-type production process, the water used during the production process is also significantly reduced. There is high water consumption during the production stage of wood and pulp, which comprise the raw materials used to make paper as well as during the paper-making stage, but this technology obviates the need for this production, thus limiting water consumption during the paper-making stage.
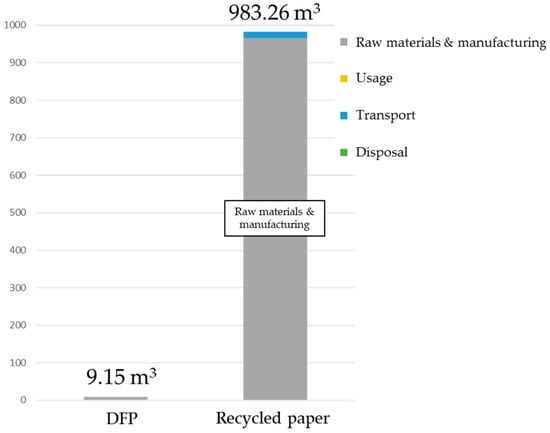
Figure 11.
Comparative results in water consumption between the office paper-making machine and recycled paper.
4. Discussion
This study used the production of 1 ton of paper as its functional unit. Note that the environmental burden per unit will differ depending on the utilization rate of the office paper-making machines. Fundamentally, evaluations based on actual specification data are desirable; however, since this system has only just entered the market, there is insufficient data to set usage scenarios. Therefore, this evaluation was based on 8 h of operation per day.
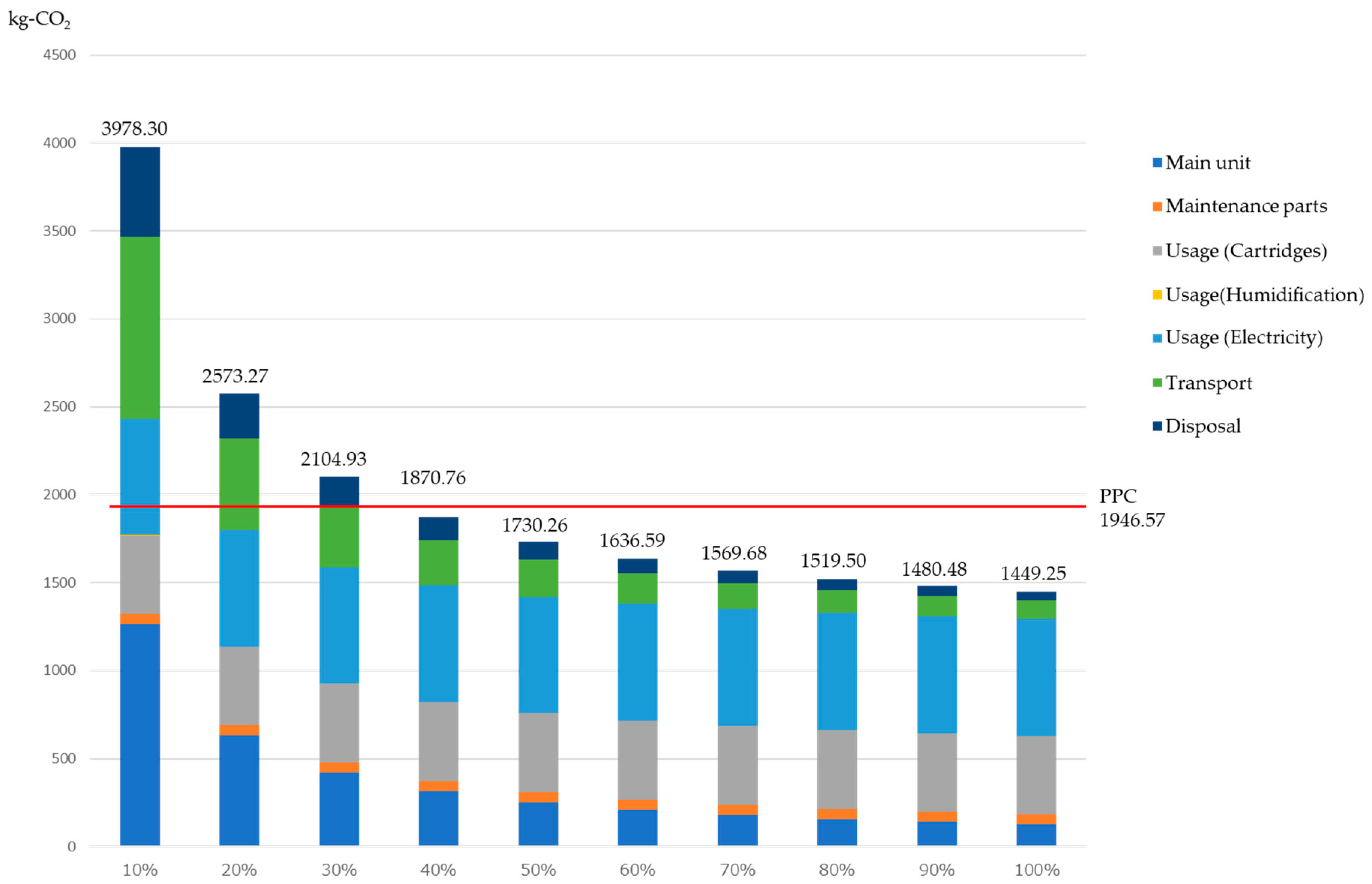
This section evaluates the sensitivity of CO2 emissions to variances in the product utilization rate. With 100% utilization set at 8 h per day, we ran simulations at between 10% to 100%, with results of the comparisons of CO2 emissions for the manufacture of recycled paper (Japan Paper Association) shown in Figure 12. The lowest CO2 emissions were obtained for the 100% utilization rate scenario, at 1449 kg-CO2, whereas emissions for the 10% scenario were 2.8 times higher, at 3975 kg-CO2. A breakdown of CO2 emissions shows the environmental burden from cartridges as 31% and that of electrical power usage as 46% in the 100% utilization rate scenario, comprising approximately 80% of the total emissions in the usage stage. On the other hand, in the 10% utilization rate scenario, the manufacture of the main unit comprised 32%, transport 26%, and disposal 13%, with emissions in other than the usage stage comprising more than half of the total.
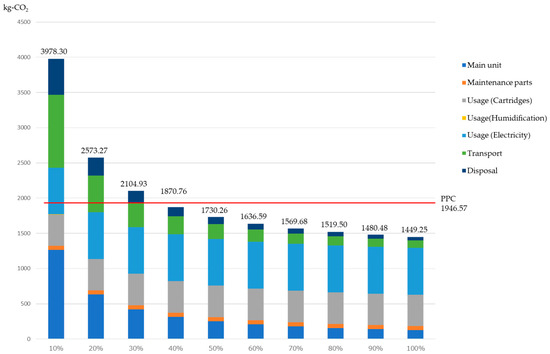
Figure 12.
Sensitivity analysis and comparison when changing the utilization rate of the office paper-making machine.
The reason for this is while the per-unit environmental burden for the production of paper at the usage stage is unchanged, that for manufacturing and transport changes, and becomes relatively higher as the utilization rate lowers. From the above, it is clear that effective reduction strategies will differ depending on how this technology is utilized by users. Usage of the office paper-making machine at the 100% utilization rate is expected to provide a reduction in CO2 emissions of roughly 500 kg. However, lower utilization rates have a corresponding increase in per-unit CO2 emissions, giving less of a reduction in the environmental burden than with recycled paper. The environmental burdens intersect at a utilization rate of 36%. Results showed that with a utilization rate above this, the office paper-making machine has a lower environmental burden, but with a utilization rate below 36%, the environmental burden increases. A utilization rate of 36% corresponds to approximately 3 h of usage daily. This should act as a guide for users who are anticipating using this product to reduce their environmental burden.
The study above clarified the following. Firstly, increasing the utilization rate can increase the per-unit environmental burden reduction effect. Therefore, it is important to promote usage of this technology as an alternative. There is a need to visualize environmental information and convey this to a wide range of stakeholders, including manufacturers, users of paper-making machines, and users of paper, and to strive towards increasing the collection rate for used paper. We need to communicate to not only manufacturers but also users of the office paper-making machines and of paper the fact that the utilization rate has a large impact on the overall results, and to increase the collection rate for used paper. Next, given that environmental burden reduction measures differ depending on the utilization rate, it is absolutely necessary that we fully understand the usage conditions of users. If there is a high utilization rate, there will also be high power consumption and burden from the usage of the bonding agent. Therefore, there is a need to make further energy savings and increase usage efficiency for the bonding agent, as well as to prioritize the usage of renewable energy. On the other hand, a low utilization rate means that the environmental burden from the manufacture of paper-making machines and from transport becomes relatively higher; therefore, this becomes an issue of reviewing raw materials, costs, and parts, as well as achieving efficiencies in delivery.
5. Conclusions
Recycled paper has been widely used to reduce the land usage required for forestry; however, substantial consumption of energy and water is still required in the production of recycled paper, and this requires the development of further measures in order to reduce the environmental burden. This study focused on an innovative technology for the dry-type production of paper as developed by Seiko Epson Corporation. Using this technology not only eliminates the need for both water disposal and drying processing, but also by producing paper within the office, reduces the environmental burden from transport required for paper collection. The aim of this study was to analyze from an LCA perspective the environmental performance of this innovative paper recycling technology.
The study showed that the use of this technology enables a reduction of 26% in CO2 emissions, and a 99% reduction in water consumption over similar general PPC paper. Focusing on CO2 emissions, when compared to PPC paper, this shows a large contribution in reductions in the production and transport stages, and a large contribution to decreased water consumption attributable to reduced usage of raw materials. The CO2 emissions results show that there is a high environmental burden from power consumption in the production and usage of cartridges. Therefore, further studies will need to look at making this technology more environmentally friendly, including considerations of the used quantities of and materials selection for the bonding agent used within the cartridge, as well as energy savings during usage. Additionally, evaluation results differ significantly depending on users’ utilization rates. Therefore, it is necessary to convey information to the users of office paper-making machines and paper, and to improve the collection rate of paper. As a limitation of this study, this study was evaluated assuming that all processes were performed in Japan. Therefore, it is not right to compare with other countries’ PPC paper. In case of comparisons, it is necessary to make evaluations using primary data, usage conditions, and an environmental load database in specific countries and regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.O. and N.I.; methodology, Y.O. and N.I.; software, Y.O.; validation, Y.O.; formal analysis, Y.O.; investigation, Y.O.; resources, Y.O., M.H., K.Y. and T.O.; data curation, Y.O.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.O. and N.I.; writing—review and editing, Y.O. and N.I.; visualization, Y.O.; supervision, N.I.; project administration, Y.O. and N.I.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessments. Available online: http://www.fao.org/forest-resources-assessment/past-assessments/fra-2015/en/ (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- MAFF. Annual Report on Forest and Forestry in Japan. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/e/data/publish/attach/pdf/index-169.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- NIKKEI. Amazon Fires. Available online: https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXMZO50483600S9A001C1000000/ (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- METI. Production Dynamic. Available online: https://www.meti.go.jp/statistics/tyo/seidou/result/ichiran/08_seidou.html (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- Nakayama, M. Development of The Dry Paper Recycling Technology Which Realizes a New Office Papermaking System. Jpn. Tech. Assoc. Pulp Paper Ind. 2018, 72, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Paper Recycling Promotion Center. Japanese Paper Recycle. Available online: http://www.prpc.or.jp/document/publications/japan/ (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- Gaudreault, C.; Samson, R.; Stuart, P.R. Energy decision making in a pulp and paper mill: Selection of LCA system boundary. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A.; Wenzel, H. Paper waste—Recycling, incineration or landfilling? A review of existing life cycle assessments. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, S29–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, D.K.; Gustafsson, S.; Wangel, J.; Höyer, M.; Lundqvist, P.; Svane, Ö. Energy at your service: Highlighting energy usage systems in the context of energy efficiency analysis. Energy Effic. 2011, 4, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Yaguchi, T. The LCI Calculation Method for LCA of Pulp and Paper Products. Japan Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry. Kami Pa Gi Kyo Shi 2002, 56, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, E.; Dias, A.; Arroja, L.; Capela, I.; Pereira, F. Application of life cycle assessment to the Portuguese pulp and paper industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2003, 11, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.C.; Arroja, L.; Capela, I. Life Cycle Assessment of Printing and Writing Paper Produced in Portugal. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2007, 12, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manda, B.M.K.; Blok, K.; Patel, M.K. Innovations in papermaking: An LCA of printing and writing paper from conventional and high yield pulp. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 439, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghose, A.; Chinga-Carrasco, G. Environmental aspects of Norwegian production of pulp fibres and printing paper. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 57, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghinea, C. Life cycle assessment of waste management and recycled paper systems. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Sevigne-Itoiz, E.; Gasol, C.M.; Rieradevall, J.; Gabarrell, X. Methodology of supporting decision-making of waste management with material flow analysis (MFA) and consequential life cycle assessment (CLCA): Case study of waste paper recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 105, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Li, X. Environmental assessment of recycled printing and writing paper: A case study in China. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurijssen, J.; Marsidi, M.; Westenbroek, A.; Worrell, E.; Faaij, A. Paper and biomass for energy? The impact of paper recycling on energy and CO2 emissions. Resources. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Y. Comparisons of four categories of waste recycling in China’s paper industry based on physical input–output life-cycle assessment model. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatoutchoup, F.D. Optimal rate of paper recycling. For. Policy Econ. 2016, 73, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’hamdi, A.I.; Kandria, N.I.; Zerouale, A.; Blumberga, D.; Guscac, J. Life cycle assessment of paper production from treated wood. Energy Procedia 2017, 128, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Footprint Network. The Green and Blue Water Footprint of Paper Products: Methodological Considerations and Quantification. Available online: http://waterfootprint.org/media/downloads/Report46-WaterFootprintPaper_1.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- NISE. 3EID Embodied Energy and Emission Intensity Data for Japan Using Input-Output Tables. Available online: http://www.cger.nies.go.jp/publications/report/d031/jpn/datafile/index.htm (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. IDEA. Available online: http://www.idea-lca.jp/index.html (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- Agency for Natural Resources and Energy. Power Survey Statistics. Available online: https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/statistics/electric_power/ep002/results_archive.html#h30 (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- Ono, Y.; Motoshita, M.; Itsubo, N. Development of water footprint inventory database on Japanese goods and services distinguishing the types of water resources and the forms of water uses based on input-output analysis. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Paper Association. Outline of Calculation of Paper LCI Data. 2006. Available online: https://www.jpa.gr.jp/en/ (accessed on 25 December 2019).
- EHSA. Toward the Promotion of Green Procurement using Environmental Hotspot Analysis. Available online: http://www.comm.tcu.ac.jp/itsubo-lab/lcaproject/products/research/files/research_01.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2019).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).