Below the water column depths, marine sediments harbor a vibrant tapestry of life that underpins a variety of ecological balances. From the tiniest microbes to complex multicellular organisms, benthic communities play pivotal roles in nutrient cycling, energy flow, and habitat formation. Understanding these intricate ecosystems is paramount, especially as they face intensive evolutionary fluctuation and natural succession. Changing climate conditions and the increasing influence of other threats from human activities are putting pressure on communities in benthic marine ecosystems and require adaptations within short periods of time.
In this Special Issue, we wanted to delve into the multifaceted world of benthic biodiversity, exploring the dynamic interactions among its diverse communities and their impacts on marine ecosystem functioning. We were lucky to collect 13 articles, totaling 252 pages, that have been co-authored by 65 researchers from 8 countries.
The contributions span a broad spectrum of topics, beginning with microbial communities that form the foundation of benthic ecosystems. Advanced metabarcoding techniques have unveiled the astonishing diversity and versatility of benthic protists, shedding light on their roles in biogeochemical processes and food webs and addressing their resilience to environmental perturbations. Transitioning to meiofauna and macrofauna, several studies investigate species distribution patterns in response to natural gradients and anthropogenic pressures like bottom trawling, sea level rise, or organic and pollutant influences from the river plume, suggesting species that suffer most from these perturbations and spotting those that are tolerant. These findings underscore the sensitivity of benthic organisms to habitat alterations, emphasizing the need for comprehensive monitoring and conservation strategies.
Interdisciplinary approaches featured in this issue highlight the functional interplays between different benthic compartments, but also the need for more integrated assessments. For instance, research on bioturbation and bioirrigation demonstrates how macrofaunal activities enhance microbial processes, facilitating nutrient exchange across the sediment–water interface. Such interactions are crucial for maintaining ecosystem health and productivity. However, establishing robust quantitative relationships to improve predictive capacity remains a challenge.
The contributions in this issue primarily focus on observational and modeling approaches to understand benthic biodiversity distribution and ecosystem functioning (Table 1). Purely experimental studies were unfortunately lacking. We therefore advocate for more of them in the future, as they can reveal not only species-specific responses but also potential cascading effects on community structure and ecosystem services. Such insights remain missing for many organism groups but are vital for predicting future changes and formulating adaptive management plans.

Table 1.
Summary of 13 papers included in this Special Issue, distinguishing between organism groups studied and methodologies and highlighting key findings.
To serve as a quick reference for readers to navigate the diverse topics covered in this Special Issue and to synthesize the wealth of information presented, Table 1 categorizes the 13 published studies based on their focal organism groups (microbes, meiofauna, macrofauna, fish) and methodological approaches (observational, experimental, modeling) and outlines key findings related to ecosystem functions. In conclusion, this compilation of research offers a snapshot of some current advancements in benthic biodiversity studies. It underscores the importance of integrative approaches to unravel the complexities of marine ecosystems and informs strategies for their understanding and preservation amidst a rapidly changing world.
Additionally, Figure 1 illustrates schematically the expected interconnections between different benthic biodiversity components, depicting how microbial, meiofaunal, and macrofaunal interactions might drive or alter essential processes like nutrient cycling, carbon remineralization, deoxygenation, and overall energy transfer.
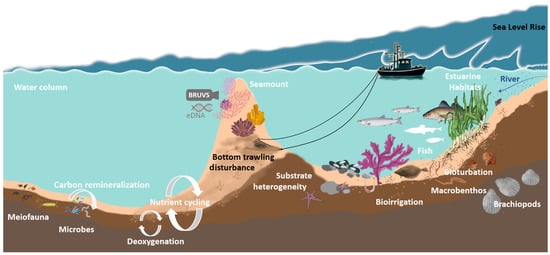
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the expected interconnections between different benthic biodiversity components and processes (labeled in white), exemplary pressures (labeled in black), as well as some currently actively developed monitoring methods (shown in gray).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gogina, M.; Renz, J.R.; Forster, S.; Zettler, M.L. Benthic Macrofauna Community Bioirrigation Potential (BIPc): Regional Map and Utility Validation for the South-Western Baltic Sea. Biology 2022, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsikopoulou, I.; Smith, C.J.; Papadopoulou, K.N.; Austen, M.C. Linking Species Functional Traits to Specific Biogeochemical Processes under Trawling Pressure. Biology 2022, 11, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, O.; Gammal, J.; Clark, D.; Ellis, J.I.; Pilditch, C.A. Estimating Effects of Sea Level Rise on Benthic Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning in a Large Meso-Tidal Coastal Lagoon. Biology 2023, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miernik, N.A.; Janas, U.; Kendzierska, H. Role of Macrofaunal Communities in the Vistula River Plume, the Baltic Sea—Bioturbation and Bioirrigation Potential. Biology 2023, 12, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, T.; Tu, K.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhou, L.; Sun, X. Population Genetics of Manila Clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) in China Inferred from Microsatellite Markers. Biology 2023, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, A.; Stubbs, T.L. A Highly Diverse Olenekian Brachiopod Fauna from the Nanpanjiang Basin, South China, and Its Implications for the Early Triassic Biotic Recovery. Biology 2023, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romoth, K.; Darr, A.; Papenmeier, S.; Zettler, M.L.; Gogina, M. Substrate Heterogeneity as a Trigger for Species Diversity in Marine Benthic Assemblages. Biology 2023, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istomina, A.A.; Zhukovskaya, A.F.; Mazeika, A.N.; Barsova, E.A.; Chelomin, V.P.; Mazur, M.A.; Elovskaya, O.A.; Mazur, A.A.; Dovzhenko, N.V.; Fedorets, Y.V.; et al. The Relationship between Lifespan of Marine Bivalves and Their Fatty Acids of Mitochondria Lipids. Biology 2023, 12, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, M.; Dünn, M.; Arndt, H. Benthic Heterotrophic Protist Communities of the Southern Baltic Analyzed with the Help of Curated Metabarcoding Studies. Biology 2023, 12, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baletaud, F.; Lecellier, G.; Gilbert, A.; Mathon, L.; Côme, J.-M.; Dejean, T.; Dumas, M.; Fiat, S.; Vigliola, L. Comparing Seamounts and Coral Reefs with eDNA and BRUVS Reveals Oases and Refuges on Shallow Seamounts. Biology 2023, 12, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, D.; Feldens, A.; Papenmeier, S.; Feldens, P.; Darr, A.; Zettler, M.L.; Heinicke, K. Habitats and Biotopes in the German Baltic Sea. Biology 2024, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogina, M.; Hahn, S.J.; Ohde, R.; Brandt, A.; Forster, S.; Kröncke, I.; Powilleit, M.; Romoth, K.; Sonnewald, M.; Zettler, M.L. Baseline Inventory of Benthic Macrofauna in German Marine Protected Areas (2020–2022) before Closure for Bottom-Contact Fishing. Biology 2024, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gintowt, N.A.; Kendzierska, H.; Janas, U. Seasonal Dynamics of Benthic Infauna Communities in Zostera marina Meadows: Effects of Plant Density Gradients. Biology 2025, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).