Abstract
Gelatin fibers have been prepared by dry spinning based on the sol-gel transition phenomena of aqueous gelatin solutions. This method is simple and environmentally friendly because only water is used for the spinning, thereby avoiding the use of any toxic organic solvents. A sol-state aqueous solution of gelatin at 50 °C was extruded into air through a thin nozzle at room temperature followed by high-speed stretching in air. As a result, a stretched and shiny gelatin fiber was produced. To improve the mechanical and water-resistant properties of the fibers, a crosslinking treatment by the addition of sugars, denacol, and glutaraldehyde vapor was used. Despite their smooth surfaces, the gelatin fibers exhibited a multi-porous phase on the inside, probably owing to the retention of water during the spinning process. The mean diameters of the obtained fibers with all crosslinking agents were approximately 50–60 μm. Furthermore, the mean tensile strength was increased by all crosslinking agents. In particular, the use of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine and glutaraldehyde as the crosslinkers resulted in a remarkable increase in tensile strength and water resistance. Moreover, their properties were further improved after heat treatment. These fibers also exhibited good water resistance and maintained their morphologies for more than 90 days.
1. Introduction
Gelatin is known as a natural glue and is generally prepared by the acid or alkaline hydrolysis of animal bones and skins. Gelatin has been utilized for a wide range of applications, including in foods, food supplements, drinks, and glues, owing to its ability to undergo sol-gel transformation in aqueous solutions. Since gelatin is biocompatible, low in toxicity, and biodegradable in the bodies of animals, it has also been applied in biomedical materials, such as capsules for drug delivery and as biomedical membranes. The low toxicity of gelatin in animals mainly depends on the absence of telopeptides, which induces the immunological response of collagen at a fairly high level [1,2,3].
Gelatin fiber is expected to find biomedical applications as a biomaterial. However, gelatin is difficult to regenerate owing to its insolubility in common organic solvents and the sol-gel transition of gelatin in aqueous solution. Previously, gelatin fibers were prepared using a wet spinning method with a lithium (or calcium) chloride-N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc) system [4]. In this system, gelatin dissolved in LiCl-DMAc or CaCl2-DMAc at room temperature was coagulated by exposure to methanol. However, the tensile strength of the obtained gelatin fibers was less than 30 MPa, which is not sufficient for practical applications, and long-term immersion in methanol was necessary to remove the salts from the fibers. Some researchers have also reported the spinning methods of gelatin fibers using organic or aqueous organic solvent [5,6,7,8]. Fukae and Midorikawa prepared the fibers by the gel spinning of gelatin solution dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide or ethylene glycol. Stoessel et al. succeeded the high speed spinning of gelatin fiber in the mixed solvent of 2-propanol and water [8]. Although these fibers showed excellent mechanical strength and water-resistance and was outstanding for industrial products, the use of a large amount of organic solvent in the spinning process or post-treatment was unsuitable for practical use in biomedical applications.
Since the aqueous gelatin sol formed upon heating is highly viscous before the formation of a hard gel, spinning the sol formed from a high-concentration aqueous solution of gelatin on heating was investigated by the quick removal of water with the orientation of gelatin molecules on the first stage of spinning [4]. This method is simple and environmentally friendly because the only solvent used is water. Although the tensile strength of the fibers produced by this method was much greater than that of wet-spun fibers, the fibers are easily dissolved in water. Therefore, it is necessary to crosslink the fibers to improve their water resistance. Gelatin microspheres and disks crosslinked with sugars have been prepared for pharmaceutical applications [9]. Crosslinking with sugars was shown to enhance the water resistance of gelatin and increase the mechanical strength of gelatin materials [10,11]. This reaction is referred to as the Maillard reaction, which crosslinks between the amino groups of proteins by furfural compounds resulting from the Amadori rearrangement of reducing sugars [12] and induces physical changes in gelatin and other protein matrices [13,14,15,16]. The crosslinking of soft collagen with epoxy compounds has been reported to enhance biomechanical properties while maintaining good biocompatibility [17,18]. Epoxy compounds have also been used as crosslinkers to coat gelatin onto the inner surface of polyurethane for vascular graft applications, resulting in significantly improved cell adhesion, spreading, and proliferation [16]. Glutaraldehyde (GTA) is a bifunctional reagent that is usually used to chemically modify proteins and polymers for various applications owing to its commercial availability, low cost, and high reactivity [19]. GTA reacts rapidly with amine groups at or close to neutral pH to form crosslinks [20,21].
In this study, we describe the preparation and characterization of gelatin fibers from the high-concentration aqueous solutions of gelatin by dry spinning. The gelatin fibers were crosslinked with various crosslinking agents including sugars, denacol, and GTA, and the properties of the crosslinked fibers were investigated using tensile and water-resistance tests.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
Bovine gelatin JS200 (Mw 100,000; 200 bloom, Type B) was supplied by Koei Co., Ltd. (Himeji, Japan). Ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (denacol EX-810) was supplied by Nagase ChemteX Coorporation (Osaka, Japan). The other crosslinking agents, sucrose (Suc), d-glucose (Glc), d-glucosamine (GlcN), N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (GlcNAc), and GTA solution (25%), were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Co., Ltd. (Osaka, Japan).
2.2. Dry Spinning of Gelatin Fiber
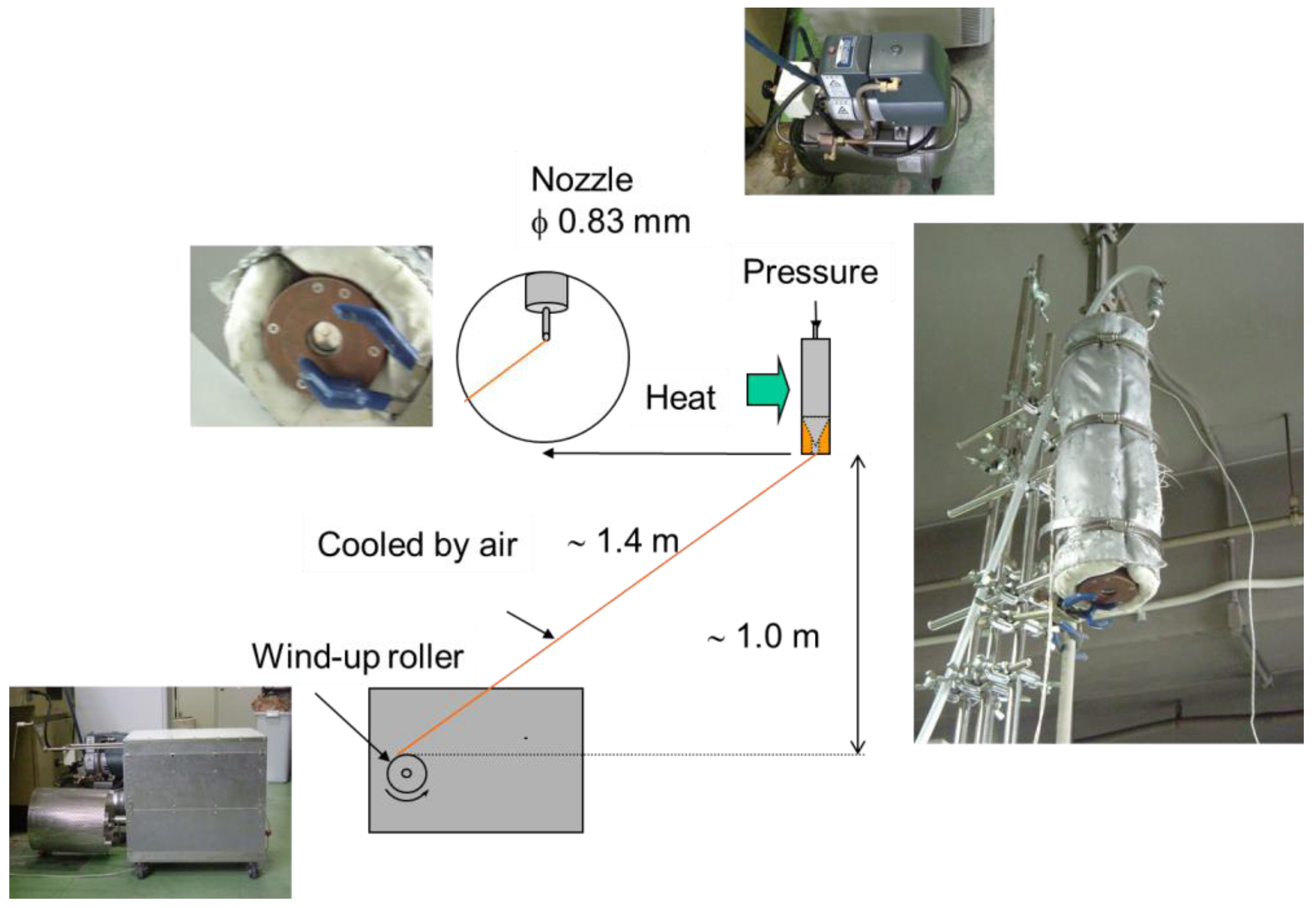
A 50 g gelatin granule was mixed with 50 g of water to prepare a 50 wt% gelatin aqueous solution. The mixture was then placed into a water bath at 50 ± 2 °C for 30 min and agitated every 10 min to remove any bubbles from the highly viscous solution; thus, a homogeneous dope solution was obtained. A cylinder (50 ± 2 °C) connected to a nozzle (inner diameter = 0.83 mm) was filled with the dope solution, and the solution was squeezed out through the nozzle under slight pressure (0.10 ± 0.04 MPa). The separation distance between the nozzle and the wind-up roller (diameter = 35 cm) was set to 1.4 m (Figure 1). The fiber was rolled up at a constant speed (50 ± 10 m/min) to an aluminum foil wrapped on a wind-up roller. The fiber was retained on the wind-up roller at room temperature for 24 h to remove residual moisture.
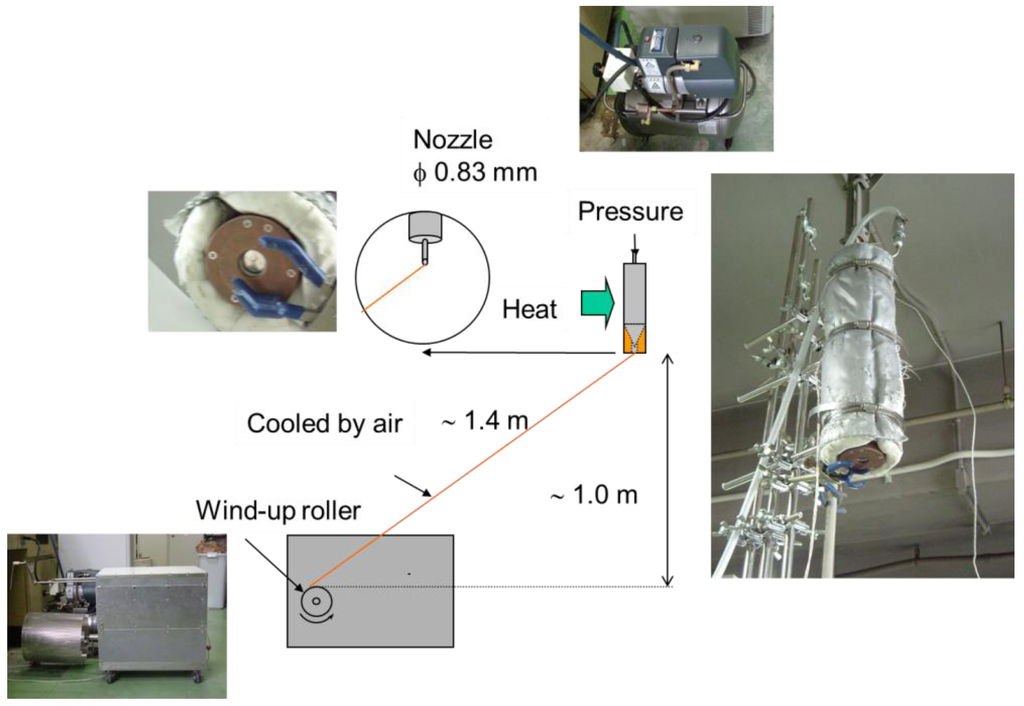
Figure 1.
Dry-spinning apparatus.
Figure 1.
Dry-spinning apparatus.
2.3. Preparation of Crosslinked Gelatin Fibers
2.3.1. Crosslinking with Sugars
The 50 wt% gelatin dope solution containing 5 wt% sugar (Suc, Glc, GlcN, or GlcNAc, with respect to the gelatin mass) mass was prepared and spun by the procedure described in Section 2.2. The obtained fibers were heat treated at 120 °C for more than 24 h to accelerate the crosslinking via the Maillard reaction.
2.3.2. Crosslinking with Denacol
Gelatin dope solutions (50 wt%) containing various concentrations of denacol (3, 4, and 5 wt% with respect to the gelatin mass) were prepared. To investigate the spinnability before spinning, the changes in viscosity of the dope solutions after the addition of denacol were observed at 50 °C for 10–70 min. After a suitable crosslinking time, the dope solution was spun by the procedure described in Section 2.2. The obtained fibers were treated with heat at 100 °C for 24 h and crosslinked with the remaining epoxide groups.
2.3.3. Crosslinking by GTA Treatment
After the spinning of gelatin fibers, the GTA-crosslinking process was carried out by placing the obtained fibers into a desiccator containing an aqueous solution of GTA at room temperature. After crosslinking, the fibers were rinsed by immersing them three times in methanol for 15 min each to remove the residual GTA. To study the effects of crosslinking time in the desiccator and heat treatment, the fibers were placed in the desiccator for 1–3 days and treated with heat at 100 °C for 24 h.
2.4. Water Resistance
Each fiber was immersed in distilled water at room temperature for 90 days. Fiber morphology was determined by its water-resistant property evaluated by the observations.
The swelling degree of the fibers was calculated from each weight according to Equation (1):
where W0 and W1 are the weights of the dry and wet fibers, respectively.
2.5. Measurements
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observations were made using a JSM6700 microscope (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). The mechanical properties were analyzed using a universal testing machine STA-1150 (A & D company, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The fibers were fixed between cardboard by maintaining a 1-cm length of fibers or the fibers tied in a knot. The tensile and knot strengths were measured 15 times using the fixed fiber samples. The cross-head loading speed was set at 10 mm/min for a loading of 5 N. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) analysis was performed using a Varian 670-IR spectrometer (Agilent Tech. Int. Japan, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was measured using a SII EXSTER TG6200 thermal analyzer (Chiba, Japan). The temperatures scanned ranged from 20 °C to 700 °C with a heating rate of 10 °C/min.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Gelatin Fibers
Gelatin fibers were dry spun from a high-concentration solution of gelatin. If the hot aqueous gelatin solution (sol state) was reeled off by a glass rod, the solution solidified (gel state) owing to the decrease in temperature. To obtain the gelatin fibers in a continuous manner, a simple apparatus was employed for automatic spinning. In this procedure, it was important that the temperature and concentration of the dope solution, de-bubbling process, and rate of the wind-up roller were controlled to quickly obtain highly oriented gelatin molecules. Since the water was quickly removed in this spinning procedure, no fiber cohesion occurred at the wind-up roller during spinning. In fact, after spinning, the water content of the immediate gelatin fibers decreased to 20% from 50% in the dope solution from TGA result. The fibers were crosslinked using the dope solutions containing sugars and denacol and by GTA treatment. Figure 2 shows the images of the gelatin solution after being kept in an electric water bath for 30 min and the crosslinked fibers. The dope solution was almost homogeneous, and bubbles were observed on the solution surface. The denacol-crosslinked fibers were smooth and white in color. On the other hand, the GlcNAc-crosslinked fibers showed a characteristic brown color after heat treatment owing to the Maillard reaction resulting in the crosslinking between the amino groups of gelatin and the furfural derivatives generated from the sugars. The GTA-treated fibers were yellow in color owing to the formation of imine linkages between the free amine groups of lysine or hydroxylysine residues of the gelatin chain and the aldehyde groups of GTA [22,23,24,25].
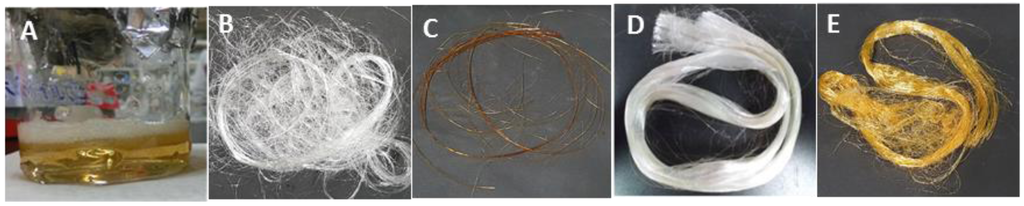
Figure 2.
Appearances of the dope solution and resultant fibers: (A) aqueous gelatin solution before spinning; (B) gel fibers without crosslinking; (C) GlcNAc-crosslinked fibers; (D) denacol-crosslinked fibers; and (E) GTA-treated fibers.
Figure 2.
Appearances of the dope solution and resultant fibers: (A) aqueous gelatin solution before spinning; (B) gel fibers without crosslinking; (C) GlcNAc-crosslinked fibers; (D) denacol-crosslinked fibers; and (E) GTA-treated fibers.
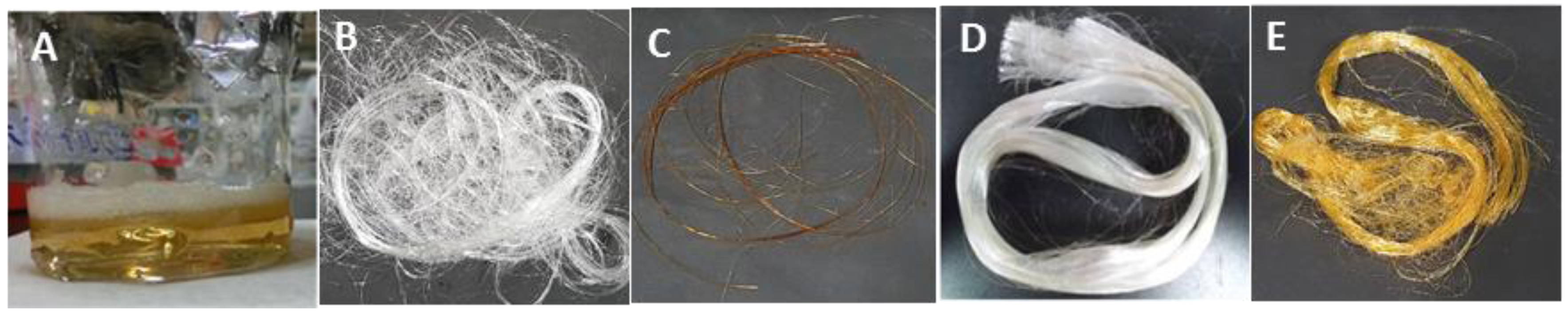
Figure 3 shows SEM images of a non-crosslinked and three crosslinked fibers. Furrows attributed to the nozzle were observed in the longitudinal direction (arrows in Figure 3A,D). The gelatin fiber without crosslinking and denacol-crosslinked fiber exhibited smooth surfaces (Figure 3A,C). The GlcNAc-crosslinked fiber showed a slightly heterogeneous surface because of the complex Maillard reactions (Figure 3B), and the GTA-treated fiber showed a slightly rough surface (Figure 3D). The results indicate that only the surfaces of the fibers were crosslinked by GTA vapor, causing it to swelling slightly owing to moisture. The mean diameter of the GTA-treated fibers was 60 ± 5 μm, slightly larger than those of the other fibers (55 ± 5 μm). Figure 3E shows the SEM images of cross-section of a gelatin fiber without crosslinking. An interconnected porous structure was observed in the cross-section of the fiber. The fiber exhibited a high porosity with a pore diameter of less than 1 μm.
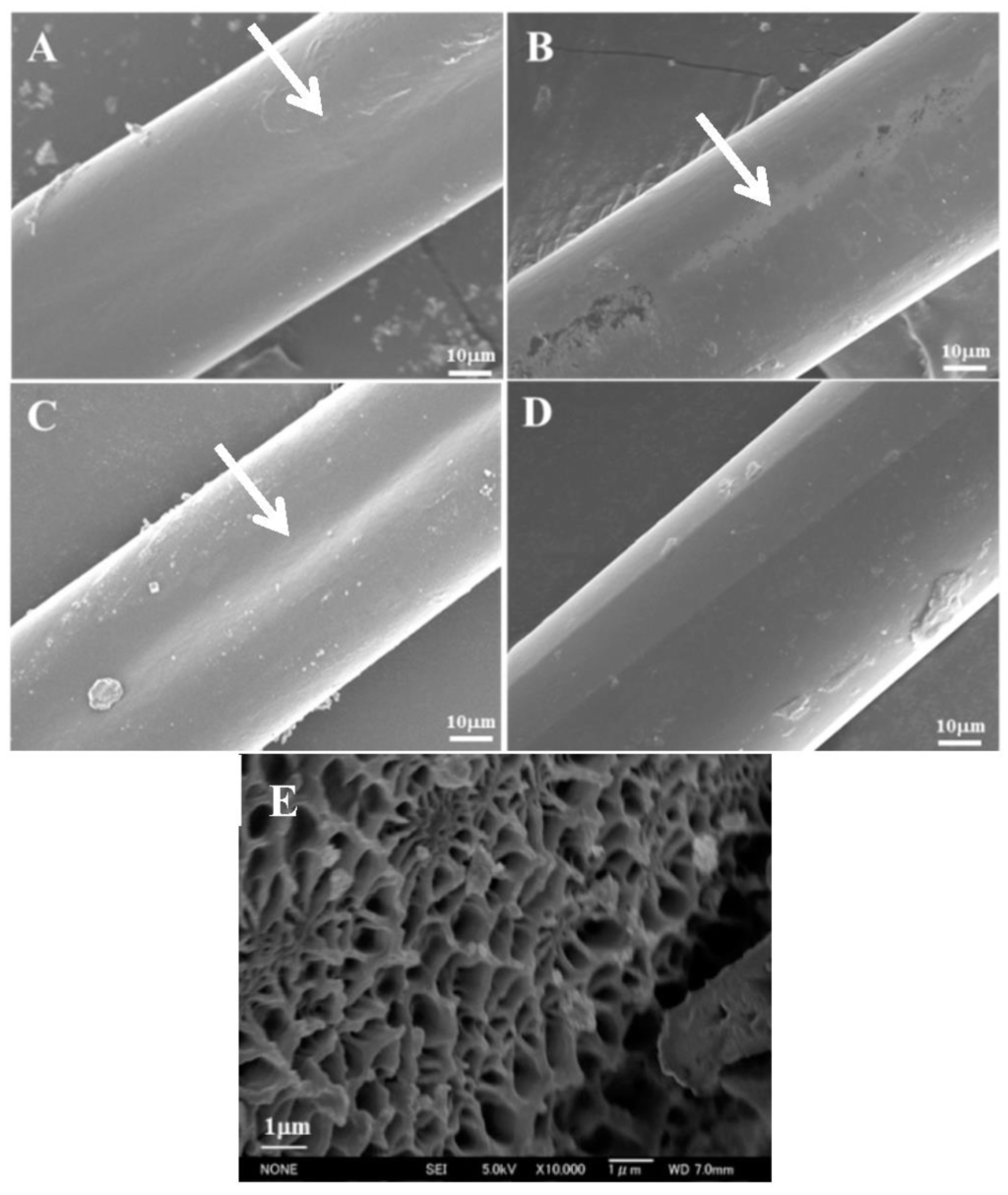
Figure 3.
SEM images of (A) gelatin fiber without crosslinking; (B) GlcNAc-crosslinked fiber; (C) denacol-crosslinked fiber; (D) GTA-treated fiber; and (E) the cross-section of the gelatin fiber without crosslinking (high magnification).
Figure 3.
SEM images of (A) gelatin fiber without crosslinking; (B) GlcNAc-crosslinked fiber; (C) denacol-crosslinked fiber; (D) GTA-treated fiber; and (E) the cross-section of the gelatin fiber without crosslinking (high magnification).
3.2. Effects of Crosslinkers
When the reducing sugars were treated at high temperature, the Maillard reaction occurred rapidly via the Amadori rearrangement, resulting in crosslinking between the molecules. Thus, we attempted to improve the strength and water resistance using this reaction. The dope solutions containing Suc, Glc, GlcN, and GlcNAc were spun using the aforementioned procedure and dried at room temperature for 24 h. The mechanical strengths of the obtained fibers were measured to investigate the effects of crosslinking with sugars (Figure 4). The tensile stress of the fibers crosslinked with sugars was higher than that of the non-crosslinked fibers (70 MPa). This indicates that the Maillard reaction proceeded at the temperature inside the cylinder (50 °C) during spinning. After heat treatment at 120 °C for 24 h, the tensile stress of the fibers containing the reducing sugars increased remarkably; the values for the fibers with Glc, GlcN, and GlcNAc were 174, 179, and 205 MPa, respectively. However, since the sugar-crosslinked fibers were generally stiff and lacked ductility compared with the other crosslinked fibers, the knot strength could not be measured.
Denacol, which contains two epoxide groups, reacts readily with amino groups under neutral conditions, resulting in crosslinking between the molecules. Accordingly, the viscosity of the dope solution increases gradually with crosslinking. The effects of the addition of the different concentrations of denacol and the crosslinking time on the spinnability were investigated (Table 1). For crosslinking intervals under 30 min, the dope solution remained incompletely-dissolved and was not homogeneous. For intervals above 50 min, spinning was impossible owing to the high viscosity of the solution. To obtain a viscosity suitable for spinning, a crosslinking time between 30 and 40 min was found to be ideal at all concentrations of denacol. The results of the tensile and knot strength tests are shown in Figure 5. Both the tensile and knot strengths of the non-crosslinked fiber were improved by crosslinking with denacol. In addition, both strengths were enhanced with increasing denacol concentration. The tensile and knot stresses for the fiber containing 5% denacol were 203 and 160 MPa, respectively. After heat treatment at 100 °C for 24 h, the stress values were almost the same or somewhat lower, probably owing to the thermal decomposition of the gelatin molecular chain [26]. These results suggest that the heat treatment was not effective in this case.
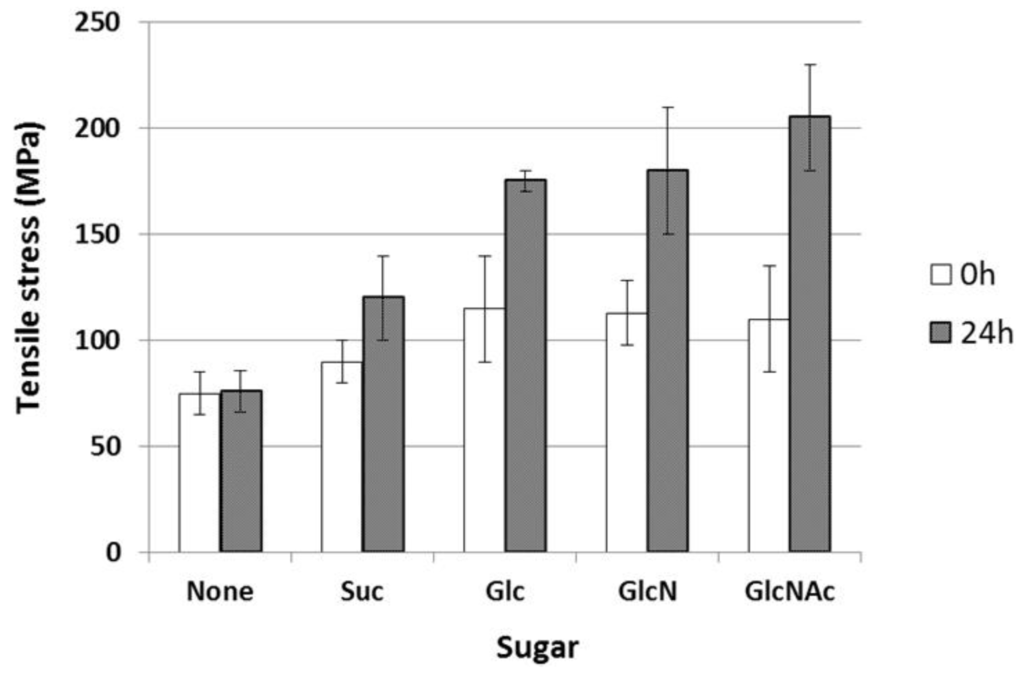
Figure 4.
Mechanical strengths of sugar-crosslinked gelatin fibers.
Figure 4.
Mechanical strengths of sugar-crosslinked gelatin fibers.
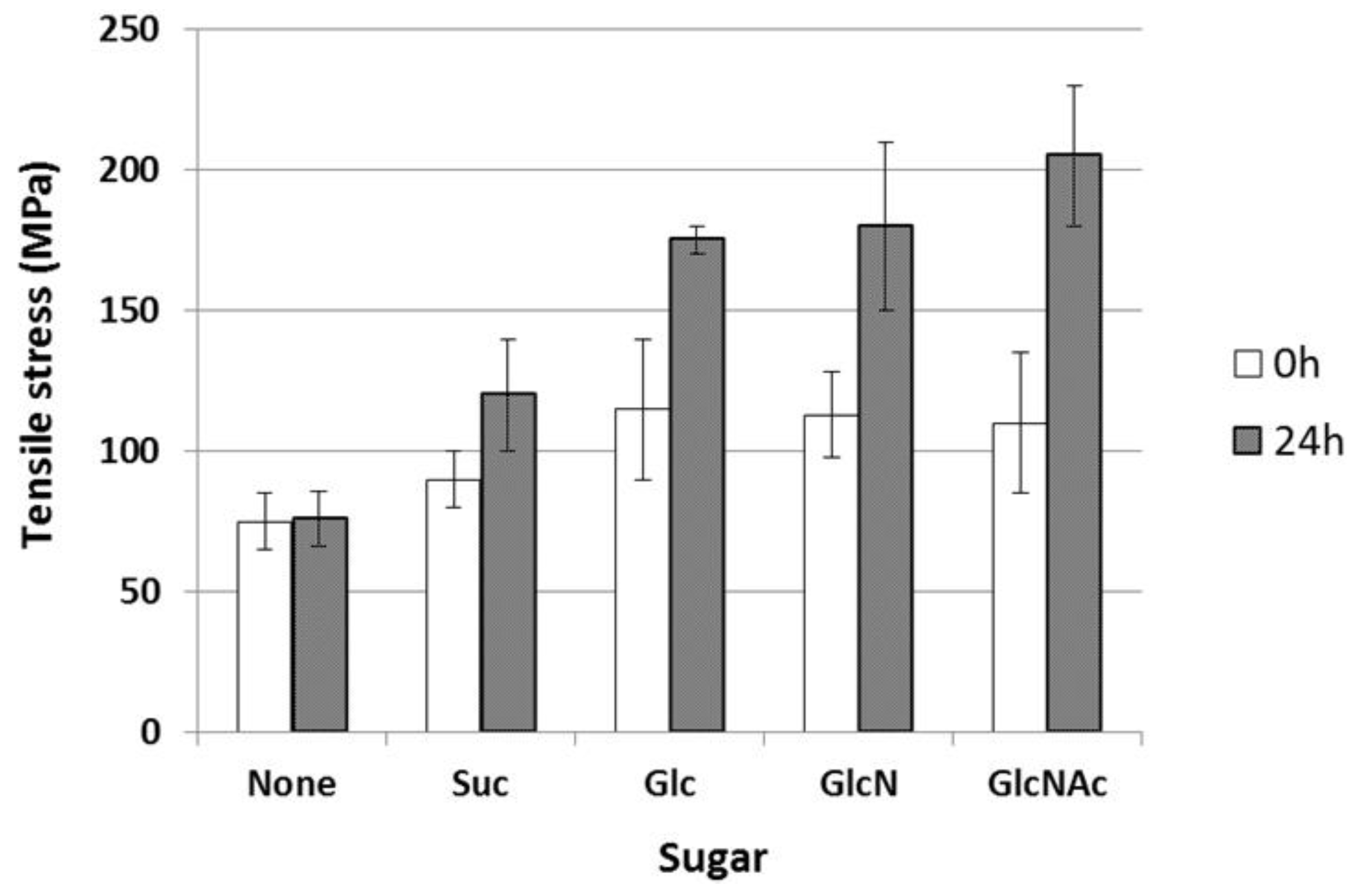

Table 1.
Spinnability of gelatin solutions containing denacol at different crosslinking time intervals.
| Denacol (%) | Crosslinking Time (min) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | |
| 0 | × | × | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| 3 | × | △ | ○ | ○ | △ | △ | × |
| 4 | × | △ | ○ | ○ | △ | △ | × |
| 5 | × | △ | ○ | ○ | △ | × | × |
Notes: ○: good spinnability; △: bad spinnability; ×: spinnability impossible.
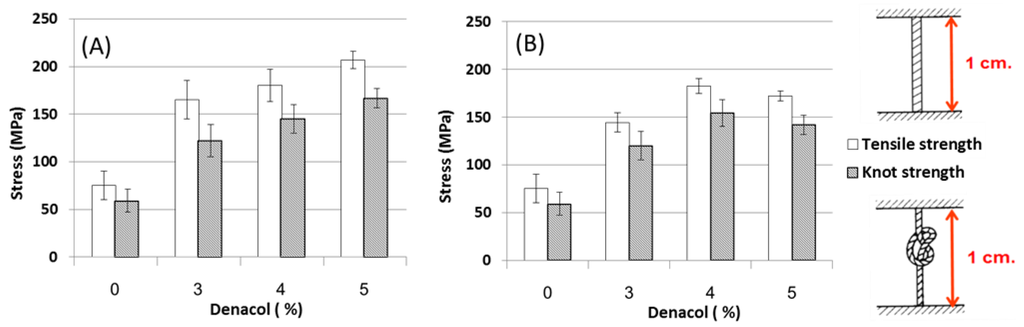
Figure 5.
Mechanical strengths of denacol-crosslinked fibers: (A) no heat treatment and (B) heat treatment at 100 °C for 24 h.
Figure 5.
Mechanical strengths of denacol-crosslinked fibers: (A) no heat treatment and (B) heat treatment at 100 °C for 24 h.
GTA also has two aldehyde groups and reacts rapidly with amino groups to form Schiff bases [19]. However, as gelatin is soluble in water, the fibers cannot be crosslinked via immersion in GTA solution. Therefore, the crosslinking reaction in this study was performed using GTA vapor. The results of the tensile and knot strength tests are shown in Figure 6. Both stresses of the GTA-treated fibers were greater than those of the gelatin fiber without GTA. The stresses increased as crosslinking time increased from 1 to 3 days. After heat treatment at 100 °C for 24 h, the tensile and knot stresses of the fibers crosslinked for 3 days were enhanced from 131 and 103 MPa to 170 and 125 MPa, respectively. These results suggest that post-treatment by heat is necessary for crosslinking in this case [25,27].
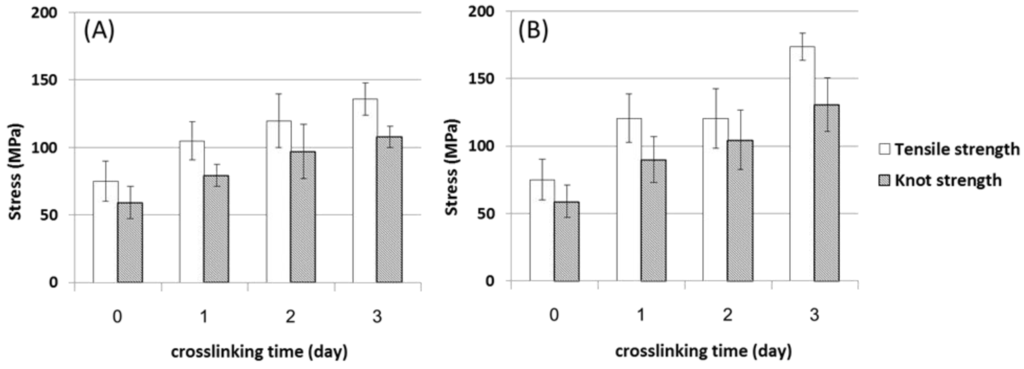
Figure 6.
Mechanical strengths of GTA-treated gelatin fibers: (A) no heat treatment and (B) heat treatment at 100 °C for 24 h.
Figure 6.
Mechanical strengths of GTA-treated gelatin fibers: (A) no heat treatment and (B) heat treatment at 100 °C for 24 h.
3.3. FT-IR Spectroscopy
Figure 7 shows the FT-IR spectra of the gelatin fibers. Gelatin peaks due to the amide I (C=O stretch), amide II (N–H bend and C–H stretch), and amide III (C–N stretch plus N–H in phase bending) were observed at 1636–1640, 1542–1544, and 1240 cm−1, respectively. However, no significant differences were observed in the spectra of the gelatin fibers with and without crosslinking.
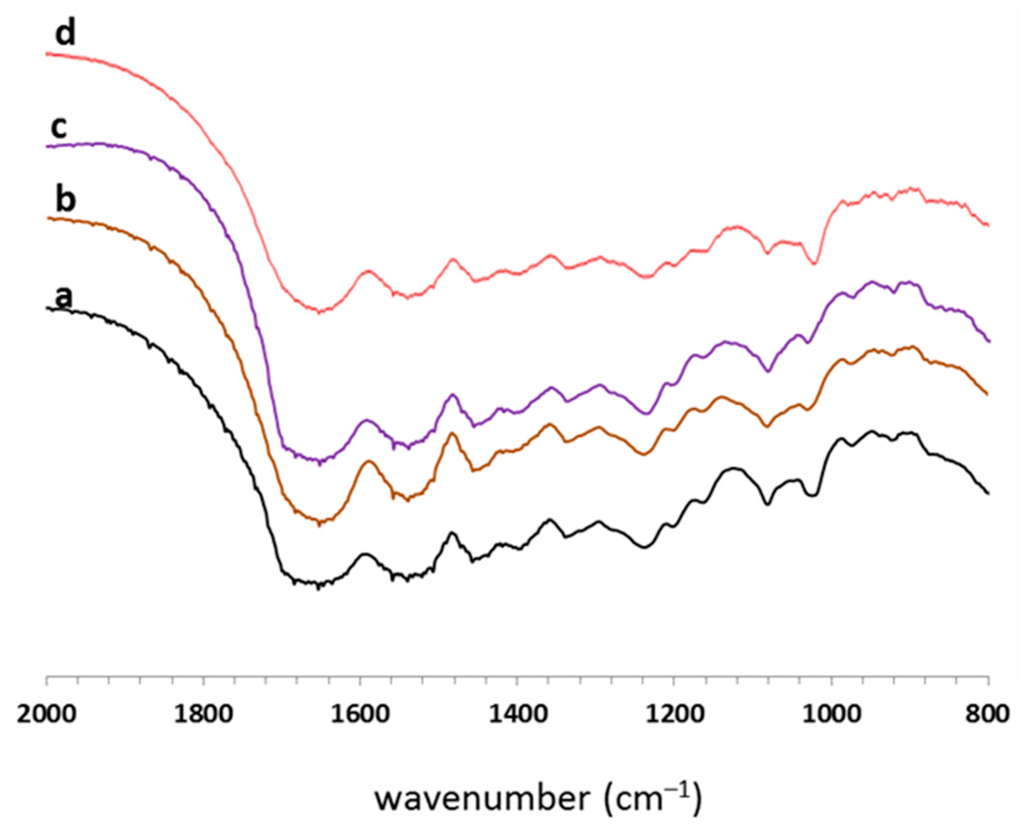
Figure 7.
FT-IR spectra of gelatin fibers: (a) gelatin fibers without crosslinking; (b) GlcNAc-crosslinked fibers; (c) denacol-crosslinked fibers; and (d) GTA-treated fibers.
Figure 7.
FT-IR spectra of gelatin fibers: (a) gelatin fibers without crosslinking; (b) GlcNAc-crosslinked fibers; (c) denacol-crosslinked fibers; and (d) GTA-treated fibers.
3.4. Water Resistance
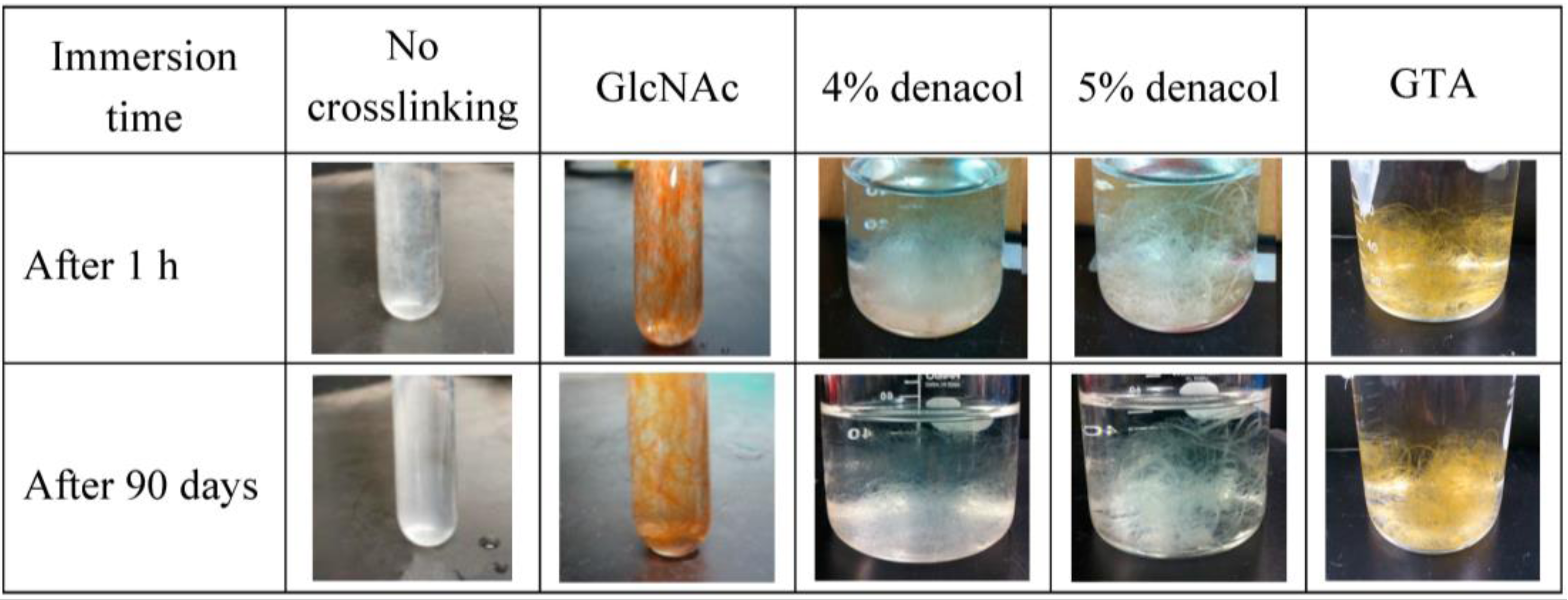
To compare the water-resistance properties of the different crosslinked fibers, the fibers were immersed in deionized water and kept at room temperature. The images of the non-crosslinked gelatin fibers, the fibers crosslinked with GlcNAc, 4% and 5% denacol, and GTA after 1 h and 90 days are shown in Figure 8. The non-crosslinked fibers and fibers crosslinked with 4% denacol swelled rapidly after immersion. After 1 day, the gelatin fibers were completely dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution. Although the gelatin fiber containing 5% denacol swelled a little, its shape was maintained more than that of the fiber containing 4% denacol. In contrast, the gelatin fibers crosslinked with GlcNAc and GTA and heat-treated for 3 days showed good water resistance and maintained their morphologies for more than 90 days. The swelling ratios of GlcNAc-, 5% denacol-, and GTA-crosslinked fibers after immersion in deionized water at room temperature for 1 day were 240%, 377%, and 196%, respectively.
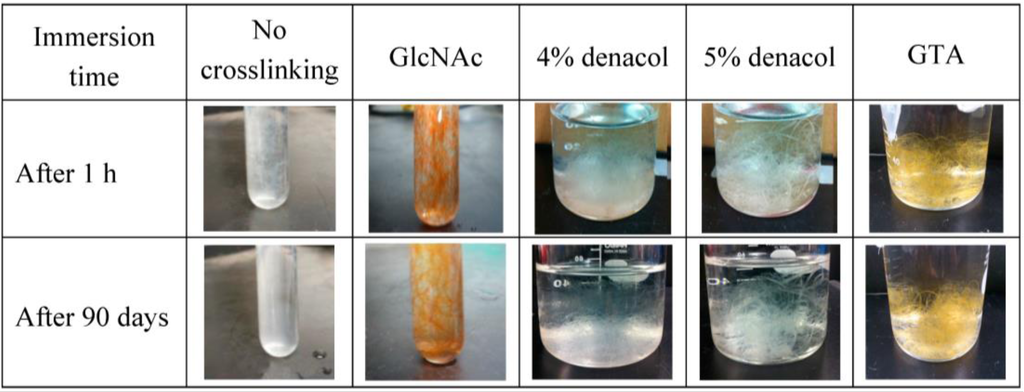
Figure 8.
Water resistance of each crosslinked fiber.
Figure 8.
Water resistance of each crosslinked fiber.
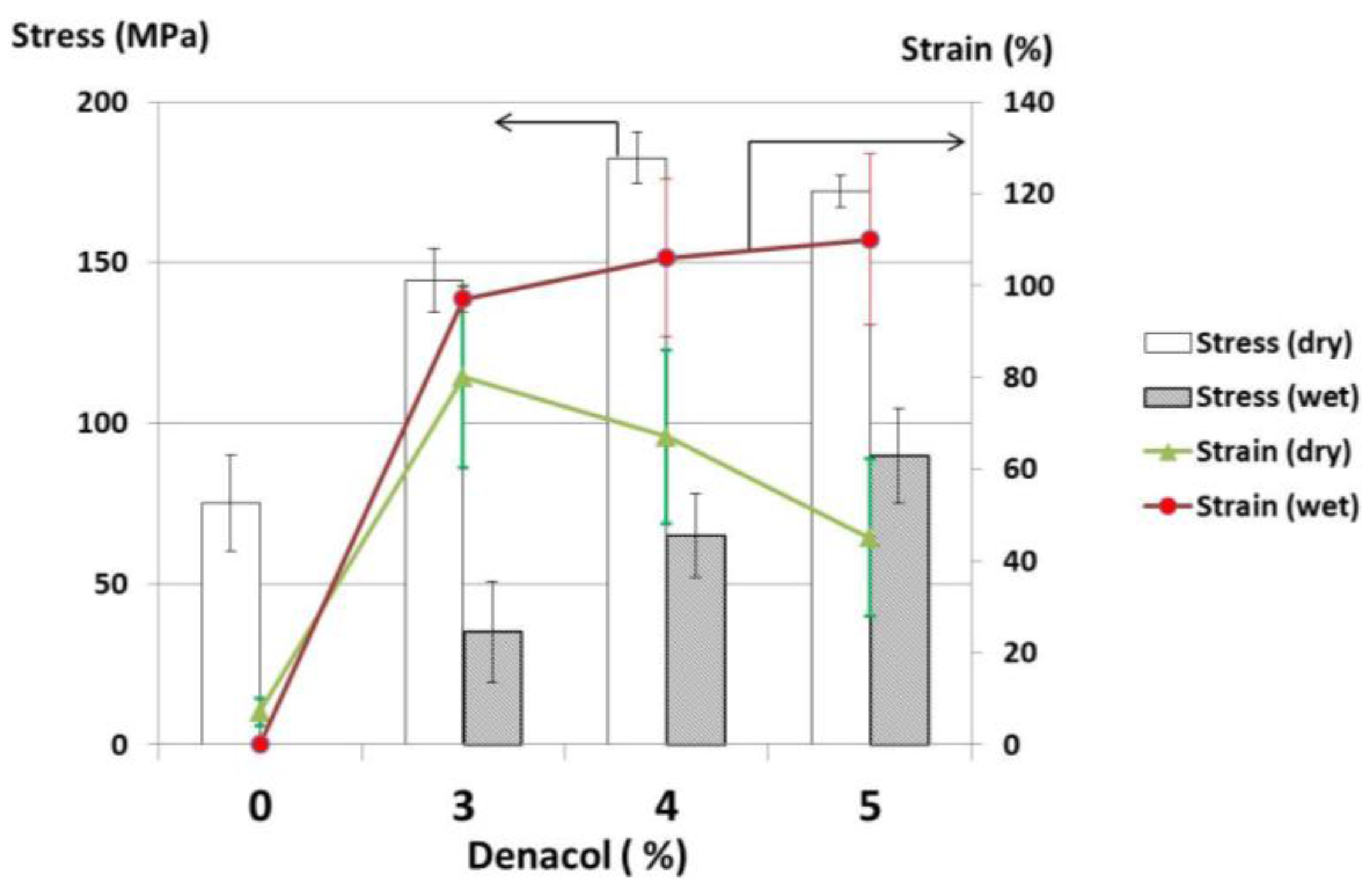
In addition, the mechanical properties of the gelatin fiber at wet condition were also investigated. The mechanical strength at wet condition was measured after immersing the fiber into deionized water for 2 min. Figure 9 shows the results of strength (tensile and knot) and strain of denacol-crosslinked fiber (after heat treatment at 100 °C for 24 h) at dry and wet conditions. The results showed that the strength of the fibers at wet condition decrease and the strain of the fibers increase remarkably, compared with those at dry condition because of the swelling of the fibers by the absorption of water. This means that the gelatin fibers in this study are excellent in compatibility against water, which is required for biomedical applications. However, the further improvement of the mechanical property may need for the applications that are necessary for the strength.
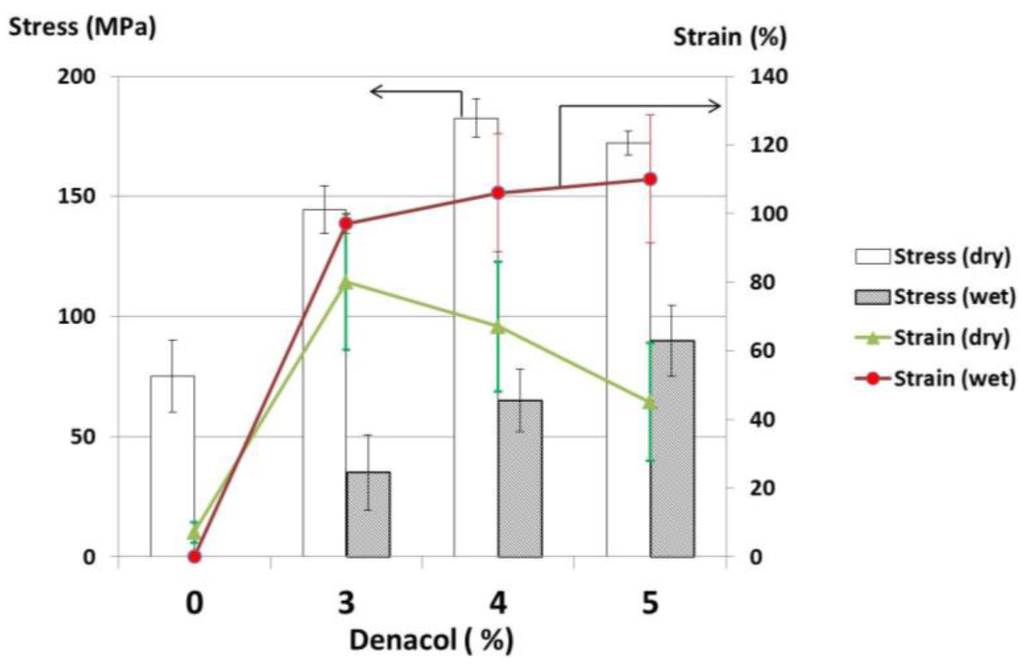
Figure 9.
Mechanical properties of denacol-crosslinked gelatin fibers at dry and wet conditions.
Figure 9.
Mechanical properties of denacol-crosslinked gelatin fibers at dry and wet conditions.
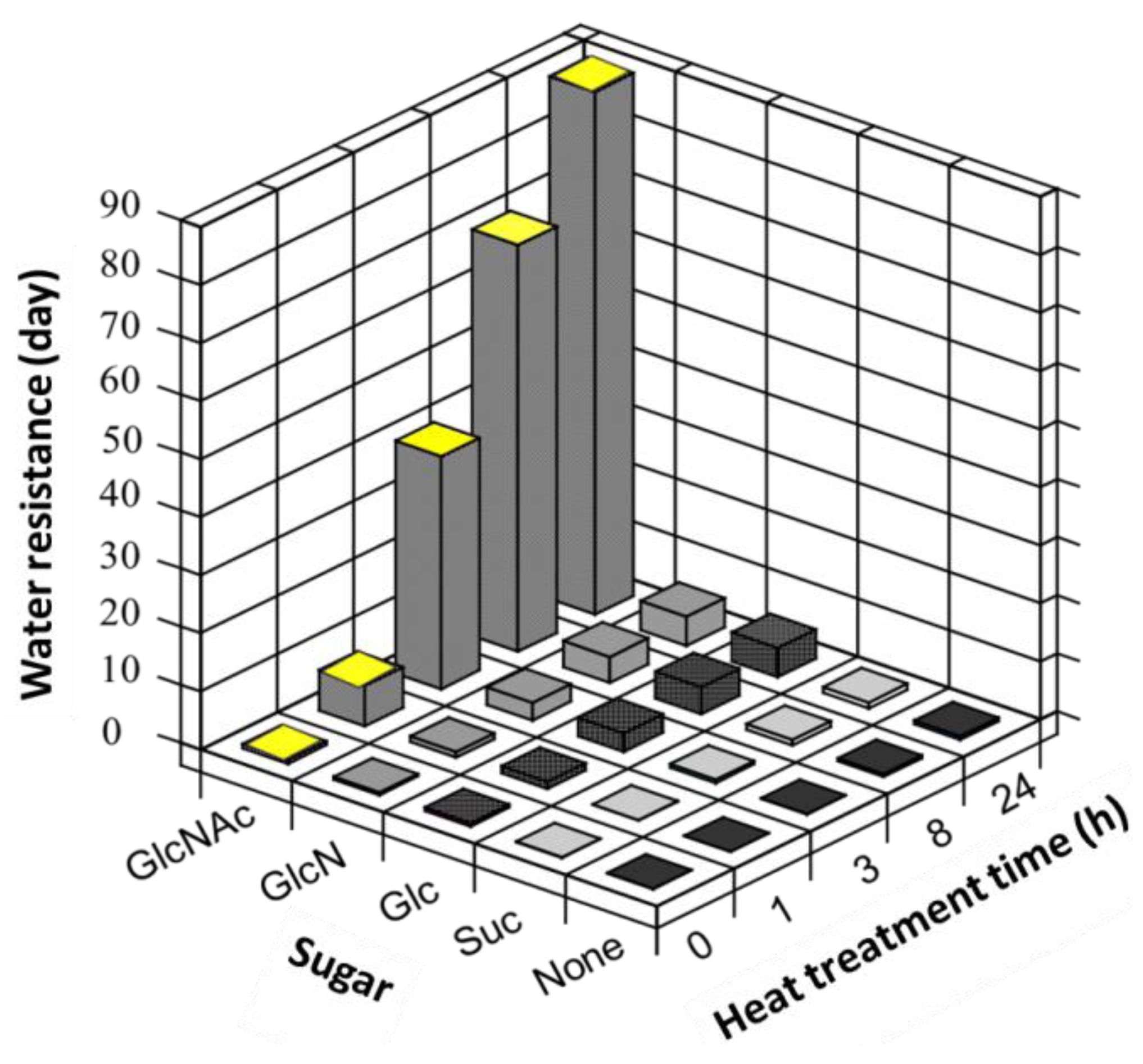
The water-resistant properties of the sugar-crosslinked fibers heat-treated for different amounts of time were investigated (Figure 10). The weakest crosslinker of gelatin fibers in this study was found to be Suc. This result is attributed to the fact that Suc is a non-reducing sugar, making the Millard reaction weaker. In the cases of GlcN and Glc, the mechanical strengths and water resistances were almost the same and increased slightly with the duration of heat treatment. In contrast, crosslinking with GlcNAc remarkably increased the water resistance of the fibers, and the crosslinked fibers retained their shapes for more than 90 days. These results indicate that GlcNAc was the most effective crosslinker among the sugars employed in this study.
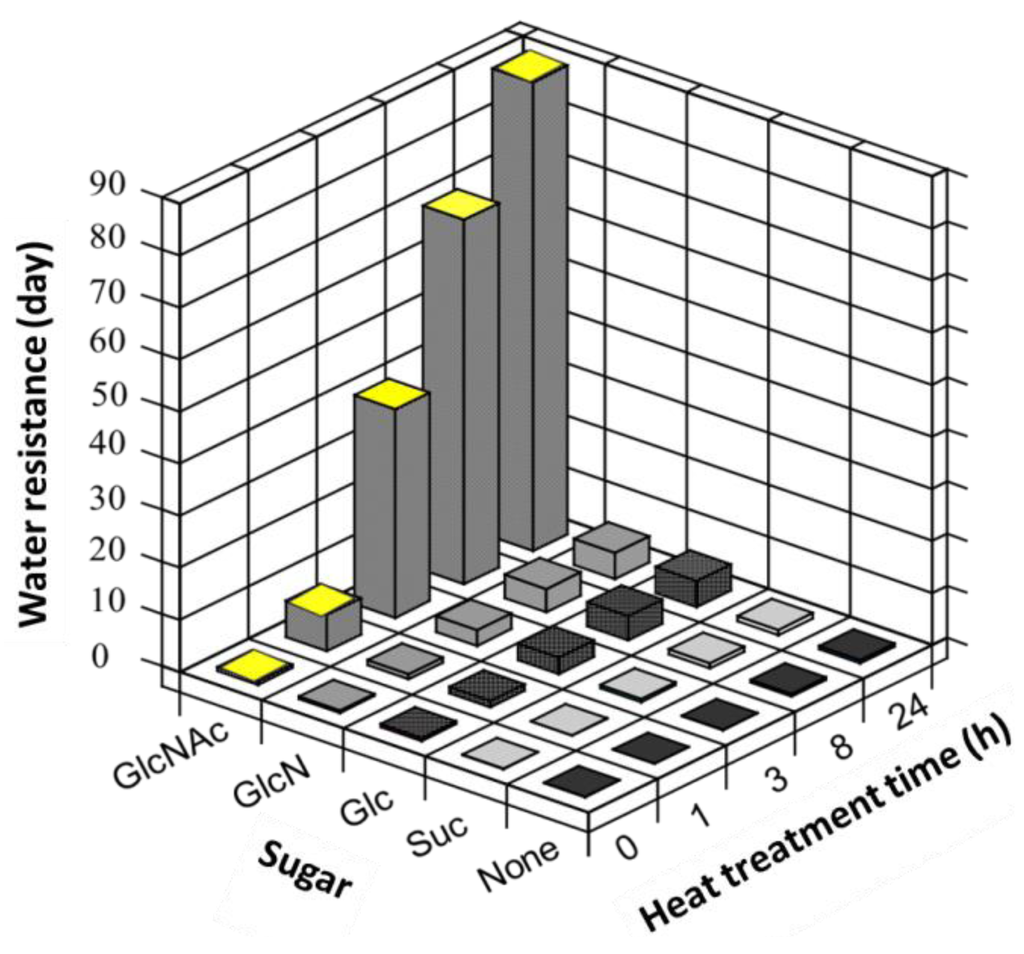
Figure 10.
Effect of heat treatment time on the water resistances of gelatin fibers crosslinked with different sugars.
Figure 10.
Effect of heat treatment time on the water resistances of gelatin fibers crosslinked with different sugars.
4. Conclusions
Gelatin fibers were prepared from the high-concentration aqueous solutions of gelatin by dry spinning based on the sol-gel transition phenomenon of the solutions. To obtain the gelatin fibers in a continuous manner, a simple apparatus was developed for automatic spinning. Since the spinning procedure quickly removed excess water, no fiber cohesion occurred at the wind-up roller during spinning. The fibers exhibited smooth surfaces with a multi-porous phase on the interior, probably owing to the retention of water during the spinning process. To improve the mechanical strengths and water resistances of the fibers, crosslinked fibers were prepared using sugars, denacol, and GTA as crosslinking agents. The mean diameters of the obtained fibers were approximately 50–60 μm. The mechanical strengths of all the crosslinked fibers were increased compared with those of the non-crosslinked fibers. Among the tested sugars, GlcNAc was the most effective crosslinker, and GTA was also effective. The heat treatment of the GTA-crosslinked fibers significantly enhanced both the mechanical and water-resistant properties. Although the denacol crosslinking showed the poor water resistance compared with the others, the smooth fiber surface might be an advantage to develop for biomaterial application, which is less needed by mechanical strength such as gel drug delivery. Additionally, these fibers maintained their shapes in deionized water for more than 90 days. The spinning method used in this study is simple and environmentally friendly as it uses only water and not any toxic organic solvents. Furthermore, because of the low toxicity of gelatin, the developed gelatin fibers and fiber assemblies are expected to be useful not only as systems for the sustained release of flavors but also as biomedical applications, such as sutures and drug delivery carriers. The biomedical applications of the gelatin fibers are now under investigation and the results will be reported as soon as possible.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Kansai University Grant-in-Aid of the Promotion and Upgrading of Education and Research, 2015, “Generation of bio-interactive polymers leading future-oriented medicals”.
Author Contributions
Tetsuya Furuike and Hiroshi Tamura designed experiments, and Thitirat Chaochai and Yusuke Imai performed the experiments. Thitirat Chaochai wrote the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Djagny, K.B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S. Gelatin: A valuable protein for food and pharmaceutical industries: Review. CRC Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 41, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Giménez, B.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Montero, M.P. Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariod, A.A.; Adam, H.F. Review: Gelatin, source, extraction and industrial applications. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2013, 12, 135–147. [Google Scholar]
- Tokura, S.; Tamura, H.; Itoh, N. Gelatin Fiber and Process for Producing the Same. Patent WO2005,054,553, 14 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fukae, R.; Midorikawa, T. Preparation of gelatin fiber by gel spinning and its mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 4011–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midorikawa, T.; Lawal, O.S.; Sasaki, Y.; Fukae, R. Structure and physical properties of gelatin fibers prepared by gel-spinning in ethylene glycol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, E332–E338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoessel, P.R.; Raso, R.A.; Kaufmann, T.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J. Fibers mechanically similar to sheep wool obtained by wet spinning of gelatin and optional plasticizers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoessel, P.R.; Krebs, U.; Hufenus, R.; Halbeisen, M.; Zeltner, M.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J. Porous, water-resistant multifilament yarn spun from gelatin. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortesi, R.; Nastruzzi, C.; Davis, S.S. Sugar cross-linked gelatin for controlled release: Microspheres and disks. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, A.; Beckman, J.A.; Schmidt, A.M.; Creager, M.A. Advanced glycation end products: Sparking the development of diabetic vascular injury. Circulation 2006, 114, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomihata, K.; Burczak, K.; Shiraki, K.; Ikada, Y. Crosslinking and biodegradation of native and denatured collagen. In Polymers of Biological and Biomedical Significance; Shalaby, S.W., Ikada, Y., Langer, R., Williams, J., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Nagahama, H.; Kashiki, T.; Nwe, N.; Jayakumar, R.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H. Preparation of biodegradable chitin/gelatin membranes with GlcNAc for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, M.O.; Gerum, F.; Severin, T. Cross-linking of proteins by Maillard processes-model reactions of d-glucosecor methylglyoxal with butylamine and guanidine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1998, 6, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Sato, M.; Hattori, M.; Yoshida, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Takahashi, K. Soft textural and emulsifiable gelatin formed by conjugating with fatty-acylated saccharide. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.; Cui, C.; Ren, J.; Yang, B.; Zhao, M. Effect of xylose on the molecular and particle size distribution of peanut hydrolysate in Maillard reaction system. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2457–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masutani, E.M.; Kinoshita, C.K.; Tanaka, T.T.; Ellison, A.K.D.; Yoza, B.A. Increasing thermal stability of gelatin by UV-induced cross-linking with glucose. Int. J. Biomater. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, R.; Shen, S.H.; Lin, D.; Hata, C.; Thyagarajan, K.; Noishiki, Y.; Quijano, R.C. Fixation of bioprosthetic tissues with monofunctional and polyepoxy compounds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1994, 28, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.H.; Tseng, H.J.; Wu, M.S. Comparative in vitro evaluation of two different preparations of small diameter polyurethane vascular graft. Artif. Organs 2000, 24, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.J.S.M.; Sousa, F.; Gübitz, G.; Paulo, A.C. Chemical modifications on proteins using glutaraldehyde. Food Technol. Biotech. 2004, 42, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Okuda, K.; Urabe, I.; Yamada, Y.; Okada, H. Reaction of glutaraldehyde with amino and thiol compounds. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1991, 71, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migneault, I.; Dartiguenave, C.; Bertrand, M.J.; Waldron, K.C. Glutaraldehyde: Behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. BioTechniques 2004, 37, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olde Damink, L.H.H.; Dijkstra, P.J.; van Luyn, M.J.A.; van Wachem, P.B.; Nieuwenhuis, P.; Feijen, J. Glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent for collagen-based biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, H.; Hasirci, N. Preparation and characterization of crosslinked gelatin microspheres. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 58, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harland, R.S.; Peppas, N.A. Solute diffusion in swollen membranes. VII Diffusion in semicrystalline network. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1989, 267, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Venugopal, J.; Huang, Z.M.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Crosslinking of the electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannas, I.V.; Tobolsky, A.V. Cross-linking of gelatine by dehydration. Nature 1967, 215, 509–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruijgrok, J.M.; de Wijn, J.R.; Boon, M.E. Optimising glutaraldehyde crosslinking of collagen: Effects of time, temperature and concentrations as measured by shrinkage temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1994, 5, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
