Protein-Based Films and Coatings: An Innovative Approach
Abstract
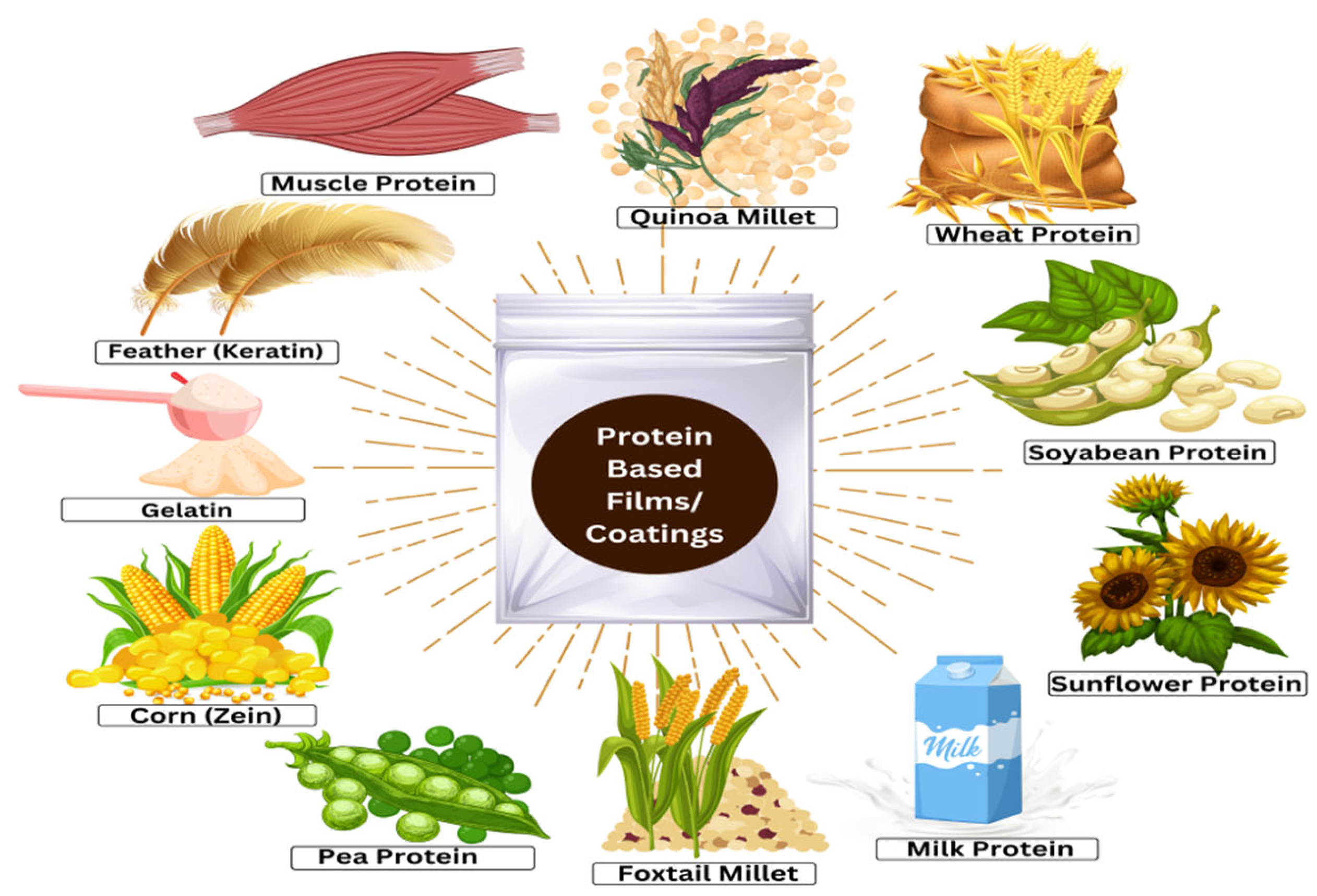
:1. Introduction
2. Historical Development
3. Improvement of Protein-Based Films and Coatings
3.1. Chemical Treatment
3.2. Enzyme-Based Treatment
3.3. Irradiation Treatment
3.4. Modification Using Hydrophobic Material
4. Physiochemical Properties
4.1. Mechanical Characteristics
4.2. Thickness
4.3. Water Vapor Permeability
4.4. Biodegradability
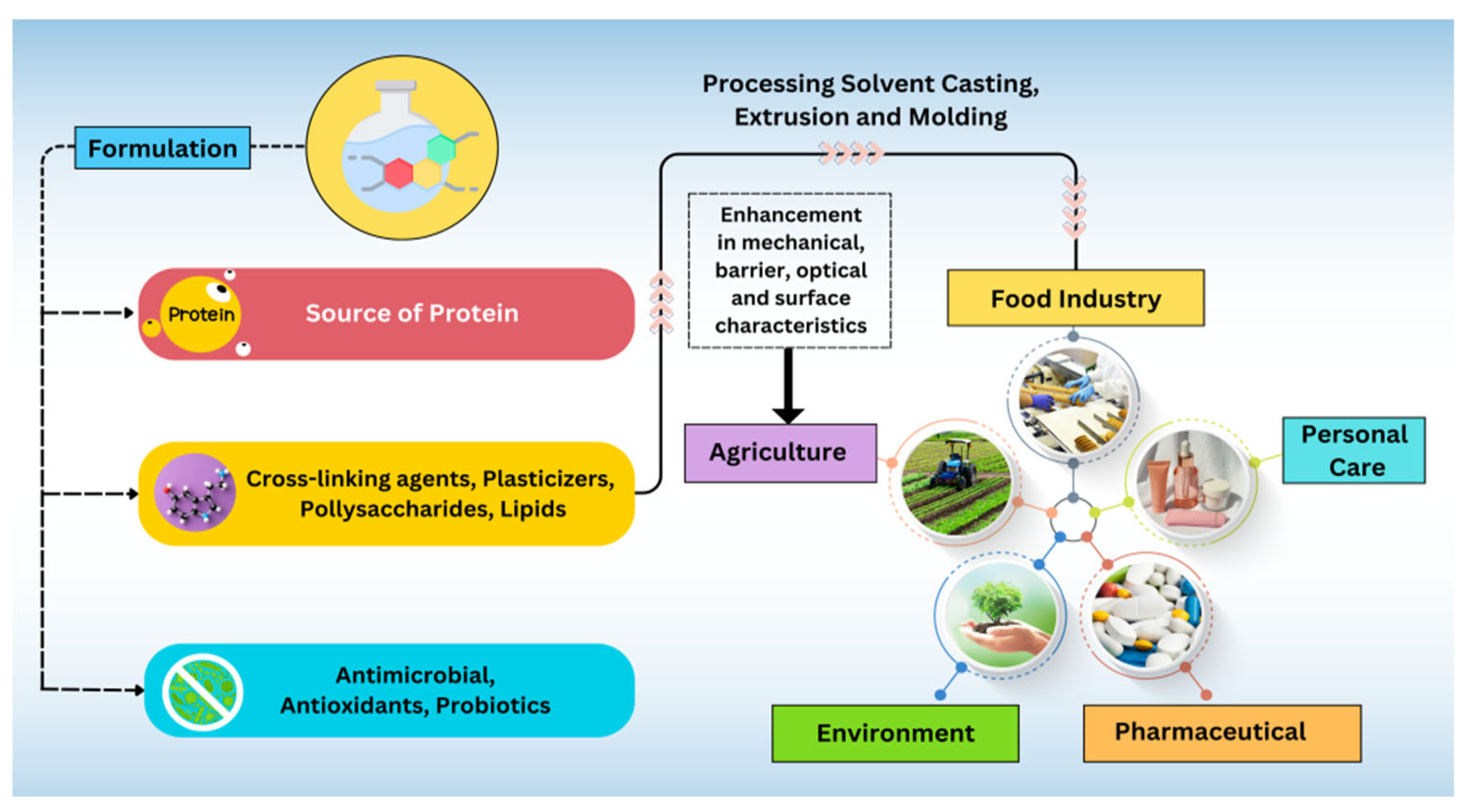
5. Applications of Protein-Based Films and Coatings
5.1. Role in Food Industries
5.2. Protein-Based Films/Coatings in Pharma Sector
5.3. Personal Care Products
5.4. Environmental Applications
5.5. Biodegradability and Sustainability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mihalca, V.; Kerezsi, A.D.; Weber, A.; Gruber-Traub, C.; Schmucker, J.; Vodnar, D.C.; Dulf, F.V.; Socaci, S.A.; Farcas, A.; Muresan, C.I.; et al. Protein-Based Films and Coatings for Food Industry Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, S.; Yoo, J.; Yun, J.; Kang, H.B.; Seol, K.H.; Kim, H.W.; Ham, J.S. Application of whey protein-based edible films and coatings in food industries: An updated overview. Coatings 2021, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Punia, S.; Dhakane-Lad, J.; Dhumal, S.; Changan, S.; Senapathy, M.; Berwal, M.K.; Sampathrajan, V.; Sayed, A.A.S.; et al. Plant-based proteins and their multifaceted industrial applications. LWT 2022, 154, 112620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Tang, P.; Yang, C.; Ran, R.; Li, G. Development of active packaging films based on collagen/gallic acid-grafted chitosan incorporating with ε-polylysine for pork preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 140, 108590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittaya, T. Protein-Based Edible Films: Characteristics and Improvement of Properties. In Structure and Function of Food Engineering; Eissa, A.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 43–70. ISBN 9789535106951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hossen, M.A.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. Gelatin-based composite films and their application in food packaging: A review. J. Food Eng. 2022, 313, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Valdes, A.; Beltran, A.; Garrigos, M.C. Gelatin-based films and coatings for food packaging applications. Coatings 2016, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, F.M.; Costa, D.; Yamashita, F.; Martelli, S.M.; Jesus, R.C.; Alganer, K.; Collares-Queiroz, F.P.; Innocentini-Mei, L.H. Comparative study of processing methods for starch/gelatin films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Sandhu, K.S.; Bangar, S.P.; Whiteside, W.S. Effect of edible coating from octenyl succinic anhydride modified rye starch to extend shelf life of plums. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Li, J.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, R.; Yu, X.; Hu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Ding, J.; et al. Supertough and highly stretchable silk protein-based films with controlled biodegradability. Acta Biomater. 2022, 153, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliarini, N.; Figoli, C.B.; Piermaria, J.; Bosch, A.; Abraham, A.G. Unraveling molecular interactions in whey protein-kefiran composite films to understand their physicochemical and mechanical properties. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Leng, X. Effects of curcumin, phycocyanin, or modified lycopene colorants on the physicochemical and sensory properties of whey protein–cellulose nanocrystal packaging films. Food Chem. 2023, 412, 135541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadaki, A.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Lappa, I.K.; Andriotis, H.; Eriotou, E.; Mandala, I.; Kopsahelis, N. Tuning the physical and functional properties of whey protein edible films: Effect of pH and inclusion of antioxidants from spent coffee grounds. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 27, 100700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, C.; Feng, X.; He, M.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y. Effects of two fatty acids on soy protein isolate/sodium alginate edible films: Structures and properties. LWT 2022, 159, 113221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shi, L.; Ren, Z.; Weng, W. Preparation and characterization of soy protein isolate films by pretreatment with cysteine. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetia, P.; Bharadwaj, C.; Purbey, R.; Bora, D.; Yadav, A.; Lal, M.; Rajulu, A.V.; Sadiku, E.R.; Selvam, S.P.; Jarugala, J. Influence of silylated nano cellulose reinforcement on the mechanical, water resistance, thermal, morphological and antibacterial properties of soy protein isolate (SPI)-based composite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Yu, D. Structural and physical properties of soybean protein isolate films with ohmic heating treatment: Impacts of electric field. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 82, 103213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Lema, S.; Nilsson, K.; Langton, M.; Trifol, J.; Gomez-Caturla, J.; Balart, R.; Garcia-Garcia, D.; Moriana, R. The effect of pine cone lignin on mechanical, thermal and barrier properties of faba bean protein films for packaging applications. J. Food Eng. 2023, 339, 111282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilah, Z.A.M.; Lyn, F.H.; Nabilah, B.; Jamilah, B.; Hean, C.G.; Hanani, Z.A.N. Enhancing the physicochemical and functional properties of gelatin/graphene oxide/cinnamon bark oil nanocomposite packaging films using ferulic acid. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Tian, L.; Li, J.; Jia, J.; Dong, Y.; Tu, Y.; Liu, X.; Tan, C.; Duan, X. Improving physicochemical properties of edible wheat gluten protein films with proteins, polysaccharides and organic acid. LWT 2022, 154, 112868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroti, G.K.; Saini, C.S. Development of edible films from protein of brewer’s spent grain: Effect of pH and protein concentration on physical, mechanical and barrier properties of films. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahsiri, Z.; Hedayati, S.; Niakousari, M. Improving the functional properties of wild almond protein isolate films by Persian gum and cold plasma treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, X. Biodegradable composite films based on egg white protein and tea polyphenol: Physicochemical, structural and antibacterial properties. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 38, 101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zi, Y.; Peng, J.; Shi, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, J. Gelatin as a bioactive nanodelivery system for functional food applications. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Liu, G.; Ye, W.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Lei, B.; Hu, C.; et al. Multifunctional carbon dots reinforced gelatin-based coating film for strawberry preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yu, R.; Zheng, H.; Wang, P. Acylated pectin/gelatin-based films incorporated with alkylated starch crystals: Characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities, and coating preservation effects on golden pomfret. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Lin, S.; Wu, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, J.; Zhu, W.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Emulsifier free fish gelatin based films with excellent antioxidative and antibacterial activity: Preparation, characterization and application in coating preservation of fish fillets. J. Food Eng. 2023, 343, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Hoang, H.T.; Trinh, C.D.; Bui, Q.T.P.; Phung, T.K.; Nguyen, T.T. Development of gelatin/agarose active coatings functionalized with Ocimum gratissimum L. essential oil for enhancing storability of ‘Booth 7’ avocado. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da-Silva, A.C.P.; Barbosa, J.R.; Araujo, C.S.; Batista, J.T.S.; Neves, E.M.P.X.; Cardoso, D.N.P.; Joele, M.R.S.P.; Lourenco, L.F.H. A new edible coating of fish gelatin incorporated into açaí oil to increase the post-harvest shelf life of tomatoes. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 138047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segu, D.Z.; Liyew, G.; Kim, C.L. Influence of gelatin-TiO2-Al2O3 nanocomposite coatings on enhancement of wear and corrosion resistance of SKD11 steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 312, 128658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Yang, L.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L. Development of electrospun fish gelatin film containing lauroyl arginate ethyl and its application in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) preservation. Food Control 2023, 153, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Ahmad, H.N.; Zhu, J. Photodynamic-responsive gelatin-based coating with high utilization curcumin loaded bilayer nanoencapsulation: A promising environmental food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzebieniarz, W.; Tkaczewska, J.; Juszczak, L.; Nowak, N.; Krzysciak, P.; Guzik, P.; Kasprzak, M.; Zimowska, M.; Jamroz, E. Design of active double-layer gel coatings based on furcellaran-gelatin and aqueous butterfly pea (Clitoria ternatea) flower extract for prolonging the shelf-life of salmon (Salmo salar). Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 186, 107945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, N.M.; Milani, J.M.; Amiri, Z.R. Fabrication of nanocomposite gelatin-based film by the pickering emulsion containing nanoparticles of chitin. J. Food Eng. 2024, 367, 111885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsallah, A.A.; Rashid, S.O. Development in gelatin-matrix composite films: The incorporation of vitamin C adducts enhances the optical behaviors of gelatin films. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, L.; Thanh, N.C.; Obaid, S.A.; Alfarraj, S.; Jhanani, G.K. Organic gelatin-coated ZnNPs for the production of biodegradable biopolymer films. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Song, G.; Huang, R.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Shi, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Fish gelatin films incorporated with cinnamaldehyde and its sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex and their application in fish preservation. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, S.T.W.; Adiningsih, S.N.; Widiyastuti, W.; Nurtono, T.; Setyawan, H.; Panatarani, C.; Praseptiangga, D.; Nazir, N.; Syamani, F.A. Novel cross-linking of toxic-free biopolymers for cellulose-gelatin films from avocado seed waste. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 25, 101725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erge, A.; Guler, B.Z.; Ergen, O. Optimization and characterization of biodegradable films from chicken gelatin crosslinked with oxidized phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadef, K.; Chaari, M.; Akermi, S.; Ennouri, K.; Hlima, H.B.; Fourati, M.; Mtibaa, A.C.; Ennouri, M.; Sarkar, T.; Shariati, M.A.; et al. Gelatin-sodium alginate packaging film with date pits extract: An eco-friendly packaging for extending raw minced beef shelf life. Meat Sci. 2024, 207, 109371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Huertas, T.K.; Mleko, M.T.; Mleko, S.; Garcia-Gareta, E.; Pakhlov, E.; Gonzalez-Caballero, F. Tailoring the surface and rheological properties of gelatine-based hydrogel films via indirect cold plasma treatment for engineering applications. J. Food Eng. 2024, 363, 111781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erceg, T.; Sovljanski, O.; Stupar, A.; Ugarkovic, J.; Acimovic, M.; Pezo, L.; Tomic, A.; Todosijevic, M. A comprehensive approach to chitosan-gelatine edible coating with β-cyclodextrin/lemongrass essential oil inclusion complex—Characterization and food application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, H.; Li, C.; Shi, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Ethyl cellulose/gelatin-carboxymethyl chitosan bilayer films doped with Euryale ferox seed shell polyphenol for cooked meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyeaka, P.O.; Dai, H.; Feng, X.; Wang, H.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Effect of different types of nanocellulose on the structure and properties of gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 108972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Kou, X. Direct addition of vanillin improved the physicochemical properties and antibacterial activities of gelatin/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose composite film. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 206, 117653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haririan, Y.; Asefnejad, A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Farahpour, M.R. Carboxymethyl chitosan-gelatin-mesoporous silica nanoparticles containing Myrtus communis L. extract as a novel transparent film wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Xie, P.; Sun, B.; Yang, X.; Lang, Y. Effect of chitosan-gelatine edible coating containing nano-encapsulated clove ethanol extract on cold storage of chilled pork. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Liu, X.; Li, H. Antibacterial castor oil-based waterborne polyurethane/gelatin films for packaging of strawberries. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 36, 101055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, J.S.; Han, J.; Chang, Y. Development of gelatin–sodium caseinate high-oxygen-barrier film containing elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) extract and its antioxidant capacity on pork. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekarina, A.S.; Supriyadi Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Susanto, E.; Show, P.L.; Ningrum, A. Effects of edible coatings of chitosan–fish skin gelatine containing black tea extract on quality of minimally processed papaya during refrigerated storage. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 5, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangapai, F.; Iwamoto, S. Influence of blending and layer-by-layer assembly methods on chitosan–gelatin composite films enriched with curcumin nanoemulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 126061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Mei, C.; Shi, C.; Li, C.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.; Cui, H. Preparation and characterization of gelatin active packaging film loaded with eugenol nanoparticles and its application in chicken preservation. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeogu, I.H.; Bako, H.K.; Yar, M.S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, M.; Ke, W.; Shan, K.; Zhou, G.; et al. Gelatin-serum plasma film incorporated with curcumin for improvement of antioxidant and antibacterial properties for fresh pork packaging application. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhuang, D.; Feng, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J. Novel “all-in-one” multifunctional gelatin-based film for beef freshness maintaining and monitoring. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 136003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, H.; Kai, Y.; Yang, H. Preservative effect of gelatin/chitosan-based films incorporated with lemon essential oil on grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets during storage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 407, 110437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, K.Y.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Extending cheese shelf-life using eco-friendly sodium alginate-gelatin films reinforced with nanoclay. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshkalampour, A.; Ghorbani, M.; Ghasempour, Z. Cross-linked gelatin film enriched with green carbon quantum dots for bioactive food packaging. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhai, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Sun, C.; Wang, W.; Hou, H. Effects of natural wax types on the physicochemical properties of starch/gelatin edible films fabricated by extrusion blowing. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obas, F.L.; Thomas, L.C.; Terban, M.W.; Schimdt, S.J. Characterization of the thermal behavior and structural properties of a commercial high-solids confectionary gel made with gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 148, 109432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammam, A.R.A. Technological, applications, and characteristics of edible films and coatings: A review. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapper, M.; Chiralt, A. Starch based coatings for preservation of fruits and vegetables. Coatings 2018, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, B.D.; Lule, V.K.; Vyawahare, S.; Rani, R. Application of Edible Packaging in Dairy and Food Industry. In Food Processing and Packaging Technologies; Tumuluru, J.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaldia, K.; Perez, C.; Banon, S.; Desobry, S.; Hardy, J. Milk proteins for edible films and coatings. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girdhar, V.; Patil, S.; Dubey, S.K.; Singhvi, G. Pharmaceutical applications of gelatin. In Natural Polymers for Pharmaceutical Applications; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2019; Volume 24, ISBN 9780429328350. [Google Scholar]
- Marianela, A.N.; Caballo-Gonzalaez, M.A.; Mata, F.J.; Garcia-Gallego, S. Shell formulation in soft gelatin capsules: Design and characterization. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 2023, 2302250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marianela, C.R.; Daniel, A.A.; Madrigal-Redondo, G.L. Gelatin and non-gelatin soft gel capsules: A review. J. Excip. Food Chem. 2021, 12, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Damian, F.; Harati, M.; Schwartzenhauer, J.; Cauwenberghe, O.V.; Wettig, S.D. Challenges of dissolution methods development for soft gelatin capsules. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullapalli, R.P.; Mazzitelli, C.L. Gelatin and non-gelatin capsule dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Chu, Y.; Tao, N.; Deng, S.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Application of gelatin in food packaging: A review. Polymers 2022, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, N.S.; Howell, N.K.; Sarbon, N.M. A review on potential use of gelatin-based film as active and smart biodegradable films for food packaging application. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 39, 1063–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Pratibha; Prasad, J.; Yadav, A.; Upadhyay, A.; Neeraj; Shukla, S.; Petkoska, A.T.; Heena; Suri, S.; et al. Recent trends in edible packaging for food applications-perspective for the future. Food Eng. Rev. 2023, 15, 718–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.S.; Olawuyi, I.F.; Lee, W.Y. Pectin hydrogels: Gel-forming behaviors, mechanisms, and food applications. Gels 2023, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Puello, V.; Figueroa-Lopez, K.J.; Ortega-Toro, R. Gelatin-based hydrogels containing microcrystalline and nanocrystalline cellulose as moisture absorbers for food packaging applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, Z.A.N.; Roos, Y.H.; Kerry, J.P. Use and application of gelatin as potential biodegradable packaging materials for food products. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Rios, D.A.; Nakamoto, M.M.; Cavalcante-Braga, A.R.; Silva, E.M.C. Food coating using vegetable sources: Importance and industrial potential, gaps of knowledge, current application, and future trends. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Lin, X.; Li, S.; Wu, X.; Mu, G.; Jiang, S. The coexistence of carboxymethylcellulose and transglutaminase modified the physicochemical properties and structure of whey protein concentrate films. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, H.; Airouyuwaa, J.O.; Hamed, F.; Wang, Y.; Maqsood, S. Structural, mechanical, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of soy protein isolate (SPI)-based edible food packaging films as influenced by nanocellulose (NC) and green extracted phenolic compounds from date palm leaves. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 38, 101124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, T.; Trinh, B.M.; Mekonnen, T.H.; Sarkar, P.; Aluko, R.E.; Bandara, N. Improving properties of canola protein-based nanocomposite films by hydrophobically modified nanocrystalline cellulose. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 35, 101018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Z.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Shi, S.Q.; Gao, Q. Development of a strong and multifunctional soy protein-based adhesive with excellent coating and prepressing in wet state by constructing a radical polymerization and organic-inorganic mineralization bionic structure. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 400, 136730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, W.R.; Capezza, A.J.; Kuktaite, R.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Johansson, E. Green Chemistry to Modify Functional Properties of Crambe Protein Isolate-Based Thermally Formed Films. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 20342–20351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chai, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, M.; Zeng, X.; Xu, X. Development of edible films by incorporating nanocrystalline cellulose and anthocyanins into modified myofibrillar proteins. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, N.A.; Riar, C.S.; Singh, S. Effect of film forming solution pH on antibacterial, antioxidant and structural characteristics of edible films from modified quinoa protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, W.; Gao, J.; Liao, X.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Y.; Sui, X.; et al. Influence mechanism of wheat bran cellulose and cellulose nanocrystals on the storage stability of soy protein isolate films: Conformation modification and molecular interaction perspective. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Bian, H.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, W. Application of protein-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Han, J. Rheological insight of polysaccharide/protein based hydrogels in recent food and biomedical fields: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1642–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, F.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Teng, L.; Haroon, M.; Khan, R.U.; Mehmood, S.; Amin, B.U.; Ullah, R.S.; Khan, A.; et al. Advances in chemical modifications of starches and their applications. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 476, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirsa, S.; Aghbolagh Sharifi, K. A review of the applications of bioproteins in the preparation of biodegradable films and polymers. J. Chem. Lett. 2020, 1, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Cui, L. Effects of high-intensity ultrasound on the structural, optical, mechanical and physicochemical properties of pea protein isolate-based edible film. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 80, 105809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zink, J.; Wyrobnik, T.; Prinz, T.; Schmid, M. Physical, chemical and biochemical modifications of protein-based films and coatings: An extensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Mu, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, X.; Tuo, Y.; Qian, F. Evaluation of the properties of whey protein films with modifications. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, L. Application of Whey Protein-Based Emulsion Coating Treatment in Fresh-Cut Apple Preservation. Foods 2023, 12, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Dong, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, H. Improved viability of probiotics encapsulated in soybean protein isolate matrix microcapsules by coacervation and cross-linking modification. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schräder, C.U.; Heinz, A.; Majovsky, P.; Mayack, B.K.; Brinckmann, J.; Sippl, W.; Schmelzer, C.E. Elastin is heterogeneously cross-linked. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15107–15119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Al-Asmar, A.; Mariniello, L. Transglutaminase protein substrates of food interest. In Enzymes in Food Technology: Improvements and Innovations; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 293–317. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Wang, W. Improved thermal-stability and mechanical properties of type I collagen by crosslinking with casein, keratin and soy protein isolate using transglutaminase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, H.; Shen, X. Effect of ultrasound pretreatment on structural, physicochemical, rheological and gelation properties of transglutaminase cross-linked whey protein soluble aggregates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 74, 105553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbah, M.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Esposito, M.; Di Pierro, P.; Mariniello, L.; Porta, R. Transglutaminase cross-linked edible films and coatings for food applications. In Enzymes in Food Biotechnology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 369–388. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, K.; Kazmi, S.; Nanda, A.; Bashir, K.; Khan, A.L.; Jan, S. Methods for the Improvement of Barrier and Mechanical Properties of Edible Packaging. In Edible Food Packaging: Applications, Innovations and Sustainability; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 353–368. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Wang, G.; Guo, M. Effects of Radiation on Cross-Linking Reaction, Microstructure, and Microbiological Properties of Whey Protein-Based Tissue Adhesive Development. Polymers 2022, 14, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Xia, N.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, H. Preparation, characterization and application of SPI-based blend film with antioxidant activity. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 27, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Wang, C.N.; Zhang, Y.C.; Liu, T.T.; Lv, J.P.; Shen, X.; Guo, M.R. Effects of gamma radiation on microbial, physicochemical, and structural properties of whey protein model system. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrin, M.; Macerata, E.; Consolati, G.; Quasso, F.; Genovese, L.; Soccio, M.; Giola, M.; Lotti, N.; Munari, A.; Mariani, M. Gamma radiation effects on random copolymers based on poly (butylene succinate) for packaging applications. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 142, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, Y.; Onal-Ulusoy, B.; Mutlu, M. Detoxification of hazelnuts by different cold plasmas and gamma irradiation treatments. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, S.; Sharma, N.; Mohite, A.M. Edible coatings and films for shelf-life extension of fruit and vegetables. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 154, 213632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Pant, K.; Brar, D.S.; Dar, B.N.; Nanda, V. Exploring the versatility of diverse hydrocolloids to transform techno-functional, rheological, and nutritional attributes of food fillings. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 146, 109275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourtoom, T. Factors affecting the properties of edible film prepared from mung bean proteins. Int. Food Res. J. 2008, 15, 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kanmani, P.; Lim, S.T. Development and characterization of novel probiotic-residing pullulan/starch edible films. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, T.; Leceta, I.; Cabezudo, S.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Tailoring soy protein film properties by selecting casting or compression as processing methods. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 85, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavand, F.; Rouhi, M.; Razavi, S.H.; Cacciotti, I.; Mohammadi, R. Improving the integrity of natural biopolymer films used in food packaging by crosslinking approach: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 687–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falguera, V.; Quintero, J.P.; Jiménez, A.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ibarz, A. Edible films and coatings: Structures, active functions and trends in their use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, P.L.M.; Pires, A.T.N.; Soldi, V. Thermal degradation of edible films based on milk proteins and gelatin in inert atmosphere. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 79, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialamas, H.; Zinoviadou, K.G.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Development of a novel bioactive packaging based on the incorporation of Lactobacillus sakei into sodium-caseinate films for controlling Listeria monocytogenes in foods. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2402–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chang, P.R.; Yu, J. Properties of biodegradable thermoplastic pea starch/carboxymethyl cellulose and pea starch/microcrystalline cellulose composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Lenart, A. Development and characterization of composite edible films based on sodium alginate and pectin. J. Food Eng. 2013, 115, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukoulis, C.; Behboudi-Jobbehdar, S.; Yonekura, L.; Parmenter, C.; Fisk, I.D. Stability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in prebiotic edible films. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianina, I.B.; Jrb, A.G.O.; Pimentelc, T.C.; Hernandesa, N.F.; Costaa, G.N. Edible Biofilms Formulated with Whey Protein Isolate and L. casei Probiotic Culture: Characterization and Application in Tomatoes and Grapes. Chem. Eng. 2019, 75, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.O.; Soares, J.; Sousa, S.; Madureira, A.R.; Gomes, A.; Pintado, M. Edible films as carrier for lactic acid bacteria. LWT 2016, 73, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzakhani, M.; Moini, S.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Physical and mechanical features investigation of protein-based biodegradable films obtained from trout fish waste. J. Food Bioprocess. Eng. 2018, 2, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, O.L.; Pop, C.R.; Dufrechou, M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Dulf, F.V.; Minervini, F.; Suharoschi, R. Edible Films and Coatings Functionalization by Probiotic Incorporation: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Won, M.; Song, K. Antioxidant activities of distiller dried grains with solubles as protein films containing tea extracts and their application in the packaging of pork meat. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.B.; Lee, J.H.; Mijan, M.A.; Song, K.B. Development of a chicken feather protein fi lm containing clove oil and its application in smoked salmon packaging. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, Y.; Darbe, S.; Hayashi, S.; Kudasheva, A.; Misawa, H.; Shibata, Y.; Kasuya, K.I. Environmental biodegradability of recombinant structural protein. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Forough, M.; Garavand, F.; Alizadeh, S.; Salehabadi, A.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Jafari, S.M. Plant protein-based food packaging films; recent advances in fabrication, characterization, and applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 154–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadermazi, R.; Hamdipour, S.; Sadeghi, K.; Ghadermazi, R.; Asl, A.K. Effect of various additives on the properties of the films and coatings derived from hydroxypropyl methylcellulose—A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3363–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, R.; Zo, S.M.; Narayanan, K.B.; Purohit, S.D.; Gupta, M.K.; Han, S.S. Recent development of protein-based biopolymers in food packaging applications: A review. Polymer Test. 2023, 124, 108097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Kajla, P.; Kumari, P.; Bangar, S.P.; Rusu, A.; Trif, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Milk protein-based active edible packaging for food applications: An eco-friendly approach. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 942524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visan, A.I.; Cristescu, R. Polysaccharide-Based Coatings as Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzoghby, A.O.; Samy, W.M.; Elgindy, N.A. Protein-based nanocarriers as promising drug and gene delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, A.A.; Ullah, A.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Marei, H.E.; Madappura, A.P.; Hassan, M.; Rizwan, M.; Gomes, V.G.; Amirfazli, A.; Hasan, A. Oxygen releasing patches based on carbohydrate polymer and protein hydrogels for diabetic wound healing: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirjalili, F.; Mahmoodi, M. Controlled release of protein from gelatin/chitosan hydrogel containing platelet-rich fibrin encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles for accelerated wound healing in an animal model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agwa, M.M.; Sabra, S.; Atwa, N.A.; Dahdooh, H.A.; Lithy, R.M.; Elmotasem, H. Potential of frankincense essential oil-loaded whey protein nanoparticles embedded in frankincense resin as a wound healing film based on green technology. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 71, 103291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosas, K.K.A.; Chandrasekar, A.R.; Dasan, A.; Pakseresht, A.; Galusek, D. Recent Advancements in Materials and Coatings for Biomedical Implants. Gels 2022, 8, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basova, T.V.; Vikulova, E.S.; Dorovskikh, S.I.; Hassan, A.; Morozova, N.B. The use of noble metal coatings and nanoparticles for the modification of medical implant materials. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.; Bernard, J.; Ganachaud, F.; Miserez, A. Protein-Based Encapsulation Strategies: Toward Micro- and Nanoscale Carriers with Increased Functionality. Small Sci. 2022, 2, 2100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffo, R.A.; Han, J.H. 17—Edible films and coatings from plant origin proteins. In Innovations in Food Packaging; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosowska, A.; Wawrzynczak, A.; Feliczak-Guzik, A. Microencapsulation as a Route for Obtaining Encapsulated Flavors and Fragrances. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Pan, X.; Rong, L.; Dong, A.; He, Y.; Song, X.; Li, J. Polymer carriers for controlled fragrance release. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 82001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, R.; Santos, L. Encapsulation of cosmetic active ingredients for topical application—A review. J. Microencapsul. 2015, 33, 1115900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Shams, R.; Dash, K.K. Techno-functional characteristics, and potential applications of edible coatings: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowicz, M.; Galus, S.; Ciurzynska, A.; Nowacka, M. The Potential of Edible Films, Sheets, and Coatings Based on Fruits and Vegetables in the Context of Sustainable Food Packaging Development. Polymers 2023, 15, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.S.; Khorshidian, N.; Mohammadi, M. An insight to potential application of synbiotic edible films and coatings in food products. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 875368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Montes, E.; Castro-Munoz, R. Edible Films and Coatings as Food-Quality Preservers: An Overview. Foods 2021, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kola, V.; Carvalho, I.S. Plant extracts as additives in biodegradable films and coatings in active food packaging. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Biswas, D.; Roy, S. A Comprehensive Review of Biodegradable Polymer-Based Films and Coatings and Their Food Packaging Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharanathan, R.N. Biodegradable films and composite coatings: Past, present and future. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.M.; Guimaraes, J.T.; Pimentel, T.C.; Esmerino, E.A.; Freitas, M.Q.; Carvalho, C.W.P.; Cruz, A.G.; Silva, M.C. Chapter 7—Edible whey protein films and coatings added with prebiotic ingredients. In Agri-Food Industry Strategies for Healthy Diets and Sustainability; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, E.; Schmid, M.; Nerney, O.M.; Wildner, J.; Smykala, L.; Lazzeri, A.; Cinelli, P. Processing and Validation of Whey-Protein-Coated Films and Laminates at Semi-Industrial Scale as Novel Recyclable Food Packaging Materials with Excellent Barrier Properties. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 496207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.T.; Subramanian, B.; Arockiarajan, A. A comprehensive review on biocompatible thin films for biomedical application. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 437–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Xu, J.; Zhong, F.; Rotello, V.M. Strategies for Fabricating Protein Films for Biomaterials Applications. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2000167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, D.; Lei, X.; Zheng, H. Recent Advances in Biomass-Based Materials for Oil Spill Cleanup. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, B.; Sillanpaa, M.; Kalliola, S. A review of bio-based materials for oil spill treatment. Water Res. 2018, 135, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.S.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Luther, D.C.; Rotello, V.M. Protein-Based Films as Antifouling and Drug-Eluting Antimicrobial Coatings for Medical Implants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48301–48307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.A.A.; El-Sakhawy, M.; El-Sakhawy, M.A. Polysaccharides, Protein and Lipid -Based Natural Edible Films in Food Packaging: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y. Wheat gluten-based coatings and films: Preparation, properties, and applications. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Joo, E.; Song, H.G.; Choi, I.; Yoon, C.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Han, J. Development of Protein-Based High-Oxygen Barrier Films Using an Industrial Manufacturing Facility. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravartula, S.S.N.; Soccio, M.; Lotti, N.; Balestra, F.; Dalla Rosa, M.; Siracusa, V. Characterization of Composite Edible Films Based on Pectin/Alginate/Whey Protein Concentrate. Materials 2019, 12, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, B.L.; Richardson, J.J.; Nithipipat, V.; Kempe, K.; Guo, J.; Cho, K.L.; Rahim, M.A.; Ejima, H.; Caruso, F. Protein Adsorption and Coordination-Based End-Tethering of Functional Polymers on Metal-Phenolic Network Films. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubner, P.; Donati, N.; Quines, L.K.M.; Tessaro, I.C.; Marcilio, N.R. Gelatin-based films containing clinoptilolite-Ag for application as wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 107, 110215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, P.; Schmid, M.; Bugnicourt, E.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Recyclability of PET/WPI/PE Multilayer Films by Removal of Whey Protein Isolate-Based Coatings with Enzymatic Detergents. Materials 2016, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, A.R.; Goulão, M.; Santo, C.E.; Anjos, O.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Pintado, C.M.B.S. Novel, Edible Melanin-Protein-Based Bioactive Films for Cheeses: Antimicrobial, Mechanical and Chemical Characteristics. Foods 2023, 12, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartore, L.; Schettini, E.; de Palma, L.; Brunetti, G.; Cocozza, C.; Vox, G. Effect of hydrolyzed protein-based mulching coatings on the soil properties and productivity in a tunnel greenhouse crop system. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés-Rodríguez, M.; Villegas-Yépez, C.; Gil González, J.H.; Rodríguez, P.E.; Ortega-Toro, R. Development and evaluation of edible films based on cassava starch, whey protein, and bees wax. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Iqbal, M.H.; Meyer, F.; Ball, V.; Boulmedais, F. Physical Chemistry Study of Collagen-Based Multilayer Films. Gels 2023, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajdnik, U.; Luxbacher, T.; Vesel, A.; Štern, A.; Žegura, B.; Trček, J.; Fras Zemljič, L. Polysaccharide-Based Bilayer Coatings for Biofilm-Inhibiting Surfaces of Medical Devices. Materials 2021, 14, 4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.S.; Gupta, A.; Duncan, B.; Ramanathan, R.; Yazdani, M.; Rotello, V.M. Biocidal and Antifouling Chlorinated Protein Films. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1862–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, P.W.; Dingley, A.J.; Swift, S.; Nelson, A.R.J.; Martin, J.; McGillivray, D.J. Using Neutron Reflectometry to Characterize Antimicrobial Protein Surface Coatings. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 5908–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdecke, N.; Bekir, M.; Eickelmann, S.; Hartlieb, M.; Schlaad, H. Toward Protein-Repellent Surface Coatings from Catechol-Containing Cationic Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 19582–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, W.; Dang, X. Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Gelatin-Based Nanocomposite Films toward Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Prinz, T.K.; Stäbler, A.; Sängerlaub, S. Effect of Sodium Sulfite, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate, and Urea on the Molecular Interactions and Properties of Whey Protein Isolate-Based Films. Front. Chem. 2017, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, J.; Vale, A.C.; APires, R.; Botelho, G.; Reis, R.L.; Alves, N.M. Spin-Coated Polysaccharide-Based Multilayered Freestanding Films with Adhesive and Bioactive Moieties. Molecules 2020, 25, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basiak, E.; Geyer, M.; Debeaufort, F.; Lenart, A.; Linke, M. Relevance of Interactions between Starch-based Coatings and Plum Fruit Surfaces: A Physical-Chemical Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.G.; Leal-Egaña, A.; Scheibel, T.R. Engineered spider silk protein-based composites for drug delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Tártara, L.I.; Palma, S.D.; Alvarez Igarzabal, C.I. Crosslinked soy protein films and their application as ophthalmic drug delivery system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 51, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, E.; Winter, G.; Engert, J. Water-based preparation of spider silk films as drug delivery matrices. J. Control. Release 2015, 213, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Gnutt, P.; Wanka, R.; Krause, L.M.K.; Finlay, J.A.; Clare, A.S.; Rosenhahn, A. Layer-by-Layer Deposited Hybrid Polymer Coatings Based on Polysaccharides and Zwitterionic Silanes with Marine Antifouling Properties. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, C.J.; Wright, K.J.; Hyun, S.H.; Krynski, K.; Yu, G.; Bajaj, R.; Guo, F.; Stauffacher, C.V.; Jiang, W.; Thompson, D.H. Nonfouling NTA-PEG-Based TEM Grid Coatings for Selective Capture of Histidine-Tagged Protein Targets from Cell Lysates. Langmuir 2016, 32, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Gunari, N.; MacNeil, D.; Finlay, J.; Callow, M.; Callow, J.; Walker, G.C. Aqueous-Based Fabrication of Low-VOC Nanostructured Block Copolymer Films as Potential Marine Antifouling Coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20342–20351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Peydayesh, M.; Li, M.; Yao, Y.; Wu, D.; Mezzenga, R. Functional Coating from Amyloid Superwetting Films. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2205072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, I.; Bittante, A.M.Q.B.; Lourenço, R.V.; do Amaral Sobral, P.J. Properties of gelatin-based films incorporated with chitosan-coated microparticles charged with rutin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siontorou, C.G.; Georgopoulos, K.N.; Nikoleli, G.P.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Karapetis, S.K.; Bratakou, S. Protein-Based Graphene Biosensors: Optimizing Artificial Chemoreception in Bilayer Lipid Membranes. Membranes 2016, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Molino, P.J.; Harris, A.R.; Yue, Z.; Moulton, S.E.; Wallace, G.G. Conductive and protein resistant polypyrrole films for dexamethasone delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Moisture Sensitivity, Optical, Mechanical and Structural Properties of Whey Protein-Based Edible Films Incorporated with Rapeseed Oil. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 54, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rubio, A.; Blanco-Padilla, A.; Oksman, K.; Mendoza, S. Strategies to Improve the Properties of Amaranth Protein Isolate-Based Thin Films for Food Packaging Applications: Nano-Layering through Spin-Coating and Incorporation of Cellulose Nanocrystals. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Shi, C.; Cui, Y. Preparation and physicochemistry properties of smart edible films based on gelatin-starch nanoparticles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5470–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calva-Estrada, S.J.; Jimenez-Fernandez, M.; Vallejo-Cardona, A.A.; Castillo-Herrera, G.A.; Lugo-Cervantes, E.D.C. Cocoa Nanoparticles to Improve the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Whey Protein-Based Films to Extend the Shelf Life of Muffins. Foods 2021, 10, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopf-Marques, H.; Barthes, J.; Lachaal, S.; Mutschler, A.; Muller, C.; Dufour, F.; Rabineau, M.; Courtial, E.J.; Bystroňová, J.; Marquette, C.; et al. Multifunctional polymeric implant coatings based on gelatin, hyaluronic acid derivative and chain length-controlled poly(arginine). Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 104, 109898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type of Film | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Thickness (µm) | Water Content (%) | Water Vapor Permeability | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silk protein-based film | 0.4–19 | -- | -- | -- | [10] |
| Whey protein–kefiran composite films | 3.16–3.95 | 129.9–153.3 | 24.44–28.80 | -- | [11] |
| Whey protein–cellulose nanocrystal packaging films | -- | 166.05–173.2 | 14.84–18.05 | 2.82–3.18 (g·s−1·m−1·Pa−1) | [12] |
| Whey protein-based edible film | 0.7–1.8 | 100–160 | -- | 6.2–12.8 (g⋅mm/d⋅m2⋅kPa) | [13] |
| Soy protein isolate/sodium alginate edible films | 3.52–7.12 | -- | -- | 3.55–5.15 (g⋅mm/(m2⋅h⋅kPa)) | [14] |
| Soy protein isolate film | 7.09–7.88 | -- | -- | 0.86–1.19 (×10−10 g·m−1·s−1·Pa−1) | [15] |
| Soy protein-isolate-based film | 2.01–4.4 | 150–180 | 11.4–14.5 | -- | [16] |
| Soybean protein isolate films | -- | 126–232 | 17.93–20.11 | 0.60–0.76 (g⋅mm h−1 m−2 kPa−1) | [17] |
| Faba bean protein films | 4.8–9.3 | 258.7–372.5 | 13.7–15.5 | -- | [18] |
| Graphene oxide/cinnamon bark oil nanocomposite packaging films | 8–23 | 19–29 | 0.06–0.10 | 1.3–2.9 (×10−10 g m−1 s−1 Pa−1) | [19] |
| Wheat gluten protein films | -- | 47.89–69.37 | 1.73–2.13 | 7.16–17.07 ((g⋅mm)/(m2⋅d⋅kPa)) | [20] |
| Edible films from the protein of a brewer’s spent grain | -- | -- | 17.7–29.69 | 3.03–4.58 (g·m/m2·s·Pa) × 10−10 | [21] |
| Almond protein isolate films | 5.55–12.77 | 104–126 | -- | 165–166.1 (×10 g m−1 s−1 Pa−1) | [22] |
| Composite films based on egg-white protein | -- | -- | 9.38–13.95 | -- | [23] |
| Source | Purpose | References |
|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | Utilizing gelatin as a bioactive nanodelivery system for applications in functional foods | [24] |
| Gelatin-based coating | A gelatin-based coating film reinforced with multifunctional carbon dots for the preservation of strawberries | [25] |
| Acylated pectin/gelatin-based films | Characterization of acylated pectin/gelatin-based films containing alkylated starch crystals: Assessment of antioxidant and antibacterial activities, and examination of coating preservation effects on golden pomfret | [26] |
| Fish gelatin | Preparation, characterization, and application of emulsifier-free fish gelatin-based films exhibiting outstanding antioxidative and antibacterial activity for coating preservation of fish fillets | [27] |
| Gelatin/agarose-active coatings | Formulation of gelatin/agarose active coatings incorporating Ocimum gratissimum L. essential oil to improve the storability of ‘Booth 7’ avocados | [28] |
| Fish gelatin | A novel edible coating comprising fish gelatin infused with açaí oil to extend the postharvest shelf-life of tomatoes | [29] |
| Gelatin–TiO2–Al2O3 nanocomposite | Impact of gelatin-TiO2-Al2O3 nanocomposite coatings on improving the wear and corrosion resistance of SKD11 steel | [30] |
| Fish gelatin | Creation of electrospun fish gelatin film incorporating lauroyl arginate ethyl and its utilization in the preservation of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) | [31] |
| Gelatin | Environmentally promising food packaging utilizing a photodynamic-responsive gelatin-based coating with high-utilization curcumin-loaded bilayer nanoencapsulation | [32] |
| Furcellaran–gelatin | Formulation of active double-layer gel coatings using furcellaran-gelatin and aqueous butterfly pea (Clitoria ternatea) flower extract to extend the shelf-life of salmon (Salmo salar) | [33] |
| Nanocomposite gelatin | Creation of a nanocomposite gelatin-based film using Pickering emulsion containing chitin nanoparticles | [34] |
| Gelatin | Advancements in gelatin-matrix composite films: The incorporation of vitamin C adducts improves the optical characteristics of gelatin films | [35] |
| Gelatin-coated ZnNPs | Coating of biodegradable biopolymer films with organic gelatin-encapsulated ZnNPs | [36] |
| Fish gelatin | Utilization of fish gelatin films containing cinnamaldehyde and its sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex, with application in fish preservation | [37] |
| Cellulose–gelatin | Innovative cross-linking of nontoxic biopolymers for cellulose-gelatin films derived from waste avocado seeds | [38] |
| Chicken gelatin | Optimization and characterization of biodegradable films made from chicken gelatin crosslinked with oxidized phenolic compounds | [39] |
| Gelatin–sodium alginate | Eco-friendly packaging for extending the shelf-life of raw minced beef using a gelatin-sodium alginate film incorporated with date pits extract | [40] |
| Gelatin-based hydrogel | Customizing the surface and rheological properties of hydrogel films based on gelatin through indirect cold plasma treatment for engineering applications | [41] |
| Chitosan–gelatin | A holistic approach to edible coating with chitosan-gelatin incorporating β-cyclodextrin/lemongrass essential oil inclusion complex—Characterization and application in the food industry | [42] |
| Cellulose/gelatin-carboxymethyl chitosan | Bilayer films of ethyl cellulose/gelatin-carboxymethyl chitosan, enriched with polyphenols from Euryale ferox seed shells, for the preservation of cooked meat | [43] |
| Gelatin | Influence of various nanocellulose types on the structure and characteristics of gelatin films | [44] |
| Gelatin/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose | The direct incorporation of vanillin enhanced the physicochemical properties and antibacterial activities of gelatin/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose composite films | [45] |
| Carboxymethyl chitosan–gelatin | A novel transparent film wound dressing composed of carboxymethyl chitosan-gelatin-mesoporous silica nanoparticles incorporating Myrtus communis L. extract | [46] |
| Chitosan–gelatin | Influence of an edible coating comprising chitosan-gelatin with nano-encapsulated clove ethanol extract on the cold storage of chilled pork | [47] |
| Polyurethane/gelatin film | Antibacterial films for strawberry packaging using waterborne polyurethane/gelatin based on castor oil | [48] |
| Gelatin–sodium caseinate | Creation of a high-oxygen-barrier film comprising gelatin and sodium caseinate, enriched with elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) extract, and assessment of its antioxidant capacity on pork | [49] |
| Chitosan–fish skin gelatine | Impact of edible coatings made from chitosan and fish skin gelatin containing black tea extract on the quality of minimally processed papaya during refrigerated storage | [50] |
| Chitosan–gelatin | Impact of blending and layer-by-layer assembly techniques on chitosan–gelatin composite films enhanced with curcumin nanoemulsion | [51] |
| Gelatin | Formulation and characterization of an active packaging film based on gelatin loaded with eugenol nanoparticles, with application in the preservation of chicken | [52] |
| Gelatin–serum | Gelatin-serum plasma film infused with curcumin to enhance antioxidant and antibacterial properties for application in fresh pork packaging | [53] |
| Gelatin | Innovative “all-in-one” multifunctional gelatin-based film designed for the preservation and monitoring of beef freshness | [54] |
| Gelatin/chitosan-based film | Preservative impact of films based on gelatin and chitosan infused with lemon essential oil on the storage of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets | [55] |
| Alginate–gelatin | Prolonging the shelf-life of cheese through the use of eco-friendly sodium alginate-gelatin films reinforced with nanoclay | [56] |
| Gelatin | Cross-linked gelatin film enhanced with green carbon quantum dots for bioactive food packaging | [57] |
| Starch/gelatin | Impact of various natural wax types on the physicochemical properties of starch/gelatin edible films produced through extrusion blowing | [58] |
| Gelatin | Analysis of the thermal behavior and structural properties of a commercially produced high-solids confectionery gel containing gelatin | [59] |
| Protein | Method of Film Formation | Modification/Additive | Observation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canola meal-derived protein isolates | Solvent casting | Using fillers (oleic acid(OA)-modified (NCC) (OA-NCC)) | OA-NCC enhanced the canola protein nanocomposite film tensile strength by 3%. The OA-NCC 7% nanocomposite films increased the break elongation by 130%. The protein and OA-NCC cohesion increased the thermal stability and water barrier properties. | [78] |
| Soy protein isolate | - | Free-radical polymerization (temperature, 60 °C; time, 2 h; initiator, AIBN) | The multifunctional soy protein (SP)-based adhesive had a strong bonding, with a good coating and pressing strength for the wet veneer. The pressing strength was 0.45–0.85 MPa, the bond strength was 0.35–0.65 MPa, the water contact angle was 105θ, and the oil contact angle was 115θ. | [79] |
| Whey protein concentrate (WPC) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) | Solvent casting method | Modified by transglutaminase (TG) (concentration—0.5, 1, 1.5%; pH—−7; casting temperature—25 °C) | CMC as a protein network filler increased the WPC film characteristics, while TG improved the mechanical qualities. Compared to the WPC film, the composite (1:1) film with 10 U/g protein of TG had a maximum tensile strength of 13.34 MPa. | [76] |
| Crambe protein isolates (CPI) | Compression molding | pH modification (pH of 4–10) | Chemical modification of CPI increased the cross-linking by 20%, increased the tensile strength by 15%, and decreased the water vapor permeability by 10%. | [80] |
| Myofibrillar protein | Casting method | Changing the strength of the interaction between a protein and a filler material | Superior mechanical and water barrier properties using nanocrystalline cellulose, which improved the mechanical strength (elongation at break: 94.43% and tensile strength: 6.68 MPa) and the water vapor barrier (10.01 × 10−9 g m−1 s−1 Pa−1). | [81] |
| Quinoa protein | Casting method | pH modification | Antibacterial and antioxidant properties of the film decreased with improved physicochemical and structural properties. | [82] |
| Soy protein isolates | - | Conformation modification | Strengthened the hydrophobic interaction, which created a strong network structure and increased the SPI-based film-storage stability and tensile strength. | [83] |
| Place/Country | Type of Work/Purpose | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| University of Massachusetts at Amherst, United States | Protein-based films for Medical Implants: Antifouling and Drug-Eluting Antimicrobial Coatings | [152] |
| College of Applied Medical Sciences, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia | A Review of Natural Edible Films in Food Packaging: Polysaccharide, Protein, and Lipid-Based Approaches | [153] |
| Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas | Coatings and Films Derived from Wheat Gluten: Preparation, Properties, and Applications | [154] |
| College of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea | Creating High-Oxygen Barrier Films from Proteins in an Industrial Manufacturing Facility | [155] |
| University of Bologna, Italy | Characterization of Edible Composite Films Comprising Pectin, Alginate, and Whey Protein Concentrate | [156] |
| The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia | Adsorption of Proteins and Coordination-Based End-Tethering of Functional Polymers on Metal-Phenolic Network Films | [157] |
| Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), ZC, Brazil | Gelatin-Based Films with Clinoptilolite-Ag for Wound Dressing Applications | [158] |
| University of Pisa, Via Diotisalvi, Pisa | Recyclability of PET/WPI/PE Multilayer Films through Enzymatic Detergent Removal of Whey Protein Isolate-Based Coatings | [159] |
| Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal | Innovative Edible Bioactive Films with Melanin-Protein Base for Cheeses: Antimicrobial, Mechanical, and Chemical Characteristics | [160] |
| University of Brescia, Italy | Impact of Mulching Coatings Based on Hydrolyzed Protein on Soil Properties and Productivity in a Tunnel Greenhouse Crop System | [161] |
| Universidad Nacional de Colombia sede Medellín, Colombia | Creation and Assessment of Edible Films Derived from Cassava Starch, Whey Protein, and Beeswax | [162] |
| Université de Strasbourg, CNRS, France | Investigation into the Physical Chemistry of Multilayer Films Based on Collagen | [163] |
| University of Maribor, Smetanova, Slovenia | Bilayer Coatings Comprising Polysaccharides for Surfaces of Medical Devices with Biofilm-Inhibiting Properties | [164] |
| University of Massachusetts-Amherst, United States | Chlorinated Protein Films with Biocidal and Antifouling Properties | [165] |
| University of Auckland, New Zealand | Utilizing Neutron Reflectometry for the Characterization of Surface Coatings with Antimicrobial Proteins | [166] |
| University of Potsdam, Karl-Liebknecht-Straße, Germany | Moving Towards Protein-Repellent Surface Coatings Utilizing Catechol-Containing Cationic Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) | [167] |
| Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan, China | Gelatin-Based Nanocomposite Films Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles for Improved Mechanical Properties and Antibacterial Activity | [168] |
| Technische Universität MünchenFreising, Germany | Influence of Sodium Sulfite, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate, and Urea on the Molecular Interactions and Characteristics of Films Based on Whey Protein Isolate | [169] |
| Headquarters at University of Minho, Avepark, Barco, Portugal | Polysaccharide-Based Multilayered Freestanding Films with Adhesive and Bioactive Elements Fabricated via Spin Coating | [170] |
| University of Burgundy, France | Significance of Interactions between Coatings Derived from Starch and Plum Fruit Surfaces: A Physical-Chemical Examination | [171] |
| Universität Bayreuth, Universitätsstraße, Germany | Composite Materials for Drug Delivery Utilizing Engineered Spider Silk Proteins | [172] |
| Ciudad Universitaria, Córdoba, Argentina | Utilization of Crosslinked Soy Protein Films for Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Applications | [173] |
| Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Germany | Preparation of Spider Silk Films as Drug Delivery Matrices Using Water-based Methods | [174] |
| Newcastle University, United Kingdom | Hybrid Polymer Coatings with Marine Antifouling Properties, Formed through Layer-by-Layer Deposition of Polysaccharides and Zwitterionic Silanes | [175] |
| Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, United States | TEM Grid Coatings Based on Nonfouling NTA-PEG for Selective Capture of Histidine-Tagged Protein Targets from Cell Lysates | [176] |
| University of Toronto, Canada | Water-Based Production of Low-VOC Nanostructured Block Copolymer Films for Prospective Marine Antifouling Coatings | [177] |
| Department of Health Sciences and Technology, ETH Zurich, Zurich, 8092, Switzerland | Amyloid Superwetting Films as Functional Coatings | [178] |
| University of São Paulo, Brazil | Characteristics of Gelatin-Based Films Containing Chitosan-Coated Microparticles Loaded with Rutin | [179] |
| University of Piraeus, Piraeus, Greece | Optimizing Artificial Chemoreception in Bilayer Lipid Membranes Using Protein-Based Graphene Biosensors | [180] |
| University of Wollongong, NSW 2500, Australia | Polypyrrole Films with Conductive and Protein-Resistant Properties for the Delivery of Dexamethasone | [181] |
| University of Life Sciences-SGGW (WULS-SGGW), Poland | Moisture Sensitivity, Optical, Mechanical, and Structural Characteristics of Edible Films Based on Whey Protein Incorporating Rapeseed Oil | [182] |
| Universidad Autónoma de Querétaro, Querétaro 76010, Mexico | Enhancing the Characteristics of Thin Films Based on Amaranth Protein Isolate for Food Packaging Applications: Nano-Layering through Spin-Coating and Integration of Cellulose Nanocrystals | [183] |
| University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan, China | Formulation and Physicochemical Characteristics of Intelligent Edible Films Derived from Gelatin-Starch Nanoparticles | [184] |
| Universidad Veracruzana, Av. Doctor Luis Castelazo, Industrial Las Animas, Xalapa Enríquez C.P. 91190, VER, Mexico | Utilizing Cocoa Nanoparticles to Enhance the Physicochemical and Functional Attributes of Whey Protein-Based Films for Prolonging the Shelf Life of Muffins | [185] |
| Protip Medical, 8 Place de l’Hôpital, 67000 Strasbourg, France | Versatile Polymeric Coatings for Implants Incorporating Gelatin, Hyaluronic Acid Derivative, and Chain Length-Controlled Poly(Arginine) | [186] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Purewal, S.S.; Kaur, A.; Bangar, S.P.; Singh, P.; Singh, H. Protein-Based Films and Coatings: An Innovative Approach. Coatings 2024, 14, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14010032
Purewal SS, Kaur A, Bangar SP, Singh P, Singh H. Protein-Based Films and Coatings: An Innovative Approach. Coatings. 2024; 14(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14010032
Chicago/Turabian StylePurewal, Sukhvinder Singh, Avneet Kaur, Sneh Punia Bangar, Poornima Singh, and Harinder Singh. 2024. "Protein-Based Films and Coatings: An Innovative Approach" Coatings 14, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14010032
APA StylePurewal, S. S., Kaur, A., Bangar, S. P., Singh, P., & Singh, H. (2024). Protein-Based Films and Coatings: An Innovative Approach. Coatings, 14(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14010032







