Efficacy and Safety of Sitafloxacin in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Infection: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Search and Selection
2.2. Definition and Outcome
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
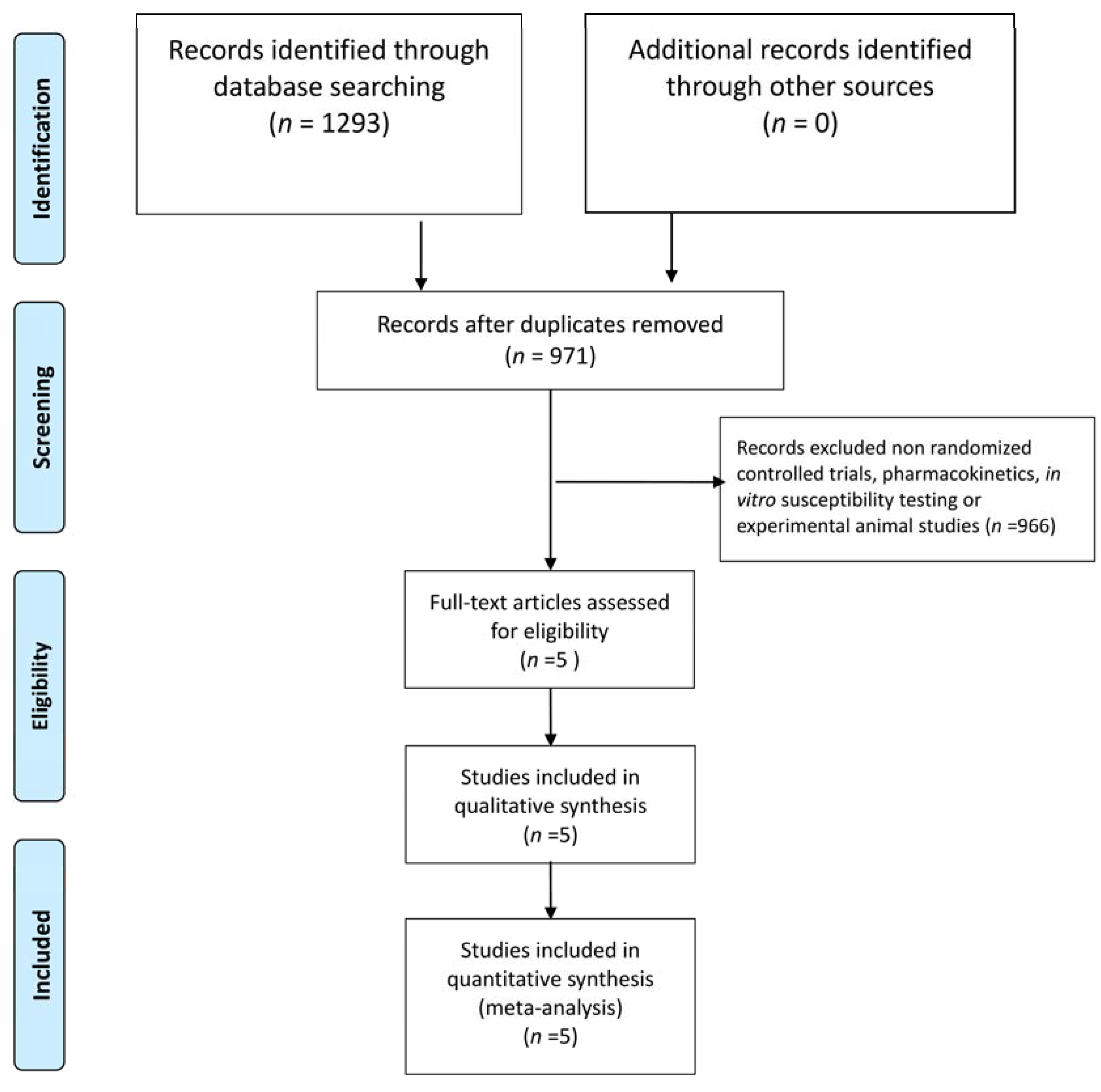
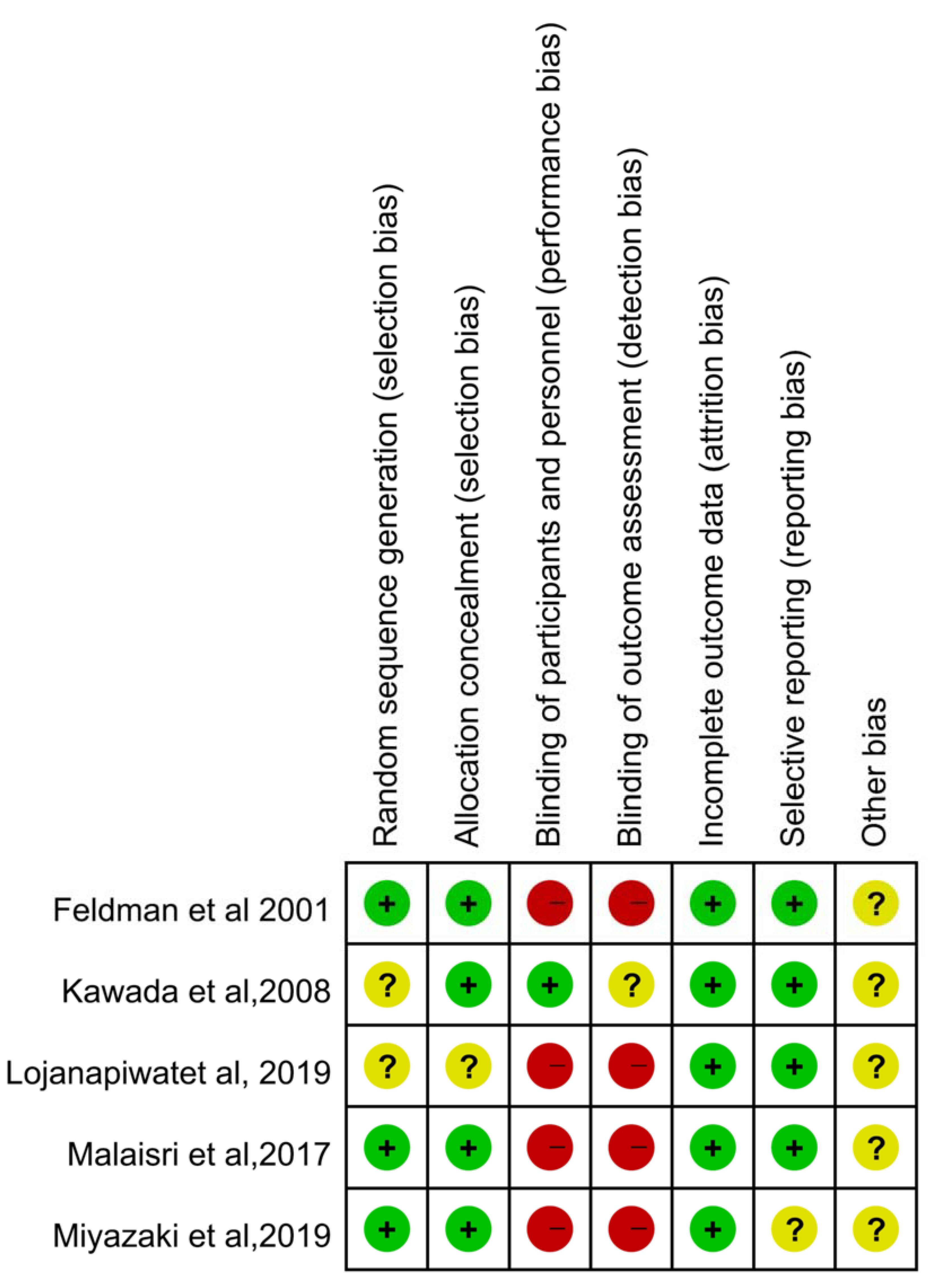
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
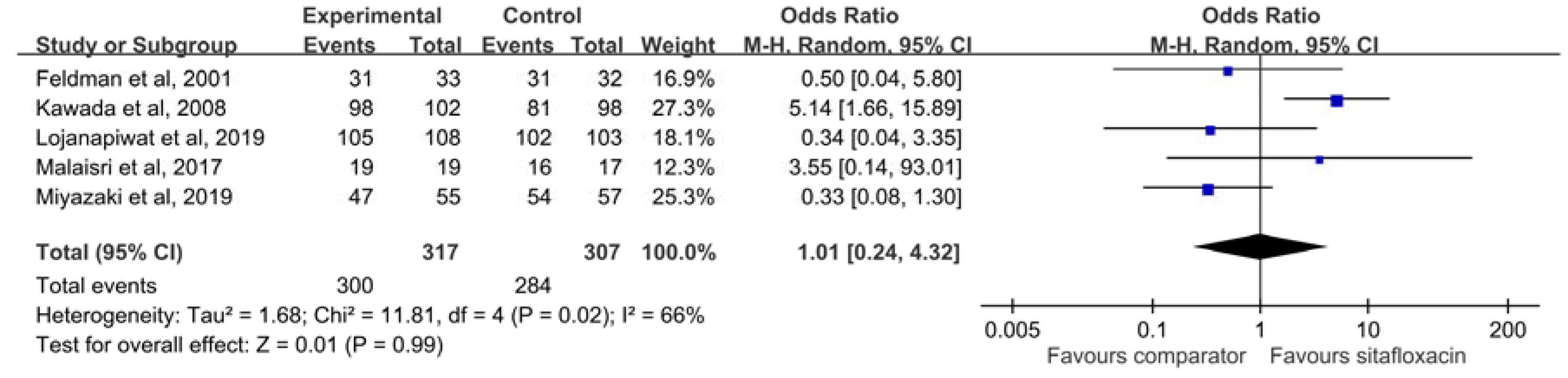
3.2. Clinical Efficacy
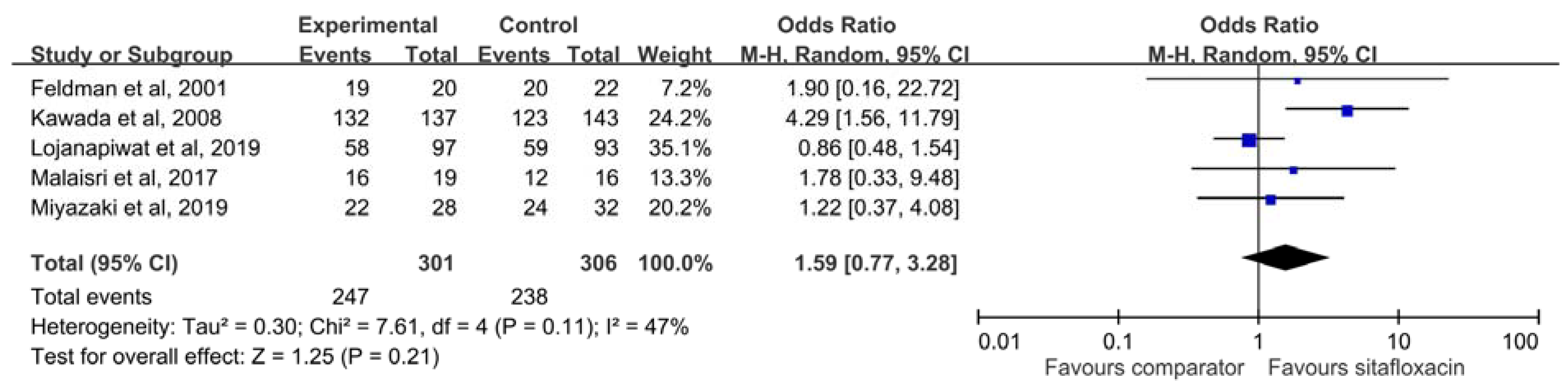
3.3. Microbiological Response
3.4. Risk of Adverse Event
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keating, G.M. Sitafloxacin: In bacterial infections. Drugs 2011, 71, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, A.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kishi, N.; Koyama, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Ikeda, F.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yokomizo, A.; Mizuno, M. In vitro activity of sitafloxacin against clinical isolates in 2012. Jpn. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amano, A.; Kishi, N.; Koyama, H.; Matsuzaki, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Uchino, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yokomizo, A.; Mizuno, M. In vitro activity of sitafloxacin against atypical bacteria (2009–2014) and comparison between susceptibility of clinical isolates in 2009 and 2012. Jpn. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.S.; Wang, J.T.; Sheng, W.H.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chang, S.C. Comparative in vitro activity of sitafloxacin against bacteremic isolates of carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii complex. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2015, 48, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, C.; White, H.; O’Grady, J.; Flitcroft, A.; Briggs, A.; Richards, G. An open, randomised, multi-centre study comparing the safety and efficacy of sitafloxacin and imipenem/cilastatin in the intravenous treatment of hospitalised patients with pneumonia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 17, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, J.; Niki, Y.; Kadota, J.; Yanagihara, K.; Kaku, M.; Watanabe, A.; Aoki, N.; Hori, S.; Tanigawara, Y.; Cash, H.L.; et al. Clinical and bacteriological efficacies of sitafloxacin against community-acquired pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae: Nested cohort within a multicenter clinical trial. J. Infect. Chemother. 2013, 19, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lojanapiwat, B.; Nimitvilai, S.; Bamroongya, M.; Jirajariyavej, S.; Tiradechavat, C.; Malithong, A.; Predanon, C.; Tanphaichitra, D.; Lertsupphakul, B. Oral sitafloxacin vs. intravenous ceftriaxone followed by oral cefdinir for acute pyelonephritis and complicated urinary tract infection: A randomized controlled trial. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaisri, C.; Phuphuakrat, A.; Wibulpolprasert, A.; Santanirand, P.; Kiertiburanakul, S. A randomized controlled trial of sitafloxacin vs. ertapenem as a switch therapy after treatment for acute pyelonephritis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli: A pilot study. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 23, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Nakamura, S.; Hashiguchi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukushima, K.; Fukuda, Y.; Kondo, A.; Inoue, Y.; Koga, H.; Sasaki, E.; et al. The efficacy and safety of sitafloxacin and garenoxacin for the treatment of pneumonia in elderly patients: A randomized, multicenter, open-label trial. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, N.; Wilson, A.P. Sitafloxacin in the treatment of patients with infections caused by vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, Y.; Matsui, T.; Matsui, T.; Tsugawa, M.; Mastumoto, T.; Nakashima, M. Comparative study on sitafloxacin and levofloxacin in complicated urinary tract infections. Jpn. J. Chemother. 2008, 56, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateda, K.; Ohno, A.; Ishii, Y.; Murakami, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Levofloxacin Surveillance Group. Investigation of the susceptibility trends in Japan to fluoroquinolones and other antimicrobial agents in a nationwide collection of clinical isolates: A longitudinal analysis from 1994 to 2016. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 594–604. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L. In vitro activities of sitafloxacin tested alone and in combination with rifampin, colistin, sulbactam, and tigecycline against extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8135–8140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Komatsu, M.; Yamasaki, K.; Fukuda, S.; Higuchi, T.; Ono, T.; Nishio, H.; Sueyoshi, N.; Kida, K.; Satoh, K.; et al. Susceptibility of various oral antibacterial agents against extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Infect. Chemother. 2014, 20, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Ohno, A.; Ishii, Y.; Tateda, K.; Iwata, M.; Kanda, M.; Tsujio, Y.; Kimoto, H.; Kaimori, M.; Nakamura, T.; et al. In-vitro susceptibilites to levofloxacin and various antibacterial agents of 18,639 clinical isolates obtained from 77 centers in 2004. Jpn. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 428–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Study, Published Year | Study Design | Study Site | Study Period | Study Population | No of Patients (ITT Population) | Dose regimen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sitafloxacin | Comparator | Sitafloxacin | Comparator | |||||
| Feldman et al., 2001 | phase II, randomized, open-label, parallel trial | 10 centers in three countries | NA | Acute bacterial pneumonia requiring hospitalization | 35 | 34 | Intravenous sitafloxacin 400 mg qd | Imipenem 500 mg q8h |
| Kawada et al., 2008 | randomized double-blind trial | 58 hospitals in Japan | 1998–2000 | Complicated urinary tract infection | 122 | 121 | Oral sitafloxacin 50 mg b.i.d | Oral levofloxacin 100 mg t.i.d |
| Malaisri et al., 2017 | prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled trial | Single hospital in Thailand | 2012–2015 | Acute pyelonephritis caused by ESBL E. coli | 19 | 17 | Oral sitafloxacin 100 mg bid followed by initial 3-day carbapenem | Intravenous ertapenem 1 g qd followed by initial 3-day carbapenem |
| Lojanapiwat et al., 2019 | prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled, noninferiority, clinical trial | 9 medical centers in Thailand | 2013 to 20159 | Acute pyelonephritis or complicated urinary tract infection | 141 | 148 | Oral sitafloxacin 100 mg bid | Intravenous ceftriaxone 2 g qd x 2–3 days, followed by oral cefdinir 100 mg q8h |
| Miyazaki et al., 2019 | randomized, open-label clinical trial | 11 medical centers or hospitals in Japan | 2013–2017 | Elderly patients with pneumonia | 58 | 61 | Oral sitafloxacin 100 mg qd | Oral garenoxacin 400 mg qd |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-K.; Cheng, I.-L.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-C. Efficacy and Safety of Sitafloxacin in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Infection: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9030106
Chen C-K, Cheng I-L, Chen Y-H, Lai C-C. Efficacy and Safety of Sitafloxacin in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Infection: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(3):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9030106
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chao-Kun, I-Ling Cheng, Yu-Hung Chen, and Chih-Cheng Lai. 2020. "Efficacy and Safety of Sitafloxacin in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Infection: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Antibiotics 9, no. 3: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9030106
APA StyleChen, C.-K., Cheng, I.-L., Chen, Y.-H., & Lai, C.-C. (2020). Efficacy and Safety of Sitafloxacin in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Infection: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Antibiotics, 9(3), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9030106





