Abstract
Background/Objective: Platelet concentrates (PCs) are used in transfusion medicine to treat bleeding disorders. Staphylococcus aureus, a predominant PC contaminant, has been implicated in several adverse transfusion reactions. The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of PC storage on S. aureus resistance to quinolones, which are commonly used to treat S. aureus infections. Methods/Results: Four transfusion-relevant S. aureus strains (TRSs) were subjected to comparative transcriptome analyses when grown in PCs vs. trypticase soy broth (TSB). Results of these analyses revealed differentially expressed genes involved in antibiotic resistance. Of interest, the norB gene (encodes for the NorB efflux pump, which is implicated in quinolone resistance and is negatively regulated by MgrA) was upregulated (1.2–4.7-fold increase) in all PC-grown TRS compared to TSB cultures. Minimal Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin in PC-grown TRS compared to TSB showed increased resistance to both quinolones in PC cultures. Complementary studies with non-transfusion-relevant strains S. aureus RN6390 and its norB and mgrA deletion mutants were conducted. MBC of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin and RT-qPCR assays of these strains showed that not only norB, but also norA and norC may be involved in enhanced quinolone resistance in PC-grown S. aureus. The role of norB in S. aureus virulence was also tested using the silkworm Bombyx mori animal model; lethal dose 50 (LD50) assays revealed slightly higher virulence in larvae infected with the wild-type strain compared to the norB mutant. Conclusions: The PC storage environment enhances quinolone resistance in S. aureus and induces differential expression of efflux pump nor genes. Furthermore, our preliminary data of the involvement of NorB in virulence of S. aureus using a silkworm model merit further investigation with other systems such as a mammal animal model. Our results provide mechanistic insights to aid clinicians in the selection of antimicrobial treatment of patients receiving transfusions of S. aureus-contaminated PCs.
1. Introduction
Platelet concentrates (PCs) are used to treat patients with bleeding disorders and consist of platelets suspended in plasma or a mix of plasma and platelet additive solution [1]. Platelet function and quality is maintained in the well-established PC storage conditions including incubation at 20–24 °C under constant agitation. Although important to maintaining platelet functionality, these conditions also sustain the growth of bacteria that may enter the blood collection bag during venipuncture [2]. To minimize the risk of transfusing bacterially contaminated PCs, Canadian Blood Services employ several strategies, including donor skin disinfection, diversion of the first 30–40 mL of collected blood, PC screening using the BACT/ALERT 3D automated culture system, and, more recently, PC treatment with the pathogen reduction technology INTERCEPT [2,3].
PC screening with the BACT/ALERT system is a gold standard method to improve PC safety; unfortunately, bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis can escape detection, posing a risk to transfusion recipients [3,4,5]. Recent research studies have demonstrated that both staphylococcal species grown in PCs exhibit increased expression of virulence-associated genes [6,7]. Additionally, S. epidermidis displays enhanced virulence when grown in PCs compared to laboratory media using the Caenorhabditis elegans animal model [8].
S. aureus is a facultative aerobic Gram-positive bacterium naturally present in the skin and mucosa of healthy humans and responsible for a wide range of community- and healthcare-associated infections [9]. Importantly, S. aureus is a predominant PC contaminant which has been involved in septic transfusion reactions worldwide and has therefore become an important safety risk to PC transfusion recipients due to its ability to escape detection during routine PC screening, grow to clinically significant levels, and produce exotoxins during PC storage [5,9].
Furthermore, S. aureus is known as a superbug due to the difficulty of treating infections caused by this organism with antimicrobial drugs [9]. There are several mechanisms involved in antimicrobial resistance in S. aureus including modifications of drug targets, drug inactivation, or drug extrusion via efflux pumps [10,11,12]. In Canada, quinolones are used to treat S. aureus infections [13]. However, this species has developed mechanisms of quinolone resistance. One of the strategies that S. aureus uses to resist quinolones involves target alteration. Specifically, mutations in the gyrA and gyrB genes which encode for the DNA gyrase or in the parC and parE genes which encode for the topoisomerase IV result in decreased binding affinity to quinolones [12]. Furthermore, the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) NorA, NorB, and NorC efflux pumps are involved in resistance to quinolones such as norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin [14]. As illustrated in Figure 1, MgrA is phosphorylated by the PknB kinase [15,16]; while norA expression is repressed by MgrA in its dephosphorylated state, norB is repressed when phosphorylated MgrA (MgrA-P) binds to its promoter [15,16,17,18]. Additionally, MgrA can be dephosphorylated by the RsbU phosphatase [16]. RsbU has a major role in the alternative sigma factor SigB regulon, which consists of four proteins, RsbV, RsbW, RsbU, and SigB [19]. When the bacterium is exposed to a stressful environment, RsbU dephosphorylates RsbV-P; dephosphorylated RsbV then binds to RsbW releasing SigB to form a complex with RNA polymerase resulting in the holoenzyme RNAP [19,20] (Figure 1). This holoenzyme drives the transcription of genes involved in housekeeping functions, virulence, biofilm formation, persistence, cell internalization, membrane transport, and antimicrobial resistance [20].
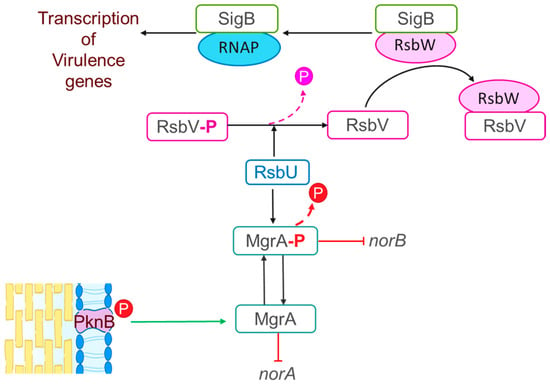
Figure 1.
Proposed model for the regulatory cascade for the “nor” family efflux in S. aureus. MgrA phosphorylation is driven by the PknB kinase resulting in repression of norA by MgrA in its dephosphorylated state and repression of norB by phosphorylated MgrA (MgrA-P). MgrA can be dephosphorylated by the RsbU phosphatase, which has a major role in the alternative sigma factor SigB regulon comprising four proteins, RsbV, RsbW, RsbU, and SigB. The SigB regulon is involved in expression of virulence genes as follows: RsbU dephosphorylates RsbV-P; dephosphorylated RsbV then binds to RsbW releasing SigB to form a complex with the RNA polymerase resulting in the holoenzyme RNAP. This holoenzyme drives the transcription of virulence genes [16,20].
In addition to antibiotic resistance, S. aureus produces several virulence factors including exotoxins, immune evasion factors, and membrane proteins that facilitate bacterial infection, making this bacterium a major threat for PC recipients [9]. Several animal models, including C. elegans, have been used to study S. aureus virulence in settings different from the PC storage environment [21]. Invertebrate animal models are amenable to investigate bacterial virulence and antimicrobial resistance as they are genetically simpler compared to other animal models, have low cost, and allow for a large sample size in research studies [22,23]. Within the invertebrate animal models, the Bombyx mori silkworm has been used to test S. aureus resistance to antimicrobial peptides [24]. More recently protocols have been established to test the virulence of the transfusion relevant bacterium Cutibacterium acnes using B. mori larvae [25].
Previous studies have demonstrated that Staphylococcus species grown in PCs display upregulation of genes encoding for antimicrobial resistance and virulence. A study from Loza et al. [7] has shown that exposure to the storage conditions and selective pressures present in PCs can lead to upregulation of genes associated with antibiotic resistance and enhanced virulence traits of S. epidermidis. Moreover, it has been shown that the PC environment triggers the upregulation of several virulence genes in PC-grown S. aureus compared to media [6,9]. These findings suggest that the PC environment provides a niche that not only supports staphylococcal survival but may also drive the expression of genes that contribute to pathogenicity and resistance to antibiotic treatment. The molecular mechanisms by which PC induces changes in bacterial virulence factors, including antibiotic resistance genes, are unknown.
Our previous studies have provided evidence of differential expression of antibiotic resistance genes in S. aureus grown in PCs [6,9]. To expand the current knowledge, this study aimed to directly test whether the increased gene expression observed under PC conditions translates into heightened antibiotic resistance with focus on resistance to quinolones by conducting comparative minimal bactericidal concentration assays. Furthermore, the work presented herein explored the role of the NorB efflux pump on virulence of S. aureus using a silkworm animal model.
2. Results
2.1. The PC Storage Milieu Triggers Upregulation of the norA, norB, and norC Efflux Pumps in a Strain-Dependent Manner
Differential expression of virulence factors between staphylococci grown in PCs and media have shown that genes involved in antibiotic resistance are upregulated in PC-grown S. epidermidis [7], and therefore we tested whether a similar phenotype was observed in S. aureus. Four transfusion-relevant S. aureus strains (TRSs), CBS2016-05, CI/BAC/25/13/W, PS/BAC/169/17/W, and PS/BAC/317/16/W) [26,27,28,29] were used for this study (Table 1). S. aureus CBS2016-05 was involved in a false-negative screening septic transfusion event in Canada while S. aureus CI/BAC/25/13/W was isolated in the National Health Service Blood and Transplant (NHSBT) in England, from a unit with false-negative screening results that presented aggregates and was therefore not transfused (near-miss). The other two strains, S. aureus PS/BAC/169/17/W and S. aureus PS/BAC/317/16/W, were detected during routine PC screening at the NHSBT. All isolates were grown in PCs and trypticase soy broth (TSB) and then subjected to comparative transcriptome analyses which showed differential regulation of antimicrobial resistance genes. This analysis revealed differentially expressed genes involved in various mechanisms of resistance to antibiotics, including the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS), the Multidrug and toxin extrusion family (MATE), ATP-binding cassette superfamily (ABC), and genes encoding for enzymes that modify the cellular targets of antibiotics and enzymes that modify or metabolize antimicrobial drugs (Figure 2).

Table 1.
List of S. aureus isolates investigated in this study and their origin.
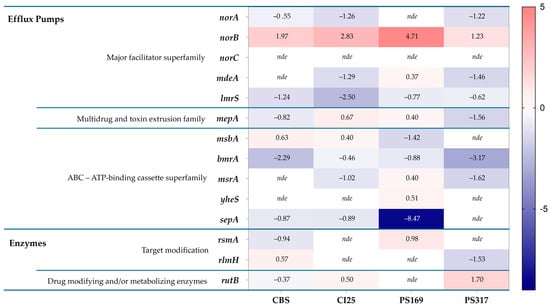
Figure 2.
Heatmap of S. aureus differentially expressed genes encoding antibiotic resistance mechanisms (PCs vs. TSB) [CBS: CBS2016-05, CI25: CI/BAC/25/13/W; PS169: PS/BAC/169/17/W and PS317: PS/BAC/317/16/W]. nde: Not differentially expressed. Heatmap prepared with GraphPad Prism (version 9.0.0).
The norB gene was the only one that was upregulated in the four TRSs with a significant log2 fold change ranging from 1.23 to 4.71 when S. aureus was grown in PCs compared to TSB (Figure 2). However, the other efflux pump genes of the nor family, norA and norC, were either downregulated or not differentially expressed (i.e., log2 fold change = 0) in PC-grown TRS compared to TSB cultures (Figure 2). The norB gene encodes for the efflux pump NorB, which is involved in quinolone resistance and is negatively regulated by MgrA [16,17,18]. Transcriptome data were verified with RT-qPCR assays, which confirmed the upregulation of norB in PC-grown S. aureus compared to TSB cultures in all four TRSs (Figure 3). Therefore, the role of NorB in S. aureus resistance to quinolones was further investigated using non-transfusion-relevant strains which included wild-type S. aureus RN6390 and its derivative mutants norB and mgrA. Interestingly, RT-qPCR showed that expression of all three genes, norA, norB, and norC, was increased (one to six-fold) in S. aureus RN6390 when this strain was grown in PCs and expression of both norA and norC genes was enhanced in PC cultures of the norB mutant (Figure 4). Unexpectedly, only norB was upregulated in the mgrA mutant despite that the global regulator MgrA represses expression of all three nor genes. Downregulation of norA and norC in the mgrA mutant strain could be due to the action of other regulators such as NorG, which is known to negatively regulate NorC [32] and the two-component regulatory system ArlR-ArlS, which is a negative regulator of NorA [33]. Importantly, in wild-type S. aureus RN6390, MgrA represses expression of NorG; therefore, in its absence, NorG can be active. Furthermore, NorG is a positive regulator of NorB and ArlS [17]. This complex interaction between regulators supports the findings presented in Figure 4 for the mgrA mutant. However, further experiments are needed to confirm this hypothesis and test the expression of other regulators in a mgrA- background. The differences observed in nor gene expression between TRS and RN6390 strains indicate that gene regulation of S. aureus grown in PCs depends on the strain’s genetic background.
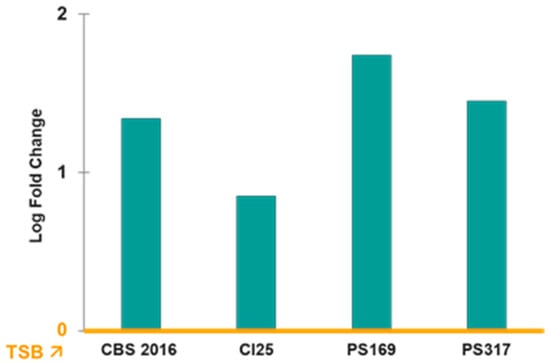
Figure 3.
RT-qPCR of norB expression in PCs compared to TSB (yellow line). Relative expression of norB genes in transfusion-relevant S. aureus strains cultured in platelet concentrates (PCs) compared to trypticase soy broth (TSB). TSB is the baseline (yellow line). Gene expression levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene (16S RNA) and calculated using the ΔΔCt method. Bars represent mean fold change from three pooled replicates. Expression of norB in PCs versus TSB was significantly different (p < 0.05).
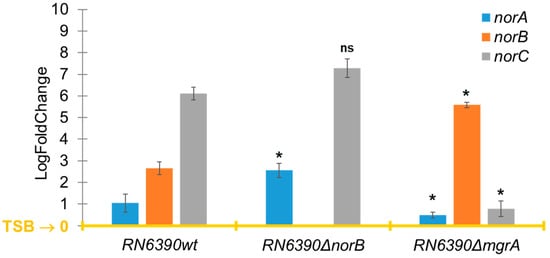
Figure 4.
Expression of efflux pumps genes norA, norB, and norC measured by RT-qPCR. Relative expression of norA, norB, and norC in S. aureus RN6390 and its deletion mutants norB and mgrA cultured in platelet concentrates (PCs) compared to trypticase soy broth (TSB). TSB is the baseline (yellow line). Gene expression levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene 16SRNA and calculated using the ΔΔCt method. Bars represent mean fold-change ± standard deviation from three biological replicates. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA, * p < 0.05; ns: not significant.
2.2. S. aureus Grown in PCs Displays Heightened Resistance to Quinolones
In Canada, quinolones are included as part of the treatment regimen for infections caused by S. aureus. [13]. Therefore, ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin were chosen to test quinolone resistance in PC-grown S. aureus. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimal Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) assays for both antibiotics were determined for the four TRSs, S. aureus RN6390, its derivative norB and mgrA mutants, and control S. aureus ATCC 29213. MIC data are shown in Supplementary Table S1. For MBC assays, all strains were cultured in PCs and TSB. MBC values in TSB were comparable to MIC results (Table 2 and Supplementary Table S1); however, MBC results for both quinolones were higher in PC-grown bacteria compared to TSB cultures reaching significant difference for ciprofloxacin (p < 0.05) in all strains tested except S. aureus PS/BAC/317/16/W, which was marginally different (p = 0.057) (Table 2). While only increased expression of norB may be associated with enhanced quinolone resistance in the TRS grown in PCs (Table 2 and Figure 2), all three norA, norB, and norC genes were upregulated in S. aureus RN6390 (Figure 4), which could play a role in increased quinolone resistance in this strain (Table 2). Comparative genomic analyses between TRSs and S. aureus RN6390 revealed no major differences in the genomic content and structure (Supplementary Table S2, Supplementary Figure S1) except for the mutation in the phosphatase rsbU gene in S. aureus RN6390. Therefore, the differences in nor gene expression between TRSs and the RN6390 strain, and consequent quinolone resistance, is likely due to the rsbU- background of S. aureus RN6390. It is anticipated that a mutation in the rsbU gene, which encodes for the RsbU phosphatase involved in MgrA dephosphorylation [16], would alter the ratio between MgrA and MgrA-P (Figure 1), resulting in differential expression of the nor genes, which warrants further studies.

Table 2.
Minimal Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin in S. aureus grown in TSB and PCs, and statistical comparison (n > 3).
Importantly, MBC values for ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin in wild-type S. aureus RN6390 and the norB mutant grown in PCs were not significantly different (p = 0.065 and p = 0.27, respectively, Table 2) indicating that norA and norC, which are upregulated in the norB mutant (Figure 4), confer resistance to these quinolones in a norB- background. However, resistance to ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin was significantly higher in the mgrA mutant compared to the wild-type strain (p = 0.0002 and p = 0.0011, respectively; Table 2), due mostly to the overexpression of norB in this strain as shown in Figure 4.
2.3. NorB Is Involved in Virulence of S. aureus in a Silkworm Model
It has been shown that the PC storage environment enhances the virulence of transfusion-relevant S. aureus CBS2016-05 and that overexpression of NorB increases S. aureus survival in a mouse abscess model [25,34]. With this information, we hypothesized that NorB could be involved in increased growth in PCs and enhanced virulence of S. aureus.
As shown in Figure 5, the growth dynamics of wild-type S. aureus RN6390 was not different from the growth displayed by the norB and mgrA mutants in PCs; therefore, norB does not seem to confer a growth advantage to S. aureus during PC storage.
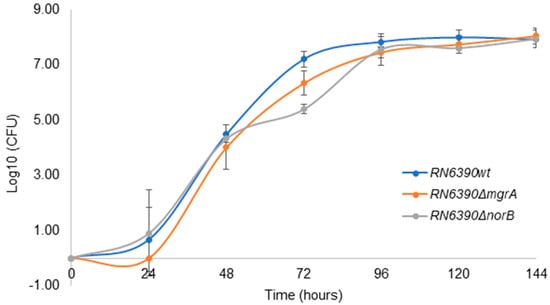
Figure 5.
S. aureus RN6390, RN6390ΔnorB and RN6390ΔmgrA grown in PCs. PC units inoculated with ~30 CFU/PC unit were incubated at 22 ± 2 °C, 60 rpm for 5 days (144 h). Results are presented as a mean of 3 independent trials. Error bars with standard deviation (±SD).
In virulence studies using animal models, lethal dose (LD50) values indicate the bacterial load needed to kill 50% of the population [35]. In this study, three groups of 10 B. mori larvae per bacterial isolate (S. aureus RN6390 and norB and mgrA mutants) were injected with 10-fold bacterial suspensions to determine the bacterial load that kills 50% of each group. LD50 studies in B. mori larvae showed that the S. aureus norB mutant (RN6390∆norB) had a higher LD50 than the wild-type strain. Two-log more of S. aureus RN6390∆norB were needed to kill 50% of larvae compared to wild-type S. aureus RN6390, indicating a decrease in the virulence of the mutant strain (Table 3). Although no statistical significance was attained (p > 0.05), biologically, a difference in 2-log of bacteria is meaningful indicating that NorB could be involved in resistance to immune clearance probably by exporting silkworm immune factors such as antimicrobial peptides from staphylococcal cells. Efflux pumps are involved in resistance to antimicrobial peptides in other bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa [36]. This provides novel evidence of the NorB role in S. aureus virulence. As norB is overexpressed in the S. aureus mgrA mutant (Figure 4), it was expected to observe increased virulence of this mutant compared to the wild-type strain. However, LD50 values of the mgrA mutant were higher than those of the wild-type strain. As MgrA is a global regulator, the absence of the mgrA gene can trigger the repression of virulence genes that would be normally expressed in the wild-type strain.

Table 3.
LD50 results for wild-type and mutant norB and mgrA S. aureus strains in a silkworm animal model (n = 3, Student t-test p > 0.05).
3. Discussion
This study validated previous gene expression studies that indicated that the PC storage environment triggers increased antibiotic resistance in contaminant bacteria. We demonstrated that quinolone resistance significantly increased in S. aureus grown in PCs compared to media, independently of the genetic background of the strains. Furthermore, novel evidence of the role of the efflux pump NorB in S. aureus virulence was provided using a silkworm model organism.
PC storage at room temperature under agitation safeguards platelet functionality, which is critical for therapeutic efficacy. Unfortunately, these conditions are amenable for growth of most bacterial contaminants introduced during venipuncture [3]. Storage of PCs is limited to a maximum of seven days to minimize the platelet storage lesion (PSL), which encompasses a series of morphological and metabolic changes that platelets undergo as a result of an increase in lactate levels, with consequential decrease in pH, loss of surface membrane glycoproteins, and reduced aggregation response [37,38]. A study by Yousuf et al. showed that S. aureus proliferation to clinically significant levels in PCs enhances the PSL [6]. Importantly, changes in the PC storage environment not only affect platelet metabolism but also impact gene expression of bacterial contaminants. Immune stressors released by activated platelets during PC storage trigger differential expression of virulence genes such as those involved in biofilm formation and antimicrobial resistance in S. aureus and S. epidermidis [6,7,39].
S. aureus is the predominant PC contaminant involved in septic transfusion reactions worldwide [9]. In this study, we demonstrated that different isolates of S. aureus, including transfusion-relevant strains, displayed increased MBC values to the fluoroquinolones ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin when the bacterium was grown in PCs compared to TSB cultures. Transcriptome and RT-qPCR analyses of four transfusion-relevant strains showed upregulation of the norB efflux pump gene, which was associated with resistance to quinolones in all tested strains grown in PCs versus TSB. Importantly, genes encoding for other efflux pumps such as norA and norC were not differentially regulated in transfusion-relevant strains. However, upregulation of norA, norB, and norC was observed in S. aureus RN6390 strains suggesting that NorA and NorC may also participate in increased quinolone resistance in PC cultures in a strain-dependent manner.
Previous studies have shown that overexpression of S. aureus norA is directly related to increased resistance to ciprofloxacin [40,41,42]. Nevertheless, our results should be analyzed with caution as S. aureus RN6390 lacks the RsbU phosphatase [30], which is involved in dephosphorylation of the global regulator MgrA [16]. It is intriguing to investigate whether other phosphatases (bacterial or platelet-derived) can change the phosphorylation status of MgrA and whether consequent expression of nor genes during PC storage, as repression of norA and norB depends on the phosphorylation state of MgrA [20]. The quinolone resistance results presented herein are likely the consequence of complex interactive regulatory processes that merit further investigation.
It has been shown that NorB favors the growth of S. aureus at low pH [43], which is one of the characteristics of the PSL as mentioned above. However, no differences in bacterial proliferation were observed between wild-type S. aureus RN6390 and its norB mutant during PC storage, indicating that NorB does not confer advantageous S. aureus proliferation in PCs.
In addition to antibiotic resistance, overexpression of NorB confers advantageous survival of S. aureus in skin abscesses [34]. The PC storage environment also poses challenges for S. aureus survival due to the presence of immune stressors [9]. Furthermore, the virulence of the transfusion-relevant strain S. aureus CBS2016-05 is enhanced when grown in PCs compared to media as recently demonstrated using a silkworm animal model [25]. We therefore tested the role of norB in virulence of non-transfusion-relevant strains of S. aureus using silkworms. Our data showed a 2-log higher LD50 for the S. aureus norB mutant compared to wild-type S. aureus RN6390, indicating loss of virulence. It is important to recognize that the rsbU-negative background of the RN6390 strains may have contributed to our observations in silkworms, which warrants more extensive studies using different S. aureus strains, animal models, or cell cultures [44,45,46]. As RsbU has a major role in the SigB regulon, it is also critical to consider how the expression of other virulence factors driven by SigB played a role in the virulence results presented herein. This can be studied by performing comparative assays between S. aureus RN6390 and a rsbU+ strain such as S. aureus SH1000. We propose that NorB may be involved in excreting antimicrobial peptides produced by silkworm larvae during infection as shown for other efflux pumps in P. aeruginosa [36]. It would therefore be interesting to investigate how expression of norB in a rsbU+ background influences virulence in silkworms as overexpression of sigB has been associated with in vitro resistance to antimicrobial peptides produced by nematodes in S. aureus [47].
We provided novel information on the complex regulation of S. aureus nor efflux pump genes in contaminated PCs. Additionally, we showed evidence of the potential role of norB in S. aureus virulence using a silkworm model. Our findings highlight the need to deepen our knowledge on the molecular mechanisms involved in resistance to antibiotics and virulence when bacteria proliferate in PCs. Understanding the complex processes involved in platelet–bacteria interactions in the unique PC storage environment could be used to propose mechanisms for the prevention of septic transfusion reactions involving S. aureus-contaminated PCs.
Recommendations for Further Investigation
- Downregulation of norA and norC in the mgrA mutant strain could be due to the action of other regulators which could be investigated by performing gene expression studies in mgrA mutant strains compared to their parental wild-type counterparts.
- We discussed that our MBC data depend on the expression of efflux pump nor genes in different bacterial backgrounds and potentially the phosphorylation status of the global regulator MgrA. Investigating changes in phosphorylation of MgrA when S. aureus is grown in PCs and consequent expression of nor genes will provide new insight to advance the interpretation of our data.
- Our virulence experiments were conducted in S. aureus RN6390, which has a negative sigB phenotype due to a mutation in rsbU. Therefore, it would be interesting to create a norB mutant in a strain with rsbU+ background and study the role of norB in virulence with a functional SigB regulon.
- We showed that the silkworm model was an appropriate tool to obtain preliminary data on the role of norB in virulence. However, these results could be complemented with assays that reflect human immune response such as experiments using human cell lines or mammalian animal models.
- Our hypothesis of the role on NorB in exporting antimicrobial peptides from cells of infected silkworm larvae could be tested by performing in vitro experiments to test resistance to antimicrobial peptides produced by silkworms using S. aureus with different genetic backgrounds.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
The origin of S. aureus strains CBS2016-05, CI/BAC/13/W, PS/BAC/169/17/W, PS/BAC/317/16/W, RN6390, RN6390ΔnorB, RN6390ΔmgrA, and ATCC 29213 is described in Table 1. S. aureus isolates were routinely cultured on trypticase soy agar (TSA) for colony isolation or trypticase soy broth (TSB) and incubated with agitation at 20–24 °C for 6 days, or static at 37 °C for 24 h. In PCs, the strains were grown with agitation at 20–24 °C for 6 days (PC storage conditions). All bacterial strains were stored in a brain–heart infusion broth with 15% glycerol (v/v) at −80 °C. TSA was used to sub-culture frozen stocks and for bacterial enumeration.
4.2. Pooled Platelet Concentrates
Leukocyte-reduced buffy coat pooled platelet concentrates suspended in 100% plasma were used for this study following standard manufacturing protocols established at the Canadian Blood Services netCAD Blood4Research Facility (netCAD, Vancouver, BC, Canada). This study was granted ethical approval by the Canadian Blood Services Research Ethical Board (REB 2015.024, 24 June 2019).
4.3. Comparative Genomic Analyses
The genomes of five S. aureus isolates, the four TRS and RN6390, which were previously published [26,27,28,29,30], were aligned and visualized using Mauve Progressive (Mauve 2015226 built10, assessed on 8 April 2025). Genome files (FASTA format) were uploaded onto the software for comparison using a guide tree constructed from pairwise comparisons to identify conserved segments, insertions, deletions, and rearrangements within the genomes. Genome inversion features were visualized using Proksee (assessed on 10 April 2025).
4.4. Transcriptome Analyses (PCs vs. TSB) and Selection of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
Three independent S. aureus TSB and PC cultures were prepared with an initial inoculum of approximately 4 × 106 CFU/mL. S. aureus RNA was isolated from bacterial samples grown to mid-stationary phase following previously established protocols [6,39]. Briefly, total RNA was isolated using the commercial kit FastRNA™ Pro Blue Kit (MP Biologicals, Santa Ana, CA), followed by DNase treatment for purification. RNA extracted from S. aureus grown in PCs was subject to a mammalian depletion treatment. RNA samples were sent to the StemCore Laboratories located at the Core Facilities at University of Ottawa and the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute (https://www.ohri.ca/bioinformatics/, accessed on 17 June 2025) for RNA sequencing and differential gene expression (DGE) analysis as described previously [42,43]. RNA samples with RIN > 8 were used to prepare paired-end libraries and sequenced. The libraries were normalized, pooled, and diluted as required to achieve acceptable cluster density on the NextSeq 500 sequencer (Illumina SY-414-1001) (Illumina Inc., Baltimore, MD, US). The transcriptome dataset of antibiotic resistance genes was further analyzed considering a log2-fold difference of ≥1.0 as a significant change in DGE. This cut-off was chosen to capture relatively small but biologically meaningful gene expression changes.
4.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
RT-qPCR assays were developed following established procedures [6,39]. Total RNA served as a template in the synthesis of cDNA using the QuantiTect RT kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, US). Primers (Supplementary Table S3) were designed targeting nor genes and qPCR was performed using QuantiNova SYBR green PCR kit (Qiagen, Hilden, German) according to manufacturer recommendations, the 16S RNA gene served as the housekeeping gene, and a blank control reaction was conducted for all the samples using ddH2O instead of template. Primer efficiency is shown in Supplementary Figures S2 and S3.
4.6. Construction of a S. aureus RN6390 norB Deletion Mutant
A norB in-frame deletion mutant was prepared following an allelic exchange protocol previously optimized [47]. Briefly, upstream and downstream sequences of the gene/locus to be deleted were amplified by overlay polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and the two fragments were linked by overlay PCR (primers used for this procedure are listed in Supplementary Table S3). PCR products and plasmid pIMAY were double-digested with KpnI and SacI, ligated together, transformed into E. coli DC10B, and incubated on Luria–Bertani (LB) containing chloramphenicol at 10 μg/mL at 37 °C. The construct pIMAY-ΔnorB was extracted and transformed into S. aureus strain RN4220 and then into S. aureus RN6390 for subsequent allelic exchange. Positive RN6390 transformants were cultured at 28 °C on TSA supplemented with chloramphenicol at 10 μg/mL. Each step was verified with DNA sequencing to confirm the plasmid construction. RN6390-positive transformants were diluted between 10- and 1000-fold and plated with chloramphenicol at 10 μg/mL and grown at 37 °C to integrate the construct pIMAY-ΔnorB into the chromosome. Absence of extrachromosomal plasmid was confirmed by PCR using primers designed from the plasmid pIMAY. Colonies were selected, plated on brain–heart infusion agar plates supplemented with anhydrotetracycline at 1 μg/mL, then grown at 28 °C for 48 h. Chloramphenicol-sensitive colonies were selected and verified by DNA sequencing. The deletion mutants were named RN6390ΔnorB and the absence of norB was verified by DNA sequencing.
4.7. Antibiotic Resistance Assays
These assays were performed for all isolates to assess bacterial potential resistance to the fluoroquinolones ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin. S. aureus ATCC 29213 was used as a control for MIC and MBC assays. MIC values were determined according to the microdilution broth method described in the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines [48]. Antibiotic stock solutions were prepared as per manufacturers’ specifications. Bacterial colonies were re-suspended in cation-adjusted Müeller–Hinton broth (MHBca+) to 0.5 Densimat, which corresponds to approximately 1 × 108 CFU/mL, and then diluted to a bacterial load of approximately 2 × 106 CFU/mL. Bacterial suspensions were distributed into a 96-well plate within 15 min of preparation. The 96-well plates were loaded as follows: wells of the outer rows and columns were filled with 200 μL of MHBca+ and the internal wells were filled with 100 μL of serially diluted antibiotics in MHBca+ to obtain antibiotic concentration gradients across the plates. Antibiotics were added in double concentration since they were diluted 2-fold once the bacterial suspensions were added (e.g., stock solution of 512 μg/mL to ensure a final concentration of 256 μg/mL in the well). Following antibiotic dispensing, 100 μL of the bacterial suspensions were added to each well and were thoroughly mixed. The top only had unspiked MHBca+ (negative control) while the last row was filled with the bacterial suspension without antibiotics (positive control). Plates were incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. After incubation, well absorbance (OD600) was recorded using a plate reader and MIC values were determined as the lowest concentration of the antibiotic inhibiting bacterial growth. MBC assays were optimized in collaboration with Dr. Thien-Fah Mah (University of Ottawa) [49]. Briefly, an antibiotic gradient was prepared and 50 μL was pre-loaded onto 48-well plates, overnight bacterial cultures were adjusted to 0.5 Densimat and inoculated in TSB or PCs to approximately 5.5 × 105 CFU/mL, and 450 μL were loaded onto the 48-well plates previously loaded with an antibiotic and incubated. Plates loaded with PCs were incubated at PC conditions (22 ± 2 °C, for 5 days with constant agitation) and plates loaded with inoculated TSB were incubated at optimal conditions for bacterial growth (37 °C, for 24 h without agitation). After incubation, samples from each well were spotted in TSA (~3.5 μL/spot) and incubated overnight at 37 °C. The presence or absence of bacterial growth was recorded to establish the MBC value. MIC and MBC assays were performed three independent times with technical duplicates.
4.8. Bacterial Growth Curves
S. aureus RN6390 and its derivative norB and mgrA mutants were cultured in PCs by inoculating units with an approximate initial inoculum of 30 CFU/PC unit to mimic real-life bacterial loads in PCs. Bacterially inoculated PCs were incubated under standard PC storage conditions (22 ± 2 °C, agitation). Samples of 1 mL were taken every 24 h for a total of 5 days for plating in duplicate on TSA plates, which were incubated for 24 h at 37 °C for colony counts and determination of bacterial loads. Growth curves were repeated three independent times.
4.9. Silkworm Rearing
Silkworm assays were established following recently optimized protocols [26]. Briefly, B. mori eggs were acquired from coastal silk and were kept at room temperature until hatched. Silkworm larvae were fed on commercially bought de-hydrated silkworm chow (coastal silk) supplemented with 300 mg of vancomycin/Kg upon re-hydration. Fifth in-star larvae (day 1 and 2 post molt) were fed food free of vancomycin for a minimum of 24 h prior to use in downstream assays.
4.10. Determination of Lethal Dose 50 (LD50)
S. aureus isolates were grown overnight aerobically at 37 °C with agitation in TSB media. The load required to kill 50% of the silkworm test population (LD50) was determined as recently described [26]. Briefly, overnight cultures were centrifuged, resuspended in insect saline (0.6% NaCl), serially diluted (ten-fold), and inoculated into the haemolymph of silkworm larvae (30 μL/10 larvae/dilution). Bacterial load of each suspension was determined by plating on TSA plates followed by incubation at 37 °C for 24 h and colony counting. Silkworm larvae were incubated at 37 °C for three days (72 h) and inspected daily to assess larval survival and death. Insect saline served as control; LD50 studies were performed in triplicate.
4.11. Statistical Analyses
Statistical analysis of the RNA-seq data was performed in R. Statistical comparisons of MBC values and LD50 values were done with GraphPad Prism (version 9.0.0) software using Mann–Whitney U test and T-test with Welch’s correction, respectively. Values were expressed as mean ± SE and a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
Our studies aimed to investigate the impact of the PC storage environment on S. aureus transcriptional changes with a focus on genes involved in antibiotic resistance. The findings of this study demonstrate that the PC storage environment triggers S. aureus resistance to quinolones and upregulation of nor efflux pump genes in a strain-dependent manner. Notably, NorB was shown to be involved in virulence of S. aureus using a silkworm model. Overall, we generated novel information advancing knowledge on platelet–S. aureus interaction in the unique PC storage environment, opening avenues for future studies that can contribute with knowledge in the prevention of septic transfusion reactions involving contaminated PCs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics14070635/s1. Table S1. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin in S. aureus grown in Müeller–Hinton (n ≥ 3). Table S2. Overview of S. aureus isolates genome features (two TRS and RN6390); Table S3. List of primers in this study (5′ → 3′). Figure S1: S. aureus genomic comparison. (A) Multiple genome alignment comparing S. aureus TRS with RN6390 using Mauve [50] algorithm, red arrow pointing at genome inversion; (B) Prophage φ6390 features using Proksee [51]. Figure S2—norB primers efficiency for the TRS (CBS2016-06; CI/BAC/25/13/W; PS/BAC/169/17/W and PS/BAC/317/16/W). Figure S3—Primer efficiency for RN6390 “wild type”, and deletion mutants RN6390ΔnorB and RN6390ΔmgrA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.R.-A.; Data curation, C.P. and S.R.-A.; Formal analysis, C.P. and Q.C.T.-B.; Funding acquisition, S.R.-A.; Investigation, C.P.; Methodology, C.P. and Y.W.; Resources, S.R.-A.; Software, C.P.; Supervision, Q.C.T.-B. and S.R.-A.; Validation, C.P. and Y.W.; Writing—original draft, C.P.; Writing—review and editing, Q.C.T.-B., D.C.H. and S.R.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Canadian Blood Services (intramural grant IG2019-SR to S.R-A.) and Health Canada. C.P. received a graduate student fellowship from Canadian Blood Services. The views expressed herein does not necessarily represent the views of the federal government of Canada.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study reported in this manuscript is part of a larger study entitled “Understanding factors that influence bacterial proliferation and biofilm formation in platelet concentrates” approved by the Research Ethical Board of Canadian Blood Services, REB2015.024 (24 June 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data of all results in this study are included in the manuscript. Raw data will be provided by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the volunteer blood donors and staff at the Blood4Research Facility in Vancouver for whole blood collection and PC manufacturing. The authors also acknowledge the assistance of the Ottawa Bioinformatics Core Facility (uOttawa/OHRI), RRID:SCR_022466.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Meliciano, A.; Salvador, D.; Mendonça, P.; Louro, A.F.; Serra, M. Clinically Expired Platelet Concentrates as a Source of Extracellular Vesicles for Targeted Anti-Cancer Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Arcos, S.; Goldman, M. Bacterial Contamination. In Practical Transfusion Medicine; Murphy, M.F., Roberts, D.J., Yazer, M.H., Dunbar, N.M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 221–228. ISBN 978-1-119-66581-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Arcos, S.; Evans, S.; McIntyre, T.; Pang, C.; Yi, Q.; DiFranco, C.; Goldman, M. Extension of Platelet Shelf Life with an Improved Bacterial Testing Algorithm. Transfusion 2020, 60, 2918–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brailsford, S.R.; Tossell, J.; Morrison, R.; McDonald, C.P.; Pitt, T.L. Failure of Bacterial Screening to Detect Staphylococcus Aureus: The English Experience of Donor Follow-up. Vox Sang. 2018, 113, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.I.; Kumaran, D.; Zeller, M.P.; Ramirez-Arcos, S. Transfusion of a Platelet Pool Contaminated with Exotoxin-Producing Staphylococcus aureus: A Case Report. Ann. Blood 2022, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, B.; Pasha, R.; Pineault, N.; Ramirez-Arcos, S. Modulation of Staphylococcus aureus Gene Expression during Proliferation in Platelet Concentrates with Focus on Virulence and Platelet Functionality. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loza-Correa, M.; Yousuf, B.; Ramirez-Arcos, S. Staphylococcus epidermidis Undergoes Global Changes in Gene Expression during Biofilm Maturation in Platelet Concentrates. Transfusion 2021, 61, 2146–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, S.D.; Greco-Stewart, V.; Jimenez, C.S.; Sifri, C.D.; Brassinga, A.K.C.; Ramirez-Arcos, S. Enhanced Pathogenicity of Biofilm-negative Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolated from Platelet Preparations. Transfusion 2014, 54, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.I.; Ramirez-Arcos, S. Platelet Concentrates Safety: A Focus on the Challenging Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus—A Narrative Review. Ann. Blood 2025, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinski, J.M.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections: Pathogenesis and Regulatory Mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 53, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Amaral, L.; Couto, I. Multidrug Efflux Pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: An Update. Open Microbiol. J. 2013, 7, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brdová, D.; Ruml, T.; Viktorová, J. Mechanism of Staphylococcal Resistance to Clinically Relevant Antibiotics. Drug Resist. Updates 2024, 77, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, L.; Pepin, J.; Toulouse, K.; Ouellette, M.-F.; Coulombe, M.-A.; Corriveau, M.-P.; Alary, M.-E. Fluoroquinolones and Risk for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, J.; Salam, F.; Lekshmi, M.; Kumar, S.H.; Varela, M.F. The Major Facilitator Superfamily and Antimicrobial Resistance Efflux Pumps of the ESKAPEE Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Dunman, P.M.; Eidem, T.; Hooper, D.C. Transcriptional Profiling Analysis of the Global Regulator NorG, a GntR-like Protein of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 6207–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Hooper, D.C. Phosphorylation of MgrA and Its Effect on Expression of the NorA and NorB Efflux Pumps of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Hooper, D.C. The Transcriptional Regulators NorG and MgrA Modulate Resistance to Both Quinolones and β-Lactams in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 2996–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Dunman, P.M.; Strahilevitz, J.; Projan, S.J.; Hooper, D.C. MgrA Is a Multiple Regulator of Two New Efflux Pumps in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachino, P.; Engelmann, S.; Bischoff, M. ςB Activity Depends on RsbU in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pané-Farré, J.; Jonas, B.; Hardwick, S.W.; Gronau, K.; Lewis, R.J.; Hecker, M.; Engelmann, S. Role of RsbU in Controlling SigB Activity in Staphylococcus aureus Following Alkaline Stress. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifri, C.D.; Begun, J.; Ausubel, F.M.; Calderwood, S.B. Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model Host for Staphylococcus aureus Pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2208–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irazoqui, J.E.; Troemel, E.R.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Luhachack, L.G.; Cezairliyan, B.O.; Ausubel, F.M. Distinct Pathogenesis and Host Responses during Infection of C. elegans by P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ségalat, L. Invertebrate Animal Models of Diseases as Screening Tools in Drug Discovery. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, H.A.; Srinivasulu, C.; Venkatappa, B. A Critical Assessment of Bombyx mori Haemolymph Extract on Staphylococcus aureus an In Vitro and In Silico Approach. J. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 9, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, D. Assessing the Impact of Collection, Production, and Storage of Platelet Concentrates on Bacterial Contamination and Product Safety. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2024. Available online: https://ruor.uottawa.ca/server/api/core/bitstreams/8c06e3dd-af9c-42ad-a866-a72918cb941f/content (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Yousuf, B.; Flint, A.; Weedmark, K.; Pagotto, F.; Ramirez-Arcos, S. Genome Sequence of Staphylococcus aureus Strain CBS2016-05, Isolated from Contaminated Platelet Concentrates in Canada. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00288-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, C.; Chi, S.I.; Flint, A.; Weedmark, K.; McDonald, C.; Bearne, J.; Ramirez-Arcos, S.; Pagotto, F. Complete Genome Sequence of Staphylococcus aureus CI/BAC/25/13/W, Isolated from Contaminated Platelet Concentrates in England. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00840-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, C.; Chi, S.I.; Flint, A.; Weedmark, K.; McDonald, C.; Bearne, J.; Ramirez-Arcos, S.; Pagotto, F. Complete Genome Sequence of Staphylococcus aureus PS/BAC/169/17/W, Isolated from a Contaminated Platelet Concentrate in England. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00841-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, B.; Flint, A.; Weedmark, K.; McDonald, C.; Bearne, J.; Pagotto, F.; Ramirez-Arcos, S. Genome Sequence of Staphylococcus aureus Strain PS/BAC/317/16/W, Isolated from Contaminated Platelet Concentrates in England. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00577-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, S.R.; Mariano, G.; Palmer, T. Genomic Analysis of the Progenitor Strains of Staphylococcus aureus RN6390. Access Microbiol. 2022, 4, acmi000464.v3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Zhang, X.; Hooper, D.C. Characterization of NorR Protein, a Multifunctional Regulator of norA Expression in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3127–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H. Unraveling Gene Regulation of MDR and ABC-Transporters in Bacteria. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2012. Available online: https://fse.studenttheses.ub.rug.nl/10095/1/LST_Bc_2012_HWang.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Li, X.-Z.; Nikaido, H. Efflux-Mediated Drug Resistance in Bacteria: An Update. Drugs 2009, 69, 1555–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Onodera, Y.; Lee, J.C.; Hooper, D.C. NorB, an Efflux Pump in Staphylococcus aureus Strain MW2, Contributes to Bacterial Fitness in Abscesses. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 7123–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government of Canada, C.C. for O.H. and S. CCOHS. What Is a LD50 and LC50? Available online: https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/chemicals/ld50.html (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Neidig, A.; Strempel, N.; Waeber, N.B.; Nizer, W.S.d.C.; Overhage, J. Knock-out of Multidrug Efflux Pump MexXY-OprM Results in Increased Susceptibility to Antimicrobial Peptides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 67, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trochanowska-Pauk, N.; Walski, T.; Bohara, R.; Mikolas, J.; Kubica, K. Platelet Storage—Problems, Improvements, and New Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Su, Y.; Guo, W.; Ma, X.; Qiao, R. The Platelet Storage Lesion, What Are We Working For? Clin. Lab. Anal. 2024, 38, e24994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.I.; Yousuf, B.; Paredes, C.; Bearne, J.; McDonald, C.; Ramirez-Arcos, S. Proof of Concept for Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Platelet Concentrates as a Novel Safety Mitigation Strategy. Vox Sang. 2023, 118, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Strahilevitz, J.; Hooper, D.C. NorC, a New Efflux Pump Regulated by MgrA of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1104–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Hao, Z.H.; Liu, P.L.; Liu, M.M.; Zhao, L.L.; Zhao, X. Increased Expression of Efflux Pump norA Drives the Rapid Evolutionary Trajectory from Tolerance to Resistance against Ciprofloxacin in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e00594-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamady, A.B.; Abd El-Fadeal, N.M.; Imbaby, S.; Nassar, H.M.; Sakr, M.G.; Marei, Y.E. Expression of norA, norB and norC Efflux Pump Genes Mediating Fluoroquinolones Resistance in MRSA Isolates. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2024, 18, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Bolduc, G.R.; Okumura, R.; Celino, B.; Bevis, J.; Liao, C.-H.; Hooper, D.C. Implication of the NorB Efflux Pump in the Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus to Growth at Acid pH and in Resistance to Moxifloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3214–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollin, G.; Tan, X.; Tros, F.; Dupuis, M.; Nassif, X.; Charbit, A.; Coureuil, M. Intracellular Survival of Staphylococcus aureus in Endothelial Cells: A Matter of Growth or Persistence. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebaier, C.; Chamberland, R.R.; Allen, I.C.; Gao, X.; Broglie, P.M.; Hall, J.D.; Jania, C.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Tilley, S.L.; Duncan, J.A. Staphylococcus aureus α-Hemolysin Mediates Virulence in a Murine Model of Severe Pneumonia through Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.; Diep, B.A.; Mai, T.T.; Vo, N.H.; Warrener, P.; Suzich, J.; Stover, C.K.; Sellman, B.R. Differential Expression and Roles of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Determinants during Colonization and Disease. mBio 2015, 6, e02272-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Wang, Y.; Hooper, D.C. Role of Staphylococcus aureus Tet38 in Transport of Tetracycline and Its Regulation in a Salt Stress Environment. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e0014222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; CLSI supplement M100, Table 2C (58-67); Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-68440-066-9; ISBN 978-1-68440-067-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mah, T.-F. Establishing the Minimal Bactericidal Concentration of an Antimicrobial Agent for Planktonic Cells (MBC-P) and Biofilm Cells (MBC-B). J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 83, e50854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple Genome Alignment with Gene Gain, Loss and Rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-Depth Characterization and Visualization of Bacterial Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).