Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent “Off–On” Probe for Selective Ascorbic Acid Detection via H2O2-Mediated Quenching
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
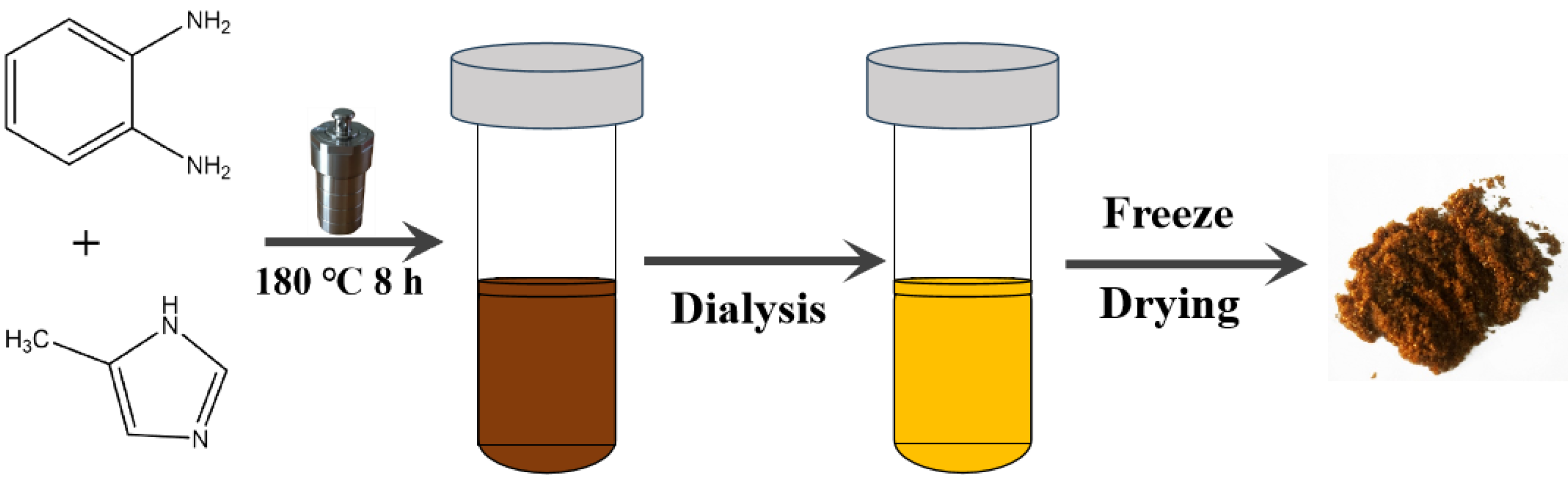
2.2. Synthesis of NCDs
2.3. QY of NCDs
2.4. Detection of H2O2
2.5. The Procedure of AA Detection
2.6. Analysis of Real Sample
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation Optimization
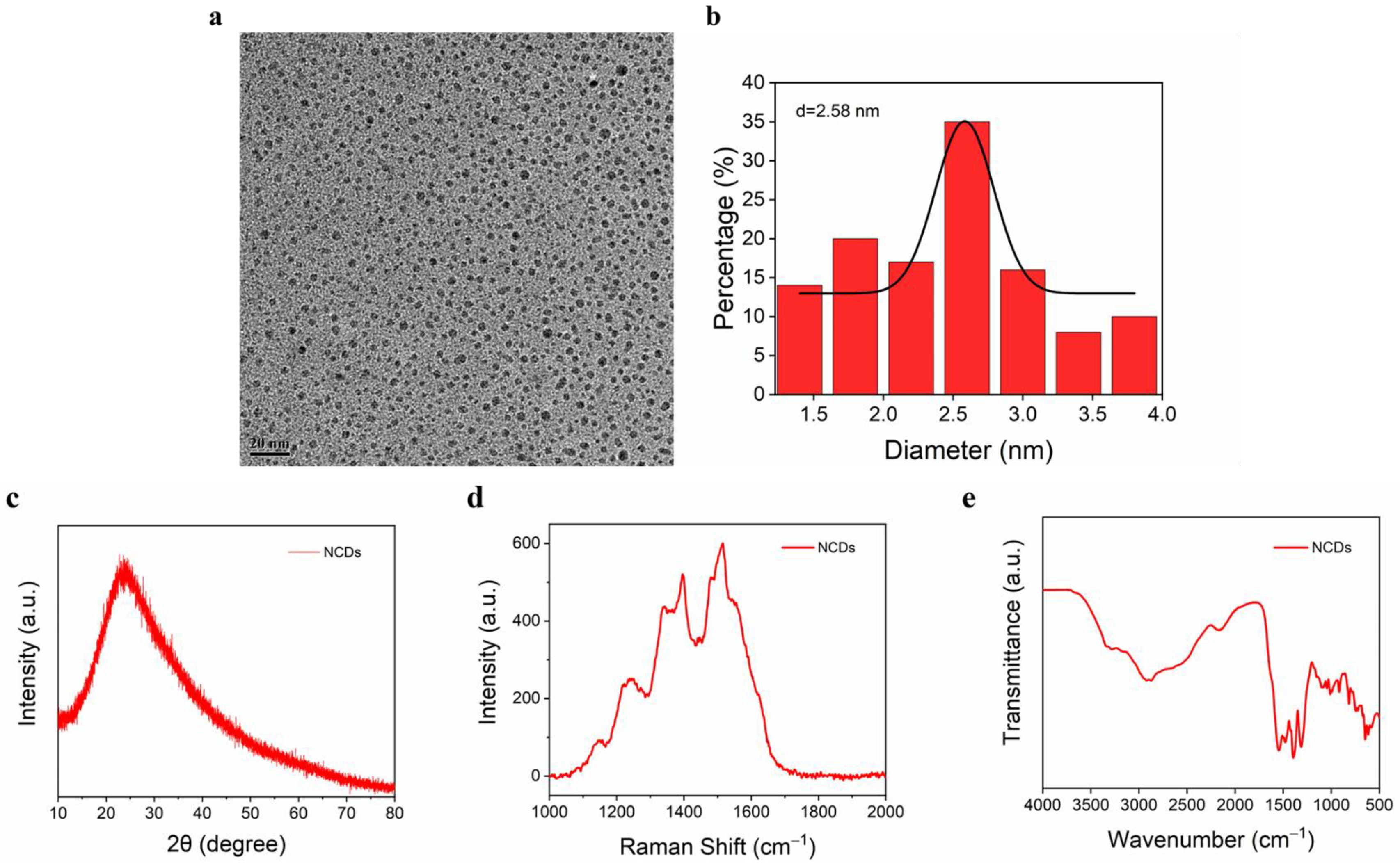
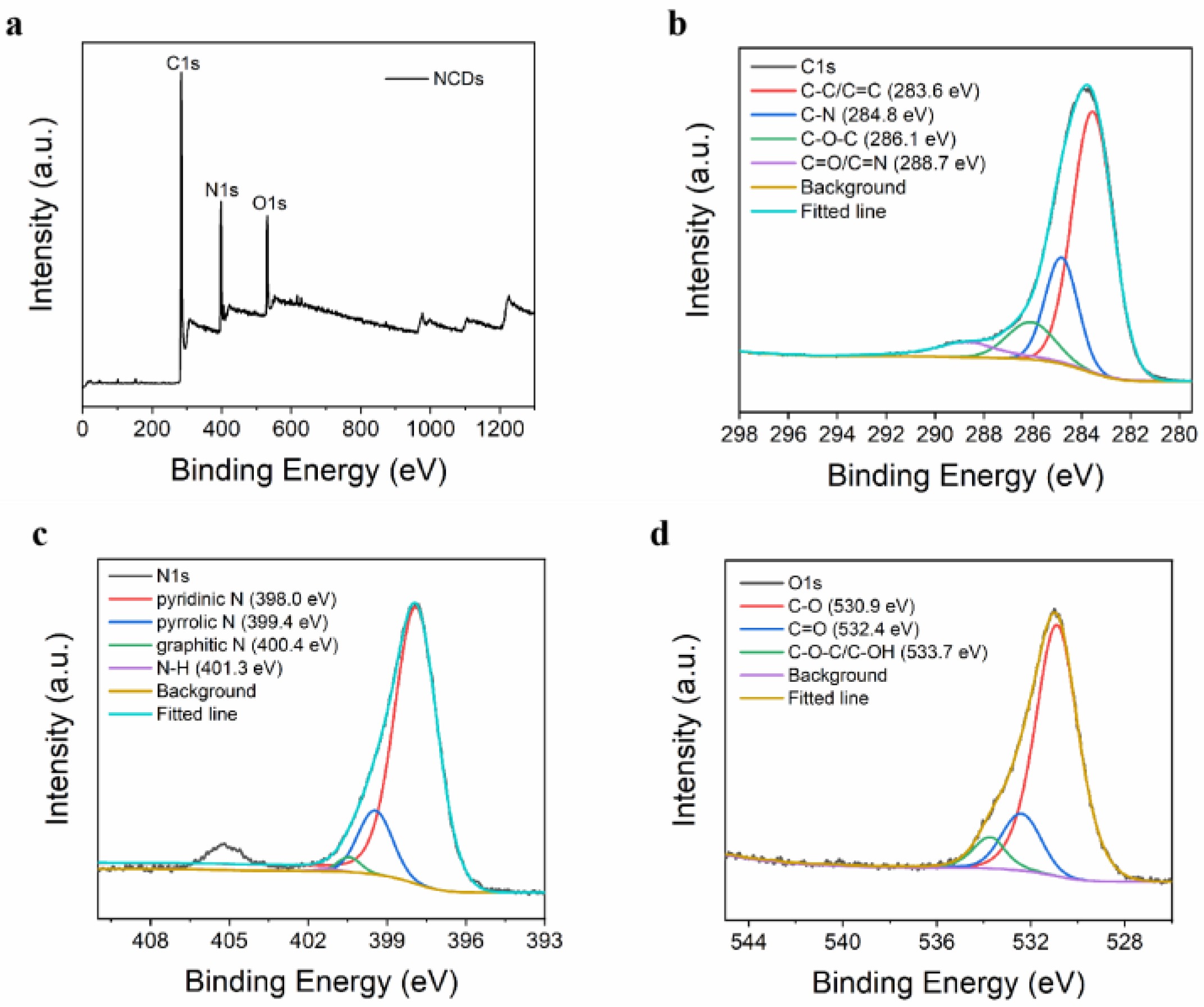
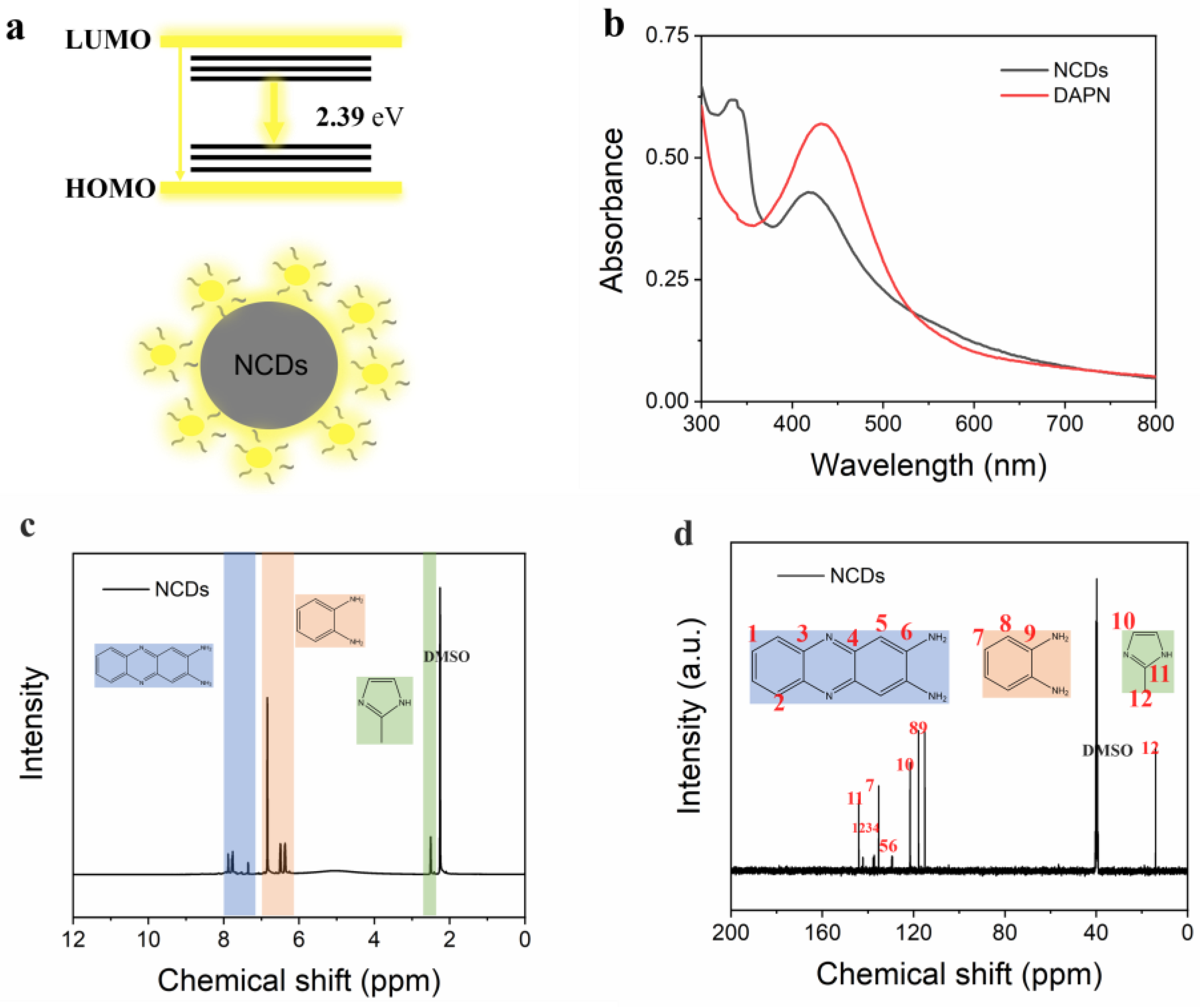
3.2. NCD Characterization
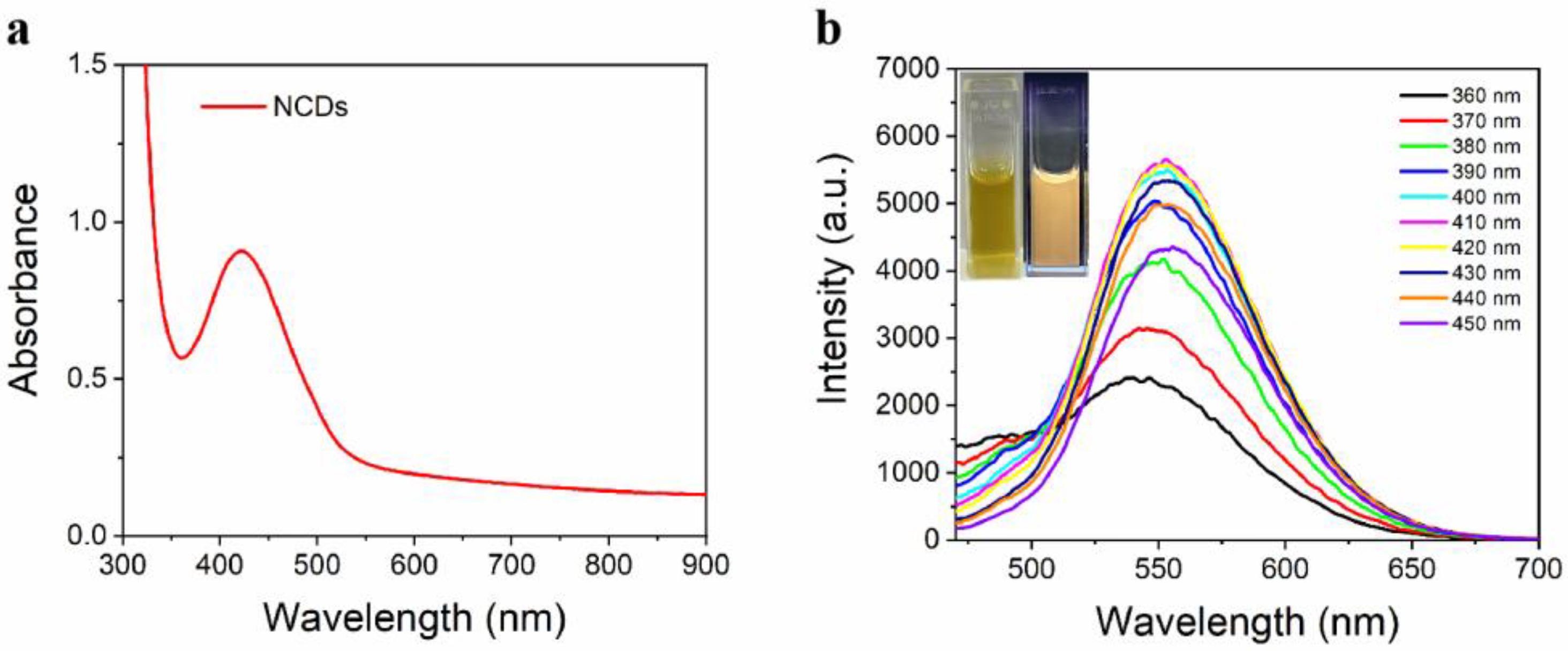
3.3. Optical Properties of NCDs
3.4. Luminescence Mechanism of NCDs
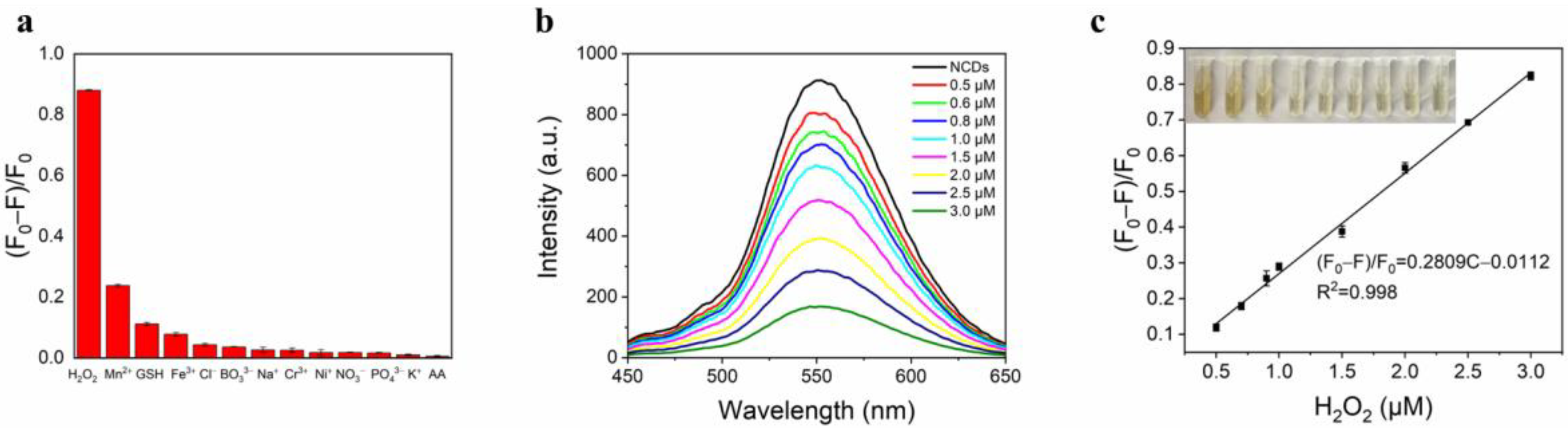
3.5. Detection of NCDs Toward H2O2
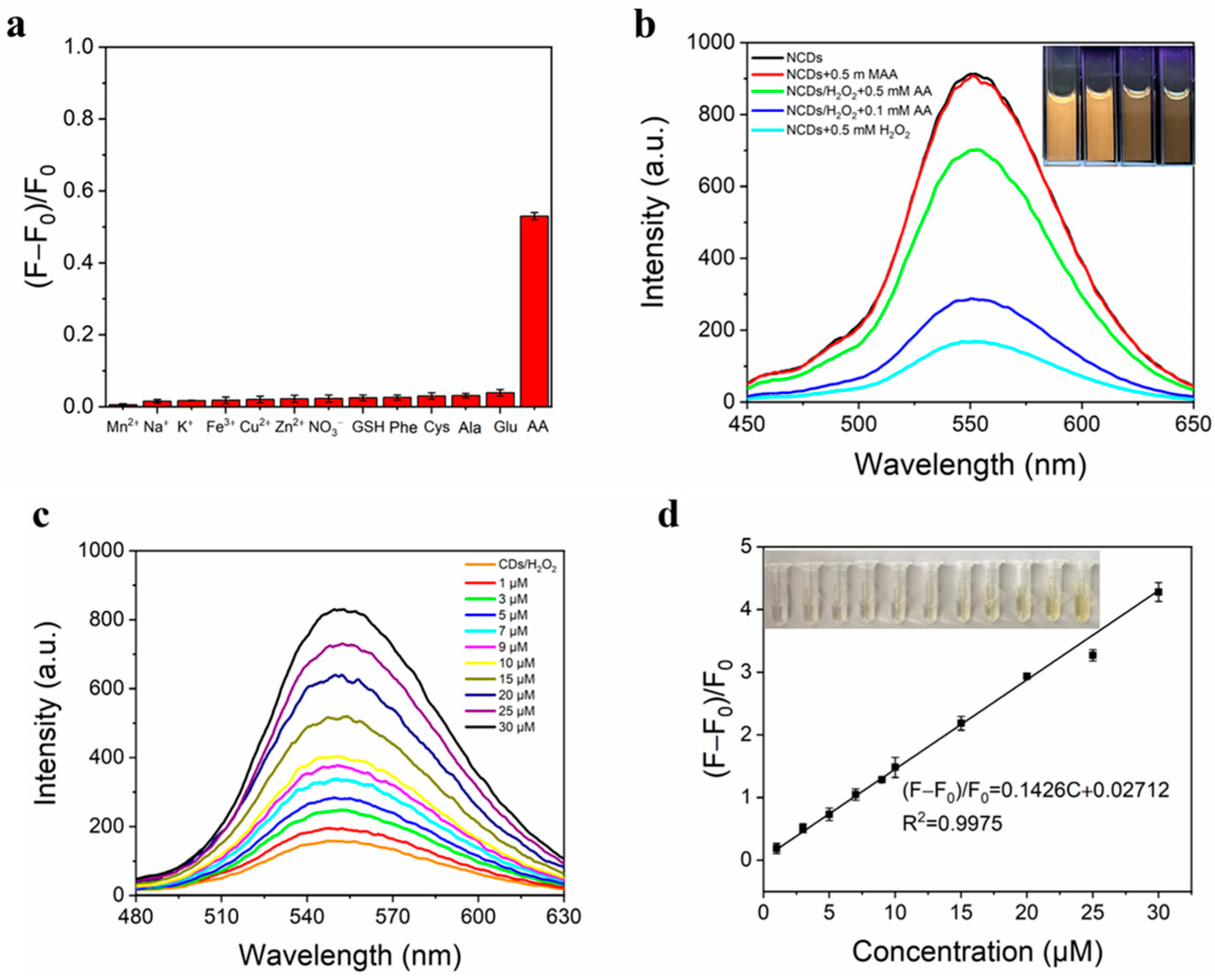
3.6. Detection of AA
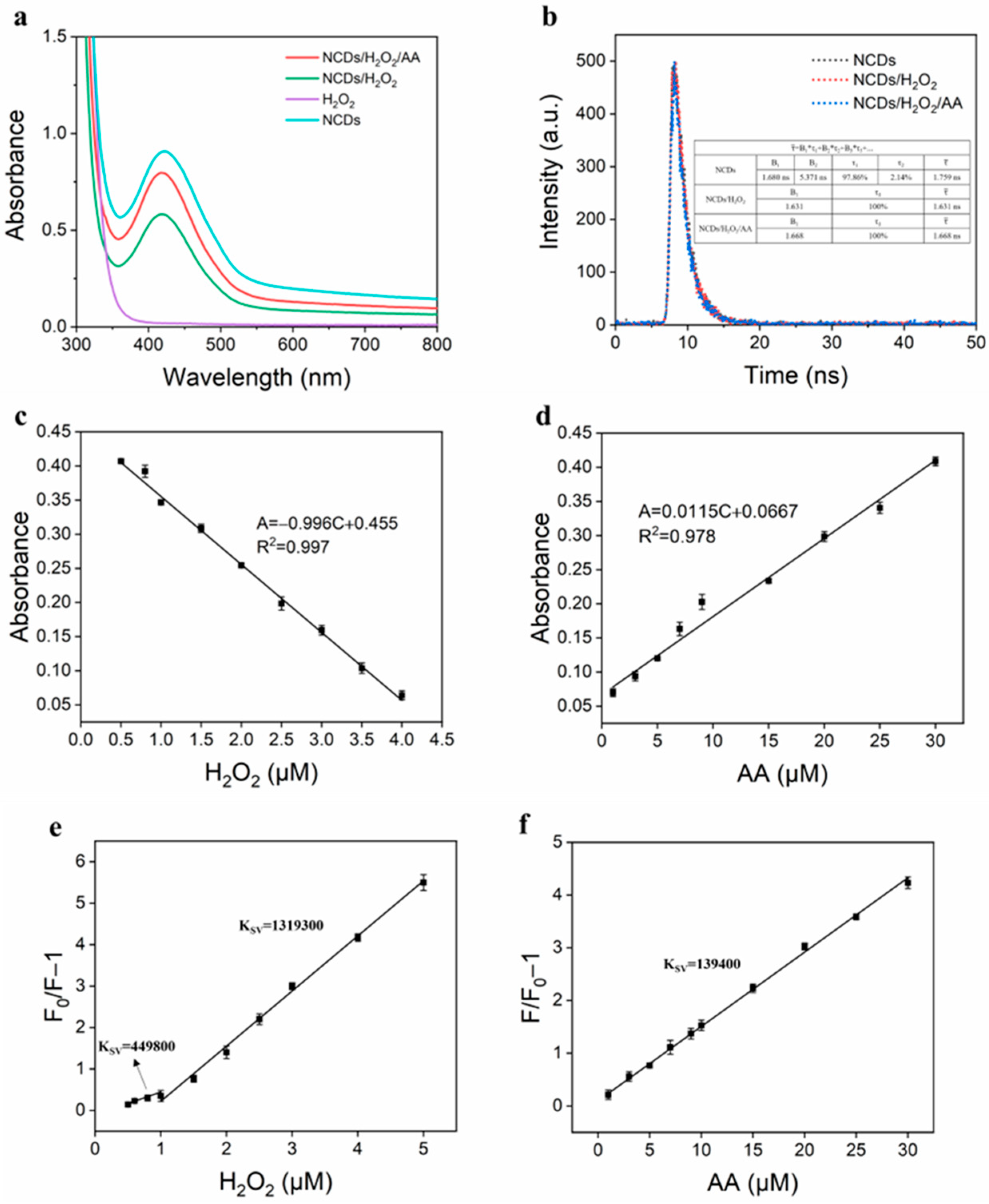
3.7. Quenching Mechanism of Fluorescence “Off” and “On”
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, C.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Yang, M.; Yang, B. Evolution and Synthesis of Carbon Dots: From Carbon Dots to Carbonized Polymer Dots. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadia, F.Y.; Ghosh, S.; Mehta, V.N.; Jha, S.; Malek, N.I.; Park, T.J.; Kailasa, S.K. Fluorescence “Turn OFF-ON” detection of Fe3+ and propiconazole pesticide using blue emissive carbon dots from lemon peel. Food Chem. 2023, 428, 136796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lei, Y. Fluorescent carbon dots and their sensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehvari, K.; Chiu, S.-H.; Lin, J.-S.; Girma, W.M.; Ling, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-Y. Heteroatom doped carbon dots with nanoenzyme like properties as theranostic platforms for free radical scavenging, imaging, and chemotherapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 114, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.T.; Loo, A.H.; Sofer, Z.; Klímová, K.; Pumera, M. Coke-derived graphene quantum dots as fluorescence nanoquencher in DNA detection. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckmeier, C.J.; Schneider, J.; Susha, A.S.; Rogach, A.L. Luminescent colloidal carbon dots: Optical properties and effects of doping [Invited]. Opt. Express 2015, 24, A312–A340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holá, K.; Sudolská, M.; Kalytchuk, S.; Nachtigallová, D.; Rogach, A.L.; Otyepka, M.; Zbořil, R. Graphitic Nitrogen Triggers Red Fluorescence in Carbon Dots. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12402–12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Sudolská, M.; Dubecký, M.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Rogach, A.L.; Zbořil, R.; Otyepka, M. Graphitic Nitrogen Doping in Carbon Dots Causes Red-Shifted Absorption. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.G.; Huš, M.; Baragau, I.; Bowen, J.; Heil, T.; Nicolaev, A.; Abramiuc, L.E.; Sapelkin, A.; Sajjad, M.T.; Kellici, S. Engineering Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots: Tailoring Optical and Chemical Properties through Selection of Nitrogen Precursors. Small 2024, 20, e2310587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Feng, B.; Zhong, X.; Ostrikov, K. Photoluminescence mechanism of carbon dots: Triggering high-color-purity red fluorescence emission through edge amino protonation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, L. Nitrogen–silicon Co-doped carbon dots synthesized based on lemon peel for copper (II) detection via a dynamic quenching mechanism. Opt. Mater. 2024, 155, 115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, R.R.; de Lima, G.G.; Perissutti, G.E.; Bassi, M.d.J.; Jacumazo, J.; Schiavon, M.A.; Roman, L.S.; de Muniz, G.I.B.; Magalhães, W.L.E.; de Cademartori, P.H.G. Pyrolytic Lignin: A Promising Precursor for the Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 11054–11062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zan, M.; Chen, F.; Kou, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Mei, Q.; Hou, Z.; Dong, W.-F.; Li, L. Formation mechanism of carbon dots: From chemical structures to fluorescent behaviors. Carbon 2022, 194, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Haydel, P.; Sui, N.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.; Yu, W.W. Wide emission shifts and high quantum yields of solvatochromic carbon dots with rich pyrrolic nitrogen. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, L.; Tang, K.; Guan, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Yu, W.W. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots used as an “on–off–on” fluorescent sensor for Fe3+ and glutathione detection. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 178, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, W.; Han, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Yue, T.; Li, Z. N,S co-doped carbon dots based fluorescent “on-off-on” sensor for determination of ascorbic acid in common fruits. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Ding, H.; Zhang, W.; Rao, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, X. A colorimetric and fluorescence turn-on probe for the detection of ascorbic acid in living cells and beverages. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.K.; Singh, V.K.; Chandra, S.; Bano, D.; Kumar, V.; Talat, M.; Hasan, S.H. Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots from Azadirachta indica Leaves and Their Peroxidase-Mimetic Activity for the Detection of H2O2 and Ascorbic Acid in Common Fresh Fruits. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Singh, V.K.; Yadav, P.K.; Bano, D.; Kumar, V.; Pandey, V.K.; Talat, M.; Hasan, S.H. Mustard seeds derived fluorescent carbon quantum dots and their peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric detection of H2O2 and ascorbic acid in a real sample. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1054, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Li, F. pH and H2O2 dual-responsive carbon dots for biocatalytic transformation monitoring. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacker, P.T. Reactive oxygen species in cancer cells: Live by the sword, die by the sword. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Conti, M.; de Castro, A.; Assis, L.; Lima, N.; Escriba, A.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Ramalho, T.; La Porta, F. Carbon dots in the center of the spotlight: A full evaluation of their synthesis and understanding of their fundamental properties and applications. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 27, 100937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.N.d.S.; Ghosh, A.; Nascimento, A.; Vieira, L.H.S.; Costa, R.S.; Ferreira, O.P.; Abreu, G.J.; Fujisawa, K.; Silva-Filho, E.C.; Filho, A.G.d.S.; et al. Advanced sustainable carbon material from babassu biomass and its adsorption performance. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 176, 111188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xue, S.; Sun, L.; Zong, X.; An, L.; Qu, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Formation and fluorescent mechanism of red emissive carbon dots from o-phenylenediamine and catechol system. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam Sk, M.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Huang, L.; Lim, K.H.; Chen, P. Revealing the tunable photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6954–6960. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, L.; Deng, Y.; Peng, K.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, X. A multi-color carbon quantum dots based on the coordinated effect of quantum size and surface defects with green synthesis. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 16647–16651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C.; Yue, G.; Wang, Y.; Rao, H.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X. One-pot synthesis of CeO2-carbon dots with enhanced peroxidase-like activity and carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescence detection of H2O2 and cholesterol. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 862, 158323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yang, X.; Yao, C. High Quantum Yield Fluorescent Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots for the Turn-On-Off-On Detection of Cr(VI) and H2O2. Nano 2021, 16, 2150103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Song, J.; Zhao, L. Metallic deep eutectic solvents-assisted synthesis of Cu, Cl-doped carbon dots as oxidase-like and peroxidase-like nanozyme for colorimetric assay of hydroquinone and H2O2. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, R.; Zhao, B.; Fang, M.; Tian, Y.; Lei, Y.; Li, Y.; Geng, L. Multifunctional N, Fe-doped carbon dots with peroxidase-like activity for the determination of H2O2 and ascorbic acid and cell protection against oxidation. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Jiang, X. Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots with Fe(III/II) Irons as Bridge for the Detection of Ascorbic Acid and H2O2. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, K.F.; Abdullah, C.N. A Dual-Mode Detection Sensor Based on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Visual Detection of Fe(III) and Ascorbic Acid via a Smartphone. J. Fluoresc. 2024, 35, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhai, W.; Fodjo, E.K.; Kong, C. Green preparation of carbon quantum dots with wolfberry as on-off-on nanosensors for the detection of Fe3+ and l-ascorbic acid. Food Chem. 2022, 376, 131898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, D.; Fang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y. Detection of Ascorbic Acid Using Green Synthesized Carbon Quantum Dots. J. Sens. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zeng, J.; Guo, D.; Liu, L.; Xiong, L.; Luo, X.; Hu, Z.; Wu, F. Cobalt-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots with Peroxidase-Mimetic Activity for Ascorbic Acid Detection through Both Fluorometric and Colorimetric Methods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 49453–49461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, F.; Liao, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. Carbon Quantum Dots from Pomelo Peel as Fluorescence Probes for “Turn-Off–On” High-Sensitivity Detection of Fe3+ and L-Cysteine. Molecules 2022, 27, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Bian, W.; Choi, M.M.F. Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots as a “turn-off-on” fluorescence probe for the detection of Hg2+ and GSH and cell imaging. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5803–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Kang, M.; Payne, G.F.; Wang, X.; Sun, R.-C. Probing Energy and Electron Transfer Mechanisms in Fluorescence Quenching of Biomass Carbon Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17478–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Gu, Z.; Lei, W.; Wang, W.; Xia, X.; Hao, Q. Graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for highly efficient detection of copper(II) ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xiang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Yang, B. Investigation into the fluorescence quenching behaviors and applications of carbon dots. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4676–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Liang, N.; Liu, C.; Xia, L.; Qu, F.; Song, Z.-L.; Kong, R.-M. Silver ion-regulated ratiometric fluorescence assay for alkaline phosphatase detection based on carbon dots and o-phenylenediamine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 282, 121682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, W.; Jin, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, T.; Wang, F. A ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on Mn doped ZnS QDs for highly selective detection of ascorbic acid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 701, 134868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Material | Linear Range (µM) | LOD (µM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2-CDs | 1.67–2.01 | 0.35 | [28] |
| Cs-oPD-CDs | 1–200 | 0.51 | [29] |
| Cu, Cl-CDs | 1–600 | 0.35 | [30] |
| N, Fe-CDs | 1–200 | 0.40 | [31] |
| N, S-CDs | 10–140 | 1.9 | [32] |
| NCDs | 0.5–3 | 0.28 | This work |
| Probe | Linear Range | LOD (µM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6,9-diamino-2-ethoxyacridine-CDs | 40–90 µM | 0.69 µM | [33] |
| Wolfberry-CDs | 10–100 µM | 1.80 µM | [34] |
| Leaf extracts of neem-CDs | 5–40 µM | 1.773 µM | [18] |
| DA-UA-CDs | 0.01–3 mM | 10 µM | [35] |
| Co-CDs | 0.6–1.6 mM | 18 µM | [36] |
| NCDs | 1–30 µM | 0.605 µM | This work |
| Beverage Samples | Dilution | Added AA Amount (µM) | Fluorometric (µM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (n = 3, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alienergy Vitamin C | 200 | 0 | 0.3 | ||
| 20 | 19.48 | 95.9% | 0.56% | ||
| 25 | 25.10 | 99.2% | 1.1% | ||
| Nongfu Spring C100 | 200 | 0 | 0.62 | ||
| 20 | 20.39 | 98.9% | 0.87% | ||
| 25 | 25.50 | 99.6% | 0.45% | ||
| Lemon Soda | 150 | 0 | 0.52 | ||
| 20 | 20.56 | 100.2% | 0.85% | ||
| 25 | 25.15 | 98.5% | 0.35% | ||
| Minute Maid Orange | 50 | 0 | 0.37 | ||
| 20 | 20.18 | 99.1% | 1.3% | ||
| 25 | 25.23 | 99.5% | 0.67% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent “Off–On” Probe for Selective Ascorbic Acid Detection via H2O2-Mediated Quenching. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130976
Jia J, Liu X, Wang W. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent “Off–On” Probe for Selective Ascorbic Acid Detection via H2O2-Mediated Quenching. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(13):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130976
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Jingjing, Xue Liu, and Wenjing Wang. 2025. "Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent “Off–On” Probe for Selective Ascorbic Acid Detection via H2O2-Mediated Quenching" Nanomaterials 15, no. 13: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130976
APA StyleJia, J., Liu, X., & Wang, W. (2025). Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent “Off–On” Probe for Selective Ascorbic Acid Detection via H2O2-Mediated Quenching. Nanomaterials, 15(13), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130976






