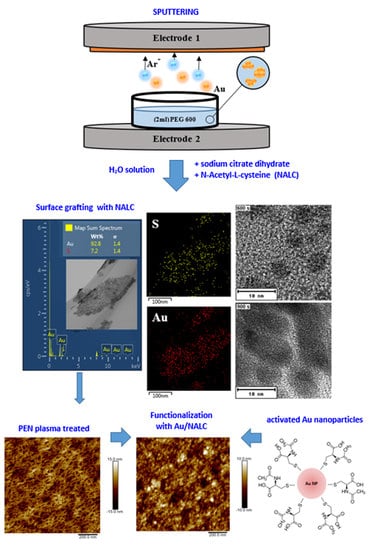
PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Grafted with N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine for Polymer Modification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results
3.1. Stability Studies of AuNP Solutions in Sodium Citrate Dihydrate
3.2. Study of AuNP Stability in N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine
3.3. Modification of PEN Using AuNP/PEG/NALC/H2O
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamkhande, P.G.; Ghule, N.W.; HaqueBamer, A.; Kalaskar, M.G. Metal nanoparticles synthesis: An overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, K.; Tsubaki, T.; Kato, T.; Okuyama, T.; Muto, H. Preparation of catalytically active Au nanoparticles by sputter deposition and their encapsulation in metal-organic framework of Cu3(BTC)2. Mater. Lett. 2020, 261, 127124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepička, P.; Slepičková Kasálková, N.; Siegel, J.; Kolská, Z.; Švorčík, V. Methods of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Preparation. Materials 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Sakata, M. Temperature dependence on the size control of palladium nanoparticles by chemical reduction in nonionic surfactant/ionic liquid hybrid systems. J. Mol. Liquids 2020, 311, 113255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.D.; Ribeiro Nogueira, B.; Rostelato, M.E.C.M. Review of the methodologies used in the synthesis gold nanoparticles by chemical reduction. J. Alloys Compound. 2019, 798, 714–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, H.; Sugahara, T.; Hirasawa, I. Preparation of dispersed metal nanoparticles in the aqueous solution of metal carboxylate and the tetra-n-butylammonium carboxylate. J. Crystal Growth 2019, 514, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ralston, J.; Sedev, R.; Beattie, D.A. Functionalized gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, structure and colloid stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 331, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, M.; Günther, B. Sputtering on liquids—A versatile process for the production of magnetic suspensions? J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torimoto, T.; Okazaki, K. Sputter deposition onto ionic liquids: Simple and clean synthesis of highly dispersed ultrafine metal nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 24311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.X.; Zhang, Q.R.; Feng, C.M.; Ge, H.L.; Jiao, Z.K. Structural and electrical properties of a metallic rough-thin-film system deposited on liquid substrates. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 1996, 54, 14754–14757. [Google Scholar]
- Slepička, P.; Elashnikov, R.; Ulbrich, P.; Staszek, M.; Kolská, Z.; Švorčík, V. Stabilization of sputtered gold and silver nanoparticles in PEG colloid solutions. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepička, P.; Přibyl, M.; Fajstavr, D.; Ulbrich, P.; Siegel, J.; Řezníčková, A.; Švorčík, V. Grafting of platinum nanostructures on biopolymer at elevated temperature. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 546, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznickova, A.; Slepicka, P.; Slavikova, N.; Staszek, M.; Svorcik, V. Preparation, aging and temperature stability of PEGylated gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 523, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Ullah, S.; Sgarbi, R.; Tremiliosi-Filho, G. One-pot ligand-free synthesis of gold nanoparticles: The role of glycerol as reducing-cum-stabilizing agent. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 565, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, N.; Chiş, V.; Mircescu, N.E.; Marişca, O.T.; Buja, O.M.; Leopold, L.F.; Socaciu, C.; Braicu, C.; Irimie, A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. One step synthesis of SERS active colloidal gold nanoparticles by reduction with polyethylene glycol. Colloids Surf. A 2013, 436, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Fu, D.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, F. Gold nanoparticles amplified microcantilever biosensor for detecting protein biomarkers with high sensitivity. Sens. Actuators A 2021, 321, 112563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Yu, T.; Liu, D.; Xianyu, Y. Recent advances in gold nanoparticles-based biosensors for food safety detection. Biosensors Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-García, S.; Solórzano, R.; Novio, F.; Alibés, R.; Busqué, F.; Ruiz-Molina, D. Coordination polymers nanoparticles for bioimaging. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 432, 213716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Langley, R.J.; Tamshen, K.; Harms, J.; Middleditch, M.J.; Maynard, H.D.; Jamieson, S.M.F.; Perry, J.K. Enhanced Bioactivity of a Human GHR Antagonist Generated by Solid-Phase Site-Specific PEGylation. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhira, T.; Sakai, H. Entropy-Driven Supramolecular Ring-Opening Polymerization of a Cyclic Hemoglobin Monomer for Constructing a Hemoglobin–PEG Alternating Polymer with Structural Regularity. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Murakami, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Che, Y. Highly efficient and controllable PEGylation of gold nanoparticles prepared by femtosecond laser ablation in water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 23293–23298. [Google Scholar]
- Takae, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Otsuka, H.; Nakamura, T.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Ligand density effect on biorecognition by PEGylated gold nanoparticles: Regulated interaction of RCA120 lectin with lactose installed to the distal end of tethered PEG strands on gold surface. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimmin, R.G.; Schoch, A.B.; Braun, P.V. Polymer size and concentration of effects on the size of gold nanoparticles cappped by polymeric thiols. Langmuir 2007, 20, 5613–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, D.; Fu, W.; Li, J.; Crasto, C.; Jones, G.; DiMarzio, C.; Amiji, M. Surface functionalization of gold nanoparticles using hetero-bifunctional poly (ethylene glycol) spacer for intracellular tracking and delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkenier, H.; Malytskyi, V.; Blond, P.; Retout, M.; Mattiuzzi, A.; Goole, J.; Raussens, V.; Jabin, I.; Bruylants, G. Orcid Controlled Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with Mixtures of Calix[4]arenes Revealed by Infrared Spectroscopy. Langmuir 2017, 33, 8253–8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Shenoy, D.; Li, J.; Crasto, C.; Jones, G.; Dimarzio, C.; Sridhar, S.; Amiji, M. Biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles functionalized using hetero-bifunctional poly(ethylene glycol) spacer. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2004, 1, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangoo, N.; Bhasin, K.; Mehta, S.; Suri, C. Synthesis and capping of water-dispersed gold nanoparticles by an amino acid: Bioconjugation and binding studies. J. Colloids. Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russier-Antoine, I.; Bertorelle, F.; Kulesza, A.; Soleilhac, A.; Bensalah-Ledoux, A.; Guy, S.; Dugourd, P.; Brevet, P.; Antoine, R. Chiral supramolecular gold-cysteine nanoparticles: Chiroptical and nonlinear optical properties. Prog. Natur. Sci. Mater. Int. 2016, 26, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. Functional Gold Nanoparticle−Peptide Complexes as Cell-Targeting Agents. Langmuir 2008, 24, 10293–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Ge, J.; Zhao, X.S. Kinetics and thermodynamics of DNA hybridization on gold nanoparticles. Nucl. Acid Res. 2009, 37, 3756–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.L.; Tsai, C.Y.; Sun, C.C.; Uppala, R.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, P.H. Electrical detection of DNA using gold and magnetic nanoparticles and bio bar-code DNA between nanogap electrodes. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipka, J.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Sperling, R.A.; Wenk, A.; Takenaka, S.; Schleh, C.; Kissel, T.; Parak, W.J.; Kreyling, W.G. Biodistribution of PEG-modified gold nanoparticles following intratracheal instillation and intravenous injection. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6574–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.S.; Cho, M.; Jeong, J.; Choi, M.; Han, B.S.; Shin, H.S.; Hong, J.; Chung, B.H.; Jeong, J.; Cho, M.H. Size-dependent tissue kinetics of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 245, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolska, Z.; Valha, P.; Slepička, P.; Švorčík, V. Refractometric study of systems water-poly (ethylene glycol) for preparation and characterization of Au nanoparticles dispersion. Arabian J. Chem. 2019, 12, 5019–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Otsuka, H.; Kataoka, K.; Nagasaki, Y. Preparation of functionally PEGylated gold nanoparticles with narrow distribution through autoreduction of auric cation by alpha-biotinyl-PEG-block-[poly(2-N, N-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate)]. Langmuir 2004, 20, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Bae, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.R.; Park, T.G. Amine functionalized gold nanoparticles as non-cytotoxic and efficient intracellular siRNA delivery carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.A.; Kim, J.P.; Oyama, M. Preparation of monodispersed carboxylate-functionalized gold nanoparticles using pamoic acid as a reducingand capping reagent. Gold Bull. 2014, 47, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Selegård, R.; Ailic, D.; Liedberg, B. Peptide functionalized gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of matrilysin (MMP-7) activity. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8973–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastis, N.G.; Sanchez-Tillo, E.; Pujals, S.; Farrera, C.; Kogan, M.J.; Giralt, E.; Celada, A.; Iloberas, J.; Puntes, V. Peptides conjugated to gold nanoparticles induce macrophage activation. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier, D.J.; Nitin, N.; Levy, M.; Ellington, A.; Richards-Kortum, R. Aptamer-targeted gold nanoparticles as molecular specific contrast agents for refelectance imaging. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jang, H.H.; Ryou, S.M.; Kim, S.; Bae, J.; Lee, K.; Han, M.S. A functionalized gold nanoparticles-assisted universal carrier for antisense DNA. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4151–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neděla, O.; Slepička, P.; Švorčík, V. Surface Modification of Polymer Substrates for Biomedical Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepicka, P.; Slepickova Kasalkova, N.; Siegel, J.; Kolska, Z.; Bacakova, L.; Svorcik, V. Nano-structured and functionalized surfaces for cytocompatibility improvement and bactericidal action. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slepicka, P.; Siegel, J.; Lyutakov, O.; Slepickova Kasalkova, N.; Kolska, Z.; Bacakova, L.; Svorcik, V. Polymer nanostructures for bioapplications induced by laser treatment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 839–855. [Google Scholar]
- Slepička, P.; Malá, Z.; Rimpelová, S.; Švorčík, V. Antibacterial properties of modified biodegradable PHB non-woven fabric. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 65, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | Element Concentration (at%) | |
|---|---|---|
| S | Au | |
| Pristin PEN; PEN modif. 200 s; PEN modif. 400 s | - | - |
| PEN modif. 200 s, AuNP 600 s | 1.26 | 0.12 |
| PEN modif. 200 s, AuNP 900 s | 1.26 | 2.32 |
| PEN modif. 400 s, AuNP 600 s | 1.96 | 2.61 |
| PEN modif. 400 s, AuNP 900 s | 0.83 | 0.59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fajstavr, D.; Karasová, A.; Michalcová, A.; Ulbrich, P.; Slepičková Kasálková, N.; Siegel, J.; Švorčík, V.; Slepička, P. PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Grafted with N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine for Polymer Modification. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061434
Fajstavr D, Karasová A, Michalcová A, Ulbrich P, Slepičková Kasálková N, Siegel J, Švorčík V, Slepička P. PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Grafted with N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine for Polymer Modification. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(6):1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061434
Chicago/Turabian StyleFajstavr, Dominik, Adéla Karasová, Alena Michalcová, Pavel Ulbrich, Nikola Slepičková Kasálková, Jakub Siegel, Václav Švorčík, and Petr Slepička. 2021. "PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Grafted with N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine for Polymer Modification" Nanomaterials 11, no. 6: 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061434
APA StyleFajstavr, D., Karasová, A., Michalcová, A., Ulbrich, P., Slepičková Kasálková, N., Siegel, J., Švorčík, V., & Slepička, P. (2021). PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Grafted with N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine for Polymer Modification. Nanomaterials, 11(6), 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061434