Effect of Hydration Time in Saline on the Swelling and Uniaxial Tensile Response of Annulus Fibrosus of the Intervertebral Disc
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
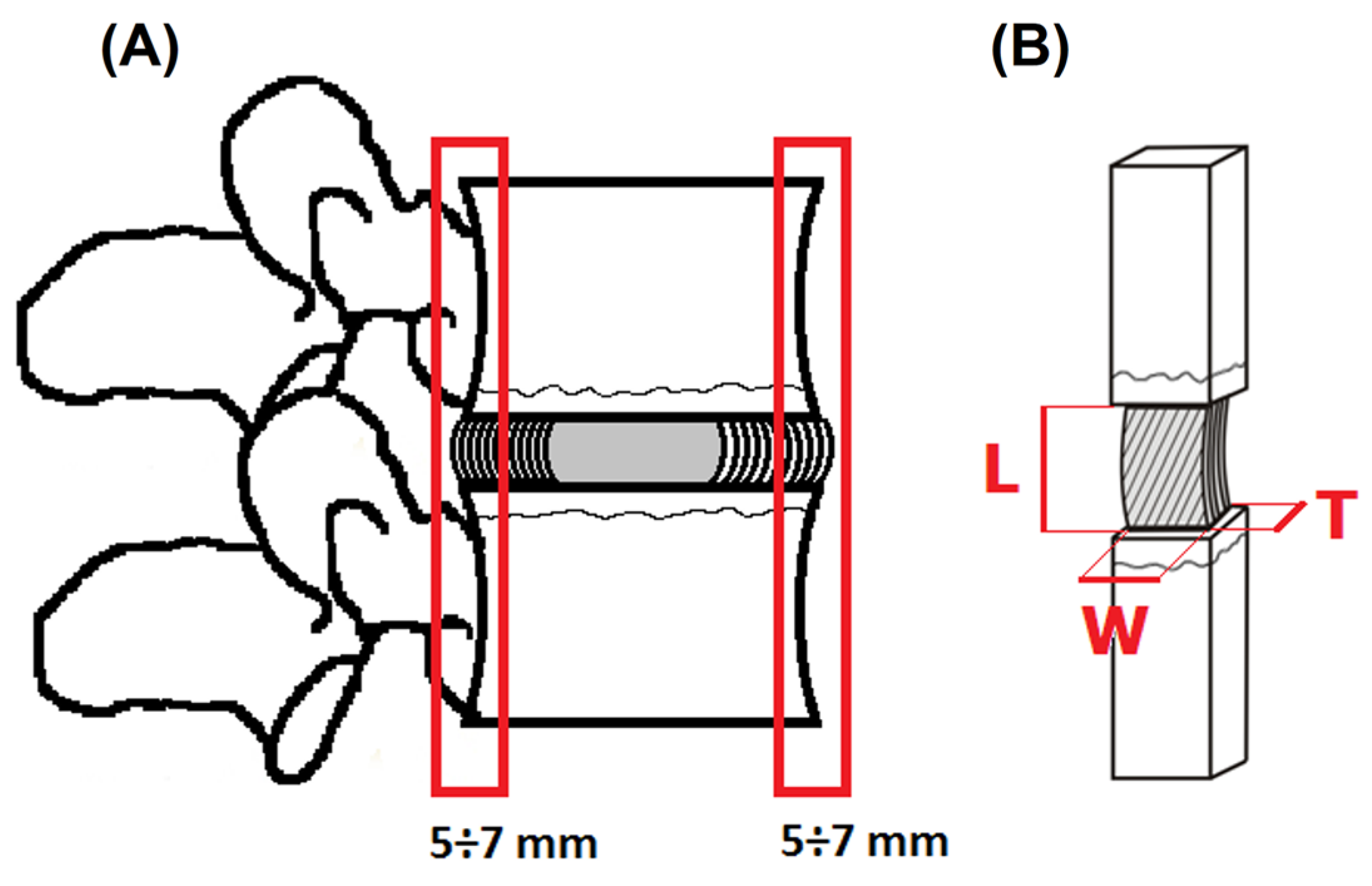
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Hydration
- -
- Cross-sectional area (AC) as the product of the width and thickness defining the changes in the radial direction of the IVD;
- -
- Longitudinal sectional area (AL) as the product of the length and width defining the changes in the circumferential direction of the IVD.
2.3. Mechanical Test
2.4. Statistical Analysis
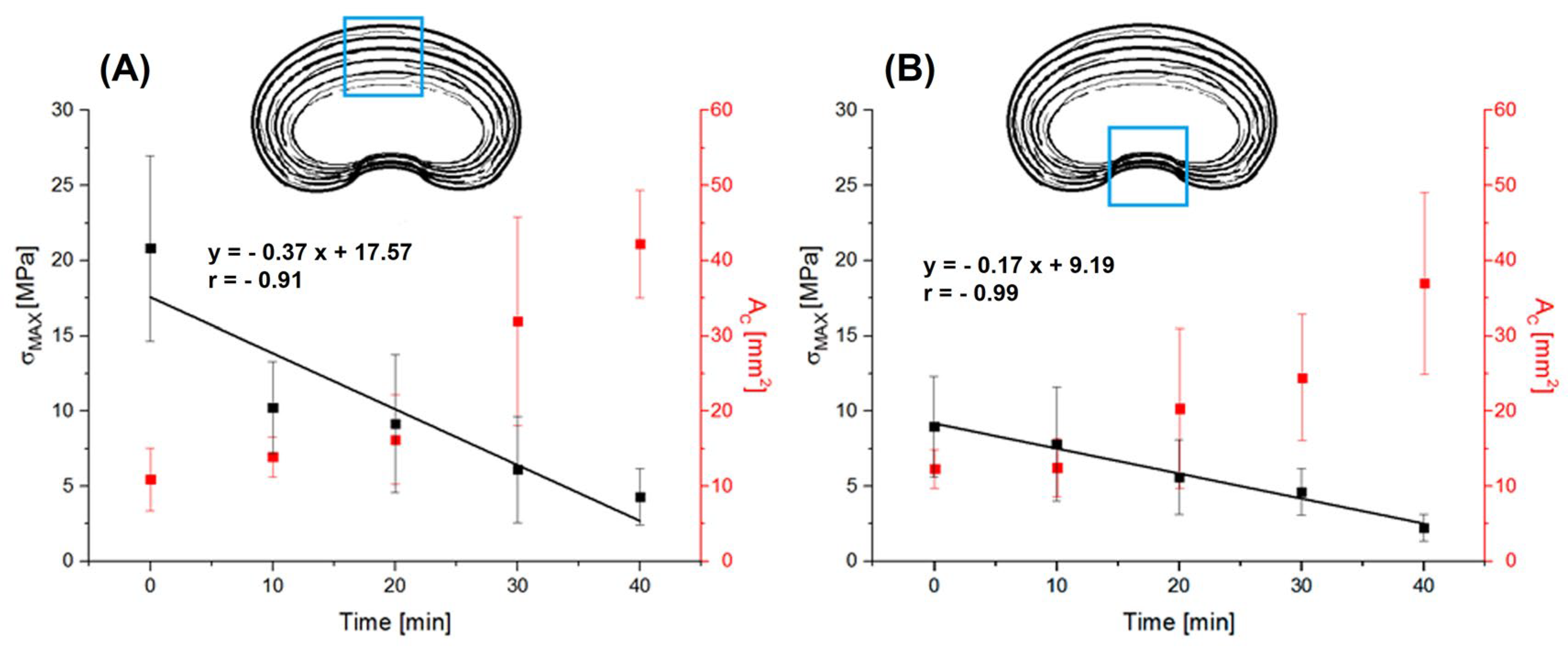
3. Results
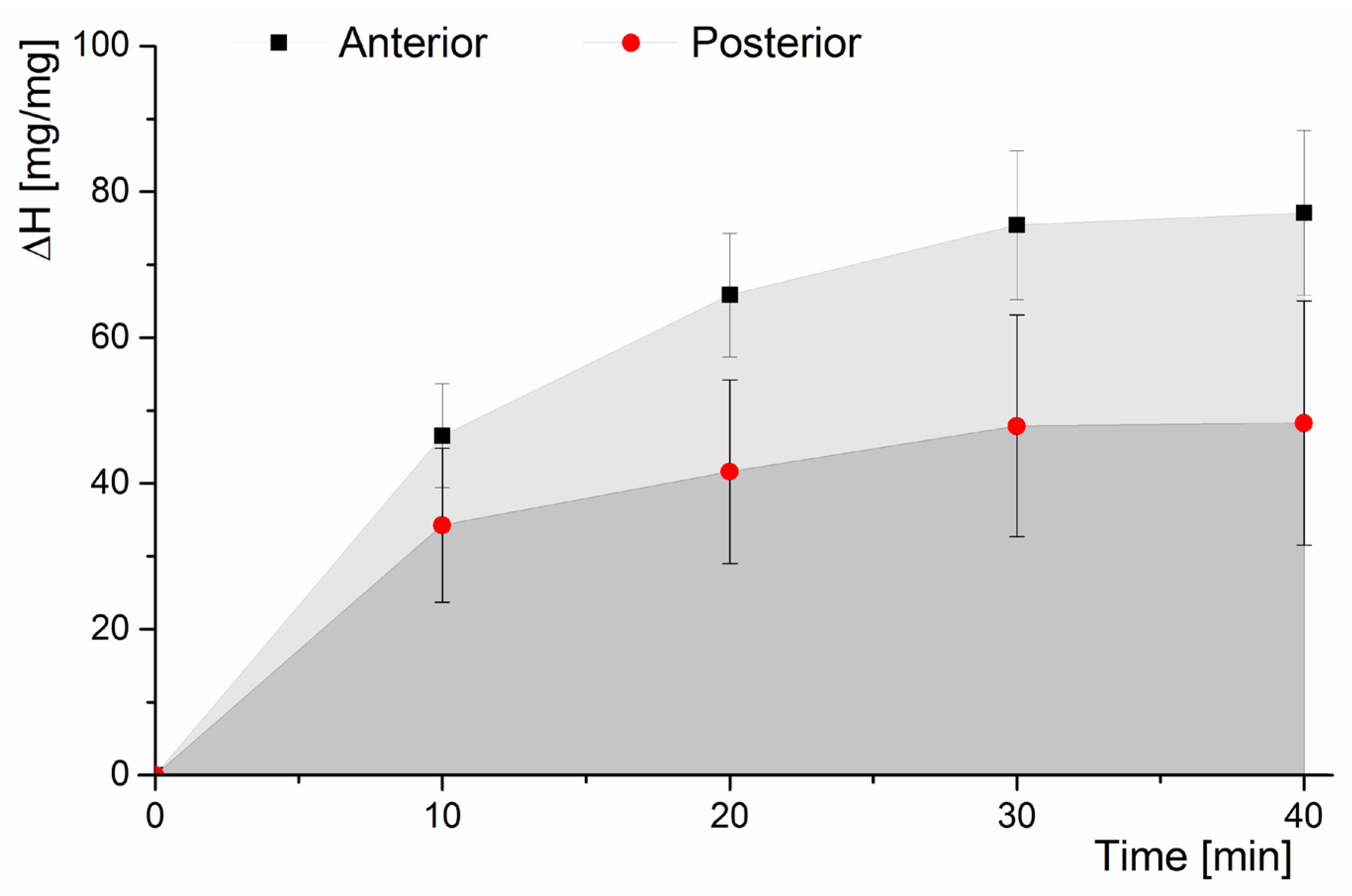
3.1. Hydration
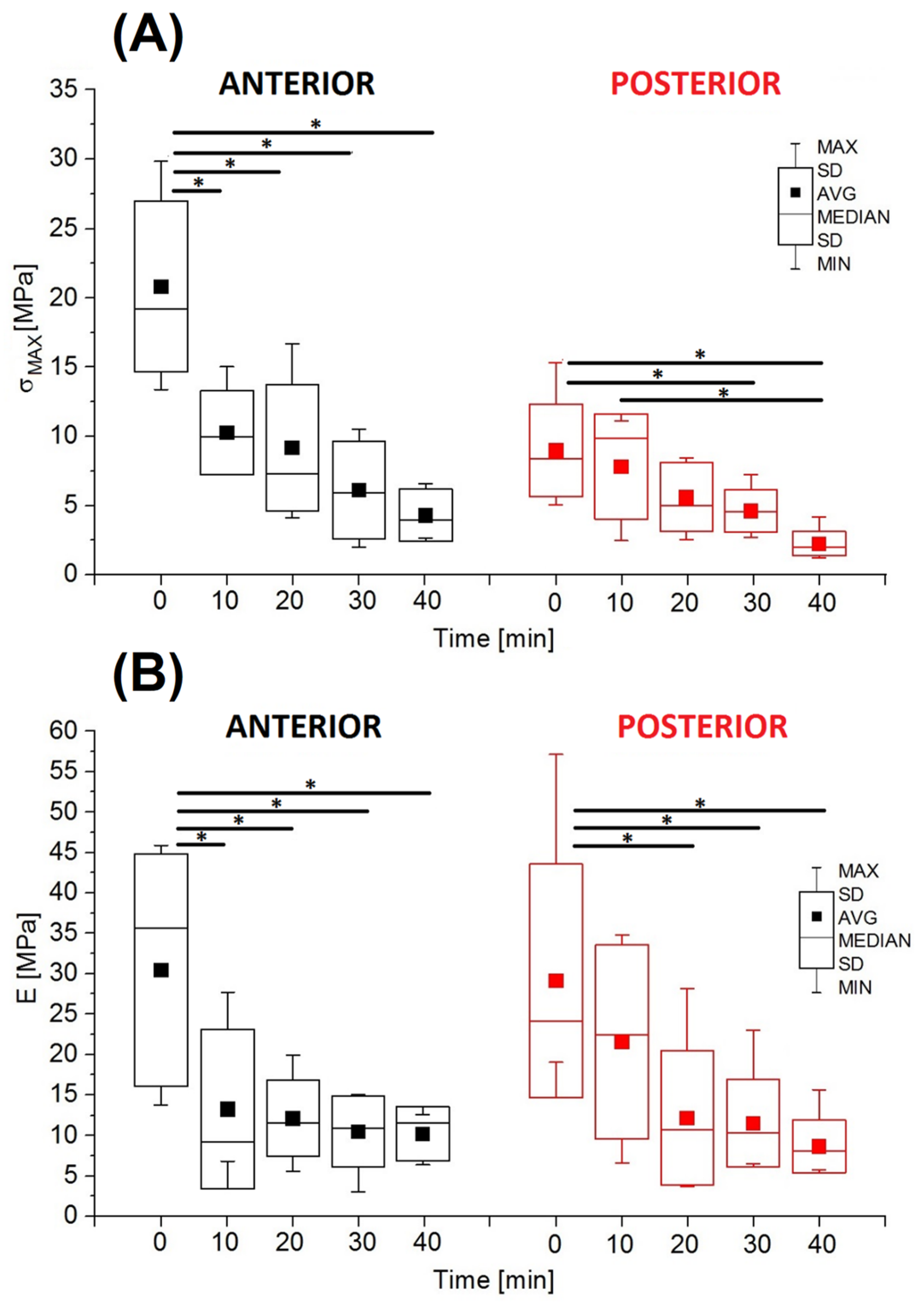
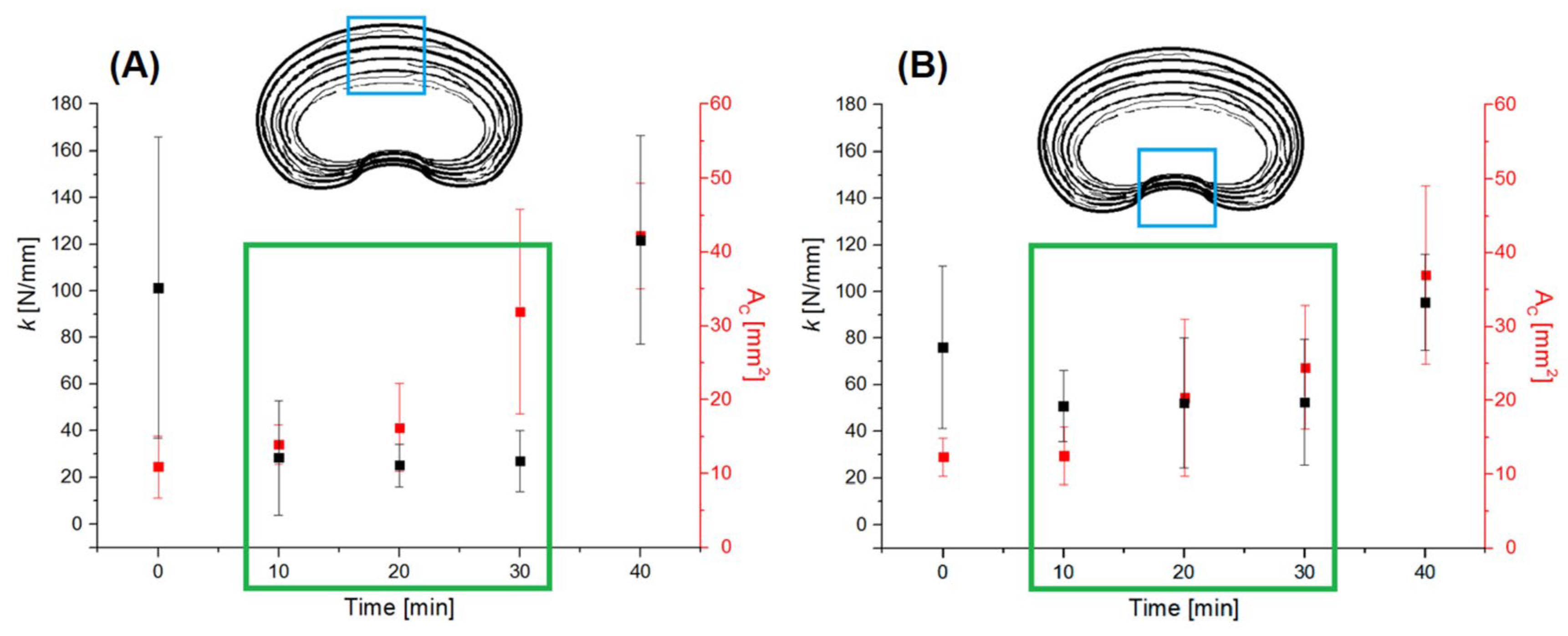
3.2. Mechanical Test
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruehlmann, S.B.; Rattner, J.B.; Matyas, J.R.; Duncan, N.A. Regional variations in the cellular matrix of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. J. Anat. 2002, 201, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Maitre, C.L.; Pockert, A.; Buttle, D.J.; Freemont, A.J.; Hoyland, J.A. Matrix synthesis and degradation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35 Pt 4, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singha, K.; Singha, M. Biomechanism Profile of Intervertebral Discs (IVD): Strategies to Successful Tissue Engineering for Spinal Healing by Reinforced Composite Structure. J. Tissue Sci. Eng. 2012, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobielarz, M.; Szotek, S.; Głowacki, M.; Dawidowicz, J.; Pezowicz, C. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of collagen and elastin in annulus fibrosus of the physiologic and scoliotic intervertebral discs. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 62, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Mi, C. On the identification of the ultra-structural organization of elastic fibers and their effects on the integrity of annulus fibrosus. J. Biomech. 2023, 157, 111728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, C.P.; Rodrigues, L.M.; Fregni, M.V.; Gotfryd, A.; Made, A.M.; Pinhal, M.A. Extracellular matrix remodeling in experimental intervertebral disc degeneration. Acta Ortop. Bras. 2013, 21, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, J.P.; Winlove, C.P. Pathophysiology of the intervertebral disc and the challenges for MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, M.; Pack, C.; Osborn-King, Z.; Raterman, B.; Kolipaka, A.; Bentil, S.A.; Walter, B.A. Modeling the effects of hydration on viscoelastic properties of nucleus pulposus tissue in shear using the fractional Zener model. J. Biomech. 2024, 164, 111965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.; Gu, W. Transport properties of cartilaginous tissues. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2009, 5, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wendland, M.F.; O’Connell, G.D. Direct Quantification of Intervertebral Disc Water Content Using MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, S.; Merkher, Y.; Wachtel, E.; Ehrlich, S.; Maroudas, A. Correlation of swelling pressure and intrafibrillar water in young and aged human intervertebral discs. J. Orthop. Res. 2006, 24, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Justiz, M.A.; Flagler, D.; Gu, W.Y. Effects of swelling pressure and hydraulic permeability on dynamic compressive behavior of lumbar annulus fibrosus. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 30, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezci, S.E.; Nandy, A.; O’Connell, G.D. Effect of Hydration on Healthy Intervertebral Disk Mechanical Stiffness. J. Biomech. Eng. 2015, 137, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raftery, K.; Rahman, T.; Smith, N.; Schaer, T.; Newell, N. The role of the nucleus pulposus in intervertebral disc recovery: Towards improved specifications for nucleus replacement devices. J. Biomech. 2024, 166, 111990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costi, J.J.; Ledet, E.H.; O’Connell, G.D. Spine biomechanical testing methodologies: The controversy of consensus vs. scientific evidence. JOR Spine 2021, 5, e1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflaster, D.S.; Krag, M.H.; Johnson, C.C.; Haugh, L.D.; Pope, M.H. Effect of test environment on intervertebral disc hydration. Spine 1997, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costi, J.J.; Hearn, T.C.; Fazzalari, N.L. The effect of hydration on the stiffness of intervertebral discs in an ovine model. Clin. Biomech. 2002, 17, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żak, M.; Pezowicz, C. Analysis of the impact of the course of hydration on the mechanical properties of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.P.; Adams, M.A.; Dolan, P. Tensile properties of the annulus fibrosus II. Ultimate tensile strength and fatigue life. Eur. Spine J. 1993, 2, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, D.L.; Weidenbaum, M.; Iatridis, J.C.; Ratcliffe, A.; Mow, V.C. Regional variation in tensile properties and biochemical composition of the human lumbar anulus fibrosus. Spine 1994, 19, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acaroglu, E.R.; Iatridis, J.C.; Setton, L.A.; Foster, R.J.; Mow, V.C.; Weidenbaum, M. Degeneration and aging affect the tensile behavior of human lumbar anulus fibrosus. Spine 1995, 20, 2690–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebara, S.; Iatridis, J.C.; Setton, L.A.; Foster, R.J.; Mow, V.C.; Weidenbaum, M. Tensile properties of nondegenerate human lumbar anulus fibrosus. Spine 1996, 21, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szotek, S.; Szust, A.; Pezowicz, C.; Majcher, P.; Będziński, R. Animal models in biomechanical spine investigations. Bull. Vet. Inst. Puławy 2004, 48, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, N.; Bass, E.C.; Lotz, J.C. Effect of frozen storage on the creep behavior of human intervertebral discs. Spine 2001, 26, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.A.; Green, T.P. Tensile properties of the annulus fibrosus. I. The contribution of fibre-matrix interactions to tensile stiffness and strength. Eur. Spine J. 1993, 2, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żak, M.; Pezowicz, C. Spinal sections and regional variations in the mechanical properties of the annulus fibrosus subjected to tensile loading. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2013, 15, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, J.; Kolditz, D.; Gowin, R. Water and electrolyte content of human intervertebral discs under variable load. Spine 1985, 10, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.A.; Hutton, W.C. The effect of posture on the fluid content of lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine 1983, 8, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.W.; Garbutt, G.; Adams, M.A. Effect of sustained loading on the water content of intervertebral discs: Implications for disc metabolism. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1996, 55, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyghe, J.M.; Jongeneelen, C.J. 3D non-affine finite strains measured in isolated bovine annulus fibrosus tissue samples. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2012, 11, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezci, S.E.; Lim, S.; O’Connell, G.D. Nonlinear stress-dependent recovery behavior of the intervertebral disc. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 110, 103881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogduk, N. Clinical Anatomy of the Lumbar Spine and Sacrum, 3rd ed.; Churchull Livingstone: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Culav, E.M.; Clark, C.H.; Merrilees, M.J. Connective tissues: Matrix composition and its relevance to physical therapy. Phys. Ther. 1999, 79, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Region | Geometric Parameters | Hydration Time [min] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | ||
| A | L [mm] | 4.51 ± 0.69 | 4.66 ± 0.44 | 4.71 ± 0.39 | 4.77 ± 0.26 | 4.88 ± 0.63 |
| P | 3.46 ± 0.59 | 3.65 ± 0.42 | 3.68 ± 0.36 | 3.70 ± 0.50 | 3.84 ± 0.60 | |
| A | W [mm] | 10.46 ± 2.01 | 10.86 ± 1.23 | 11.93 ± 2.05 | 12.29 ± 2.43 | 13.50 ± 1.29 |
| P | 9.47 ± 0.35 | 10.40 ± 1.14 | 10.78 ± 2.17 | 11.00 ± 2.00 | 12.33 ± 0.58 | |
| A | T [mm] | 1.04 ± 0.28 *# | 1.28 ± 0.20 *# | 1.36 ± 0.38 *# | 2.60 ± 0.78 * | 3.13 ± 0.25 # |
| P | 1.30 ± 0.27 # | 1.20 ± 0.25 # | 1.89 ± 0.78 # | 2.22 ± 0.71 | 3.00 ± 0.89 # | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Żak, M.; Szotek, S. Effect of Hydration Time in Saline on the Swelling and Uniaxial Tensile Response of Annulus Fibrosus of the Intervertebral Disc. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16100365
Żak M, Szotek S. Effect of Hydration Time in Saline on the Swelling and Uniaxial Tensile Response of Annulus Fibrosus of the Intervertebral Disc. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(10):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16100365
Chicago/Turabian StyleŻak, Małgorzata, and Sylwia Szotek. 2025. "Effect of Hydration Time in Saline on the Swelling and Uniaxial Tensile Response of Annulus Fibrosus of the Intervertebral Disc" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 10: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16100365
APA StyleŻak, M., & Szotek, S. (2025). Effect of Hydration Time in Saline on the Swelling and Uniaxial Tensile Response of Annulus Fibrosus of the Intervertebral Disc. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(10), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16100365






