Eye Gaze Patterns during Reasoning Provide Insights Regarding Individual Differences in Underlying Cognitive Abilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study 1
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Participants
2.1.2. Instruments
2.1.3. Apparatus
2.1.4. Procedure
2.1.5. Eye-Tracking Measures
2.1.6. Data Analysis
2.2. Results
2.2.1. Descriptive
2.2.2. LASSO Regression Model
3. Study 2
3.1. Methods
3.1.1. Participants
3.1.2. Instruments
3.1.3. Apparatus
3.1.4. Procedure
3.1.5. Eye-Tracking Measures
3.1.6. Data Analysis
3.2. Results
3.2.1. Descriptive
3.2.2. Comparing the Correlations
3.2.3. LASSO Regression Models
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, Patricia A. 2016. Relational thinking and relational reasoning: Harnessing the power of patterning. NPJ Science of Learning 1: 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, Irai Cristina Boccato. 2007. Teste D.70: Manual revisado e ampliado [D.70 Test: Revised and Extended Manual]. São Paulo: Centro Editor de Testes e Pesquisas em Psicologia. [Google Scholar]
- Bethell-Fox, Charles E., David F. Lohman, and Richard E. Snow. 1984. Adaptive reasoning: Componential and eye movement analysis of geometric analogy performance. Intelligence 8: 205–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birney, Damian P., and Jens F. Beckmann. 2022. Intelligence IS Cognitive Flexibility: Why Multilevel Models of Within-Individual Processes Are Needed to Realise This. Journal of Intelligence 10: 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, John B. 1993. Human Cognitive Abilities. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Cattell, Raymond B. 1973. Measuring Intelligence with the Culture Fair Tests. Champaign: Institute for Personality and Ability Testing. [Google Scholar]
- Chartier, P. 2009. Les tests dominos (D70 et D2000): Comment dépasser le constat du seul score total? Propositions d’analyses des réponses [The domino-type tests (D70 and D2000): How to go beyond the report of the only total score? Proposals for analyses of the answers]. Pratiques Psychologiques 15: 287–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuderski, Adam. 2013. When are fluid intelligence and working memory isomorphic and when are they not? Intelligence 41: 244–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colzato, Lorenza S., Nelleke C. Van Wouwe, Tristan J. Lavender, and Bernhard Hommel. 2006. Intelligence and cognitive flexibility: Fluid intelligence correlates with feature “unbinding” across perception and action. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 13: 1043–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, Andrew R. A., Michael J. Kane, and Randall W. Engle. 2003. Working memory capacity and its relation to general intelligence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 7: 547–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, Andrew R., Nelson Cowan, Michael F. Bunting, David J. Therriault, and Scott R. Minkoff. 2002. A latent variable analysis of working memory capacity, short-term memory capacity, processing speed, and general fluid intelligence. Intelligence 30: 163–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, Pierre, Jerry S. Carlson, and J. P. Das. 1990. Planning ability and cognitive performance: The compensatory effects of a dynamic assessment approach. Learning and Individual Differences 2: 437–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, Phillip M. 1972. Human Memory and the Medial Temporal Region of the Brain. Ph.D. thesis, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada. [Google Scholar]
- Dehn, Milton J. 2017. How working memory enables fluid reasoning. Applied Neuropsychology: Child 6: 245–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drodick, Lisa Whipple, Dustin Wahlstrom, Jianjin Zhu, and Lawrence G. Weiss. 2012. The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Fourth Edition and the Wechsler Memory Scale—Fourth Edition. In Contemporary Intellectual Assessment: Theories, Tests, and Issues. Edited by Dawn P. Flanagan and Patti L. Harrison. New York: The Guilford Press, pp. 99–144. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, Randall W., Stephen W. Tuholski, James E. Laughlin, and Andrew R. A. Conway. 1999. Working memory, short-term memory, and general fluid intelligence: A latent-variable approach. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 128: 309–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, Dawn, and Patti L. Harrison. 2012. Contemporary Intellectual Assessment: Theories, Tests, and Issues. New York: The Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Gonthier, Corentin, and Jean-Luc Roulin. 2020. Intraindividual strategy shifts in Raven’s matrices, and their dependence on working memory capacity and need for cognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 149: 564–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, Taylor R., Alexander A. Petrov, and Per B. Sederberg. 2011. A novel method for analyzing sequential eye movements reveals strategic influence on Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices. Journal of Vision 11: 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, Robert K., Gordon J. Chelune, Jack L. Talley, Garry G. Kay, and Glenn Curtiss. 2004. Teste Wisconsin de Classificação de Cartas [Wisconsin Card Sorting Test]. São Paulo: Casa do Psicólogo. [Google Scholar]
- Heinze, George, Christine Wallisch, and Daniela Dunkler. 2018. Variable selection—A review and recommendations for the practicing statistician. Biometrical Journal 60: 431–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, Timothy L., Adnan Bajwa, Adrian M. Owen, and Christopher Kennard. 2000. The strategic control of gaze direction in the Tower of London task. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 12: 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, Tatiana A. 2018. Análise do padrão dos movimentos oculares em uma multitarefa de busca visual em ambiente real e suas relações com as funções executivas [Analysis of the pattern of eye movements in a visual search multitasking in a real environment and its relationships with executive functions]. Unpublished Master’s thesis, Mackenzie Presbyterian University, São Paulo, Brazil. [Google Scholar]
- Jarosz, Andrew F., Megan J. Raden, and Jennifer Wiley. 2019. Working memory capacity and strategy use on the RAPM. Intelligence 77: 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffreys, Harold. 1961. Theory of Probability. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Scott B. 2014. Working Memory and Fluid Reasoning: Same or Different? Scientific American. Available online: https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/beautiful-minds/working-memory-and-fluid-reasoning-same-or-different/ (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Krikorian, Robert, John Bartok, and Nancy Gay. 1994. Tower of London procedure: A standard method and developmental data. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 16: 840–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharský, Šimon, Ingmar Visser, Gabriela Olivia Truțescu, Paulo Guirro Laurence, Martina Zaharieva, and Maartje E. J. Raijmakers. 2020. Cognitive strategies revealed by clustering eye movement transitions. Journal of Eye Movement Research 13: 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, Paulo Guirro, and Elizeu C. Macedo. 2022. Cognitive strategies in matrix-reasoning tasks: State of the art. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 30: 147–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, Paulo Guirro, Tatiana Pontrelli Mecca, Alexandre Serpa, Romain Martin, and Elizeu C. Macedo. 2018. Eye movements and cognitive strategy in a fluid intelligence test: Item type analysis. Frontiers in Psychology 9: 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, Juhani E. 2004. A test for children’s goal-directed behavior: A pilot study. Perceptual and Motor Skills 98: 223–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luke, Steven G., Emily S. Darowski, and Shawn D. Gale. 2018. Predicting eye-movement characteristics across multiple tasks from working memory and executive control. Memory & Cognition 46: 826–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrew, Kevin S. 2009. CHC theory and the human cognitive abilities project: Standing on the shoulders of the giants of psychometric intelligence research. Intelligence 37: 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghanathan, Radha N., Cees van Leeuwen, and Andrey R. Nikolaev. 2015. Fixation duration surpasses pupil size as a measure of memory load in free viewing. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 8: 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, Rik, and Michel Wedel. 2012. Ad gist: Ad communication in a single eye fixation. Marketing Science 31: 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, John, J. C. Raven, and J. Court. 1998. Manual for Raven’s Progressive Matrices and Vocabulary Scales. Oxford: Oxford Psychologists Press. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, Robert M., Charles E. Lance, Peter K. Isquith, Aadina S. Fischer, and Peter R. Giancola. 2013. Confirmatory factor analysis of the behavior rating inventory of executive function-adult version in healthy adults and application to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 28: 425–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, Robert M., Peter K. Isquith, and Gerard A. Goia. 2005. Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Functions—Adult Version. Lutz: Psychological Assessment Resources. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, Flavia H., C. B. Mello, Orlando F. A. Bueno, and Georges Dellatolas. 2005. Cross-cultural differences for three visual memory tasks in Brazilian children. Perceptual and Motor Skills 101: 421–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlottfeldt, Carlos Guilherme, and Leandro Fernandes Malloy-Diniz. 2018. Teste Matrizes de Vienna 2: Versão Informatizada. [Vienesse Matrices Test 2: Informatized Version]. São Paulo: Editora Hogrefe Cetepp. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, W. Joel, and Kevin S. McGrew. 2012. The Cattell-Horn-Carroll model of intelligence. In Contemporary Intellectual Assessment: Theories, Tests, and Issues. Edited by Dawn P. Flanagan and Patti L. Harrison. New York: The Guilford Press, pp. 99–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shallice, Timothy. 1982. Specific impairments of planning. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences 298: 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, Richard E. 1978. Eye Fixation and Strategy Analyses of Individual Differences in Cognitive Aptitudes. In Cognitive Psychology and Instruction. Edited by A. M. Legold, J. W. Pellegrino, S. D. Fokkema and R. Glaser. New York: Plenum Press, pp. 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, Richard E. 1980. Aptitude processes. In Aptitude Learning, and Instruction: Cognitive Process Analysis of Aptitude. Edited by Richard E. Snow, Pat-Anthony Federick and William E. Montague. Hillsdale: N Erlbaum, pp. 27–63. [Google Scholar]
- Starr, Ariel, Elena R. Leib, Jessica W. Younger, Project iLead Consortium, Melina R. Uncapher, and Silvia A. Bunge. 2022. Relational thinking: An overlooked component of executive functioning. Developmental Science 26: e13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, James H. 1980. Tests for comparing elements of a correlation matrix. Psychological Bulletin 87: 245–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabalas, Andrius, Emma Gowen, Ellen Poliakoff, and Alexander J. Casson. 2019. Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size. PLoS ONE 14: e0224365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneau, François, André F. Caissie, and Douglas A. Bors. 2006. Eye-movement analysis demonstrates strategic influences on intelligence. Intelligence 34: 261–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, David. 2004. WAIS-III. São Paulo: Casa do Psicólogo. [Google Scholar]
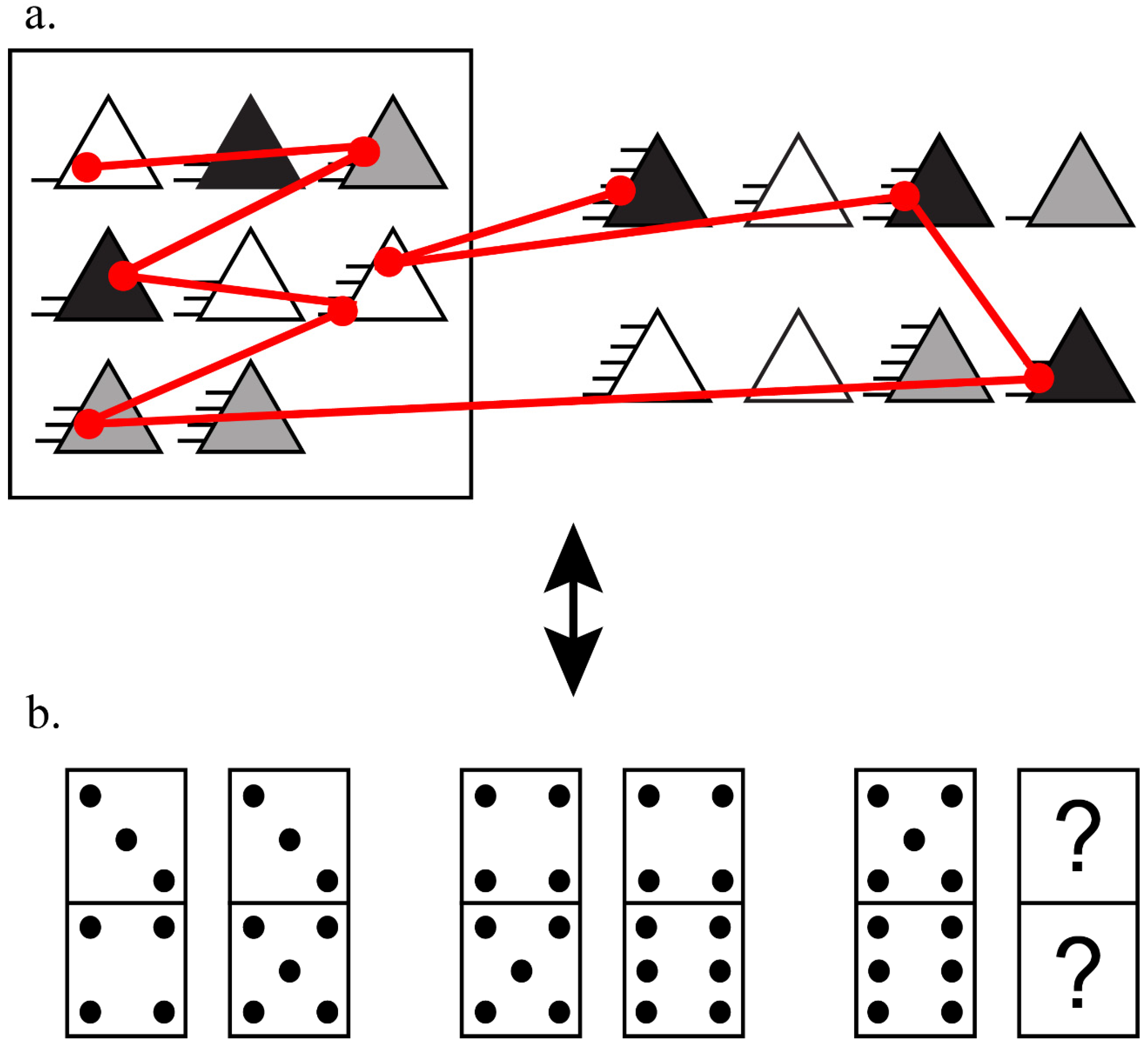
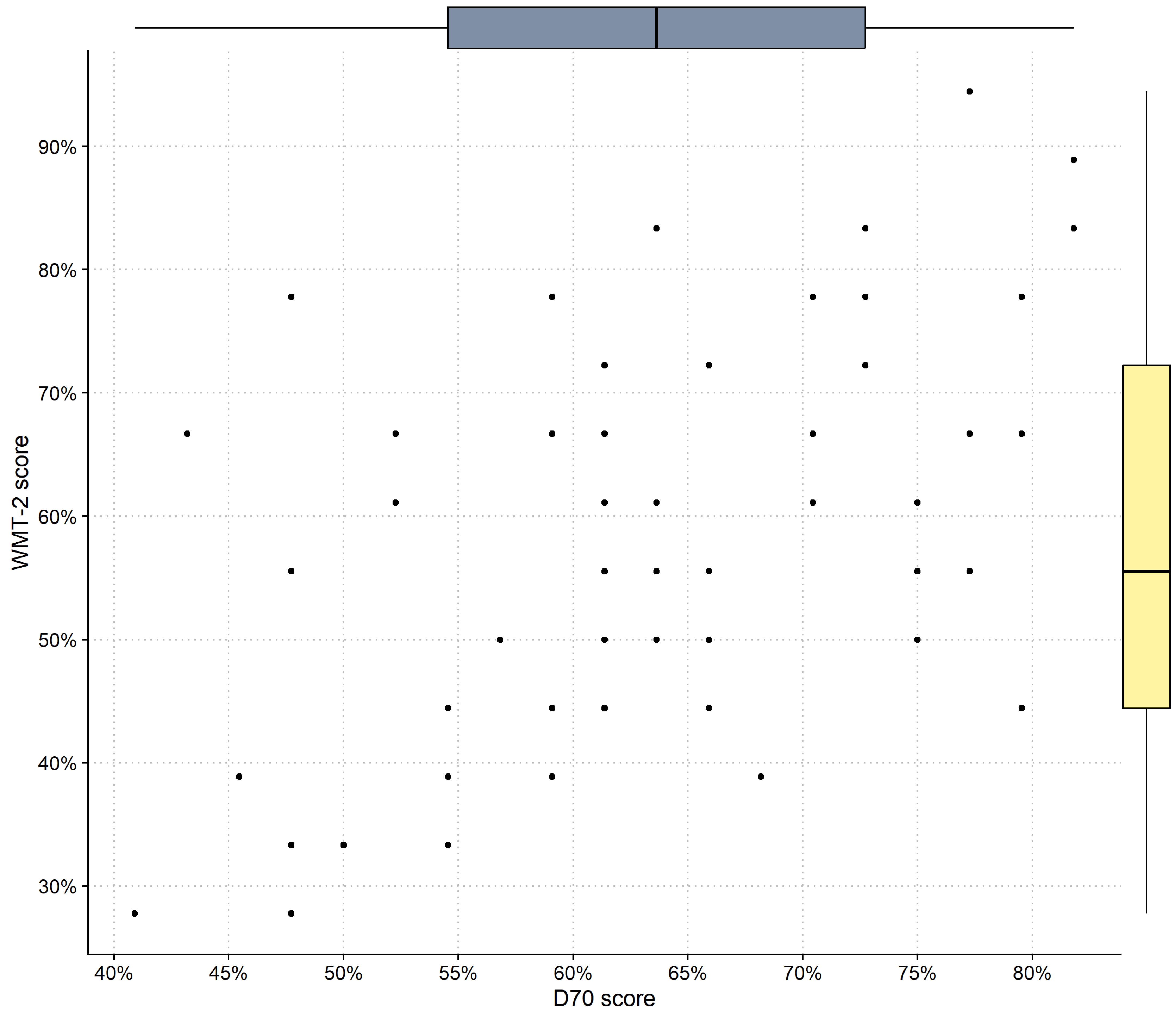

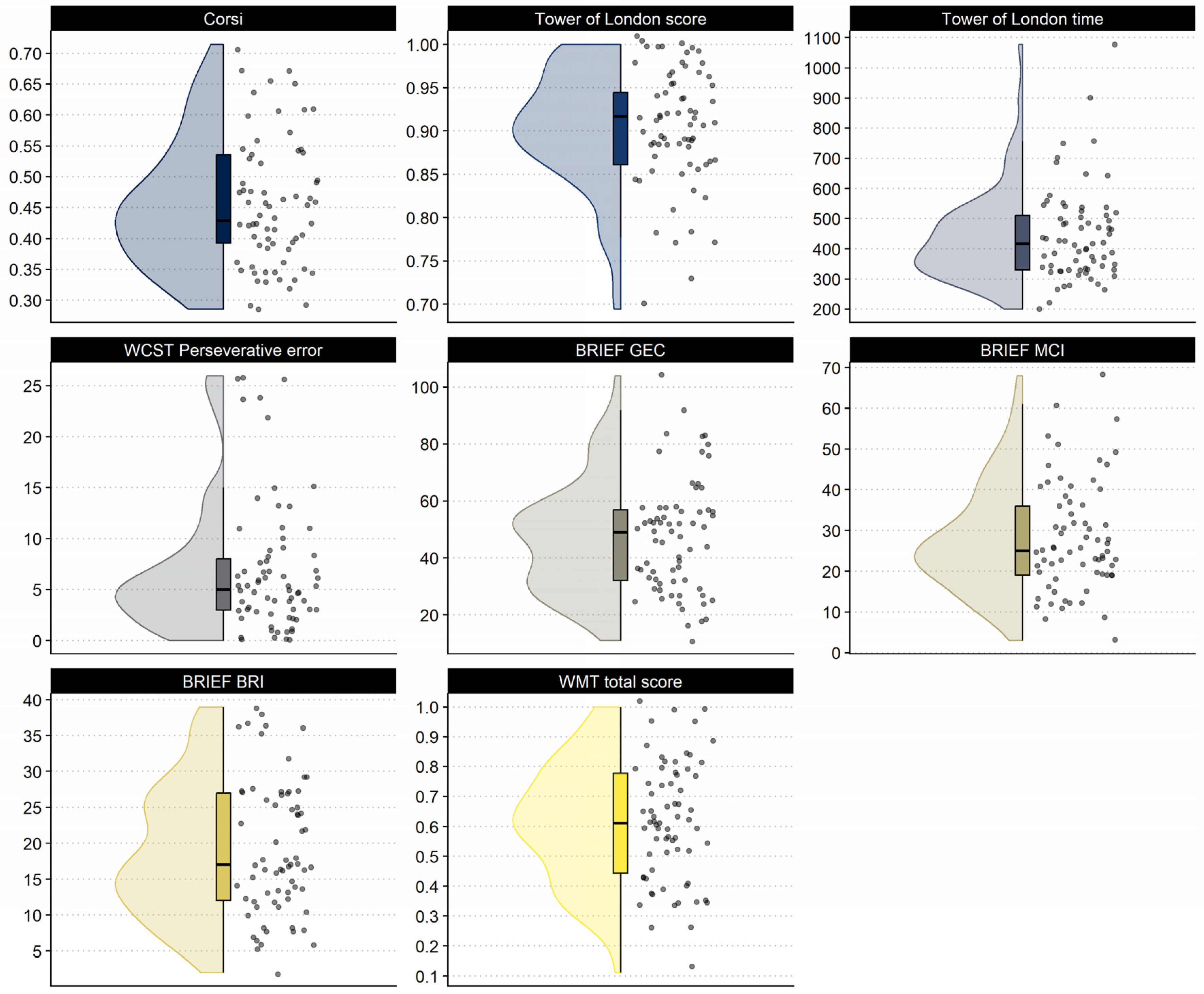

| Eye-Tracking Metrics | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Average time in each test item |
| 2 | Number of matrix–matrix transitions (number of times that a participant gazed from a matrix cell to another matrix cell) |
| 3 | Number of matrix–answer transitions (number of times that a participant gazed from the matrix to the answer choices or vice versa) |
| 4 | Number of answer–answer transitions (number of times that a participant gazed from an answer choice to another answer choice) |
| 5 | Latency to the first fixation on an answer choice (the time it took for a participant to perform the first fixation on the answer choices) |
| 6 | Ratio of time spent on the matrix vs. answer choices (time spent on the matrix divided by the time spent on the answer choices) |
| 7 | Average number of visits to a given matrix cell (the mean of the number of visits to each cell in all test items) |
| 8 | Average number of visits to a given incorrect answer choice (the mean of the number of visits to each answer choice, excluding the correct choice, in all test screens) |
| 9 | Total number of fixations on matrix cells |
| 10 | Average fixation duration for a matrix cell |
| 11 | Total number of fixations on answer choices |
| 12 | Average fixation duration for an answer choice |
| 13 | Percent of trials classified as cluster 2 scanpath (the percent of the items that the participant had their eye gaze classified as the cluster 2 scanpath) |
| 14 | Rate of matrix–answer transitions (the number of matrix–answer transitions divided by the average time in each test item; this conversion equalizes the number of matrix–answer transitions by how much time each participant spent gazing at each item. Higher rate indicates that participants gazed more times their eyes between the matrix and answer choices per second) |
| Metric | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gaze direction | Row-wise | Row-wise and Column-wise | Transition matrices (see supplementary file) |
| Probability of transition to answer choices from top or middle row | Low | Low to moderate | Transition matrices probabilities (see supplementary file) |
| Average time in each test item | - | - | BF10 = 0.07 (±<0.00) oo |
| # Matrix–matrix transitions | - | - | BF10 = 0.21 (±<0.00) o |
| # Matrix–answer transitions | - | - | BF10 = 0.08 (±<0.00) oo |
| # Answer–answer transitions | More transitions | Fewer transitions | BF10 = 10.19 (±<0.00) ** |
| Latency to the first fixation on an answer choice | - | - | BF10 = 1.09 (±<0.00) |
| Ratio of time spent on the matrix vs. answer choices | - | - | BF10 = 0.07 (±<0.00) oo |
| # Visits to a given matrix cell | - | - | BF10 = 0.17 (±<0.00) o |
| # Visits to a given incorrect answer choice | - | - | BF10 = 0.46 (±<0.00) |
| # Fixations on matrix cells | - | - | BF10 = 0.07 (±<0.00) oo |
| Average fixation duration for a matrix cell | Longer fixations | Shorter fixations | BF10 > 1000 (±<0.00) *** |
| # Fixations on answer choices | - | - | BF10 = 0.38 (±<0.00) |
| Average fixation duration for an answer choice | Longer fixations | Shorter fixations | BF10 > 1000 (±<0.00) *** |
| Rate of matrix–answer transitions | More transitions per second | Less transitions per second | BF10 = 8.13 (±<0.00) * |
| Measures | Standardized Coefficients |
|---|---|
| Predictors 1 | |
| Average time in each test item | −1.68 |
| Matrix–answer transitions | 1.40 |
| Answer–answer transitions | 1.80 |
| Latency to first fixation in answer choices | −0.09 |
| Ratio of time spent on matrix vs. answers | −0.25 |
| Visits in wrong answer choices | −2.61 |
| Total number of fixations on matrix cells | 0.84 |
| Average fixation duration for a matrix cell | −0.07 |
| Total number of fixations on answer choices | −0.01 |
| Average fixation duration for an answer choice | 0.39 |
| Percent of trials classified as cluster 2 scanpath | 0.15 |
| Rate of matrix–answer transitions | −1.10 |
| Performance estimates | |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.77 |
| MAE | 0.52 |
| RMSE | 0.61 |
| R2 | 0.57 |
| Metric | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gaze direction | Row-wise | Row-wise and Column-wise | Transition matrices (see supplementary file) |
| Probability of transition to answer choices from top or middle row | Low | Low to moderate | Transition matrices probabilities (see supplementary file) |
| Average time in each test item | - | - | BF10 = 0.07 (±<0.00) oo |
| # Matrix–matrix transitions | - | - | BF10 = 0.40 (±<0.00) |
| # Matrix–answer transitions | - | - | BF10 = 0.06 (±<0.00) oo |
| # Answer–answer transitions | Fewer transitions | More transitions | BF10 = 72.79 (±<0.00) ** |
| Latency to the first fixation on an answer choice | - | - | BF10 = 0.06 (±<0.00) oo |
| Ratio of time spent on the matrix vs. answer choices | - | - | BF10 = 0.08 (±<0.00) oo |
| # Visits to a given matrix cell | - | - | BF10 = 0.32 (±<0.00) o |
| # Visits to a given incorrect answer choice | - | - | BF10 = 0.83 (±<0.00) |
| # Fixations on matrix cells | - | - | BF10 = 0.08 (±<0.00) oo |
| Average fixation duration for a matrix cell | Shorter fixations | Longer fixations | BF10 > 1000 (±<0.00) *** |
| # Fixations on answer choices | - | - | BF10 = 1.91 (±<0.00) |
| Average fixation duration for an answer choice | Shorter fixations | Longer fixations | BF10 > 1000 (±<0.00) *** |
| Rate of matrix–answer transitions | - | - | BF10 < 0.16 (±<0.00) o |
| Variables | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. | 8. | 9. | 10. | 11. | 12. | 13. | 14. | 15. | 16. | 17. | 18. | 19. | 20. | 21. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.TowerofLondonscore | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.Corsiscore | 0.16 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3.WSCTPerseverativeerrors | −0.01 | −0.04 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4.BRIEF−ABRI | −0.18 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| 5.BRIEF−AMCI | −0.07 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.51 *** | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| 6.BRIEF−AGEC | −0.13 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.81 *** | 0.91 *** | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| 7.WMT−2totalscore | 0.50 *** | 0.31 ** | −0.28 * | −0.23 | −0.11 | −0.18 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| 8.Averagetimeineachtestitem | 0.19 | −0.27 * | −0.00 | −0.30 * | −0.09 | −0.21 | 0.31 * | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| 9.#Matrix−matrixtransitions | 0.16 | −0.28 * | 0.13 | −0.30 * | −0.17 | −0.26 * | 0.35 ** | 0.75 *** | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| 10.#Matrix−answertransitions | 0.03 | −0.37 ** | 0.21 | −0.20 | −0.12 | −0.17 | −0.10 | 0.62 *** | 0.58 *** | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 11.#Answer−answertransitions | −0.02 | −0.41 *** | 0.19 | −0.19 | −0.13 | −0.18 | −0.02 | 0.66 *** | 0.74 *** | 0.85 *** | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| 12.Latencytothefirstfixationonananswerchoice | 0.37 ** | 0.10 | −0.20 | −0.14 | −0.05 | −0.10 | 0.32 ** | 0.29 * | −0.01 | −0.27 * | −0.28 * | 1.00 | |||||||||
| 13.Ratiooftimespentonthematrixvsanswerchoices | 0.26 * | 0.11 | −0.15 | −0.26 * | −0.15 | −0.22 | 0.36 ** | 0.05 | 0.07 | −0.26 * | −0.38 ** | 0.53 *** | 1.00 | ||||||||
| 14.#Visitstoagivenmatrixcell | 0.15 | −0.30 * | 0.15 | −0.30 * | −0.17 | −0.26 * | 0.31 ** | 0.77 *** | 1.00 *** | 0.66 *** | 0.79 *** | −0.04 | 0.03 | 1.00 | |||||||
| 15.#Visitstoagivenincorrectanswerchoice | −0.03 | −0.43 *** | 0.21 | −0.19 | −0.12 | −0.17 | −0.11 | 0.67 *** | 0.67 *** | 0.94 *** | 0.97 *** | −0.27 * | −0.36 ** | 0.73 *** | 1.00 | ||||||
| 16.#Fixationsonmatrixcells | 0.17 | −0.30 * | 0.11 | −0.32 ** | −0.18 | −0.27 * | 0.34 ** | 0.84 *** | 0.98 *** | 0.63 *** | 0.74 *** | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.98 *** | 0.70 *** | 1.00 | |||||
| 17.Averagefixationdurationforamatrixcell | −0.25 * | −0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.07 | −0.21 | −0.19 | −0.16 | −0.11 | 0.00 | −0.12 | −0.18 | −0.16 | −0.04 | −0.22 | 1.00 | ||||
| 18.#Fixationsonanswerchoices | 0.01 | −0.40 *** | 0.17 | −0.20 | −0.11 | −0.17 | −0.02 | 0.72 *** | 0.74 *** | 0.92 *** | 0.98 *** | −0.24 * | −0.33 ** | 0.80 *** | 0.99 *** | 0.77 *** | −0.08 | 1.00 | |||
| 19.Averagefixationdurationforananswerchoice | −0.20 | −0.11 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.19 | −0.18 | −0.10 | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.17 | −0.26 * | −0.37 ** | −0.02 | 0.13 | −0.11 | 0.86 *** | 0.08 | 1.00 | ||
| 20.Percentoftrialsclassifiedascluster2scanpath | −0.03 | −0.16 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.14 | −0.02 | −0.07 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.24 * | −0.09 | −0.12 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.41 *** | 0.17 | 0.41 *** | 1.00 | |
| 21.Rateofmatrix−answertransitions | −0.21 | −0.23 | 0.28 * | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.06 | −0.50 *** | −0.26 * | −0.11 | 0.51 *** | 0.29 * | −0.69 *** | −0.46 *** | −0.04 | 0.39 *** | −0.15 | 0.04 | 0.31 ** | 0.16 | 0.08 | 1.00 |
| Measures | Corsi | TOL Score | TOL Time | WSCT Perseverative Errors | BRIEF-A BRI | BRIEF-A MCI | BRIEF-A GEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictor’s standardized coefficients 1 | |||||||
| Average time in each test item | - | - | −0.65 | - | −0.09 | - | - |
| Matrix–answer transitions | - | - | −2.00 | - | - | - | - |
| Answer-answer transitions | - | - | −3.66 | - | - | - | - |
| Latency to first fixation in answer choices | - | 0.14 | −0.22 | - | - | - | - |
| Ratio of time spent on matrix vs. answers | - | 0.02 | −0.16 | - | −0.10 | - | - |
| Visits to a given matrix cell | - | - | −0.96 | - | - | - | - |
| Visits in wrong answer choices | −0.27 | - | 3.38 | - | - | - | - |
| Total number of fixations on matrix cells | - | - | 1.83 | - | - | - | - |
| Average fixation duration for a matrix cell | - | −0.13 | 0.02 | - | −0.14 | - | - |
| Total number of fixations on answer choices | - | - | 2.13 | - | - | - | - |
| Average fixation duration for an answer choice | - | - | 0.30 | - | 0.03 | - | - |
| Percent of trials classified as cluster 2 scanpath | −0.03 | - | −0.40 | - | - | - | - |
| Rate of matrix–answer transitions | - | - | −0.18 | - | - | - | - |
| Performance estimates | |||||||
| Correlation coefficient | 0.48 | 0.59 | 0.14 | - | 0.09 | - | - |
| MAE | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.94 | - | 0.73 | - | - |
| RMSE | 0.68 | 0.92 | 1.11 | - | 0.95 | - | - |
| R2 | 0.18 | 0.16 | −2.13 | - | −0.03 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laurence, P.G.; Jana, T.A.; Bunge, S.A.; Macedo, E.C. Eye Gaze Patterns during Reasoning Provide Insights Regarding Individual Differences in Underlying Cognitive Abilities. J. Intell. 2023, 11, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11040075
Laurence PG, Jana TA, Bunge SA, Macedo EC. Eye Gaze Patterns during Reasoning Provide Insights Regarding Individual Differences in Underlying Cognitive Abilities. Journal of Intelligence. 2023; 11(4):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11040075
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaurence, Paulo Guirro, Tatiana Abrão Jana, Silvia A. Bunge, and Elizeu C. Macedo. 2023. "Eye Gaze Patterns during Reasoning Provide Insights Regarding Individual Differences in Underlying Cognitive Abilities" Journal of Intelligence 11, no. 4: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11040075
APA StyleLaurence, P. G., Jana, T. A., Bunge, S. A., & Macedo, E. C. (2023). Eye Gaze Patterns during Reasoning Provide Insights Regarding Individual Differences in Underlying Cognitive Abilities. Journal of Intelligence, 11(4), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11040075





