Abstract
In this paper, we propose a new approach to couple formation and dynamics that abridges findings from sexual strategies theory and attachment theory to develop a framework where the sexual and emotional aspects of mating are considered in their strategic interaction. Our approach presents several testable implications, some of which find interesting correspondences in the existing literature. Our main result is that, according to our approach, there are six typical dynamic interaction patterns that are more or less conducive to the formation of a stable couple, and that set out an interesting typology for the analysis of real (as well as fictional, as we will see in the second part of the paper) mating behaviors and dynamics.
1. Introduction
The process of reproductive mating is a clear example of a complex socio-biological phenomenon, of paramount evolutionary importance. Effective mating is indispensable to individuals’ reproductive success, and is therefore subject to huge selection pressures, which have generated all kinds of ingenious adaptations throughout the animal realm. Human mating is a particularly complex instance in that reproductive concerns are embedded in a wider sphere of social meaning, individual motivations, and lifetime goals. This makes the problem-solving component of mating behaviors for humans particularly challenging in that, unlike most animals, mating choices are not the solution to a single-dimensional optimization problem (maximizing reproductive fitness), but rather to a multi-dimensional one, where the various dimensions are often deeply intertwined and sometimes difficult to monitor, measure, and evaluate in terms of actual achievement. The fact that human mating is such a manifold driver of personal and collective life occurrences causes its implications to be particularly far-reaching and intricate across all aspects of human activity, social organization, and culture. Consequently, mating-related problem-solving is far from being confined to the individual sphere, but is a central focus of social problem-solving, in all human environments of all times.
Human societies differ wildly as to the level of self-determination of individuals in making mating choices, in the nature of the social environment in which mating search and finalization occurs, and in socially admissible solutions to couple formation, maintenance, and dissolution issues. Likewise, apart from reproductive success, successful vs. unsuccessful mating entails very different levels of social stigma across societies. However, in spite of this, mating behavior is also characterized by some surprisingly universal features, the most remarkable of which, as shown by Buss [1] in a study covering 37 different cultures, are certain stable differences between sexes in terms of mating strategies and preferences, although, as found by Schmitt [2] on an even larger sample of 48 countries, their extent tends to be mediated by the level of difficulty of the reproductive environment. That men and women have markedly different attitudes toward finding and retaining a mate, and that such attitudes must be somehow related to evolutionary pressures, is even part of conventional wisdom. In many societies, there is a tendency to depict men as constitutionally oriented toward multiple sexual relationships, and to legitimate a sort of dualism where spousal sexual life is basically driven by reproductive concerns and household development, and out-of-wedlock sex is mainly recreational and finalized to establishing a social image of masculinity. Likewise, according to complementary stereotypes, women are depicted as uniquely interested in long-term relationships finalized to family creation and maintenance, and to children care-giving. Such preconceptions are often claimed to be supported by a vague evolutionary rationale that transposes the “hunting men” vs. “gathering and agricultural women” stereotypical dyad into distinctive sperm dissemination vs. (good) sperm acquisition and retention strategies.
What certain types of commonsense regard as an essential component of human nature proves in fact to be, at closer inspection, a product of social norms. In appropriate social environments, women are psychologically prepared for short-term sexual relationships, and may even pursue them actively on the basis of a solid evolutionary rationale in terms of mate selection and resource acquisition [3]. However, remarkable differences are found at the dispositional level as to short-term sexual relationships: compared to men, women show less desire for short-term relationships, prefer less sexual diversity, and need more time to decide to have sex with a partner [4]. Mating strategies are therefore sex-specific and much less straightforward than a mechanical evolutionary rationale would suggest. As a consequence, rather than reasoning in terms of Males Compete/Females Choose mating models which implicitly presume static sex roles, it is more appropriate to reason in terms of Mutual Mate Choice models, where mating-directed interaction is the outcome of sophisticated strategic behavior shaped by subtle and highly specialized evolutionary pressures [5], with an important context-sensitive component [6].
In fact, for all animals, but in particular for humans, mating calls for the solution of two distinct although strongly complementary problems: selecting the right partner and generating an offspring, and rearing the offspring as optimally as possible. In the first situation, men behave as sperm distributors and women must appropriately select which genetic material should combine with theirs to generate the offspring. In the second, man and woman must cooperate so that their offspring receives all the care and the resources needed to secure the best survival and development chances. In the first situation, success strategies for both men and women need not entail stable mating, whereas in the second they do. In the first situation, men can diversify their sexual activity and compete to win women’s consensus to intercourse; in the second, a child-bearing woman must win the consensus of the fecundating male to form a stable couple and to divert attention from other potentially fertile women. It is the relationship between the two situations that creates a very complex strategic interaction with subtle tradeoffs, and in particular there is one between men’s genetic fitness and their willingness to cooperate with the woman in offspring rearing [7].
The formation of a stable couple which gives its offspring good prospects of survival and reproductive success therefore depends upon two different kinds of compatibility: a sexual and genetic one (that provides both mates with enough incentives to sexual intercourse), and an emotional and relational one (that allows the couple to self-regulate into a psychologically rewarding and mutually sustainable family life). Although there is today a vast literature that explores the details of sex differences in mating strategies, and in particular sexual strategy theory [8], and there are many different theoretical paradigms that study the dynamics of affective behavior in new as well as already established couples—from the cognitive-affective processing system model [9] to interdependence theory [10] and attachment theory [11,12,13], there is still a lack of a simple theoretical framework that allows to model the male/female couple interlock as the chain effect of sex-specific solutions to the two problems above.
In this paper, we propose a simple approach to modeling the male/female mating interaction, which has an explicitly dynamic character. Our approach systematizes several results from the literature and provides clear-cut implications. It is not an alternative to existing ones, but rather builds upon basic complementarities between some of them in shaping up a more comprehensive picture of sex roles in mating. In particular, our approach points out how the condition for long-term stability of heterosexual mating depends on a particular combination of male and female strategies that optimize the sexual/emotional compatibility tradeoff through their dynamic unfolding. In our perspective, the eventual short- vs. long-term orientation of mating is not a pre-determined feature that reflects the subjects’ mating dispositions, but rather an endogenous outcome of the interaction itself. A subject could start an interaction with short-term expectations and objectives and become tied-up into a long-term relationship, or, vice versa, could be initially orientated to a long-term perspective and losing incentive to go beyond a short-term one, depending on how the interaction actually evolves. The novelty of our approach lies in elucidating the different role, and the different relative functioning, of the sexual and emotional dimensions of the mating interaction in men and women. Each sex turns out to have a distinctive, biologically motivated way of balancing the sexual and emotional spheres. This asymmetry gives rise to peculiar strategic patterns, which lead to a range of possible final outcomes depending, in particular, on how each sex sends/gets exposed to a certain combination of sexual and relational stimuli, which are in part the effect of sophisticated socio-biological programming. We call our approach the “tie-up theory” because, as we shall see, the dynamic interaction between sexes will lead or not to a stable mating, depending on whether or not both players will be reciprocally “tied-up” to the other through a suitable interlock of behavioral signals that could be only partially conscious and intentional.
The structure of the remainder of the paper is the following. Section 2 briefly reviews some of the psychological literature on mating and couple dynamics, with a special emphasis on sexual strategy theory and attachment theory. Section 3 presents our model. Section 4 discusses its relationships with recent findings in the neurosciences literature. Section 5 provides a short recapitulation and sets the background for the analysis and results reported in the second part of the paper.
2. The Sexual and Emotional Components of Mating Strategies and Couple Dynamics
Problems of mating and couple dynamics are one of the most preferred areas of research in evolutionary psychology, and it could not be otherwise. As already observed in the introduction, mating is the engine of evolutionary selection. On the other hand, mating can be regarded in evolutionary terms from a multitude of different angles, which privilege one of the two poles of the within-couple interaction: the sexual and the emotional one. Of course, most psychological theories of mating do not limit themselves to the exclusive consideration of one of these and aim at providing a comprehensive explanation. However, as a matter of fact, their driving explanatory mechanisms tend to focus upon one dimension, and to consider the other as a consequence. In the approach of the present paper, it is instead the dynamic interaction of the two poles that becomes the driving explanatory force.
It is beyond the scope of this paper to offer a thorough review of the psychological literature on the issue, which would amount to a lengthy paper itself (if not a whole book). Here, we rather focus attention on some specific theoretical approaches that can be taken as particularly representative of the sexual vs. emotional analytical tradeoff in mating and couple dynamics. In particular, we consider sexual strategy theory (see [14] for an introduction and discussion in historical perspective) and adult attachment theory (see [15] for an updated formulation) in the wider context of person-by-situation approaches [16] as representative of the sexual vs. emotional poles, respectively. It is interesting to remark that both theories can be conveniently framed into an evolutionary psychology perspective. Moreover, if this is rather straightforward for sexual strategy theory, whose evolutionary rationale is entirely explicit, it also applies, although less obviously, to attachment theory [17].
2.1. Sexual Strategy Theory: Sex as Evolutionary Calculus
Sexual strategy theory (SST) provides a thorough account of human mating and couple formation, evolution, and dissolution within an evolutionary strategic interaction framework. In so doing, it does justice of naïve accounts that mechanically apply an evolutionary logic to sexual relationships, roles, and functions. In particular, SST postulates that both males and females have an interest in both short-term and long-term mating and that the emergence of a specific mating arrangement is the consequence of a certain constellation of incentives which influence the short-term vs. long-term mating tradeoff. This does not mean that both sexes have the same propensities for short-term and long-term mating, though. As already noted, women are relatively less prone than men to short-term relationships, sexual diversity, and impulsive sexual intercourse [4], and are more oriented to self-sacrifice [18]. More generally, mate preferences are characterized by a robust sexual dimorphism which allows for the safe identification of the sex of a subject on the sole basis of the mate preferences [19]. As far as long-term mating is concerned, sex differences that show a certain stability across cultures are women’s preferential valuation of social status and men’s preferential valuation of physical attractiveness [20]. Additionally, reasons for having sex tend to differ between men and women, with men prioritizing physical attractiveness of the partner and experience seeking, and women prioritizing emotional expression motivations [21].
Long-term mating is an evolutionary puzzle from many points of view, and sexual behaviors are no exception in this regard. Intuitively, its evolutionary rationale is linked to the large parental investment that is the other side of the coin of human cognitive advancement. This implies slow maturation and high demand of resources during the developmental phase to adulthood, as well as overlapping rearing cycles for different offspring, with a compounding effect on investment [22] and, with the transition toward socio-economically developed societies, an extension of the investment phase well into adult age [23]. In this respect, stable cooperation between parents to support joint investment in offspring is a solution to a typical public goods game, which enables sophisticated regulations such as female fecundity management [24]. Moreover, marital satisfaction reduces the costs associated to the spouse’s personality, susceptibility to infidelity, and mate guarding, thus favoring the self-enforcement of a stable, satisfactory mating [25]. On the other hand, this does not mean that short-term mating cannot have its evolutionary rationale and advantages, both for men and women. In particular, women may find short-term mating especially useful as a strategy for resource acquisition and for optimal screening of potential mates in a longer-term perspective [3], and this may induce in turn in long-term mating-oriented men the deployment of mate retention tactics and semen-displacement practices to hedge against the risk of successful insemination of the partner by male rivals, especially if the woman is judged sexually attractive [26]. In terms of mating-relevant cues, moreover, men differentiate between (women) body-focused short-term cues and face-focused long-term ones, whereas no such differentiation exists in women’s mating orientations [27].
Whereas for men short-term mating can be psychologically very rewarding [4], especially sexually arousing [28] and even linked under certain conditions to mentally healthy personality characteristics [29], the emotional response of women the morning after occasional sexual encounters is significantly less positive than men’s, even when the episode was never regarded by them as a possible prelude to a longer-term relationship, the main drive being regret for having been sexually exploited [30]. In fact, the existence of these asymmetries in orientation toward short-term mating between men and women reflect into differential forms of regret for sexual choices. Men typically regret about untapped sexual opportunities, whereas women about acceptance of casual sex [31]. Such asymmetry also creates a potential issue of sexual exploitation of women insofar as an ambiguity exists concerning the real purpose of sexual interaction. In fact, the sexual exploitability of women can be a sexually attractive character that may foster an adaptation in men to systematically pursue accessible women through the development of sophisticated exploitative strategies [32], whose actual incidence in men’s sexual strategies are the outcome of a complex interplay of personality traits and contextual conditions [33]. For instance, men who perceive themselves as successful in mating display a particular preference for short-term mating, and their preferences are driven by the potential partner’s physical attractiveness or earning potential, whereas it is the combination of these two characteristics that elicits the best response in women [34]. On the other hand, women who are more oriented to short-term mating are more effective than men in avoiding emotional intimacy [35], may make an intentional use of sexual exploitability cues to attract mates [36], as a risky signaling strategy which is not necessarily used by women with low confidence in their mating attractiveness potential [37], and which can be further incentivized by biological clock pressures [38]. In fact, attractive women tend to have more sexual activity and a less restricted orientation [39], while at the same time setting very demanding standards on all dimensions of male partners’ desirability [40], including emotionality. As a general rule, women put a stronger, and inter-culturally stable, mate selection focus upon personality traits than upon intelligence [41], and are more sensitive than men to the partner’s positive personality traits. More generally, both men and women tend to prefer mates with similar psychological characteristics to theirs [42]. In certain cultural contexts, risk-taking mate selection by women is stigmatized, and this causes a further asymmetry in male vs. female mating strategies [43].
The deployment of long-term- vs. short-term-oriented mate attraction tactics is easily readable at the social level by third parties and tends to be coherent with the subject’s real intentions [44]. However, there are also sex-specific misperceptions of sexual interest cues: Specifically, women tend to underestimate men’s sexual interest, whereas men tend to overestimate the sexual interest of women, all the more when the woman is physically attractive and when they are oriented to short-term mating and perceive themselves as attractive [45]. Conditional strategies where short-term and long-term mating goals are jointly pursued are also possible though, and even likely as a sophisticated open-loop strategy on the mate search space [46]. Such an open-ended strategic attitude is all the more necessary when taking into account the possibility of forms of strategic manipulation such as deception, which again assume sex-specific forms. Women focus on the male partner’s commitment, which may lead the latter to simulate it to have access to sexual intercourse, which in turn leads women to test men’s real willingness to commit, and leads men to develop even more sophisticated forms of simulation [47]. This clearly mirrors into how actual sexual intercourse tends to impact upon the long-term vs. short-term orientation of men vs. women. For very sexually active men, first-time intercourse causes a decrease in the partner’s attractiveness, whereas this does not happen to men with a low number of sexual partners. Women, on the contrary, tend to experience increased feelings of partner commitment after first-time sex [48]. Sexually active men, though, are the ones that are more likely to capture the attention of women, as the latter are more attracted if a man is shown as surrounded by other women, rather than by other men or alone; men, on the contrary, are less attracted to a woman if she is shown as surrounded by other men than by other women or alone [49]. Somewhat consequently, men are less willing to forgive sexual infidelity than emotional infidelity and are more likely to break down the couple in the former case, whereas it is the other way round for women [50]. Moreover, such a gender difference is only found in heterosexual subjects and is fairly independent of contextual conditions [51].
As far as opposite-sex friendships are concerned, although both sexes tend to regard this kind of relationship as valuable to acquire useful information on how to attract other-sex partners, there is a marked difference in terms of the other salient potential benefits. Men give more value to possible opportunities of sexual intercourse with the opposite-sex friend, whereas women are more interested in the opposite-sex friend protecting them [52]. Disappointment of such sex-specific interests increases the likelihood of termination of the friendship itself [53]. Subsequent studies have confirmed the strict relationship between opposite-sex friendships and mating goals in that men consistently give priority to the opposite-sex friend’s physical attractiveness and women to the opposite-sex friend’s affluence and physical prowess [54]. However, women also give value to physical attractiveness in opposite-sex friendship, and sexually unrestricted women place special emphasis on physical prowess [55].
Even from this short survey, it is therefore apparent how sex-related differences in both short-term and long-term mating strategies are the norm, and that such differences reflect into characteristic behavioral and motivational patterns that make strategic interaction between sexes complex and full of subtle nuances. Nevertheless, such patterns are remarkably structured, stable across cultures, and internally consistent—enough to reason in terms of a “science of human mating strategies” [5].
2.2. Attachment Theory: Managing Emotions
Whereas sexual strategy theory focuses upon the sexual dimension and its adaptive subtleties, attachment theory (AT) concentrates upon emotions and draws attention more upon the psychological history and traits of individuals than on sex-specific characteristics. This does not mean, of course, that sex differences do not matter for attachment theory; quite the contrary. However, the role of sex differences in the explanatory framework of AT is certainly less pronounced, comparatively, than in SST [56].
The evolutionary rationale of attachment is rooted in parent-child care-giving, and builds in particular upon the infantile drive to conquer the attention of rearing adults in order to secure the necessary resources to survive and develop effectively, and to protect themselves from external threats [57]. In its application to romantic relationships, couple formation and dynamics, AT postulates that the nature of the links that are created through this sort of interactions is the same as that regulating care-giving relationships, and reflects the same basic behavioral patterns: secure, anxious-ambivalent, and avoidant [58]. It is therefore heavily conditioned by individuals’ past history of parental relationships, especially as to their past experience of affective and physical security [59], while implying different patterns of information seeking, depending on the nature of the affective insecurity [60], and different interpretations of the acquired information [61]. AT also provides useful insight on the dynamic adjustment of partners during the early couple formation process, and in particular about how the consistency between ideal partner representations (whose more relevant aspects are trustworthiness, attractiveness, and resourcefulness—see [62]) and actually perceived ones is a crucial element of perceived relationship quality (whose more relevant aspects are intimacy and passion—see [62]). Such consistency is moreover conducive to the salience of shared ideals over time and lowers the chances of couple dissolution conditional to a continuing perception of relationship quality [63]. One of the most critical aspects of AT, though, is that of postulating that all romantic or couple relationships can be interpreted in terms of attachment [64], with a potential risk of failing to adequately differentiate the attachment dimension, the sexual one, and that of actual care-giving.
A very interesting aspect of AT is how it models the couple relationship as a reciprocal regulation process between the two partners [65], which is dynamically intertwined with the emotional climate among them [66], and whose stability is affected by the reciprocal level of trust [67], thus emphasizing the evolving, transformational nature of a romantic couple relationship as reflected into the dynamic regulatory adjustment attempts between actual partner perceptions and ideal standards of reference [68]. Fincham et al. [69] show, for example, how the level of marital satisfaction crucially controls the kind of attributional bias, which is more benign for the other compared to self in case of a happy relationship, but more negative for the other compared to self in case of a distressful one. On the other hand, the attachment perspective reveals how romantic relationships are directly affected by experiences at pivotal stages of individual developmental histories, as well as by the care-giving style of subjects’ same-sex parent [70]. This determines a virtuous vs. vicious circle of affective development moving from security of attachment in early childhood to development of social competence in infancy, to security of relationships in adolescence, and to quality of emotional experiences in early adulthood [71]. Moreover, a direct relationship between parental representations in terms of affective security, actual care-giving/receiving attitudes and reaction in couple dynamics [72], and increased capacity of recovery from conflict is established, with a positive post-conflict buffering (i.e., affective regulation) of less affectively secure partners [73], whose forms are strongly dependent on the type of affective insecurity [74]. The vicious circle of affective insecurity also causes individuals to become the “weak link” in couple dynamics, showing less commitment than the partner and thus subjecting the couple to breakup when the gap in commitment becomes too large [75]. One can therefore regard attachment security as a sort of key asset in developing a stable and satisfactory couple relationship [76], although romantic attachment representations have an impact on a couple relationship that is not mediated by general attachment representations, so that a complex interplay between the two factors emerges [77]. One can regard the construction of intimacy as a shared sense of connectedness [78], that is, the effect of a prolonged virtuous circle that removes affective insecurity through acts of self-disclosure and partner disclosure of emotions (more than facts or information), as mediated by partner responsiveness [79,80].
One of the areas where attachment-related couple dynamics shows a considerable predictive power is in stress management within the couple, where affectively insecure partners can spark a self-fulfilling rejection fear dynamics [81], fueled by biased perceptions of partners’ emotions, where the nature of the bias once again depends on the type of insecurity [82]. The regulation of emotions in stressful situations is particularly critical, and differences in regulatory focus [83], in levels of trust [84], and in attachment orientations imply different reactions and solution approaches at all levels—cognitive, emotional, and behavioral [85], with complex effects. Even emphatic accuracy, which in principle should be helpful to partners to manage conflict by helping them restore intimacy, can backfire when the other partner displays relation-threatening feelings [86]. On the other hand, perception of a partner’s emphatic effort is more beneficial than emphatic accuracy for relationship satisfaction [87]. As a rule, attachment anxious people perceive higher conflict and quicker escalation and become more stressed, but are more positively sensitive to support [88]. Highly attachment-avoidant people (but not moderately attachment-avoidant ones) are on the contrary negatively sensitive to partner support, but respond positively to uncommonly high levels of support [89]. Avoidant people are also sensitive to partners’ emotional buffering through softened communication, suggesting that skillful regulation has a central role in de-structuring conflict within the couple, even with defensive partners [90].
In this context, sex differences play a relatively minor role, although a closer consideration of their effects has been long advocated [91,92]. However, significant sex effects are also found in attachment-related couple dynamics. Holtzworth-Munroe and Jacobson [93] report, for instance, differences in attributional attitudes between men and women in conflictual relationships: Men increase their attributional thoughts in case of distress, whereas women do not—a critical feature given the role of attributions in negatively stabilizing distressed couple relationships. Overall et al. [94] show that women tend to perceive more than men the transformational potential of direct communication strategies with a positive valence in change-oriented interaction within intimate relationships. Cohen et al. [87] show that men tend to link their relationship satisfaction to the capacity to read the partner’s positive emotions, whereas women are more focused upon the partner’s negative emotions. Tran and Simpson [95] show that, provided that relationship commitment acts as a buffer against the effects of attachment insecurities, wives’ degree of relationship commitment is more impacting on the emotional outcome of both couple members than husbands’. On the other hand, women are the ones who are more likely to be sexually compliant, and more generally to sacrifice for the sake of the (committed) relationship [96]. More generally, the sexual dimension has received little attention in AT literature though. Schachner and Shaver [97] show how different forms of attachment insecurity are associated with different motives for sex: Anxious subjects focus on insecurity reduction and intimacy building, whereas avoidant subjects on recognition-seeking among peers. More generally, higher levels of attachment insecurity predict higher levels of sexual dissatisfaction in couples and of sexual dysfunction [98].
In concluding this brief and necessarily sketchy review, we notice how SST and AT, although both addressing issues of couple formation and maintenance, present radically different perspectives, which are potentially complementary to some extent, but that for the moment are characterized by little dialogue. In this paper, we develop an approach that makes this dialogue possible by integrating the sexually-centered perspective of SST and the emotionally-centered perspective of AT within a single, dynamic framework, where the subtle interplay of sexual and emotional components in mating can be appreciated in all of its complexity and structural inter-relatedness, more than it usually does within these already established perspectives.
3. A Tie-Up Theory of Mating
In this section, we present our approach that unifies sex-focused and emotion-focused streams of literature on mating and couple formation and maintenance within a common framework, whose dynamic structure consists of sexual-emotional feedback loops, thus abridging the particular theoretical perspectives of SST and AT. For reasons that will become clear shortly, we refer to our model as the Tie-Up Theory. We regard it as a parsimonious representation and explanation of certain aspects of the dynamic interaction of heterosexual partners in romantic relationships. In particular, in the spirit of [46], our scheme is designed to analyze open-loop mating strategies where long-term vs. short-term orientation of the relationship is the endogenous outcome of the interaction itself, rather than a dispositional precondition of subjects—where such an outcome is the result of a complex interplay of the sexual and emotional dimensions. Likewise, our approach develops within a biosocial perspective that fully acknowledges the role of biological factors in determining male-female differences regarding the sexual and emotional aspects of mating, but also takes into account the regulatory role of social factors, in the spirit of [99].
Our approach is consistent with much of the literature that has been presented in Section 2. However, to ease readability and to keep the argument compact, in presenting it we will not emphasize all the correspondences that can be found with the literature review, as this would make the paper difficult to read and would subtract clarity and conciseness to the explanation of new concepts. As mere examples, the asymmetry in male vs. female roles and psychological structures in our model can be easily traced back to the concepts and findings of SST, and we will not generally restate them during our presentation. The same applies to more specific aspects such as, say, courtship as a seduction strategy, sexual exploitation as the result of affective insecurity, deferment of sexual intercourse to incite attachment, and so on. We will limit ourselves to spare references, when they are of special importance, and will leave to the reader the task of re-formulating single aspects and implications of our model in the context of the literature review of Section 2. As can be expected, not all aspects or implications of our approach find a specific corroboration in the existing literature, and further experimental and empirical work will be needed to this purpose, as it is common when a new theoretical approach is proposed.
3.1. Basic Concepts
Let us consider two subjects, Male (M) and Female (F), both of which characterized by two complementary psychological structures, which we call the Active Area (AA) and the Receptive Area (RA), respectively. We therefore speak of Male Active Area (M-AA) and Male Receptive Area (M-RA), and likewise of Female Active Area (F-AA) and Female Receptive Area (F-RA)—see Figure 1, where red codes AAs, and blue codes RAs. AAs and RAs are the components of a dynamical system that determines whether or not M and F are bonded by some type of more or less stable, prolonged (sexual and/or emotional) relationship. If the nature of this bond gets stabilized from M’s point of view, from F’s point of view or from the point of view of both, we say that a Tie-Up (TU) has occurred. If the bond only concerns F, we speak of a Female Tie-Up (F-TU); if it only concerns M, we speak of a Male Tie-Up (M-TU). If a bond has been created for both, we speak of a Double Tie-Up (D-TU)—see Figure 2.
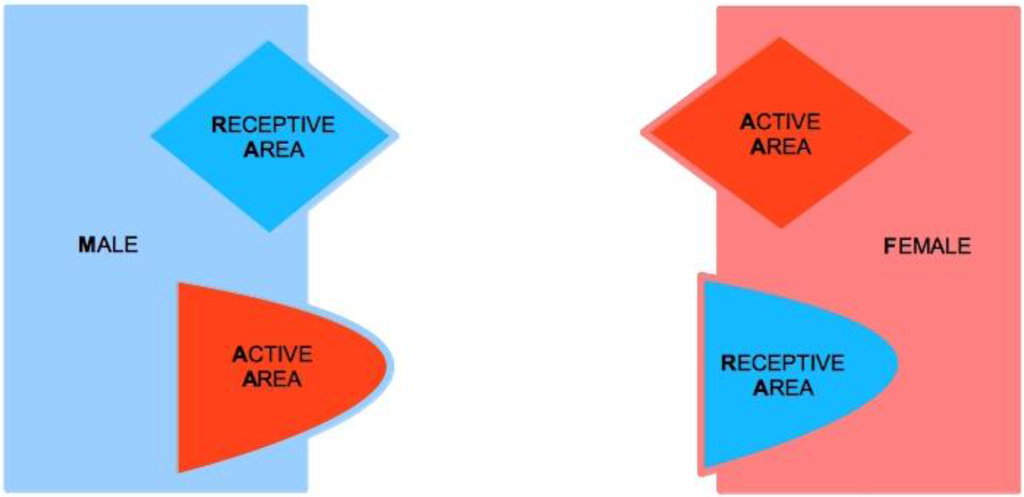
Figure 1.
Male Receptive Area (M-RA), Male Active Area (M-AA), Female Active Area (F-AA), and Female Receptive Area (F-RA).
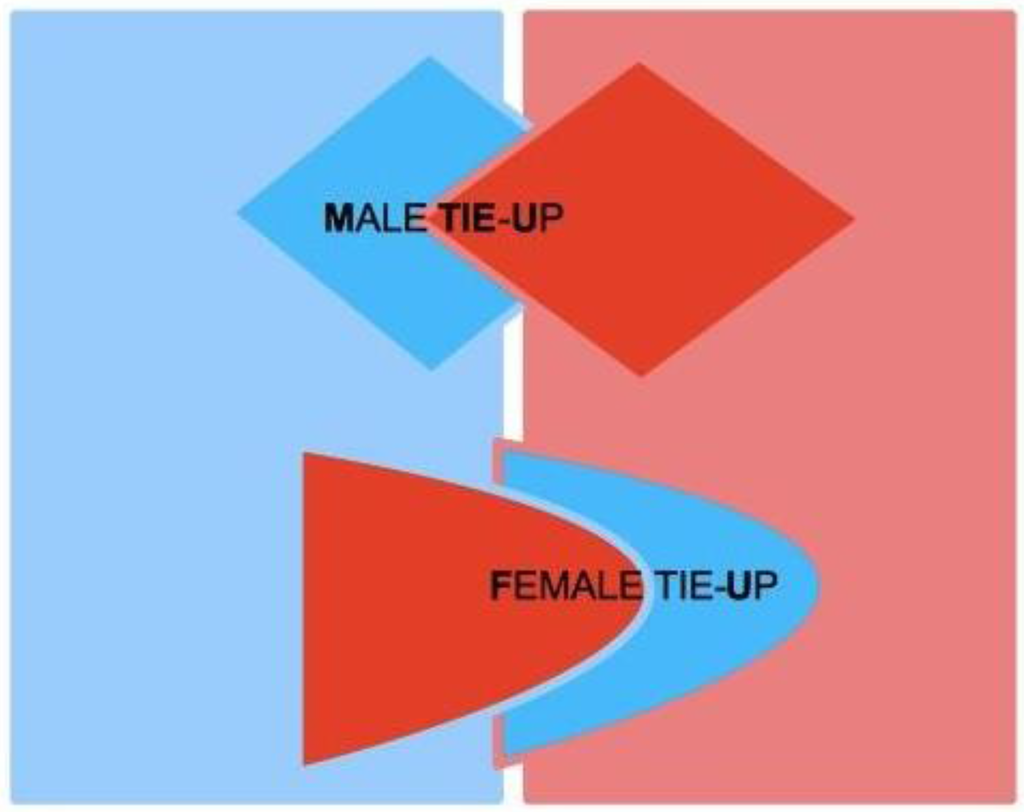
Figure 2.
Double Tie-Up.
AAs are psychological structures that build up attraction for and to the opposite sex. They are defined as active in that they elicit behaviors that are aimed at seducing partners, and that, in particular, are aimed at “tying up” potential mates. AAs are regulated by a psychological reward mechanism, which is connected to their mere usage. The optimal reward is reached when the partner’s TU is attained, for either M or F. In particular, M’s reward is optimal when the action of M-AA causes F to tie-up, i.e., F-TU is created, and vice versa for F-AA when M is caused to be tied-up and M-TU is created.
A key feature of our approach lies in the asymmetric characterization of the nature of AAs and RAs in the two sexes. For M, AA corresponds to M’s sexual dimension (see Figure 3). M can be regarded as sexually active in that his active strategy toward the other sex is deployed on a sexual, i.e., physical level, and is accompanied by physical correlates of sexual arousal [100] and primarily aimed at genital contact [101]. A component of M-AA (sexual) reward is pride for sexual performance: M’s ability in the usage of his AA results in a sexual seduction of F, which at its best outcome causes F to be tied-up (F-TU). M’s reward is increasing in the level of F’s outward display of sexual availability response, as well as in the effective willingness to engage in a sexual intercourse.
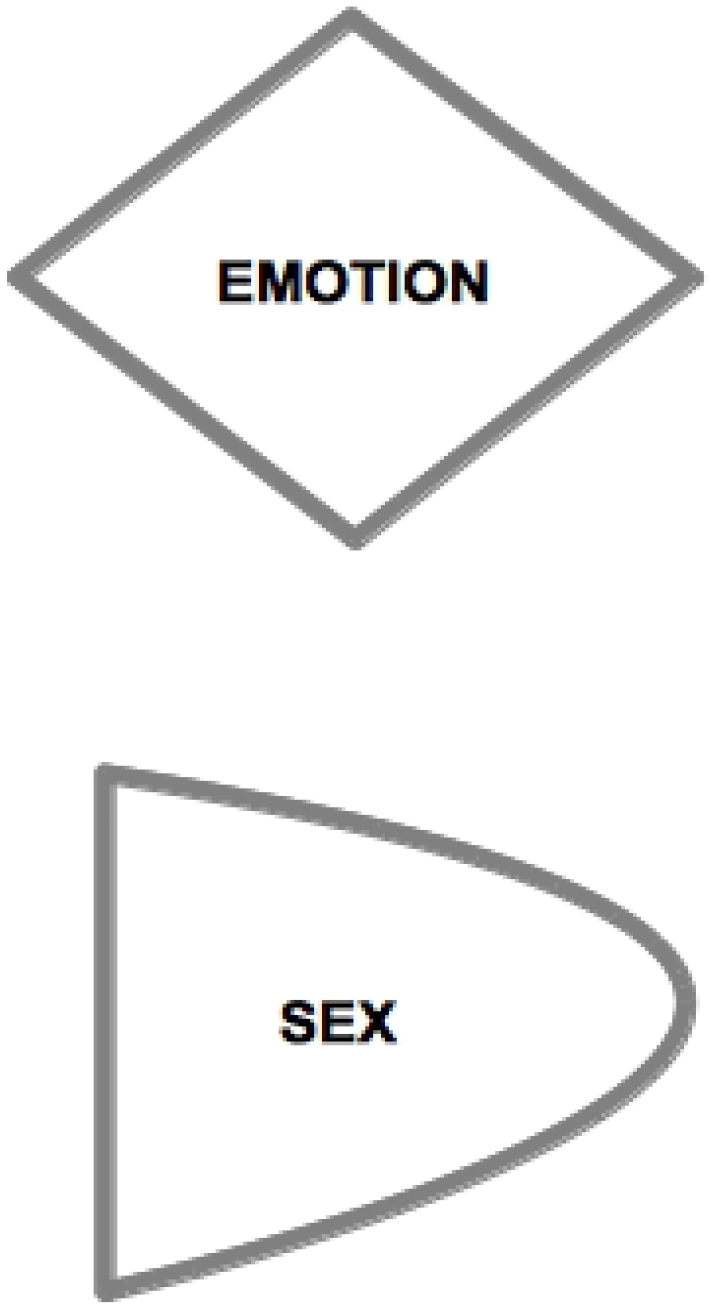
Figure 3.
Emotional vs. sexual components.
For F, AA corresponds to F’s emotional dimension. F elaborates her attraction toward the opposite sex from a mental-emotional viewpoint. F’s active seductive approach has an emotional nature, and reward is accompanied by physical correlates of emotional activation (e.g., [102]). In female sexual function, the emotional and sexual dimensions are deeply connected [103], and female implicit sexual desire increases once being romantically stimulated, whereas the same does not occur to men [104]. The reason of such a difference is that women associate with the romantic situation, and in particular to the first physical contacts aimed at the creation of a possible intimacy, a sexual connotation, while men on the contrary in such a situation are led to momentarily inhibit their sexual response. In both cases, as we will see, these reactions are finalized to each one carrying out the respective compatibility test for the sake of the future formation of the couple. For F, causing M to tie-up (M-TU) as a consequence of the action of F-AA means involving M in her mental process of emotional bonding construal. When M gets bonded in turn, the reward of F reaches its peak, as this signals that F-AA has been able to cause the Tie-Up of M. It is significant to note that Ms’ preference for sexual over-romantic stimuli (and the other way round for Fs) does not depend on pleasantness of the association—in fact, in terms of pleasantness, both Ms and Fs associate romantic stimuli more strongly with the pleasant condition than sexual ones, which further strengthens the idea of a biological programming of the content of each sex’s AAs [105]. Additionally, from the cognitive point of view, the structure of conceptual associations about sex-related matters is distinctively more focused on the emotional dimension for women and on the physical one for men [106], and the corresponding sex-related differences in word frequency and vocabulary use are clearly reflected in communication styles [107]. However, concluding from the previous discussion that Fs are emotionally oriented whereas Ms are sexually oriented would be misleading. For both men and women, the sexual and emotional dimensions are equally central for mating purposes. What changes substantially is their relative role and functioning. To understand this better, we now turn to a closer examination of RAs.
RAs are passive psychological structures where the Tie-Up happens or not, that is, where F gets sexually seduced and/or M gets emotionally involved. RAs test effective compatibility with mates. For this reason, it is not granted that RAs are activated, even when the opposite-sex potential partner actively engages the subject to this purpose. AAs command more personal (and social) awareness than RAs, so that RAs are effectively perceived only when they are successfully activated by the opposite-sex partner. The reason is that AAs function as safety systems in that they guarantee the perpetuation of the species, even if they do not manage to activate RAs, and become thus potentially conducive to a lasting mating. RAs, on the contrary, are mating stabilizers, which come into function when TU-oriented stimulation is effective, and their activation peaks when the TU takes place.
For M, RA has an emotional nature. M gets tied-up by F on a mental-emotional level, and is seduced in his imagination and feelings. M gets tied-up to F only if she is able to involve him emotionally. Otherwise, once the sexual intercourse has taken place and an optimal reward has been reached, M walks away from the relationship. M-RA has the task of checking the psychological compatibility with the female partner, as well as the right level of complementarity in pursuing joint couple goals such as child rearing, with the consequent evolutionary benefits.
For F, RA has a sexual nature, but its physical correlate is not limited to the genital area [108]. A wide range of cues, including subliminal ones [109], can generate a significant activation of RA [110]. RA has a passive function; thus, the fact that F’s sexuality resides in F-RA tends to (erroneously) characterize F as ‘sexually passive’ when compared to M’s AA-driven sexual initiative. F-TU is therefore the outcome of physical contact with potential sexual implications. If F’s physical interaction with M is rewarding, the conditions for F-TU will be created; otherwise, F will divert attention toward other potential partners. F-RA is devoted to checking the biological compatibility with the M potential partner. In evolutionary terms, the role of F-RA is the screening of the appropriateness of M’s genetic endowment; thus, as one could expect, for Fs the spectrum of motivational factors that determine sexual satisfaction is wider and more heterogeneous than for men, as the sexual dimension plays a more relevant role in mate selection than for men [111]. It would be interesting to test whether the opposite holds for emotional satisfaction, i.e., satisfaction related to the dimension that is more relevant for M’s mate selection. To our knowledge, no results in this regard are available as yet, but this is an interesting subject for future inquiry. To sum up, when RA is stimulated (sexually for F, emotionally for M), a potential interest is sparked for the opposite-sex subject who has performed the activation. Humans have evolved special abilities to recognize signs of romantic interest from others, and such abilities extend cross-culturally [112], although other research provides evidence of higher accuracy in detecting a lack of romantic interest than its actual presence [113]. Even minimal stimuli might function in principle as an activation. For instance, F could be stimulated by a visual excitement without any close contact, an olfactory stimulus such as pheromone signals, or a casual touch entailing an energetic perception under the form of body heat, or vocal features such as modulation, tone, frequency, rhythm, vigor, and so on. Such signals, before they intensify or cumulate, anticipate and prepare F-RA to the biological compatibility test. For M, instead, a typical effective stimulation of M-RA might take the form of (non-sexual) curiosity toward an opposite-sex subject, but equally effective might be strong emotional states such as disappointment, scorn, or even hatred, as far as they manage to convey attention toward F, whether positive or negative in that all that is needed is the emotional drive that sparks the psychological test to be carried out by M. The more M considers F in non-sexual terms, the more concrete the possibility of M-TU becomes. M-RA might be stimulated even by a gesture, a posture, a way of walking or of addressing others by an opposite-sex subject, or by emotional cues such as a smile, a laughter, or an uncommon or intriguing situation. In other cases, similarities with a previous situation, or associations with another opposite-sex subject with which an emotional bond was once established, might also work. What drives attention is affinity, in addition to perception of commonality of interests and passions. For some male personalities, M-RA might also be activated by a challenge that creates a clash of opposite wills, or by a mystery that arouses curiosity. M’s psychological state and emotional context have a role. A refusal of attention by F may induce a psychological interest in M, with a consequent activation of M-RA as the effect of frustration. Generally, for both M and F, testing mode is favored by the absence or deterioration of TU.
It is important to point out here the complex interplay between two different, interacting oppositions in the functioning of AAs and RAs: active/passive vs. conscious/unconscious. In particular, identifying active character with consciousness and passive character with unconsciousness would not be accurate. RAs, given their passive character, are often operating below the level of consciousness, but they can become the object of conscious attention, as, for example, when someone realizes s/he has become tied-up to another subject. AAs, on the contrary, given their active character are often functioning consciously, but they could also operate unconsciously in certain conditions, as, for example, when one unintentionally sends signals (e.g., staring at someone) that others can mistakenly interpret as evidence of romantic interest. Therefore, all possible combinations of conscious/unconscious and active/passive modes of functioning of AAs and RAs are possible. We will return on this point later on, when the full dynamic unfolding of the interaction between AAs and RAs will be presented.
3.2. M-TU vs. F-TU
TU is a psychological state where an emotional bond toward an opposite-sex individual is created with a potential purpose of long-term mating. If the bond is solid enough, the subject is tied-up, i.e., is constrained into the relationship until some major force or perturbing event intervenes. In F, this bond is mediated by the physical response of F-RA; in M, by the emotional response of M-RA. TU always contemplates a passive and an active element—one player who gets tied-up, and another player that elicits the Tie-Up. TU takes place when the subject’s AA successfully stimulates the opposite-sex’s partner RA. If this does not happen, TU fails.
Stable mating occurs when each partner gets tied-up to the other, and a D-TU occurs (Figure 2 above). Stable mating thus calls for two distinct TUs: one where F is active and M passive, and one where M is active and F passive. If only one TU occurs, then one of the two partners is not tied-up, and as a consequence the mating is not stable and poses a dissolution threat to the couple, if previously formed (Figure 4). When, instead, in a previously stable mating, one of the TUs deteriorates for some reason, the couple stability is threatened, and once again there is a risk of dissolution.
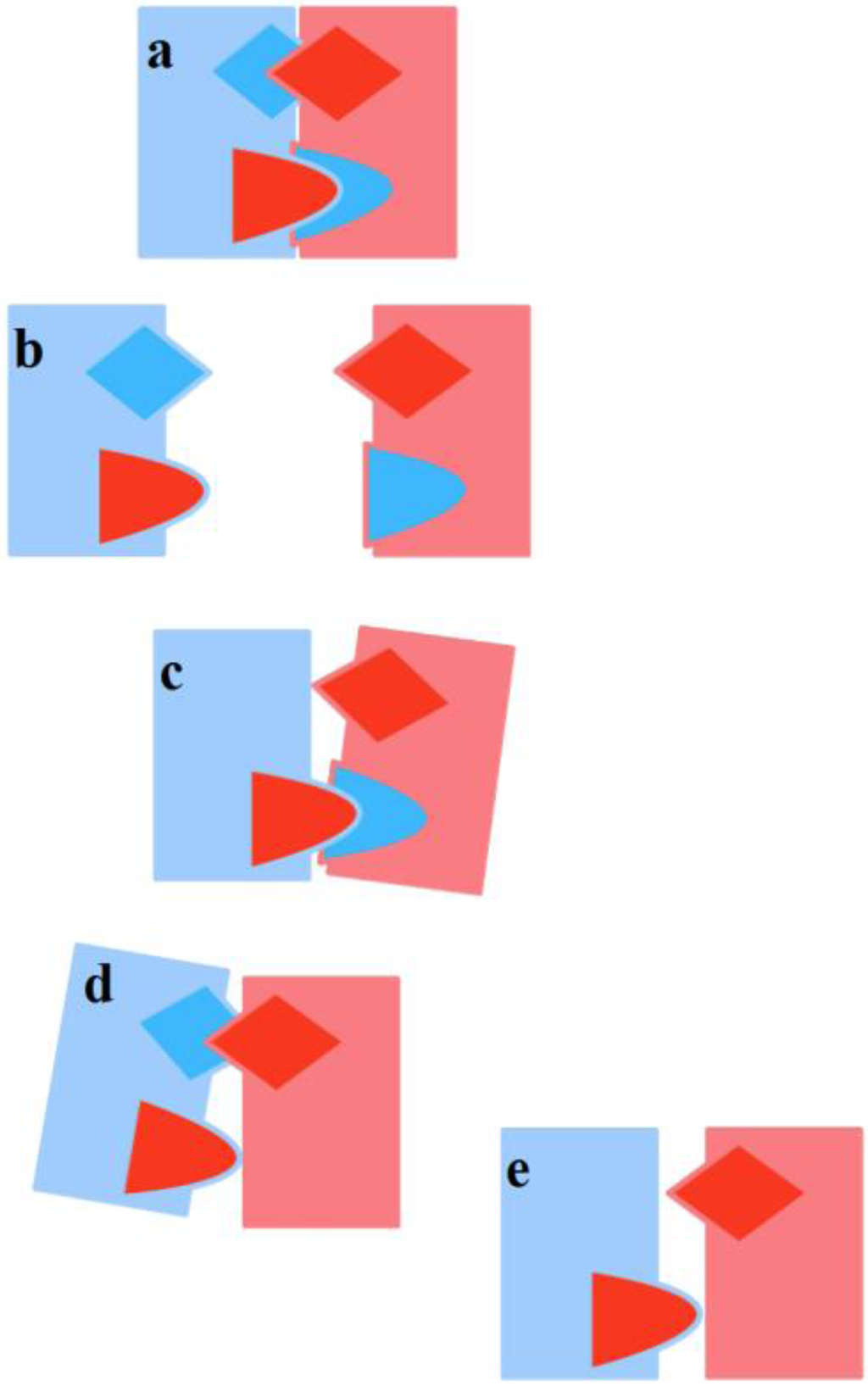
Figure 4.
Possible cases. (a): Formation of a stable couple with Double Tie-Up (D-TU); (b): Lack of TU and non-existence of the couple; (c): F-TU only; (d): M-TU only; (e): Couple without TUs. RAs not shown are not activated.
When RA is successfully stimulated by the other-sex partner’s action, as a result of the consequent positive response, there is a feedback toward the acting partner’s AA itself. Such positive response leads the active subject to intensify his/her action, and the process starts to self-catalyze. It must be pointed out that the positive signal arrives from RA in an indirect way, RA being a passive component of the subject who needs the active one, AA, to communicate. An effectively stimulated RA, thus, will send a positive signal to the same subject’s AA, which will be activated to respond to the opposite-sex partner. When RA’s response signal is elaborated by the AA of the same subject (who was originally passive), the subject now becomes active, and starts in turn to stimulate the partner who receives the new signal, this time passively, through his/her own RA. In this way, a flow of transmission/reception of signals is created that goes through AAs and RAs of both subjects, being progressively amplified at every passage, thus favoring the occurrence of the compatibility tests and the formation of the TUs and, due to their occurrence, feeding and strengthening them.
To sum up, the process requires the AA to send signals to the RA of the opposite-sex partner and that the RA directly communicates only with the same subject’s AA. In this way, each subject is passive in his/her own RA and active in his/her own AA, and the alternation between the two phases determines a communication flow, anti-clockwise and cyclical, that self-catalyzes (see Figure 5). It may happen that, despite the correct and repeated occurrence of the transmission/reception flow, a one-sided TU by one subject only is determined and persists. Moreover, if there are sufficient incentives for each one to keep the relationship alive anyway, the result may be an opposite-sex friendship. If a F-TU occurs, this may lead to a (short-term) sexual friendship, without the formation of a proper couple in that M is not tied-up (see Figure 4c above). A sexual friendship may be frustrating for F-AA. On the contrary, an emotional friendship where only M-TU occurs and F is not tied-up may frustrate M-AA (see Figure 4d above).
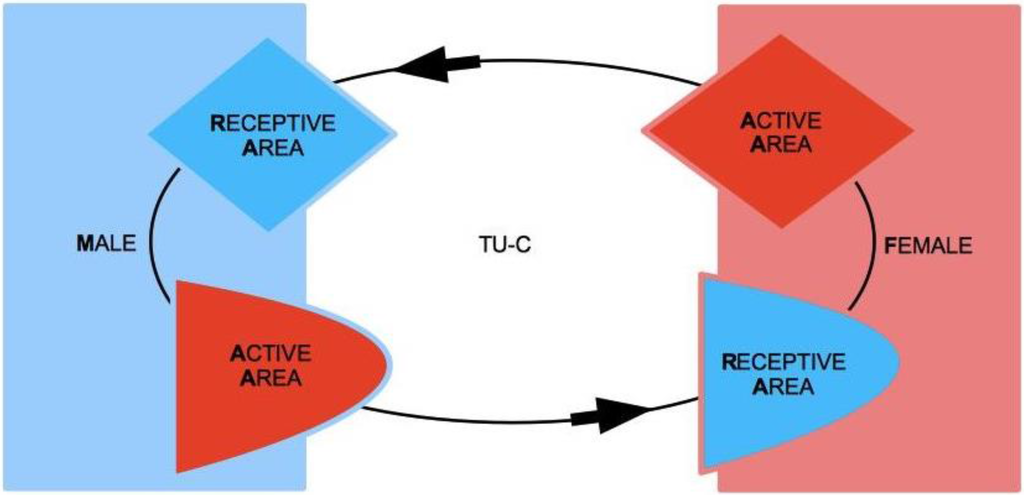
Figure 5.
The sequence of activation of the four Areas.
F-TU is sexual: In this type of TU, F gets bonded to M, through her being tied-up at F-RA, which has a sexual nature, as a consequence of the active stimulation by M. F-TU can only happen when F-RA has successfully tested M’s biological compatibility. As the whole female body reacts sensitively to the stimulation of her RA, F starts to test M’s compatibility from the very first physical and chemical contacts (smell, taste through kissing, bodily energy through touch). In this way, F can carry out the screening without having to undergo an excessive number of sexual intercourses (in the limit, even none) with different potential mates, minimizing the risk of inefficient selection of genetic endowment. For instance, in some societies where women are sexually secluded before marriage, dancing may represent a relatively effective way to carry out the biological compatibility test in the absence of sexual intercourse [114].
Significantly, women consistently manifest more negative feelings for sex than men both at the implicit and explicit level [115]; moreover, although women display a relatively more liberal attitude toward sexual invitations in low-risk social environments then in high-risk ones, a significantly higher propensity of men to casual sex still remains in the most favorable conditions [116]. Men also display a more positive affective response to sexual rejection than women [117]. F can be mentally and emotionally attracted to M, but physical attraction is not consequential if the biological compatibility test is not successfully passed. Thus, M can emotionally seduce F without causing F-TU to occur. This is the case where F is only interested in a friendship relationship with M, as she feels rewarded in her F-AA by the signal coming from M, without, however, having an impact upon F-RA.
M-TU is emotional: In this type of TU, M is the passive player who gets tied-up in M-RA by the seductive action of F. This form of mental seduction compounds with the physical one, although the two components may decouple to ensure that M-AA keeps on functioning: M can be sexually attracted to F, but the emotional compatibility with F cannot be taken for granted. If the two types of seduction are decoupled, TU does not take place for M: M-AA is strongly stimulated, but M-RA is not. Sperm is distributed anyway if sexual intercourse takes place, thus guaranteeing a “mechanical” perpetuation of the species, but it is not granted that a stable couple that would secure safer child rearing will form. F is therefore able to seduce both emotionally and sexually, but it is only the emotional seduction that is able to induce M-TU in M-RA. M, on the other hand, can also be stimulated in M-AA as a consequence of a merely emotional stimulation in that the emotional M-TU affects M-AA anyway. This explains the difficulties in-built in an opposite-sex friendship: M gets emotionally tied-up; thus, as a consequence, it is possible that his sexual M-AA gets stimulated in turn. Only if M is already stably tied-up in another couple relationship, or if F has a very low short-term mate value for M, does it become possible for M to take part in the friendship with a limited level of frustration of M-AA.
3.3. The Tie-Up Cycle
The interplay between M and F’s AAs and RAs determines what we call the Tie-Up Cycle (TU-C). To understand how it takes place, it is important to distinguish two different kinds of rewards to M and F actions: direct (active) reward and indirect (passive) reward. Reward is what sparks TU-C and keeps it working. Direct reward is originated in AA and depends on its functioning. The more used, well operating, and successful AA is in eliciting (and feeding) the other-sex partner’s TU, the larger the direct reward. Indirect reward is again perceived in AA but is the consequence of a stimulation of RA and thus comes from RA. Indirect reward thus induces a further stimulation of AA and, in particular, desire for a more direct reward. To appreciate the different nature of direct vs. indirect rewards, one can think of them as rewards linked to carrying out an action (e.g., the dog’s satisfaction from grabbing the thrown stick and bringing it back) vs. rewards linked to passively enjoying a benefit (e.g., the dog’s satisfaction from being offered biscuits and eating them), respectively. Skillful modulation of active vs. passive responses to mating-related situations is crucial in the dynamic unfolding of TU-C, and the two different kinds of rewards may be thought of as evolved, complementary psychological incentives that regulate mating interaction. One can thus regard our approach as a first hint of a behavioral theory to make sense of the neurophysiology of mating-related rewards, and which of course calls for substantial further development [118]. Some preliminary remarks in this direction may be found in Section 4 below. It is also useful to remark that the specific content of both direct and indirect rewards is subject to cultural variation: What can be perceived as a signal of emotional attention or of sexual interest that is conducive to a certain kind of reward clearly varies in different socio-cultural settings. However, the functioning of rewards in the context of the mating interaction is largely independent of the form or content of the signal that caused the reward.
The elements from the previous discussion can now be summarized in the TU-C diagram shown in Figure 6, which presents the M/F-AA/RA interaction in terms of a specific cycle with a typical structure. In the cycle, a subject’s AA is always linked to the opposite-sex partner’s RA, whereas a subject’s RA is always linked to the same subject’s AA—two rules which are implicit in the very definitions of AA and RA. This amounts to requiring that the cycle proceeds anti-clockwise only. The cycle can moreover be started in principle at any point (although with different consequences, as we will discuss below), and, in order to successfully build up, it must not be interrupted. A full cycle is a precondition for a D-TU, and more cycles correspond to the progressive consolidation of the couple relationship. How many cycles are actually needed for a stable D-TU to happen depends on a variety of factors. If RA is activated, and the potential mate shows an interest as well, one or more test TU-Cs can be tried out. For each full iteration, the possibility of a TU for at least one of the subjects substantially increases. Activations of M/F-AA/RA may occur at different levels of intensity, response, and reward, and interactions themselves may occur at different speeds that depend on the actual frequency of stimulation. In particularly intense situations, several TU-Cs may take place very quickly, and repeated stimulation causes and strengthens TUs as a consequence of the pattern of activation of RAs. However, a slow movement along a TU-C may present advantages in terms of reinforcement of the desire for reward. Both patterns probably have an optimal interval of contextual conditions in which they work best. The varying intensities of interaction and contextual situations in which the cycle happens may cause biological/psychological testing to happen already at the very first iteration, or in the repeated, quick kick-off iterations of TU-C and, if successful, may bring about TU. In other cases, several TU-C iterations might be called for just to carry out the test, which always precedes TU, if there are resistance factors or obstacles at work, both by the subjects themselves and in the external environment.
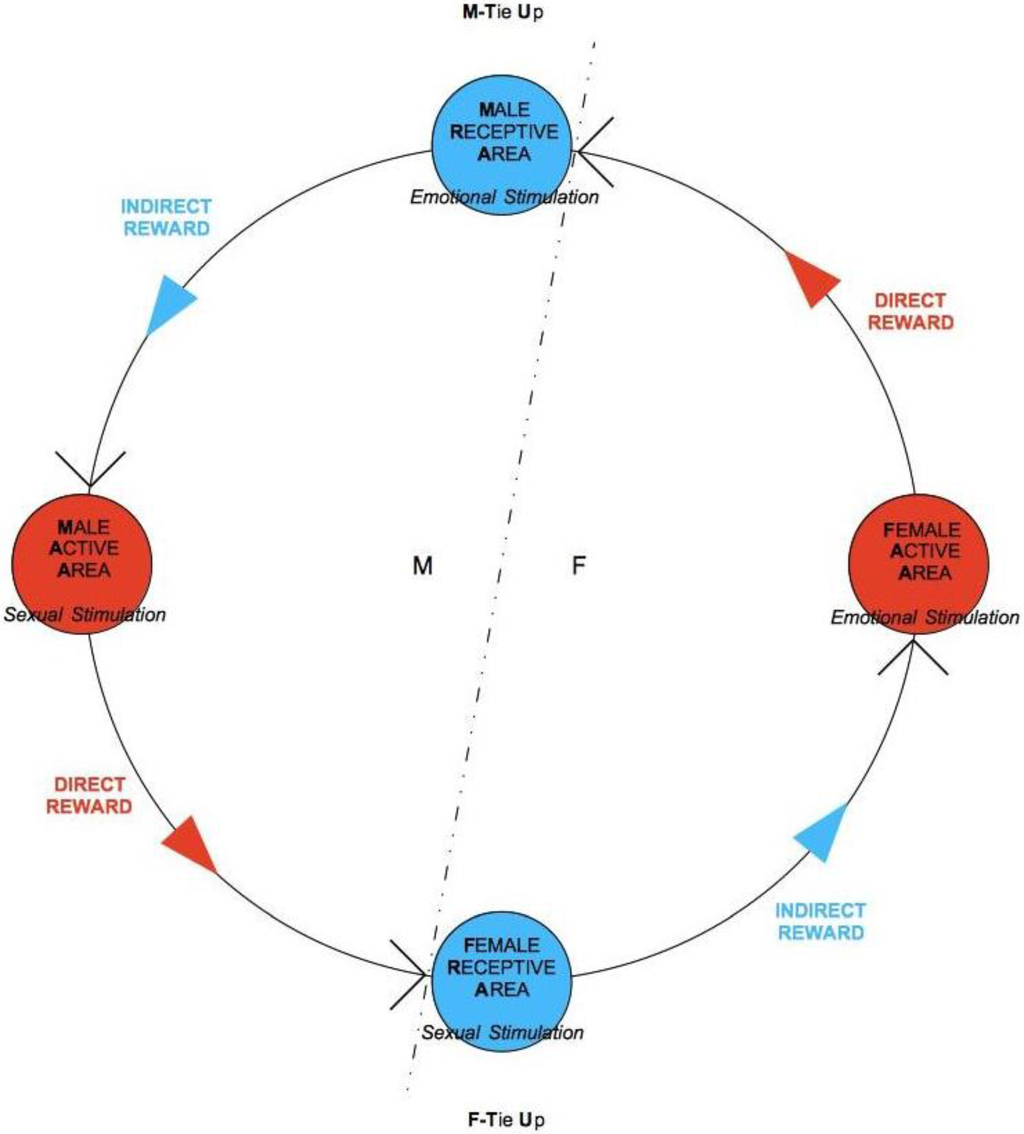
Figure 6.
The Tie-Up Cycle (TU-C) diagram.
The dynamic structure of TU-C allows us to illustrate the basic difference between the active/passive vs. conscious/unconscious functioning of AAs and RAs. M could, for example, get tied-up to a F with apparent low mate value insofar as the emotional compatibility test has been unconsciously carried out by M and successfully passed by F. M could therefore inexplicably feel incapable of drawing attention away from F despite his perception of F’s low mate value. At this point, RA is functioning in its unconscious mode. Once M realizes he has become tied-up, however, the functioning of RA moves to the conscious level; however, because of RA’s passive character, there is nothing that M can do to break the Tie-Up insofar as his RA continues to be effectively stimulated by F. Conversely, F could, for example, unconsciously stimulate M’s RA with some unintentional attitude (e.g., a certain way of speaking or paying attention). However, once she realizes that M has been stimulated and reacts accordingly, she could easily refrain from going on with the stimulation if she is not interested in tying-up M. F’s stimulation of M came from F-AA; thus, the passage from the unconscious to the conscious level is all it takes to put the stimulus under control and to block it if needed. A conscious functioning of one’s AA thus corresponds to a situation of full control in the context of the mating interaction. An unconscious functioning of the AA corresponds to a redeemable failure of control. A conscious functioning of one’s RA corresponds to an awareness of a lack of control. Finally, an unconscious functioning of one’s RA corresponds to exposure to external control. If one-sided, it leaves the subject susceptible to possible manipulation.
One can read couple dynamics as a sequence of iterations of the cycle so that interaction among partners may further consolidate D-TU or threaten its stability. If D-TU fails to be achieved or is broken at some point, the cycle dies down. Moreover, there is no consequentiality between TUs: They occur separately and therefore need not happen concurrently, but may even happen at long distances in time from one another. Therefore, the fact that a TU occurs never guarantees that D-TU will eventually take place as well. If D-TU does not occur, TU-C does not unfold effectively. However, there is a possibility that one of the two subjects simulates his/her own TU, pretending s/he is tied-up. In this case, TU-C kicks off but does not really work: Maintaining the simulation calls for continued effort, which subtracts energy from TU-C. The issue with the subject simulating TU is that his/her RA is not really activated; thus, s/he goes through TU-C by benefit only of direct reward in that RA does not yield any indirect reward. Although direct reward is attractive for the subjects in that it confirms their sex role, the true engine of TU-C, the one that guarantees its self-catalytic regeneration, is the indirect reward that further feeds the subjects’ AAs.
One interesting vantage point to understand the interaction dynamics between M and F is the moment in which sexual intercourse takes place so as to evaluate possible evolution scenarios on the basis of TU-C. Let us choose this reference point to fix ideas and to better illustrate the structure and properties of TU-C. The direction of movement along TU-C is what determines the behaviors of M and F after the sexual intercourse. If sex has been rewarding, F-RA gets stimulated and F-TU occurs (bottom circle in the cycle in Figure 6). The sexual activation that results stimulates F-AA by means of an indirect (passive) reward, because F-TU has occurred so that sexual stimulation also becomes emotional stimulation, and F-AA is prompted to generate further direct (active) reward to the benefit of M, who has been the cause of F’s indirect reward. If, however, M-TU has not occurred (top circle in the cycle), F-AA gets frustrated, TU-C is interrupted, and the couple is threatened to dissolve.
The anti-clockwise direction of movement of TU-C tells us that, for M, sexual stimulation is by no means conducive to emotional stimulation as for F in that the latter is antecedent to the former in the cycle’s flow of movement. Therefore, if M gets sexually stimulated, emotional M-TU is far from granted, while at the same time not precluding the possibility of sexual intercourse for M. In the case of M, it is emotional stimulation that transforms into sexual stimulation in the TU-C, and not vice versa. For F, likewise, emotional stimulation does not spontaneously evolve into sexual stimulation, as it is still necessary that the cycle’s flow of movement passes through M and his sexual initiative. It is, in other words, necessary that the emotionally stimulated F has the opportunity to test M’s biological compatibility, that is, the quality of the genetic endowment that would be transmitted with impregnation; thus, sexual stimulation exclusively depends upon this test, which takes place in F-RA, through a physical-chemical-energetic sampling of M which does not primarily concern M’s genitals. The kind of test taking place in M-RA instead is related to psychological (and not biological) compatibility; thus, such a test does not influence the possibility of sexual intercourse that can occur for M without the need of emotional involvement.
If M, along TU-C, moves from M-AA, he will proceed toward an increase of his direct reward, of a sexual nature, totally ignoring indirect, emotional reward. If he will manage to elicit F-TU, his level of reward will reach the optimal level, and will inevitably plunge after the intercourse as a consequence of the attainment of the goal, not evolving into any other kind of reward, as the indirect one is behind his shoulders along TU-C, and not in front of him. This is why M, having depleted any form of further reward, will break up TU-C, leaving F to realize, along with a frustration of her F-AA, that no M-TU has occurred. If, instead, M takes the move from his M-RA, that is, when M-TU has occurred, thus experiencing an emotional stimulation, his indirect reward will evolve into a direct reward (circle on the left in Figure 6), and emotional stimulation will turn into sexual stimulation and, if he manages to cause F-TU to occur, sexual intercourse; thus, F’s active stimulation will bring about further stimulation of M-RA with a consequent indirect reward that will keep the overall level of reward high even after the intercourse. The cycle closes up and becomes self-catalytic, and the premises for a stable couple are set.
For F, it is therefore always safer to enter TU-C from her F-AA in that if M does not tie-up, the inevitable frustration that results is easily solved as F is in turn not tied-up yet; it is therefore easier for her to step down the relationship and to look for other partners. If, instead, F-TU takes place via sexual intercourse to a M who is in turn not tied-up, the frustration of F-AA will be much stronger, and it will take time to solve it, as F is now emotionally linked to a M who refuses her. From M’s point of view, the situation is much different, as he can go through the sexual intercourse without having to be tied-up and without getting any frustration from this—and this guarantees female impregnation, even though a stable reproductive couple has not formed. The stable reproductive couple is, in fact, a higher-level relational arrangement that guarantees not only quantity, but also quality in child rearing, with an evolutionary advantage for offspring reared by both parents. M’s test of psychological compatibility then serves to assess F’s emotional intelligence and personality traits—two crucial aspects of a fully successful child rearing.
F-TU may occur independently of the sexual intercourse: Once the biological compatibility test is completed, if there are no obstacles in the first iterations of TU-C, that is, if rewards are correctly activated and M’s emotional and sexual responses are also satisfactory in terms of F’s active reward, with the unfolding of TU-C, sooner or later, F-TU occurs. However, if the sexual intercourse takes place, if there is biological compatibility, and if an optimal level of indirect reward is generated, F-TU is guaranteed. M-TU, on the other hand, is more likely to occur without sexual intercourse because, as pointed out earlier, if TU-C is started off with intercourse without an involvement of M-RA, M will be subsequently induced to leave TU-C to compensate for his own sudden drop in the after-peak direct reward. This is a typical problem of the earlier phases of TU-C. However, if TU-C kicks off and D-TU is established, there will no longer be a drop in reward for M within the cycle in that the indirect reward generated by M-RA will compensate and ensure a fair level of overall reward for M, stimulating M-AA to generate more reward for F.
The different implications of the sexual intercourse from the viewpoint of F vs. M thus depend on the fact that the intercourse fits into TU-C in a way that favors F-TU, but, on the contrary, plays against M-TU. M has thus an incentive toward pursuing sexual intercourse in the early stages of the interaction, whereas F has an incentive to postpone it. These two incentives are targeting two different adaptation problems: M’s drive ensures that biological reproduction may occur also in the absence of M-TU, whereas F’s conduct has the effect of restricting sexual contacts to the Ms who meet the criteria for effective child rearing, as revealed by the fact that they are willing to cooperate with F in the TU-C kickoff instead of practicing sex without attachment. By going through the first iterations of TU-C without sexual intercourse happening, M and F gradually build up their way to their peak levels of direct vs. indirect reward, respectively, and by so doing they have the possibility of effectively synchronizing their cooperative mating strategies, while at the same time being pulled in by the expectation of higher rewards in the subsequent steps. On the other hand, when D-TU has occurred, there is no need for F to strategically limit sexual intercourse any longer, and there is no reason of impatience for M in achieving it. In other words, one can regard the positioning of the sexual intercourse with respect to F-TU vs. M-TU in a proper TU-C dynamics as a sophisticated, evolved mechanism for optimal mate selection by F, which balances the evolutionary necessity of M’s attachment-free sex as a no-brainer hedging strategy against the threat of demographic decline, and, at the same time, for the sake of M’s partner selection, who is able to check the strategic-emotional intelligence of F as a psychologically (and evolutionarily) useful resource for an effective joint child rearing.
In view of the above, it is possible to better understand the role of generally acknowledged sources of mate attractiveness, namely physical (beauty) and material (wealth, power, etcetera) resourcefulness. Being beautiful, rich or powerful in itself cannot cause a TU, as the latter is regulated by biological (for F) or emotional (for M) compatibility tests, respectively, whose outcome is neither mechanically related to beauty nor to intelligence or social prestige. However, certainly resourcefulness makes a subject more attractive as a possible mate, as the carrier of a highly desirable asset with a clear reproductive value. The main effect of being rich, powerful, or beautiful is therefore that of dramatically increasing the probability that the appropriate conditions are created to be tested out by the other party in terms of close physical interaction or deeper psychological probing, according to cases. Independently of the test’s outcome, the other party could be strongly incentivized to tie-up the resourceful subject for instrumental reasons and therefore to simulate one’s own TU, relying upon direct reward as the only real incentive. If, however, the test is successful, the party attempting to tie-up the resourceful subject will enjoy an indirect reward as well, and the mating interaction will at least partially lose its instrumental character, improving the chances of a successful TU-C and of a stable mating.
3.4. M vs. F Rewards
According to sentimental common sense, the partner who suffers the most in a couple is the one who is most attached. In fact, from what we have learned from our previous analysis, the partner who suffers the most is likely to be the one who is tied-up to someone who pretends to be tied-up, but in fact is not. The reason is that, if a partner is not tied-up, once s/he has got the desired reward, s/he will show very little concern for the reward of the other. A failed TU in a couple may be in turn the response to a specific constellation of incentives. Some men, for instance, systematically avoid hooking up with a woman, as they expect a progressive consummation of direct reward through repeated sexual intercourse, and are unwilling to face the risky prospects of an emotional commitment. Looking for another partner is a possible solution, but it is once again necessary not to tie-up, i.e., not establishing emotional bonds with the new F as well. The ideal target for attachment-free sex is a sexually attractive F who, however, does not pair well with M’s personality and intimate world and possibly lacking strategic mating intelligence, so that it will be easier to walk away once M’s direct reward takes the downward slope, without having to overcome sophisticated mate retention tactics by F, or to resist the temptation of settling in with an emotionally rewarding mate. For M, therefore, the indirect, emotional reward coming from M-RA may look risky and unattractive if M is convinced that life satisfaction depends upon unrestricted sexual choice and lack of couple-related responsibility.
Another common belief, that is, that women are more prone to be bonded to men than the other way round, illustrates a constellation of incentives that is the mirror image of the former, in terms of a failed TU, this time from F’s side: Social pressures, the biological clock, or the achievement of economic security urge them to find a mate no matter what and thus, to keep biologically undemanding standards for mate choice to prioritize instrumental mating. Occurrence of F-TU is therefore not a precondition. However, men who marry a non-tied-up woman face no less trouble than women marrying a non-tied-up man. What is at stake for M is not only his direct reward, but his very masculine identity: Living together without being tied-up entails a very high temptation to frustrate the partner, and this is typically what will happen during marital conflict. If M cares for having children and a family without being exposed to frustration on a daily basis in both his direct and indirect reward, it is not enough to look for a physically attractive woman, but it is necessary that she is also emotionally intelligent, and well-matched in terms of feelings and personality, world views, and ideals, so that indirect rewards can be generated for M. Moreover, F will have to be tied-up in turn so as to generate also direct (sexual) reward. A non-tied-up F is sexually detached and could easily deny, or more generally strategically manipulate, sexual access by M. The existence of a D-TU is therefore a precondition for a TU-C where the continued exchange of rewards between M and F will make marital life satisfactory and desirable.
Notice how, despite the strong reproductive rationality of direct and indirect rewards, mating interaction leaves space for cultural variation. For women, the test has a biological nature, but the conditions under which women can actually carry out the test are often strongly regulated, if not restricted, in ways that clearly depend on the socio-cultural environment. For men, the test has an emotional nature; therefore, the criteria with which psychological compatibility is defined and established are clearly culturally influenced. The limitation of women’s discretional power in mating choices observed in many cultures could therefore be regarded as a male-controlled form of limitation of the scope of the female compatibility test, whose content can be otherwise culturally manipulated only to a limited extent.
A sphere in which the interaction of M and F rewards lends itself to interesting exemplification is that of chivalric courtship. When M chivalrously courts F, he is feeding F’s direct reward. Here, courting is nothing but emotionally pleasing F, hoping for an active response from her. Courtship can thus be regarded as a persuasive technique of M, targeting F-AA. F is certainly pleased by it, also in the absence of any level of sexual involvement or even interest. Such kind of male courtship simulates, or is a concrete manifestation of, male romantic love. This is always gratifying for F in that it confirms the effective functioning of her F-AA, aimed at conquering M’s emotional attentions (not necessarily of the M actually courting her). Some direct reward for F occurs even if it is apparent that M’s courtship is not really aimed at sexual conquering, and this is because in this case courtship purely acts upon F-AA, and not upon F-RA. F perceives a discreet courting from M who appreciates femininity in general, as a gentle, refined form of attention and respect. Chivalrous courting could thus also be directed at women with very low mating value for M (e.g., a very elder woman) while still making sense for him as a way to test his courtship abilities.
If M expresses sexual attention instead, with explicit appreciations and no courtship, no direct reward will be generated for F, and not because F is not interested in sex, but because such an un-mediated approach does not gratify her F-AA, which has an emotional nature. M’s crude sexual approach clearly signals not only no real propensity to tie-up, but an exclusive desire to gratify his own M-AA, totally ignoring F-AA: In other words, a plain intention of sexual exploitation. Frustrating F’s direct reward, in the absence of any F-TU, leads to an abrupt interruption of the flow in TU-C. F ceases to show interest toward M, who signals he is not orientated toward M-TU and thus rejects him all the more in sexual terms, even if he turned out to be biologically compatible. If, instead, M shows an ability to generate a direct reward for F, F will in turn activate F-AA so as to stimulate him and to eventually arrive, through the steps of TU-C, to test his biological characteristics.
In case of F’s affective insecurity and/or low self-appreciation, sexual attention from M can be misunderstood for emotional interest, leading to classical sexual exploitation dynamics. In this case, M’s crude sexual request generates an “anomalous” direct reward for F. This sparks a rather problematic TU-C, which will lead with difficulty to a stable couple. Affective insecurity might in particular make F willing to sexually comply with the requests of a non-tied-up M simply to get some manipulative emotional, or even merely sexual, attention.
In the absence of self- or hetero-directed manipulative distortions, we can claim in general that F’s direct reward sparks an emotional interest toward M, and F’s indirect reward sparks sexual attraction toward M. The actual starting point of TU-C will depend on which area of F will be stimulated first: AA or RA. If F meets a physically attractive male, appreciating his posture, gesture, prowess, voice, smell, energy, touch, even merely through a simple, close handshake, her F-RA gets passively stimulated, and the reward that follows is an indirect one. The signs of an indirect reward for F are all the more evident in the early phases of her psycho-sexual development, when her capacity of strategic dissimulation is still limited: blushing, embarrassment, giggling, smiles, laughter, excitement—a typical attitude, for instance, of young fans of pop stars at their idols’ live acts. Their hysteria is the result of an indirect reward that reaches paroxysm. Indirect reward being passive, if there is no F-TU, it does not generate any frustration and is therefore psychologically innocuous for F. It is just F’s body that responds to a sensory stimulus, even a mere visual one, and F can decide to stop at this point and not to go for a direct reward. This is just the premise of a potential TU, and not an actual one in that the biological test has just started. This is what is commonly called an infatuation.
If, in general, the early phases of an interaction escalate to kissing, and if the experience is pleasing, F’s indirect reward reaches a first peak. For teenagers, kissing may actually cause TU, and it may be highly persuasive even for adult women as a very direct and effective way to sample M’s chemistry and energy. The more the indirect reward generated by the kiss, the more promptly TU-C will start. If kissing in itself will most likely not be enough to cause a TU, provided that it generates enough indirect reward for F, it will certainly stimulate F-AA, thus producing a direct reward. Beyond physical response, there will be an emotional response as well. F will begin to act emotionally, that is, actively, with respect to the M who kissed her, even by means of complex signals that may lead to significant strategic interaction. For instance, the face slap that M may receive in certain circumstances after the kiss is a concrete signal of an active emotional response by F and not necessarily with a negative valence. If F did not like the kiss, she would clearly show disgust and would try to escape; however, if M, say, gets simply slapped, the message may be more ambiguous, and it is, however, a signal that an indirect reward has reached F-AA. The impulse behind the slap may then possibly be a way for F to brake or interrupt a process that has generated some level, however small, of indirect reward. In this case, if M wants to take advantage of the kiss with the intent of getting closer to F, the best move is not to react to the physical offence and to stop the sexual approach immediately. Surrendering makes a winning move here in that it amplifies the overall reward for F as a sum of the indirect sexual reward from the kiss and of the direct emotional reward from realizing how her active response has proven effective.
The fact that there is a fundamental asymmetry between M and F with regard to the positioning of their sexual/emotional sphere into the AA/RA reflects, as briefly anticipated in Section 3.1, different modes of management of the relationship between the two spheres in each sex. As to such differences, there are also substantial misunderstandings though, especially about the role of emotions in the female sexual response. The fact that women get sexually excited by a romantic situation (for instance, a movie scene) is not, as it is erroneously believed, the consequence of the activation of her emotional sphere, but on the contrary derives from the excitement of her RA due to the simulation (with the movie’s male lead character as the potential mate) of the test of biological compatibility that is connected to romantic physical contact. This is the reason why the actors who play the male lead character in romantic movies (from Rodolfo Valentino to Leonardo DiCaprio) turn into sex symbols; the female audience gets potentially tied-up to them. The excitement of the F-RA is immediately processed by the F-AA, which receives in turn a considerable increase of its direct reward, thus generating the emotional response, which, however, follows the sexual one. Thus, contrary to what is commonly believed, the driver of mating-oriented attraction for women has a sexual nature. In the case of the man, instead, the romantic situation excites his emotional RA, and the man thus interprets this situation as the simulation of a test of psychological compatibility with the partner (in this case, the female lead character of the movie) that calls for a momentary inhibition of his sexual response, which will possibly follow the emotional one should the test be successful. Again, contrary to common beliefs, the driver of mating-oriented attraction for men has thus an emotional nature. The romantic movie, being centered upon the creation of the conditions for the possible formation of a couple (and thus of a D-TU) is in other words designed in order to activate the RAs of both sexes, which will however react in opposite ways because of the different sphere of pertinence of the respective RAs. The consequence of such asymmetry is that, in the romantic situation, in the case of the woman, the rapid firing of the sexual response becomes synergetic to the emotional one that follows, whereas for the man the sexual response must be momentarily inhibited so that the emotional signal may become legible to him for the purpose of the possible formation of the couple.
If M’s direct reward calls for continued shots of confirmation about his masculinity, F’s direct reward calls for attention and consideration by M, who must show sensitivity toward F’s emotional world and, more generally, a genuine interest for her. Many Ms are able to simulate such interest without an actual TU, but in case an easy capitulation from F is not obtained, they may get easily discouraged, revealing their lack of TU and their mere appetite for a direct reward. The only possibility for F, at the beginning of a TU-C, to expose a manipulative tactic of this sort is thus to take time, that is, being able to go through several iterations of TU-C without conceding to sexual intercourse: An optimal mechanism to frustrate a sexually opportunistic M and to dissuade him from insisting further. For a tied-up M, instead, the same situation is less difficult to manage, as he can benefit anyway from the indirect reward deriving from the activation of his M-RA, that is, the gratification experienced from the emotional involvement with F. In this case, then, postponing the intercourse may even result in an amplification of future sexual pleasure, when F will become stably tied-up, thus generating an even greater direct reward for M. This request to wait, however stressing for him, further produces in the tied-up M, as already remarked, a reassurance as to having chosen a F with an appropriate level of emotional intelligence. If M is really tied-up, the resulting indirect reward will induce him to explore F’s psychological world in search of more emotional stimulation, and the interaction with F will then be able to generate further psychological and emotional advantage.
The well-known gender differences as to the sensitivity to sexual vs. emotional forms of infidelity may thus also be read, in terms of M vs. F rewards, as gender-specific sensitivity toward the kind of infidelity that directly threatens the partner’s TU, that is, that attacks the betrayed subject’s monopoly of the partner’s indirect reward: M’s emotional infidelity for F, and F’s sexual infidelity for M. It is interesting to remark that such differences are still distinctively found in societies with very high levels of gender egalitarianism like Norway [119].
3.5. Frustration
The positioning of M-TU in M-RA explains how M can easily abandon F after having obtained his optimal level of direct reward. The positioning of F-TU in F-RA explains why some F bind themselves to some M who are totally unfit at the emotional level. Therefore, the M–F interaction may easily degenerate from the point of view of a stable mating. However, an effective strategy to achieve TU may be found in frustration. Frustrating the direct reward in an early phase of the M–F interaction leaves two possibilities open, depending on whether an indirect reward of some sort has already been generated or not, and the implications are different for M and F. When M is sexually attracted to F, his M-AA starts to be stimulated, that is, direct reward begins to be produced, which leads M to attempt a sexual approach. If, however, F refuses the approach, M’s direct reward gets frustrated. The two possibilities are then the following: M gives up and turns attention toward another F, or M insists. The difference lies in indirect reward, that is, in the actual starting point of TU-C. If M, even without being tied-up, has been stimulated in his M-RA by F, even unintentionally, some level of indirect reward (however small) will be generated for him. If direct reward thus gets coupled to indirect reward, the frustration of the former will induce an urge for the achievement and consolidation of the latter. It is as if frustration calls for a compensation via the type of available gratification that is more proximate to the frustrated one, which in this case is provided by indirect reward—or otherwise is sought for elsewhere.
Therefore, if M is intrigued by F, the denial of his desire will end up intensifying it, leading M to persist, and to seek emotional attention from F. In this way, frustration encourages further strategic effort by M to achieve his goal, temporary shifting attention from his own direct reward to that of F. M thus goes searching for an entrance way to F’s psychology, for an access key to her interiority in that he instinctively, and sometimes consciously, knows that stimulating F emotionally, raising her active interest, and thus aiming at her direct reward, provided that the indirect one seems blocked, amplifies his chances of mating with her. What M fails to realize, however, is that in so doing he also amplifies his own chances to get tied-up in turn, as in this way he cultivates his own indirect, passive reward. In practice, M gets exposed to F’s emotional fascination, in addition to the sexual one, and carries out his own compatibility test on F, which if successful will expose M to a further, increasing indirect reward, that is, to a possible M-TU.
The activation of M-RA, as a precondition for the TU, is thus for M the ideal starting point of a long-lasting TU-C in that the lack of indirect reward, if the direct one gets frustrated, causes M to lose any interest for F.
A minimum level of indirect reward achievable by M is, for instance, feeling courted and the object of female emotional attention as, at least, M will in this way feel pleased to arise an active interest in F. However, if F looks like she did not even notice M, to obtain any level of indirect reward it will not be enough for M that F be sexually attractive, but it will also be needed that F has noticeable qualities in terms of emotional fascination—for instance, a particular sense of style and elegance, or inspiring tenderness and sense of protection, or, to the opposite, displaying a challenging attitude or an unconventional personality, and so on. The mere display of such non-sexual qualities may cause in some M an indirect reward linked to psychological curiosity and to the propensity to experiment with mystery. Lack of sympathy, or a strong initial disappointment, or even hatred, provided that they cause a destabilization of M’s certainties, such as questioning his emotional equilibrium and at the same time prospecting a different, unexpected one, might in principle become the basis for M’s emotional entrapment. Whether this kind of circumstance may lead to a M-TU ultimately depends upon the context, partners’ personality traits, their personal histories, and the details of the interaction itself. M might be willing to defend himself from the possibility of a TU by developing some form of emotional insensitivity toward F, which might be due to an exclusive interest for short-term mating, but also reveal pathological personality traits (for instance, a narcissistic, Machiavellian, or psychopathic syndrome [120]). In this latter case, the simulation of an interaction aiming at the TU might be brought forward through a purely instrumental psychological exploration to enable a more effective manipulation of F, also by means of sophisticated usage of the signals and strategies of attraction [121,122]. Frustration might be thus the first step of a risky manipulative strategic interaction for the opposite sex partner [123].
Similar remarks to those concerning manipulative frustration can be made, in a mirror-like manner, for rewards. Here, manipulation does not amount to taking the reward away but, on the contrary, to instrumentally providing it to get something from the partner. One must consider that the effect upon TU-C of reward increases is no longer that of a suspension of the flow, but of a flow acceleration within the cycle, which will, however, become increasingly demanding for the manipulative partner and will inevitably imply for him some simulation effort. The effort to sustain an accelerated rhythm of iterations of TU-C, though they are not so pleasing for those with merely manipulative goals, may unveil with time the instrumental intent. If the ultimate goal is that of inflicting some suffering to the other person, as in the above-mentioned pathological cases, the partner of the manipulative subject will be exposed to sudden accelerations followed by equally sudden brakes of the TU-C flow. The manipulator will make use of rounds of reward combined with frustration, thus mixing up the effects of both, and making the interruption of the cycle even more painful in its abrupt reversal of the acceleration of the flow of rewards along TU-C. Unlike frustration, which becomes effective for manipulation purposes only if targeting a direct reward, a manipulative action that makes use of the partner’s reward increases is equally effective whether it targets direct or indirect reward.
As to F, in this case an effective strategy to achieve F-TU may also be found in frustration. One, however, must keep in mind the actual functioning of TU-C in that if F does not feel herself sexually considered by a M she is interested in and is therefore sexually frustrated, in her case resentment will be felt not on a merely sexual level, as it happens to M, but will be felt on an emotional level, whereas M will perceive himself as sexually inadequate, F will not feel herself emotionally appreciated. This occurs because, in TU-C, F’s sexual area lies in RA and not in AA as for M. Sexually frustrating F means interrupting the flow of female indirect reward so that the affected area will still be F-AA, which will register the overall decrease of its reward, depleted of its indirect component coming from RA, and reacts on its (pertinent) emotional level: F will feel frustrated in her aspiration to perceive herself as emotionally and not sexually desired.
It is now appropriate to ask why, in an initial phase of TU-C, we only focus upon frustration of direct reward, and not upon frustration of indirect reward. Indeed, frustration of indirect reward, both for F and M, in this delicate phase of the TU build-up, would amount to a sort of suicide for the subject who frustrates with the ultimate goal of kicking off TU-C in that in this case one would undermine from the start the possibility of TU itself by blocking the compatibility tests for both sexes. Sexually frustrating a F while aiming to seduce her sexually is obviously counterproductive, and likewise it is far from convenient, to psychologically conquer M, to highlight an apparent conflict of character or even worse an inadequacy in terms of intelligence and mental capacity, be it the partner’s or the subject’s. More generally, if F frustrates M’s indirect reward, this means that F is no longer emotionally stimulating M, that is, she becomes emotionally repelling—therefore, the only reward that F may now offer to M has a sexual nature and is devoid of emotional attachment, as it happens, for instance, in prostitution. If M frustrates F’s indirect reward, this is equally counterproductive in that he devaluates his own sexual profile, thus only becoming able to offer F an emotional reward close to the one that is characteristic of same-sex friendship. The momentary, targeted frustration of direct reward, instead, does not endanger TU in that it does not act upon RAs, but rather addresses the AAs of both sexes, stimulating their active response.
The strategy also remains the same as far as F is concerned: denying a desire only to intensify it. If one wants to use frustration to induce F-TU, it must be realized that, in this latter case, it is necessary to administer the signal more parsimoniously than for M, and this derives from the basic difference between M-AA and F-AA, which are the actual targets of frustration so as to carry out an adequate calibration of the intensity of the effect brought about by frustration. The sexual nature of M-AA requires that the F willing to frustrate M exerts a sharp, peremptory action, with unequivocal implications and matching the sexual energy to be countervailed with an opposite push of equal intensity. However, the emotional nature of F-AA calls instead for greater precision on M’s side so as to modulate a much more sensitive, susceptible response. The finer emotional sensitivity of women with respect to men [124] may be interpreted in our context in terms of the association of the emotional dimension with women’s AA and with men’s RA. M will thus have to avoid any form of frustration that derives from tactics and behaviors that have been validated and are generally accepted in male-only relational environments (in which agonistic fight, real or symbolic, has its own evolutionary rationale), such as name calling or ironical mocking of the other. To emotionally frustrate F, then, a simple, momentary suspension of interest may be enough already.
The frustration of F-AA based upon a temporary suspension of interest is, for instance, a common strategy among M teenagers, sometimes as an involuntary consequence of affective insecurity in relating to attractive potential female partners. A typical scenario of interaction is the following: When F enters the room, M acts as if F were not there, not speaking to her and not even looking at her, or, in more strategically sophisticated cases, even courting other Fs. In fact, with these premises, the young M’s strategy might prove ineffective unless he did not previously display at least a minimum level of emotional involvement toward F, or attract her attention, for example, through a non-incidental eye contact, before carrying out the suspension. Without a preexisting emotional anchoring, a suspension becomes entirely meaningless. Once framed into an appropriate emotional context, though, the suspension strategy of the M teenager carries over practically unaltered to the adult age: After having intensely courted F, M momentarily ceases to show attention, as if any interest would have suddenly died down. F’s frustration would be immediate, and all the more so provided that F previously grew accustomed to the constant direct reward from the courtship.
Additionally, in this case, frustration of F’s direct reward will open up two different, alternative scenarios, depending upon the implications for F’s indirect reward. If F has no sexual interest in M, the frustration of F’s indirect reward by M will have no consequence other than provoking a short-lived disappointment in F, which will be soon wiped out by new opportunities for reward. If, on the other hand, F-RA was effectively stimulated during the previous courting by M, and F experienced some level of indirect reward (however small), thus beginning or even completing the biological compatibility test, for instance, as a consequence of an incidental physical contact with M, then frustration would turn out to be considerably amplified, and F would suddenly miss the reward value of that experience. Therefore, when direct and indirect reward are coupled, frustrating the former practically amounts to intensifying the latter, and F will consequently be sexually attracted to the potential, biologically compatible other sex partner she fears to have lost. The extent of the attraction will depend also upon a possible preexisting TU situation with another partner, which might have been weakened through time, making F susceptible to new opportunities of mating. The more solid the preexisting TU condition, the stronger the needed impulse in terms of indirect reward in order to make frustration effective and to open up further relational developments.
However potentially effective, though, the suspension of interest strategy needs skillful implementation: If the suspension is too evident and emphasized, exposing its manipulative character, F will realize this, and all the emotional impact will be lost, possibly together with the chance to give it another try. The crucial aspect of the successful frustration of F’s direct reward is its nuanced character, at the border with non-intentionality so as to feel natural and authentic. A similar effect can be generated by a sudden absence of M preceded by a period of successful courting. Additionally, in this case, the effect is the activation of F-RA in that M’s absence is perceived as equivalent to the frustration of F’s direct reward. In the case of benign manipulation, this sort of strategizing is used only once, in the most appropriate moment to foster F-TU, that is, when F is emotionally pleased and has surrendered to the pleasure of the emotional reward despite not having to feel any obligation to concede at the sexual level. By experiencing a frustration of her direct reward, F turns attention toward the only viable reward left, that is, the indirect, sexual one, which is still attainable through the memory of M’s rewarding physical approaches and of F’s bodily reactions.
If M frequently adopts a suspension of interest strategy, however, his manipulative intention may be more radical and less benign: M could only be interested in his own direct reward, the sexual one; in this case, the name of the game is rapidity in that a prolonged phase of indirect reward not adequately supported by a direct one would not be sustainable for long. If the suspensive technique is instead applied after the sexual intercourse and F-TU has taken place, the manipulative intention is potentially even more dangerous in that the frustration of F’s direct reward would in this case amount to an outright act of (implicit) hostility, as typical, in extreme cases, of pathological narcissistic personalities. Misuse of frustration of a tied-up F is therefore tantamount to sending her a negative signal of lack of attachment and of manipulative intention. Likewise, if F abuses the frustration of M’s direct reward, letting him believe that she will sexually concede, only to perpetually postpone the intercourse, we find the female equivalent of the manipulative male narcissistic personality just mentioned. If F’s manipulative intention is (benignly) limited to inducing M-TU, she will frustrate M in an explicit, clearly interpretable way.
In already formed couples engaging in conflict and/or subject to emotional distress, frustration can be used as a proper marital weapon. In these cases, not only direct reward, but also indirect reward can be attacked by the partner, with the specific purpose of inflicting emotional pain. This is a typical consequence of the breakup of TU and of the consequent interruption of TU-C. Analyzing these issues in depth is beyond the scope of the present paper. However, what may be of interest here is the implication that an effective maintenance of the TU is strictly connected to refraining from frustrating one’s partner, for whatever reason, whether intentionally or not. Once this erroneously happens, apologizing becomes necessary to prevent the negative impact of the action on either direct or indirect reward, or on both. A basic level of emotional intelligence as to preventing and detecting unnecessary frustration seems to be fundamental for couple maintenance and stability.
In a nutshell, we may conclude that:
- -
- M’s indirect reward begins to be frustrated when F loses interest and consideration for her male partner and when M consequently feels he is no longer important for his female partner;
- -
- F’s indirect reward begins to be frustrated when F feels no longer sexually desired by M and when M consequently avoids approaching her and maintaining physical contact;
- -
- M’s direct reward begins to be frustrated when F subtracts herself, physically and mentally, to the pleasure of physical contact with her male partner;
- -
- F’s direct reward begins to be frustrated when M does not pay attention anymore to what F says and shows no sign of interest toward her.
Without a continued interest in the partner, TU is seriously threatened, and the situation may easily escalate into a sequence of frustration, wrongdoing, provocation, and revenge, where of course past emotional openness offers to each party plenty of opportunity to harm the partner in a carefully targeted, extremely effective way. On the contrary, reciprocal care strengthens TUs, creating with time couple solidity and psychological enrichment, as continued reciprocal reward within the couple is a clear sign of psychological well-being and personal development [125].
To sum up, frustration is an interruption in the flow of rewards within TU-C. If such an interruption persists, the cycle is irreparably compromised as TUs are dissolved. Frustration causes distress in AA, in RA, or in both, depending on whether the object of frustration is direct or indirect reward, and may unfold in time in many different ways. A crucial difference is whether the TU has already taken place or not when frustration occurs. Without TU, frustrating indirect reward, the one concerning (passive) RA, does not cause significant distress in both sexes, whereas frustrating direct reward, even in the absence of TU, causes real distress in that it is the AA which is being hit, and the offence is then perceived by the subject, M or F, as a personal attack to one’s own identity—of sexual nature for M, and of emotional nature for F. The situation is turned upside down once TU has taken place. In this case, frustrating indirect reward causes a devastating distress, which deeply undermines F’s sexual self-confidence and M’s affective self-confidence, with serious repercussions upon esteem, trust, balance, and so on. Attacking RA equals to attaching TU itself, as RA is the area where TU occurs.
Once TU-C is started, there are self-regulating mechanisms that come into play in case TU-C is threatened by some intervening situation—in particular in the case of a momentary interruption of the flow of direct rewards, that is to say, of compromised AAs. If, instead, the compromised areas are the RAs, and the interruption affects indirect reward, the issue rapidly escalates to a critical level, and the dissolution of TU may arrive quickly and painfully. In non-secularized societies, this sort of issue is solved by means of socio-cultural compensation mechanisms, generally acting upon Fs who, even when compromised in their sexual RAs, are kept bound to their partner by religious constraints and social stigma, while at the same time socially incentivizing AAs for both couple members, through family affects and protection for F, and through the acknowledgement to M of his masculine rule, which also guarantees a buffer of social acceptance for out-of-wedlock sexual conduct. In secularized societies, such mechanisms have been gradually dismantled, and today TU dissolution as a consequence of interruption of indirect rewards is typically conducive to couple disintegration.
3.6. Inversion of TU-C Flow
The practical consequence of frustration of direct reward from the point of view of TU-C is a blockage of the flow of rewards, which tends to be compensated with an inversion in the direction of the flow itself. If frustration is momentary, the cycle is therefore able to self-regulate effectively and to restore normal anti-clockwise flow direction. If it persists, the whole cycle is compromised. In terms of our TU-C diagram, interruption of the flow amounts to turning off one of the two RAs, which closes itself to the interaction with the other areas, stopping any circulation of rewards. In this case, the first area to be exposed to distress is the RA that is opposed to the one that has closed down. The cycle’s self-regulation mechanisms are immediately activated, trying to produce a compensation, by exposing the distressed area to an increase in stimulation in order to restore the correct direction of the flow that has been broken. The acting components are AAs, as frustration emanates from an AA to hit the opposed AA. For instance, let us imagine that it is M who is willing to frustrate F. M-AA sends an impulse in the opposite direction with respect to the normal flow (Figure 7), which, once his own M-RA is reached, turns it off and moves forward, always in opposition to the normal flow direction, to hit its final target, F-AA. We speak in this case of emotional frustration. F’s emotional frustration, in turn, contrasts and blocks F’s direct reward, preventing it from reaching M-RA. The repression of F’s direct reward sparks a regulatory mechanism of the system, which consequently leads F-AA to send, always in the opposite direction with respect to the normal one, a balancing signal to F-RA, which we will simply call compensation (the inner flow in the bottom part of the diagram in Figure 7). In this case, compensation is an impulse of sexual drive that stimulates F-RA to generate sexual desire. The direction of the flow is still inverted, as F-RA, once stimulated, instead of sending signals to F-AA, as would ordinarily happen, now sends a signal—more specifically, a request for sexual attention, to M-AA. If M-AA responds sexually, then the anti-clockwise direction of the cycle is re-established and starts again flowing in the normal direction. A further passage through F-AR, at this point, may also cause F-TU (if it was not previously established yet) in that F-RA has been highly stimulated. With the sexual response of M-AA, and with its landing onto F-RA, an indirect reward is generated, which, once F-AA is reached, in turn causes a further direct reward, targeting M-RA. At this point, M-AA, which with its sexual response has generated a direct reward for M, could then suspend its emotional frustration impulse toward F and allow F’s direct reward to activate its own M-RA again. If this happens, TU-C is safely restored. If, instead, M persists in his action of frustration, the flow will be inverted again, exposing F-RA to further stress. The repeated exposure to frustration may thus lead to a dysfunctional dynamic, where M aims at the domination of F through a stable condition where only F ends up being tied-up and D-TU is strategically avoided by M.
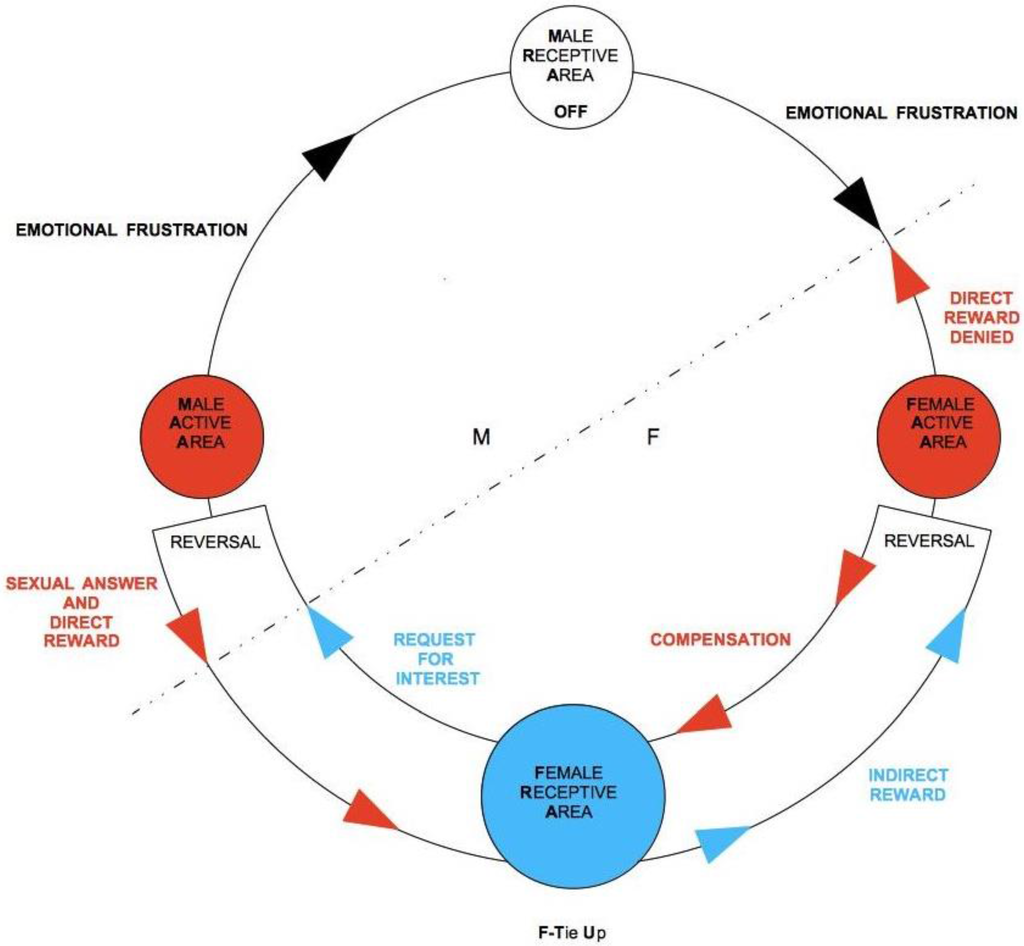
Figure 7.
M-driven inversion of TU-C: frustration of F’s direct reward.
Observation of the graph clarifies what happens when M is not tied-up and is not interested in activating his M-RA in order to get an indirect reward. In this case, a proper TU-C does not even exist, as the flux is persistently confined in the bottom part of the diagram. However, F might interpret this situation as a momentary suspension and, being frustrated by the lack of M’s attention, could end up accommodating the cycle’s regulation mechanism. If several iterations through F-RA occur without causing M to unblock his ongoing emotional frustration of F, F’s distress will tend to become more and more painful at each round. If, in particular, F gets tied-up by means of a sexual intercourse, the suffering may be quite intense. It is unfortunately not easy to discern when a potential partner, whether M or F, is simulating a TU. Particularly for F, whose testing has a merely biological nature and thus does not give any guarantee for the long-term commitment of M, the only truly effective counter-strategy is to slow down the unfolding of the cycle and to frequently screen M’s actual intentions through temporary frustrations of M’s direct reward (see Figure 8). F must exert special caution and be aware that for her, in the context of TU-C, the sexual intercourse is the situation that exposes her to the higher risk of premature and possibly unilateral TU. On the other hand, deferring the intercourse moves the psychological cost on the shoulders of the manipulating M, who is only interested in his own direct reward. Such a strategy works as a revealing mechanism for M’s true intentions [126]. In case of a real lack of M-TU, with time the non-existence of TU-C becomes apparent. In the early phases of mating, as a consequence of uncertainty about M’s true intentions, F should learn to modulate with emotional intelligence all possible gradations of sexual reward. A cycle broken through frustration can be correctly restarted without necessarily having to engage in full sexual intercourse. If M shows patience, this increases the likelihood that he is actually engaged and allows him to learn to synchronize to F’s psychological states—an important asset for both sexual and emotional satisfaction. The above analysis tells us that, whereas the evolutionary benchmark for male selection in mating is on the sexual and genetic level, for females it is related to emotional intelligence—women who manage to engage men emotionally through a skillful strategic manipulation of direct rewards and thus to overcome M’s potential sexual opportunism face a higher chance of stable mating by signaling to Ms that, thanks to their psychological qualities, M’s investment in a stable couple may be worthwhile in terms of the quality of marital relationship and of successful child rearing.
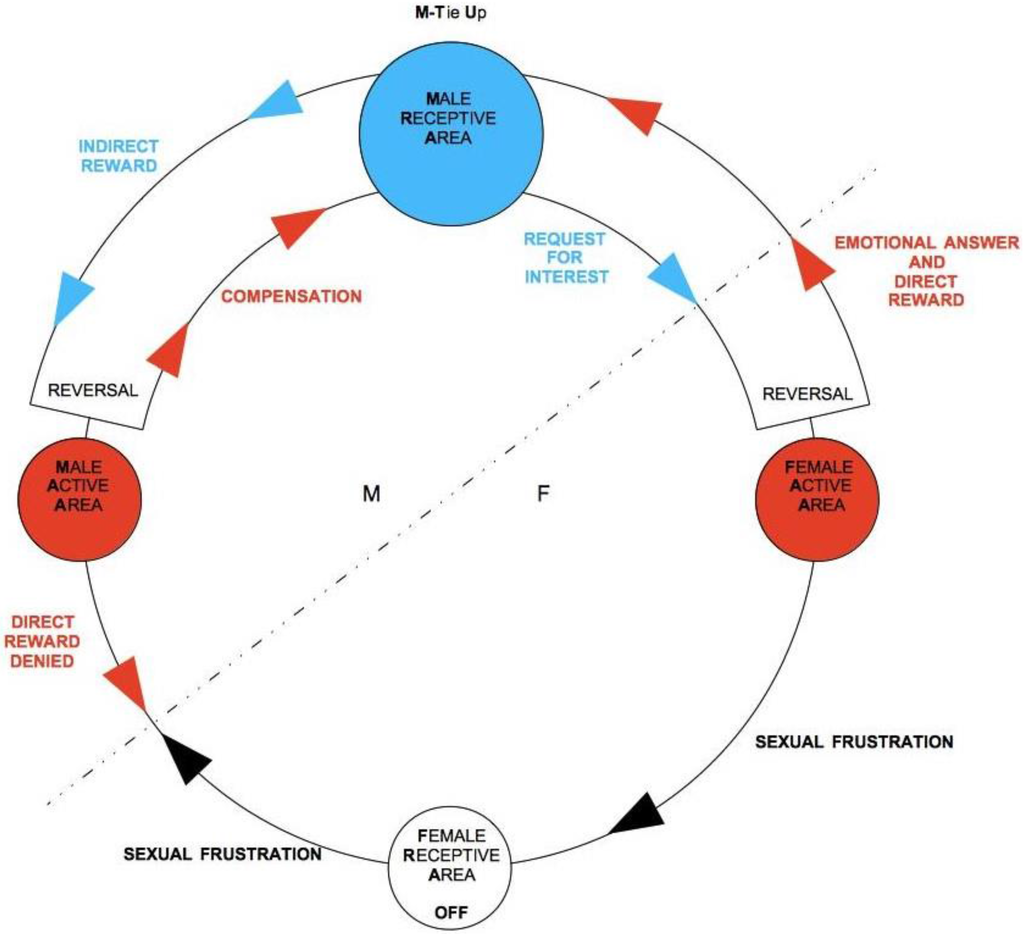
Figure 8.
F-driven inversion of TU-C; frustration of M’s direct reward.
The mirror-like situation of a F-driven inversion of TU-C is shown in Figure 8. When it is F who is willing to frustrate M, it is F-AA that sends an impulse in the opposite direction with respect to the anti-clockwise flow. Once F-RA is reached, the impulse turns it off and proceeds further against the normal flow by hitting its final target, M-AA. We can speak here of sexual frustration. M’s sexual frustration, in turn, blocks M’s direct reward, preventing M-AA from reaching out to F-RA. Additionally, in this case, the repression of M’s direct reward activates a regulatory mechanism of the system, which consequently makes M-AA send an equilibrating signal in the opposite direction with respect to the normal flow for the purpose of compensation (the internal flow in the top part of the diagram in Figure 8). This time, the compensation is no longer an impulse of a sexual nature, as it was for M-sparked frustration, but rather an emotional impulse that stimulates M-RA. The direction of the flow is still opposite with respect to the normal anti-clockwise one; therefore, M-RA, once stimulated, rather than sending signals to M-AA as it would ordinarily happen, now sends a request for emotional attention to F-AA so as to encourage F to suspend the frustration. If F-AA responds emotionally, the anti-clockwise normal flow is restored. The emotional response of F-AA (external flow in the top part of the diagram in Figure 8) reaches M-RA and an indirect reward is generated, which moves on to M-AA, generating in turn a direct reward and thus a further impulse toward F-RA. At this point, F-AA, which with its emotional response has generated a direct reward for F, might suspend its sexual frustration, and allow the consequent M’s direct reward to cause M-AA to activate F-RA again. If this happens, TU-C is finally re-established. The structure of this second diagram of flow inversion is thus the perfect mirror image of the former, shown in Figure 7. The difference is that, in this case, the flow persists in the top part of the diagram rather than in the bottom one. Inspection of the diagram suggests how M’s sexual frustration caused by F produces, as a compensation to restore TU-C, a repeated stimulation of M-RA and an increase of the emotional interest of M toward F. The high level of stimulation of M-RA, analogously to the effect of M-sparked frustration upon F-RA described in Figure 7, may cause M to carry out the psychological compatibility test and thus lead to M-TU (if not previously established yet). Sexual frustration administered by F may therefore be regarded as expedient to increase M’s possibility of a TU. Moreover, Figure 8 clarifies what happens when F is not tied-up and is not sexually interested in M, but is nevertheless willing to exploit M’s emotional attentions to her own advantage, for instance, through a promise of future direct reward for M, which will not necessarily occur.
It is useful to remark that sexual frustration of M implies a failed achievement of M’s maximum level of direct reward, i.e., full sexual intercourse. There is, however, a full range of intermediate forms of sexual reward that ensure a gradual satisfaction in the early phases of couple formation, allowing F to check to what extent M is willing to accommodate his frustration with an inversion of the flow of rewards. The more M is willing to compensate the frustration of his direct reward with a request for emotional attention from F, the more likely the production of indirect reward for M and an eventual M-TU. For this reason, in an early phase, going through TU-C without seeking to achieve maximum levels of reward may allow F to check whether M-TU has actually taken place, and M to test in turn F’s psychological compatibility, by amplifying the response of M-RA and consequently the emotional interaction with F-AA.
3.7. The Six Ways: the Role of Entry Points in TU-C
A TU-C may kick off from any of the four Areas, that is, it may start from active Areas (M-AA and F-AA) or from passive ones (M-RA and F-RA). If the Area lies in the F hemicycle, it is the woman that initiates TU-C; if, instead, the Area is in the M hemicycle, it is the man who starts. There are three possibilities for each sex, for a total of six, of which only four will have a chance to bring about the partner’s TU. Whereas starting from AA entails only one possible path, with a quick transition into the partner’s hemicycle, by simply following the anti-clockwise direction of movement of the cycle itself, without crossing other Areas of one’s own hemicycle, starting from RA opens up two possibilities to reach the partner’s hemicycle, one of which calls for the inversion of the cycle’s flow of movement.
In the former case, we have that AA directly communicates with the opposite sex’s RA (Ways 1–2, Figure 9), and no inversion in the flow of rewards is contemplated, that is, no change in the direction of movement of the cycle, which remains anti-clockwise. This depends on the fact that AA constitutionally relates to the opposite sex’s RA, which always follows up in the TU-C diagram, in addition to representing the most proximate access to the opposite hemicycle, and being excited by AA on its same sphere of pertinence, be it emotional-psychological or sexual. This means that, in the case of the woman, there is an emotional excitement of F-AA toward the male’s psychological sphere, that is, M-RA (Way 1), whereas in the case of the man there is sexual excitement, and the sexual M-AA will directly address the (sexual) F-RA of the woman (Way 2). This represents a classical approach to the other sex and thus depends on the characteristics of each sex’s AAs. If the action of AA is successful, a TU in the opposite sex’s RA will be caused, generating a peak of direct reward for AA—and this may occur at the first iteration or may call for several rounds of the cycle by repeating and strengthening at each passage the excitement of RA, keeping in mind that, at each round, the possibility that the other TU occurs in the starting hemicycle keeps on increasing. In case the compatibility test fails, instead, RA is not activated, and the cycle does not start at all.
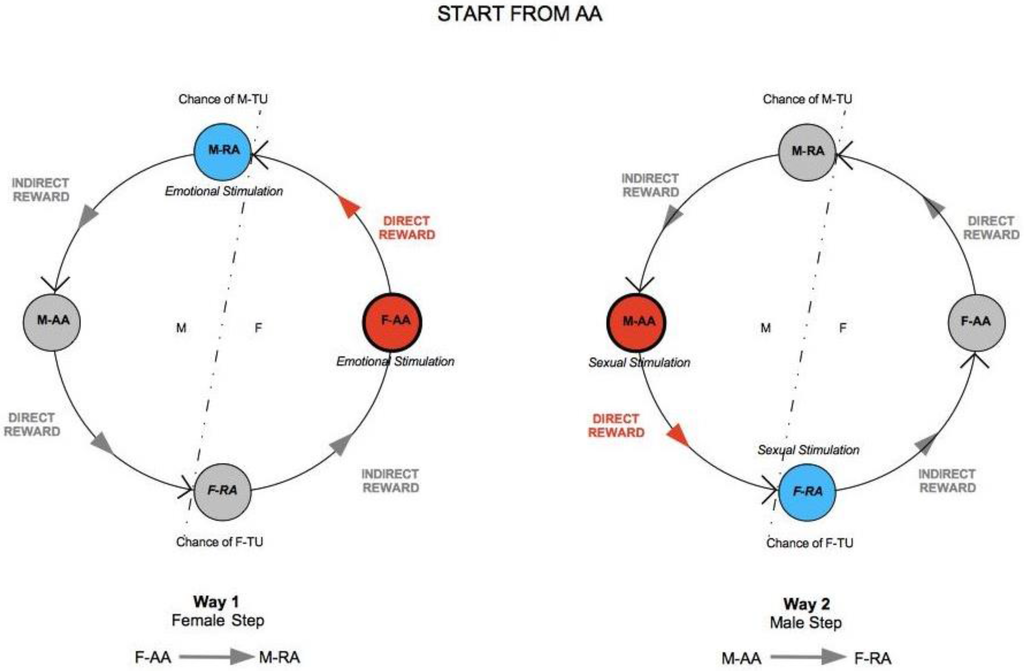
Figure 9.
Ways 1–2.
When the cycle moves from the AAs, this entails a larger probability of an opposite sex’s TU, while as regards the second TU in the same hemicycle of the starting AA, this depends upon the capacity of the potential partner to complete his/her own half cycle within TU-C, preserving the same anti-clockwise direction of movement. Thus, in Way 1, if M does not succeed in correctly stimulating F-RA, there will be no possibility of a F-TU, and F will only experience a direct reward, maintaining a friendship relation with M, especially if the latter has inverted the direction of the flow. In Way 2, likewise, if F does not manage to correctly stimulate M-RA, there will be no chance of a M-TU. At best, if F inverts the direction of the flow and responds to the sexual offer, M will enjoy his direct reward through a sexual friendship. If the cycle is not successfully completed by the involved partner, then there will be only one possibility of direct reward for the acting AA and thus for the sex of the starting hemicycle, whereas, for the opposite sex partner, in case s/he fails to stimulate the other’s RA or decides to invert the direction of the flow, the lack of direct reward may result in frustration, especially in case his/her TU has occurred.
This mechanism also ensures the efficacy of the system when the cycle is not activated and the couple is not formed in that there will be in any case a high propensity to insemination on M’s side, balanced by a low propensity of F to being frequently inseminated by different partners, consequently preserving the sperm from the possibility of being displaced by that of competing males, and at any rate not being conveniently selected (Way 2). At the same time, F will not be engaged into relations with a bad probability of insemination, remaining available for other mating and TU opportunities, whereas Ms will be concurrently selected in terms of their conformity to the TU-C demands and of transmission of the best generic material (Way 1).
If, instead, the cycle moves from RAs, we need to keep in mind that these are passive areas, which, once activated and excited, must, however, make use of the respective AAs, which are designated for action, to engage into an active interaction with the other hemicycle. If the response of RA takes an active character, RA connects to its own AA. One must realize, however, that RA has its own autonomy of passive response to the stimulating AA, for instance, in female sexual surrender with a strong passive connotation or in sending out invitation signals that M-AA is easily able to decode. Allowing the partner to act sexually in an active fashion, therefore, is a typical response of F-RA to M-AA. When the flow is inverted, instead, it is always F-AA that operates to actively seduce M-AA within the sexual F-RA sphere. If, in particular, we consider male courtship as a form of seduction, when courting has sexual implications, its active nature accommodates the natural flow of TU-C, heading toward F-RA. However, if courting is devoid of sexual implications and only aims at F’s emotional sphere as in chivalry, it will be M-RA that interacts with F-AA, and this happens through an inversion of the flow, that is, when M-RA involves M-AA in an active mode of emotional seduction.
When the cycle starts from a RA, the first step will always be toward one’s own AA (Ways 3, 4, 5, and 6; Figure 10), but at that point there are two options: reaching the opposite-sex partner’s RA, continuing along the anti-clockwise direction of movement (Way 3, Way 4), or inverting the direction of the flow to head back toward the partner’s AA with a second passage through one’s own RA (Way 5, Way 6). This latter possibility could be regarded as resource economizing, as AA will reach the area that has determined its own excitement more quickly, that is, the other hemicycle’s AA (Way 5, Way 6), whereas in the latter option, despite not having to invert the cycle’s direction of movement, the partner’s AA will only be reachable once the partner’s RA has been crossed, and this implies a switch in the sphere of pertinence, from sexual to emotional or vice versa, depending on whether we are in the M or F hemicycle, to subsequently return to the initial sphere in which the excitement has originated (Way 3, Way 4).
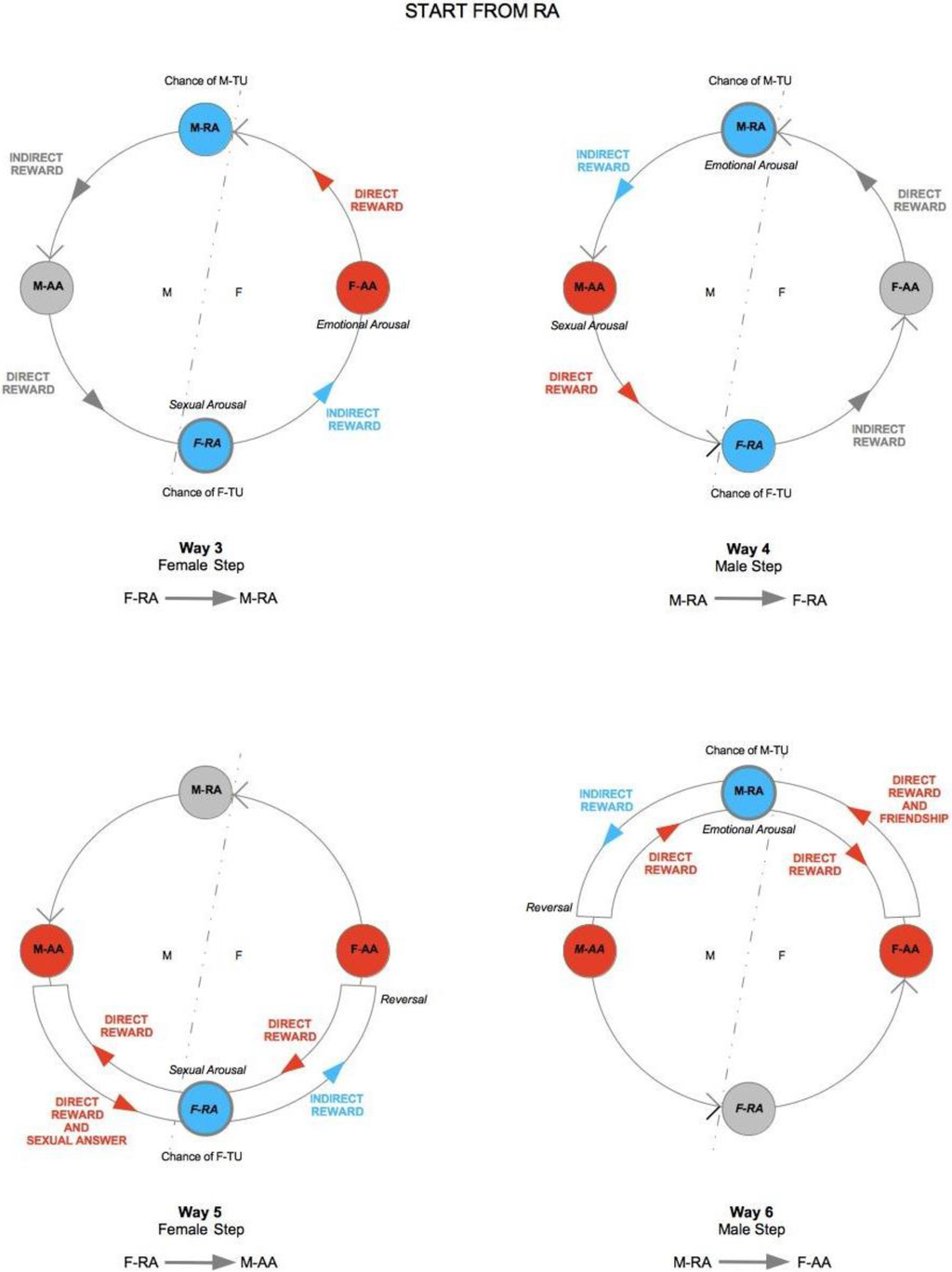
Figure 10.
Ways 3–6.
In other words, we must realize that, if we start from AAs, these get excited through their forward-heading action (in terms of the normal anti-clockwise direction of TU-C) toward the other hemicycle’s RA. However, if we start from RAs and an indirect reward is produced anyway, the AAs will also be excited by this other reward that comes from behind, that is, from the same hemicycle’s RA, for which there is, instead, only a possibility of passive excitement that depends upon the opposite hemicycle’s AA, which still precedes according to the anti-clockwise direction of the flow of rewards.
It is thus understandable that, when we start from RAs, for the same hemicycle’s AAs, there will be a temptation to invert the direction of the flow. Now, the AA, through its own RA, will experience the attraction toward the partner’s AA from which the reward comes, this time no longer direct but indirect, and which it can achieve in two ways: moving along and generating direct reward in the direction of the other hemicycle’s RA (Way 3, Way 4), in the hope of managing to excite it to reach, with a further step, the AA it sought for (so that it commands the production of further indirect reward). Or rather, inverting the flow and generating direct reward in the direction of the partner’s AA (Way 5, Way 6). Obviously, we are not dealing with the same kind of direct reward in the two cases because the one addressing the other hemicycle’s RA will remain within the same sphere of pertinence, be it emotional-psychological or sexual, whereas the direct reward that moves clockwise toward the opposite hemicycle’s AA by crossing its own RA will switch to the latter’s sphere of pertinence so as to be able to dialogue with the partner’s AA.
For more clarity: If, for instance, the cycle has started from the F hemicycle, the direct reward that travels in the direction of M-RA will express itself on an emotional level, whereas the direct reward that moves toward M-AA will adjust to the sphere of pertinence of the F-RA it crosses along the way and will approach M-AA sexually. In a sense, each sex can decide whether to go along the faster, easier path in the economy of the cycle, which entails carrying out the inversion, or choosing the longer, more exacting path, which requires a complete round. From the point of view of couple formation, however, the system remunerates the most expensive option, which is the one that accommodates the TU-C direction of flow, with a concrete possibility of a TU of the partner who has actively sparked the cycle. The inversion of the flow indeed represents the only case that does not contemplate the TU of the partner who has excited, and possibly also tied-up, the initially engaged RA. The inversion of the flow moreover represents a real risk of one-sided TU for the subject that practices it, with a cycle that has not even properly started, in that the opposite sex’s AA, once obtained and its reward enjoyed, does not follow up with more action, whereas the respective RA remains turned off, not having been crossed at all.
In evolutionary terms, the short path ensures the species’ survival in that: if in one case (when it is F who inverts the flow), the sexual intercourse is quickly reached; in the other (when it is M who inverts the flow), what is favored, instead, is the selection of the fittest subjects for insemination purposes, ruling out those M who proved themselves less competitive on sexual grounds, and who therefore did not manage to tie-up any female subject. The long path conversely favors the species’ cultural evolution, as it is the only one that, once the positive outcome of the compatibility test for both sexes is checked, ensures the unfolding of a complete TU-C and the constitution of the stable couple that will rear the offspring.
Some simple exemplification may help to better appreciate the specific characteristics of each Way from the viewpoint of the dynamics of TU-C. Way 1 (F-AA → M-RA) may, for instance, represent the case of a woman who admires a man for his endowment of psychological resources and skills (gentleness, sympathy, intellectual brightness, talent, professionalism), or of material resources (wealth, power, etc.), which constitute for her a source of attraction with a clear evolutionary rationale. In Way 1, F thus admires M to the point of feeling psychologically attracted to him, independently of his aspect and physical characteristics. This psycho-emotional approaching of F allows M to interact on the same sphere and to test his psychological compatibility with F. If the test succeeds and M, in turn, will feel emotionally attracted to F, some level of indirect reward in the M hemicycle will be produced, which will push the cycle toward the sexual sphere (M-AA), but not necessarily—if, for instance, preexisting M-TU and F-TU with other partners are already in place, or if F is not sexually attractive for age reasons or other factors, if M has his own inhibitions or is just not into heterosexual sex, the flow could stop anyway. M could then accept a friendship with F, without even approaching her enough to enable the test of biological compatibility in her own F-RA.
Way 2 (M-AA → F-RA) represents, instead, the classical case when a man notices a woman who attracts him physically, that is, excites him in a sexual way, thus activating his own AA and consequently leading him to deploy all of his seductive ability. M-AA will produce ever increasing shots of direct reward, which will prompt M to approach F physically, and the choice of the how, and of the how much, will be a key part of the seductive strategy, successful or not according to cases. F, on the other hand, could already be happily tied-up to someone else. In this case she will try to keep herself out of (physical) reach to prevent the kickoff of a biological compatibility test (ranging from simple visual, olfactory, and vocal examination to move to a tactile-energetic sampling, and finally a chemical one). The test is automatic, and can be avoided only by maintaining physical distance, but even if it would turn out positive and would generate a shot of indirect reward in the F hemicycle, F might not be interested and avoid accommodating M for various reasons, especially if there is an absence of F-TU toward him. However, for other possible reasons, F could accept the approach of M, actively responding in sexual terms with an inversion of the cycle, or instead following the anti-clockwise direction of movement of the rewards, and become interested in M from a psychological point of view. The cycle, however, will not move further in two cases: if F sexually gratifies M from the very early phase of the approach with full sexual intercourse before M-TU is brought about, or if M does not tie-up because there is not an equivalent psycho-emotional attraction toward the F who attracted him physically, that is, if the psychological compatibility test with F fails.
Way 3 (F-RA → M-RA) is the fortuitous case where a positive test of biological compatibility occurs in the woman without anyone noticing, including the man who is the object of the test. The woman thus starts to feel physical attraction for the man, thereby resolving to seduce him primarily on an emotional, psychological level. This Way concerns examples of women who proceed carefully, without exposing themselves to a F-TU too precociously, but that at the same time emotionally re-elaborate their sexual instincts. The activation of the F-RA is generally quicker the younger she is and the less sexually mature she is, as in this case the test will be less detailed and demanding. For example, in the case of a teenager, it may happen that the sight and the sound of the voice of a potential male partner that corresponds to some ideal standard of underage male attractiveness may be enough to activate her F-RA and to generate indirect reward, even if this will not be conducive to an effective, full-fledged TU, the biological compatibility test not having been completed (that is, what is commonly meant by an experience of Platonic infatuation). What is interesting to observe with very young subjects is that F instinctively starts to experiment and to practice with her own AA by attempting an approach toward the M-RA of the male subject who has stimulated her F-RA. The first teenage love experiences may thus represent an entirely natural way to learn about future romantic interactions, and especially about how to successfully move along a fully functioning TU-C.
In Way 4 (M-RA → F-RA), the man feels psychologically attracted to a woman, up to the point of tying-up, and thus attempts to make her tied-up in turn by means of an appropriate physical approach. This is the Way that best represents a male subject who is fit for long-term mating and child rearing. M instinctively operates the choice of his partner in this regard already, by primarily looking for a psychological compatibility with the F who could interest him sexually, while ruling out instead those Fs who are only interesting on a merely sexual level. The M of Way 4 represents the man who wants to be intrigued by a woman both mentally and sexually, and who moreover feels the confidence to engage himself sexually once he has found the right F partner, showing a stronger persistence and determination in the construction of the relationship with respect to the M of Way 2, who, instead, could just be satisfied with his own (tied-up) achievement of direct reward of a sexual nature.
Way 5 (F-RA → M-AA) represents the case, rather frequent today, of single women who finally find the recognition of their right to make their own sexual choices freely and autonomously. However, this option does not necessarily guarantee fulfillment from the psycho-emotional viewpoint, and many women still realize, bitterly, how it may be difficult to achieve a satisfactory level of direct reward in the sentimental sphere with the same ease of men. The reason is because, for F, the inversion of the cycle according to the logic of Way 5 indeed allows an immediate access to sexuality, but at the same time, in the absence of a tied-up male, strongly limits the opportunity for direct reward and thus the full social acknowledgement of her sex identity, which is linked to the expression of her AA. The male partner, on the contrary, receives a full direct reward from a relationship centered upon the sexual dimension, consequently feeling perfectly socially confirmed in his sex identity. The only reward which F can access in Way 5 is thus the indirect one, with a perennial exposure to the risk of a one-sided TU. There is moreover a further complication of a social nature: A woman who freely makes her sexual choices outside the context of a stable couple must still face, even in the most permissive social environments, a strong social prejudice, and may, for instance, encounter difficulties to enforce her rights and her reasons vis-à-vis retaliations from former partners who aim at devaluating her identity and social dignity via stigmatization of her previous sexual availability toward them (think, for instance, of the sadly escalating phenomenon of revenge porn [127]). The achievement of a real sex parity in this regard is far from simple, and, to this purpose, women need to acquire specific relational competences, maturing a deep awareness of their as well as of male nature, and of the associated social perceptions, and to avoid surrender to the simplification that identifies emancipation with a mechanical imitation of the respective male role models.
Way 6 (M-RA → F-AA), finally, is, for instance, the classical case of the shy, immature teenager who, having fallen in love, does not know how to make use of his M-AA to win the sexual attention of his loved one, and attempts an inversion of the flow in the hope that she will make the first step. This is a passive attitude typical of M-RA, which is rarely remunerated by selection in couple formation. The problem is exacerbated when M must face the competition of more expert and proactive males. The possibilities opened by Way 6 may, however, be widely utilized to gratify women, even with a simple exercise in chivalry or a bland courtship which will please women of any age and social extraction. The man who practices Way 6 skillfully will thus be able to obtain an ascendant on many women, consolidating a situation that might also be conducive to a relational development in the sexual sphere. Way 6, in the absence of competition with other males, may represent a good preparation strategy to obtain feminine esteem and respect before the sexual approach, but at the same time is very risky in that it may confine M into the role of the friend-confident of F, making the passage to the sexual sphere increasingly more difficult the more the relationship gets locked into its original mode.
A last possibility, which is not, however, contemplated among the six Ways just presented, but that may happen anyway, is that of a simulated TU-C sparked by F, in a sort of manipulative mirror reflection of Way 1. Here F starts from her AA but moves in the opposite direction with respect to the normal anti-clockwise direction. The reason why we do not include it among the Ways is that, in this case, interaction is programmatically started in a logic of manipulation in which TU-C is entirely simulated, from the very beginning and with purely instrumental purposes. An F who moves from her F-AA to launch a cycle of interaction in the opposite direction of the anti-clockwise movement corresponds, for instance, to the case of a sexual approach toward M to get material benefits, in the absence of a F-TU, or even of a simple activation of F-RA (for example, if M has considerable financial or power resources). Moving in the opposite direction with respect to TU-C, F first crosses her inactive F-RA to proceed further toward M-AA and stimulate M sexually so as to amplify as much as possible his direct reward, and therefore the whole interaction is shaped by a manipulative logic. To the contrary, a manipulative M has no need to move from the beginning in the opposite direction with respect to the natural flow of TU-C to cause an instrumental, one-sided TU in a F with considerable material resources, as this goal can simply be achieved by following the flow of TU-C and going, first of all, for an active sexual seduction of F-RA and subsequently for a passive one, by simulating M-TU once F emotionally responds on the F-AA sphere.
When F sexually seduces M in an instrumental way, it is not necessary that M gets unilaterally tied-up, but it is, however, necessary that the relationship be stabilized to allow F to extract the material benefits she craves for. If F would limit herself to stimulate M-AA, once obtained his reward M would simply abandon the relationship in search of more rewards elsewhere. F has therefore two alternatives. The first, risky in the short term but convenient in the long term, is that of attempting M-TU, to stabilize the relationship and hedge against the competition of other Fs who could approach M with a similar tactic. In this case, once having sexually stimulated M-AA, F could follow the natural direction of flow of the cycle and emotionally activate her own F-AA to stimulate M-RA. The risk lies in the fact that, in case M’s test of the psychological compatibility of F fails, F could be discarded by M. F should in this case invert the flow again and attempt a new sexual seduction of M through a further stimulation of M-AA. If the attempt turned out successful, F would have gained more time for the pursuit of her personal material advantage. The alternative strategy is that of not undergoing the psychological test by M, thus minimizing the risk of abandonment in the short term, but remaining exposed to the substantial risk of being discarded sooner or later in favor of other competing Fs.
A summing up of the basic characteristics of each Way is presented in Figure 11.
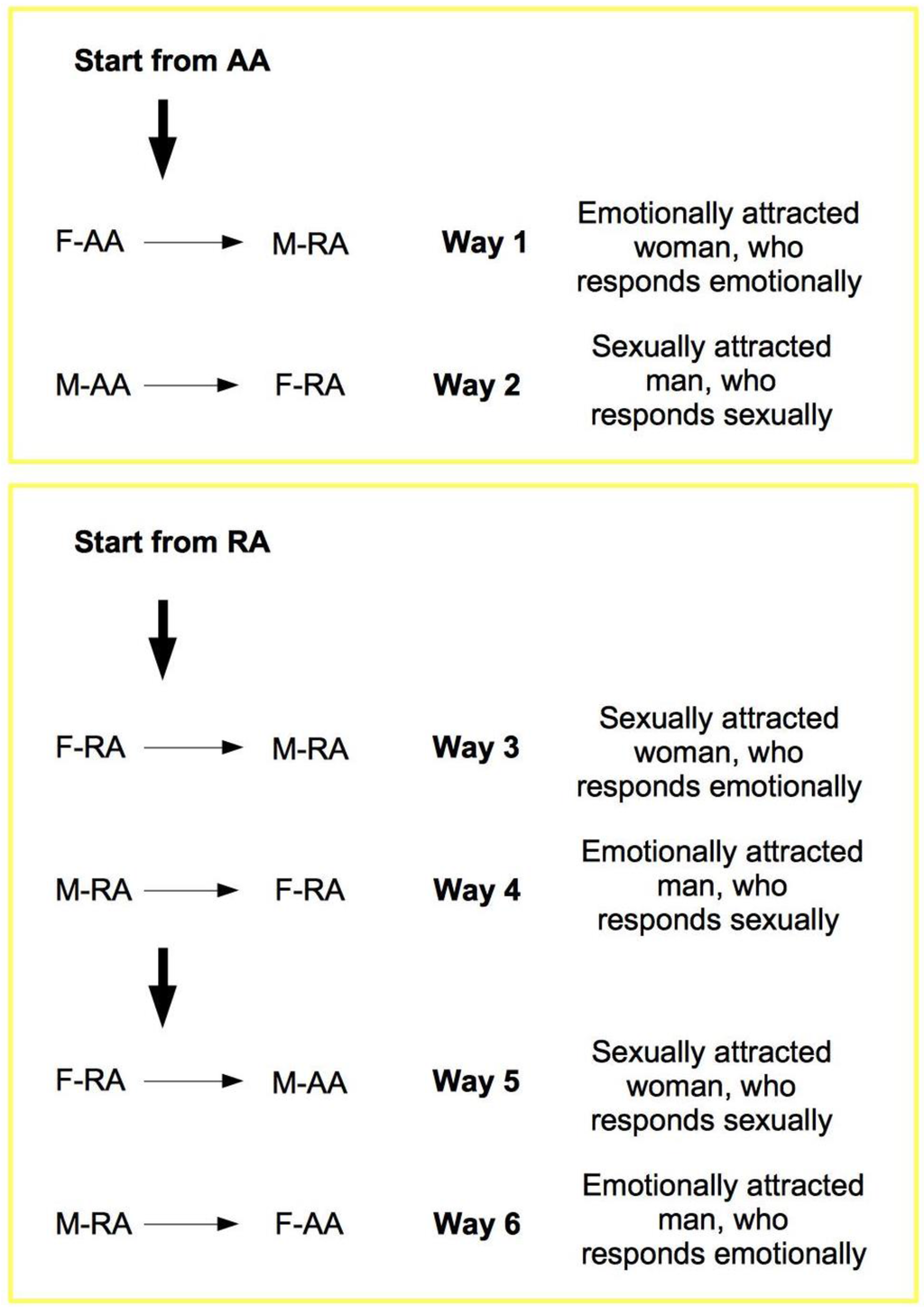
Figure 11.
Summary scheme for the six Ways.
4. TU-C and the Neuroscience of Mating
In this paper, we have presented the basic structure of the TU model from a purely behavioral point of view. A possible development of special interest is to explicitly connect it to recent findings from the neuroscience of mating. This is an endeavor that is mainly left for future research, but it is useful to give a few preliminary hints here.
An obvious relationship between the TU model and neuroscience is in terms of the neuro-endocrine activity involved in the administration of direct vs. indirect rewards. The role of oxytocin in pair bonding dynamics in the early phases of romantic relationships is, for example, well studied [128]. Oxytocin levels are not only high at the beginning of TU-C, but also remain high at a later stage in case the couple has successfully stabilized, whereas they drop if TU-C has been broken and the couple has split. In particular, oxytocin is linked to the couple’s interactive reciprocity independently of sex, relationship duration, and the partner’s oxytocin levels, which in our framework shows its role in the administration of rewards, both direct and indirect. The fact that high oxytocin levels are observed during female orgasm [129] moreover suggests a possible neuroendocrine basis to understand why sexual intercourse is a powerful route to F-TU. Likewise, cortisol levels clearly mark marital conflict situations linked to TU-C frustrations [130]. More generally, Pietromonaco et al. [131] show how attachment processes are regulated by the Hypotalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis in terms of stress responses, thus highlighting the existence of a specific neuroendocrine strategy for tackling attachment-related stressors.
Other typical markers are found in the initial phase of screening and selection of potential mates. Roney et al. [132] show how salivary testosterone of young males is differentially activated by brief encounters with females (i.e., potential mates), and that males’ testosterone levels, in particular, are high in the conditions where the female reported visible signs that the male was trying to impress her, and where the male reported a significant potential mating value of the female—in our framework, this suggests that the activity of M-AA is marked by high testosterone levels.
Diamond and Dickenson [133] carry out a neuroimaging analysis of emotional vs. sexual desire brain activation patterns showing how, on the one side, the two aspects are associated to different patterns of brain activation, although there are specific brain regions that remain active in both cases (caudate, putamen, insula, and anterior cingulated cortex), thus indicating the possibility that, whereas certain forms of romantic attachment and sexual desire are sharply separated and independent, other ones may be closely connected. This suggests differences in sexual desire for strangers vs. partners, as well as the possibility of more responsive vs. mechanical forms of sexual drive, and of more or less emotionally-driven forms of sexual drive—an evidence that relates interestingly to the different functions and connotations of sexual and/or emotional responses at different stages and in different phases of TU-C. As a consequence, the brain activation pattern of subjects is likely to be influenced by whether or not a TU has previously occurred at the moment a given sexual or emotional stimulation is being administered.
One aspect that has been not analyzed in the neuroscientific literature so far, and that could become an interesting line of research in the context of the TU model, is the endocrine pattern of biological vs. emotional testing of mates by F vs. M, respectively. If specific patterns of endocrine activation are found in Fs in the case of physical contact with potential M partners with high (subjective) mating value, and if, likewise, for Ms in the case of psychological involvement with potential F partners with high (subjective) mating value, this would help us understand better the exact nature of the test being carried out, its criteria, and success parameters.
Even from a small sample of studies, we therefore find ample room for possible research in this new, exciting interdisciplinary field. As the neuroscience of sexual and emotional response is at its early stages, we look forward to future findings that may help us better understand the deep endocrine nature of direct and indirect rewards, of the respective frustrations, and of their complex interactions.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have tried to provide a conceptual synthesis of part of the vast literature on mating by developing a framework in which the sexual and emotional components act in a dynamic, complementary way in determining mating behavior. Our approach generates implications that show many points of contact with the empirical evidence documented in the literature, but it is obvious that a substantially higher level of empirical check is needed to provide even a preliminary corroboration. Moreover, in many points our approach presents speculations that are to our knowledge lacking specific favorable or contrary evidence in existing studies and therefore call for further scrutiny. Our hope is to contribute to the formulation of interesting research questions that can stimulate significant empirical and experimental research.
Such research will likely be time and resource consuming and calls for a vast range of specialist competences. At this stage, we think, however, that a first level of testing of our approach can be carried out by following a relatively unconventional route, that is, by evaluating the structure and implications of our approach in the sphere of movie fiction. Although surprising at first sight, this choice has a clear rationale. There is today a growing stream of literature that is studying fiction as a sophisticated form of social cognition that allows the transmission of key knowledge about events and situations of which subjects could only have a limited direct experience (see e.g., [134]), and certainly mating is not just one area where this kind of “inherited” knowledge can be most useful for novices (and often also for more expert subjects), but also one that has historically stimulated an impressive amount of narrative effort, practically in any human culture.
In this perspective, of major meaning are these fictional narratives that have attracted an especially intense interest, i.e., that have met a significant success with audiences in that such interest can be regarded, at least in part, as a social validation of the relevance of that narrative for specific social learning purposes. In our case, we will therefore focus attention on that particular narrative universe that is Hollywood romantic movies—the productive sphere of fictional creations that has more than any other contributed to shape the global popular narrative on mating of today. In the second part of this paper, we will in particular discuss the methodological implications of this choice, and select a certain number of very successful romantic Hollywood movies that provide neat illustrations of the dynamics of the six Ways that are the main corollaries of our approach. By so doing, we will argue that the specific mating-related strategic interaction that we have described here is mirrored in a certain sphere of socially transmitted knowledge that has been strongly validated by very large movie audiences worldwide. This is not to be meant as an empirical corroboration of our approach, but as a preliminary test that can inspire, on the one side, specific empirical and experimental research and, on the other side, new fields of inter-disciplinary analysis and research that combine methods from social psychology, social sciences, and the humanities.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous referees of this journal for their useful comments and suggestions that greatly improved the paper. The usual disclaimer applies.
Author Contributions
Lorenza Lucchi Basili developed the theoretical framework and its graphical representation. Pier Luigi Sacco contributed to the framework’s conceptual development and placed it in the context of the existing literature. The paper has been jointly written.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Buss, D.M. Sex differences in human mate preferences: Evolutionary hypotheses tested in 37 cultures. Behav. Brain Sci. 1989, 12, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.P. Sociosexuality from Argentina to Zimbabwe: A 48-nation study of sex, culture and strategies of human mating. Behav. Brain Sci. 2005, 28, 247–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiling, H.; Buss, D.M. Women’s sexual strategies: The hidden dimension of extra-pair mating. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2000, 28, 929–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.P.; Shackelford, T.K.; Buss, D.M. Are men really more “oriented” toward short-term mating than women? A critical review of theory and research. Psychol. Evolut. Gend. 2001, 3, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D.M. The science of human mating strategies: An historical perspective. Psychol. Inq. 2013, 24, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D.M. The evolution of human intrasexual competition: Tactics of male attraction. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 54, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangestad, S.W.; Simpson, J.A. The evolution of human mating: Trade-offs and strategic pluralism. Behav. Brain Sci. 2000, 23, 573–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buss, D.M.; Schmitt, D.P. Sexual strategies theory: An evolutionary perspective on human mating. Psychol. Rev. 1993, 100, 204–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mischel, W.; Shoda, Y. A cognitive-affective system theory of personality: Reconceptualizing situations, dispositions, dynamics and invariance in personality structure. Psychol. Rev. 1995, 102, 246–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, H.H.; Thibaut, J.W. Interpersonal Relationships: A Theory of Interdependence; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and loss: Volume 1. In Attachment; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and loss: Volume 2. In Separation: Anxiety and Anger; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and Loss: Volume 3. Loss; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, D.M. Sexual strategies theory: Historical origins and current status. J. Sex. Res. 1998, 35, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietromonaco, P.R.; Feldman Barrett, L.; Powers, S.I. Adult attachment theory and affective reactivity and regulation. In Emotion Regulation in Couples and Families: Pathways to Dysfunction and Health; Snyder, D.K., Simpson, J.A., Hughes, J.N., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.A.; Winterheld, H.A. Person-by-situation perspectives on close relationships. In The Oxford Handbook of Personality and Social Psychology; Deaux, K., Snyder, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 493–516. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.A.; Belsky, J. Attachment theory within a modern evolutionary framework. In Handbook of Attachment, Second Edition: Theory, Research, and Clinical Applications; Cassidy, J., Shaver, P.R., Eds.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 131–157. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, D.M. Unmitigated agency and unmitigated communion: An analysis of the negative components of masculinity and femininity. Sex. Roles 1990, 22, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy-Beam, D.; Buss, D.M.; Pham, M.N.; Shackelford, T.K. How sexually dimorphic are human mate preferences? Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2015, 41, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackelford, T.K.; Schmitt, D.P.; Buss, D.M. Universal dimensions of human mate preferences. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2005, 39, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meston, C.M.; Buss, D.M. Why Humans have sex. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2007, 36, 477–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, H.S.; Hill, K.; Lancaster, J.; Hurtado, A.M. A theory of human life history evolution: Diet, intelligence, and longevity. Evolut. Anthropol. Issues News Rev. 2000, 9, 156–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrdy, S.B. Mother Nature: A History of Mothers, Infants, and Natural Selection; Pantheon Books: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Conroy-Beam, D.; Goetz, C.D.; Buss, D.M. Why do Humans form long-term mateships? An evolutionary game-theoretic model. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2015, 51, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford, T.K.; Buss, D.M. Marital satisfaction and spousal cost-infliction. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2000, 28, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, A.T.; Shackelford, T.K.; Weekes-Shackelford, V.A.; Euler, H.A.; Hoier, S.; Schmitt, D.P.; LaMunyon, C. Mate retention, semen displacement, and human sperm competition: A preliminary investigation of tactics to prevent and correct female infidelity. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2005, 38, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confer, J.C.; Perilloux, C.; Buss, D.M. More than just a pretty face: Men’s priority shifts toward bodily attractiveness in short-term versus long-term contexts. Evolut. Hum. Behav. 2010, 31, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.A.; Shackelford, T.K.; Goetz, A.T. Sexual arousal and the pursuit of attractive mating opportunities. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2011, 51, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.P.; Shackelford, T.K.; Duntley, J.; Tooke, W.; Buss, D.M. The desire for sexual variety as a key to understanding basic human mating strategies. Pers. Relatsh. 2001, 8, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A. The morning after the night before. Affective reactions to one-night stands among mated and unmated women and men. Hum. Nat. 2008, 19, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galperin, A.; Haselton, M.G.; Frederick, D.; Poore, J.; von Hippel, W.; Buss, D.M.; Gonzaga, G.C. Sexual regret: Evidence for evolved sex differences. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2013, 42, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.D.; Easton, J.A.; Lewis, D.M.G.; Buss, D.M. Sexual exploitability: Observable cues and their link to sexual attraction. Evolut. Hum. Behav. 2012, 33, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.M.G.; Easton, J.A.; Goetz, C.D.; Buss, D.M. Exploitative male mating strategies: Personality, mating orientation, and relationship status. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2012, 52, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, M.A.; Lalumiere, M.L.; Quinsey, V.L. Sex differences in intra-sex variations in human mating tactics: An evolutionary approach. Ethol. Sociobiol. 1995, 16, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonason, P.K.; Buss, D.M. Avoiding entangling commitments: Tactics for implementing a short-term mating strategy. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2012, 52, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.D.; Easton, J.A.; Meston, C.M. The allure of vulnerability: Advertising cues to exploitability as a signal of sexual accessibility. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2014, 64, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.D.; Easton, J.A.; Buss, D.M. Women’s perceptions of sexual exploitability cues and their link to sexual attractiveness. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2014, 43, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easton, J.A.; Confer, J.C.; Goetz, C.D.; Buss, D.M. Reproduction expediting: Sexual motivations, fantasies, and the ticking biological clock. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2010, 49, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perilloux, C.; Cloud, J.M.; Buss, D.M. Women’s physical attractiveness and short-term mating strategies. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2013, 54, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D.M.; Shackelford, T.K. Attractive women want it all: Good genes, economic investment, parenting proclivities, and emotional commitment. Evolut. Psychol. 2008, 6, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.A.; Shackelford, T.K.; Buss, D.M. Is variability in mate choice similar for intelligence and personality traits? Testing a hypothesis about the evolutionary genetics of personality. Intelligence 2012, 40, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botwin, M.D.; Buss, D.M.; Shackelford, T.K. Personality and mate preferences: Five factors in mate selection and marital satisfaction. J. Personal. 1997, 65, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Shengua, J.; Davis, H.M.; Peng, K.; Shao, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Mating strategies in Chinese culture: Female risk avoiding vs. male risk taking. Evolut. Hum. Behav. 2012, 33, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleske-Rechek, A.L.; Buss, D.M. Sexual strategies pursued and mate attraction tactics deployed. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2006, 40, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perilloux, C.; Easton, J.A.; Buss, D.M. The misperception of sexual interest. Psychol. Sci. 2012, 23, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.J.; Kirkpatrick, L.A. The structure and measurement of human mating strategies: Toward a multidimensional model of sociosexuality. Evolut. Hum. Behav. 2007, 28, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselton, M.G.; Buss, D.M.; Oubaid, V.; Angleitner, A. Sex, lies, and strategic interference: The psychology of deception between the sexes. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2005, 31, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselton, M.G.; Buss, D.M. The affective shift hypothesis: The functions of emotional changes following sexual intercourse. Pers. Relatsh. 2001, 8, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.E.; Buss, D.M. The mere presence of opposite-sex others on judgments of sexual and romantic desirability: Opposite effects for men and women. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2008, 34, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackelford, T.K.; Buss, D.M.; Bennett, K. Forgiveness or breakup: Sex differences in responses to a partner’s infidelity. Cogn. Emot. 2002, 16, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, D.A.; Fales, M.R. Upset over sexual versus emotional infidelity among gay. Lesbian, bisexual, and heterosexual adults. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2016, 45, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleske, A.L.; Buss, D.M. Can men and women be just friends? Pers. Relatsh. 2000, 7, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleske-Rechek, A.L.; Buss, D.M. Opposite-sex friendship: Sex differences and similarities in initiation, selection, and dissolution. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2001, 27, 1310–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.M.G.; Conroy-Beam, D.; Al-Shawaf, L.; Raja, A.; DeKay, T.; Buss, D.M. Friends with benefits: The evolved psychology of same- and opposite-sex friendship. Evolut. Psychol. 2011, 9, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.M.G.; Al-Shawaf, L.; Conroy-Beam, D.; Asao, K.; Buss, D.M. Friends with benefits II: Mating activation in opposite-sex friendships as a function of sociosexual orientation and relationship status. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2012, 53, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman Barrett L. Robin, L.; Pietromonaco, P.R.; Eyssell, K.M. Are women the ‘more emotional’ sex? Evidence from emotional experiences in social context. Cogn. Emot. 1998, 12, 555–578. [Google Scholar]
- Mikulincer, M.; Shaver, P.R. The attachment behavioral system in adulthood: Activation, psychodynamics, and interpersonal processes. In Advances in Experimental Social Psychology; Zanna, M., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 53–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hazan, C.; Shaver, P.R. Romantic love conceptualized as an attachment process. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1987, 52, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, M. Sex, attachment, and the development of reproductive strategies. Behav. Brain Sci. 2009, 32, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rholes, W.S.; Simpson, J.A.; Tran, S.S.; Martin, A.M., III; Friedman, M. Attachment and information seeking in romantic relationships. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2007, 33, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, N.L.; Ford, M.B.; Guichard, A.C.; Allard, L.M. Working models of attachment and attribution processes in intimate relationships. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2006, 32, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, G.J.O.; Simpson, J.A.; Thomas, G.; Giles, L. Ideals in intimate relationships. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1999, 76, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, G.J.O.; Simpson, J.A.; Thomas, G. Ideals, perceptions, and evaluations in early relationship development. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2000, 79, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, R.C.; Shaver, P.R. Adult romantic attachment: Theoretical developments, emerging controversies, and unanswered questions. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2000, 4, 132–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overall, N.C.; Simpson, J. Regulation processes in close relationships. In The Oxford Handbook of Close Relationships; Simpson, J., Campbell, L., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 427–451. [Google Scholar]
- Waldinger, R.J.; Schulz, M.S. Linking hearts and minds in couple interactions: Intentions, attributions, and overriding sentiments. J. Fam. Psychol. 2006, 20, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, L.; Simpson, J.A.; Boldry, J.G.; Rubin, H. Trust, variability in relationship evaluations, and relationship processes. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2010, 99, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overall, N.C.; Fletcher, G.J.O.; Simpson, J.A. Regulation processes in intimate relationships: The role of ideal standards. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2006, 91, 662–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fincham, F.D.; Beach, S.R.; Beaucom, D.H. Attribution processes in distressed and nondistressed couples: 4. Self-partner attribution differences. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1987, 52, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnelley, K.B.; Pietromonaco, P.R.; Jaffe, K. Attachment, caregiving, and relationship functioning in couples: Effects of self and partner. Pers. Relatsh. 1996, 3, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.A.; Collins, W.A.; Tran, S.S.; Haydon, K.C. Attachment and the experience and expression of emotions in romantic relationships: A developmental perspective. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2007, 92, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.A.; Winterheld, H.A.; Rholes, W.S.; Oriña, M.M. Working models of attachment and reactions to different forms of caregiving from romantic partners. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2007, 93, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, J.E.; Kuo, S.I.-C.; Steele, R.D.; Simpson, J.A.; Collins, W.A. Recovering from conflict in romantic relationships: A developmental perspective. Psychol. Sci. 2011, 22, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.A.; Overall, N.C. Partner buffering of attachment insecurity. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 23, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oriña, M.M.; Collins, W.A.; Simpson, J.A.; Salvatore, J.E.; Haydon, K.C.; Kim, J.S. Developmental and dyadic perspectives on commitment in adult romantic relationships. Psychol. Sci. 2011, 22, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulincer, M.; Florian, V.; Cowan, P.A.; Pape Cowan, C. Attachment security in couple relationships: A systemic model and its implications for family dynamics. Fam. Process. 2002, 41, 405–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydon, K.C.; Collins, W.A.; Salvatore, J.E.; Simpson, J.A.; Roisman, G.I. Shared and distinctive origins and correlates of adult attachment representations: The developmental organization of romantic functioning. Child. Dev. 2012, 83, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurenceau, J.P.; Rivera, L.; Shaffer, A.R.; Pietromonaco, P.R. Intimacy as an interpersonal process: Current status and future directions. In Handbook of Closeness and Intimacy; Mashek, D., Aron, A., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Laurenceau, J.P.; Feldman Barrett, L.; Pietromonaco, P.R. Intimacy as an interpersonal process: The importance of self-disclosure, partner disclosure, and perceived partner responsiveness in interpersonal exchanges. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1998, 74, 1238–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, H.T. Responsiveness: Affective interdependence in close relationships. In Mechanisms of Social Connection: From Brain to Group; Mikulincer, M., Shaver, P.R., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 255–271. [Google Scholar]
- Downey, G.; Freitas, A.L.; Michaelis, B.; Khouri, H. The self-fulfilling prophecy in close relationships: Rejection sensitivity and rejection by romantic partners. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1998, 75, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overall, N.C.; Fletcher, G.J.O.; Simpson, J.A.; Fillo, J. Attachment insecurity, biased perceptions of romantic partners’ negative emotions, and hostile relationship behavior. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2015, 108, 730–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterheld, H.A.; Simpson, J.A. Seeking security of growth: A regulatory focus perspective on motivations in romantic relationships. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2011, 101, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shallcross, S.L.; Simpson, J.A. Trust and responsiveness in strain-test situations: A dyadic perspective. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 102, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.A.; Rholes, W.S. Adult attachment orientations, stress, and romantic relationships. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 45, 279–328. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.A.; Oriña, M.M.; Ickes, W. When accuracy hurts, and when it helps: A test of the empathic accuracy model in marital interactions. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 85, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Schulz, M.S.; Weiss, E.; Waldinger, R.J. Eye of the beholder: The individual and dyadic contributions of empathic accuracy and perceived emphatic effort to relationship satisfaction. J. Fam. Psychol. 2012, 26, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, L.; Simpson, J.A.; Boldry, J.; Kashy, D.A. Perceptions of conflict and support in romantic relationships: The role of attachment anxiety. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2005, 88, 510–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girme, Y.U.; Overall, N.C.; Simpson, J.A.; Fletcher, G.J.O. “All or nothing”: Attachment avoidance and the curvilinear effects of partner support. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2015, 108, 450–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overall, N.C.; Simpson, J.A.; Struthers, H. Buffering attachment-related avoidance: Softening emotional and behavioral defenses during conflict discussions. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 104, 854–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, L.A.; Davis, K.E. Attachment style, gender, and relationship stability: A longitudinal analysis. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1994, 66, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietromonaco, P.R.; Carnelley, K.B. Gender and working models of attachment: Consequences for perceptions of self and romantic relationships. Pers. Relatsh. 1994, 1, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzworth Munroe, A.; Jacobson, N.S. Causal attributions of married couples: When do they search for causes? What do they conclude when they do? J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1985, 48, 1398–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overall, N.C.; Fletcher, G.J.O.; Simpson, J.A.; Sibley, C.G. Regulating partners in intimate relationships: The costs and benefits of different communication strategies. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 96, 620–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, S.S.; Simpson, J.A. Prorelationship maintenance behaviors: The joint roles of attachment and commitment. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 97, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impett, E.A.; Peplau, L.A. Sexual compliance: Gender, motivational, and relationship perspectives. J. Sex. Res. 2003, 40, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachner, D.A.; Shaver, P.R. Attachment dimensions and sexual motives. Pers. Relatsh. 2004, 11, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanou, C.; McCabe, M.P. Adult attachment and sexual functioning: A review of past research. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 2499–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, J.D.; Baldwin, J.I. Gender differences in sexual interest. Arch. Sex. Behav. 1997, 26, 181–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, J. The endocrinology of sexual arousal. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 186, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denney, N.W.; Field, J.K.; Quadagno, D. Sex differences in sexual needs and desires. Arch. Sex. Behav. 1984, 13, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esch, T.; Stefano, G.B. The neurobiology of love. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2005, 26, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalmbach, D.A.; Pillai, V. Daily affect and female sexual function. J. Sex. Med. 2014, 11, 2938–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewitte, M. Gender differences in liking and wanting sex: Examining the role of motivational context and implicit versus explicit processing. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2015, 44, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.E.; O’Sullivan, L.F. Gender differences in associations of sexual and romantic stimuli: Do young men really prefer sex over romance? Arch. Sex. Behav. 2012, 41, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geer, J.H. Gender differences in the organization of sexual information. Arch. Sex. Behav. 1996, 25, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, H.A.; Eichstaedt, J.C.; Kern, M.L.; Dziurzynski, L.; Ramones, S.M.; Agrawal, M.; Shah, A.; Kosinski, M.; Stillwell, D.; Seligman, M.E.P.; et al. Personality, gender, and age in the language of social media: The open-vocabulary approach. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, C.M. The use of magnetic resonance imaging for studying female sexual function: A review. Clin. Anat. 2015, 28, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillath, O.; Collins, T. Unconscious desire: The affective and motivational aspects of subliminal sexual priming. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, C.A.; Sanders, S.A.; Milhausen, R.R.; McBride, K.R. Turning on and turning off: A focus group study of the factors that affect women’s sexual arousal. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2004, 33, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, K.R.; Ahrold, T.K.; Meston, C.M. The association between sexual motives and sexual satisfaction: Gender differences and categorical comparisons. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2011, 40, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Place, S.S.; Todd, P.M.; Zhuang, J.; Penke, L.; Asendorpf, J.B. Judging romantic interest of others from thin slices is a cross-cultural ability. Evolut. Hum. Behav. 2012, 33, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.A.; Xing, C.; Brooks, S. Accurately detecting flirting. Error management theory, the traditional sexual script, and flirting base rate. Commun. Res. 2015, 42, 939–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugill, N.; Fink, B.; Neave, N. The role of human body movements in mate selection. Evolut. Psychol. 2010, 8, 66–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geer, J.H.; Robertson, G.G. Implicit attitudes in sexuality: Gender differences. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2005, 34, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowski, A.M.; Hecht, H. Gender differences and similarities in receptivity to sexual invitations: Effects of location and risk perception. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2015, 44, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Graaf, H.; Sandfort, T.G.M. Gender differences in affective responses to sexual rejection. Arch. Sex. Behav. 2004, 33, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, W. Behavioral theories and the neurophysiology of reward. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2006, 57, 87–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendixen, M.; Ottesen Kennair, L.E.; Buss, D.M. Jealousy: Evidence of strong sex differences using both forced choice and continuous measure paradigms. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2015, 86, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonason, P.K.; Kavanagh, P. The dark side of love: Love styles and the dark triad. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2010, 49, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufner, M.; Rauthmann, J.F.; Czarna, A.Z.; Denissen, J.J.A. Are narcissist sexy? Zeroing in on the effect of narcissism on short-term mate appeal. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2013, 39, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzman, N.S.; Strube, N.J. People with dark personalities tend to create a physically attractive veneer. Soc. Psychol. Personal. Sci. 2012, 4, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.D.; Shrira, I.; Campbell, W.K. Theoretical models of narcissism, sexuality, and relationship commitment. J. Soc. Pers. Relatsh. 2006, 23, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chentsova-Dutton, Y.E.; Tsai, J.L. Gender differences in emotional response among European Americans and Hmong Americans. Cogn. Emot. 2007, 21, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzer, A.; Frey, B.S. Does marriage make people happy, or do happy people get married? J. Socio-Econ. 2006, 35, 326–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmusen, E. Games and Information; Blackwell: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Calvert, C. Revenge porn and freedom of expression: Legislative pushback to an online weapon of emotional and reputational destruction. Fordham Intell. Prop. Media Entertain. Law J. 2015, 24, 673–702. [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman, I.; Zagoory-Sharon, O.; Leckman, J.F.; Feldman, R. Oxytocin during the initial stages of romantic attachment: Relations to couples’ interactive reciprocity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magon, N.; Kalra, S. The orgasmic history of oxytocin: Love, lust and labor. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 15, S156–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, L.A.; Pietromonaco, P.R.; DeBuse, C.J.; Powers, S.I.; Sayer, A.G. Spouses’ attachment pairings predict neuroendocrine, behavioral, and psychological responses to marital conflict. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 105, 388–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietromonaco, P.R.; DeBuse, C.J.; Powers, S.I. Does attachment get under the skin? Adult romantic attachment and cortisol responses to stress. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 22, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roney, J.R.; Mahler, S.V.; Maestripieri, D. Behavioral and hormonal responses of men to brief interactions with women. Evolut. Hum. Behav. 2003, 24, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.M.; Dickenson, J.A. The neuroimaging of love and desire: Review and future directions. Clin. Neuropsychiatr. 2012, 9, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, B. On the Origin of Stories, Evolution, Cognition, and Fiction; Belknap Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).