Potential for Reuse of E-Plastics through Processing by Compression Molding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. E-Waste
- (1)
- metals-containing wastes (e-metals), and
- (2)
- plastics (e-plastics).
1.2. E-Plastics
1.3. Analysis of E-Plastics
1.4. E-Plastics Processing
1.5. Project Background
- Investigate the feasibility of using e-plastics for compression molding instead of disposal;
- Obtain information on the FR and metals content from samples of e-plastics used for compression molding testing;
- Identify and if possible test, lower cost, simpler, and more portable analytical methods for FR concentration in e-plastics
2. Results
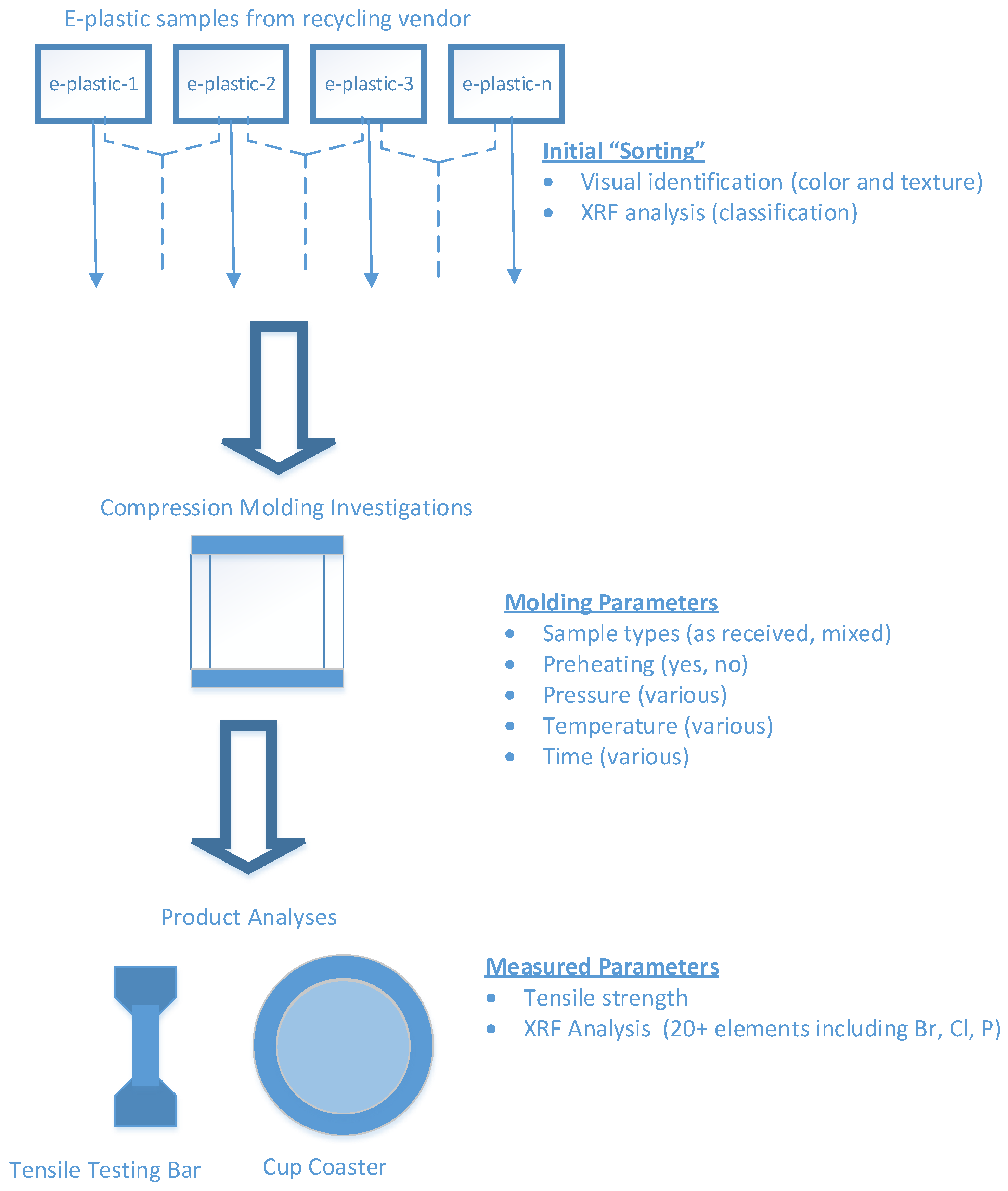
2.1. Compression Molding of Some Sample E-Plastics
2.2. Preliminary Screening Analysis
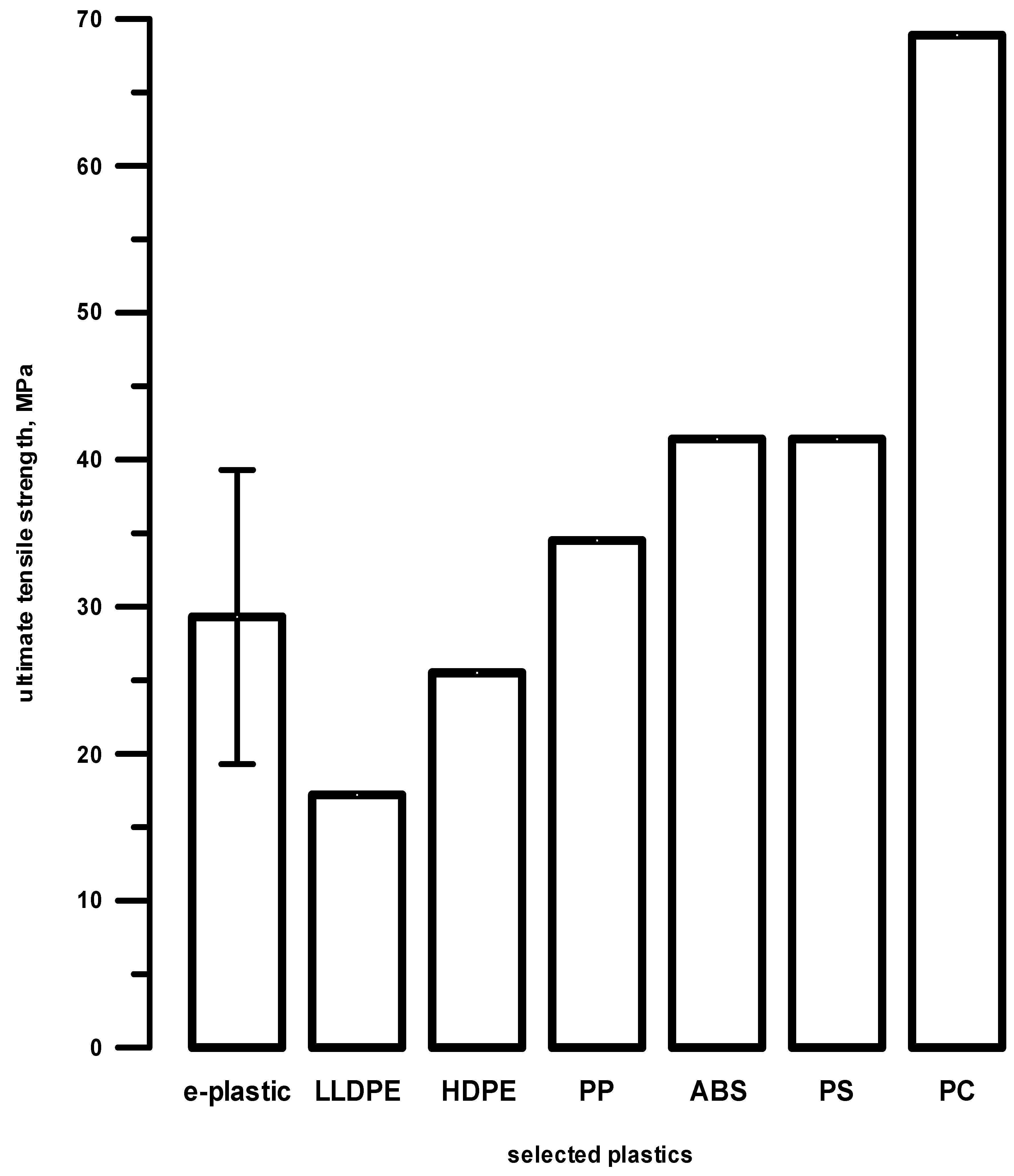
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compression Molding
4.2. Hand-Held XRF Analysis
5. Future Research and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABS | acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
| BFR | Brominated flame retardante-wa(s) |
| DOE | Design of Experiments |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| e-metals | Metals derived from e-waste |
| e-plastics | Plastics derived from e-waste |
| EU | European Union |
| e-waste | Electronic waste (e-waste), see also WEE |
| EHS | Environmental and Health and Safety |
| FR | Flame retardant(s) |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| HDPE | high-density polyethylene |
| HIPS | high impact polystyrene |
| HHEs | NIOSH Health Hazard Evaluations |
| HRGCxGC-TOFMS | Two-dimensional high-resolution gas, tomography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| IBA | ion beam analysis, see also IBS |
| IBS | ion beam spectrometry, see also IBA |
| ICP-MS | Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry |
| ICP-OES | inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| LLDPE | linear low-density polyethylene |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| NDIR | non-dispersive infrared spectroscopy |
| NIOSH | National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health |
| NIU | Northern Illinois University |
| OPFR | Organophosphorus flame retardant(s) |
| PBDE | polybrominated diphenyl ethers |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PVC | Polyvinylchloride |
| TD-GC-MS | Thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| TD-HRGC-TOFMS | Thermal desorption-high-resolution gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| US | United States |
| USEPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| UTS | Ultimate tensile strength |
| WEEE | Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment |
| XRF | X-ray fluorescence |
References
- Kang, H.Y.; Schoenung, J.M. Electronic waste recycling: A review of US infrastructure and technology options. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2005, 45, 368–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.R.; Forssberg, E. Mechanical recycling of waste electric and electronic equipment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 99, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElectronicsTakebackCoalition. Facts and Figures on E-Waste and Recycling. Available online: http://www.electronicstakeback.com/wp-content/uploads/Facts_and_Figures_on_EWaste_and_Recycling.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2014).
- Buekens, A.; Yang, J. Recycling of WEEE plastics: A review. J. Mater. Cycl. Waste Manag. 2014, 16, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations University. 2008 Review of EU Directive on Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) —Final Report. 2007. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/weee/pdf/final_rep_unu.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- USEPA. Statistics on the Management of Used and End-of-Life Electronics. 2012. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/osw/conserve/materials/ecycling/manage.htm (accessed on 19 October 2014). [Google Scholar]
- ILEPA. Electronic Waste Recycling: Public Act 97-0287—Electronic Products Recycling & Reuse Act. Available online: http://www.epa.state.il.us/land/electronic-waste-recycling/ (accessed on 19 October 2014).
- Wang, R.X.; Xu, Z.M. Recycling of non-metallic fractions from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE): A review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1455–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schut, J.H. Recycling E-Plastics New Material Stream Brings its Own Set of Problems. Available online: http://www.ptonline.com/articles/recycling-e-plastics-new-material-stream-brings-its-own-set-of-problems (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philosoph. Transac. Royal Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.T.; Buranakarn, V. Emergy indices and ratios for sustainable material cycles and recycle options. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 38, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlummer, M.; Gruber, L.; Maurer, A.; Wolz, G.; van Eldik, R. Characterisation of polymer fractions from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) and implications for waste management. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1866–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wäger, P.; Boni, H.; Buser, A.; Morf, L.; Schluep, M.; Streicher, M. Recycling of Plastics from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)—Tentative Results of a Swiss Study. 2009. Available online: http://ewasteguide.info/files/Waeger_2009_R%2709.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- USEPA. High Speed Plastic Recycling. 2010. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-06/documents/nrt.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, D.W. How well are we handling electronic-waste? In Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Network and Optical Communications, Vilanova i la Geltru, Spain, 20–22 June 2012.
- Deng, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J.H.; Li, H.F. A Mini-review on disposal of WEEE plastics containing PBDEs with a special focus on China. In Selected Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Waste Management and Technology; Li, J., Hu, H., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 600–608. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.N.; Sun, L.S.; Xiang, J.; Hu, S.; Su, S. Pyrolysis and dehalogenation of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE): A review. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tue, N.M.; Takahashi, S.; Subramanian, A.; Sakai, S.; Tanabe, S. Environmental contamination and human exposure to dioxin-related compounds in e-waste recycling sites of developing countries. Environ. Sci. Proc. Impact. 2013, 15, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, S.D.; Berger, M.L.; Harris, J.H.; Yun, S.H.; Wu, Q.; Liao, C.; Blum, A.; Stefani, A.; Kannan, K. Persistent organic pollutants including polychlorinated and polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in firefighters from northern California. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nnorom, I.C.; Osibanjo, O. Sound management of brominated flame retarded (BFR) plastics from electronic wastes: State of the art and options in Nigeria. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2008, 52, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sthiannopkao, S.; Wong, M.H. Handling e-waste in developed and developing countries: Initiatives, practices, and consequences. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodder, N.G.; Strandberg, B.; Hites, R.A. Concentrations and spatial variations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and several organochlorine compounds in fishes from the northeastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, A.; Isobe, T.; Ramu, T.; Tue, N.M.; Sudaryanto, A.; Davanathan, G.; Viet, P.H.; Tana, R.S.; Takahashi, S.; Subramanian, A.; et al. Soil contamination by brominated flame retardants in open waste dumping sites in Asian developing countries. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, A.; Nomiyama, K.; Devanathan, G.; Subramanian, A.; Bulbule, K.A.; Parthasarathy, P.; Takahashi, S.; Tanabe, S. Different profiles of anthropogenic and naturally produced organohalogen compounds in serum from residents living near a coastal area and e-waste recycling workers in India. Environ. Int. 2012, 47, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos, D.; Gong, W.; Page, E. Health Hazard Evaluation Report: A Pilot Assessment of Occupational Health Hazards in the U.S. Electronic Waste Recycling Industry. 2014. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/hhe/reports/pdfs/2012-0100-3217.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos, D.; Chen, L.; Page, E.; Echt, A.; Oza, A.; Ramsey, J. Health Hazard Evaluation Report: Evaluation of Occupational Exposures at an Electronic Scrap Recycling Facility. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2014. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/hhe/reports/pdfs/e-scrap_survey_report.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.M.; Yolton, K.; Rauch, S.A.; Webster, G.M.; Hornung, R.; Sjodin, A.; Dietrich, K.N.; Lanphear, B.P. Prenatal polybrominated diphenyl ether exposures and neurodevelopment in U.S. children through 5 years of age: The HOME study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjodin, A.; Hagmar, L.; Klasson-Wehler, E.; Kronholm-Diab, K.; Jokobsson, E.; Bergman, A. Flame retardant exposure: Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in blood from Swedish workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osibanjo, O.; Nnorom, I.C.; Ogbonna, K.C. Modelling waste generation by the telecom sector in Nigeria: The grey side of the impressive outing. Waste Manag. Res. 2008, 26, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osibanjo, O.; Nnorom, I.C. Material flows of mobile phones and accessories in Nigeria: Environmental implications and sound end-of-life management options. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2008, 28, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needhidasan, S.; Samuel, M.; Chidambaram, R. Electronic waste—An emerging threat to the environment of urban India. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BFR 2014 Submitted Abstracts. 2014. Available online: http://www.bfr2014.indiana.edu/All%20Abstracts.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2014).
- Zhang, W.H.; Wu, Y.X.; Simonnot, M.O. Soil contamination due to e-waste disposal and recycling activities: A review with special focus on China. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 434–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V. Evaluating overall quality of recycling of e-waste from end-of-life computers. J. Clean. Produc. 2012, 20, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, P.A.; Schluep, M.; Muller, E.; Gloor, R. RoHS regulated substances in mixed plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wäger, P.; Schluep, M.; Müller, E. RoHS Substances in Mixed Plastics from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment. 2010. Available online: http://ewasteguide.info/files/Waeger_2010_Empa-WEEEForum.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Characterization and Failure Analysis of PLASTICS; Lampman, S. (Ed.) ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2003.
- Portoles, T.; Sales, C.; Gomara, B.; Sancho, J.V.; Beltran, J.; Herrero, L.; Gonzalez, M.J.; Hernandez, F. Novel analytical approach for brominated flame retardants based on the use of gas chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-tandem mass spectrometry with emphasis in highly brominated congeners. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9892–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsonek, J.; Puype, F. Occurrence of brominated flame retardants in black thermo cups and selected kitchen utensils purchased on the European market. Food Add. Contam. A Chem. Anal. Control Exposure Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Veen, I.; de Boer, J. Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1119–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, W.J.; Williams, P.T. Analysis of products from the pyrolysis of plastics recovered from the commercial scale recycling of waste electrical and electronic equipment. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2007, 79, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajka, T.; Hajslova, J.; Kazda, R.; Poustka, J. Challenges of gas chromatography-high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry for simultaneous analysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and other halogenated persistent organic pollutants in environmental samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2005, 28, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, E.K.; Fromme, H.; Volkel, W. Analysis of common and emerging brominated flame retardants in house dust using ultrasonic assisted solvent extraction and on-line sample preparation via column switching with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1241, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.N.; Reiner, E.J.; Marvin, C.; Helm, P.; Riddell, N.; Dorman, F.; Misselwitz, M.; Shen, L.; Crozier, P.; Macpherson, K.; et al. Development of liquid chromatography atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of halogenated flame retardants in wastewater. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilaplana, F.; Karlsson, P.; Ribers-Greus, A.; Ivarsson, P.; Karlsson, S. Analysis of brominated flame retardants in styrenic polymers—Comparison of the extraction efficiency of ultrasonication, microwave-assisted extraction and pressurised liquid extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1196, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debrauwer, L.; Riu, A.; Jouahri, M.; Rathahao, E.; Jouanin, I.; Antignac, J.P.; Cariou, R.; Le Bize, B.; Zalko, D. Probing new approaches using atmospheric pressure photo ionization for the analysis of brominated flame retardants and their related degradation products by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1082, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Forssberg, E. Characterization of shredded television scrap and implications for materials recovery. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrian, A.; Ledersteger, A.; Pomberger, R. Monitoring of WEEE plastics in regards to brominated flame retardants using handheld XRF. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallen, C.; Banks, A.; Brandsma, S.; Baduel, C.; Thai, P.; Eaglesham, G.; Heffernan, A.; Leonards, P.; Bainton, P.; Mueller, J.F. Towards development of a rapid and effective non-destructive testing strategy to identify brominated flame retardants in the plastics of consumer products. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 491, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taurino, R.; Cannio, M.; Mafredini, T.; Pozzi, P. An efficient and fast analytical procedure for the bromine determination in waste electrical and electronic equipment plastics. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 3147–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peaslee, G.F. Methods for Identification of Flame Retardants in Polyurethane Foam. Available online: http://www.pfa.org/abstracts/abmay13.html (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Peaslee, G.F.; DeYoung, P.A. An Undergraduate Ion Beam Analysis Laboratory in International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Research Applications and Utilization of Accelerators. 2009. Available online: http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/P1433_CD/datasets/papers/sm_ae-02.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Lazarov, B.; Swinnen, R.; Spruyt, M.; Maes, F.; Van Campenhout, K.; Goelen, E.; Covaci, A.; Strager, M. Air sampling of flame retardants based on the use of mixed-bed sorption tubes-a validation study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18221–18229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JEOL. Analysis of Additives in Plastic by Thermal Desorption (TD) GC-TOFMS—Accurate Mass Measurement and Isotope Pattern Matching. MS-Tips 2009. Available online: http://www.jeol.co.jp/en/applications/pdf/ms/mstips138e.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2014).
- Hosaka, A.; Watanabe, C.; Tsuge, S. Rapid determination of decabromodiphenyl ether in polystyrene by thermal desorption-GC/MS. Anal. Sci. 2005, 21, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatara, R. Compression molding. In Applied Plalstics Engineering Handbook; Kutz, M., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Athalya, A.S. Plastic Materials Handbook; Multi Tech Publishing Co.: Bombay, India, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.; Kumar, V. Polymer Systems and Applications; Stadium Press (India) Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- OTA. Chapter 7 Case Study: Polymer Matrix Composites in Automobiles, in Advanced Materials by Design; Office of Technology Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Malnat, P. Inside Manufacturing: A Reinforced Thermoplastic Car Hood? Available online: http://www.compositesworld.com/articles/inside-manufacturing-a-reinforced-thermoplastic-car-hood (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Lakshmi, R.; Nagan, S. Utilization of waste E plastic particles in cementitious mixtures. J. Struct. Eng. 2011, 38, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.C.; Alston, S.; Holder, A. Void formation due to gas evolution during the recycling of Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene copolymer (ABS) from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Polymer Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balart, R.; Lopez, J.; Garcia, D.; Salvador, M.D. Recycling of ABS and PC from electrical and electronic waste. Effect of miscibility and previous degradation on final performance of industrial blends. Eur. Polymer J. 2005, 41, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, D.; Dayanidhi, S.A.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of recycled polycarbonate/recycled poly(acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene) blend nanocomposites. Polymer Comp. 2012, 33, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.B. Plastics: Materials and Processing; Pearson Education, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, W.; Tracy, A.; Cline-Thomas, A. Integrated application of field screening: A case study. In Proceedings of 3rd International Symposium on Field Screening Methods for Hazardous Wastes and Toxic Chemicals, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1993.
- Carver Bench Top Standard Auto Series Model Presses. Available online: http://www.carverpress.com/benchtop_auto_standard.html (accessed on 24 April 2016).
- ASTM. Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. 2014. Available online: http://www.astm.org/Standards/D638.htm (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Lloyd Instruments EZ Series EZ50 50 kN Universal Materials Testing Machine. 2007. Available online: http://www.jlwinstruments.com/index.php/products/products-library/ez50-50-kn-universal-materials-testing-machine-ez-series/ (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Olympus. Delta Professional XRF Analyzers. Available online: http://www.olympus-ims.com/vi/xrf-xrd/delta-handheld/delta-prof/ (accessed on 21 February 2016).
- Coleman, K.; Olympus USA, Center Valley, PA, USA; Mills, W.; INorthern Illinois University, DeKalb, IL, USA. Personal communication, 2015.
- EU. Restriction of Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment. 2002. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/rohs_eee/legis_en.htm (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- ThermoFisher. Handheld XRF. 2014. Available online: http://www.thermoscientific.com/content/tfs/en/products/handheld-xrf.html (accessed on 19 October 2014).
- Maley, A.M.; Falk, K.A.; Hoover, L.; Earlywine, E.B.; Seymour, M.D.; DeYoung, P.A.; Blum, A.; Stapleton, H.M.; Peaslee, G.F. Detection of halogenated flame retardants in polyurethane foam by particle induced X-ray emission. Nuclear Instr. Method. Phys. Res. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atom. 2015, 358, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SGS. Ultratrace. 2014. Available online: http://www.sgsgroup.us.com/en/Environment/Soil/Laboratory-Analysis/Specialty-Analyses/Ultratrace.aspx (accessed on 19 October 2014).


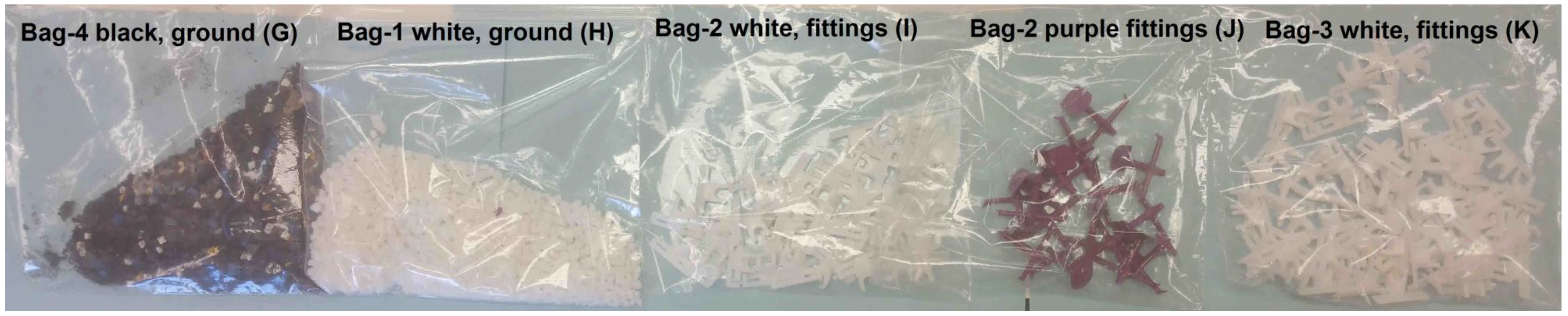
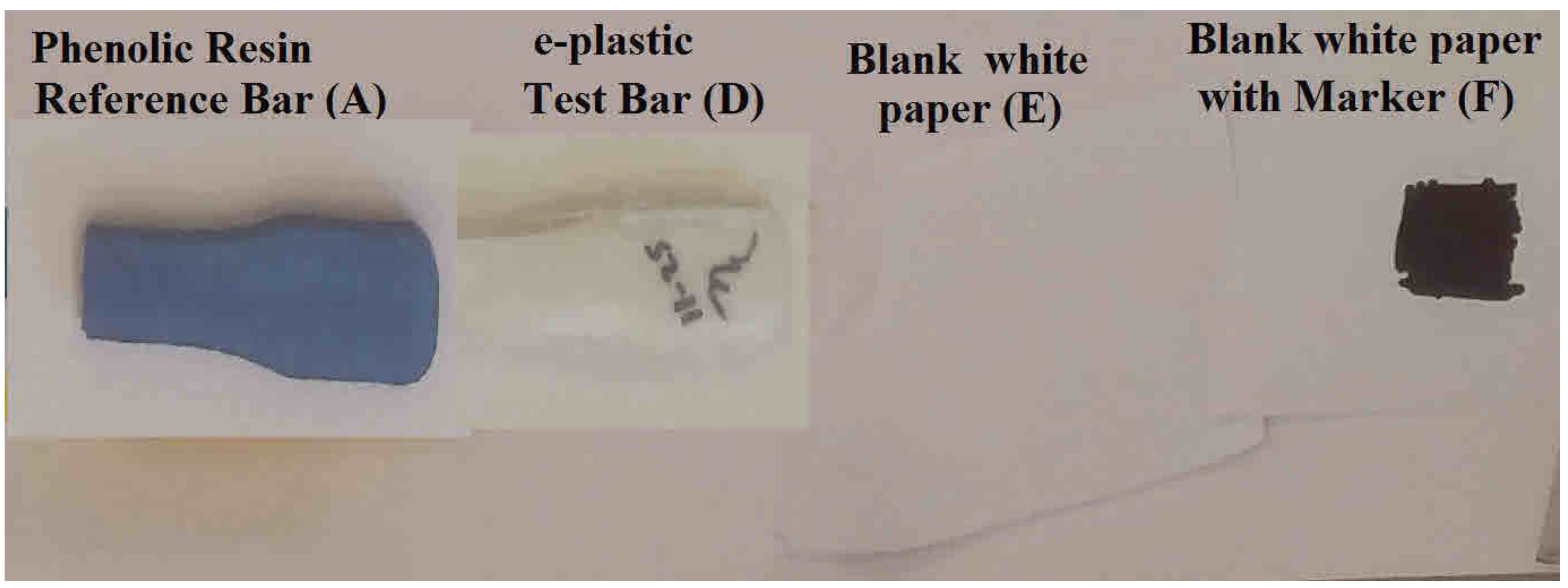
| Material Source | Letter ID (Figure 5 & Figure 6) | Elapsed Time Total | Br | Cl | P | Hg | Pb | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic Resin—Reference Bar | A | 44.13 | 399 | <LOD 1 | <LOD | 9 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 961 | |
| Phenolic Resin—Reference Bar | A | 44.12 | 420 | <LOD | <LOD | 6 | 11 | <LOD | <LOD | 983 | |
| e-Plastic Test Bar | B (no photo) | 44.68 | 208 | <LOD | <LOD | 9 | 11 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Phenolic Resin (powder) | C (no photo) | 44.13 | 43 | 69 | <LOD | <LOD | 36 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 2600 |
| e-Plastic—Test Bar | D | 43.57 | 547,244 | 43 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 170 |
| e-Plastic—Test Bar | D | 43.65 | 545,085 | 36 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 143 |
| Blank white paper | E | 45.06 | <LOD | 1705 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 382 | <LOD | <LOD | 324 |
| Blank white paper with Black Marker | F | 44.97 | <LOD | 4292 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 575 | 2641 | <LOD | <LOD |
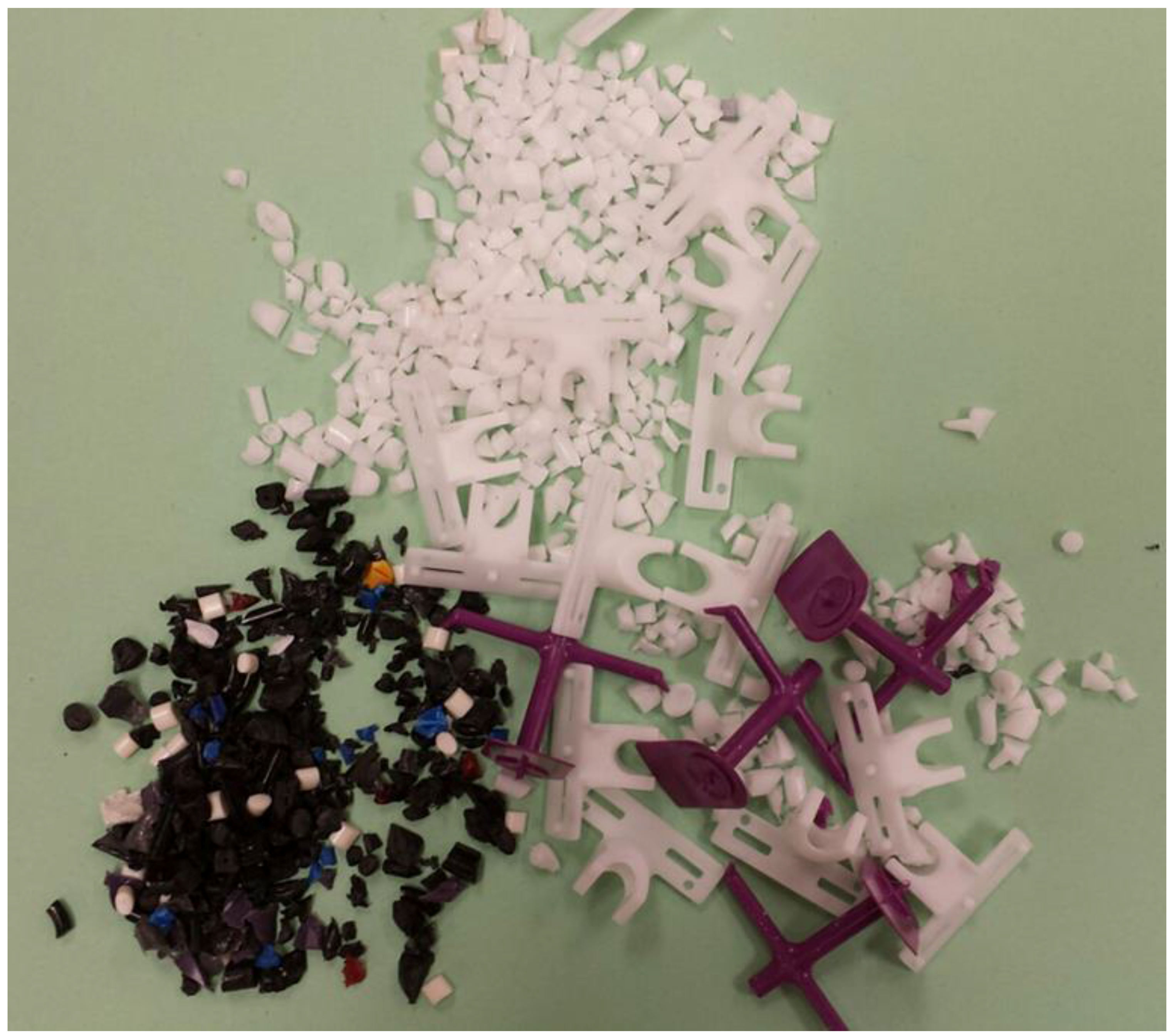
| Black e-plastic, ground up (Bag-4) | G | 43.56 | 77,904 | 532 | <LOD | <LOD | 259 | 134 | <LOD | <LOD | 484 |
| White e-Plastic, ground up (Bag-1) | H | 43.71 | 2560 | 11 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| White e-Plastic , fittings (Bag-2) | I | 44.56 | 44 | 25 | <LOD | <LOD | 37 | 65 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Purple e-Plastic , fittings (Bag-3) | J | 44.42 | 50 | 63 | <LOD | <LOD | 30 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| White e-Plastic , fittings (Bag-3) | K | 44.18 | 44 | 15 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
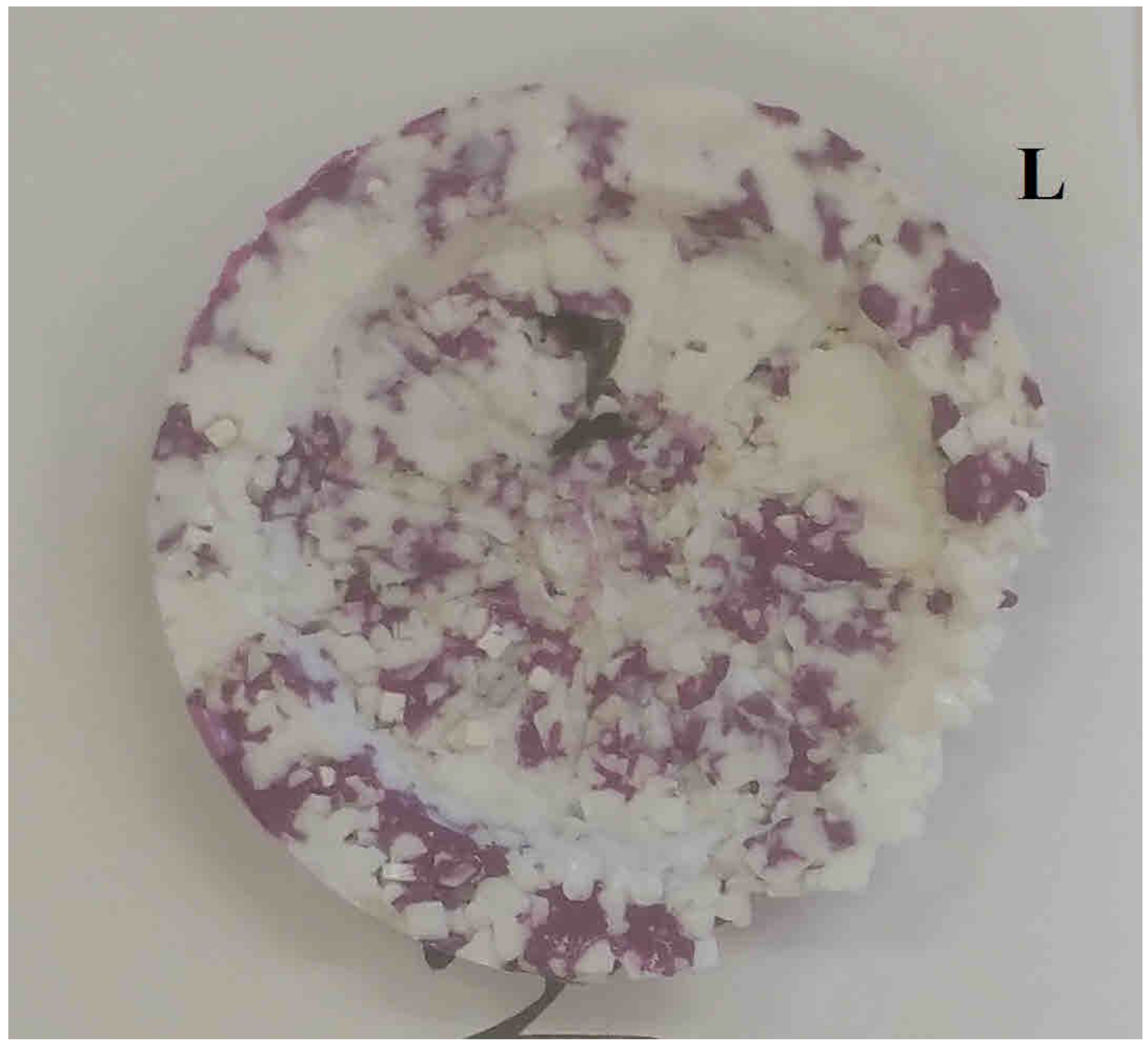
| Purple/White e-Plastic, compression mold test | L | 43.77 | 526 | 21 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| Purple/White e-Plastic, Test Bar | M (no photo) | 44.38 | 77 | 19 | <LOD | <LOD | 30 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| White e-Plastic Test Bar (repeat) | D | 44.28 | 118,564 | 34 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 28 |
| Br | Cl | P | Hg | Pb | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | 43 | 11 | LOD | LOD | 5.6 | 9.7 | 2641 | LOD | 28 |
| max | 547,244 | 4292 | LOD | LOD | 259 | 575 | 2641 | LOD | 2600 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mills, W.; Tatara, R.A. Potential for Reuse of E-Plastics through Processing by Compression Molding. Challenges 2016, 7, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe7010013
Mills W, Tatara RA. Potential for Reuse of E-Plastics through Processing by Compression Molding. Challenges. 2016; 7(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe7010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMills, William, and Robert A. Tatara. 2016. "Potential for Reuse of E-Plastics through Processing by Compression Molding" Challenges 7, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe7010013
APA StyleMills, W., & Tatara, R. A. (2016). Potential for Reuse of E-Plastics through Processing by Compression Molding. Challenges, 7(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe7010013