Abstract
Observations of water level, current velocity, river discharge, wind and salinity were collected in the Maroni estuary, on the border of French Guiana and Suriname during the wet season of 2018 to explore subtidal circulation patterns. Measurements are complimented by the application of analytical models with an aim to diagnose forcing mechanisms responsible for producing subtidal flows during the day of data collection and to extrapolate these findings to other time periods with variable wind and river forcing. Subtidal along-channel flows were found to be dominated by river discharge, with seaward directed velocities found throughout the channel section reaching 40 cm s. This pattern was altered with strong southwesterly winds, which produced and inverse gravitational circulation pattern despite the elevated river discharge. Secondary, or cross-channel flows, displayed a three-layer vertical structure in the main channel due to a combination of channel curvature and tidal asymmetry in the lateral baroclinic pressure gradient. The pressure gradient was produced by a salinity intrusion front that only manifested in the channel during flood tide. This is the first comprehensive study of tidal and subtidal flow dynamics in the Maroni estuary.
1. Introduction
Subtidal circulation, or the flow that remains after tidal currents have been removed, is responsible for the transport and fate of sediments, pollutants, larvae, and all other water-borne materials in estuaries. Some of the major components contributing to subtidal flow generation are density gradients, river discharge, wind velocities and bathymetric and topographic changes in estuary shape [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Classically, estuarine circulation has been attributed to gravitational circulation which results from along-channel density gradients and subsequently produces a two layer flow structure with inflow at depth and outflow near the surface [2]. In estuaries that experience high river-inflow the ebb phase of the tide can be longer than the flood and the salinity intrusion length limited, resulting in tidally averaged, or subtidal flows, that are directed out-estuary over the entire estuarine cross-section. However, in tropical estuaries that are known to experience persistent wind influence, the subtidal outflow could be augmented or opposed.
The Northern coast of South America, including French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana and Venezuela experience persistent southwesterly winds that are therefore blowing directly on-shore and thus, up-estuary [7]. This could be an important (yet unexplored) feature of this region in terms of estuarine dynamics since studies have found that onshore winds can reduce or even reverse estuarine exchange flows [8,9]. In fact, [8] used observations from the microtidal and partially mixed York River Estuary in Virginia to demonstrate how along-channel wind plays a dominant role in governing the estuarine circulation. They found that up-estuary winds reduce or even reverse the tidally averaged vertical shear which ultimately reduces vertical stratification while down-estuary winds enhance the tidally averaged vertical shear, which interacts with the along-channel density gradient to increase stratification. These findings are revealing, but it is unknown if they will translate to estuaries with a larger tidal range or systems with different stratification patterns.
Another estuary feature that can produce subtidal flows is the along-channel shape of an estuary. Reference [10] found that the curvature of an estuary can produce complex lateral flow patterns that differ from one phase of the tide to the other, subsequently producing subtidal lateral flows. These lateral flows have been found to play a major role in how estuaries function, as they redistribute momentum and dictate scalar transport, such as salt, across an estuary. Conversely, it has been shown that stratification can alter lateral circulation patterns [11,12] since lateral flows can be generated by lateral straining of along-channel density gradients [13]. In fact, even when density gradients are not important, lateral shear stresses have still been found to be influential in estuarine function [14]. All of the above mentioned studies indicate the importance of understanding lateral flow and salinity structure in estuaries, yet have been carried out in temperate estuarine systems that feature either continual partial stratification or are well-mixed, leaving a gap in understanding if these results translate to high-inflow systems that become partially stratified only on certain phases of the tide.
To date, there have been very few studies on estuaries located on the Northern coast of South America [15,16,17], as most studies have focused on the coastal area under the influence of the Amazon River ([18,19] and references therein). In fact, in the Maroni estuary, the focus of research has been the geochemistry of suspended matter and bottom deposits [20] with the first observations on hydro-sedimentary dynamics conducted very recently [21]. As the Maroni estuary is a tropical high-inflow system that has yet to be modified by anthropogenic change, it presents a unique opportunity to study circulation patterns and forcing mechanisms in a natural (i.e., not dredged, not dammed, no bridges, no armoring or coastal reinforcements) estuarine environment. Therefore, the goal of this study is to determine the subtidal circulation patterns in a high river-inflow tropical estuary during the wet season. In order to address this goal, three specific research questions will be answered. First, what are the forcing mechanisms responsible for driving the subtidal circulation near the salt intrusion limit? Second, how would varying the strength of these forcing mechanisms alter the subtidal flow patterns? And finally: What is the effect of up-estuary winds and channel curvature on the subtidal circulation patterns? These questions will be answered using both data collection and analysis in addition to analytical modeling. The remainder of the manuscript will include a description of the study site in Section 2 followed by an explanation of the methods used including data analysis and a description of the analytical models in Section 3. Section 4 will detail the results including the intra-tidal and subtidal flow patterns and the comparison of data with the idealized models. The discussion will follow in Section 5, where the results will be expanded to consider how variations in forcing mechanisms will alter subtidal flow strength and structure, and finally, the conclusions will be presented in Section 6.
2. Study Site
French Guiana, located on the border between Suriname and Brazil in northern South America (Figure 1), features a wet equatorial climate. Seasonal variations in climate of this region are driven by the meridional migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). When the ITCZ is in its southern position (January to July), French Guiana experiences northeast trade winds and an abundance of rainfall (wet season). During the dry season (July to December), corresponding to when the ITCZ is at its northern position, this region experiences southeast trade winds [22]. During the wet season, the mesoscale North Brazil Coastal Current and the Guianas Current (which is an extension of the North Brazil Coastal Current), flow toward the northwest and bring low-salinity, sediment and nutrient rich waters from the Amazon River along the shorelines of French Guiana, Suriname, Guiana and Venezuela. During the other months of the year the North Brazil current travels westward bringing more saline and less turbid surface waters to much of the continental shelf [18].
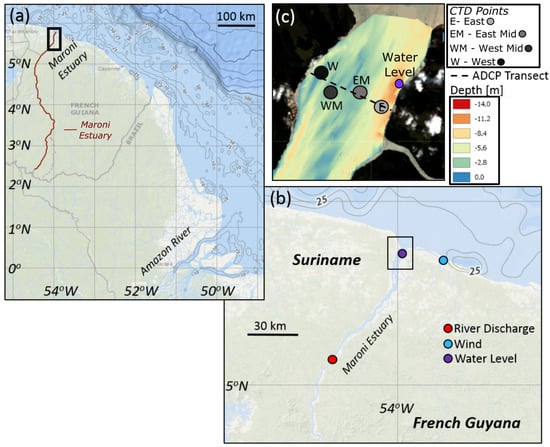
Figure 1.
(a) The study area, the Maroni estuary, outlined in black rectangle in relation to South America. Note the Amazon River on the bottom right of the figure. (b) A zoom in on the Maroni estuary depicting the locations where river discharge (red dot), wind (blue dot) and water level (purple dot) measurements were collected. (c) Zoom in on ADCP transect (dashed black lines) and locations of CTD profiles taken on the East (E) side of the estuary near the French Guiana coast, at a East-Mid (EM) location, at a West-Mid (WM) location and on the West (W) side of the estuary near the Suriname coast and the location of water level measurements (purple dot). (a,b) are from NOAA Bathymetric Data Viewer (https://maps.ngdc.noaa.gov/viewers/bathymetry/).
The coastal waters off of French Guiana contain large amounts of sediments, suspended materials and fresh water discharged from the Amazon River [23] and from several rivers located in the country (the Maroni, the Mahury, and the Oyapock being the largest). However the sediment loads in the local rivers are minor when compared with the suspended sediment concentrations observed in coastal waters. In fact, the coast of French Guiana is part of the longest stretch of muddy coastline found worldwide and experiences drastic morphological instability due to the longshore migration of mudbanks under wave forcing [24,25]. The Maroni estuary, which separates French Guiana from Suriname, is located approximately 700 km to the northwest of the Amazon and features a mean discharge of ∼1680 m s [19]. The Maroni watershed covers 66,814 square kilometers and is characteristic of the Guiana shield basins that drain the neotropical rainforest. This discharge, combined with the influence of the Amazon river, make the estuary waters highly turbid [20] and add to the high volumes of freshwater on the coast, especially during the rainy season [19]. The tide in French Guiana is mesotidal and semidiurnal dominant with an amplitude up to 2.5 m during spring tide [24]. Salinity intrusion length in the Maroni Estuary was found to vary from dry to wet seasons with the intrusion limit reaching ∼12 km and ∼5 km upstream from the mouth, in each respective season [20,21]. To date there have been no studies on the tidal dynamics of the Maroni Estuary.
3. Methods
3.1. Data Collection
Surveys of current velocities, salinity and temperature were conducted throughout a semidiurnal tidal cycle (∼12.42 h) near the salt intrusion limit of the Maroni estuary on 20 April 2018. Horizontal current velocities were collected with a vessel-towed 1200 kHz RDI Workhorse Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) in 0.25 m bins at 120 pings per ensemble over the tidal cycle. Measurements were then averaged over 10 ensembles to reduce noise. In addition, a SonTek Castaway Conductivity, Temperature, Depth (CTD) profiler measured salinity and temperature at 5 Hz with ±0.1 PSS accuracy for salinity and ±0.05 °C accuracy for temperature. The ADCP measured horizontal velocities in cross-channel transects from the eastern bank (French Guiana coast) to the western bank (Suriname coast) of the estuary with measurements directly linked with a Garmin GPS for navigation and to correct for boat heading and speed. CTD profiles were collected on the return transect at 4 locations across the estuary (Figure 1). A total of 20 full transects (ADCP and CTD) were completed (∼30 min per transect). The tidal range during the sampling was ∼2 m, three days after spring tide.
River discharge measurements collected every two hours at Apatou (∼80 km from the estuary mouth; Figure 1) were provided by the French agency Direction de l’Environnement de l’Aménagement et du Logement (DEAL, www.guyane.developpement-durable.gouv.fr). Wind velocity measurements averaged every 10 min were provided by the Mana airport (5°3948 N, 53°4542 W). Water level measurements were collected every minute approximately 10 km from the estuary mouth (5°4254 N, 53°5756 W) using a NKE Instrumentation SPT data logger with 0.02 m accuracy.
3.2. Data Analysis
The instantaneous velocity measurements were collected with a boat speed maintained at approximately 2.5 knots. After the data were ensemble averaged (10 ensembles per average) they were interpolated onto a uniform grid of 10 m length (cross-channel) and 0.5 m depth for each of the 20 transects measured throughout the semidiurnal tidal cycle. The ADCP data were trimmed to exclude measurements within 10% of the bottom to eliminate side lobe effects. Any data ensemble that produced less than an 85% signal return of good data were excluded. Also, error velocities, which are quantified as the difference between two estimates of vertical velocities from all independent pairs of beams, were quantified. If the error velocity values were found to be greater than 5% of the maximum horizontal velocity, that measurement was marked bad. All remaining data were corrected by comparing the bottom track velocities collected by the ADCP to instrument velocities that were derived from the GPS following the method of [26]. Finally the North-South and East-West velocities derived from the ADCP were rotated to the primary flow direction (along- and cross-estuary) using a regression analysis [27].
To isolate the subtidal flows, a least-squares regression analysis was applied to the interpolated and rotated current velocities. This allows for the instantaneous velocity data to be represented as a sum of multiple tidal harmonic species. In this case, the included harmonic species were the semi-diurnal (D2 with period of ∼12 h) and its first and second overtides, the quarter-diurnal (D4 with a period of ∼6 h) and the sixth-diurnal (D6 with a period of ∼4 h) species [28]. The least-squares fit analysis to the three above-mentioned tidal species was applied to the along- and cross-channel velocities (u and v) as,
where u is the instantaneous velocity, is the subtidal flow, , and are velocity amplitudes, , and are the frequencies, and , and are the phases of the D2, D4 and D6 tidal species, respectively. Therefore, the subtidal signal includes the effects of wind, density gradients (river input) and tidal rectification.
3.3. Wind, River and Density-Induced Flow
Analytical model solutions were used to verify the forcing mechanisms of the observed along-channel subtidal flows by isolating the effects of wind, river and along-channel density gradients in producing long-term circulation. The solution is derived from the one-dimensional (depth-dependent) along-channel momentum balance between the pressure gradient (barotropic and baroclinic) and friction (surface and bottom) which was first presented in [2] but has been applied by other studies since [29],
where z denotes the vertical coordinate (positive up from surface), P is pressure (barotropic and baroclinic), is the vertical eddy viscosity, which is considered constant to maintain the analyticity of the solution, is a reference density of 1000 kg m which is an average density over the tidal cycle and across the channel quantified from the collected data. The boundary conditions are no slip at the bottom, wind stress at the surface, and a river discharge (per unit width) at the head. The solution for the along-channel residual flow is,
where H is the depth, R is the river discharge (per unit width), is the variable water density (kg m) and is the wind stress. The first term on the right hand side of the equation represents the density driven flow, the second term is the river-induced flow and the third term is the wind-induced flow. The prescription of the along-channel density gradient is estimated using in-situ collected density data. As was not able to be pre-determined, it was considered as a free parameter, which is a crude approximation, but nonetheless produced revealing results. To further investigate the role of the pressure gradient, in particular the baroclinic and barotropic (driven by changes in density) pressure gradients influence on the lateral variability of along and cross-channel flow structure, a second analytical solution was used.
3.4. Cross-Channel Variation in Density-Induced Flow
This analytical solution assesses the influence of along- and cross-channel variations in density on the transverse variability of subtidal circulation in frictional estuaries with an arbitrary bottom profile [30]. The governing equations are as follows,
where u and v are the along and cross-channel velocities in the x and y directions, respectively, g is gravitational acceleration (9.81 m s), is the water level variation (m) and f is the Coriolis parameter at 5° latitude (s). Equations (5) and (6) can be represented in a compact way (as done in [30]), which is as the real and imaginary part of a complex velocity, and complex barotropic and baroclinic pressure gradients, and , respectively, where denotes the imaginary number. Using this formulation we can replace Equations (5) and (6) with
The flow w includes contributions from both the BCPG and the BTPG (or sea level slope), which following [30,31] can be represented as,
yet it should be noted that the BTPG is directly linked to the BCPG (which is prescribed in this application) and thus does not explicitly depend on an influx of fresh water from the upstream boundary. Using no stress at the surface and no slip at the bottom boundary conditions, and assuming that the horizontal density gradient is independent of depth, and there is no net volume flux across the channel, Equation (8) can be plugged into Equations (5) and (6) to arrive at,
which have solutions
In Solutions (11) and (12), the parameter , where is the Ekman layer depth. The parameter h denotes an arbitrary cross-channel bathymetry (function of y). If the BCPG and are prescribed, then a solution can be derived for the BTPG using the above-mentioned boundary conditions, namely,
where B is the width of the channel. The prescription of the BCPG is able to be estimated using in-situ collected density data. The solution to Equation (8) can then be obtained using Equations (11)–(13). Readers are referred to [30,31] for more details on the derivations.
4. Results
4.1. River, Wind, Tide and Salt
River discharge remained at or above ∼3000 m s from 15–24 April 2018 (Figure 2a). The maximum river discharge was 4000 m s on 15 April and decreased to ∼3000 m s on the day of the ADCP transects (20 April 2018). The river discharge during the dry season is on average 500 m s (not shown), indicating the significant increase in river flow during the wet season months. Wind measurements collected concurrently with river discharge is almost consistently from the northeast (blowing toward the southwest; Figure 2b,c). During the day ADCP measurements were collected the wind was blowing south-southeastward at ∼4.4 m s, which is calmer than the surrounding days (Figure 2b). Water level data were collected from 17–21 April 2018 (Figure 2d). The tidal range was ∼2 m throughout this sampling period, including the day of the ADCP transects and the water level is ∼45° out of phase with the current velocity (Figure 2e) indicating that the tide behaves as a partially standing wave.
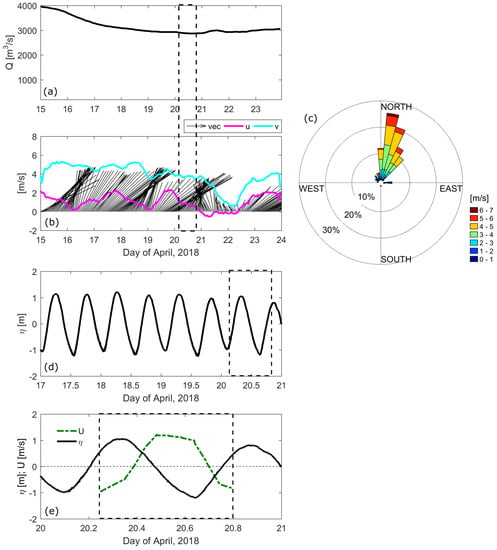
Figure 2.
(a) River discharge, (b) Wind velocity vectors as well as North-South (cyan) and East-West (magenta) wind velocity components showing the incoming wind direction, (c) Wind rose of the wind data shown in (b). Subplots (a–c) depict nine days (15–24 April 2018) surrounding the ADCP transect date (20 April 2018), (d) water level from the 17–21 April 2018 and (e) a zoom in of the water level (black line) and the depth-averaged current velocity (green dashed line) during the day of ADCP data collection. The dashed black line in subplots (a,b) and (d,e) indicated the ADCP transect measurement time.
Absolute salinity (hereafter referred to as salinity; http://www.teos-10.org/) varied both throughout the tidal cycle and across the channel on 20 April 2018 (Figure 3). The most pronounced intratidal variability in salinity occurred at the East and East Mid Station where salinity reached 4 g kg at the bottom during maximum flood (Day 20.38, Figure 1 and Figure 3a,b) and decreased to 0 g kg at slack after flood, through ebb tide and at the start of the consecutive flood tide. East Mid station is located ∼1 km to the west of East station and is shallower than the East Station by approximately 4 m (Figure 3b). The two stations on the western side of the estuary remained fresh (salinity of 0 g kg) throughout the tidal cycle and were significantly shallower (<4 m deep) than the eastern stations (Figure 3c,d). Tidally averaged salinity indicates negligible values at the West Mid and West stations (∼0 g kg) and a top to bottom salinity gradient reaching 0.7 and 0.6 g kg m at the West Mid and West stations respectively, indicating the presence of a salinity intrusion front that only manifests in the channel during flood tide (Figure 4). It is interesting to note that although the East station is deeper, there is a more pronounced vertical salinity gradient at the East Mid station.
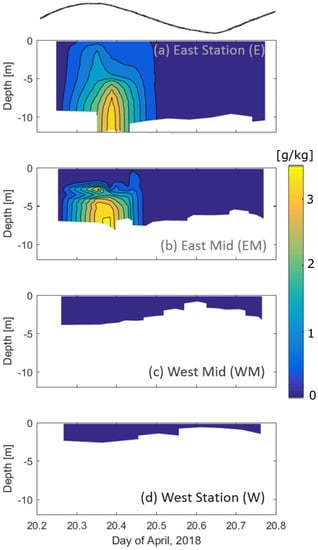
Figure 3.
Absolute salinity (g kg) throughout depth (y-axis) and time (x-axis) at (a) the East station (E), (b) the East-Mid station (EM), (c) the West-Mid station (WM), (d) the West station (W). The black line at the top of the figure indicates the water level variation throughout time.
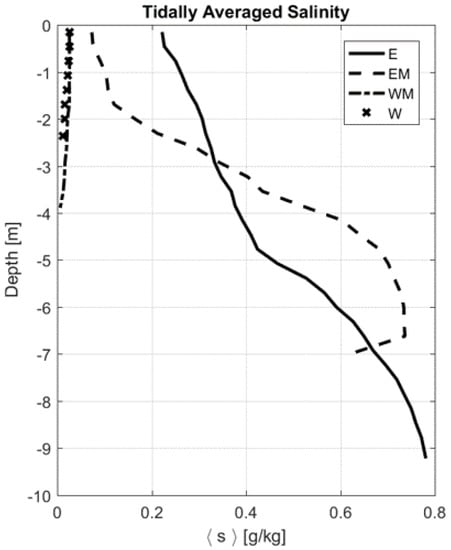
Figure 4.
Tidally averaged salinity over depth at East station (E, solid line), East-Mid station (EM, dashed line), West-Mid station (WM, dash-dotted line) and at West station (W, crosses).
4.2. Intratidal Flow
Intratidal along-channel flows indicate a longer ebb (7.7 h) than flood tide (4.6 h), which is due to a combination of the elevated river discharge during wet season and the flood-dominance of this funnel-shaped estuary. The first ADCP transect was collected during max flood tide (20.24–20.27 d), with current velocities reaching ∼1.5 m s over the deepest part of the channel (eastern side) near the surface (Figure 5). Slack after flood was captured between 20.35–20.37 d showing flow over the shoals beginning to ebb while flow over the channel continued to flood. Maximum ebb tide currents occurred during the transect collected from 20.49 to 20.51 d, reaching ∼−1.3 to −1.5 m s over the cross section. Slack after ebb occurred from 20.69 to 20.71 d showing the flow over the shoals starting to flood before the channel (Figure 5).
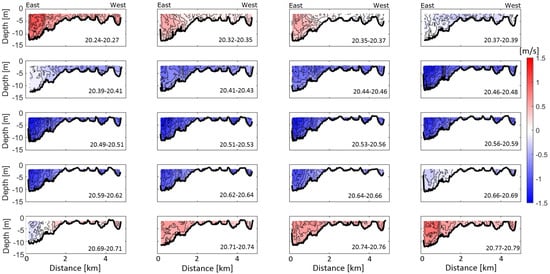
Figure 5.
Along-channel current velocity through depth (y-axis) and cross-channel distance (x-axis) throughout the tidal cycle in m s. A distance of x = 0 km is on the eastern side of the river and a distance of x = 4.75 km is on the western side. Time is indicated at the bottom right of each subplot. Red colors indicated in-estuary flow and blue colors indicate out-estuary flow and the vantage point is looking in-estuary.
Intratidal cross-channel flows exhibit a three-layer vertical structure that is only present during late flood tide (20.24–20.35 d), slack after flood (20.35–20.37 d) and early ebb tide (20.37–20.41 d), with the three-layer structure transitioning to a uni-directional eastward (toward French Guiana) lateral flow by 20.43 d (Figure 6). The three layer circulation is present in the channel (from 0–2 km across) with surface flows directed to the east (up to −0.18 m s, towards French Guiana), mid-depth flows to the west (up to 0.15 m s, towards Suriname), and near-bottom flows directed to the east (up to −0.12 m s, towards French Guiana). The lateral flows are also stronger when the three-layer flow structure is present compared to the remainder of the tidal cycle (Figure 6). The tidal asymmetry in the strength of the lateral flows, as well as the three-layer vertical structure only being present during end of flood and early ebb tide is similar to that found by [32] in the Hudson River estuary. Their study showed that lateral advection produced a three-layer lateral circulation during flood tide in addition to a tidal asymmetry in the strength of lateral flows with this effect diminishing as river discharge increased. They found that this was due to the enhanced stratification stifling advection (as found in [33]). In the Maroni, the large river discharge combined with the influence of fresh coastal waters from the Amazon River produce a water column that is typically fresh throughout the tidal cycle, indicating well-mixed conditions, which could explain the similarities to [32]. This will be explored further in the Section 5.
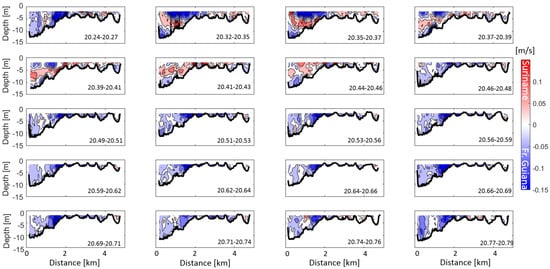
Figure 6.
Cross-channel current velocity through depth (y-axis) and cross-channel distance (x-axis) throughout the tidal cycle in m s. Time is indicated at the bottom right of each subplot. Red colors indicated flow directed toward the Suriname coast and blue colors indicate flows directed toward the French Guiana coast and the vantage point is looking in-estuary.
A least squares fit to the semi-diurnal (D2), quarter-diurnal (D4) and sixth-diurnal (D6) harmonic species was applied to the intratidal along- and cross-channel flows. The D2 species indicates maximum along-channel tidal velocity amplitudes (∼1.3 m s) near the surface (2–5 m depth) in the channel (∼0.25–0.5 km across-channel; Figure 7a). The cross-channel D2 tidal amplitude indicates maximum lateral flows (∼0.2 m s) at the channel-shoal interface (1.5–2.25 km) throughout the water column (Figure 7d). The D4 tidal velocity amplitude is elevated (∼0.3 m s) in the channel and at the channel-shoal interface (0.25–1 km and 1.25–2 km; Figure 7b). The cross-channel D4 tidal velocity amplitude is also elevated (up to 0.16 m s) at the channel-shoal interface, likely a product of the elevated cross-channel D2 tidal velocity amplitudes at this location (Figure 7d,e), since D4 is the first overtide of D2. The D6 along- and cross-channel amplitudes are less pronounced than their D4 counterparts, reaching 0.13 m s and 0.08 m s, respectively. Since D6 is a product of quadratic friction, with the effect reducing as mean flows (river discharge) enhance, the energy in the D6 harmonic is likely transferred to its asymmetric counterpart, D4 [34]. The subtidal flows are also quantified from the least squares fit analysis.
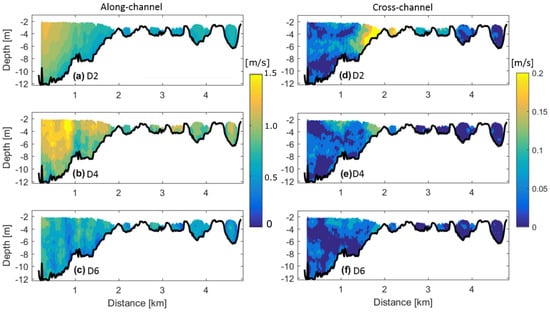
Figure 7.
Along-channel current velocity amplitude of the (a) semi-diurnal, (b) quarter-diurnal and (c) sixth-diurnal tidal species. Cross-channel current velocity amplitude for the (d) semi-diurnal, (e) quarter-diurnal and (f) sixth-diurnal tidal species.
4.3. Subtidal Flow
The semi-diurnal (D2), quarter-diurnal (D4) and sixth-diurnal (D6) bands were removed from the tidal signal, and the subtidal flow was quantified. The along-channel subtidal flow indicates outflow over the entire cross-section reaching −0.4 m s near the surface in the channel (Figure 8a), which is the same location as the maximum D2 tidal velocity (Figure 7a), and over the shoal (3.75 to 4.25 km across channel). The subtidal outflow is due to the consistent mean flow from the river producing a much longer ebb tide than flood (7.7 h for ebb and 4.6 h for flood).
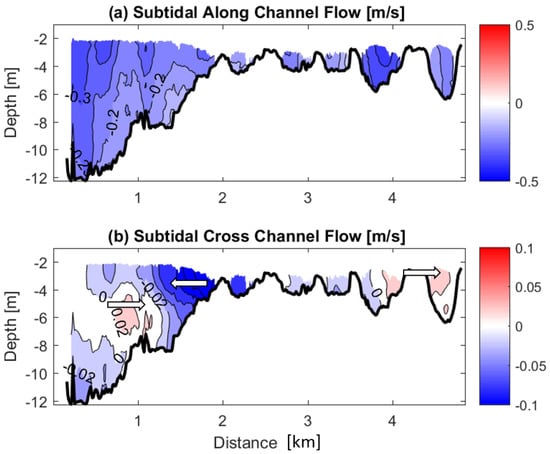
Figure 8.
(a) Subtidal along-channel flows where blue colors denote out-estuary flows and (b) subtidal cross-channel flows where blue colors denote currents directed toward the French Guiana coast and red colors denote currents directed toward the Suriname coast. The white arrows in subplot (b) are for ease in determining the current direction.
The cross-channel subtidal flow reiterates the importance of the three-layer flow in the cross-channel intratidal velocities at the end of flood tide, slack after flood and the start of ebb (Figure 6 and Figure 8b). In the channel (0.25 to 2 km) there is a three layer circulation with flow at the surface towards the French Guiana coast, mid-depth toward the Suriname coast and near bottom again toward the French Guiana coast. Over the shoal, the flow is directed toward the French Guiana coast from 2 to 3.75 km and toward the Suriname coast from 3.75 to 5 km across the channel. The multi-directional flow over the shoals can be a product of the barotropic pressure gradient building up over the shoals and essentially ‘spilling over’ toward the deeper channel (French Guiana coast) and the Suriname channel (∼6 m deep from 4.5 to 5 km; Figure 8b).
4.3.1. Analytical Solutions for Wind, River and Density Driven Flow
The solutions for the depth-dependent, tidally-averaged flow driven by density, river and wind (Equation (3)) were used to determine the subtidal flow driven by these forcing mechanisms in the channel section (∼12 m deep) of the estuary (∼0.25–2 km across). The along channel density gradient was assumed to be constant (3 g kg change over 6 km) from the 15–24 April. Although only the cross-channel density was measured on the day of the field campaign, salinity intrusion measurements collected during the wet season in this estuary (April 2019) indicated that the salt intrusion does not penetrate further than 6 km upstream from the mouth (not shown), making this assumption a prudent approximation. The river discharge per unit width, R, was quantified using the river discharge data divided by the width of the channel at the measurement section ∼4.5 km, to be input into the model solution. As river discharge data were available from the 15–24 April 2018, this term varies with both depth and time. Wind data were also available through this time period and therefore the wind-induced residual flow was quantified with both depth and time as well. The total residual flow is a sum of the three above-mentioned components. The most limiting assumption made was the vertical eddy viscosity, which was assumed constant and used a free parameter ( m s) to best fit the total subtidal flows (both structure and magnitude) to the channel average of the data. A more detailed account of how varying the vertical eddy viscosity will alter the results of this analysis will be explored in the Section 5. However, future work would benefit from turbulence measurements to verify assumed values of vertical eddy viscosity.
The density-driven flow in the channel section shows outflow at the surface and inflow at depth throughout the time series, due to the constant along-channel density gradient (Figure 9a). The density-driven inflow and outflow never exceed ∼0.05 m s. The assumption of a constant along-channel density gradient is crude, but as the river discharge remains relatively constant throughout this time period (∼3000 m s), from the 18 to 24 April of 2018 (Figure 2a), it is a sufficient assumption. The river-discharge induced flow indicates consistent outflow with strongest velocities (reaching −0.15 m s) at the start of the time series (15–18 April) due to the elevated river discharge at this time (reaching 4000 m s; Figure 2a and Figure 9b). During the ADCP sampling campaign on 20 April, the river-induced flows reached −0.1 m s at the surface, decreasing to 0 m s at depth due to the no-slip bottom boundary condition. The wind-induced residual flow is the most variable of the three components over the time series and with depth (Figure 9c). Throughout the time series the wind-driven flow indicates inflow at the surface, due to the southward directed wind (Figure 2b) and a return flow at depth. The wind-driven flow reaches ±0.2 m s during the 15, 18, 20 and 21 April 2018. The wind pattern of the day of the ADCP transects (20 April) would augment the flood tide velocites at the surface and oppose them at depth, with the opposite effect during ebb (Figure 5 and Figure 9c). However, the wind-driven flow is consistently opposing the density driven-flow, which will suppress the wind-driven flows contribution to the total residual velocity (Figure 9a,c). Despite this, the total residual flows quantified by the model reproduce the pattern and magnitude of the subtidal velocities from the ADCP data (Figure 8a and Figure 9d), indicating that they are primarily driven by river discharge. When the wind speed is strong (5 m s) toward the southwest, the total residual inflows decrease, approaching 0 m s since the wind-driven flow can overpower both the density driven flow and reverse the river-induced flows near surface (less than 4 m deep) and augment them near bottom (below 4 m depth). This phenomenon starts to occur on the day of the ADCP transects (20 April), but the wind velocities die down by the start of the field campaign (day 20.35 of April; Figure 5 and Figure 9).
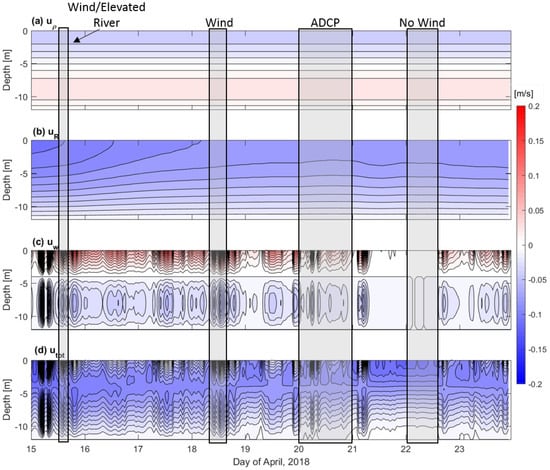
Figure 9.
Analytical model solutions that show (a) the density-driven flow, (b) river-discharge driven flow, (c) wind-driven flow and (d) the total residual flows through time (x-axis) and depth (y-axis) in m s. Black shaded boxes indicates time periods when different residual flow forcing mechanisms are dominant. 15 April represents elevated wind and river forcing, 18 April represents elevated wind forcing, 20 April is the ADCP measurement date and 22 April represents a time period with no wind forcing.
The results of the total residual flow from the analytical solution match well in structure and magnitude to the observed subtidal flows (Figure 8a and Figure 9d). This implies that the barotropic pressure gradient induced by the river input is the main driver of along-channel subtidal flows during the wet season. However, it should be noted that the analytical solution is limited in that it only considers depth-dependent tidally averaged flow at one cross-section location, it does not include nonlinear terms, such as advection which can be influential in tidally energetic estuaries, and there is no indication of the lateral flow structure or magnitude. In order to determine the role of lateral variations in baroclinicity in driving subtidal flows, a second analytical solution is considered.
4.3.2. Analytical Solution for Lateral Variations in Pressure Gradient Driven Flow
To better understand the role of the pressure gradient driven residual flows the analytical model solutions based on [30] were used. The model solutions show the lateral variability of the along- and cross-channel subtidal flows driven by a combination of the baroclinic and barotropic (as a function of a prescribed density gradient) pressure gradients (Figure 10). The along-channel subtidal flows show outflow in the main channel throughout depth reaching ∼0.25 m s at the surface and weak inflow (∼0.01 m s) at depth over the channel shoal interface (from 1 to 2 km across-estuary) and over the shoals. Overall, the along-channel subtidal flows are underestimated by the model (reaching −0.3 m s at the surface in the channel and remaining near 0 m s over the shallower shoals; Figure 8a). This is due to the model not including the wind-induced flow that counteracts the density driven flow as well as the barotropic pressure gradient not including river discharge, which would produce enhanced outflow throughout the cross-section. The cross-channel subtidal flows are overestimated by the model (reaching ∼−0.1 m s in the channel; Figure 10b). The modeled cross-channel flows also indicate a single-cell circulation from the channel shoal interface (1 km across estuary) to the Suriname coast (5 km across estuary). The overestimation of the subtidal flow magnitude and the difference in structure indicates that the lateral pressure gradient driven by density is at least not solely responsible for driving the actual cross-channel subtidal flow pattern (Figure 8b). The model does ignore influence of a river-discharge induced barotropic pressure gradient that could alter the cross-channel variation in water levels, thus driving lateral subtidal flows. Also, along-channel variations in estuary shape, such as curvature and convergence, and nonlinear terms are considered negligible (not included in momentum balance), but in systems with strong tidal currents interacting with complex bathymetry, the influence of advective accelerations could be important, altering the subtidal current structure. Further, it is unknown how the subtidal flow structure during the wet season would be altered when river discharge decreases.
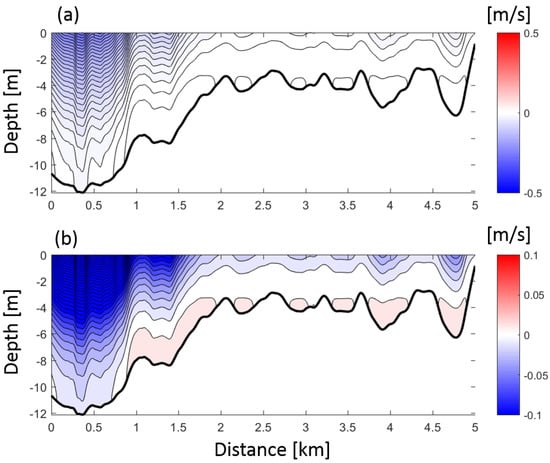
Figure 10.
Analytical model solution of pressure-gradient driven (a) along-channel residual flow (blue colors denote out-estuary flow and (b) cross-channel residual flows (blue colors denote flow directed toward the French Guiana coast) over depth (y-axis) and cross-channel distance (x-axis). The vantage point is looking in-estuary.
5. Discussion
The goal of this study is to determine the magnitude of and forcing mechanisms driving subtidal circulation in a tropical high-inflow estuary during wet season. Further, this work investigates how modified forcing mechanisms will subsequently alter subtidal flows and will elucidate the role of wind forcing and along-channel variations in estuary shape on producing subtidal flows. Results have shown that along-channel subtidal flows during the day of data collection were driven by river discharge since the wind-driven flow opposed density-driven flow. It was also shown that the lateral subtidal flows featured a three-layer circulation that was not driven by the pressure gradient (at least not solely). This section of the paper will expand on these findings in two ways: (1) explore how expected intra-seasonal and seasonal (wet and dry season) variations in along-channel subtidal flow forcing mechanisms (such as river discharge, wind forcing and density gradient) will alter the along-channel subtidal flow structure and (2) determine the role of curvature in producing the three-layer vertical structure of lateral intratidal and subtidal flows found during wet season.
5.1. Along-Channel Subtidal Flows
Variations in subtidal flow drivers during the wet season in the Maroni are primarily driven by fluctuations in wind velocities and river discharge. This is because the extent of salinity intrusion during the wet season is limited to the first 6 km (from the mouth) of the estuary as well as the results of this study showing that pressure gradients (both along and cross-channel) do not reproduce the expected subtidal circulation patterns. Investigating the nine day time series of wind and river discharge during the wet season and using the one-dimensional (vertical) analytical model revealed that variations of wind and river flow could alter subtidal flows patterns (Figure 2 and Figure 9).
Profiles of residual flows driven by wind, river and density (from the analytical solution) during the nine day period surrounding the day of the ADCP transects (20 April 2018) depict how variations in wind and river alter the depth-dependent residual flows during the wet season (Figure 11a). We chose four representative days with varying river flow and wind conditions (as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 9) and investigated the residual flow profile. The first day chosen is an instance of elevated southwestward wind (∼8 m s) and river discharge (3800 m s) found on day 15.5 April 2018. The second was chosen for average river flow (for wet season, 3000 m s) and elevated southwestward wind (∼10 m s) on day 18.5 of April. The day of the ADCP transects was considered for comparison purposes (20 April) and featured wind velocities less than that of days 15.5 and 18.5, reaching ∼5 m s and river discharge of approximately 2800 m s. The fourth day was chosen as it featured slack winds (∼1 m s) with river flow the same as the day of the ADCP transect (∼2800 m s) on day 22 to 22.5, allowing for the wind influence on the ADCP sampling day to directly be determined. The density gradient was held constant throughout the nine day period as it was above.
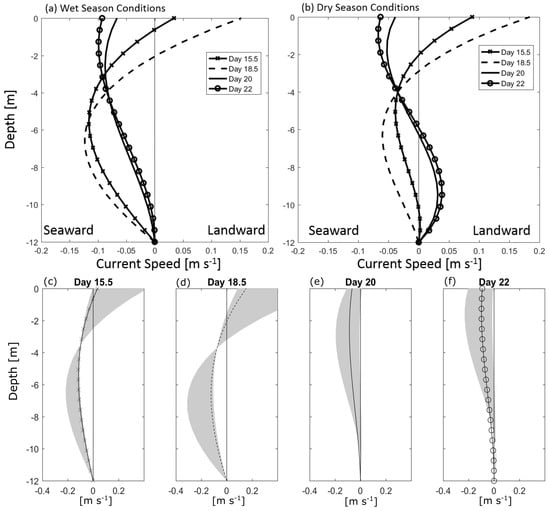
Figure 11.
(a) Residual flow profiles during wet season on days where different dominant forcing mechanisms are found as shown in Figure 9. Day 15.5 (solid line with cross) represents elevated river discharge and wind velocity, day 18.5 (dashed line) represents elevated wind velocity, day 20 (solid line and averaged over the day) is the day of ADCP measurements and day 22 (solid line with circles) represents no wind forcing and elevated river. (b) Residual flow profiles for dry season (river discharge of 500 m s) under the influence of the same wind conditions used in (a). (c–f) show the residual profiles from (a) with shaded areas representing vertical eddy viscosity values ranging from to m s. Note that m s for all line plots.
Figure 11a depicts the vertical structure of the residual flows during each of the above-mentioned days. On day 15.5 and 18.5, the two days featuring the strongest wind velocities, the residual flows show two vertical layers, with the near-surface layer directed landward and the bottom layer directed seaward, which indicates that the wind can produce a reverse estuarine circulation in this system, even during high river flow (wet season). In addition, the seaward directed flow at depth augments the river-induced outflow, producing elevated seaward flows (up to −0.13 m s) compared to the days with weaker wind forcing (−0.05 m s). The day of the ADCP field campaign (day 20 of April) and day 22–22.5 of April featured weaker wind velocities and showed residual flows directed seaward throughout the water column. The maximum residual flows were ∼−0.1 m s near surface. During the day of the ADCP velocity transects (day 20), the vertical structure of the residual flow in the main channel of the estuary (Figure 8a) shows a similar structure to the theoretical results (Figure 11a), yet the magnitude is underestimated by the analytical solution (reaches −0.1 m s at the surface where the data shows −0.3 m s). This could be due to a forcing mechanism not considered in the momentum balance for the analytical solution (e.g., neglecting nonlinear terms) or invoking simplifying assumptions, like a spatially and temporally constant vertical eddy viscosity or only a one dimensional solution. To understand how the solutions would vary for different values of vertical eddy viscosity, the same solutions were considered ranging from 10 to 10 m s (Figure 11c–f). Results show that for day 15.5 and 18.5, varying will still, for the most part, result in a two-layer circulation. Further, for day 20, the residual flow pattern remains seaward throughout depth, yet even varying does not produce residual flows of the same speed as the data (maximum of ∼0.2 m s).
There is evidence of strain induced periodic stratification (SIPS, [35]) in the main channel (Figure 3), yet since the subtidal flow pattern is uni-directional seaward (Figure 5a), and tidal straining circulation manifests as a two-layer flow, it is likely that another forcing mechanism is at work. [6] found that channel convergence can itself produce a residual flow that weakens estuarine circulation driven by tidal straining and gravitational circulation even when horizontal density gradients are significant and convergence effects are minimal. Typical tidal straining circulation features more stratification during ebb tide that stifles mixing, ensuring that the covariance between vertical eddy viscosity () and vertical shear of the along-channel flow () is larger during flood tide than ebb, which ultimately produces the typical two-layer estuarine circulation pattern. The convergence-driven residual flows found by [6] produce an inverse tidal straining circulation that features landward flow at the surface and seaward flow at depth. This is explained by the covariance between vertical eddy viscosity and the vertical shear of along-channel flows being more pronounced during ebb tide than flood, opposite to tidal-straining circulation. As the Maroni is a convergent system (∼4.5 km near the mouth and ∼750 m near the tidal excursion limit 80 km upstream), this is likely reinforcing the river-induced subtidal flows near surface, and explaining the discrepancy between the idealized solution and the subtidal flow measurements. It is unlikely that advection is reinforcing the density-driven flow as it has been found that lateral advection acts as a seaward driving force for near-surface waters and a landward driving force at depth [33], which would augment density-driven flow. Future studies would benefit from gathering detailed bathymetry data along the estuary in order to quantify the convergence number to confirm that this is indeed augmenting the subtidal flows.
During the dry season, the salinity intrusion reaches approximately 12 km upstream [20,21], implying that density gradients could play a more substantial role in producing subtidal flows. The direction of the wind does not vary much throughout the year in French Guiana with the dry season featuring slightly weaker winds and a daily sea breeze rather than persistent wind toward the southwest as during the wet season. In order to have a more direct comparison between seasons, the same wind velocities measurements from the wet season (days 15.5, 18.5, 20 and 22) were considered for the dry season. The average river discharge during the dry season is 500 m s, therefore this value was held constant. Figure 11b depicts the vertically varying residual flows during dry season conditions. Day 15.5 and 18.5 feature strong winds producing a two-layer residual flow structure with landward flow at the surface due to wind stress and a seaward return flow at depth, reversing the typical estuarine circulation pattern. During day 20 and 22–22.5, when the wind has settled, the residual flows indicate that the horizontal density gradient is producing a typical estuarine circulation pattern with inflow at the bottom and out-estuary flow at the surface. Of course, measurement of current velocities throughout at least one full tidal cycle in the dry season are needed to verify these results. We suspect that the role of convergence will counteract the density-induced flow and will augment wind-induced flow, which could result in a weak or inverse gravitational circulation pattern during time periods with elevated southwestward winds.
5.2. Lateral Subtidal Flows
Investigation by [36] demonstrated how along-channel winds can modify both along and cross-channel current structure in the Chesapeake Bay. They found that under the influence of rotation, Ekman transport drives a counterclockwise lateral circulation under the influence of down-estuary winds and vice-versa for up-estuary winds (vantage point looking into the estuary, in the northern hemisphere). As the Maroni estuary is located at 5° N latitude, the Coriolis force is negligible, leaving out wind as a driver for the complex lateral flow pattern found during late flood and early ebb tide (Figure 6). However, the curvature of the channel could play a role.
In fact, [10] investigated how curvature affects lateral flows in both well-mixed and stratified conditions. Their study, carried out in Elkhorn Slough, California, showed that stratification strengthens curvature-induced lateral circulation, but the development of a lateral baroclinic pressure gradient opposes the lateral flows, which results in a three-layer circulation. They found that variations in stratification and tidal velocity amplitudes from flood to ebb tide strongly affected lateral transport and generation of residual currents in regions of curvature. The results of [10] reinforced the findings of [12], who found that during the wet season in Kill van Kull between Newark Bay and New York Harbor, during neap tide conditions, the lateral flows depicted a three-layer vertical structure.
The lateral baroclinic pressure gradient found between the main channel near the French Guiana coast and the shoals near the Suriname coast could counteract the effect of the curvature around the headland at the mouth of the estuary during flood tide (Figure 12). Although there is also an ebb channel that indicates that curvature effects should be important during this phase of the tide as well, there is no lateral baroclinic pressure gradient to oppose the curvature force and therefore the three-layer circulation pattern is not present (Figure 5 and Figure 12). In fact, quantifying the order of magnitude of the baroclinic pressure gradient during flood tide, , we arrive at m s using m s, kg m, kg m, m and m as the average depth of the cross-section, and comparing this to acceleration due to curvature, m s, where u is the tidal velocity amplitude of the semi-diurnal tide (∼1 m s) and km is the radius of curvature of the headland measured from the location of largest along-channel velocities during flood tide, it becomes apparent that these two forces are in competition. Figure 12 shows a simplified diagram of how the channel curvature during flood produces an along-channel velocity maximum at the location of the flood tide channel on the outside of the bend and lateral flows near the surface directed toward the French Guiana coast with a return flow below. The baroclinic pressure gradient (Figure 12c) opposes this flow structure producing flow again directed toward the French Guiana coast at depth.
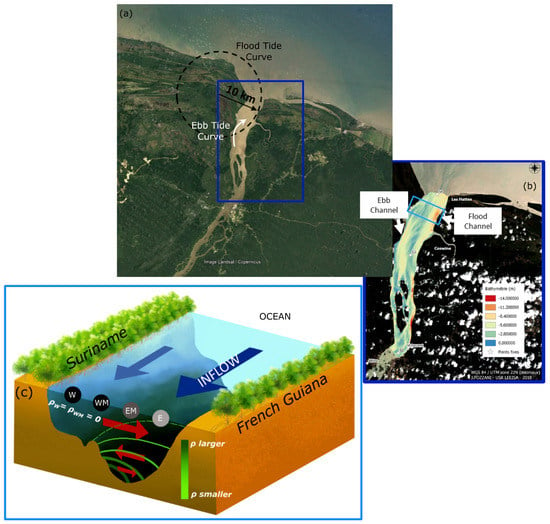
Figure 12.
(a) Ariel view of the Maroni estuary that depicts the flood tide headland (and radius of curvature) and the ebb tide curve. The blue box is the area that is zoomed in for subplot (b). (b) Bathymetry of the Maroni estuary showing evidence of a flood tide channel toward the French Guiana coast due to the headland and a ebb tide channel due to the upstream channel bend. The light blue box is the area that is zoomed in for subplot (c). (c) illustration of the density contours across channel during the flood tide (green lines) as well as the along-channel velocity (blue arrows) and cross-channel velocity (red arrows).
The role of curvature inducing the lateral circulation would be more compelling if the direction of tidal approach into the Maroni was available. Although the coastal residual flows are directed to the northwest due to the Guiana Current, the co-tidal lines in this region converge on the northeast coast of South America [37] making it unclear from which direction the tide is approaching the mouth of the Maroni estuary. A study by [38] uses a numerical model to describe the tidal and residual flows along the coast of French Guiana. Their study indicates that for the majority of the coast, the tide approaches from the southwest, however, at the Maroni estuary, which is at the border between French Guiana and Suriname (and is the boundary of their model), the tidal currents are more rectilinear, indicating that the tide approaches directly from offshore. They do not offer explanation for why this is the case. Investigating the bathymetry outside of the estuary mouth could also provide a clue into tidal propagation direction. A recent study by [39] includes bathymetry surveys between Suriname and French Guiana and reveals a main tidal channel extending rectilinearly from the estuary mouth and a second less pronounced channel extending along the Suriname Coast. Although this does not confirm that the flood tide enters the estuary from directly offshore and the northeast, it evidences a flood channel at both locations, driven by flow around the headland. Future work in this area should consider a numerical model that can simulate the tidal propagation on the French Guiana and Suriname coasts as well as the tidal currents in the Maroni in order to verify the findings of this study.
6. Conclusions
A field experiment was conducted to measure the intratidal and subtidal current and salinity structure in a tropical estuary during wet season. Analytical solutions were used to complement measurements and determine how subtidal flow patterns are altered under a range of wind, river discharge and along-channel density conditions. During the day measurements were collected, the along-channel subtidal flows were directed out-estuary over the channel cross-section and depth due to the enhanced river-discharge during wet season and relatively weak wind velocities. However, in this region wind velocities can persistently blow in the southwesterly direction, which was found to alter the subtidal outflow found during the day of the measurement campaign.
When wind velocities are enhanced, blowing in-estuary (southward), the subtidal flows indicate a two-layer structure with landward flow at the surface and strengthened seaward flow at depth, despite the river discharge being maintained above 3000 m s, and having implications for the long term transport of sediments and other suspended materials in the estuary. In addition, the lateral flows revealed a three-layer circulation in the main channel that is due to flow curvature around a headland during flood tide which is opposed by a lateral baroclinic pressure gradient. As the lateral baroclinic pressure gradient develops only during flood tide, this is not found during ebb, despite the presence of a slight channel bend. The tidal asymmetry in lateral flows could cause sediment accretion near the Suriname coast, contributing to the extensive shoals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.R., A.S., A.G. and S.L.; methodology, L.R., A.S. and A.G.; instrumentation and software, T.M., A.G. and S.L.; formal analysis, L.R., T.M.; investigation, L.R., A.S., T.M., S.L. and A.G.; resources, A.G., T.M.; data curation, L.R., T.M.; writing–original draft preparation, L.R.; writing–review and editing, A.S., T.M., S.L. and A.G.; visualization, L.R., T.M.; supervision, A.S., A.G.; project administration, A.S., A.G.; funding acquisition, A.G., A.S.
Funding
We acknowledge financial support from the French Guiana Water Agency for the Project EFHEMAR. Additional funding was provided from the European Regional Development Fund for the project OYAMAR. This is a contribution from the French GDR LIGA researcher network.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Guillaume Detandt and Sylvain Morvan for their help with data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ADCP | Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler |
| CTD | Conductivity, Temperature, Depth profiler |
| BTPG | Barotropic Pressure Gradient |
| BCPG | Baroclinic Pressure Gradient |
References
- Pritchard, D.W. Salinity distribution and circulation in the Chesapeake estuarine system. J. Mar. Res. 1952, 11, 106–123. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, D.V.; Rattray, M., Jr. Gravitational circulation in straits and estuaries. J. Mar. Res. 1965, 23, 104–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.C. On the nature of transverse variability in a coastal plain estuary. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 14209–14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winant, C.D. Three-dimensional wind-driven flow in an elongated, rotating basin. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.A.; Geyer, W.R.; Lerczak, J.A. Subtidal salinity and velocity in the Hudson River estuary: Observations and modeling. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, H.; Schulz, E.; Schuttelaars, H.M. Impact of estuarine convergence on residual circulation in tidally energetic estuaries and inlets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garreaud, R.D.; Falvey, M. The coastal winds off western subtropical South America in future climate scenarios. Int. J. Climatol. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E.; Friedrichs, C.T.; Brubaker, J.M. Control of estuarine stratification and mixing by wind-induced straining of the estuarine density field. Estuaries 2005, 28, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, S.N.; MacCready, P. Reverse estuarine circulation due to local and remote wind forcing, enhanced by the presence of along-coast estuaries. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 10184–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidzieko, N.J.; Hench, J.L.; Monismith, S.G. Lateral circulation in well-mixed and stratified estuarine flows with curvature. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 831–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seim, H.; Gregg, M.C. The importance of aspiration and channel curvature in producing strong vertical mixing over a sill. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 3451–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chant, R.J. Secondary circulation in a region of flow curvature: Relationship with tidal forcing and river discharge. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.A.; Simpson, J.H. Axial convergence in a well-mixed estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1985, 20, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, J.R.; Monismith, S.G. Secondary currents in a curved, stratified, estuarine channel. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthois, L.; Hoorelbeck, J. Etude Dynamique de la Sedimentation dans trois Cours d’eau de la Guyane Française: La riviere Mahury, la Riviere de Cayenne, et le Fleuve Maroni; Memoires ORSTOM; ORSTOM: Marseille, France, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Jouanneau, J.; Pujos, M. Suspended matter and bottom deposits in the Mahury estuarine system (French Guiana): Environmental consequences. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1987, 21, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orseau, S.; Lesourd, S.; Huybrechts, N.; Gardel, A. Hydro-sedimentary processes of a shallow tropical estuary under Amazon influence. The Mahury Estuary, French Guiana. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 189, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas, L.F.; Vendeville, P.; Leopold, M.; Guiral, D.; Ternon, J.F. Marine biodiversity in French Guiana: Estuarine, coastal and shelf ecosystems under the influence of Amazonian waters. Guiana 2003, 67, 302–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambs, L.; Muller, E.; Fromard, F. The Guianese paradox: How can the freshwater outflow of the Amazon increase the salinity of the Guianan shore? J. Hydrol. 2007, 342, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanneau, J.M.; Pujos, M. Suspended matter and bottom deposits in the Maroni estuarine system (French Guiana). Neth. J. Sea Res. 1988, 22, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottolichio, A.; Gardel, A.; Huybrechts, N.; Maury, T.; Morvan, S.; Lesourd, S. Premières observations de la dynamique hydro-sédimentaire de l’estuaire du Maroni (Guyane). In Proceedings of the XV National Conference on Coastal and Civil Engineering (GCGC), La Rochelle, France, 29–31 May 2018; pp. 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratiot, N.; Gardel, A.; Anthony, E.J. Trade-wind waves and mud dynamics on the French Guiana coast, South America: Input from ERA-40 wave data and field investigations. Mar. Geol. 2007, 236, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Master, D.J.; Mckee, B.A.; Moore, W.S.; Nelson, D.M.; Showers, W.J.; Smith, W.O., Jr. Geochemical processes near the mouth of the Amazon River/ocean boundary. Oceanography 1991, 4, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anthony, E.J.; Gardel, A.; Gratiot, N.; Proisy, C.; Allison, M.; Dolique, F.; Fromard, F. The Amazon-influenced high mud-supply shores of South America: A review of mud bank-shoreline interactions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 103, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Brunier, G.; Gardel, A.; Hiwat, M. Chenier Morphodynamics on the Amazon-Influenced Coast of Suriname, South America: Implications for Beach Ecosystem Services. Front. Earth Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, T.M. In situ “calibration” of ship-board ADCPs. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1989, 6, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.E.; Emery, W.J. Data Analysis Methods in Physical Oceanography, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jay, D.A.; Kukulka, T. Revising the paradigm of tidal analysis—The uses of non-stationary data. Ocean. Dyn. 2003, 53, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R. Influence of wind on dynamics and flushing of shallow estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Levinson, A.; Reyes, C.; Sanay, R. Effects of bathymetry, friction and rotation on estuary-ocean exchange. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2003, 33, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, A.; Hill, A.E.; Fujiwara, T.; Simpson, J.H. Effect of the Earth’s rotation on the circulation in regions of freshwater influence. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 16961–16969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E.; Geyer, W.R.; Lerczak, J.A. The influence of lateral advection on the residual circulation: A numerical modeling study of the Hudson River estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerczak, J.A.; Geyer, W.R. Modeling the lateral circulation in straight, stratified estuaries. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 1410–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.B. The relative importance of the various nonlinear mechanisms in a wide range of tidal interactions (review). In Tidal Hydrodynamics; Parker, B., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 237–268. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.H.; Brown, J.; Matthews, J.; Allen, G. Tidal straining, density currents, and stirring in the control of estuarine stratification. Estuaries 1990, 13, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M. Wind-driven lateral circulation in a stratified estuary and its effects on the along-channel flow. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C09005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdrup, H.U.; Johnson, M.W.; Fleming, R.H. The Oceans; Prentice-Hall, INC.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 516–604. [Google Scholar]
- Bourret, A.; Devenon, J.-L.; Chevalier, C. Tidal influence on the hydrodynamics of the French Guiana continental shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolievt, M.; Anthony, E.J.; Gardel, A.; Brunier, G. Multi-decadal to short-term beach and shoreline mobility in a complex river-mouth environment affected by mud from the Amazon. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).