Abstract
F_TIDE has been proven to be effective in obtaining the time-varying harmonic parameters of nonstationary tidal signals, and the results near the two endpoints of the analyzed time series are more accurate than those obtained by S_TIDE, which provides good conditions for the prediction of future sea levels. In this paper, F_TIDE is used for the short-term prediction of nonstationary tides in Nome (Alaska) and South Beach (Oregon). The significance of each standard parameter of F_TIDE is quantified by calculating its signal-to-noise ratio to determine the appropriate parameters that can be used for prediction. F_TIDE performs well in forecasting the sea level for three weeks at the Nome gauge and one week at the South Beach gauge. F_TIDE causes 30.1% and 42.0% decreases in the mean absolute errors between the forecasts and the observations compared to T_TIDE. F_TIDE is applied to the original signal at the Nome gauge, and the results show a strong correlation between the variation in M2 amplitude and the variation in the mean sea level. A potential mechanism is speculated in that changes in tides are affected by the changes in water depth on different time scales, which the sea level pressure, wind, sea ice, and other marine motions may contribute to.
1. Introduction
Tides are closely related to human activities. Tide level forecasting is vital for the development of marine resources and coastal structures and the prevention of marine disasters. As a ubiquitous movement in the ocean, tides greatly affect coastal erosion [1], navigation to and from ports [2], and coastal ecosystems [3].
Under the traditional assumption of stationarity, tides are regular changes in sea levels, driven by the tide-generating force of the Sun and Moon [4]. Tide levels can be predicted well due to regular variations in the relative positions of the planets [5]. However, over the past few decades, oceanographers have realized that the nonstationary properties of tides are ubiquitous worldwide [6,7], which greatly increases the difficulty of tidal simulation and prediction. The accurate extraction of the nonstationary properties of tides can help us understand the interaction of different marine motions and the cause of nonstationarity and improve prediction results. Therefore, the study of tidal variations holds both scientific significance and practical value, representing a key focus in contemporary tidal research.
There are many mechanisms for tidal changes. Astronomical forces generally cause the variations in tidal amplitudes to have fixed periods (such as semiannual, annual, 4.4-year, 8.85-year, and 18.61-year) or secular trends [4,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Some non-astronomical forces can also make tides undergo quasiperiodic and aperiodic changes, which are difficult to capture. According to some studies, tidal changes may be caused by variations in water depth [16,17,18,19,20], sea ice [21,22], internal tides [11], bottom friction [9,23], non-linear interactions between tides [24], other physical processes [25,26,27], and some anthropogenic factors (such as the construction of ports, land reclamation, etc.) [28,29].
Over recent decades, tidal prediction techniques have undergone continuous refinement, driven by advances in numerical modeling, statistical methods, and machine learning approaches. Generally, the numerical models used for water level forecasting are constantly being developed [30,31,32,33], but hydrodynamic models rely on input data and the forecast value of the boundary, leading to uncertainty in prediction results. A time series analysis based on water levels can also predict the nonstationary properties of a tide. Rashid and Wahl [34] used discrete wavelet transform and formulated regression models for each frequency separately, to establish a prediction model for low-frequency variations (decadal to multidecadal) of extreme sea levels. Chen et al. [35] used autoregressive analysis and the NS_TIDE model to improve the short-term water level prediction (24 h) of the Yangtze estuary. Tu et al. [36] used residual analysis to predict short-term nonstationary water levels (3 h). A pure mathematical method, cardinal B-spline basis functions, has been proposed for high tide forecasts (4 h) at the Venice lagoon [37,38,39,40,41,42]. In addition, neural networks and deep learning are also widely used for nonstationary tidal prediction [40,41].
Wang et al. [43] indicated that F_TIDE is an effective approach for dealing with nonstationary tides through the analysis of tidal gauge observations and comparisons between different harmonic analysis methods. The present study further explores improvements of F_TIDE in forecasting nonstationary tides and investigates the underlying causes of nonstationary tidal phenomena at the Nome gauge station. This article is organized as follows: The second part gives a description of materials and methods. The third part presents the applications of F_TIDE and preliminarily explores the physical significance of F_TIDE. The fourth part gives the conclusions of the paper.
2. Materials and Methods
In this paper, the sea level observations at two tidal gauges (Figure 1) are selected, which are provided by the University of Hawaii Sea Level Center (UHSLC, https://uhslc.soest.hawaii.edu/, accessed on 23 August 2021). A 17-year record (from 1998 to 2014, Figure 2a) at Nome (Alaska) and a 20-year water level record (from 1997 to 2016, Figure 2b) at South Beach (Oregon) with hourly intervals are used.
Figure 1.
Map of the west coast of North America.
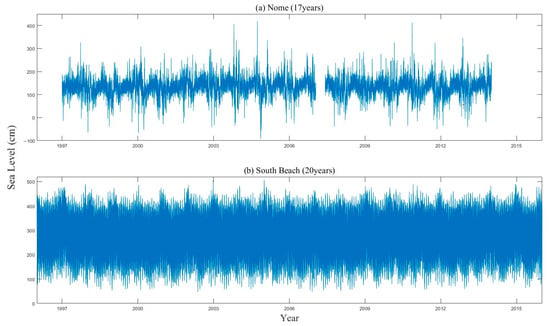
Figure 2.
Water level records at (a) Nome (Alaska) and (b) South Beach (Oregon) in the US (unit: cm).
F_TIDE combines Fourier series and classical harmonic analysis, and the sea level can be expressed by:
where Z(t) is the sea level at time t. σj is the tidal frequency corresponding to the j-th tidal constituent. λi = 2πi/L is the frequency of the harmonic parameter, meaning that the harmonic parameter has the period L/i; L is the time length of the analyzed data; N and Ns are the maximum cycle numbers (CNs) in the analyzed data corresponding to the highest frequency term in the Fourier series for the harmonic parameters and the mean sea level (MSL); sj and kj are the background value and the coefficient of trend term on the j-th tidal constituent. J is the number of constituents with a changing harmonic parameter and J-J1 is the number of constituents with a constant harmonic parameter. N, Ns, J1, and J are adjustable variables and a1j,i, a2j,i, b1j,i, b2j,i, a3i, b3i, Aj, Bj, k1j, k2j, k3, s1j, s2j, and s3 are unknown parameters, which can be solved by the least squares method with sufficient observations Z(t). Refer to Zhang et al. [43] for details on data and methods. T_TIDE [44] and F_TIDE are used to forecast the future sea level at the two tidal gauges and explore the reason for nonstationary tides.
3. Results
3.1. Prediction in F_TIDE
The accuracy of F_TIDE results has been validated by Zhang et al. [43]. Compared to S_TIDE [45], F_TIDE still yields satisfactory results near the endpoints, which provides a favorable basis for future sea level predictions. Since the harmonic parameters in F_TIDE are constructed using trigonometric functions, the future sea level can be calculated by substituting the values to t in Equation (1). According to Zhang et al. [43], CN is the important parameter for adjusting the scale of results. It is necessary to choose the appropriate CN value or select some appropriate coefficients for effective prediction. In the classical harmonic analysis [10], the tidal constituents obtained according to the Rayleigh criterion do not all participate in the prediction, but the tidal constituents with the signal to noise ratios (SNRs) of amplitudes greater than 2 (significant tidal constituents) are selected to participate in the prediction, thereby reducing the uncertainty of the predictive model. Similarly, the uncertainty of F_TIDE is quantified by the SNRs of the standard parameters (amplitudes, MSL, slopes, etc.) with the aim of enhancing predictive performance. This approach helps distinguish which coefficients are statistically significant during the study period and which may be attributable to noise or observational error.
According to Pawlowicz et al. [44], for a non-linear function z = F(x,y) = (x2 + y2)1/2, an estimate of the standard error of z is converted non-linearly from the standard errors of x and y by using:
where ξ is the standard error. According to Equation (1), the standard parameters are defined as follows: hmj,i = F(amj,i,bmj,i), m = 1,2. Hj,i = F(h1j,i,h2j,i) is the amplitude to the j-th tidal constituent with CN = i. h3i = F(a3i,b3i) is the amplitude to MSL with CN = i. Kj = F(k1j,k2j) is the slope of the amplitude to the j-th tidal constituent, Hsj = F(s1j,s2j) is a constant amplitude to the j-th tidal constituent. The estimate of the standard error for these standard parameters are converted non-linearly using Equation (2). Then, 90% confidence intervals can be estimated using the standard errors, and the SNR of these standard parameters can be computed based on the square of the ratio of their values to standard errors.
Table 1 shows the estimation of the standard parameter at the Nome gauge in 1999 (the largest two constituents M2 and K1 and the MSL are considered to change with time). The trend of MSL and tidal constituents have extremely small values and can be ignored. The values of the parameter for changes in MSL is larger than those for changes in M2 and K1. The SNR for changes in MSL is mostly greater than 2 (only parameters with an SNR greater than 10 are shown for changes in MSL shown in Table 1), which indicates that sea level changes are mainly affected by MSL changes at the Nome gauge. Parameters with an SNR > 2 are considered statistically significant, as they are less susceptible to noise or observational errors and account for a substantial portion of the variance in the original signal. These significant parameters contribute effectively to the prediction process.

Table 1.
Parameter estimates obtained by analyzing the original signal in 1999 at the Nome gauge by F_TIDE (unit: cm). Only parameters with SNR greater than 10 are shown for changes in MSL.
Through the parameter estimates, the parameters of MSL with an SNR > 5 and the parameters of tidal constituents with an SNR > 2 are used to analyze the original observations made in 1999 by F_TIDE (including the first day of 2000 in order to distinguish 68 constituents for T_TIDE according to the Rayleigh criterion), and the sea levels for the next three weeks are predicted (Figure 3). The results show that the forecast result obtained by F_TIDE is obviously better than that of T_TIDE. The forecast obtained by T_TIDE has a root-mean-square error (RMSE) of 48.5 cm and a mean absolute error (MAE) of 40.2 cm, while F_TIDE yields an RMSE of 28.7 cm and an MAE of 24.5 cm, causing a 40.8% and 39.1% decrease in the RMSE and MAE, respectively. The maximum absolute error of the forecast is 112.5 cm and 60.6 cm in T_TIDE and F_TIDE.
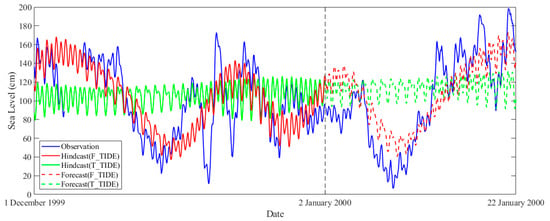
Figure 3.
The forecast for 3 weeks (2–22 January 2000) using F_TIDE and T_TIDE to analyze the data in 1999 (1 January 1999 to 1 January 2000). For clarity, the figure only shows the results from 1 December 1999 to 22 January 2000; the vertical black dashed line indicates the start time of the prediction.
The effective prediction of F_TIDE indicates that the nontidal perturbations (variation of MSL) have some significant periodic signals in a period of time, and the parameters corresponding to these frequencies are significant, and so can be used for prediction. F_TIDE can find the quasi-periodic variation of MSL with relatively fixed frequencies (low frequencies) at the Nome gauge, and has the ability to predict nonstationary tides in a short time. To evaluate the predictive capability of F_TIDE, the raw annual signals are analyzed, and sea level predictions are generated for a three-week horizon at the Nome station. The average MAE of the forecast results is reduced by 30.1% compared with T_TIDE, which shows that F_TIDE can effectively improve the prediction results.
Similarly, F_TIDE is applied to the prediction of the sea level at the South Beach gauge. Figure 4 shows that the sea levels for one week are predicted by analyzing the original observations in 1999 by T_TIDE and F_TIDE. Since the sea level is relatively stable at the South Beach gauge, T_TIDE has been able to obtain the hindcast of the original sea level and realize the effective prediction of the future sea level (68 constituents according to the Rayleigh criterion). F_TIDE can obtain more accurate hindcast and forecast results (7 days). The forecast obtained by T_TIDE has an RMSE of 21.2 cm, an MAE of 19.8 cm, and a relative error of 7.9%, while F_TIDE yields an RMSE of 9.4 cm, an MAE of 7.6 cm, and a relative error of 2.8%, causing a 55.7% and 61.6% decrease in the RMSE and MAE, respectively. However, the prediction results by F_TIDE are similar to or worse than those by T_TIDE after 9 January 2000. Consistent with the procedure applied at the Nome tide gauge, the raw annual data are analyzed, and sea level predictions are generated for a one-week horizon at the South Beach tide gauge. Compared to T_TIDE, the predictions yield a 42.0% reduction in mean absolute error.
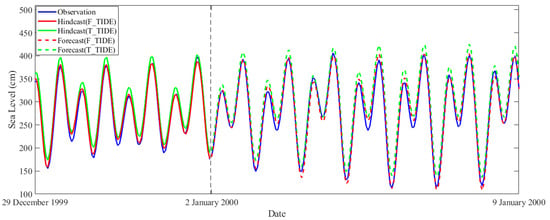
Figure 4.
The forecast for 1 weeks (2–9 January 2000) using F_TIDE and T_TIDE to analyze the data in 1999 (1 January 1999 to 1 January 2000). For clarity, the figure only shows the results from 29 December 1999 to 9 January 2000; the black dashed line indicates the start time of the prediction.
When different CNs are employed, certain standard parameters may exhibit statistical significance during specific time periods; however, their influence on predictions is often time-varying. For a certain frequency in a nonstationary signal, the significance of the corresponding parameter may be changed in different time periods. The fitting coefficients can be obtained from observations and the significance of standard parameters can be quantified by SNR, but they may be insignificant in the next time period. Generally, there is a transition period (days or even weeks) for these parameters to change from significant to insignificant, because most changing tides caused by natural factors are continuous and slow. For signals with less pronounced nonstationary characteristics, the significance of parameters also diminishes more rapidly over time. This explains why the prediction result by F_TIDE is better than that by T_TIDE in the first 7 days at the South Beach gauge, but it is not as good as that by T_TIDE in some later days. Some parameters are not significant after 7 days, which negatively affects the prediction of sea levels. Nevertheless, these parameters are still conducive to the accuracy of reconstructed sea levels in the transition period, which is the basic assumption by which F_TIDE can be used for short-term prediction. Therefore, the parameters that can be used for prediction must pass the significance test in F_TIDE.
3.2. Exploring the Main Mechanisms Causing Tide Changes by F_TIDE
The selection of CN has been discussed in previous studies [43], by changing the CN, F_TIDE can extract the time-varying amplitudes in nonstationary tides at different time scales. In this section, F_TIDE is applied to explore the main mechanisms causing tide changes at the Nome gauge.
At the Nome gauge with the shallow water depth [46], the time-varying amplitudes of the M2 tidal constituent and the time-varying MSLs are obtained by F_TIDE with different CNs, and the correlation coefficients reached 0.78, 073, 0.66, and 0.52 (Figure 5). The high correlation coefficients between the M2 amplitude and the MSL indicate that tide changes may be driven by water depth changes due to MSL changes. With decreases in CN, the correlation coefficients increase, indicating that the impact of MSL changes on tidal amplitudes is principally reflected on long time scales. Recent research has shown that rising sea levels will increase the tidal range in many areas, such as the Delaware estuary [47], Gulf of Mexico [48], and some portions of the Bohai Sea [49,50]. Changes in water depth have been explored as one of the main drivers of changes in tides at the regional/global scale [17,21,51,52]. Tides behave as shallow-water waves and thus are strongly affected by water depth [7]. At the Nome gauge with the shallow water depth and weak tide, the variation of the tide is almost dominated by the variation of the MSL.
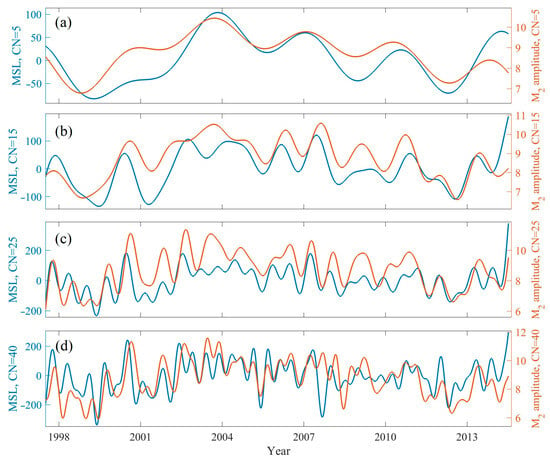
Figure 5.
(a–d) MSL (unit: cm) and M2 amplitudes (unit: cm) obtained by F_TIDE with CN= 5, 15, 25, and 40.
The factors causing the water depth changes naturally become the mechanisms that drive tide changes. In Nome at high latitudes, annual sea ice is found in Norton Sound from about early November until late May [53]. The melt and growth of sea ice will also cause variations in MSL, generally showing seasonal variation [20]. Varying sea ice is an important factor for driving tide changes [7], and cannot be neglected in forecast model predictions [22]. In addition, wind speed is also a factor affecting MSL changes on a short time scale at Nome. According to the study by Blier et al. [46], during the October 1992 storm surge event in Nome, the increase in wind speed exhibited a strong correlation with the rise in sea level. The lowest atmospheric pressure and the strongest wind gusts occurred almost simultaneously with the peak water level. Numerical modeling experiments also verify this phenomenon. As can be seen from Figure 5, with increases in CN, the M2 amplitudes have a good correlation with the MSLs in some high peak areas, which indicates that some physical processes on a shorter time scale may still cause tide changes. In conclusion, the MSL changes are caused by various factors, which in turn may cause tide changes. F_TIDE results can provide some references for studying the mechanisms of tide changes; this, however, needs to be verified by numerical models and other methods.
3.3. Parameter Setting
In analyzing the sea level by F_TIDE, the long-term or short-term variation (diurnal, weekly, semiannual, annual, three-years, five-years, or even ten-years) of amplitude may be significant. It is more likely that the amplitudes have significant high-frequency variations at a location with complex or drastic background flows. Therefore, it is important to choose the appropriate cycles (or CNs) at different locations.
In order to make it convenient to use F_TIDE in analyzing tidal data, a suggested scheme is performed according to the following steps: (1) The appropriate constituents are selected by the Rayleigh criterion, and then, the harmonic constants of each constituent are obtained by classical harmonic analysis. (2) The long-period tidal constituents are regarded as constant tidal constituents. The tidal constituents of interest (generally the tidal constituents with large amplitudes) are set to change with time, and the others are regarded as constants. (3) The CN is determined according to the length of the time series for the sea level (assuming that the length is k years). If only the interannual variation is considered, the CNs for the harmonic parameters and MSL are set to be less than k. If the annual variation is considered, the CNs for the harmonic parameters and MSL are set to be greater than k. In this way, seasonal variation and semiannual variation for tidal constituents can be obtained. (4) Insignificant parameters with a low SNR are eliminated. If the estuary tide seriously affected by the river flow is studied, higher values of CNs should be adopted to capture variations at shorter temporal scales.
The above scheme has been applied to observations at the Nome gauge. The time-varying amplitudes of the seven tidal constituents (M2, K1, Sa, Ssa, Mf, S1, and Msm) and the time-varying MSL are captured by F_TIDE for analyzing the 17-year data. The time-varying amplitudes of five tidal constituents (M2 K1, Ssa, Mf, and Msm) and the time-varying MSL are captured by F_TIDE for analyzing 1-year data (2009). Table 2 shows the results obtained by F_TIDE and T_TIDE (segmented harmonic analysis) with 17-year and 1-year data. Note that the constituents near the above constituents are considered to be stationary, and some cycles in MSL (corresponding frequencies near long-period constituents) are eliminated in advance (the detailed description in Section 3.4). According to Table 2, the tidal amplitudes and MSL obtained by F_TIDE are basically consistent with those obtained by T_TIDE for analyzing 17-year and 1-year data, which shows the wide applicability of F_TIDE.

Table 2.
The amplitudes and MSL obtained by F_TIDE and T_TIDE (unit: cm). 17 and 1 represent the analysis of 17-year and 1-year (2009) data, respectively. Bold numbers indicate the average of the time-varying parameter.
3.4. Physical Meaning of F_TIDE
The essence of F_TIDE is that the time-varying harmonic parameters and MSL can be represented by a linear combination of trigonometric functions with fixed periods. The regular variation (semiannual, annual, 2-year and 3-year) of tidal amplitude is often meaningful. For example, M2 and K1 amplitudes are added trigonometric functions with periods of 1 year and 0.5 years, which essentially expresses the seasonal variability and the semiannual variability of M2 and K1. The variability may be obvious at some tidal gauges. For example, M2 amplitude varies with a period of about two years, and K1 amplitude varies with a period of about three years at Nome gauge (Zhang et al. [43]). The quasi-periodic variation of tidal amplitudes is common in oceans and rivers. Therefore, the trigonometric function applied to the harmonic parameters plays an important role. Nevertheless, some sinusoidal terms of tidal amplitude may not be significant, potentially leading to unrealistic results due to the influence of noise. When CN increases, Equation (1) may include more sinusoidal terms whose coefficients are not significant. The fitting coefficients with low SNRs should be discarded.
The role of CN can be explained in another way. Let
where S0 is MSL. Hj(t) and θj are the time-varying amplitudes and the phase lag corresponding to the j-th tidal constituent. φj,i is phase of i-th term in a Fourier series corresponding to the j-th tidal constituent. Combining Equations (3) and (4), according to product-sum identities, we can get:
As can be seen from Equation (5), each tidal constituent can be expressed in the combination of 2N + 1 sub tidal constituents, and their frequencies are σj − λN, σj − λN−1, …, σj − λ1, σj, σj + λ1, …, σj + λN. The variation of amplitudes is of a lower frequency than that of the sea level, resulting in λi being much smaller than σj. Therefore, the frequencies of these sub tidal constituents exist around σj. In other words, the tidal constituents with a time-varying amplitude are essentially expressed as a combination of 2N + 1 tidal constituents with nearby frequencies (from σj − λN to σj + λN).
Pan et al. [44] confirmed that the time-varying tidal constituents will absorb the energy from nearby constituents in S_TIDE, and more IPs will enhance the absorption effect. In F_TIDE, the increase of CN leads to the increase of λN, so the frequency band of each constituent will become wider (from σj −λN to σj + λN). The tidal constituent with the frequency of σj includes nearby frequencies from σj − λN to σj + λN, which is shown as absorbing the energy from the nearby constituents. This also explains why the K1 constituent appears as a new cycle with a large CN (Figure 8c in Zhang et al. [43]). The large value of CN causes the wide frequency band of K1, which causes the absorption of nearby constituents (S1 and ψ1). In order to avoid unrealistic results, the constituents close to K1 should be regarded as constant constituents and extracted in advance, or the CN of K1 be set to a relatively small value, since the variations in tidal amplitude are often slow.
In Equation (1), the expression of the term a3icosλit is similar to the term Ajcosσjt (s1jcosσjt). In order to obtain a3i and Aj (s1j) accurately, λi is required not to be equal to or approximately equal to σj. Otherwise, frequency aliasing will occur, and the sensitivity of a3i and Aj (s1j) to the data will be greatly increased, which will easily lead to incorrect fitting results. Since the frequency of MSL changes is generally much less than that of diurnal tides, the value of λi is usually small, but the frequency σj of the long-period constituents is also small. Therefore, the CN of MSL may affect the results of the long-period constituents. This is why the long-period constituents are often considered constant constituents in F_TIDE. If the change of long-period constituents is considered, the CN of MSL should be selected carefully.
Increasing the value of CN allows results to be obtained at finer temporal scales; however, this approach is constrained by two main limitations. First, when the CN is excessively large, the constituent components may interfere with one another. There is an example to explain: Figure 6 shows the power spectral densities of the 10-year sea level (1998 to 2007) at the Nome gauge. It can be seen that N2 and M2 are major semi-diurnal tidal constituents with similar frequencies. In F_TIDE, the constituents M2 and N2 are assumed to vary over time for analyzing 10-year data at the Nome gauge. Their own frequencies (CN = 0) are 11.913 rad∙d−1 and 12.141 rad∙d−1, respectively. When the CN becomes larger, the frequency bands of the two tidal constituents becomes wider (blue dots in Figure 6). M2 and S2 show the frequency bands of 11.913 ± 0.114 rad∙d−1 and 12.141 ± 0.114 rad∙d−1 with CN = 66, and the two frequency bands overlap. The overlap frequency of 12.027 rad∙d−1 will greatly increase the sensitivity of the fitting coefficient, which will be easily affected by abnormal data. Therefore, CN = 66 is the upper limit of M2 and N2 for the analysis of 10-year data. Second, long-period tidal constituents and time-varying MSL may interfere with each other due to their similar periodic variations. Similarly, Figure 6b shows the power spectral densities in the low frequency band for analyzing 10-year data. In F_TIDE, MSL is considered to change with time, and the CN for MSL increases from 0 to 10, causing the frequency bands to gradually become wider. When CN is set to 10, the time-varying MSL will contain a periodic variation with a frequency of 1.721 × 10−2 rad∙d−1. If the constituents Sa (frequency is 1.720 × 10−2 rad∙d−1) is considered, the almost equal frequencies will easily lead to wrong results. The limitations of tidal constituents and MSL are essentially the same. Complicating the zero-frequency solution can improve the tidal results, but it also brings more restrictions. The Rayleigh criterion of F_TIDE is redefined as avoiding the overlap between different frequency bands.
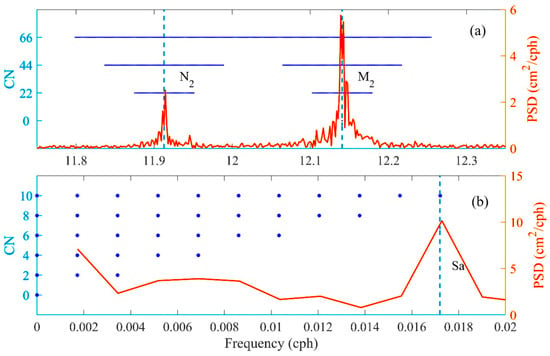
Figure 6.
The power spectral densities (red line) of the 10 yr sea level at the Nome gauge and frequency bands (blue dot) at different CNs for (a) N2 and M2 constituents and (b) MSL.
The tidal response to the variation of other physical motions is often to generate new frequencies around the original tidal frequencies, which is expressed as the energy transfer for high-frequency tidal signals. Similarly, the variation of MSL can generate new low-frequency signals. The generated frequency band (from σj − λN to σj + λN) can contain the tidal constituents whose frequencies are transferred. Therefore, the Fourier series in F_TIDE shows unique advantages in capturing time-varying amplitudes and MSL in the study of nonstationary tides.
The hindcasts of F_TIDE do not require all terms of the Fourier series to be statistically significant. The complete finite Fourier series can accurately show the tide changes at a specific time scale, which are consistent with the results of S_TIDE in Zhang et al. [43]. However, it is difficult to use the complete finite Fourier series to forecast the future sea level. The tide changes at some frequencies (some terms of the Fourier Series) are not significant, and they are difficult to exist in the next time period. Only the significant frequencies are conducive to effective short-term prediction. This is also an interesting property of Fourier series: With a high cutoff frequency, Fourier series can approximate any time series and accurately simulate the original signal. When only some terms are selected or the cutoff frequency is low, Fourier series only represent the newly added frequencies on the basis of the original frequencies, which can be used to improve the prediction of nonstationary tides.
4. Conclusions
F_TIDE has been demonstrated to effectively extract time-varying harmonic parameters from non-stationary tidal signals. Building upon previous research, this study applies F_TIDE to conduct the short-term prediction of non-stationary tides at two locations: South Beach (Oregon), and Nome (Alaska). By applying F_TIDE to the raw signal from the Nome tide gauge, we analyze and discuss potential influencing factors on tidal variations in the region.
In the short-term prediction of non-stationary tides, significant standard parameters can be selected for prediction by calculating the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of each parameter. Since both harmonic parameters and the mean sea level height can be expressed as a superposition of trigonometric functions, future sea level values can be predicted by substituting time t into Equation (1). F_TIDE was applied to the raw observational data from the Nome and South Beach tide gauges for the year 1999, generating sea level predictions for the subsequent three weeks and one week, respectively. Compared to T_TIDE, the average mean square error of the predictions was reduced by 30.1% and 42%, demonstrating that F_TIDE effectively improves short-term forecast accuracy. However, as the prediction period extends, the significance of standard parameters tends to weaken and may even adversely affect forecast performance, leading to degraded prediction quality over longer time spans.
Regarding the physical mechanisms, F_TIDE was applied to the raw signal from the Nome tide gauge. By selecting different CN values, we compared and analyzed variations in the M2 constituent amplitude and Mean Sea Level (MSL) across multiple time scales. The results indicate a strong correlation between changes in the M2 amplitude and changes in MSL, suggesting that tidal variations in Nome are likely driven by water depth changes resulting from MSL fluctuations, in the context of relatively shallow water. Changes in MSL may be influenced by factors such as sea-level pressure, wind forcing, and dynamic sea ice conditions, which could in turn contribute to variations in tidal behavior. While the results from F_TIDE can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying tidal changes, this conclusion remains preliminary due to limitations in data and methodology. Further validation through the collection of multi-parameter observational data and numerical modeling is necessary in subsequent studies.
This study further explores the application of F_TIDE in the analysis of non-stationary tides and its physical implications, demonstrating its effectiveness in both short-term prediction and investigations into the mechanisms underlying non-stationary tidal variations. In the future, F_TIDE is expected to serve as a viable method for studying non-stationary oceanic tides, river tides, and internal tides. It can also be integrated with multi-parameter data analysis and numerical modeling to investigate tidal dynamics and their driving mechanisms on a global scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.C. and X.L.; methodology, Y.Z. and S.J.; software, S.J. and Y.Z.; validation, S.J. and Y.Z.; formal analysis, S.J. and Y.Z.; investigation, S.J. and Y.Z.; resources, W.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.J. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.C. and X.L.; visualization, S.J.; supervision, X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Coastal Ecosystem (202314), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42076011), and the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2022YFC3105003).
Data Availability Statement
The water level observations were provided by the University of Hawaii Sea Level Center (https://uhslc.soest.hawaii.edu/, accessed on 23 August 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Rich Pawlowicz, Bob Beardsley, and Steve Lentz for distributing the T_TIDE package. The authors thank Anzhou Cao and Yuzhe Wang for their help in the process of writing the manuscript. The numerical simulation was supported by the High-Performance Computing Division of the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Idier, D.; Bertin, X.; Thompson, P.; Pickering, M.D. Interactions Between Mean Sea Level, Tide, Surge, Waves and Flooding: Mechanisms and Contributions to Sea Level Variations at the Coast. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 1603–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akan, Ç.; Moghimi, S.; Özkan-Haller, H.T.; Osborne, J.; Kurapov, A. On the Dynamics of the Mouth of the Columbia River: Results from a Three-Dimensional Fully Coupled Wave-Current Interaction Model. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 5218–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Haines, J.W. Variations in Tidal Level in the Gulf of Mexico and Implications for Tidal Wetlands. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 46, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doodson, A.T. The Harmonic Development of the Tide-Generating Potential. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1921, 100, 305–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, D.; Woodworth, P. Sea-Level Science: Understanding Tides, Surges, Tsunamis and Mean Sea-Level Changes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Talke, S.A.; Jay, D.A. Changing Tides: The Role of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 59, 121–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, I.D.; Pickering, M.D.; Green, J.A.M.; Arbic, B.K.; Arns, A.; Dangendorf, S.; Hill, D.F.; Horsburgh, K.; Howard, T.; Idier, D.; et al. The Tides They Are A-Changin’: A Comprehensive Review of Past and Future Nonastronomical Changes in Tides, Their Driving Mechanisms, and Future Implications. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, e2018RG000636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, M.G.G. Manual for Tidal Currents Analysis and Prediction. 1977. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264782849_Manual_for_Tidal_Currents_Analysis_and_Prediction?__cf_chl_tk=5.odFP4Id_L9.RMwysrI61sTI8FUcl1OGCl6Q.nRMjE-1756797774-1.0.1.1-k6d3rqfUy176tHOn2miIfVGS5gg9W2os15Ni1db4b0E (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Godin, G. The use of Nodal Corrections in the Calculation of Harmonic Constants. Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 1986, 63, 143–162. [Google Scholar]
- Foreman, M.G.G.; Henry, R.F. The Harmonic Analysis of Tidal Model Time Series. Adv. Water Res. 1989, 12, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosi, J.A.; Munk, W. Tales of the Venerable Honolulu Tide Gauge. J. Phys. Ocean. 2006, 36, 967–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, D.A. Evolution of Tidal Amplitudes in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L04603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.D. Secular Changes in the Solar Semidiurnal Tide of the Western North Atlantic Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L19601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, I.D.; Eliot, M.; Pattiaratchi, C. Global Influences of the 18.61 Year Nodal Cycle and 8.85 Year Cycle of Lunar Perigee on High Tidal Levels. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C06025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Lv, X. Is There a Quasi 60-Year Oscillation in Global Tides? Cont. Shelf Res. 2021, 222, 104433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.C.; Najjar, R.G.; Li, M.; Lee, S.B.; Zhang, F.; Liu, W. Fingerprints of Sea Level Rise on Changing Tides in the Chesapeake and Delaware Bays. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 8102–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelegger, M.; Green, J.A.M.; Wilmes, S.B.; Haigh, I.D. Can We Model the Effect of Observed Sea Level Rise on Tides? J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 4593–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idier, D.; Paris, F.; Le Cozannet, G.; Boulahya, F.; Dumas, F. Sea-Level Rise Impacts on the Tides of the European Shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 137, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, A.T.; Jay, D.A.; Zaron, E.D.; Talke, S.A.; Pan, J.; Lin, H. Tidal Variability Related to Sea Level Variability in the Pacific Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 8445–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Cherniawsky, J.Y.; Foreman, M.G.G.; Von Storch, J.S. Seasonal Variation of the M2 Tide. Ocean. Dyn. 2014, 64, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, M.D.; Horsburgh, K.J.; Blundell, J.R.; Hirschi, J.J.M.; Nicholls, R.J.; Verlaan, M.; Wells, N.C. The Impact of Future Sea-Level Rise on the Global Tides. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 142, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgas, N. Large Seasonal Modulation of Tides Due to Ice Cover Friction in a Midlatitude Estuary. J. Phys. Ocean. 2012, 42, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, G. The Propagation of Tides up Rivers with Special Considerations on the Upper Saint Lawrence River. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1999, 48, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, L.F.; Greenberg, D.A.; Garrett, C.J.R.; Dobson, F.W. Nodal Modulation of the Lunar Semidiurnal Tide in the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine. Science 1985, 230, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsburgh, K.J.; Wilson, C. Tide-Surge Interaction and Its Role in the Distribution of Surge Residuals in the North Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, C08003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M. The Influence of Changing Stratification Conditions on Barotropic Tidal Transport and Its Implications for Seasonal and Secular Changes of Tides. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 47, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, A.T.; Jay, D.A.; Talke, S.A.; Zaron, E. Can Tidal Perturbations Associated with Sea Level Variations in the Western Pacific Ocean Be Used to Understand Future Effects of Tidal Evolution? Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 1093–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Familkhalili, R.; Talke, S.A. The Effect of Channel Deepening on Tides and Storm Surge: A Case Study of Wilmington, NC. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9138–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, M.S. Tides of History: Ocean Science and Her Majesty’s Navy; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniawan, A.; Ooi, S.K.; Gerritsen, H.; Twigt, D. Calibrating the Regional Tidal Prediction of the Singapore Regional Model Using OpenDA. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Hydroinformatics (HIC 2010), Tianjin, China, 7–11 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Karri, R.R.; Badwe, A.; Wang, X.; El Serafy, G.; Sumihar, J.; Babovic, V.; Gerritsen, H. Application of Data Assimilation for Improving Forecast of Water Levels and Residual Currents in Singapore Regional Waters. Ocean Dyn. 2013, 63, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijl, F.; Verlaan, M.; Gerritsen, H. Improved Water-Level Forecasting for the Northwest European Shelf and North Sea through Direct Modelling of Tide, Surge and Non-Linear Interaction. Ocean Dyn. 2013, 63, 823–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijl, F.; Sumihar, J.; Verlaan, M. Application of Data Assimilation for Improved Operational Water Level Forecasting on the Northwest European Shelf and North Sea. Ocean Dyn. 2015, 65, 1699–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.M.; Wahl, T. Predictability of Extreme Sea Level Variations Along the U.S. Coastline. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2020JC016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gan, M.; Pan, S.; Pan, H.; Zhu, X.; Tao, Z. Application of Auto-Regressive (AR) Analysis to Improve Short-Term Prediction of Water Levels in the Yangtze Estuary. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.Z.; Gao, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, W.; Sun, Y.; Su, D. A Novel Method for Regional Short-Term Forecasting of Water. Water 2021, 13, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.L.; Billings, S.A. An Efficient Nonlinear Cardinal B-Spline Model for High Tide Forecasts at the Venice Lagoon. Nonlin. Process. Geophys. 2006, 13, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-P.; Lee, T.-L. Back-Propagation Neural Network in Tidal-Level Forecasting. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1999, 125, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.L.; Tsai, C.P.; Jeng, D.S.; Shieh, R.J. Neural Network for the Prediction and Supplement of Tidal Record in Taichung Harbor, Taiwan. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2002, 33, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.K.; Lin, L.C. Multi-Point Tidal Prediction Using Artificial Neural Network with Tide-Generating Forces. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Jun, S.C.; Hyun, Y.; Bae, G.O.; Lee, K.K. A Comparative Study of Artificial Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines for Predicting Groundwater Levels in a Coastal Aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Wu, C.H.; Hsieh, C.M.; Wang, Y.C.; Tsen, I.F.; Tseng, S.H. Deep Learning for Imputation and Forecasting Tidal Level. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 46, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, S.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Lv, X. Exploration the Effect of Nonstationary Signals on the Tidal Phenomenon Using F_TIDE Part, I. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowicz, R.; Beardsley, B.; Lentz, S. Classical Tidal Harmonic Analysis Including Error Estimates in MATLAB Using T TIDE. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blier, W.; Keefe, S.; Shaffer, W.A.; Kim, S.C. Storm Surges in the Region of Western Alaska. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1997, 125, 3094–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Li, M.; Zhang, F. Impact of Sea Level Rise on Tidal Range in Chesapeake and Delaware Bays. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 3917–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeri, D.L.; Hagen, S.C.; Plant, N.G.; Bilskie, M.V.; Medeiros, S.C.; Alizad, K. Tidal Hydrodynamics under Future Sea Level Rise and Coastal Morphology in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Earths Future 2016, 4, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelling, H.E.; Uehara, K.; Green, J.A.M. The Impact of Rapid Coastline Changes and Sea Level Rise on the Tides in the Bohai Sea, China. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, C.; Zou, T.; Jiang, D. Influence of Rising Sea Level on Tidal Dynamics in the Bohai Sea. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 74, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, A.; Wahl, T.; Dangendorf, S.; Jensen, J. The Impact of Sea Level Rise on Storm Surge Water Levels in the Northern Part of the German Bight. Coast. Eng. 2015, 96, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, D.A.; Blanchard, W.; Smith, B.; Barrow, E. Climate Change, Mean Sea Level and High Tides in the Bay of Fundy. Atmos.—Ocean. 2012, 50, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettema, R.; Asce, F.; Baker, J.L.; Howlett, G.; Asce, M.; Hudson, B. Ice-Floe Impact with a Rubble-Mound Causeway at the Port of Nome, Alaska. J. Cold Reg. Eng. 2019, 33, 05019001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Matte, P.; Chen, H.; Jin, G. Exploration of Tidal-Fluvial Interaction in the Columbia River Estuary Using S_TIDE. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 6598–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).