Field Determination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in the Seawater of the Shandong Peninsula, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Field Surveys, Sample Collection Analysis, Study Area, and Data Processing
2.1. Field Surveys, Sample Collection, and Analysis
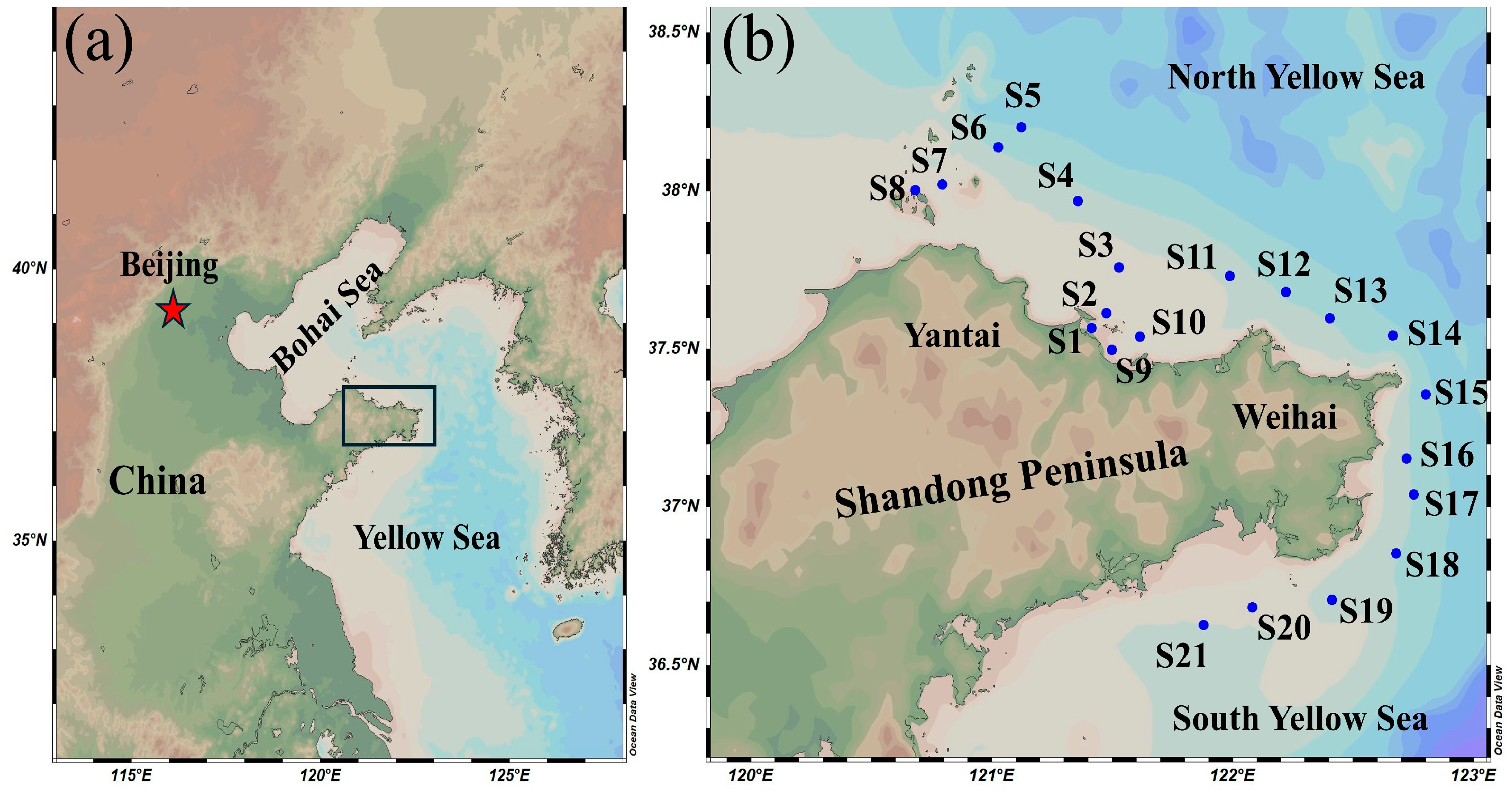
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Water Quality Assessment Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Distributions of the Hydrological Parameters and Nutrients in the Seawater
3.2. Spatial Distributions and Analysis of the Dissolved Metals in the Seawater
3.3. Comparison with Other Coastal Waters
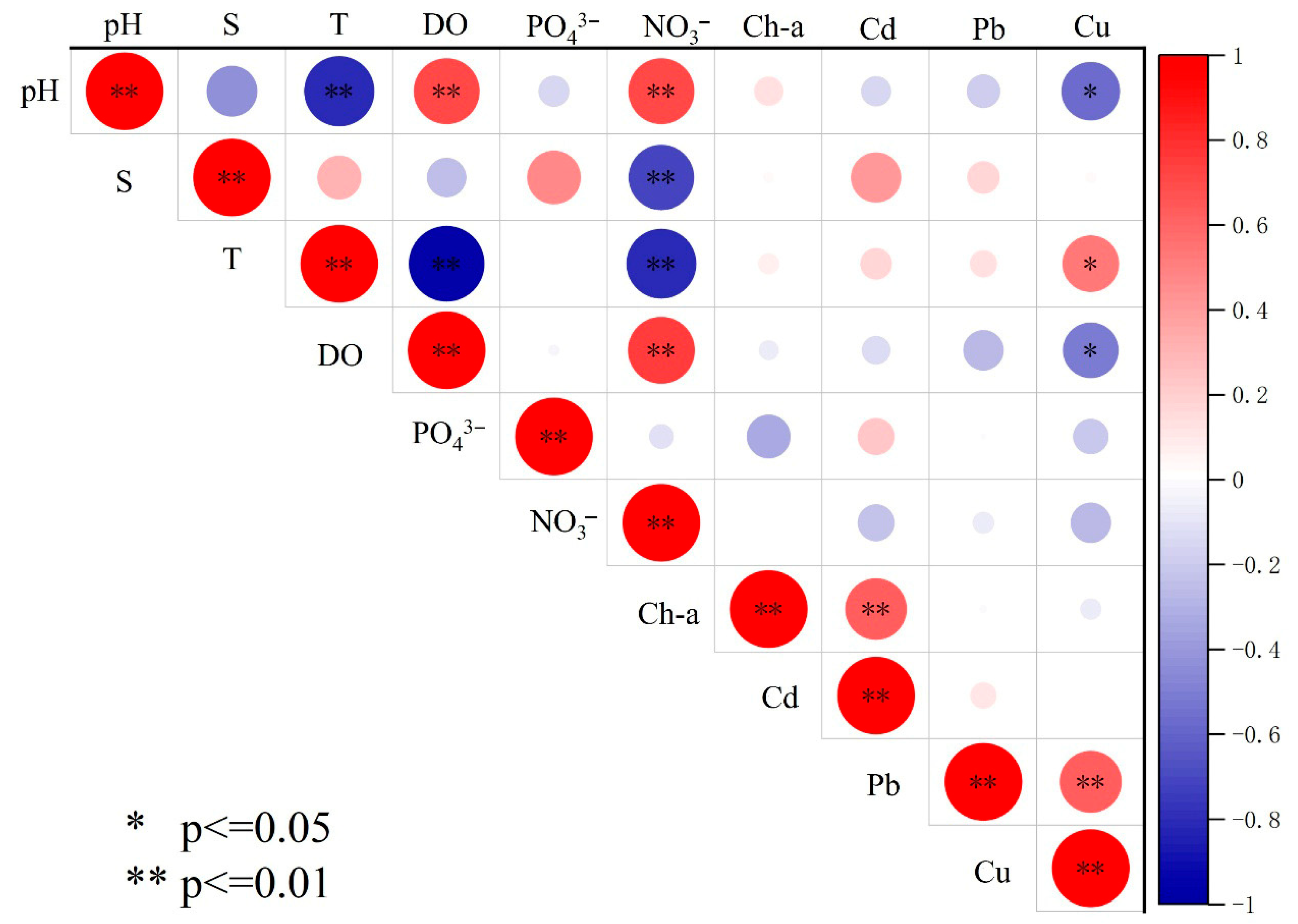
3.4. Factors Influencing the Distributions of the Total Dissolved Metals Concentrations
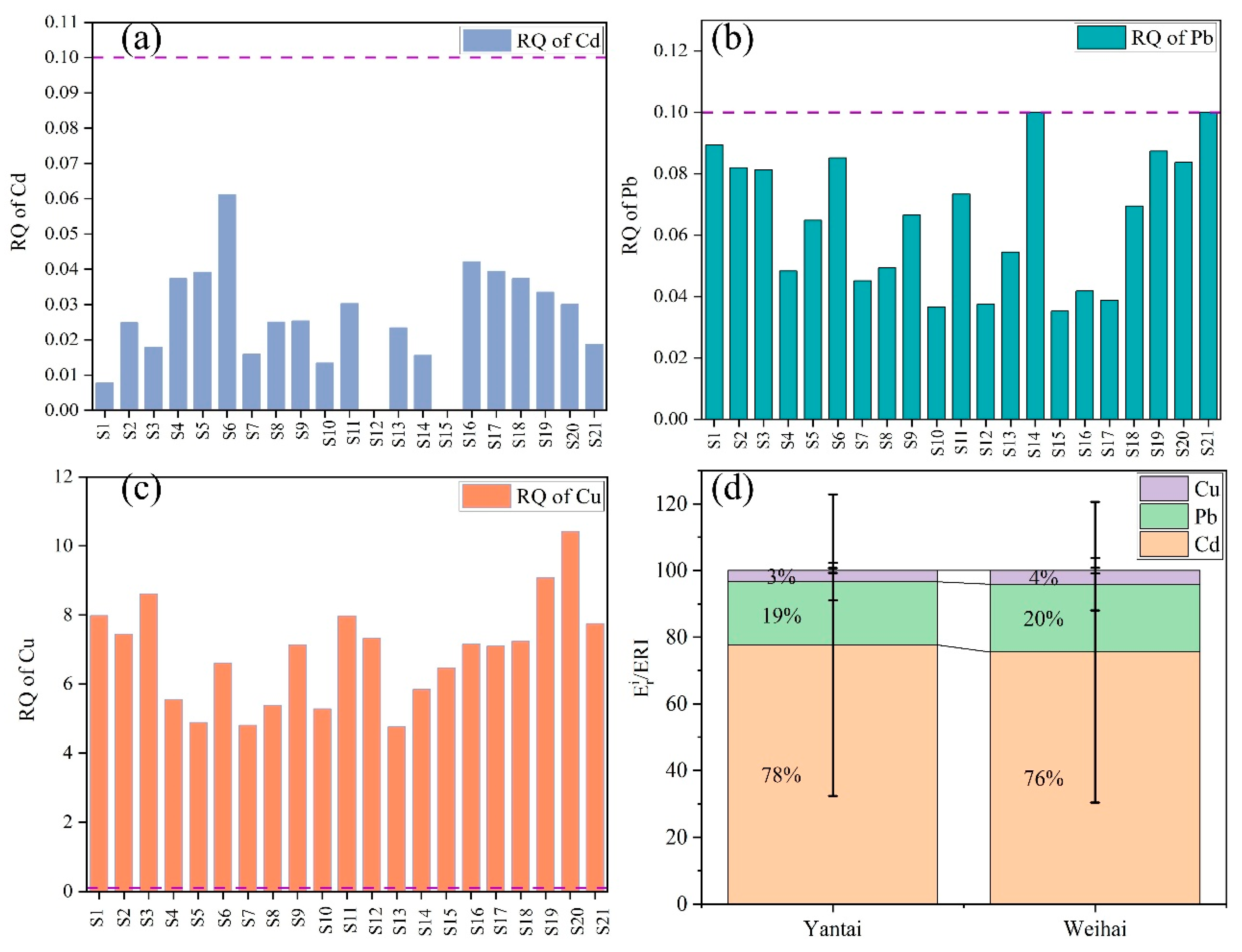
3.5. Water Quality and Ecological Risk Assessments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Frazier, M.; Afflerbach, J.; Lowndes, J.S.; Micheli, F.; O’Hara, C.; Scarborough, C.; Selkoe, K.A. Recent pace of change in human impact on the world’s ocean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.; Alotaibi, M.O.; Li, J.; Du, D.; Mahmoud, E. Heavy Metal Pollution in Coastal Environments: Ecological Implications and Management Strategies: A Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achary, M.S.; Panigrahi, S.; Satpathy, K.; Prabhu, R.; Panigrahy, R. Health risk assessment and seasonal distribution of dissolved trace metals in surface waters of Kalpakkam, southwest coast of Bay of Bengal. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 6, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Feng, H.; Shen, G.; Cao, Y.; Yu, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Spatiotemporal variation and potential risks of seven heavy metals in seawater, sediment, and seafood in Xiangshan Bay, China (2011–2016). Chemosphere 2018, 212, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fu, J.; Shi, J.; Jiang, G. Biomonitoring: An appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 606, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.L.; Xu, X.R.; Sun, Y.X.; Liu, J.L.; Li, H.B. Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of South China: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Bao, K.; Wang, H.; Dai, Y.; Wu, S.; Yan, K.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, J. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metals in the coastal zone of yantai, China. Water 2024, 16, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Lin, M.; Hu, G. Heavy metals distribution and environmental quality assessment for sediments off the southern coast of the Shandong Peninsula, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Pan, D.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Fan, X. Distribution and ecological health risk assessment of dissolved trace metals in surface and bottom seawater of Yantai offshore, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 993965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, A.; Hughes, H.P.; Kilbourne, K.H.; Schijf, J. An ICP-AES method for routine high-precision measurement of seawater Sr/Ca ratios to validate coral paleothermometry calibrations. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2021, 19, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffle, J.; Tercier-Waeber, M.L. Voltammetric environmental trace-metal analysis and speciation: From laboratory to in situ measurements. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.G.M.; Carrington, P.; Rowley-Neale, S.J.; Banks, C.E. Recent advances in portable heavy metal electrochemical sensing platforms. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2676–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riso, R.D.; Le Corre, P.; Chaumery, C. Rapid and simultaneous analysis of trace metals (Cu, Pb and Cd) in seawater by potentiometric stripping analysis. J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 351, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou, M.; Ochsenkühn, K.M. Comparison of inductively coupled plasma–atomic emission spectrometry, anodic stripping voltammetry and instrumental neutron-activation analysis for the determination of heavy metals in airborne particulate matter. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 369, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Pan, D.; Li, Y.; Han, H.; Wang, X.; Gai, G. Field determination and ecological health risk assessment of trace metals in typical mariculture area of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, X.; Ma, C.; Yao, Z.; Bao, X. Case analysis of water exchange between the Bohai and Yellow Seas in response to high winds in winter. J. Oceanogr. 2020, 38, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guan, C.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, W.; Yang, B. Progress on research and construction of marine ranching along the coast of Shandong Province of China. J. Shipp. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 4, 338–347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, D.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Han, Q. Heavy metal contamination in the marine organisms in Yantai coast, northern Yellow Sea of China. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, D.; Zheng, B.; Fang, Y.; Shen, G.; Liu, H. Distribution and pollution assessment of trace metals in seawater and sediment in Laizhou Bay. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Wu, Q.; Liu, P.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Shi, B.; Zhou, Y.; Kwon, B.O.; Choi, K.; Ryu, J. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments and water from the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.; Grist, E.; Leung, K.; Morritt, D.; Crane, M. Species sensitivity distributions: Data and model choice. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.C.; Ownby, D.R.; Mézin, L.C.; Powell, D.C.; Christensen, T.R.; Lerberg, S.B.; Anderson, B.A. Applying species-sensitivity distributions in ecological risk assessment: Assumptions of distribution type and sufficient numbers of species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlı, C.; Varol, M.; Ustaoğlu, F. Ecological and health risk assessment and quantitative source apportionment of dissolved metals in ponds used for drinking and irrigation purposes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 52818–52829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, I.; Beiras, R. Ecotoxicologically based marine acute water quality criteria for metals intended for protection of coastal areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, B.J.; Hansen, B.G.; Johansson, S.; Luotamo, M.; Munn, S.J.; Musset, C.; Olsen, S.; Olsson, H.; Paya-Perez, A.B.; Pedersen, F. Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment. Part 1. Part 2; Institute for Health and Consumer Protection: Ispra, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Lao, Q.; Su, Q.; Shen, Y.; Chen, F.; Qing, S.; Wei, C.; Zhang, C. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of dissolved heavy metals in the aquaculture areas of Beibu Gulf, South China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 1957–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, D. The influences of Yellow River input and nutrient dynamics on colloidal Fe migration in the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 198, 106553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Liu, S.; Ren, J. Phosphorus utilization by phytoplankton in the Yellow Sea during spring bloom: Cell surface adsorption and intracellular accumulation. Mar. Chem. 2021, 231, 103935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kang, X.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Song, J.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y. Heavy metals in surface sediments along the Weihai coast, China: Distribution, sources and contamination assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Hu, R.; Wang, N.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Liu, B. Distribution and movement of heavy metals in sediments around the coastal areas under the influence of multiple factors: A case study from the junction of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.U.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Noh, J.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, M.; Jeong, J.; Hyun, M.J.; Won, J. Impact of vertical stratification on the 2020 spring bloom in the Yellow Sea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y.; Qiu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, S. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in seawater near the Yellow River Estuary of Laizhou Bay. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 203, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Z.; Fan, Z.; Wang, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Huang, H. Heavy metal(loid)s in multiple media within a mussel mariculture area of Shangchuan Island, China: Partition, transfer and health risks. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X. Assessment of dissolved heavy metals in the Laoshan Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Le, N.; Hoang, T.T.H.; Phung, V.P.; Nguyen, T.L.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Duong, T.T.; Pham, T.M.H.; Phung, T.X.B.; Nguyen, T.D.; Le, P.T. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the coastal aquaculture zone of the Red River Delta (Vietnam). Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.B.; Padhi, R.; Mohanty, A.; Satpathy, K. Distribution and ecological and health-risk assessment of heavy metals in the seawater of the southeast coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Pan, J.F.; Wang, M. Trace elements distribution and ecological risk assessment of seawater and sediments from Dingzi Bay, Shandong Peninsula, North China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Dei, R.C.; Hong, H. Seasonal study on the Cd, Se, and Zn uptake by natural coastal phytoplankton assemblages. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryer, S.; Schlosser, C.; Allison, N. The combined effects of ocean acidification and copper on the physiological responses of the tropical coral Stylophora pistillata. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 176, 105610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.J.; Sañudo-Wilhelmy, S.A. Impact of water temperature and dissolved oxygen on copper cycling in an urban estuary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6103–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Regions | Cd Concentration (µg L−1) | Pb Concentration (µg L−1) | Cu Concentration (µg L−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laizhou Bay, China | 0.096 (0.039–0.16) | 2.12 (0.63–4.97) | 3.64 (1.93–8.83) | [36] |
| Laoshan Bay, China | 0.11 (0.06–0.47) | 0.78 (0.32–2.74) | 1.48 (0.51–4.50) | [38] |
| Dingzi Bay, China | 0.36 (0.19–0.56) | 1.07 (0.62–1.46) | 2.02 (0.87–2.71) | [41] |
| Xiangshan Bay, China | 0.23 (0.03–1.61) | 1.70 (0.22–6.00) | 2.30 (0.60–8.40) | [6] |
| Shangchuan Island, China | N.D.-1.12 | (0.44–1.37) | (1.60–7.29) | [37] |
| Shengshan Island, China | N.D. | 6.18 (0.62–15.10) | 11.52 (3.80–18.66) | [18] |
| Southeast coast, India | 0.11 | 0.36 | 5.19 | [40] |
| Red River Delta, Vietnam | 0.44 (0.04–2.41) | 7.27 (0.80–31.20) | 26.91 (0.10–96.00) | [39] |
| Shandong Peninsula offshore, China | 0.033 (N.D.–0.079) | 0.55 (0.30–0.84) | 3.17 (2.19–4.79) | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, B.; Pan, D. Field Determination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in the Seawater of the Shandong Peninsula, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091672
Luan Y, Zhang Z, Gong B, Pan D. Field Determination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in the Seawater of the Shandong Peninsula, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091672
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuan, Yongsheng, Zhiwei Zhang, Bin Gong, and Dawei Pan. 2025. "Field Determination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in the Seawater of the Shandong Peninsula, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091672
APA StyleLuan, Y., Zhang, Z., Gong, B., & Pan, D. (2025). Field Determination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in the Seawater of the Shandong Peninsula, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091672









