Coarse and Fine-Grained Sediment Magnetic Properties from Upstream to Downstream in Jiulong River, Southeastern China and Their Environmental Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
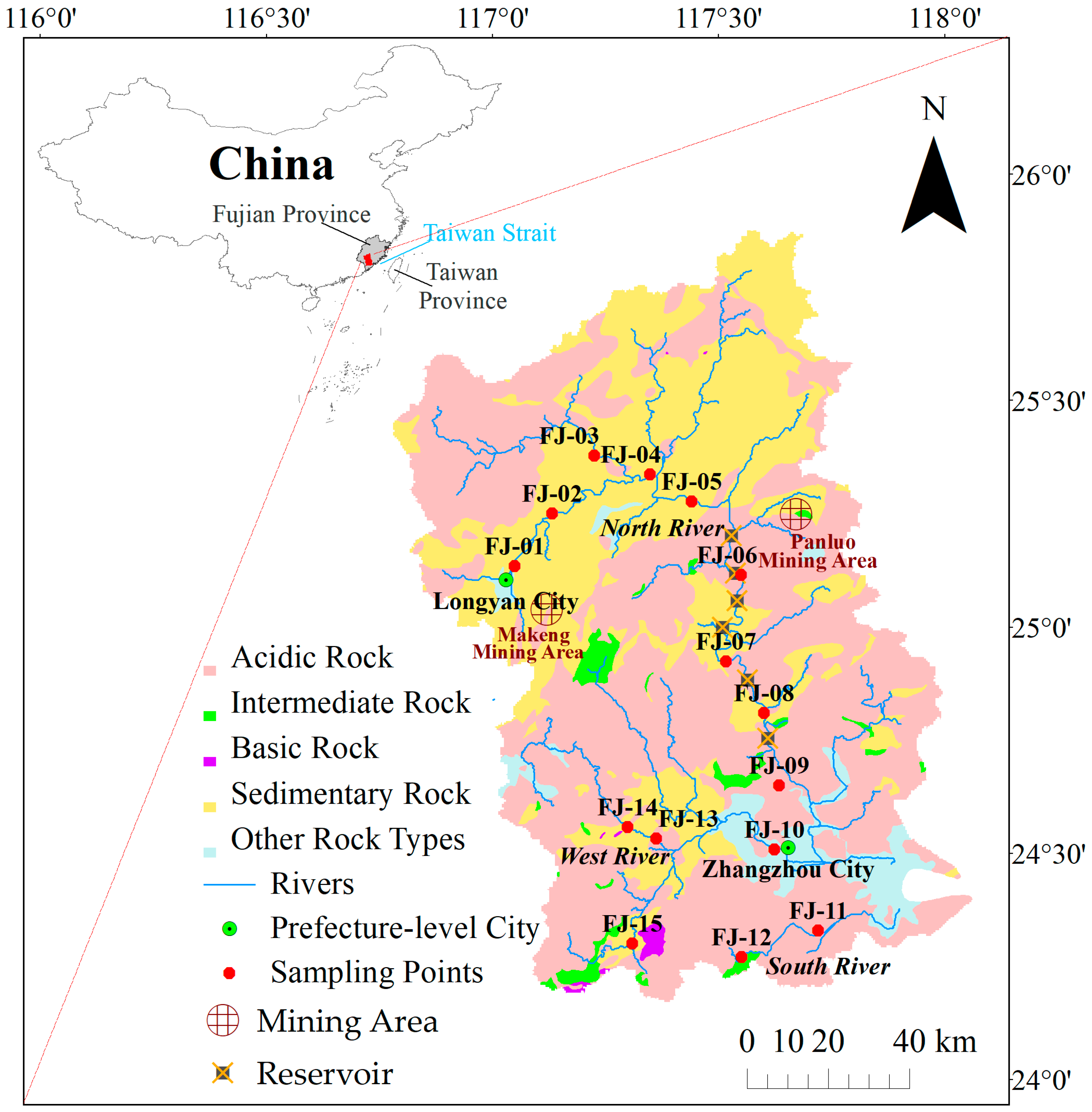
2.1. Regional Settings
2.2. Sample Acquisition
2.3. Magnetic Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Species and Features of Magnetic Minerals
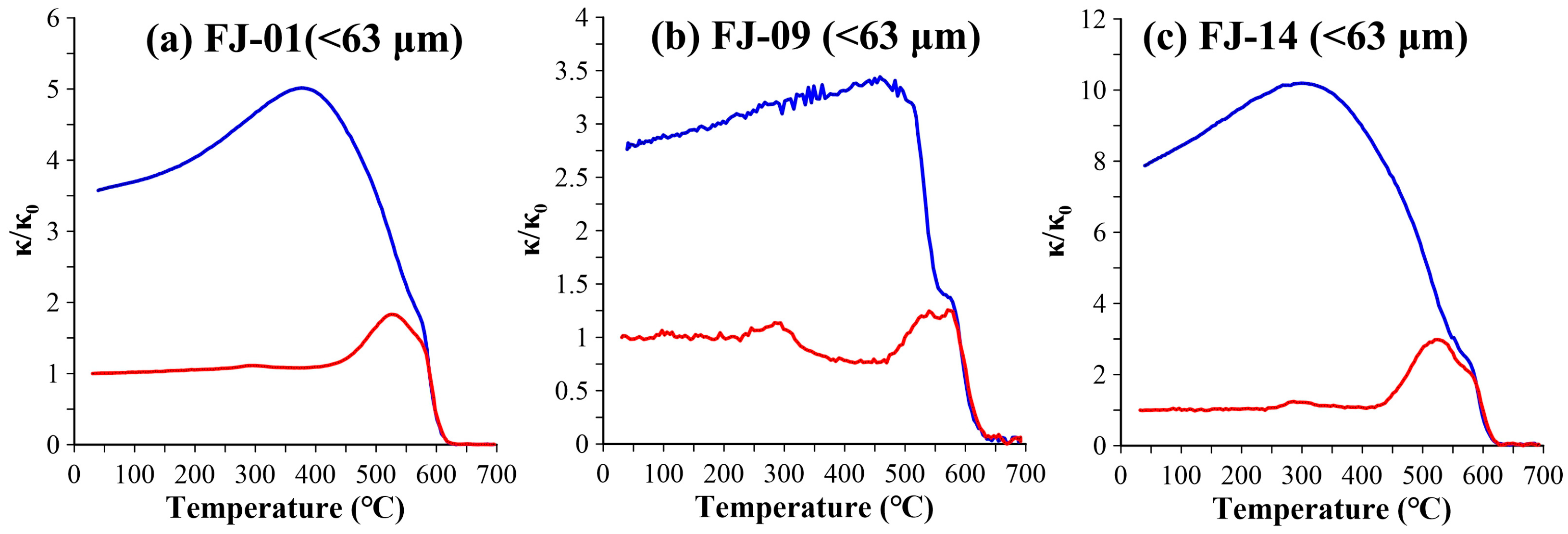
3.1.1. κ-T Curve
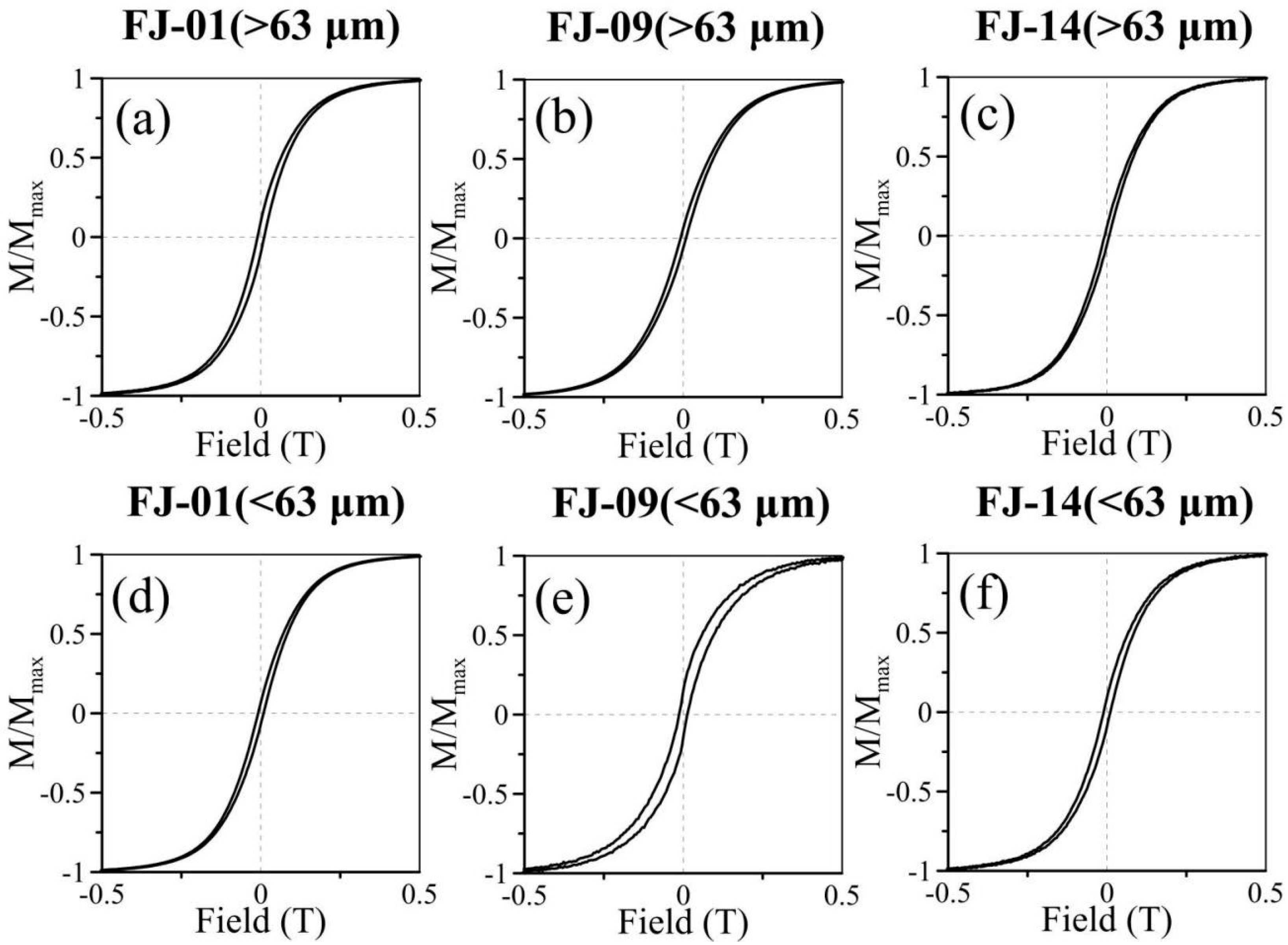
3.1.2. Magnetic Hysteresis Loops
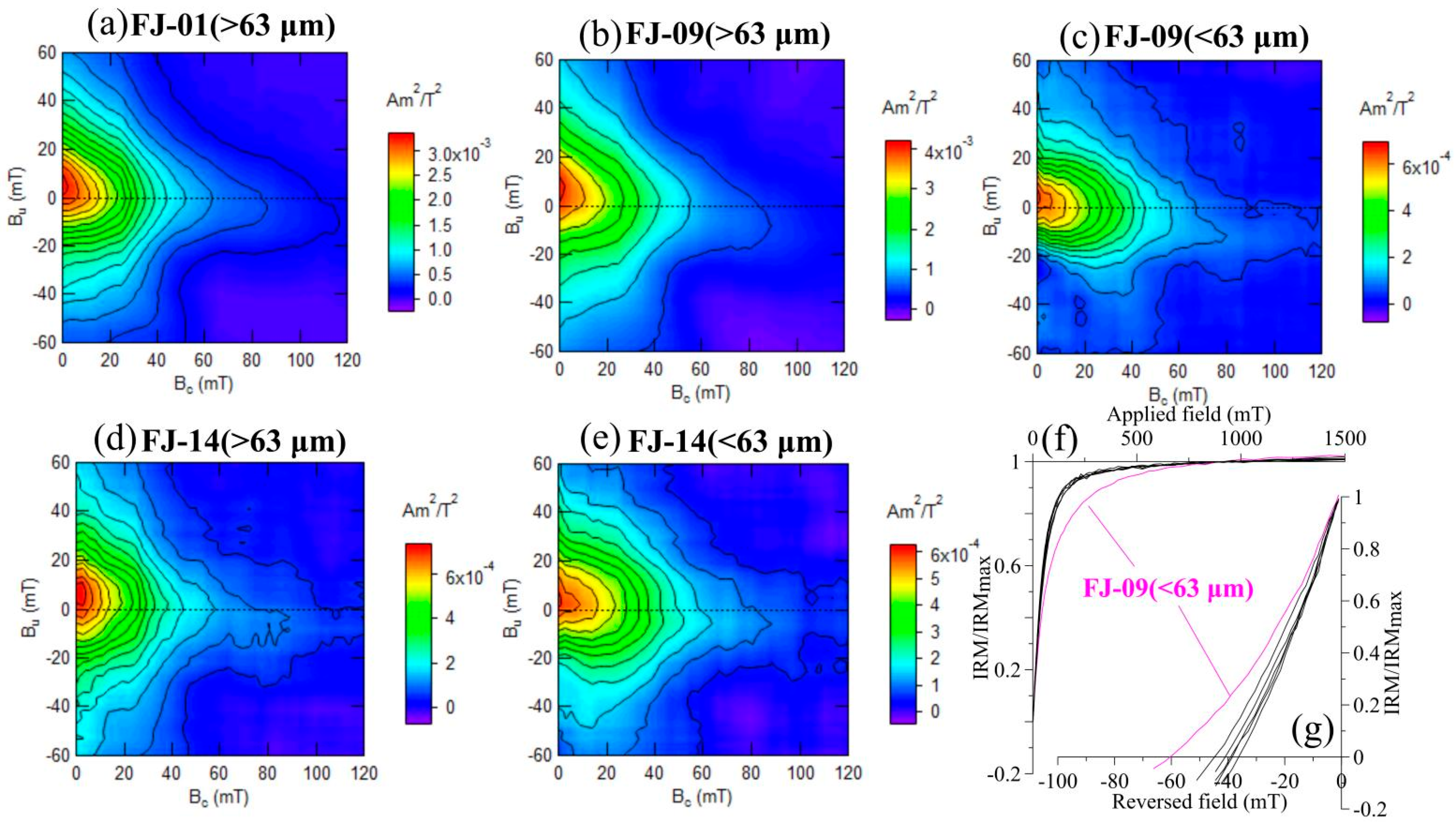
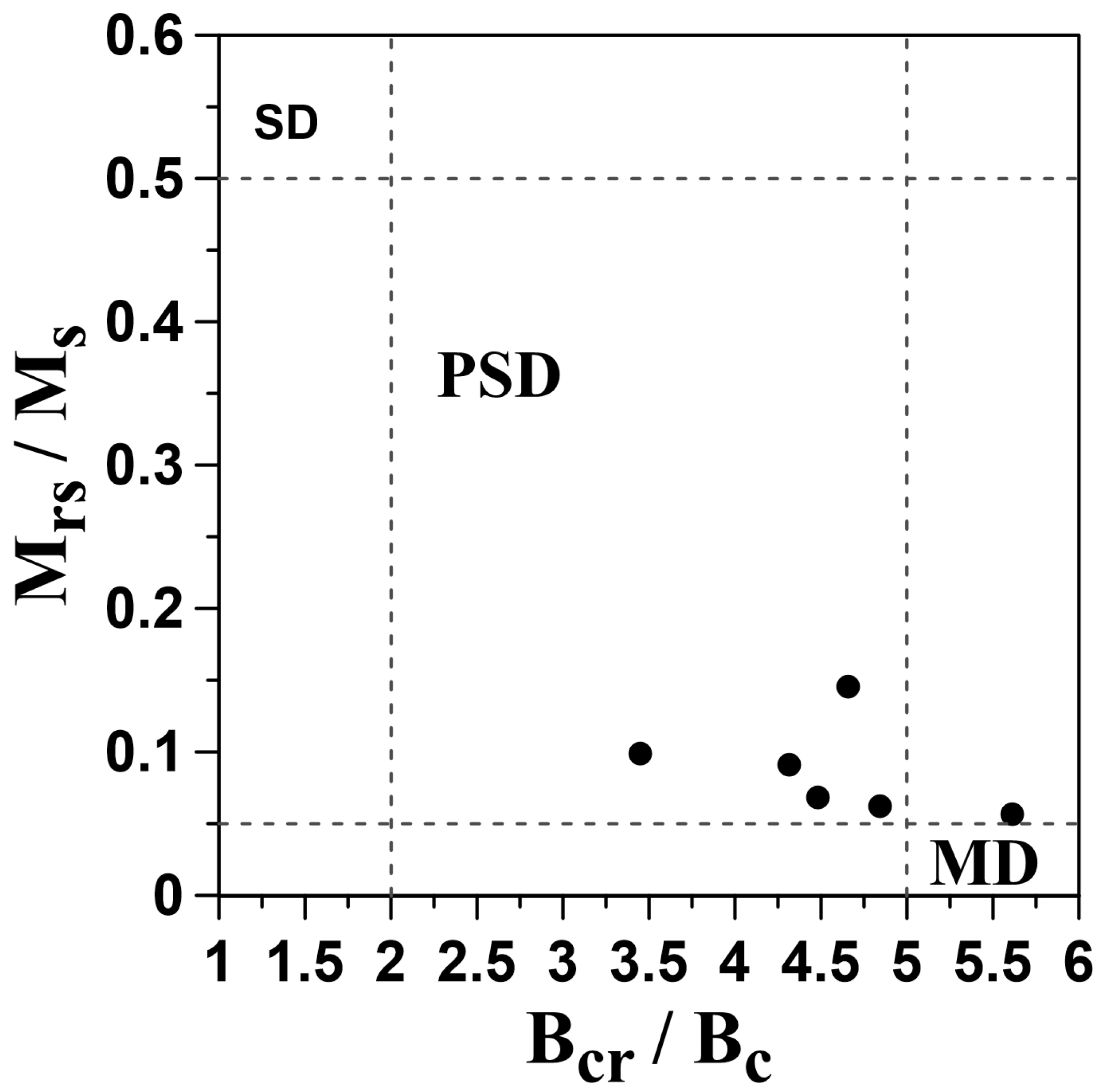
3.1.3. FORC Diagrams
3.1.4. IRM Acquisition Curve
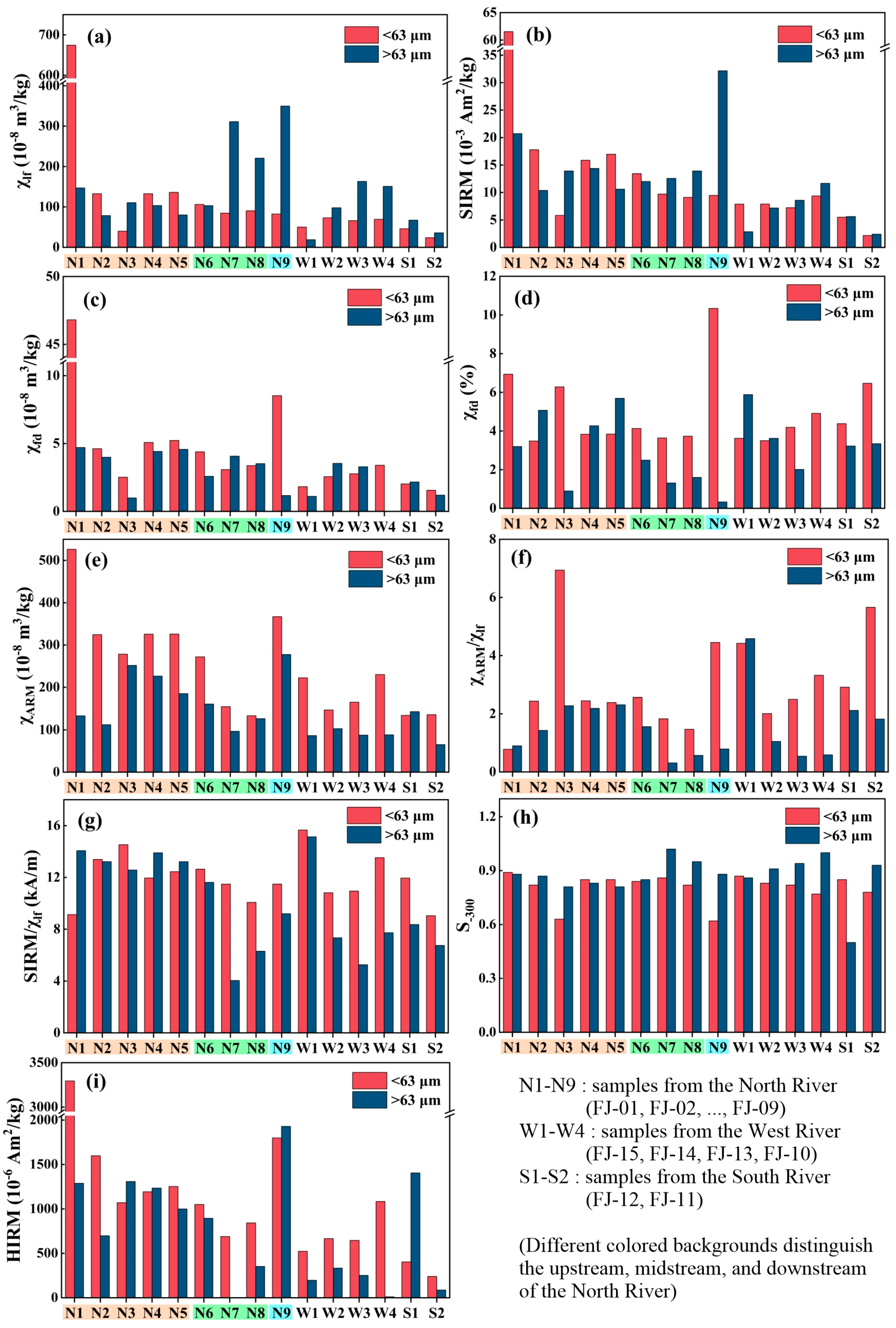
3.2. Spatial Variations in Magnetic Parameters
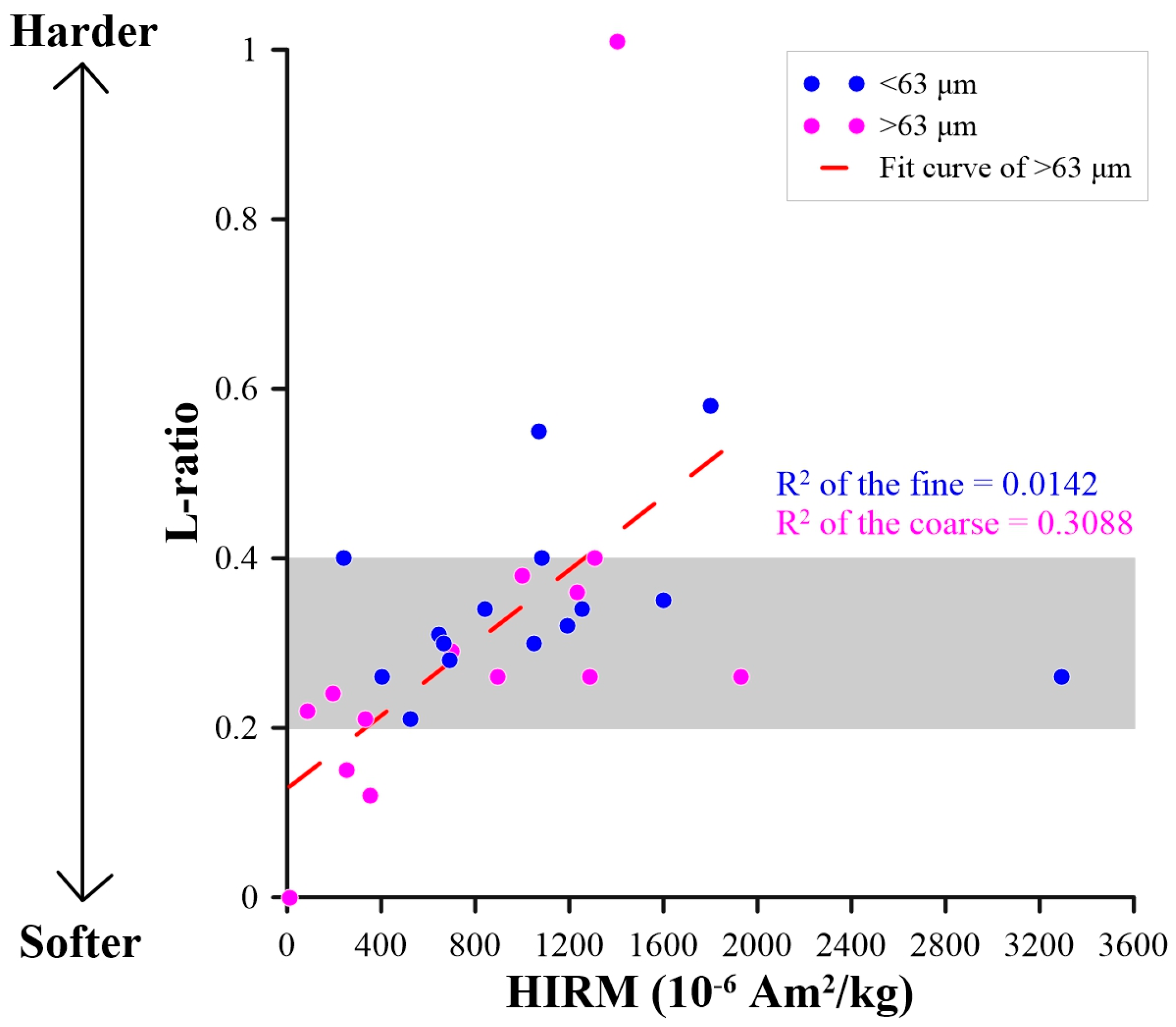
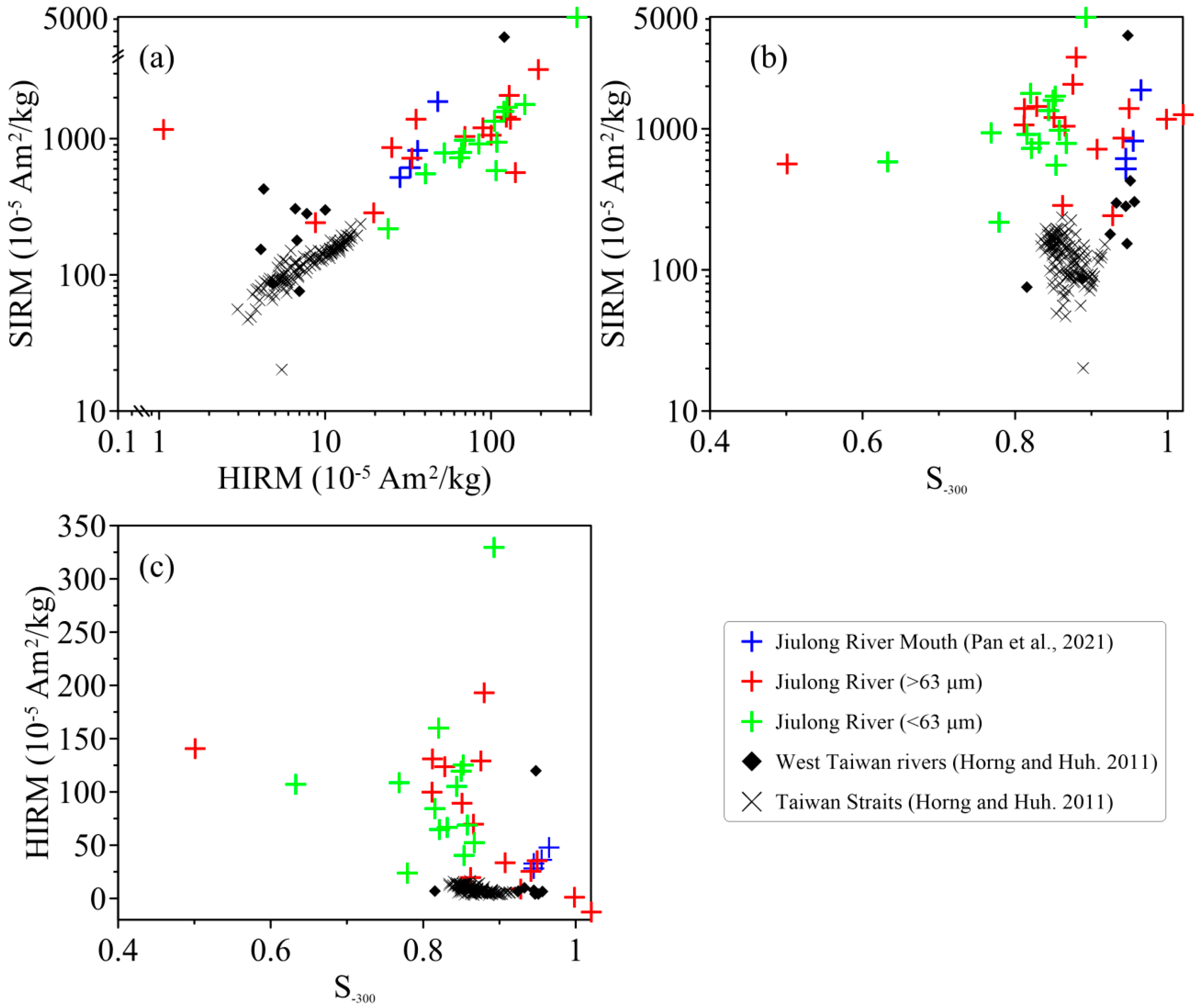
3.2.1. HIRM Usability
3.2.2. Overall Features
3.2.3. Magnetic Variation Patterns in North River
3.2.4. Magnetic Variation Patterns in West River
3.2.5. Magnetic Variation Patterns in South River
3.3. Human Activities on Magnetic Minerals
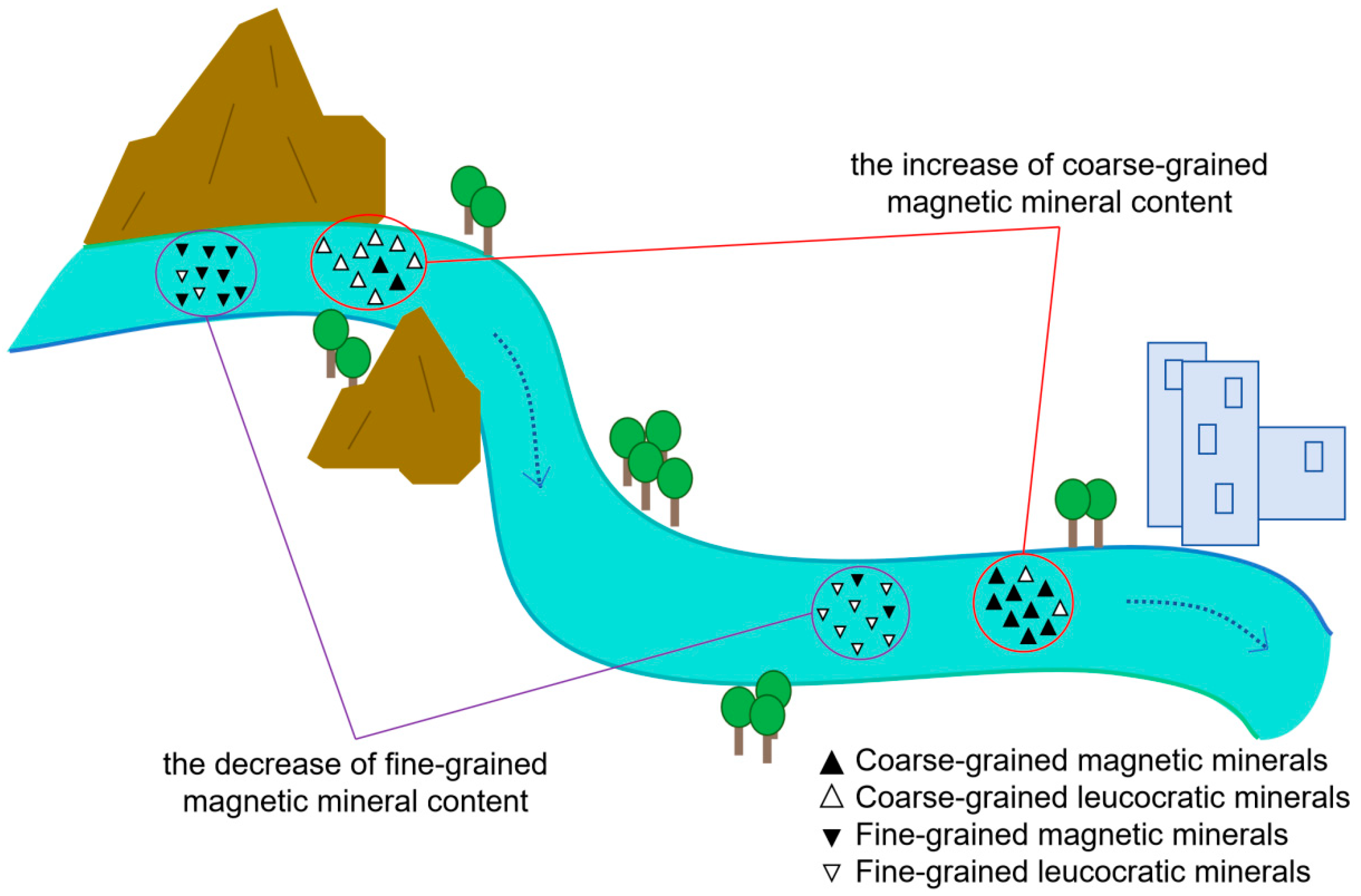
3.4. Provenance Significance of the Magnetic Parameters of the Fine and Coarse-Grained Fractions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milliman, J.D.; Farnsworth, K.L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, W.; Sanderson, R.A.; Tyson, P.D.; Jäger, J.; Matson, P.A.; Moore III, B.; Oldfield, F.; Richardson, K.; Schellnhuber, H.-J.; Turner, B.L.; et al. Global Change and the Earth System: A Planet Under Pressure; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Syvitski, J.; Ángel, J.R.; Saito, Y.; Overeem, I.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Wang, H.; Olago, D. Earth’s sediment cycle during the Anthropocene. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B. Ubiquitous magnetite. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Rajkumar, P.; Ramasamy, V.; Sinito, A.M. Magnetic parameters, trace elements, and multivariate statistical studies of river sediments from southeastern India: A case study from the Vellar River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Suresh, G.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Ramasamy, V.; Sinito, A.M. Magnetic studies and elemental analysis of river sediments: A case study from the Ponnaiyar River (Southeastern India). Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissel, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Wandres, C. Magnetic minerals in three Asian rivers draining into the South China Sea: Pearl, Red, and Mekong Rivers. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2016, 17, 1678–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissel, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Wandres, C. Magnetic signature of river sediments drained into the southern and eastern part of the South China Sea (Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Luzon and Taiwan). Sediment. Geol. 2017, 347, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Ge, C.; Liu, J.; Bai, X.; Feng, H.; Yu, L. Magnetic properties of sediments of the Red River, Vietnam: Effect of sorting on the source-to-sink pathway and its implications for environmental reconstruction. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2016, 17, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, S.; Yang, S.; Srivastava, P.; Khan, M.; Sangode, S.; Chakrapani, G. Environmental magnetic characterization of the Alaknanda and Ramganga river sediments, Ganga basin, India. Catena 2020, 190, 104529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, C.S.; Huh, C.A. Magnetic properties as tracers for source-to-sink dispersal of sediments: A case study in the Taiwan Strait. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 309, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, R.; Meadows, M.; Sengupta, D.; Zhu, L. Sources of sediment in tidal flats off Zhejiang coast, southeast China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, S.; Ouyang, T.; Tang, J.; He, C. Magnetic fingerprints of surface sediment in the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Geol. 2020, 427, 106226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xing, Y.; Yu, L.; Feng, H.; Lu, M. Distinguishing sediments from the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China: A mineral magnetic approach. Holocene 2008, 18, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, L. Correlation patterns between magnetic parameters and heavy metals of core sediments in the Yellow River Estuary and their environmental implications. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhu, S.; Ouyang, T.; Tang, J.; Tang, Z. Magnetic properties of the surface sediments in the Yellow River Estuary and Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China: Implications for monitoring heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.; Ye, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Responses of magnetic properties to heavy metals pollution recorded by sediments of Nanchang City reach of Ganjiang River, East China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 47, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, G.; Qiu, J.; Chen, B. Environmental magnetic parameter characteristics as indicators of heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments of the Zhoushan Islands in the East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 218, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Qiao, Q.; Piper, J.D.A.; Huang, B. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from a Fe-smelting plant in urban river sediments using environmental magnetic and geochemical methods. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3057–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Liao, Z.; Liang, W.; Liu, Y.; XIao, Y.; Zhu, C. Mineral magnetic characteristics of tidal flat surficial sediments and their implications for sedimentary environment identification in the Jiulong Estuary. Mar. Sci. 2021, 45, 30–41. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, X.; Yang, S.; Hong, D.; Liang, H.; Zhang, S.; Fu, H.; Zhang, W. Seasonal geochemical heterogeneity of sediments from a subtropical mountainous river in SE China. Mar. Geol. 2020, 422, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ji, R.; Nguyen, T.T.H. Influence of provenance and hydrodynamic sorting on the magnetic properties and geochemistry of sediments of the Oujiang River, China. Mar. Geol. 2017, 387, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.; Kao, S.J. Climate-dependent Sediment Composition and Transport of Mountainous Rivers in Tectonically Stable, Subtropical East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, E.; Bai, Y.; Li, M.; Ouyang, T.; Zhang, F.; Yu, M.; Lei, G.; Zhiyi, P.; Long, G. Magnetic properties of surface sediments from Liuxi River, southern China and their environmental significance. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1286–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, R.G.; Stoner, J.S.; Reilly, B.T.; Tepley, F.J.; Wheeler, B.H.; Housen, B.A. Grain size dependent magnetic discrimination of lceland and South Greenland terrestrial sediments in the northern North Atlantic sediment record. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 474, 474–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, R.G.; Wheeler, B.H.; Reilly, B.T.; Stoner, J.S.; Housen, B.A. Particle Size Specific Magnetic Properties Across the Norwegian-Greenland Seas: Insights Into the Influence of Sediment Source and Texture on Bulk Magnetic Records. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2019, 20, 1004–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, S.; Palcu, D.V.; Srivastava, P.; Hassan, M.B.; Muraszko, J.R.; Jovane, L. Changing sediment supply during glacial-interglacial intervals in the North Atlantic revealed by particle size characterization and environmental magnetism. Glob. Planet. Change 2023, 220, 104022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Huang, T.; Xu, Y.; Lai, Z. Particle-size dependent magnetic property variations in the Yangtze delta sediments of late Holocene: Effects of pedogenesis and diagenesis. Catena 2022, 209, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Han, G. Distribution, provenance, contamination, and probabilistic ecological risk of rare earth elements in surface sediments of Jiulong River estuary and adjacent watershed. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 254, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. New progress in the study of metamorphic belt along the southeast coast of Fujian. Geol. Fujian 1988, 4, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Wei, D. A comparative study of late Mesozoic volcanic stratigraphy and volcanism characteristics in western Fujian and Eastern Fujian. Geol. Fujian 2005, 04, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Fujian Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Regional Geology of Fujian Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Pan, D.; Lin, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, L.; Liang, J.; Huang, C. Temporal and spatial distribution of salinity and suspended sediment concentration in surficial water from the Jiulong estuary. J. Minnan Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 33, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A. Analysis of Water Environment Quality and Research on Pollution Prevention and Control Strategies in the Basin of South River of Jiulong River. Staits Sci. 2022, 10, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y. Distribution patterns of reduced inorganic sulfur in surface sediments and its reservoir driving mechanism during the flooding season in Jiulong River,China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield, R.G.; Stoner, J.S.; Carlson, A.E.; Reyes, A.V.; Housen, B.A. Source as a controlling factor on the quality and interpretation ofsediment magnetic records from the northern North Atlantic. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 368, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbins, D.; Herrero-Bervera, E. Encyclopedia of Geomagnetism and Paleomagnetism; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson, J. XIV. Magnetic and other physical properties of iron at a high temperature. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1889, 180, 443–465. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, A.P.; Chang, L.; Rowan, C.J.; Horng, C.-S.; Florindo, F. Magnetic properties of sedimentary greigite (Fe3S4): An update. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49, RG1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P. Magnetic properties of sedimentary greigite (Fe3S4). Earth Planet Sci Lett. 1995, 134, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Oldfield, F. Environmental Magnetism; Allen and Unwin: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop, D.J.; Özdemir, O. Rock Magnetism: Fundamentals and Frontiers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, A.P.; Zhao, X.; Harrison, R.J.; Heslop, D.; Muxworthy, A.R.; Rowan, C.J.; Larrasoana, J.C.; Florindo, F. Signatures of reductive magnetic mineral diagenesis from unmixing of first-order reversal curves. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 4500–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.; Fuller, M.; Schmidt, V. Hysteresis properties of titanomagnetites: Grain-size and compositional dependence. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1977, 13, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Moralejo, M.D.P.; Böhnel, H.; Acebal, S.G. Iron oxide mineralogy in Mollisols, Aridisols and Entisols from southwestern Pampean region (Argentina) by environmental magnetism approach. Catena 2020, 190, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Roberts, A.P.; Torrent, J.; Horng, C.-S.; Larrasoaña, J.C. What do the HIRM and S-ratio really measure in environmental magnetism? Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2007, 80, Q09011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Krishnamoorthy, N.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Lecomte, K.L.; Mullainathan, S.; Mehra, R.; Sinito, A.M. Magnetic, chemical and radionuclide studies of river sediments and their variation with different physiographic regions of Bharathapuzha River, southwestern India. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2015, 59, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Hu, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Lu, B.; Wang, P. Mineralogy study of magnetic susceptibility of rocks along the coast of the northern South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys 2011, 54, 573–587. [Google Scholar]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Sinito, A.M.; Ramasamy, V.; Marinelli, C.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Mullainathan, S.; Murugesan, S. Magnetic measurements and pollutants of sediments from Cauvery and Palaru River, India. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Ng, N.C.W.; Yang, S.; Bui, V.V.; Nguyen, D.C.; Duan, X.; Yin, P.; Tran, T.T.T.; et al. Sr-Nd isotope fingerprints of Red River sediments and its implication for provenance discrimination in the South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2023, 457, 106997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Formula | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| χlf | — | Concentration of the total magnetic minerals |
| χfd% | 100×(χlf − χhf)/χlf | Semi-quantitative contribution of superparamagnetic (SP) particles |
| χfd | χlf − χhf | Particle size of the minerals |
| χARM | — | Content of fine-grained ferrimagnetic component (such as the stable single domain (SSD)) |
| χARM/χlf | — | Grain size of the ferrimagnetic particles |
| SIRM | — | Concentration of the ferromagnetic (sensu lato) minerals |
| SIRM/χlf | — | Grain size or mineralogy of magnetic minerals |
| S−300 | −IRM−300mT/SIRM | Relative content of low and high coercive magnetic minerals |
| L-ratio | (SIRM + IRM−300mT)/ (SIRM + IRM−100mT) | Control the S−300 and HIRM to enable a more rigorous interpretation of these parameters |
| HIRM | HIRM = (IRM−300mT + SIRM)/2 | Content of high-coercive magnetic minerals |
| Sample | χlf | SIRM | χfd | χfd | χARM | χARM/χlf | SIRM/χlf | S−300 | HIRM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−8 m3/kg | 10−3 Am2/kg | % | 10−8 m3/kg | 10−8 m3/kg | kA/m | 10−6 Am2/kg | |||
| FJ-01 (<63 μm) | 674.45 | 61.55 | 6.94 | 46.81 | 526.56 | 0.78 | 9.13 | 0.89 | 3294.25 |
| FJ-02 (<63 μm) | 132.88 | 17.79 | 3.48 | 4.62 | 324.60 | 2.44 | 13.39 | 0.82 | 1598.42 |
| FJ-03 (<63 μm) | 40.12 | 5.83 | 6.28 | 2.52 | 278.40 | 6.94 | 14.53 | 0.63 | 1070.48 |
| FJ-04 (<63 μm) | 132.69 | 15.88 | 3.83 | 5.08 | 325.66 | 2.45 | 11.96 | 0.85 | 1193.17 |
| FJ-05 (<63 μm) | 136.28 | 16.96 | 3.84 | 5.23 | 326.04 | 2.39 | 12.45 | 0.85 | 1252.84 |
| FJ-06 (<63 μm) | 106.37 | 13.44 | 4.13 | 4.39 | 272.00 | 2.56 | 12.64 | 0.84 | 1050.32 |
| FJ-07 (<63 μm) | 84.71 | 9.72 | 3.64 | 3.08 | 154.91 | 1.83 | 11.48 | 0.86 | 689.73 |
| FJ-08 (<63 μm) | 90.54 | 9.12 | 3.73 | 3.37 | 133.34 | 1.47 | 10.08 | 0.82 | 843.25 |
| FJ-09 (<63 μm) | 82.48 | 9.47 | 10.34 | 8.53 | 367.21 | 4.45 | 11.49 | 0.62 | 1798.56 |
| FJ-10 (<63 μm) | 69.34 | 9.38 | 4.91 | 3.40 | 230.28 | 3.32 | 13.53 | 0.77 | 1084.73 |
| FJ-11 (<63 μm) | 24.04 | 2.18 | 6.47 | 1.56 | 136.01 | 5.66 | 9.05 | 0.78 | 240.44 |
| FJ-12 (<63 μm) | 46.07 | 5.51 | 4.38 | 2.02 | 134.17 | 2.91 | 11.95 | 0.85 | 403.81 |
| FJ-13 (<63 μm) | 66.08 | 7.24 | 4.19 | 2.77 | 165.54 | 2.50 | 10.95 | 0.82 | 646.07 |
| FJ-14 (<63 μm) | 73.05 | 7.90 | 3.50 | 2.56 | 147.06 | 2.01 | 10.82 | 0.83 | 665.63 |
| FJ-15 (<63 μm) | 50.30 | 7.88 | 3.62 | 1.82 | 222.41 | 4.42 | 15.66 | 0.87 | 523.49 |
| FJ-01 (>63 μm) | 147.15 | 20.71 | 3.20 | 4.71 | 133.07 | 0.90 | 14.07 | 0.88 | 1289.05 |
| FJ-02 (>63 μm) | 78.55 | 10.39 | 5.07 | 3.99 | 112.21 | 1.43 | 13.22 | 0.87 | 697.61 |
| FJ-03 (>63 μm) | 110.69 | 13.92 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 251.82 | 2.28 | 12.57 | 0.81 | 1309.03 |
| FJ-04 (>63 μm) | 103.54 | 14.39 | 4.27 | 4.42 | 226.38 | 2.19 | 13.90 | 0.83 | 1235.13 |
| FJ-05 (>63 μm) | 80.29 | 10.61 | 5.69 | 4.57 | 185.08 | 2.31 | 13.22 | 0.81 | 999.70 |
| FJ-06 (>63 μm) | 103.27 | 12.00 | 2.49 | 2.58 | 161.08 | 1.56 | 11.62 | 0.85 | 894.91 |
| FJ-07 (>63 μm) | 311.28 | 12.57 | 1.31 | 4.07 | 96.59 | 0.31 | 4.04 | 1.02 | - |
| FJ-08 (>63 μm) | 220.85 | 13.92 | 1.60 | 3.52 | 126.59 | 0.57 | 6.30 | 0.95 | 352.42 |
| FJ-09 (>63 μm) | 349.57 | 32.15 | 0.33 | 1.17 | 277.54 | 0.79 | 9.20 | 0.88 | 1929.09 |
| FJ-10 (>63 μm) | 150.88 | 11.67 | - | - | 88.35 | 0.59 | 7.73 | 1.00 | 10.63 |
| FJ-11 (>63 μm) | 35.91 | 2.42 | 3.34 | 1.20 | 65.25 | 1.82 | 6.75 | 0.93 | 87.31 |
| FJ-12 (>63 μm) | 67.37 | 5.63 | 3.22 | 2.17 | 143.11 | 2.12 | 8.36 | 0.50 | 1404.74 |
| FJ-13 (>63 μm) | 163.31 | 8.59 | 2.01 | 3.29 | 87.55 | 0.54 | 5.26 | 0.94 | 252.09 |
| FJ-14 (>63 μm) | 97.89 | 7.19 | 3.62 | 3.54 | 102.75 | 1.05 | 7.34 | 0.91 | 333.24 |
| FJ-15 (>63 μm) | 18.88 | 2.86 | 5.88 | 1.11 | 86.47 | 4.58 | 15.13 | 0.86 | 196.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, R.; Liang, S.; Li, M.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Yuan, Y. Coarse and Fine-Grained Sediment Magnetic Properties from Upstream to Downstream in Jiulong River, Southeastern China and Their Environmental Implications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081502
Wen R, Liang S, Li M, Chaparro MAE, Yuan Y. Coarse and Fine-Grained Sediment Magnetic Properties from Upstream to Downstream in Jiulong River, Southeastern China and Their Environmental Implications. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081502
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Rou, Shengqiang Liang, Mingkun Li, Marcos A. E. Chaparro, and Yajuan Yuan. 2025. "Coarse and Fine-Grained Sediment Magnetic Properties from Upstream to Downstream in Jiulong River, Southeastern China and Their Environmental Implications" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081502
APA StyleWen, R., Liang, S., Li, M., Chaparro, M. A. E., & Yuan, Y. (2025). Coarse and Fine-Grained Sediment Magnetic Properties from Upstream to Downstream in Jiulong River, Southeastern China and Their Environmental Implications. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081502






