Abstract
Local scour around support structures has remained a critical barrier to tidal stream turbine deployment in energetic marine channels since loss of embedment and bearing capacity has undermined stability and delayed commercialization. This review identifies key mechanisms, practical implications, and forward-looking strategies related to local scour. It highlights that rotor operation, small tip clearance, and helical wakes can significantly intensify near-bed shear stress and erosion relative to monopile foundations without turbine rotation. Scour behavior is compared across monopile, tripod, jacket, and gravity-based foundations under steady flow, reversing tides, and combined wave and current conditions, revealing their influence on depth and morphology. The review further assesses coupled interactions among waves, oscillatory currents, turbine-induced flow, and seabed response, including sediment transport, transient pore pressure, and liquefaction risk. Advances in prediction methods spanning laboratory experiments, high-fidelity simulations, semi-empirical models, and data-driven techniques are synthesized, and mitigation strategies are evaluated across passive, active, and eco-integrated approaches. Remaining challenges and specific research needs are outlined, including array-scale effects, monitoring standards, and integration of design frameworks. The review concludes with future directions to support safe, efficient, and sustainable turbine deployment.
1. Introduction
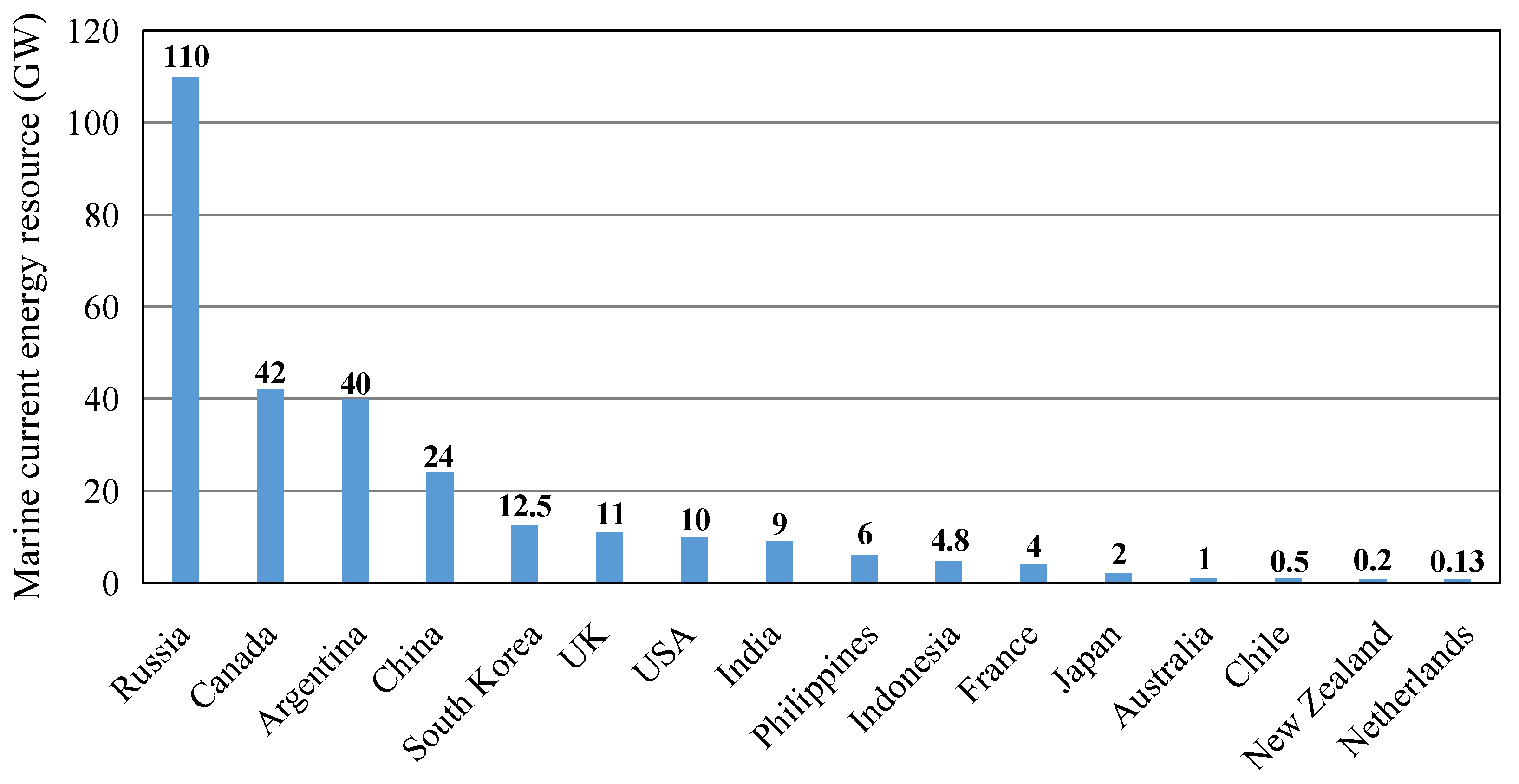
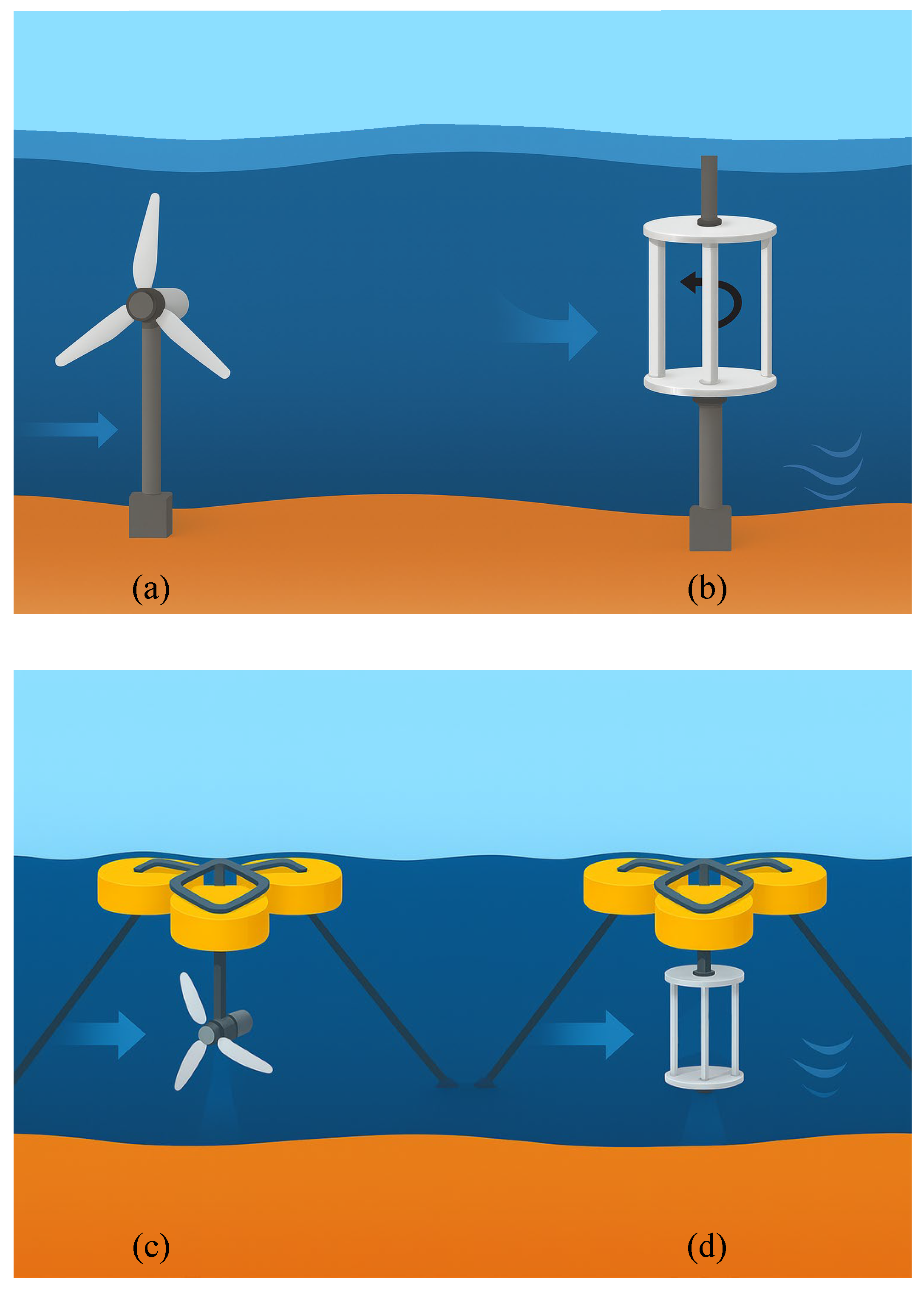
Tidal stream energy represents a key component of the global shift toward clean and renewable electricity generation [1]. Its high predictability, operational reliability, and substantial energy density provide clear advantages over other renewable sources [2]. The global technically harvestable potential of marine current energy is estimated at about 1 TW [3]. Figure 1 depicts the distribution of marine current energy resources across 16 countries. The current worldwide installed capacity is about 40 MW, and the International Energy Agency projects growth to 120 GW by 2050 [4]. Tidal energy systems operate by capturing the kinetic energy of water currents to drive turbines and generate power. As shown in Figure 2, the main energy conversion devices are horizontal axis tidal turbine (HATT) and vertical axis tidal turbine (VATT), and support structures primarily include fixed bottom and floating foundations. Recent advances in megawatt-scale HATT technology and floating platform design have supported the transition from pilot demonstrations to early commercial deployment [5]. These advancements support consistent energy extraction in high-energy tidal environments across diverse bathymetric conditions and help relax siting limitations in deeper marine channels and straits. Ongoing refinement in array hydrodynamics, environmental impact assessment, and reliability engineering is anticipated to enable the conversion of tidal resources into economically sustainable projects, characterized by predictable output and manageable life cycle costs.
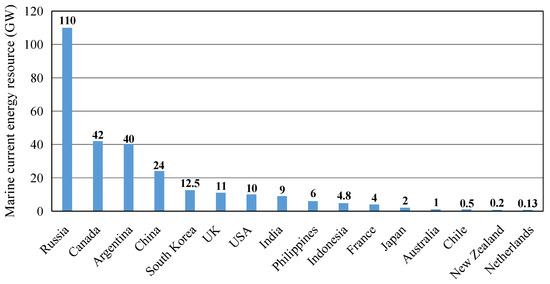
Figure 1.
Technically harvestable marine current energy reserves across 16 representative countries worldwide. Data from [3].
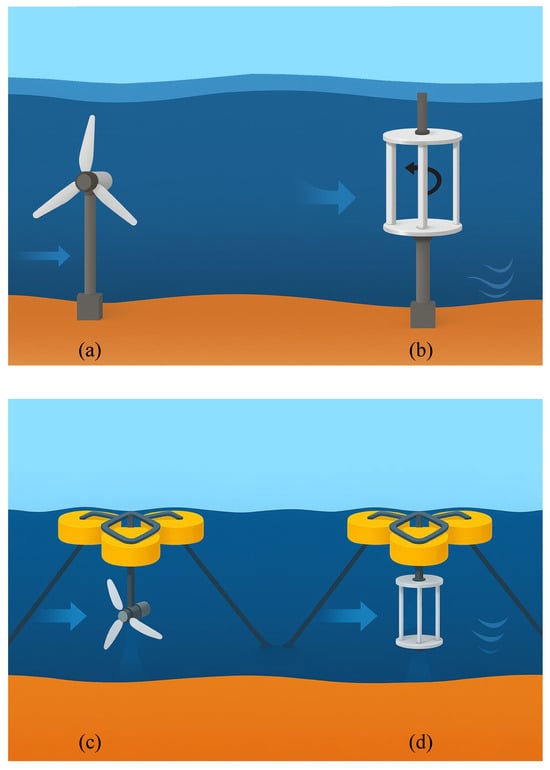
Figure 2.
Configurations of tidal energy turbines (a) fixed bottom foundations supporting a horizontal axis tidal turbine (HATT) and (b) a vertical axis tidal turbine (VATT); (c) floating tension leg platforms supporting a HATT and (d) VATT.
However, deployment of tidal stream devices, particularly bottom-fixed support structures such as monopiles and tripods, faces persistent and coupled challenges related to environmental loading and geotechnical stability throughout their service life. Among these challenges, local scour is a primary failure mechanism that demands rigorous assessment [6,7,8]. Local scour develops when the approaching flow accelerates around the foundation, forming an upstream horseshoe vortex and a downstream wake vortex system. These flow structures increase near-bed shear stress beyond the sediment motion threshold and cause removal of seabed material [7,9]. The engineering consequences may be severe, including progressive loss of embedment depth, reduced axial and lateral capacity, and amplified dynamic responses [6,8]. These effects increase the risk of fatigue damage and may lead to global instability under extreme conditions. Although tidal stream turbines are typically deployed in high-energy environments with coarse seabeds composed of gravel or exposed rock, where the potential for substantial scour development is generally limited, an increasing number of demonstration and pre-commercial arrays have now been installed in areas containing finer or mixed sediments such as sand, silty sand, or mud.
In such settings, representative deployments include tidal arrays in estuarine channels and tidal inlets, such as the East River in New York [10], Cobscook Bay in Maine [11], and smaller inlets of the St. Lawrence River [12], where sediment mobility and potential foundation erosion have been identified as primary constraints on design. Field observations and modelling studies at such sites have documented pronounced local scour around turbines installed in sandy tidal flats and estuarine channels, confirming that sediment mobility and foundation erosion become critical factors in both design and performance assessment. In seabed environments dominated by finer sediments, local scour can exert direct and significant effects on turbine performance, including reductions in foundation bearing capacity, unintentional exposure or undermining of buried cables and protection layers, increases in bending moments near the mudline, and shifts in rotor elevation or alignment that may diminish energy output or intensify fatigue loading. Taken together, these effects underscore that local scour is highly site specific and carries substantial implications for the long-term structural integrity and economic viability of tidal energy projects. From a process viewpoint, scour evolution involves coupled interactions among vortex-induced pressure gradients, bed shear stress, and sediment transport regimes in both clear-water and live-bed conditions. Wave–current interactions and bidirectional tidal flows can intensify scour development and shorten the time required to reach an equilibrium scour depth [13]. These hydrodynamic and morphodynamic considerations directly influence engineering design factors such as stability margins, inspection and monitoring schedules, and mitigation requirements. Therefore, it is essential to integrate site-specific scour prediction, continuous monitoring, and protective measures into a comprehensive reliability framework for tidal stream foundations, with particular emphasis on probabilistic design and validation against field measurements.
Relative to scour around offshore wind turbine monopiles or bridge piers, foundation scour associated with tidal stream turbines is governed by distinct mechanisms and exhibits higher hydrodynamic and geotechnical complexity. A rotating rotor above the support structure extracted momentum from the ambient flow during operation and introduced periodic wake disturbances along with additional dynamic loads. Empirical rules developed for monopiles without turbines were not directly transferable [6,7,8,9,14]. Rotor-induced acceleration of the flow, enhanced turbulence, and rotor seabed coupling modified near-bed shear stress, sediment entrainment, and scour hole morphology. These changes altered the pattern and rate of scour development and necessitated dedicated models and tailored experimental protocols [6,15]. In practical tidal channels, turbines often operate under oscillatory currents together with waves. Scour was governed by multiple coupled drivers, including cycle to cycle variation in velocity magnitude and direction, fluctuations in instantaneous bed pressure and pore water pressure under wave action, and site-specific seabed properties such as shear strength and resistance to liquefaction [16]. Additional sensitivity reflected sensitivity to tip clearance, Reynolds number, and sediment regime, where clear water and live bed conditions led to different thresholds for motion and different equilibrium depths. These interacting factors complicated mechanistic interpretation and motivated integrated approaches that linked high fidelity hydrodynamics with sediment transport modeling and targeted physical validation [17].
This review has provided a structured synthesis of international progress on local scour around tidal stream turbine foundations. Following a problem-driven organization, it first brings together experimental, numerical, and field-based evidence on rotor-induced scour, outlining the evolution of tidal stream devices and the principal support configurations for horizontal axis and vertical axis systems, and clarifying how rotor operation modifies the local flow field through near-bed acceleration and helical wakes and how tip clearance exerts a decisive control, which together intensify scour relative to monopile foundations without turbine rotation. It has compared scour characteristics and governing factors for monopiles, tripods, jackets, and gravity bases under oscillatory reversing currents and combined wave and current conditions, thereby contributing to a coherent physical picture across foundation types and loading regimes. It then summarizes recent evidence on seabed dynamic response under coupled wave, current, and turbine loading, including transient liquefaction risk. Building on this physical understanding, it brings together advances in prediction that integrate physical experiments, high fidelity Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) approaches with surrogate rotors such as the actuator line method (ALM) coupled to immersed boundaries, semi-empirical relations, and physics-informed, data-driven tools. Finally, the review synthesizes passive, active, and eco-integrated comprehensive protection strategies and highlights priority directions for engineering implementation, including array-scale scour effects, verification and validation with field data, standardization, and intelligent monitoring for the design, construction, and operation and maintenance of tidal stream energy projects.
2. Scour Mechanisms Induced by Rotor Rotation
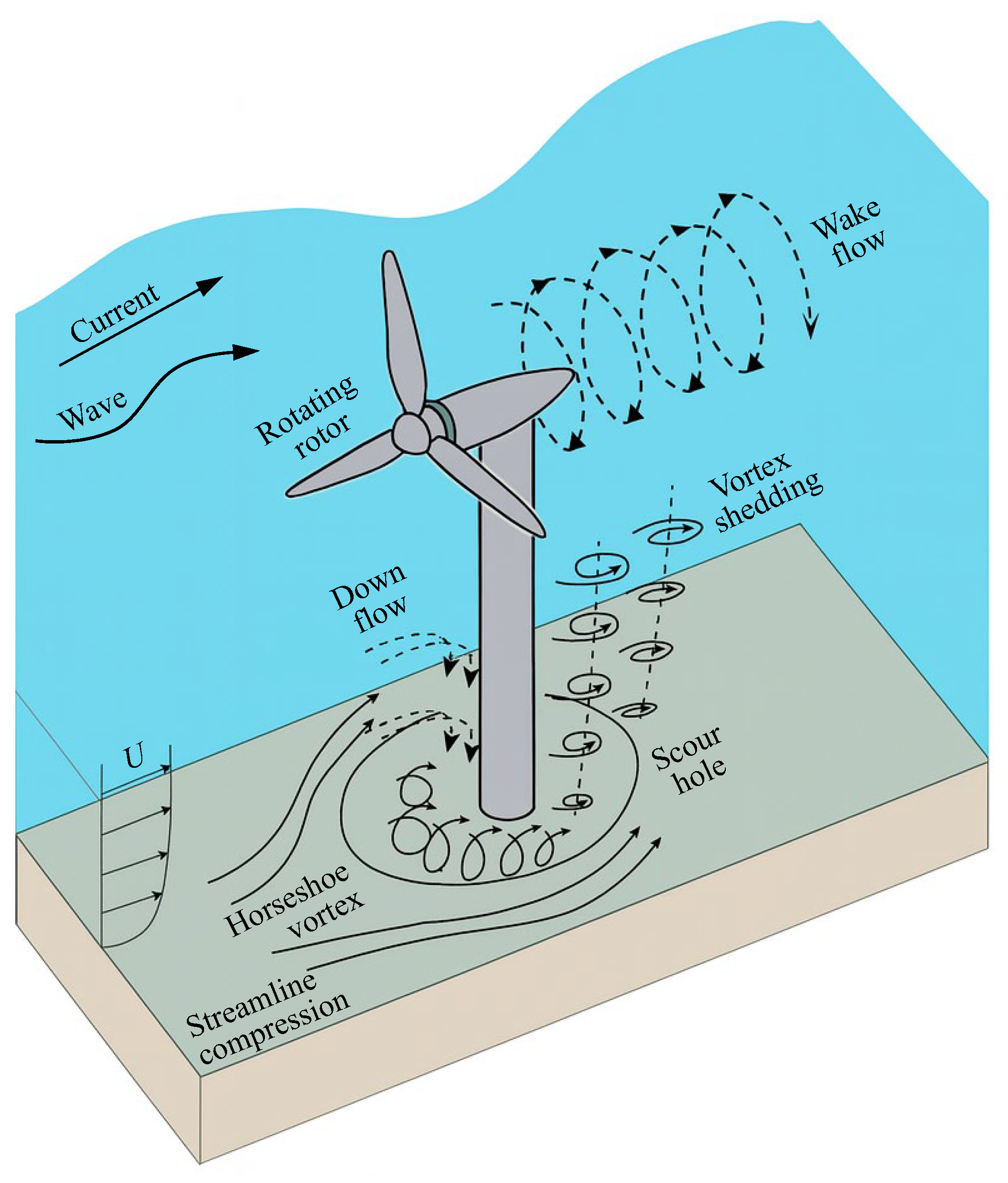
Compared with monopile foundations without turbine rotation, the periodic operation of a tidal stream rotor is a key control on local scour processes around foundations [13,18]. Figure 3 schematically illustrates how energy extraction by the rotor modifies the near-bed flow field and redistributes shear stress, strengthening the horseshoe vortex system in front of the pile and generating tip vortices, hub vortices, and a helical wake downstream that together accelerate scour development. This section first describes these rotor-induced local flow structures and then examines how the resulting near-bed velocity and shear stress patterns influence scour depth and morphology.
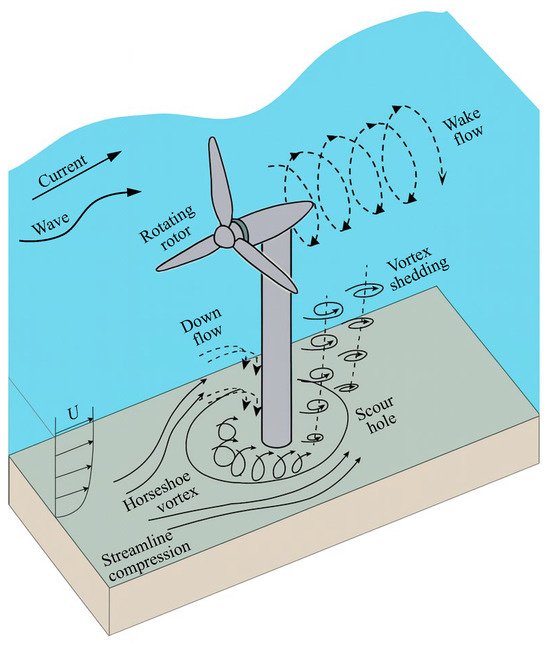
Figure 3.
Local scour and vortex system around tidal stream turbine foundations.
2.1. Hydrodynamic Acceleration Effect
Local scour induced by tidal stream turbines differs from scour around monopile foundations without turbine rotation because the moving rotor accelerates the flow and redistributes momentum in the water column. When the rotor operates, energy extraction from the incoming current produces a contracted high velocity jet beneath the rotor disk, strengthens the near-bed shear layer, and modifies the structure of the boundary layer [19]. Laboratory flume experiments and numerical simulations consistently show that, for the same upstream conditions, rotating rotor cases develop higher erosion rates and larger maximum scour depths than pile-only configurations, and that the equilibrium scour hole extends over a wider area [20]. The increase in bed shear stress is closely linked to the rise in axial velocity within the accelerated zone beneath the rotor, a characteristic feature captured in velocity measurements and computed flow fields [14]. Comparative studies indicate that rotor operation shortens the time required to reach a given scour depth and increases the final equilibrium depth, with similar trends across different geometric scales and sediment size ranges [7]. Coupled hydrodynamic and sediment transport models further confirm the simultaneous amplification of shear stress and sediment flux caused by rotor-induced acceleration, which explains the stronger erosion intensity and faster temporal evolution observed in laboratory studies [21].
Rotor rotation also introduces swirl and reorganizes the three-dimensional vortex system around the foundation. The tangential velocity component in the wake modifies the strength and position of the horseshoe vortex and the associated downflow in front of the pile, while a high vorticity region forms near the bed beneath the rotor disk and interacts with the sediment motion threshold, thereby intensifying local erosion [22]. Flow visualization and non-contact measurement systems (including Particle Image Velocimetry, Acoustic Doppler Velocimeters and Profilers, multibeam sonar, and laser-based bed scanners) reveal that the interaction between vortices shed from the blades and background turbulence produces asymmetric shear stress distributions and non-uniform sediment transport pathways. This transport pattern promotes the asymmetric development of bedforms, resulting in the characteristic asymmetric evolution of scour holes [23]. Considering that non-uniform sediment transport may induce bed armoring effects, this mechanism can significantly influence the evolution of scour morphology. Under combined wave and current forcing, rotor-induced swirl acts together with cyclic wave pressure, increasing peak shear stress around the foundation and enlarging the equilibrium scour depth and footprint [24]. Comparisons between time resolved field surveys and laboratory experiments indicate that the maximum relative scour depth around operating tidal stream turbines can exceed empirical ranges reported for bridge piers, so predictive models need to represent rotor-induced acceleration and modification of the vortex system in order to provide reliable engineering estimates [13].
2.2. The Decisive Role of Tip Clearance
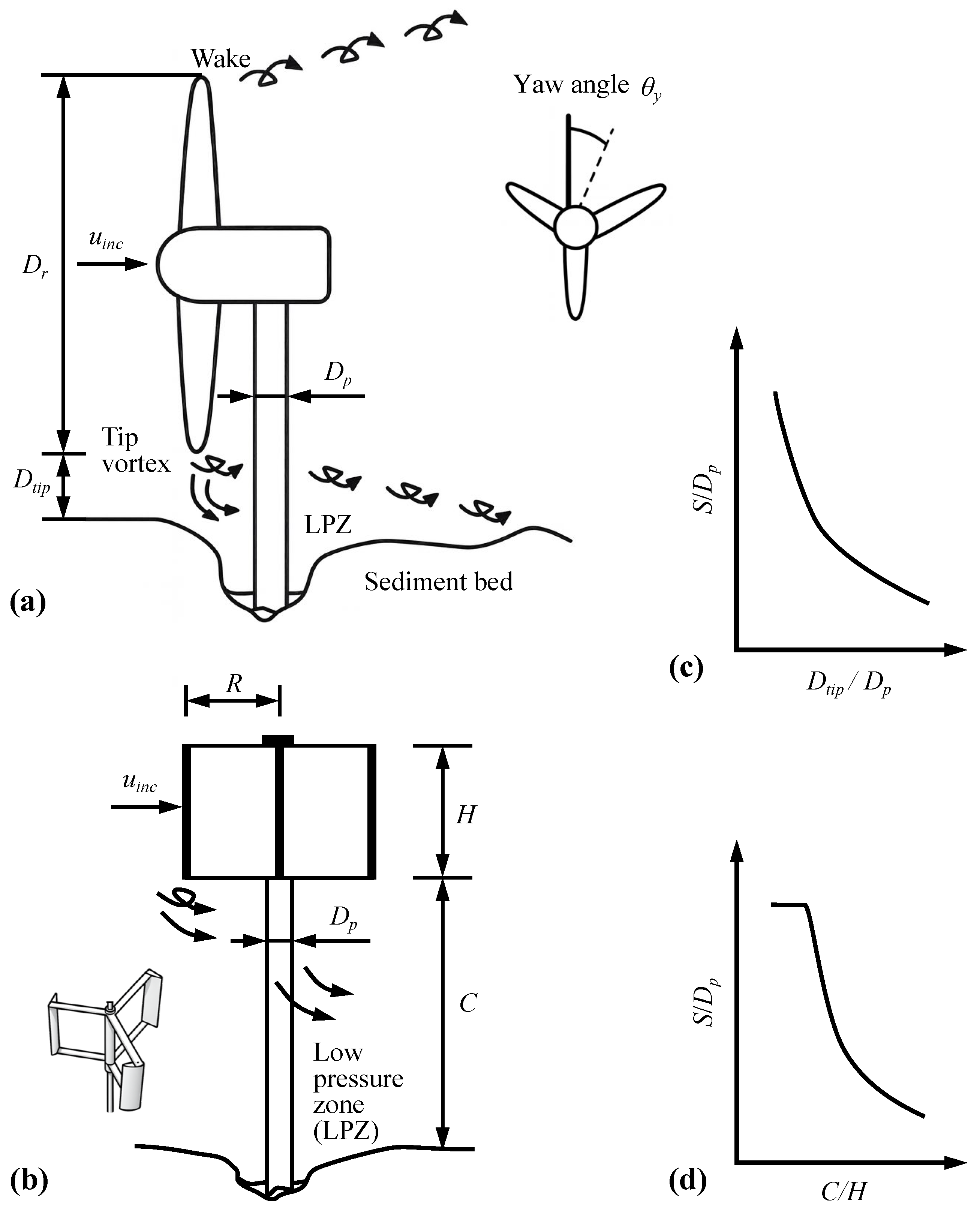
Tip clearance is a key geometric design parameter for tidal stream turbines and plays a decisive role in predicting scour depth and in selecting scour protection measures [14,18]. In this review, tip clearance is defined as the vertical distance between the blade tip and the sediment bed, as shown in Figure 4a,b. Tip clearance influences scour by modifying the flow structure in the gap between the turbine base and the seabed. The rotating rotor and its blockage effect force flow through the narrow passage between the blade tip and the bed, compressing and accelerating the local streamwise motion. The accelerated near-bed velocity, often termed the tip–bed velocity, acts as a primary driver of turbine-induced scour. Measurements and simulations indicate an acceleration ratio of about 10 to 20% in the zone between the tip and the bed [23,24], and theoretical estimates further show that when the clearance approaches zero, the maximum velocity increase can reach about 46% of the free stream velocity [23]. As tip clearance decreases, the near-bed flow becomes faster, which amplifies local bed shear stress beneath the rotor and increases the potential for scour around erodible surfaces.
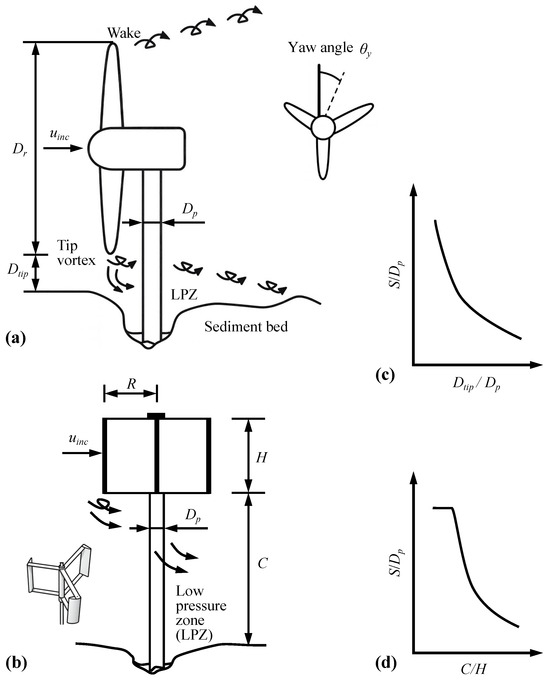
Figure 4.
Schematic of key geometric parameters for (a) a horizontal axis tidal turbine HATT and (b) a vertical axis tidal turbine VATT. Panels (c,d) show equilibrium scour depth for different tip clearance ratios for HATT and VATT.
Extensive experimental and numerical evidence shows that both scour depth and spatial extent increase as tip clearance decreases, with smaller clearance leading to greater sediment transport and faster scour development, whereas larger clearance reduces sediment mobility and slows scour growth (Figure 4c,d) [7,18,20,23]. For HATTs, when clearance approaches about three pile diameters, the accelerated near-bed velocity can exceed the threshold for sediment motion, leading to a sharp increase in scour depth and the onset of local live bed conditions [7,13]. For VATTs, the maximum relative scour depth and the affected area decrease approximately linearly with increasing clearance, and the temporal rate of scour also declines as clearance increases. When the ratio of tip clearance C to rotor height H (Figure 4b) decreases from 0.75 to 0.50, scour depth increases markedly, and when C/H is less than or equal to 0.50, the regime shifts to live bed scour with only limited additional deepening for further reduction in clearance [24]. When clearance is sufficiently large, turbine influence becomes negligible for scour assessment [23]. A practical guideline is to position the rotor so that the shaft centerline is at least one rotor diameter above the seabed, which reduces severe sediment mobilization and disturbance.
2.3. Control of Scour by Helical Wake and Yaw Effects
The three-dimensional helical wake generated by turbine rotors can influence the morphology and spatial distribution of scour pits, though its overall impact on ultimate scour depth is likely secondary compared to factors such as flow intensity, sediment properties, and foundation geometry. In contrast with the nearly axisymmetric annular pits that form around monopiles without turbines in unidirectional flow, seabeds downstream of tidal stream turbines often display asymmetric scour and deposition. The underlying cause is a coherent system of tip and hub vortices shed by the rotating blades that reorganizes the near-bed flow field downstream of the pile [25]. Numerical simulations and field observations, primarily based on small-scale experiments and turbine-scale simulations, report asymmetric bedforms behind the pile, with a deeper pit on one side and concomitant deposition on the other side, consistent with a bias in near-bed shear and sediment transport pathways imposed by the helical wake [26]. The spatial organization and recovery rate of turbulence in the wake govern the downstream velocity deficit and the distribution of bed shear stress.
Under yawed operation, the yaw angle θy (Figure 4a) between the rotor axis and the incoming flow redirects the wake and modifies the turbulence structure of the wake, which changes the layout of scour and deposition [27]. Laboratory studies under three-dimensional yaw show that increasing yaw angle induces wake deflection opposite to the direction of rotor yaw. Asymmetry appears at small angles, and for angles above about 30°, the wake moves away from the centerline and organizes into a banded pattern [27,28]. Yaw also influences power and thrust output, typically reducing both and producing thrust fluctuations that first increase and then decrease with increasing yaw angle. However, in practical deployments, the effect of yaw-induced asymmetries on ultimate scour depth is often limited unless large angles persist. When the absolute yaw angle is below about 15°, the final scour depth changes little. Larger angles can reduce power markedly and couple with scour evolution, which complicates assessment of foundation scour and fatigue [28,29]. Notably, evidence from large-scale or field measurements isolating yaw effects remains scarce, and current understanding relies heavily on controlled laboratory conditions.
3. Scour Characteristics of Different Foundations
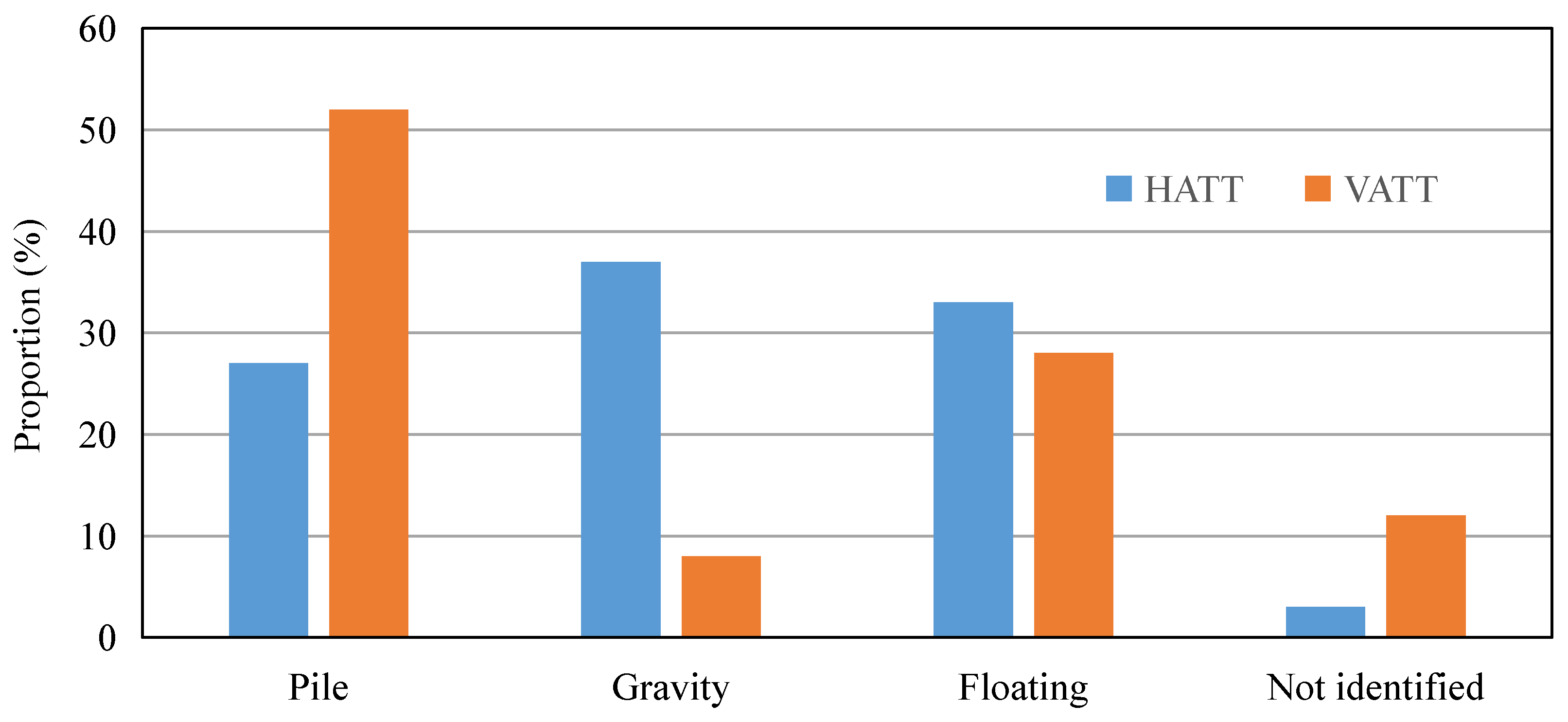
All tidal energy conversion devices require a supporting structure for secure installation in designated sea areas. Common support structures can be grouped into three categories: floating, gravity-based, and pile-based [30]. Bottom-fixed systems include monopiles, tripods, jackets, and gravity bases. Figure 5 shows the proportion of turbines that use different placement options for horizontal axis and vertical axis configurations in situ. Pile-based supports predominate for vertical axis devices, while gravity and floating supports occur more often for horizontal axis devices. Differences in geometry and stiffness alter the surrounding hydrodynamics and shape the resulting scour patterns. This section reviews principal foundation configurations under oscillatory currents and combined wave and current conditions representative of marine environments, and summarizes characteristic scour evolution and the governing factors. It also relates foundation choice to design margins, monitoring requirements, and protection strategies.
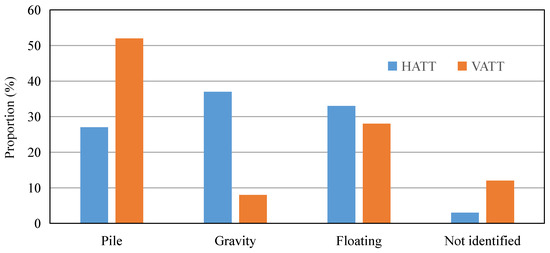
Figure 5.
Proportion of turbines adopting different placement options in situ. Data from [30]. HATT: horizontal axis tidal turbine; VATT: vertical axis tidal turbine.
3.1. Monopile Foundation
The monopile is a common fixed support for tidal turbines [7,13]. In real marine settings, tidal currents are typically oscillatory rather than steady and unidirectional [31]. Scour mechanisms under bi-directional or reversing oscillatory flow are therefore more complex than under steady current conditions [32,33]. Flume experiments that investigate monopile scour in reversing currents reveal a cyclic sequence of partial infilling and renewed excavation within each half cycle. When the tide reverses, some of the previously eroded sediment settles back into the pit, which reduces the instantaneous depth. As the flow switches direction again, this infill is removed and the pit deepens further. The cycle repeats while the net trend is progressive growth. The amplitude of these depth oscillations increases with oscillatory current strength.
A notable finding is that, for the same peak velocity, the maximum scour depth under oscillatory flow can be smaller than that under steady unidirectional flow because alternating flow provides more opportunities for deposition during reversals, which temporarily suppresses scour development [13,32]. This suppression weakens as current strength rises, and at sufficiently high amplitudes, the maximum depth approaches that observed in steady flow. The influence of velocity amplitude on scour depth is approximately linear in both flow regimes. Higher peak velocities produce larger equilibrium depths [13,34]. Design of monopiles in oscillatory tidal regions should therefore account for the modulation of scour rate and depth by flow reversal and include adequate safety margins.
3.2. Tripod and Jacket Foundations
Tripod and jacket foundations consist of multiple legs and provide high stability and load carrying capacity. They are widely used in tidal energy and offshore wind applications [6,35]. Their scour behavior is more complex because wakes generated by individual legs interact and the corresponding scour zones may overlap. For tripod systems, each leg develops a local scour pit and the arrangement of the legs governs the resulting morphology. Experiments and simulations for tripods supporting HATT indicate that, with the rotor in operation, scour around each leg increases over time and approaches a distinct equilibrium depth. Differences arise among the three pits due to the angle between the incoming flow and the symmetry axis of the foundation, often described as the installation angle [17,36]. When the flow faces one leg at zero installation angle, the central leg often experiences the largest scour, while leeward legs in the wake region show reduced erosion. If the installation angle is rotated so that the inflow is directed toward the gap between legs, scour shifts laterally, with one side deepening and the other side mitigating. These findings indicate that relative leg position and flow alignment exert primary control on scour distribution and should be considered in design to avoid excessive erosion at a single leg [36].
Jacket foundations combine multiple piles with truss members, where the key issues concern pile group interaction and the influence of the pile cap and horizontal beams on the local flow [37]. Laboratory studies under reversing currents and combined wave and current conditions show that the upstream pile develops a pit similar to a monopile, while the downstream pile experiences less scour due to wake sheltering from the upstream row. At the same time, braces accelerate the flow locally and can induce additional pits in the bays between piles. For bucket-type jackets, the scour depth depends on the bucket exposure height, with larger exposure creating a greater projected area and more severe erosion. Overall, scour around multi-pile systems is more intricate than around a single pile and requires joint consideration of leg spacing, array arrangement, and structural details that modify near-bed hydrodynamics [37].
3.3. Gravity-Based Foundations and Hybrid Structures
A gravity base anchors the device to the seabed through self weight, and some systems connect to pre-laid concrete foundations. Gravity-based structures are viewed as a leading solution for tidal turbines because installation can proceed efficiently at demanding sites with limited offshore work [38]. Representative implementations include the Open Centre Turbine, DeepGen, and DeltaStream, which are secured by gravity support frames or caissons [39]. These foundations are commonly deployed in high-energy tidal channels. Field observations under combined wave and current conditions report pronounced edge scour around the base perimeter that requires explicit consideration during design and siting [40]. In mobile bed settings, the joint action of waves and currents together with rotor-induced near-bed acceleration can intensify edge scour relative to monopiles in steady flow. Design practice can draw on experience from gravity caissons and from hybrid concepts that condition near-bed hydrodynamics to reduce equilibrium scour depth and improve long-term foundation performance in tidal applications.
To enhance resistance to scour, recent designs integrate energy conversion into the foundation itself. One example incorporates an oscillating water column (OWC) wave energy converter into an offshore wind turbine (OWT) monopile to form an OWC–OWT system. The added base plate and open-air chamber focus incident wave energy and buffer local hydrodynamics, which reduces scour depth around the foundation [6,41]. Numerical simulations indicate that such OWC configurations modify steady flow and the three-dimensional vortex field and thereby reduce the maximum scour depth. Geometry exerts a significant influence on protection efficiency. Orienting the OWC opening upstream and choosing a base plate length near one and a half times the chamber diameter provides superior mitigation relative to alternative settings [41]. For tidal stream turbine foundations, a similar hybrid approach can be adopted by integrating flow guiding skirts or OWC style chambers into gravity bases to offset rotor-induced near-bed acceleration and to reduce equilibrium scour depth at sites with strong wave–current coupling.
4. Seabed Response Under Wave–Current–Turbine Coupling
In complex sea states, the combined action of waves and tidal currents produces variations in seabed pore water pressure and redistributes soil stresses. With additional dynamic disturbance from a rotating turbine rotor, the seabed may display more intricate responses that include transient liquefaction and cyclic cumulative deformation, which extend beyond the conventional concept of scour [15]. To investigate this coupled behavior, recent work has developed numerical models that represent interactions among waves, currents, the seabed, and the turbine, and has examined the resulting characteristics of seabed response.
4.1. Multiphysics Coupling Framework
To quantify the influence of tidal stream turbine operation on seabed stability, researchers have developed one-way coupled numerical models that represent interactions among waves, tidal currents, the seabed, and the turbine foundation [15,42] primarily at the scale of an individual turbine. The hydrodynamic component solves three-dimensional turbulent flow under combined waves and currents using Reynolds averaged Navier–Stokes equations, often implemented on open-source CFD platforms such as OpenFOAM (version not specified) and, when needed, with two-phase solvers to capture the free surface [42,43]. While these models can accurately resolve the flow and turbulence field, it is important to distinguish this capability from their performance in predicting equilibrium scour depth and scour hole geometry. The seabed component applies Biot consolidation theory to represent deformation of the soil skeleton and the evolution of pore pressure in a porous medium [15]. Turbine forcing is introduced through equivalent rotor approaches that include the ALM and its unsteady variants, which apply distributed body forces along idealized blade lines and reproduce key wake features at substantially lower cost than full rotor geometry while retaining near-wake fidelity [7,21]. Transient wave pressures computed by the flow solver are passed to the seabed model as boundary loading, while the pore pressure response does not feed back to the flow field, so coupling remains one way with submodels advanced in an alternating time sequence. Most implementations treat the seabed as a saturated elasto-plastic medium and focus on pore pressure and liquefaction without explicitly resolving bedform evolution due to scour excavation and deposition, which reflects the present scope of these frameworks [15,35].
An alternative line of work uses morphodynamic coupling based on the Exner continuity equation to simulate directly the evolution of the bed surface [42,44,45]. In this formulation the turbulent flow is resolved with Reynolds Averaged Navier–Stokes equations (RANS) or with Large Eddy Simulation (LES) when higher fidelity is required near blades and support members, where LES better captures tip vortices and flow separation than RANS in comparative studies [44,45,46]. Sediment transport is represented through combined bedload and suspended load flux relations, and the bed elevation advances in time by solving the Exner equation with bed shear stress from the flow solution as input forcing [42,45,47]. Three-dimensional models that solve the Navier–Stokes and Exner systems concurrently have reproduced the formation and growth of scour pits around piles and have clarified sensitivities to hydraulic and geometric parameters for turbine foundations under waves and currents. However, a synthesis of available studies indicates that the accuracy of these numerical predictions of scour depth can vary, and they do not consistently outperform empirical formulas in terms of absolute error, due to uncertainties in sediment transport closures, boundary conditions, and long-term morphodynamic feedbacks. Taken together, these multiphysics strategies enable joint analysis of fluid motion, sediment transport, and soil response in the vicinity of a tidal stream turbine foundation and provide a more complete basis for scour protection and geotechnical stability assessment [9]. Therefore, numerical models and empirical relations should be considered complementary tools. Numerical models excel in exploring complex mechanisms and site-specific configurations, whereas empirical relations remain valuable for rapid and conservative estimates. At the farm scale, morphodynamic studies frequently use depth-averaged or three-dimensional RANS models with parameterized turbine representations to examine scour processes and sediment redistribution across turbine arrays.
4.2. Dynamic Stress Amplification and Liquefaction Risk
Coupled numerical simulations show that, under otherwise identical incident wave and current conditions, rotation of the tidal stream turbine rotor significantly intensifies the dynamic response of the seabed [15]. For a monopile foundation under combined wave and current conditions, turbine rotation increases the wave-induced pressure on the upstream face of the pile compared with the non-rotating case. First, the peak dynamic wave pressure transmitted to the seabed upstream of the pile rises by about 75% during rotor operation, which is consistent with sharper local velocity gradients and larger wave orbital motions induced by rotor-driven downflow and flow blockage, and which directly increases the cyclic loading imposed on the soil in front of the pile. Second, downstream of the pile the significant wave height in the wake region increases by about 15% relative to the non-rotating case, so that the wave energy and associated cyclic shear loading reaching the seabed are also enhanced. Near-bed turbulence strengthens and the shear field around the pile is reorganized, which elevates the peak shear stress on the pile flank by approximately 230%. The wall shear on the pile shifts from being predominantly streamwise to a state with a substantial downward component associated with rotor-induced downflow, a change that promotes deeper erosion and stronger stress concentration at the pile base.
At the soil level, this hydrodynamic amplification manifests as larger cyclic pore pressure fluctuations and deeper transient liquefaction. The combined action of waves and rotor rotation raises the magnitude of negative pore pressure behind the pile by about 24%, which indicates stronger cyclic shearing of the soil skeleton and a greater reduction in effective stress. Once the effective stress drops below a critical threshold, transient liquefaction initiates and the depth of the liquefied zone increases. Simulations show that the depth of transient liquefaction increases by about 50% compared with the non-rotating monopile reference, which implies reduced effective strength and faster enlargement of scour features with added threats to foundation stability [15]. Collectively, these results provide a step by step explanation of why rotor-induced amplification under combined wave and current forcing increases both the hydrodynamic drivers of scour and the propensity for soil failure. Design practice should therefore consider the additional loads from rotating components and apply targeted measures for liquefaction resistance and scour mitigation; for example, drainage or ground improvement near the pile together with sufficient embedment or armoring to withstand the intensified near-bed shear field.
4.3. Hydrodynamic Wake Modification Under Wave Action
Waves modify the inflow to tidal stream turbines and alter wake characteristics compared with current-only conditions [48,49,50]. Under combined wave–current forcing, the velocity distribution within the wake differs from that produced by purely tidal flow. For waves that propagate in the same direction as the mean current, Zhang et al. [48] report that moderate wave forcing can enhance wake recovery downstream, because wave orbital motion transports higher energy fluid into the wake deficit and can reduce the distance required for partial recovery of the mean velocity field in the far wake. In the near wake, the presence of waves can intensify the velocity deficit and increase turbulence levels. Under wave–current conditions with zero relative angle, periodic acceleration and deceleration of the inflow over each wave cycle modulate the blade angle of attack and produce large intra-wave fluctuations in turbine power, with the cycle averaged power either slightly increased or slightly decreased relative to the current only case depending on wave height, period, and operating point [48,49]. The associated modulation of near-bed velocity and turbulence implies an enhanced local scour potential near the foundation and may, for some wave–current combinations, modify the distance to full wake recovery in the far field. For waves that approach from other directions, for example obliquely, the detailed wake distortion and scour pattern will depend on the relative angle between wave propagation and tidal current, which remains an important topic for future investigation.
The implications for turbine arrays require attention. In wave-affected sites, wake interactions among adjacent units may deviate substantially from expectations based on current-only conditions, and the associated scour patterns can become more complex, which motivates dedicated assessment of spacing and layout at the tidal farm scale [51,52]. The combined action of waves and currents creates a harsher environment for foundations, with stronger scour drivers and an elevated likelihood of soil liquefaction in some settings [15]. Design and analysis should therefore use multiphysics models that integrate the relevant processes and should draw on test site observations for validation and calibration to ensure predictive reliability for engineering use [21,53].
5. Scour Prediction and Modeling Methodologies
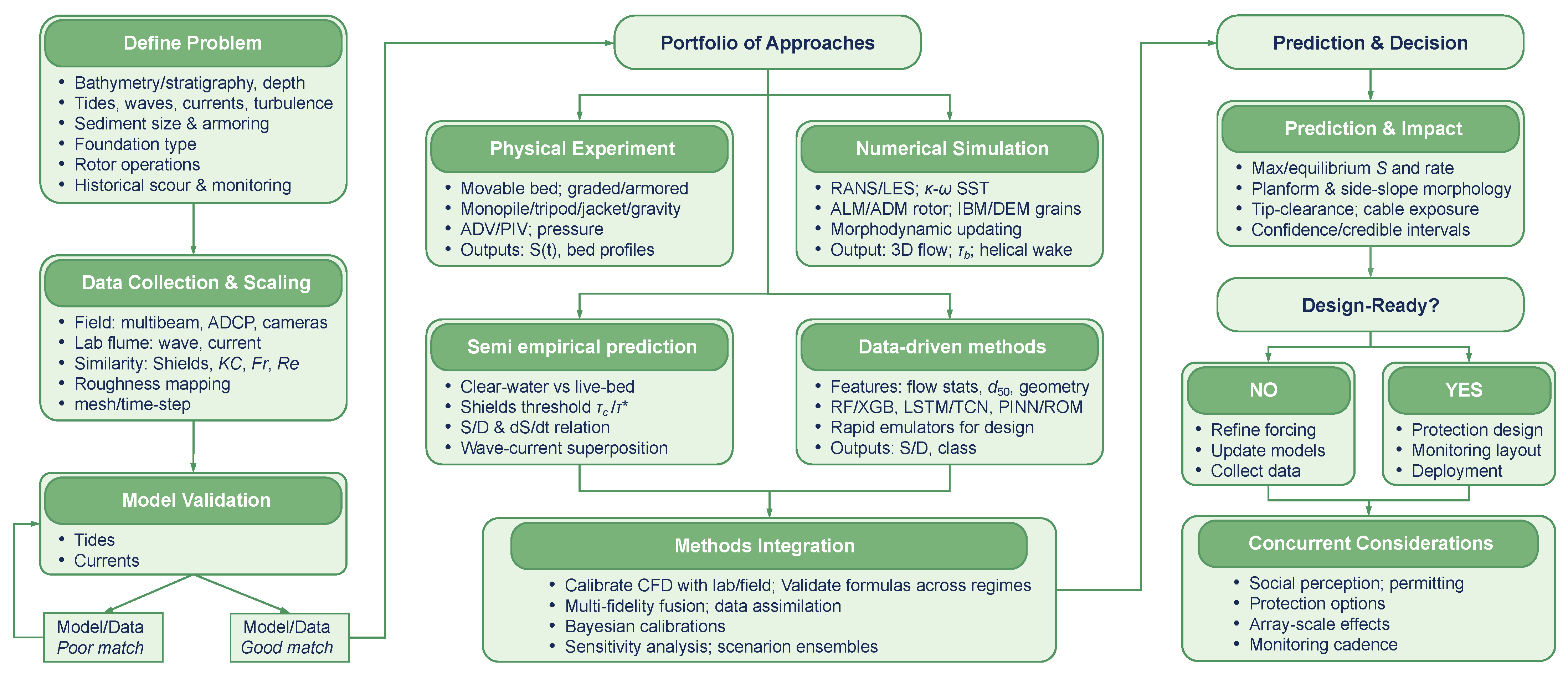
Building on the physical understanding developed in Section 2, Section 3 and Section 4, accurate prediction of scour depth and morphology around tidal stream turbine foundations relies on a portfolio that includes physical experiments, high fidelity numerical simulation, empirical and semi-theoretical formulations, and data-driven techniques. Figure 6 presents a schematic workflow for scour prediction and modeling methodologies that brings together the main numerical approaches used for tidal stream turbines and the corresponding ways in which the turbines are represented in the models. The central panel distinguishes depth-averaged morphodynamic models with enhanced drag terms, three-dimensional RANS models with actuator disk or actuator line representations, and high-resolution CFD approaches with body fitted blades and fully coupled seabed response, while the surrounding panels link each method family to its typical input data, scales of application, and main prediction outputs, as well as to design readiness and concurrent considerations such as scour protection and monitoring. Each approach addresses distinct scales of flow-sediment interaction and provides complementary constraints on the governing processes responsible for local erosion and deposition around support structures [9,54]. Progress has accelerated through systematic integration of these methods with rigorous cross-validation and explicit uncertainty quantification, where laboratory measurements inform and refine model calibration, high-fidelity numerical solvers reveal complex three-dimensional hydrodynamics and sediment pathways, and reduced-order models combined with advanced machine learning tools support rapid, data-informed assessment within design studies. This comprehensive multi-method workflow significantly strengthens mechanistic understanding and demonstrably improves predictive skill for practical engineering applications in energetic marine environments.
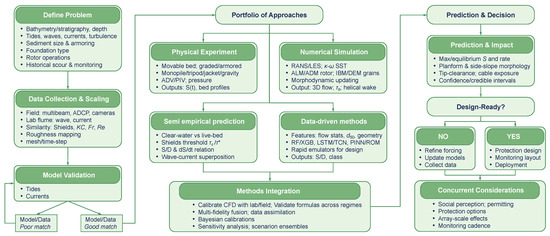
Figure 6.
Schematic workflow for scour prediction and modeling methodologies.
5.1. Physical Model Experiments
Flume and basin experiments are a primary approach to investigate scour around tidal stream turbines and to obtain key data on flow structure, wake characteristics, and scour pit morphology and depth [18,19,24], although they remain inherently idealized and usually cover a limited subset of hydraulic, geometric, and sediment conditions encountered in the field. These datasets are essential for mechanistic interpretation and for the validation of numerical models and reduced formulations, but they often emphasize well-controlled reference cases rather than the full variability of prototype environments. In typical physical model experiments, recirculating and wave flumes are employed to reproduce steady currents, reversing flows, and combined wave–current conditions. These simulations emulate site-specific conditions and are used to assess turbine performance, structural loading, and seabed morphodynamic response [7,18,29,48,49]. Most studies, however, focus on single-turbine setups in straight channels, neglecting the effects of three-dimensional bathymetry and turbine array interactions. Test matrices often vary the foundation type, such as monopile and tripod, the tip to bed clearance, the yaw condition, and predefined bedforms to isolate controlling parameters for scour development [55,56,57,58,59,60], yet interactions among these parameters are only rarely explored through systematic multi-factor designs, which limits the ability to generalize trends across sites. Measurements combine particle image velocimetry or acoustic Doppler velocimetry for velocity and turbulence with nonintrusive bed profilers, laser three-dimensional scanning, and stereophotogrammetry for morphology, thereby resolving time dependent fields that are suitable for model calibration and uncertainty assessment [61,62,63,64,65], although restricted spatial coverage, finite run durations, and measurement noise can still lead to incomplete characterization of extreme events and late stage scour evolution.
Scale effects remain a central limitation. High Reynolds number turbulence characteristic of prototypes is difficult to reproduce at laboratory scale, especially in three-dimensional separated flows near blades and support members, which challenges fidelity in turbulence structure and wake recovery [18,24,66], and only a few studies have quantified how these discrepancies translate into bias in predicted bed shear stress and scour depth. Experimental design therefore prioritizes Froude similarity to preserve free surface dynamics while seeking the highest feasible Reynolds number to mitigate distortion, and acknowledges that perfect similarity in both groups is rarely attainable, so that trade offs between free surface scaling, turbulence structure, and sediment mobility are unavoidable. Sediment scaling introduces additional uncertainty since ripple dimensions under reversing flow often exceed field values, which affects transport thresholds and equilibrium morphology, and cohesive or mixed sediment beds that are common at many tidal stream sites remain underrepresented in existing campaigns. In this context, physical experiments serve as benchmarks for validating numerical and semi empirical models and for defining defensible prediction envelopes for engineering application in energetic tidal settings, but their results are most reliable and meaningful when interpreted as process-level insight and relative trends, whereas absolute design values must be supplemented by careful extrapolation, field observations, and complementary modelling approaches.
5.2. Numerical Simulation Techniques
Computational fluid dynamics is now a primary tool to study scour driven by tidal stream turbines because it resolves local flow features that support mechanism analysis and parametric studies [67,68,69,70], although its predictive capability still depends strongly on modelling assumptions, numerical resolution, and the availability of validation data. Detailed fields of velocity, vorticity, and evolving morphology are obtained to support interpretation and model validation, but in most applications these fields are still generated for single turbines under idealized inflow and sediment conditions, so transfer to field settings requires caution. Fully resolved rotor geometry with moving grids or sliding interfaces captures blade motion but requires substantial computational cost and wall clock time, as shown by comparisons in which the fully resolved approach needs about 3.5 times the runtime of the ALM under matched conditions [7,21,47,69], which has so far limited its use mainly to short-duration or highly simplified scour campaigns. To balance accuracy and efficiency, several surrogate rotor models are widely applied. The actuator disc method, also called actuator disk theory (ADT), treats the rotor as a zero thickness porous disc within a momentum framework and applies distributed thrust, which is effective for large-scale domains, although it omits swirl and tip vortex details [71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78], so it cannot reproduce near-wake structure or tip clearance effects with sufficient fidelity for detailed scour assessment close to the foundation. The ALM distributes body forces along blade-aligned lines based on blade element momentum relations and reproduces helical wake features at far lower cost than fully resolved geometry. Reported accuracy for wake deficit, vorticity distribution, and thrust is close to that of fully resolved models in many cases, which supports its use for array and scour simulations at larger scales [21,79,80,81], yet its performance remains sensitive to grid resolution, force-smearing strategy, and empirical tuning, and systematic benchmarks for scour-related metrics are still scarce. Blade element momentum formulations embedded in CFD share similarities with the ALM and can further reduce cost, although, like the actuator disc approach, they have difficulty capturing tip vortex structure with full fidelity [71,78], and are therefore better suited to farm-scale flow modification than to near-bed scour prediction. The actuator surface model distributes forces over an idealized surface to improve three-dimensional interactions, with additional computation [74,82], but applications to turbine-induced scour are still limited and its relative advantages over ALM and ADT for morphodynamic problems remain to be quantified.
Turbulence closure represents a fundamental modeling decision. Although systematic comparisons of different turbulence models specifically for scour applications around tidal turbines remain scarce, existing studies provide important references for model selection. Reynolds averaged Navier–Stokes closures such as the k–ω Shear Stress Transport turbulence model are prevalent in tidal turbine scour studies because they provide reliable mean fields at moderate cost, yet they may under-resolve near-wake separation and anisotropy [42,73]. Furthermore, systematic comparisons of different turbulence closures specifically for sediment transport and scour prediction around tidal stream turbines remain limited, and no single model has been comprehensively validated for this application. Consequently, only a few studies have quantitatively assessed how these modeling deficiencies propagate into errors in predicted bed shear stress and scour depth. LES resolves a wide range of energetic eddies and represents transient and anisotropic turbulence more faithfully, including tip vortex dynamics and separation behind support members, so it offers a more physically detailed description of rotor–seabed interaction. The associated computational expense remains high, which limits routine engineering deployment at present, and has so far restricted LES-based scour studies to relatively short durations and simplified geometries. Careful selection of turbulence closure and grid resolution remains necessary, and sensitivity of predicted scour to turbulence intensity and spectral content continues to be an active topic [49,83], with current evidence indicating that inflow turbulence specification and unresolved small-scale motions can introduce non-negligible uncertainty into design-level scour estimates.
Recent work has advanced multiphysics coupling to represent concurrent hydrodynamics and morphodynamics. A notable development couples the ALM with an immersed boundary method (IBM) representation of the bed and structure so that the fluid solver exchanges momentum with a deformable seabed and the bed elevation updates by sediment transport and Exner-type relations. This strategy avoids dynamic remeshing associated with arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian schemes and reproduces three-dimensional scour patterns under combined waves and currents in agreement with experiments [21,42,84], although most applications remain at laboratory scale and long-term bed evolution and array interactions have yet to be demonstrated. Two-phase Eulerian formulations have also been integrated with actuator-based rotors to simulate suspended load and resettlement under turbine operation above erodible beds, although parameterization of mixture rheology can be demanding [9,21,71,78], and the scarcity of field measurements makes it difficult to constrain constitutive assumptions for realistic sediment mixtures. Overall, these developments show that high fidelity CFD combined with surrogate rotor models provides a promising but still developing basis for prediction of scour around tidal turbine foundations, and credible application requires transparent reporting of model choices, well-constrained physical parameters, and systematic validation against laboratory and, where available, field data. Further work is needed on turbulence modelling, sediment transport closures, and the explicit treatment of tip clearance and array effects before these tools can be regarded as mature for routine engineering design.
5.3. Semi-Empirical Prediction Models
Traditional semi-empirical formulas remain practical for preliminary engineering design; however, most of these formulas were originally developed for non-cohesive sandy sediments and do not account for the effects of cohesion, which significantly alters erosion thresholds and scour development in clay-rich or silt-laden environments. Moreover, only a limited number of relationships explicitly quantify the influence of rotor rotation on scour [85,86]. The transferability of these formulas is constrained by the specific experimental and field conditions under which they were derived, hindering their generalizability across broader parameter spaces and more complex site-specific environments. Table 1 consolidates a summary of representative semi-empirical models, presenting their basic forms, parameter definitions, experimental or field bases (e.g., foundation type, sediment grain size range, flow and loading conditions), intended application domains, and underlying assumptions, while highlighting key limitations such as restrictions to clear-water or live-bed scour, lack of comprehensive validation, and the inability to accurately predict scour in cohesive bed materials without modification. The accompanying discussion clearly compares the strengths and weaknesses of various formulas, enabling engineers to more effectively select and critically apply semi-empirical models in design and assessment, while interpreting predictions in conjunction with field monitoring and numerical simulation.

Table 1.
Summary of formulas for predicting scour around tidal stream turbine foundations.
Semi empirical models address these gaps by combining physical mechanisms with data-supported correlations. One recent approach integrates ADT with Phenomenological Theory of Turbulence (PTT) to predict the maximum equilibrium scour depth around foundations of HATTs under wave and current forcing [34]. In this formulation, ADT provides an estimate of the accelerated near-bed velocity in the gap between the rotor and the seabed, which is then introduced into PTT to evaluate turbulence quantities that control sediment mobilization. A wave–current factor is included so that scour depth under combined forcing can be obtained. The resulting semi-empirical relation shows positive correlations between equilibrium scour depth and the Keulegan–Carpenter number (KC = Um T/D, where Um is the maximum horizontal velocity of the wave orbital motion near the seabed, D is the diameter of the supporting pile, and T is the wave period) as well as the relative wave–current velocity [34].
5.4. Data-Driven Methods
Data-driven approaches such as machine learning offer powerful capability to represent nonlinear relationships and show clear advantages for predicting local scour in tidal stream applications. These methods excel at identifying multivariable couplings and complex behaviors that are challenging for traditional empirical formulas to represent accurately. Other representative techniques include artificial neural networks (ANN), support vector machines (SVM), and ensemble models such as XGBoost and CatBoost. When trained on experimental or field data, these models can establish strong and often statistically significant correlations, frequently achieving improved predictive accuracy within their calibration ranges compared to conventional formulas. For instance, studies such as the application of nature-inspired optimization algorithms to ANFIS for wave-induced scour around pipelines, and new stochastic strategies for pier scour in cohesive beds, illustrate the capabilities of these AI-based approaches [87,88]. These methods capture multivariable couplings and complex behaviors that traditional formulas struggle to represent, and they have been applied to current speed modeling, wake modeling, and enhancement of high-resolution bathymetry, where deep learning supports feature extraction and the construction of surrogates that link wake distribution to incident velocity and turbulence intensity [9,89]. Several challenges limit immediate engineering deployment. Models often operate as black boxes with limited interpretability, they require large and high-quality training datasets, and their generalization may be weak under rare extremes that are underrepresented in the training corpus, which undermines reliability for critical design events. It should be noted that most existing applications concern pipelines and bridge piers rather than tidal stream turbine foundations, indicating that these AI approaches represent a promising but still emerging tool for the tidal energy sector.
Current development emphasizes physics-informed machine learning that embeds governing laws from hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics into neural architectures, thereby improving reliability, generalization, and physical consistency [90]. Work is advancing on multi-scale coupling so that interactions across device, array, and regional scales are represented, including the parameterization of device scale CFD for integration into regional models for environmental assessment [22,77]. Efforts also aim to reduce uncertainty in turbulence prediction through models that represent interaction between ambient turbulence and superposed wakes and that predict wake properties under combined waves and wind. A practical balance between efficiency and accuracy is being pursued by optimizing efficient numerical frameworks such as ALM and IBM coupling and by exploring advanced closures such as LES to lower computational cost while retaining reliability and to support transition to engineering practice [9,44].
6. Scour Protection and Innovative Mitigation Strategies
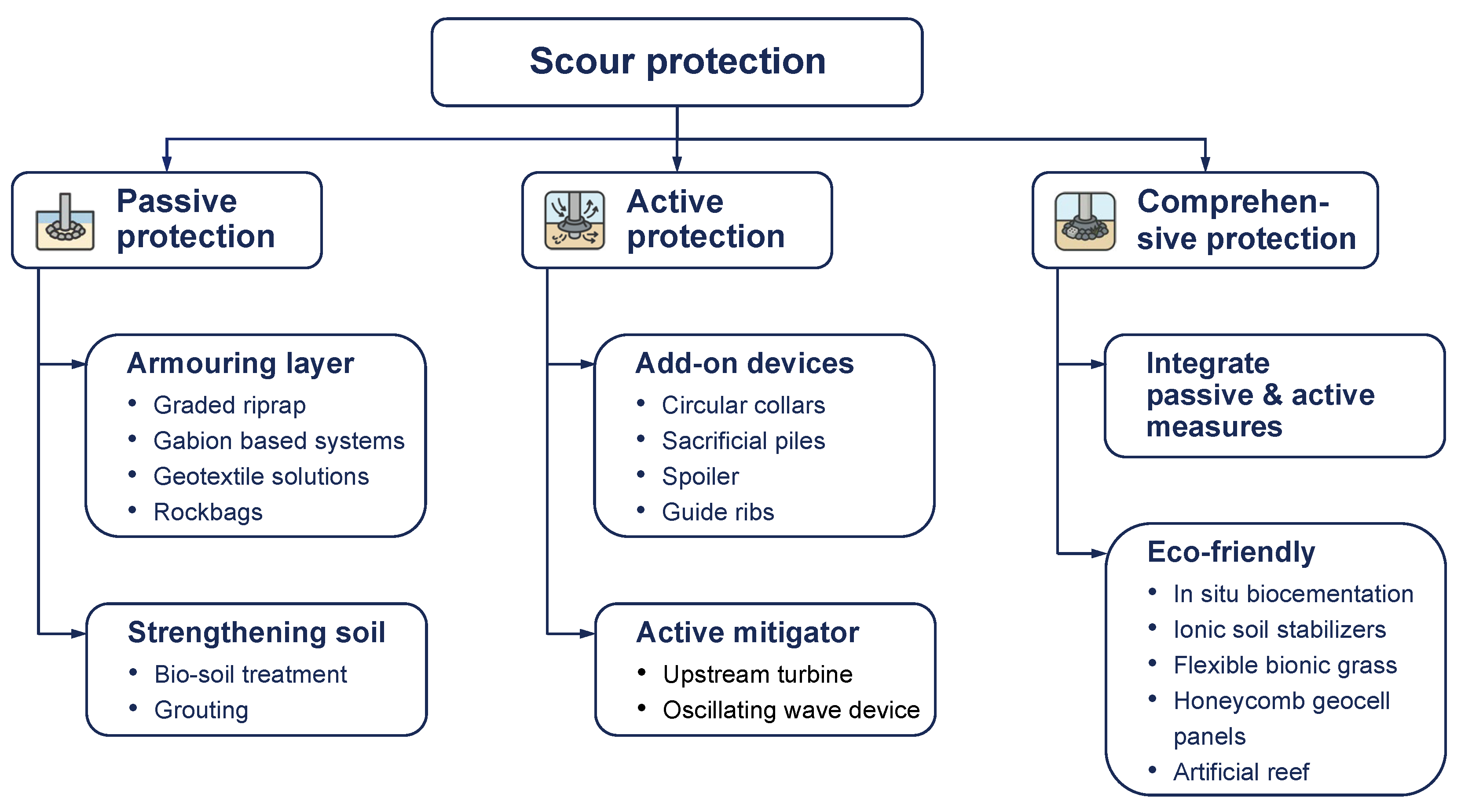
Mitigation of foundation scour around tidal stream turbines uses a combined strategy that integrates passive and active measures to manage hydraulic forcing and bed response throughout the project life cycle [91]. Figure 7 presents a classification of scour protection and mitigation strategies. The figure groups measure into passive protection, active protection, and comprehensive protection, and highlight links between armoring, flow modifiers, and eco-friendly solutions. In this section, we first summarize protection concepts that have been directly tested or implemented at tidal stream turbine sites, then draw on solutions originally developed for offshore wind monopiles and other marine structures that are considered transferable to energetic tidal channels, and finally include a limited set of generic scour protection approaches that provide relevant design principles. The catalogue of options was compiled from a targeted review of field deployments, laboratory experiments, and numerical studies conducted under strong current or combined wave–current conditions and for sediment beds that are representative of potential tidal stream sites. Selection of a strategy depends on the hydrodynamic regime, sediment type, constructability, monitoring needs, and life cycle cost. Established passive options include graded riprap and geotextile systems that stabilize the seabed and limit shear-driven sediment mobility in the near field of the support structure [92]. Recent studies emphasize active and hybrid concepts that leverage turbine operating characteristics and incorporate ecological design principles to moderate near-bed acceleration, disrupt coherent erosive structures, and deliver habitat co-benefits, which has become a central theme in current research on comprehensive protection strategies for tidal sites [93].
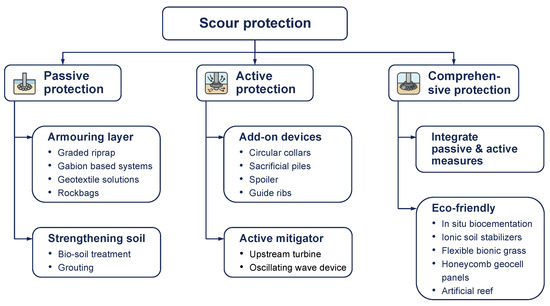
Figure 7.
Classification of scour protection and mitigation strategies.
6.1. Passive Protection
Passive protection increases seabed resistance to erosion by armoring or by strengthening the bed around foundations, thereby limiting scour under tidal stream turbines [12,93]. Many passive concepts considered here were first developed for offshore wind foundations, bridge piers, or similar marine structures. Their relevance to tidal stream turbine foundations is examined, with emphasis placed on adapting their mechanisms and design criteria. Conventional surface treatments remain the primary defense and include graded riprap and gabion systems together with geotextile solutions that increase roughness, dissipate flow energy, reduce near-bed velocity, and raise the critical shear for sediment motion [94]. Geotextile sand containers are widely used at offshore wind sites and have demonstrated good hydraulic stability at foundation edges with notable reductions in scour depth and width, as shown for gravity-based foundations that substituted rock with double layers of sand-filled geotextile bags [6,94]. Gabions filled with rock are common for riverbanks and bridge protection, although field applications for offshore turbine foundations are still limited. Partial grouting of armor units that fill about one half of the void space can deliver high stability while maintaining permeability and has been shown in laboratory studies to increase critical shear by an order of magnitude under extreme loading when compared with traditional riprap layouts. Design philosophies include static stability, which chooses stone size to prevent movement under peak flow, and dynamic stability, which allows controlled reshaping to reduce material demand while maintaining performance, supported by damage indices that distinguish dynamic behavior from failure, though further validation is needed for energetic tidal sites [91,95,96,97].
Failure modes for passive protection include shear-driven displacement, weathering of armor units, edge scour, and interactions with bedforms, among which edge scour poses a persistent long-term risk because it can progressively undermine and retreat the protection layer [91]. Flume studies on riprap aprons indicate that edge scour arises from the combined action of the primary flow and secondary circulation, where turbulent lifting in the main stream mobilizes particles that are then transported by secondary cells, leading to erosion and loss of support at the apron boundary [98]. These findings motivate careful detailing of transitions and edges, attention to layering and filter compatibility, and monitoring strategies tailored to reversing flow and wave and current environments characteristic of tidal channels, with site-specific calibration based on laboratory and field evidence before extrapolation to full-scale deployment [9].
6.2. Active Protection
Active protection aims to weaken scour at the source by reshaping local hydrodynamics around the structure to reduce downflow and the horseshoe vortex and to lower near-bed shear [9]. Two complementary avenues have been developed. The first uses add on devices that modify the flow. Circular collars mounted around the pile disrupt downflow attachment and suppress the near-bed vortex system, which produces substantial reductions in scour depth with decreases of about one third [99,100,101]. Sacrificial piles placed upstream with a smaller diameter than the main support condition the approach flow and weaken the horseshoe vortex around the primary foundation, a concept well documented in bridge pier protection and now increasingly applied to tidal settings, often together with guide panels and collars [102,103]. Spoilers or guide ribs attached to the monopile have been proposed to redistribute shear and enhance dissipation of coherent vortices, with laboratory evidence that fixed ribs attenuate the horseshoe vortex and smooth the bed shear stress field [9,94]. For tidal stream applications, these devices are of interest where hydrodynamic loading and scour patterns resemble those around monopiles, and current studies focus on assessing their performance under bi-directional tidal currents and rotor-induced near-bed acceleration.
The second avenue leverages the turbine system itself as an active mitigator. A small tidal turbine positioned upstream of a monopile can extract momentum from the inflow and disturb the approach boundary layer, thereby reducing near-bed shear and weakening the vortex system while also generating power [91,104]. Numerical and flume studies show that appropriate placement and operation of the upstream turbine can lower the maximum bed shear stress by about 8% and can reduce the maximum scour depth by up to 42%, although the benefit depends on site conditions and operating parameters [94,104,105]. Integrated hybrid concepts extend this idea by embedding a wave energy converter within the foundation layout so that wave-induced flows are redirected and local turbulence is moderated. Configurations with an oscillating wave device placed in front of a monopile report average reductions in scour depth of about 60%, which demonstrates the potential of combining energy conversion and protection within a single structural system [41].
6.3. Eco-Integrated Comprehensive Protection
Modern marine engineering increasingly emphasizes environmental compatibility, which motivates protection strategies that integrate passive and active measures with ecological components to mitigate scour around tidal stream turbine foundations while also providing habitat benefits [91]. Comprehensive protection in this sense combines flow control and bed stabilization within a unified concept and has been proposed as a distinct category where bio-based or environmentally friendly modules are incorporated into conventional layouts to increase roughness, disrupt coherent erosive structures, and enhance sediment stability. This integrated view recognizes that hydraulic forcing, sediment transport, and ecosystem function are coupled processes and therefore addresses scour reduction and ecological outcomes together during design and operation [9,93].
Several innovations illustrate this approach. Microbially-induced calcium carbonate precipitation creates in situ biocementation that strengthens the near-bed layer and raises the threshold for sediment motion, with reported reductions in relative scour depth up to 84% after treatment [6,106]. Ionic soil stabilizers that blend cationic and anionic species increase critical shear stress and have produced reductions of 90% to 95% in relative depth in controlled studies, though potential impacts on benthic communities require careful assessment [91,107]. Bio-inspired configurations such as flexible bionic grass mats and honeycomb geocell panels promote deposition and limit local erosion in the turbine near field, while artificial reef modules dissipate wave and current energy, trap sediment, and enhance biodiversity with modeled reductions in scour of 20% to 30% [91,108]. Although these eco-integrated and soil improvement techniques often achieve higher composite scores than purely active devices in multi-criteria assessments, field applications at tidal stream sites remain limited and require site-specific validation and environmental evaluation before broader deployment.
7. Engineering Context, Challenges, and Future Outlook
Progress on scour around tidal stream turbine foundations is tightly coupled to the evolving needs of tidal energy technology. Achieving deployment at scale and commercial viability requires solutions to intertwined scientific and engineering problems that span hydrodynamics, morphodynamics, and design practice, as highlighted by recent international programs and reviews [109,110,111,112]. Building on ongoing global and Chinese demonstration projects, this chapter outlines priority research directions and standardization tasks that can accelerate technology readiness, including coordinated laboratory to field validation, transferable modeling and design criteria for wave and current environments, and integrated approaches that connect turbine performance, foundation integrity, and environmental stewardship within coherent engineering frameworks.
7.1. Global Development Status
To place the foregoing engineering considerations within a broader deployment framework, the subsequent discussion reviews the global development status of tidal stream energy, a clean, renewable, and predictable resource with high energy density that plays an important role in global energy transition. International development has progressed to full-scale sea trials and is advancing toward commercial deployment, with horizontal axis devices emerging as the mainstream technology. Europe has taken a leading role, notably the United Kingdom, France, and Norway, supported by strong marine engineering capability and policy frameworks. The European Marine Energy Centre in Orkney is widely recognized as an authoritative testing and certification facility for wave and tidal devices and has produced more than 10 testing guidelines, several of which have informed International Electrotechnical Commission drafts. Multiple companies have conducted trials at EMEC, including Alstom Deepgen, Voith Hydro HyTide 1000, Andritz Hydro HS1000, and OpenHydro devices [113]. Beyond EMEC, several megawatt-scale demonstration arrays and test sites have been developed in European waters, particularly in the English Channel (for example, in the Alderney Race) and in western Brittany (for example, in the Fromveur Strait) [113,114]. These projects have provided field evidence on device performance, array-scale hydrodynamic effects, and seabed response under energetic tidal currents, complementing insights from idealized flume experiments. Long-term monitoring at these locations has highlighted the importance of scour observation, foundation optimization, and adaptive operating strategies in harsh marine environments. International demonstration projects at the megawatt scale have accumulated operational experience and point to two clear trends: rapid scaling toward 2 megawatts and beyond, and increasing use of floating platforms that reduce environmental footprint, simplify installation, and open deeper, more energetic sites [112].
China possesses abundant tidal stream resources and considerable potential in terms of installable capacity [115]. Significant advances have been made in power generation technologies and equipment, with progress in areas such as hydraulic and electrical pitch control and bidirectional generation technologies, elevating certain subsystems to a leading international level [110]. Gaps remain relative to leading programs, with the overall technology readiness broadly comparable to international status [112]. However, many prototypes are still in sea trials with limited operating hours, modest efficiency, and vulnerability to damage, and reliability and stability under real sea conditions require further improvement [116]. Industrialization has progressed at a slower rate than in Europe, which has resulted in an installed capacity that remains lower than in leading regions [110]. Dedicated test sites are being developed to bridge the final step before commercialization, including comprehensive test fields at Weihai, Zhoushan, Zhuhai, and deep-sea locations, as well as the Zhaitang Island offshore test site. Continued expansion of integrated testing platforms and a more complete standards system are needed to accelerate technology transfer and industry growth.
7.2. Array-Scale Scour Effects as a Critical Research Gap
Scaling tidal stream energy toward commercial capacity requires array deployments, since shared supports and subsea cables reduce capital and installation costs and improve overall efficiency [117,118,119,120]. Arrays introduce wake interference and blockage that reshape the internal flow field, which in turn affects power capture and the spatial distribution of local scour around foundations [51,52]. Downstream of tidal stream turbine arrays, extensive low velocity wakes are commonly observed, and full recovery distances can reach about 40 rotor diameters, while paired turbines produce slower vortex shedding and longer recovery lengths [51]. Longitudinal spacing primarily controls the velocity deficit within roughly five diameters behind a downstream unit and has weaker influence farther away, with optimal downstream tip-speed ratios near 4.5 under the tested conditions and progressive increases in power coefficient as spacing grows. When the streamwise spacing equals or exceeds 10 diameters, wake affected power coefficients approach upstream values, and practical guidance recommends 20 to 30 diameters so that mean speed recovers to more than 80% of the inflow. Lateral spacing is often selected near two diameters, although sensitivity to site conditions remains an open question [51,121].
Array operation can also disrupt the regional hydrodynamic setting. During flood and ebb, the free surface can rise on the upstream side of arrays and local velocities can be redistributed, which raises questions for sediment pathways and far field effects in constrained channels [122,123,124,125]. Despite substantial progress on scour around single turbines, systematic evidence for array-induced scour and farm-scale morphodynamic response remains limited. Fully coupled three-dimensional CFD simulations that resolve every turbine and the surrounding seabed at the scale of entire farms are still computationally demanding and therefore rare. As a result, most existing studies at the farm scale employ depth-averaged or three-dimensional RANS models with parameterized turbine representations to approximate the aggregate effects of arrays on sediment transport and seabed evolution. Layout archetypes that include aligned, staggered, center channel, and off-axis placement can alter near-bed shear and turbulence through compound wake interactions, thus reorganizing scour footprints around monopiles and jacket legs across the farm footprint [51]. Competitive effects between adjacent arrays add another layer of hydrodynamic and morphodynamic coupling that must be considered in spacing optimization and in environmental assessment for future large-scale tidal developments. The development and systematic validation of array-scale morphodynamic models therefore remains a critical research priority for reliable prediction of farm-level scour impacts.
7.3. Future Directions
To secure technological maturity and large-scale deployment of tidal stream energy, forthcoming studies need to confront the central scientific and engineering challenges that constrain performance, reliability, and environmental compatibility across the full system lifecycle. Priority areas include comprehensive characterization of wave–current seabed interactions, transferable prediction tools that couple turbine hydrodynamics with morphodynamics, validated design criteria and test protocols for array-scale installations, and integrated frameworks that align energy yield with foundation integrity and ecosystem stewardship, which are highlighted here as research priorities rather than descriptions of current routine practice.
7.3.1. Multiphysics Coupling and Advances in Experimental Methodology
Achieving progress in this field is expected to rely on fully coupled models that integrate turbine operation, hydrodynamics including waves and currents, seabed morphodynamics, and structural dynamic response including floating platform motion, which at present remain under active development rather than being widely deployed in design offices. Such models should address limitations of one-way coupling and simplified closures that mask feedback between near-bed acceleration, sediment transport, and load paths. A practical pathway is to extend efficient surrogate-rotor formulations so that the ALM is coupled with the IBM within a consistent solver, which enables concurrent resolution of wake dynamics and bed evolution at tractable cost while preserving the key physics of rotor–seabed interaction. Within this framework, systematic verification and validation across steady, wave–current, and reversing-flow regimes are needed to define model credibility for design use, together with sensitivity analyses that quantify uncertainty propagation from turbulence closures and sediment mobility parameters [21,29].
Equally important is refining the physical understanding and the experimental basis that support these models. Research should clarify how environmental turbulence interacts with compound wakes in multi-turbine settings and should evaluate the applicability of large eddy simulation for engineering prediction where coherent structures and anisotropy govern near-bed stress fields. Laboratory practice should minimize scale effects that arise from Reynolds number mismatch and should report richer turbulence descriptors that include integral length scales in addition to intensity so that inflow conditions can be transferred between facilities and into numerical boundary conditions. Future campaigns should also isolate the roles of background shear, cavitation onset and development, and unsteady loading associated with platform motions such as surge, since these factors modulate rotor wake coupling and the sequence from sediment initiation to equilibrium morphology [126].
7.3.2. Uncertainty Analysis and Scale-Effect Assessment
Uncertainty in prediction arises from the complexity of the tidal stream turbine environment that couples waves and currents, spatial velocity gradients, yawed inflow, and site-specific variability, which together modulate turbulence and sediment mobility. Priority tasks include quantifying uncertainty propagation in power output and scour metrics through sensitivity analysis and stochastic modeling, and improving model robustness by systematically addressing inflow statistics, boundary conditions, and sediment properties, so that future tools can report not only best estimates, but also transparent confidence bounds for engineering decisions. Field evidence should be expanded through longer duration deployments and higher sampling cadence so that nonstationary forcing and rare events are captured and can inform model calibration and validation. These steps will strengthen confidence bounds for turbine performance and for bed response under realistic operating envelopes [127].
Scale effects require dedicated assessment and correction so that laboratory findings can be translated to prototype conditions without bias. A coherent framework should relate laboratory and field regimes through similarity constraints on Froude number, Reynolds number, Shields parameter, and characteristic morphological timescales, and should provide correction functions that account for unresolved turbulence and sediment size disparities. Validation against multi-scale datasets and cross comparison with high fidelity computations can then constrain extrapolation error and enhance the reliability of scour prediction for design and risk evaluation at array and project scales [9,128].
7.3.3. Establishment of Relevant Technical Standards
A coherent standards system is needed to support tidal stream energy development from concept to decommissioning. Priority actions include accelerating the formulation of laws, regulations, and technical specifications that cover design, fabrication, installation, operation, maintenance, and end-of-life phases so that project delivery follows consistent and auditable criteria. Lifecycle guidance should codify hydrodynamic assessment, foundation and scour design, reliability management, monitoring protocols, and environmental safeguards in order to raise technology readiness and reduce project risk [53,110]. For tidal stream applications, these elements are only partially in place at present, so they are identified here as medium- to long-term objectives rather than a description of the current regulatory baseline.
Internationalization and harmonization are equally important. China is encouraged to engage in collaborative programs and to draw on the experience of organizations such as EMEC so that test sites are planned and operated under internationally aligned standards and results can be mutually recognized. Convergence with global practices will facilitate certification, bankability, and cross-border deployment of tidal technologies while creating feedback loops between domestic demonstration projects and international standard-setting activities.
7.3.4. Development of Intelligent Predictive Tools
Data-driven approaches are required to overcome the limitations of traditional empirical models and to improve the fidelity of scour and performance prediction around tidal stream turbines. Priority is increasingly shifting toward physical information machine learning in which governing laws from fluid and sediment dynamics are embedded within learning architectures, although practical applications to tidal stream turbine scour are still at a relatively early stage. This strategy reduces the black box character of purely statistical models, enhances extrapolation across operating envelopes, and increases reliability for design and risk assessment in wave–current environments [89].
Automated array layout optimization is advancing through high-performance computing and surrogate-assisted search so that power yield, economic cost, and environmental impact can be treated within a unified multi-objective framework. Outstanding challenges include explicit inclusion of capital and operating expenditures, sediment transport and morphology modules, and ecological response into the optimization workflow together with engineering validation at demonstration sites. These capabilities are therefore discussed as promising research directions that could underpin future digital twin style planning tools rather than as methods that are already mature for routine project design. Integration of these elements will enable transparent trade studies and support bankable decisions for commercial-scale deployments.
7.3.5. Fully Coupled Assessment of Structural Safety and Ecological Effects
A comprehensive framework is required that integrates structural safety analysis with externally forced multiphysics environments that include waves, currents, and scour. Fatigue reliability and ultimate strength need to be evaluated together with hydrodynamic loading, seabed evolution, and support interaction so that demand and capacity are assessed in a consistent manner across operating and extreme states. The trend toward larger units and deployment in deeper and more energetic waters intensifies these requirements, since harsher ocean conditions impose greater demands on load carrying capacity, resistance to extreme events, and fatigue life. Methodologies that couple response at the turbine, foundation, and mooring with site-specific metocean statistics will be essential to demonstrate adequate margins for commercial projects [111], but at present remain a target for continued model development and field-based validation rather than a fully standardized practice.
Parallel attention is needed for environmental effects associated with tidal stream energy [129]. Priority topics include modification of flow speed, suspended sediment, and bed morphology, disturbance to benthic communities and fish populations and their habitats, and potential contributions from noise, electromagnetic fields, and chemical releases. An indicators-based framework for environmental impact assessment should be established together with baseline surveys before construction and sustained monitoring after commissioning, so that cumulative effects are quantified and mitigation can be adapted throughout the project lifecycle, thereby moving environmental management from largely site-specific case studies toward a more systematic and transferable practice.
7.3.6. Novel Foundation Concepts and Strategies for Monitoring and Intervention
Advancing tidal stream energy into deeper and more energetic waters requires foundation concepts that support floating technology and enable hybrid multi-energy systems that integrate with offshore wind where appropriate. Candidate solutions include semisubmersible or spar-supported platforms with mooring layouts tailored to site-specific metocean conditions, as well as shared support structures for co-located resources that rationalize footprint and cable infrastructure while maintaining hydrodynamic performance. Most of these concepts are still being explored at the prototype or pilot scale and are therefore highlighted as emerging directions rather than established options for commercial deployment.
Operation and maintenance depend on reliable monitoring and targeted interventions. Priorities include improved sealing for nacelles and subsea equipment, corrosion control, and antifouling technologies that extend service life and reduce unplanned outages. Remote intelligent operation and maintenance together with online condition monitoring and diagnostics should provide early warning for scour progression and structural fatigue, which enables timely mitigation and adaptive maintenance planning. Scour interventions benefit from continued development of dynamically stable riprap concepts and from active and integrated protection strategies, including ecologically informed measures that couple hydraulic modification with habitat enhancement. These monitoring and intervention strategies are presented as a roadmap for future practice that builds on, but clearly extends beyond, the tools currently available at existing tidal test sites.
8. Conclusions
Scour around foundations of tidal stream turbines is central to the safe and sustainable growth of the emerging marine energy sector. This review synthesizes the present state of knowledge, and the main conclusions are as follows.
- Rotor rotation significantly intensifies scour. Compared with monopiles without turbines, periodic operation of the turbine rotor imposes strong perturbations on the near-bed flow, which increases the scour rate and elevates the equilibrium depth. The wake and tip vortices generated by rotating blades are primary drivers of this amplification, and the final depth decreases with increasing tip clearance.
- Reversing tidal currents produce distinct scour behavior. Under realistic flood and ebb conditions, depth exhibits cyclical fluctuations with cumulative growth, and the maximum depth under two-directional forcing is slightly smaller than that under an equivalent unidirectional current. Sites with intermittent strong currents require explicit consideration of tidal phase in scour evolution.
- Scour around multi-pile foundations is spatially nonuniform. For tripod and similar layouts, pit geometry depends on leg arrangement and installation heading, and different legs can experience markedly different depths. Appropriate layout and targeted local protection are important for such foundations.
- Coupled waves and currents amplify seabed response. When a rotor operates with waves present, dynamic stresses and pore pressure responses in the bed increase, and the risk of transient liquefaction grows. Assessment of coupled scour and liquefaction under extreme sea states is required, together with measures that improve resistance to liquefaction.
- Innovation in prediction and protection is advancing practice. Numerical modeling such as ALM with IBM coupling and revised empirical relations has improved predictive skill. New mitigation concepts that exploit turbine wake effects and ecologically integrated protection show promising performance and provide additional engineering options.
- Future directions emphasize stronger field evidence and standardization, attention to cumulative scour within arrays and to foundation–structure interaction, and integration of artificial intelligence into monitoring, early warning, and predictive tools so that research outcomes translate effectively into engineering application.
Tidal stream energy is a key element of the future clean energy portfolio. The scour problem presents significant challenges and also new opportunities. With sustained collaboration between industry and academia, continued research, and systematic validation in practice, it is feasible to attain effective control of this critical issue and to ensure development that is safe, efficient, and sustainable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation and methodology, R.L. and Q.Y.; validation and data curation, Y.L.; funding acquisition and writing—review and editing, D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 42176214, 41876095 and 41906183; the Joint Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers LZJWZ22E090002 and LZJWY22E090006; and the Key Program of the President of the Zhejiang Institute of Hydraulics and Estuary, grant numbers ZIHE21Z001 and ZIHE25Z003.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- von Jouanne, A.; Agamloh, E.; Yokochi, A. A review of offshore renewable energy for advancing the clean energy transition. Energies 2025, 18, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, V.; Bhuiyan, M.A. Tidal energy-path towards sustainable energy: A technical review. Clean Energy Syst. 2022, 3, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zou, T.; Liu, H.; Lin, Y.; Ren, H.; Li, Q. Status and challenges of marine current turbines: A global review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Ocean Energy and Net Zero: An International Roadmap to Develop 300GW of Ocean Energy by 2050. Available online: https://www.ocean-energy-systems.org/publications/oes-documents/market-policy-/document/ocean-energy-and-net-zero-an-international-roadmap-to-develop-300gw-of-ocean-energy-by-2050/ (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Zhang, X.; Ji, R.; Sun, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yin, M.; Kong, M.; Reabroy, R. A review of ocean tidal current energy technology: Advances, trends, and challenges. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 071308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambel, J.; Fazeres-Ferradosa, T.; Miranda, F.; Bento, A.M.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Lomonaco, P.A. comprehensive review on scour and scour protections for complex bottom-fixed offshore and marine renewable energy foundations. Ocean Eng. 2024, 304, 117829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. Scour around a mono-pile foundation of a horizontal axis tidal stream turbine under steady current. Ocean Eng. 2019, 192, 106571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Wolf, J.; Williams, A.J.; Badoe, C.; Masters, I. Local and regional interactions between tidal stream turbines and coastal environment. Renew. Energy 2024, 229, 120665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Wang, D.; Qin, C.; Duan, L. Local scour around marine structures: A comprehensive review of influencing factors, prediction methods, and future directions. Buildings 2025, 15, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RIT Energy. Roosevelt Island Tidal Energy (RITE) Environmental Assessment Project: Final Report; Prepared for the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority by Verdant Power, Report 11-04; Verdant Power: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Polagye, B.; Copping, A.; Kirkendall, K.; Boehlert, G.; Walker, S.; Wainstein, M.; Van Cleve, B. Environmental Effects of Tidal Energy Development: A Scientific Workshop; NMFS F/SPO-116, NOAA; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sangiuliano, S.J. Planning for tidal current turbine technology: A case study of the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Guan, D.; Zheng, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, B. Scour processes around a mono-pile foundation under bi-directional flow considering effects from a rotating turbine. Ocean Eng. 2023, 269, 113401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lam, W.-H. Slipstream between marine current turbine and seabed. Energy 2014, 68, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H. Seabed dynamic response of monopile foundation for tidal stream turbine. J. Changjiang River Sci. Res. Inst. 2023, 40, 88–95, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, P.; Zheng, J.; Wu, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, T. Current-induced seabed scour around a pile-supported horizontal- axis tidal stream turbine. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2015, 23, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Guan, D.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Gao, L. Scour processes around a horizontal axial tidal stream turbine supported by the tripod foundation. Ocean Eng. 2024, 296, 116891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hashim, R.; Othman, F.; Motamedi, S. Experimental study on scour profile of pile-supported horizontal axis tidal current turbine. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Musa, M.; Chamorro, L.P.; Ellis, C.; Guala, M. Local scour around a model hydrokinetic turbine in an erodible channel. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lam, W.H.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, J.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Tan, T.H.; Chuah, J.H.; et al. Empirical model for Darrieus type tidal current turbine induced seabed scour. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 171, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X. Proposal of actuator line immersed boundary coupling model for tidal stream turbine modeling with hydrodynamics upon scouring morphology. Energy 2024, 292, 130451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, T.A.A.; Draper, S.; Willden, R.H.J.; Vogel, C.R. The fluid mechanics of tidal stream energy conversion. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2021, 53, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lam, W.H.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Lam, S.S.; Hamill, G. Tip bed velocity and scour depth of horizontal axis tidal turbine with consideration of tip clearance. Energies 2019, 12, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lam, W.H.; Lam, S.S.; Dai, M.; Hamill, G. Temporal evolution of seabed scour induced by Darrieus-type tidal current turbine. Water 2019, 11, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadian, P.; Neill, S.P.; Barclay, V.M. Characterizing seabed sediments at contrasting offshore renewable energy sites. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1156486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, R.; Murdoch, L.; Jordan, L.B.; Amoudry, L.O.; McLelland, S.; Cooke, R.D.; Thorne, P.; Simmons, S.M.; Parsons, D.; Vezza, M. Asymmetric effects of a modelled tidal turbine on the flow and seabed. Renew. Energy 2020, 159, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Chen, H. Experimental investigation on wake and thrust characteristics of a twin-rotor horizontal axis tidal stream turbine. Renew. Energy 2022, 195, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.; Ravanelli, G.; Bertoldi, W.; Guala, M. Hydrokinetic turbines in yawed conditions toward synergistic fluvial installations. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S. Coupled experimental–numerical analysis of energy harvesting dynamics of tidal stream turbine: Synergistic effects of operational status and morphological evolution in wave–current environments. Appl. Energy 2025, 396, 126311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Bhuyan, G.; Iqbal, M.T.; Quaicoe, J.E. Hydrokinetic energy conversion systems and assessment of horizontal and vertical axis turbines for river and tidal applications: A technology status review. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schendel, A.; Hildebrandt, A.; Goseberg, N.; Schlurmann, T. Processes and evolution of scour around a monopile induced by tidal currents. Coastal Eng. 2018, 139, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lin, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J. Experimental study on scour process around mono-pile foundation of a tidal stream turbine under bidirectional flow. J. Hohai Univ. 2022, 50, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse, R.J.S.; Stroescu, E.I. Scour depth development at piles of different height under the action of cyclic tidal flow. Coastal Eng. 2023, 179, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Ding, Z. Experimental analysis and proposal of semi-empirical prediction model on tidal stream turbine induced local scour subjected to wave–current loading. Ocean Eng. 2025, 327, 121020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asumadu, R.; Zhang, J.; Osei-Wusuansa, H. 3-D numerical study of offshore tripod wind turbine pile foundation on wave-induced seabed response. Ocean Eng. 2022, 255, 111421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lai, J.; Lin, X.; Deng, X. Local scour depth evolution characteristics of tripod pile foundation for a tidal current energy turbine. J. Hohai Univ. 2025, 53, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Hou, D.; Guo, Y. On the local scour around a jacket foundation under bidirectional flow loading. Ocean Eng. 2024, 310 Pt 2, 118772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.; Gavin, K.; Doyle, T. Design of shallow foundations for tidal-stream energy structures. In Proceedings Fourth International Symposium on Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics; Westgate, Z., Ed.; University of Texas: Austin, USA, 2020; Volume 3587, pp. 1805–1815. [Google Scholar]
- O’Doherty, T.; O’Doherty, D.M.; Mason-Jones, A. Tidal energy technology. In Wave and Tidal Energy; Greaves, D., Iglesias, G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, O.; Cossu, R.; Heatherington, C.; Hunter, S.; Baldock, T.E. Field observations of scour behavior around an oscillating water column wave energy converter. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, T.; Tong, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, H.; Lun, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L. Design and analysis of the anti-scour offshore wind-wave energy converter: Scour characteristics and hydrodynamic mechanism. Ocean Eng. 2025, 339, 122210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Law, A.W.-K.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X. Two phase fluid-actuator line-immersed boundary coupling for tidal stream turbine modeling with scouring morphology under wave-current loading. Energy 2025, 329, 136757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Zhang, X.; Ji, R.; Wu, H.; Yin, M.; Liu, H.; Sun, K.; Reabroy, R. Effects of wave-current interaction on hydrodynamic performance and motion response of a floating tidal stream turbine. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksen, M.M.; Seyedzadeh, H.; Anjiraki, M.G.; Craig, J.; Flora, K.; Santonia, C.; Sotiropoulos, F.; Khosronejad, A. Large eddy simulation of a utility-scale horizontal axis turbine with woody debris accumulation under live bed conditions. Renew. Energy 2025, 239, 122110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sotiropoulos, F.; Conde, S.M.J.; Khosronejad, A. Large-eddy simulation of a hydrokinetic turbine mounted on an erodible bed. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjiraki, M.G.; Aksen, M.M.; Shapourmiandouab, S.; Craig, J.; Khosronejad, A. Computational study of a utility-scale vertical-axis MHK turbine: A coupled approach for flow–sediment–actuator modeling. Fluids 2025, 10, 304. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, X. Coupled BEM and two-phase mixture model for surrounding flow of horizontal axial turbine over sediment seabed. Ocean Eng. 2022, 261, 112127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, W.; Zheng, J.; Cappietti, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E. The influence of waves propagating with the current on the wake of a tidal stream turbine. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Zang, W.; Ji, R. Power fluctuation and wake characteristics of tidal stream turbine subjected to wave and current interaction. Energy 2023, 264, 126185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Mei, Y.; Shi, M.; Wang, S.Q.; Sheng, Q.H. Development of experimental methods for horizontal-axis tidal turbines. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2023, 42, 32–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.S.; Yu, S.Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.R.; Wang, F.Y. Research progress on hydrodynamics and layout optimization of tidal stream turbine array. J. Hohai Univ. 2024, 52, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, P.; Liu, X.D.; Si, X.C.; Wang, S.J.; Tan, J.Z.; Zheng, Z.S. Research on influence of horizontal axial tidal turbine array on regional tidal regime. J. Ocean Univ. China 2019, 49, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.H.; Deng, Q.; Li, J.; Shi, H.D. Progress of marine energy test sites and its inspiration. Coast. Eng. 2025, 44, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lam, W.-H. Methods for predicting seabed scour around marine current turbine. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Lin, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, H. Experimental investigation of wake and thrust characteristics of a small-scale tidal stream turbine array. Ocean Eng. 2023, 283, 115038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, R.; Amoudry, L.O.; Thorne, P.D.; Cooke, R.D.; McLelland, S.J.; Jordan, L.B.; Simmons, S.M.; Parsons, D.R.; Murdoch, L. Laboratory study on the effects of hydro kinetic turbines on hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zang, W.; Lin, X.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E. Experimental study of the wake homogeneity evolution behind a horizontal axis tidal stream turbine. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 111, 102644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lam, W.H.; Dai, Y.; Hamill, G. Prediction of seabed scour induced by full-scale Darrieus-type tidal current turbine. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Flow structures in wake of a pile-supported horizontal axis tidal stream turbine. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Experimental investigation of the seabed topography effects on tidal stream turbine behavior and wake characteristics. Ocean Eng. 2023, 281, 114682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Lam, W.H.; Robinson, D.; Hamill, G. Temporal and spatial scour caused by external and internal counter-rotating twin-propellers using Acoustic Doppler Velocimetry. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 97, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schendel, A.; Welzel, M.; Hildebrandt, A.; Schlurmann, T.; Hsu, T.-W. Role and impact of hydrograph shape on tidal current-induced scour in physical-modelling environments. Water 2019, 11, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, S.M.; McLelland, S.J.; Parsons, D.R.; Murphy, B.J.; Jordan, L.B.; Vybulkova, L. Flume measurements of the wake of two model horizontal-axis tidal stream turbines. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Hydraulic Structures, Coimbra, Portugal, 8–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zang, W.; Lin, X.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E. Experimental investigation into effects of boundary proximity and blockage on horizontal-axis tidal turbine wake. Ocean Eng. 2021, 225, 108829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoul, F.; Obregon, M.; Ortega-Casanova, J.; Fernandez-Feria, R. Experimental study of the erosion in a sand bed caused by wakes behind tidal energy extraction devices. In Proceedings of the European Seminar OWEMES 2012, Málaga, Spain, 5–7 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J. Experimental investigation into downstream field of a horizontal axis tidal stream turbine supported by a mono pile. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 101, 102257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, U.; Apsley, D.; Afgan, I.; Stallard, T.; Stansby, P. Fluctuating loads on a tidal turbine due to velocity shear and turbulence: Comparison of CFD with field data. Renew. Energy 2017, 112, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojasteh, D.; Shamsipour, A.; Huang, L.; Tavakoli, S.; Haghani, M.; Flocard, F.; Farzadkhoo, M.; Iglesias, G.; Hemer, M.; Lewis, M.; et al. A large-scale review of wave and tidal energy research over the last 20 years. Ocean Eng. 2023, 282, 114995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Amoudry, L.O.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.; Thorne, P.D.; Song, Q.; Zheng, P.; Simmons, S.M.; Jordan, L.-B.; McLelland, S.J. Three-dimensional modelling of suspended sediment transport in the far wake of tidal stream turbines. Renew. Energy 2020, 151, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, H.; Zang, W.; Lin, X. A review on numerical development of tidal stream turbine performance and wake prediction. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 79325–79337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Shi, W.; Xu, Y.; Song, Y. Actuator disk theory and blade element momentum theory for the force-driven turbine. Ocean Eng. 2023, 285, 115488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairley, I.; Masters, I.; Karunarathna, H. The cumulative impact of tidal stream turbine arrays on sediment transport in the Pentland Firth. Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Zang, W.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E. Experimental analysis and evaluation of the numerical prediction of wake characteristics of tidal stream turbine. Energies 2017, 10, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Ren, T.; Yu, F.; Cen, Y.; Li, C.; Yuan, S. Review of research on wake characteristics in horizontal-axis tidal turbines. Ocean Eng. 2024, 312, 119159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E. Numerical investigation on the wake and energy dissipation of tidal stream turbine with modified actuator line method. Ocean Eng. 2024, 293, 116608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.A.; Venugopal, V. Wake field interaction in 3D tidal turbine arrays: Numerical analysis for the Pentland Firth. J. Waterw. Port Coastal Ocean Eng. 2024, 150, 04024013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, S.P.; Haas, K.A.; Thiébot, J.; Yang, Z. A review of tidal energy—Resource, feedbacks, and environmental interactions. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2021, 13, 062702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, F. Modelization of the Interactions Between Turbine and Sediment Transport, Using the Blade Element Momentum Theory. Doctoral Thesis, Normandie Université, Caen, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S. Comparison of actuator line method and full rotor geometry simulations of the wake field of a tidal stream turbine. Water 2019, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apsley, D.D.; Stallard, T.; Stansby, P.K. Actuator-line CFD modelling of tidal-stream turbines in arrays. J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Energy 2018, 4, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, S.T.; Broström, G.; Bergqvist, B.; Lennblad, J.; Nilsson, H. Modelling Deep Green tidal power plant using large eddy simulations and the actuator line method. Renew. Energy 2021, 179, 1140–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sotiropoulos, F. A new class of actuator surface models for wind turbines. Wind Energy 2018, 21, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mycek, P.; Gaurier, B.; Germain, G.; Pinon, G.; Rivoalen, E. Experimental study of the turbulence intensity effects on marine current turbines behaviour. Part I: One single turbine. Renew. Energy 2014, 66, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; García, M.H. Three-dimensional numerical model with free water surface and mesh deformation for local sediment scour. J. Waterw. Port Coastal Ocean Eng. 2008, 134, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.; Guan, D.; Wang, R. Semi-theoretical prediction for equilibrium scour depth of a mono-pile supported tidal stream turbine. Ocean Eng. 2023, 275, 114093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.; Heisel, M.; Guala, M. Predictive model for local scour downstream of hydrokinetic turbines in erodible channels. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2018, 3, 024606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafati, A.; Tafarojnoruz, A.; Motta, D.; Yaseen, Z.M. Application of nature-inspired optimization algorithms to ANFIS model to predict wave-induced scour depth around pipelines. J. Hydroinform. 2020, 22, 1425–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafati, A.; Tafarojnoruz, A.; Yaseen, Z. New stochastic modeling strategy on the prediction enhancement of pier scour depth in cohesive bed materials. J. Hydroinform. 2020, 22, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Li, H.; Pan, Z.; Xia, W. A review of tidal current power generation farm planning: Methodologies, characteristics and challenges. Renew. Energy 2024, 220, 119603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.-W.; Xie, Y.-X.; Yao, Z.-S.; Chiew, Y.-M.; Zhang, J.-S.; Zheng, J.-H. Local scour at offshore windfarm monopile foundations: A review. Water Sci. Eng. 2022, 15, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Malekjafarian, A.; Salauddin, M. Scour protection measures for offshore wind turbines: A systematic literature review on recent developments. Energies 2024, 17, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, P.; Du, F.; Wang, L. Experimental investigation on scour development and scour protection for offshore converter platform. Mar. Struct. 2023, 90, 103440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Yan, J.; Gao, X. Countermeasures for local scour around offshore wind turbine monopile foundations: A review. Appl. Ocean Res. 2023, 141, 103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Lian, J.; Wang, H. Mechanisms, assessments, countermeasures, and prospects for offshore wind turbine foundation scour research. Ocean Eng. 2023, 281, 114893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, L.; De Rouck, J.; Troch, P.; Frigaard, P. Empirical design of scour protections around monopile foundations: Part 1: Static approach. Coast. Eng. 2011, 58, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, L.; De Rouck, J.; Troch, P.; Frigaard, P. Empirical design of scour protections around monopile foundations. Part 2: Dynamic approach. Coast. Eng. 2012, 60, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeres-Ferradosa, T.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Chambel, J. Probabilistic comparison of static and dynamic failure criteria of scour protections. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, T.U.; Sumer, B.M.; Fredsøe, J.; Raaijmakers, T.C.; Schouten, J.-J. Edge scour at scour protections around piles in the marine environment–Laboratory and field investigation. Coast. Eng. 2015, 106, 42–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafarojnoruz, A.; Gaudio, R.; Calomino, F. Evaluation of flow-altering countermeasures against bridge pier scour. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 138, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhosseini, M.; Yue, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, G. Scour depth at a pile with a collar at bed level in clear-water current. Ocean Eng. 2025, 320, 120319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Melville, B.; Shamseldin, A.; Guan, D.; Singhal, N.; Yao, Z. Experimental study of collar protection for local scour reduction around offshore wind turbine monopile foundations. Coast. Eng. 2023, 183, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liang, F.; Yu, X. Experimental and numerical investigations on the performance of sacrificial piles in reducing local scour around pile groups. Nat. Hazards 2016, 85, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Preventing scour of monopile foundations using a vertical rotation device. Ocean Eng. 2024, 311, 118879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wei, K.; Yang, W.; Li, T.; Qin, B. A feasibility study of reducing scour around monopile foundation using a tidal current turbine. Ocean Eng. 2021, 220, 108396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Kashif, A.; Liu, H.W.; Wei, S.S. Study on wake characteristics and influence of anti-scour tidal current turbine under bed interference. J. Vib. Shock 2024, 43, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J. An innovative eco-friendly method for scour protection around monopile foundation. Appl. Ocean Res. 2022, 123, 103177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Lu, Y.; Leng, H.; Liu, H.; Shi, W. A novel countermeasure for preventing scour around monopile foundations using Ionic Soil Stabilizer solidified slurry. Appl. Ocean Res. 2022, 121, 103121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Xu, S. Numerical simulation of offshore wind power pile foundation scour with different arrangements of artificial reefs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1178370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, L.; Sottolichio, A.; Huybrechts, N.; Brunet, P. Tidal turbines in the estuarine environment: From identifying optimal location to environmental impact. Renew. Energy 2021, 169, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.L.; Xu, D.H. Research on the development of tidal current energy power generation industry. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2024, 40, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, J.C.; Jia, F.Y. Current status, new opportunities and challenges of marine tidal current energy generation technology and equipment in China. Acta Energ. Sol. Sin. 2024, 45, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.M.; Ma, C.L.; Chen, F.Y.; Liu, L.; Ge, Y.Z.; Peng, J.P.; Wu, H.Y.; Wang, Q.B. Development, utilization and technological progress of marine renewable energy. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2018, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, D.; Angeloudis, A.; Greaves, D.; Hastie, G.; Lewis, M.; Mackie, L.; McNaughton, J.; Miles, J.; Neill, S.; Piggott, M.; et al. A review of the UK and British Channel Islands practical tidal stream energy resource. Proc. R. Soc. A 2021, 477, 20210469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, N.; Charpentier, J.-F.; Benbouzid, M. The Tidal Stream Energy Resource of the Fromveur Strait—A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Yu, B.T.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhu, L.N.; Wang, X.Y. Development frontiers and selection recommendations for tidal current energy generation devices. Acta Energ. Sol. Sin. 2025, 46, 690–695. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Shi, H.D.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z.; Cao, F.F.; Yu, T.S.; Wang, Y.Q.; Lun, Z.X.; Liu, H.W.; Sun, K. Research status and future development suggestions of marine energy in China. Sol. Energy 2024, 363, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Angeloudis, A.; Kramer, S.C.; He, R.; Piggott, M.D. Interactions between tidal stream turbine arrays and their hydrodynamic impact around Zhoushan Island, China. Ocean Eng. 2022, 246, 110431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apsley, D.D. CFD simulation of tidal-stream turbines in a compact array. Renew. Energy 2024, 224, 120133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoe, C.E.; Li, X.; Williams, A.J.; Masters, I. Output of a tidal farm in yawed flow and varying turbulence using GAD-CFD. Ocean Eng. 2024, 294, 116736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Ren, Z. Investigating tidal stream turbine array performance considering effects of number of turbines, array layouts, and yaw angles. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.R.; Li, S.G.; Mei, Y.L. Influence analysis of wake structure in series horizontal-axis tidal current turbine units. Ship Sci. Technol. 2025, 47, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, M.; Hill, C.; Sotiropoulos, F.; Guala, M. Performance and resilience of hydrokinetic turbine arrays under large migrating fluvial bedforms. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.; Hill, C.; Guala, M. Interaction between hydrokinetic turbine wakes and sediment dynamics: Array performance and geomorphic effects under different siting strategies and sediment transport conditions. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, P.E.; Neill, S.P.; Lewis, M.J. Impact of tidal-stream arrays in relation to the natural variability of sedimentary processes. Renew. Energy 2014, 72, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, S.P.; Jordan, J.R.; Couch, S.J. Impact of tidal energy converter (TEC) arrays on the dynamics of headland sand banks. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Lu, B.; Lin, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, S. Experimental investigation of motion response and mooring load of semi-submersible tidal stream energy turbine under wave-current interactions. Ocean Eng. 2024, 300, 117445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.N.; Wang, X.N.; Guo, Y.; Jia, N.; Chen, Q. Research on output power prediction method of tidal current energy generation device based on uncertainty analysis. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2025, 46, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Pan, D.; Cheng, W.; Pan, C. Tidal stream energy resource assessment in the Qiantang River Estuary, China. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2018, 37, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid, C.; Andonegi, E.; Depestele, J.; Judd, A.; Rihan, D.; Rogers, S.I.; Kenchington, E. The environmental interactions of tidal and wave energy generation devices. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2012, 32, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).