Abstract
Empirical green’s functions (EGFs) can be extracted from the cross-correlation of ambient ocean noise and serve as the foundation for passive ocean acoustic tomography (POAT). A critical challenge in POAT is the accurate identification of propagation paths, especially in shallow water and short-range scenarios where multipath arrivals often overlap. Traditional methods relying on absolute arrival time delays are rather sensitive to environmental variability and measurement uncertainty. In this study, we propose a path identification method based on time delay differences between extracted acoustic paths, which exhibit lower sensitivity to sound speed profile (SSP) perturbations than absolute time delays. This approach provides a more robust and stable metric for distinguishing coherent arrivals. We further analyze how accumulation time and hydrophone spacing influence the extraction of coherent wavefronts and identify trade-offs in resolution and stability. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated through both field experiments and Bellhop simulations, demonstrating consistent time delay difference patterns and improved arrival stability. The findings suggest that time delay difference-based path identification enhances robustness and provides practical guidance for optimizing POAT deployments in complex shallow water environments.
1. Introduction
The acoustic field created by ambient noises in the ocean is often considered incoherent compared to active sound sources. However, there is some coherence between signals received at two hydrophones by contributions from those noise sources that are located around extensions of the eigenrays. The Green’s function estimate that is obtained from noise cross correlation function (NCF) is referred to as the empirical Green’s function (EGF) [1,2,3,4,5,6]. EGFs approximate the Green’s function even when the noise is not perfectly diffuse [5,7,8,9,10,11,12]. One can correlate noise signals between two hydrophones by accumulation over a sufficiently long time, and then only the noise sources in the end-fire direction contribute to the EGF [13,14]. To enhance the emergence rate of EGF, researchers have implemented the beam-forming technique on a vertical array [15,16] and on two separated arrays [17,18,19,20,21]. The required accumulation time means that the ocean environment could change befor ae stable EGF is obtained, which is one of the major limitations in passive ocean acoustic tomography (POAT).
Ocean acoustic tomography (OAT), originally developed by Munk and Wunsch [22], has established itself as an efficient acoustic remote sensing technique for large-scale monitoring of ocean thermal structure and current dynamics [23]. Traditional OAT implementations employ controlled acoustic sources transmitting precisely calibrated signals, with the sound speed profile (SSP) reconstruction typically achieved through three principal methodologies: (i) ray-theoretical travel-time inversion [24], (ii) modal phase/travel-time analysis [25], and (iii) matched-field processing techniques [26]. While these active approaches have demonstrated considerable success, their operational complexity and substantial deployment costs have motivated the development of POAT. Recent advancements have validated POAT’s feasibility through successful demonstrations of noise cross-correlation tomography in shallow water environments, employing both ray-based [27,28] and normal-mode propagation models [29]. In traditional OAT, the transmitted signal is known, allowing for precise travel time estimation through matched filtering, which significantly enhances time delay resolution. In contrast, POAT relies on the accumulation frequency bandwidth of coherent wavefronts for time delay resolution. This bandwidth cannot be too wide, as a broader bandwidth may introduce more environmental noise, reducing the coherence of the extracted wavefronts and decreasing the time delay resolution. This limitation makes it more challenging to accurately distinguish different acoustic paths, adding uncertainty to subsequent SSP inversion. In addition to the long accumulation time required to obtain EGFs, POAT also faces the challenge of overcoming the inherent multi-path ambiguity.
Several factors pose challenges for POAT from short-range seafloor-moored hydrophone pairs in shallow water: the rapid temporal variation in the shallow-water SSP, the difficulty in obtaining stable arrival-time structures from a single hydrophone pair, and the limited number of distinguishable arrivals. Consequently, there is a notable scarcity in the related research literature. For path identification in POAT, the existing literature typically focuses on scenarios with greater water depths and longer hydrophone spacings, where absolute arrival time delays extracted from experiments are compared with Kraken or Bellhop models to determine specific path types [1,2,3,10,14,27]. However, when water depth decreases and hydrophone spacing is reduced, the adjacent peaks in the Green’s function arrival time delays are less than 5 ms with a total time delay span within 20 ms, making them difficult to distinguish by conventional time delay methods in near-shore, shallow-water, short-range environments of this study. As the analysis is conducted using distributed hydrophones exclusively, beamforming techniques [2,3,17] are also not applicable in this configuration. In such cases, we find that employing time delay differences for path identification can, to some extent, achieve higher path identification accuracy while exhibiting significantly greater robustness to environmental perturbations.
The main contributions of this work are the following: a time delay difference-based method is proposed for multipath arrival identification in POAT, which avoids reliance on absolute arrival time delays and is less sensitive to environmental fluctuations; the effects of hydrophone spacing and accumulation time on coherent wavefront extraction and path separability are quantitatively analyzed, providing practical guidance for hydrophone deployment; the method is validated through experiments in a shallow-water environment (∼40 m depth) using real seafloor-moored hydrophone data and Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) SSP, demonstrating its effectiveness under realistic conditions; the results support the application of this approach in future multipath-assisted environmental inversion for POAT.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents formulation for the Green’s function extraction and arrival time delay difference modeling. Section 3 analyzes the impact of varying hydrophone spacing and accumulation time on the extraction of coherent wavefront under different SSP scenarios, with a focus on evaluating the sensitivity of arrival time delay and delay differences to SSP perturbation. Section 4 presents a comparative analysis between experiment and simulation results, demonstrating that utilizing time delay difference rather than absolute time delays enables more precise path identification. Section 5 summarizes the conclusions drawn from this study.
2. Theory
2.1. Empirical Green’s Function Extraction
The cross-correlation of the signals received at two separate hydrophones, is given by [13]
where is the correlation time, is the recording duration, and are the respective locations of the two hydrophones, and is the pressure field recorded at each hydrophone. Generally, is quite relatively long, so is usually divided into K snapshots, which is processed separately and then averaged. In the frequency domain, Equation (1) becomes
where is the complex conjugate of and is the angular frequency. Pre-whitening methods [4] are applied to the raw data in the frequency domain to preserve the phase information of the signal and make the magnitude response flat for all relevant frequency. The time derivative of the NCF has been proved to be approximately the sum of two EGFs [30], i.e.,
where is the EGF from to , is the time-inversed EGF, and is the correlation time delay between those two hydrophones. Theoretical analyses have established that the ideal signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of EGFs derived from NCFs follows a scaling law [31,32].
2.2. Arrival Time Delay Difference Modeling
In a shallow-water multi-path channel, the Green’s function in the time domain between two hydrophones can be expressed as
where I is the number of paths, and and are the respective amplitude and travel-time delay for individual paths. Assuming that there are resolved arrivals, the arrival-time vector is
Assuming corresponds to the time delay of the direct arrive that usually arrives first, it is taken as the reference. Subtracting time delays of the other arrivals by , the time delay differences between other paths and the first arrival path are obtained as
By determining the reference delay of a certain arrival and calculating time delay difference with respect to the reference, it is possible to better identify the path of each arrival, which will be investigated in the following section.
3. Sensitivity Analysis of Coherent Wavefront Extraction
In realistic ocean environments, long-term accumulation is typically employed to enhance the probability of coherent wavefront structures emerging from the background noise field. Rapidly varying SSPs further complicate multipath acoustic path identification in shallow water. This section examines the sensitivity of coherent wavefront delay extraction to varying SSP conditions and hydrophone spacing configurations. Additionally, it evaluates how accumulation time affects the detection of temporal SSP variations, while leveraging arrival time delay differences, which vary with hydrophone spacing and SSP characteristics, to discriminate between distinct propagation paths.
3.1. Influence of SSP Variability and Spacing of Seafloor Hydrophones on Coherent Wavefront Extraction
The hydrophone spacing determines the spatial sampling of the wavefront curvature. Small spacing ensures the spatial coherence of the signal but may fail to resolve multipath differences, whereas large spacing provides sufficient path delay differences to improve resolution but reduces coherence between receivers. Therefore, this section analyzes the sensitivity of coherent wavefront delay extraction to varying SSP conditions and hydrophone spacing configuration. Figure 1a shows SSP obtained from the HYCOM data for the East China Sea area (30.64 N, 122.80 E), where our experiment was conducted, from 1 August to 15 August 2023 (https://www.hycom.org/), with the SSP forecasting at 3-h intervals. In this area, the HYCOM data provides SSP sampled at 13 non-uniformly spaced depth levels, with no values below 30 m in Figure 1a. Figure 1b presents the complete SSPs along the water column after linear extrapolation to the SSP data. The sound speed in seawater is primarily governed by three fundamental physical parameters: temperature, salinity, and hydrostatic pressure [33]. SSP structure in shallow water is relatively simple and typically lacks a deep-water sound channel axis like that found in the deep ocean. In summer, as illustrated by the HYCOM SSP in Figure 1a, solar heating warms the surface layer, forming a warm water mass, beneath which lies cooler water, resulting in a negative sound speed gradient [33]. The significant change in the SSP around 12 August likely corresponds to dynamic processes at the sea surface, such as typhoon. These influences cause the SSP to exhibit rapid spatiotemporal variations, which can differ significantly from hour to hour and day to day.
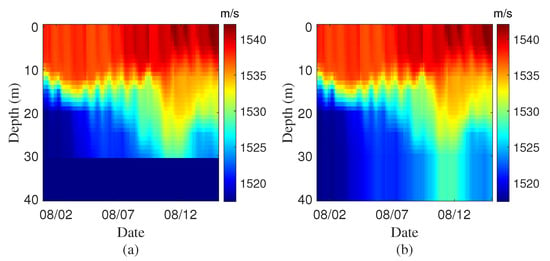
Figure 1.
Temporal variation in Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) sound speed profile (SSP): (a) Raw data; (b) Extrapolation results. The horizontal axis indicates observation times at 3-h intervals, and the vertical axis represents water depth.
The simulation environment is a range-independent environment. The homogeneous bottom halfspace parameters were chosen as a sound speed of 1800 , a density of 1.8 , and an attenuation coefficient of 0.05 . The water depth is 40 m, with two seafloor-moored hydrophones. Using HYCOM SSP in Figure 1b as the environmental parameters, the Bellhop acoustic propagation model is used to compute time delays of different multipath arrivals for varying SSPs and hydrophone spacings [34]. Here, the frequency is set to 110 Hz. The simulation parameter configuration remains consistent throughout subsequent analyses. All analyses are performed using MATLAB (version R2022b). The direct arrival, single bottom-reflected arrival, double bottom-reflected arrival, triple bottom-reflected arrival, single surface-single bottom-reflected arrival, double surface-double bottom-reflected arrival, triple surface-triple bottom-reflected arrival, and quadruple surface-quadruple bottom-reflected arrival are, respectively, abbreviated as D, B, 2B, 3B, 1S1B, 2S2B, 3S3B, and 4S4B; hereinafter, they are the same.
Figure 2 illustrates the influence of different seafloor hydrophone spacings (0.25 km, 1 km, 3.25 km, and 4.75 km) on the extraction of coherent wavefronts. The black, green, blue, and red lines represent the acoustic paths D, 3B, 1S1B, and 2S2B, respectively. At smaller hydrophone spacings, only a limited number of propagation paths exist and can be extracted (e.g., 3B and 2S2B do not exist with the spacing of 1 km, as shown in Figure 2a). As the spacing increases (e.g., 1 km in Figure 2b), the time delays become more spread out, allowing the extraction of longer paths, such as 3B (green line). At even larger spacings (e.g., 3.25 km and 4.75 km in Figure 2c,d), previously unresolved longer paths like 2S2B (red line) can also be identified.
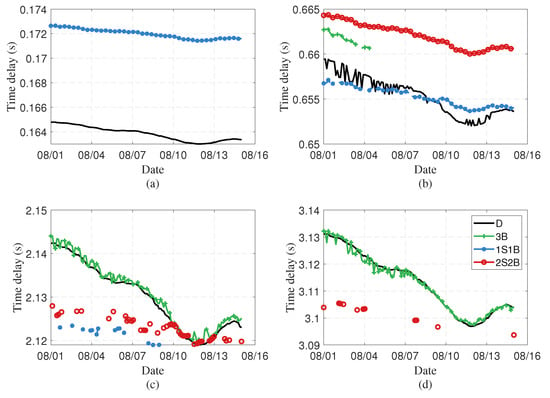
Figure 2.
Impact of different seafloor hydrophone spacings on the time delays of propagation paths: (a–d) illustrate results for hydrophone spacings of 0.25 km, 1 km, 3.25 km, and 4.75 km, respectively. The horizontal axis indicates observation times at 3-h intervals, and the vertical axis represents coherent wavefront time delay.
When the hydrophone spacing is short, for example, 0.25 km, as shown in Figure 2a, the propagation range of each path is short; thus, the change in coherent wavefront time delay caused by SSP variation is also tiny. Increasing hydrophone spacing exhibits longer ray paths and richer coherent wavefront diversity, where the change in coherent wavefront time delay caused by SSP variation becomes more significant (Figure 2b,c). For example, around August 12, there is a clear valley in the coherent wavefront that first descends and then ascends in Figure 2c,d, corresponding to a relatively obvious change in the SSP during this period in Figure 1b. In a homogeneous medium, sound waves travel in straight lines. However, the ocean is a typical layered, inhomogeneous medium where the sound speed variation with depth causes refraction. Snell’s law in underwater acoustics describes this phenomenon; sound rays always bend towards regions with lower sound speed [35]. Only D and 1S1B arrivals can be extracted at the range corresponding to Figure 2c. For seafloor-moored hydrophone pairs, the path of direct wave typically traverse the deeper part of the water column, where SSP changes are relatively small. This explains why the direct wave is consistently extracted across all four ranges, as shown in Figure 2a–d. In contrast, bottom-surface reflected waves (e.g., 1S1B, 2S2B) typically span the entire water depth. Due to the significant temporal and vertical variations in the SSP across the entire depth and the tendency of sound rays to bend towards slower sound speed regions, these bottom-surface reflected paths can sometimes fail to be extracted, as observed in Figure 2b–d.
For D (black line in Figure 2c) and 3B (green line in (Figure 2c,d) arrival, their acoustic paths span only part of the water column depth. When there are significant changes in adjacent SSPs in the time dimension, the path lengths for different rays belonging to the same arrival wave type can differ substantially. This leads to significant oscillations in the calculated time delays. In contrast, paths with specific reflection counts like 1S1B (blue line) and 2S2B (red line) traverse the entire water depth. For these arrival types, the path length changes between different paths of the same arrival wave are small, resulting in more stable time delays. This means D and 3B paths are more sensitive to various arrival types to SSP variations. For the entire observation period, the time delay variations in D (black line) and 3B (green line) in Figure 2c are generally larger than those of 1S1B (blue line) and 2S2B (red line).
Furthermore, since the SSP near the bottom is approximately 20 m/s less than the maximum SSP, the time delay of D is greater than that of 1S1B in Figure 2c. As the distance between hydrophones continues to increase, 1S1B gradually disappears in Figure 2d. By analyzing the time delays of different acoustic paths between seafloor hydrophones, it is possible to capture information about SSP variations. However, the sensitivity of these paths to SSP changes depends on their depth coverage, as paths traversing different depth ranges respond differently to SSP fluctuations. Additionally, for certain hydrophone spacings and SSP conditions, the time delays of different acoustic paths may be similar, introducing ambiguity in path identification.
3.2. Sensitivity of Arrival Time Delay and Delay Differences to SSP Perturbation
To address this, this section proposes a path identification method that utilizes the time delay differences between each path and a reference path. This approach is based on the assumption that while the mismatch between HYCOM SSP and actual SSP can introduce absolute time delay errors, the relative time delay differences between paths may still provide a stable indicator for path identification.
To verify this assumption, we evaluate the sensitivity of the arrival time and time delay differences to SSP perturbation by computing the correlation coefficients between each observed variable and the corresponding SSP perturbation. The correlation coefficients and are defined as follows [33]:
where is time delay, is time delay difference, SSP perturbation is defined as the difference between SSP and mean value of all SSP, correspond to different depths and arrivals, N is the number of SSP s at different time instants, , and
Figure 3 shows the correlation coefficients of both time delays and time delay differences with HYCOM SSP perturbation at different depths, across various ranges. For seafloor-deployed hydrophones in shallow water, most detectable acoustic paths primarily traverse deeper water layers. Due to the negative gradient of SSP with depth, upper-layer paths propagate faster than lower-layer paths of equal length. Consequently, in Figure 3a–d, time delays (green line for D, blue line for B, black line for 1S1B or 3B) exhibit higher sensitivity to SSP variations in deeper regions, resulting in stronger correlation coefficients (absolute correlation coefficient of 1) with SSP perturbation below 20 m depth.
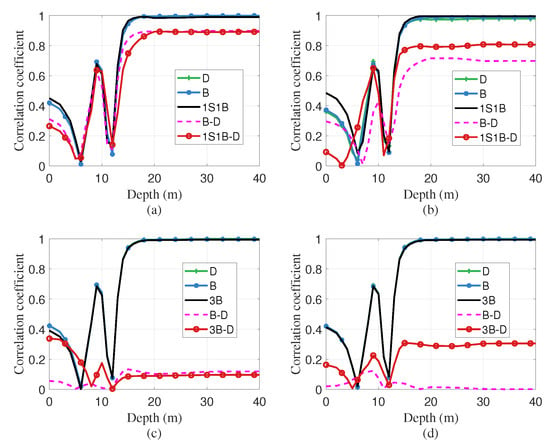
Figure 3.
Correlation coefficients of both time delays (green line for direct arrival (D), blue line for single bottom-reflected arrival (B), black line for other arrival path) and time delay differences (red and magenta line) with HYCOM SSP perturbation at different depths: (a–d) illustrate results for hydrophone spacings of 0.25 km, 1 km, 3.25 km, and 4.75 km, respectively. The horizontal axis indicates the SSP depth, and the vertical axis represents the calculated correlation coefficient.
The correlation coefficients exhibit minimal variation with range, which indicates that time delays are more sensitive to SSP mismatch than to range variations. The magenta curve (B-D) represents the time delay difference between paths B and D, while the red curves (labeled 1S1B-D and 3B-D) correspond to the time delay differences between 1S1B and D and between 3B and D, respectively. In contrast, time delay differences derived from the subtraction of different arrival path pairs show reduced sensitivity to SSP mismatches. Thus, their correlation coefficients are generally lower than those of absolute time delays and the correlation patterns vary across different ranges and arrivals in Figure 3a–d. Absolute arrival time delays are highly sensitive to environmental variability, especially in shallow-water waveguides where small changes in SSP can significantly alter ray bending and travel times. This sensitivity reduces the robustness of path identification based on direct time delay matching. In contrast, the time delay difference between paths is often more robust, as the use of relative delays cancels out both clock synchronization errors and hydrophone location uncertainties. As such, the relative time delay between two paths reflects more intrinsic features of the waveguide structure.
3.3. Impact of Accumulation Time on Coherent Wavefront Extraction
POAT typically requires long accumulation times to extract coherent wavefronts from ambient noise. However, the temporal variability in the SSP in shallow water can often occur on shorter timescales than the chosen accumulation duration, potentially reducing the accuracy of extracted wavefronts. Longer accumulation times increase the signal-to-noise ratio of the extracted wavefronts, but excessive averaging may also blur fine-scale multipath arrivals. This trade-off is physically linked to the temporal coherence of ambient noise sources and the modal dispersion of the acoustic field. Therefore, it is essential to analyze the impact of accumulation time on the extraction of coherent wavefronts and to empirically determine the optimal accumulation time for accurately capturing SSP variations.
This section examines the effects of different hydrophone spacings and accumulation times on coherent wavefront extraction under various SSP scenarios. Given that the direct path (D) is generally more robust and easier to identify in both experimental and simulated data, the following analysis primarily focuses on the time delay variations in the direct path. The conclusions for other paths are expected to be similar. Figure 4 presents the variation probability of direct path time delay error under different accumulation times for HYCOM data. Here, the error is defined as the difference between the direct path time delay at a given time instant, which is seen as the true direct path time delay and the time-accumulated direct path delay over the preceding accumulation period, which is seen as the extracted time delay.
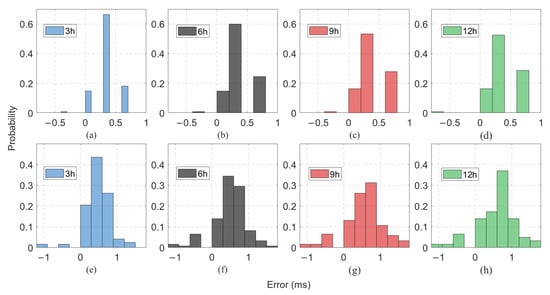
Figure 4.
The probability of direct path time delay error under different accumulation time (3 h, 6 h, 9 h, 12 h) of HYCOM SSP: (a–d) Hydrophone spacing of 1.5 km. (e–h) Hydrophone spacing of 3 km. The horizontal axis indicates time delay error, and the vertical axis represents probability.
The blue, black, red, and green histogram correspond to different accumulation times of 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, and 12 h, respectively. The simulation frequency band is 20–200 Hz. The error increases with hydrophone spacing. For example, when the hydrophone spacing is 1.5 km (Figure 4a–d), the time delay error for a 12 h accumulation period is within 1 ms in Figure 4d. In contrast, for a 3 km spacing (Figure 4e–h), the corresponding error increases to 2 ms in Figure 4h, due to the longer propagation paths being more sensitive to SSP variability.
As discussed in Section 3.1, larger hydrophone spacings tend to increase the sensitivity of different arrival paths to SSP changes and provide richer arrival diversity (e.g., multi-path reflections), but they also generally require longer accumulation times for stable coherent wavefront extraction [36]. In contrast, smaller hydrophone spacings reduce the impact of SSP variability, making it easier to obtain stable wavefronts with shorter accumulation times, but they limit the number of resolvable arrival paths; often, only the direct path exists in the extracted wave fronts [36]. This means that when the hydrophone spacing is within a certain range, the errors introduced by long-term accumulation are relatively small. Therefore, in the following experimental analysis, we will focus on the path identification accuracy without considering the impact of long-term accumulation errors.
4. Experiment
4.1. Overview of Experiment
The experiment was carried out in the East China Sea from 6 August to 13 August 2023. Five self-recording hydrophones (Hangzhou UTSIS Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China), spatially separated as shown in Figure 5a, were deployed on the seafloor in 40-m-deep water to collect ambient noises. The hydrophone is mounted at a height of about 1 m above the seabed. During the observation period, 22 SSPs were measured during daytime using a conductivity-temperature-depth (CTD) profiler at locations surrounding the five hydrophones. As shown in Figure 5b, the SSP variations in this shallow sea region are substantial, with differences of up to 10 m/s at the same depth across different times. The measurement times corresponding to the 22 CTD-obtained SSP are listed in Table 1. The clock drifts of the five hydrophones after five to six days of recording are shown in Table 2, all of which are less than 0.1 ms, which can be neglected for the EGF calculation. The distance between the five seafloor-moored hydrophones varies between 300 and 1400 m. Broadband ambient noise was recorded at a sampling frequency of 128 kHz synchronously and continuously.
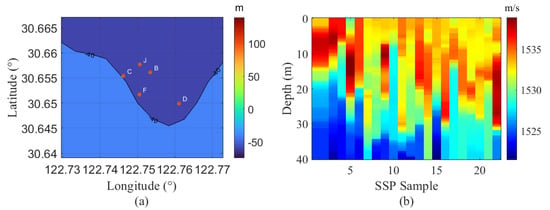
Figure 5.
(a) Deployment positions of five self-recording acoustic hydrophones (B, C, D, F, J). (b) A total of 22 SSPs at different time instants measured by the conductivity-temperature-depth (CTD) profiler.

Table 1.
Times of 22 sound speed profiles measurements by conductivity-temperature-depth (CTD) profiler.

Table 2.
Summary of seafloor hydrophones recording duration and clock drift characteristics.
The ambient noise spectrum varies with time, and the level appears to be significantly higher in the low-frequency band ( Hz). Due to the high sampling frequency, in order to reduce computational complexity, the data here initially undergo a low-pass filter, followed by 8× downsampling, and then the pre-whitening methods is applied [4]. The pre-processing results are outlined in Figure 6, along with 5 s of time data (consisting of 80,000 points) before (Figure 6a,b) and after pre-processing (Figure 6c,d). The pre-whitening preserves the phase information of the signal but makes the magnitude response flat for all relevant frequencies in Figure 6d. The processed signals are then cross-correlated, yielding a 10-s signal with 160,000 points. These 10-s long correlations are then accumulated and normalized in amplitude to create an NCF. The accumulation time will be varied in the following sections.
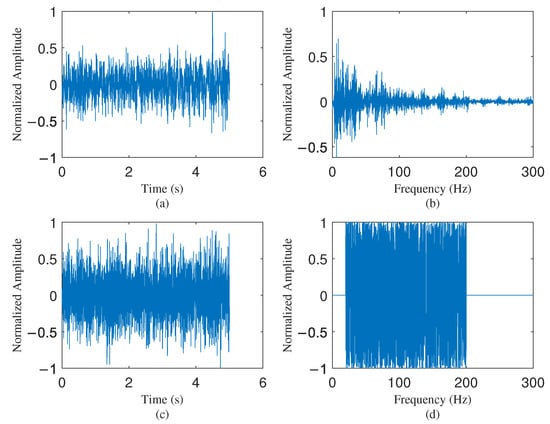
Figure 6.
A 5-s segment of data before and after pre-processing, shown in both the time and frequency domains: (a) Raw data in the time domain; (b) Raw data in the frequency domain; (c) Pre-processed data in the time domain; (d) Pre-processed data in the frequency domain.
4.2. Temporal Variability of the NCF
We evaluate extracted NCFs between different hydrophones. The accumulation procedure is the same as References [37,38,39]. Figure 7a compares the NCFs obtained from the seafloor hydrophone pair C–D under different accumulation times. For clarity, the negative and positive time delay portions are referred to as N-NCF and P-NCF, corresponding to propagation from hydrophone D to C and from C to D, respectively [13,14,30]. As the accumulation time increases, the coherent wavefront features in the NCF gradually emerge from the background noise, as shown in Figure 7a. Unlike active sound sources, ambient noise is theoretically uniformly distributed across the entire sea surface. Consequently, the NCFs in Figure 7a often exhibit a double-sided structure (forward and reverse directions) between hydrophones C and D. These features appear most prominently as strong peaks and valleys around ±1 s based on their spacing and SSP. In realistic ocean environments, long-term accumulation is typically employed to enhance the probability of coherent wavefront structures emerging from the background noise field. By cross-correlating noise signals recorded at two hydrophones over a sufficiently long duration, only noise sources located in the end-fire direction contribute. Figure 7b shows the variation in the coherent-to-incoherent amplitude ratio (CIR) with different accumulation times. [for an arbitrary hydrophone pair ] is defined as the ratio of the maximum value of its envelope (computed using the absolute value of the Hilbert transform) around the expected coherent peak arrival (i.e., within a 20 ms window centered around s for hydrophone pair C–D) to the estimated level of these residual temporal fluctuations such that [2,17]
where is the recording duration, 0.95–1.05 s is around the expected coherent peak, and the period 1.3–1.5 s has the residual temporal fluctuations. Generally, CIR increases with a longer accumulation time. However, once the accumulation time exceeds a certain threshold, no significant further improvement in CIR is observed (as shown in Figure 7b). It can be observed that after 24 h of accumulation, the CIR increases by approximately 17 dB in Figure 7b. The deterministic features of all NCFs emerge from the random background after 3 h of noise accumulation (Figure 7a). Considering the presence of interferences with varying locations and intensities across different time periods (such as passing vessels and other active sound sources in the non-endfire direction), the CIR corresponding to 3-h accumulations from different time segments consequently exhibits fluctuating values in Figure 7c. Similar conclusions can be drawn for the other three hydrophone pairs (B–J, C–B, D–F) in Figure 8, with
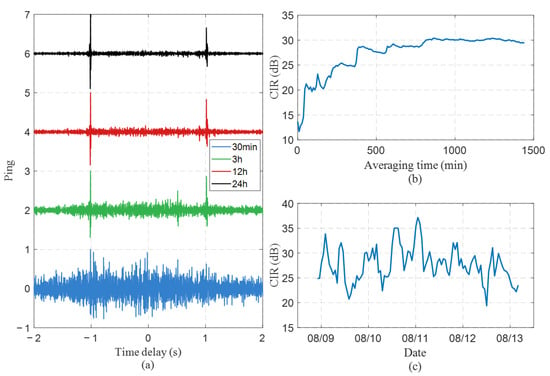
Figure 7.
(a) Envelope of noise cross-correlation function (NCF) extracted from hydrophone pair C–D for different accumulation time. Each is computed using ambient noises in successive 5 s long intervals. (b) The evolution of the relative coherent-to-incoherent amplitude ratio (CIR) of NCF between hydrophone pair C–D, for different accumulation times, starts from 16:00 on August 9th. The horizontal axis shows the accumulation times. (c) CIR evolution per 3-h accumulation at different initial times. The vertical axis represents CIR.
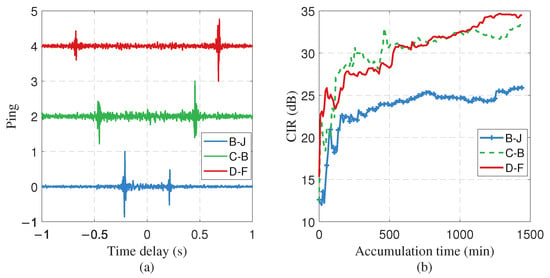
Figure 8.
(a) The 24-h NCFs for the remaining three hydrophone pairs (B–J, C–B, D–F), along with (b) their corresponding CIR variations over accumulation time.
To validate the propagation paths extracted from the experimental NCFs, we performed ray-based simulations to provide a theoretical reference for comparison [34]. These simulations help determine whether the observed arrival structures in the NCF are consistent with expected multipath arrivals under the measured ocean conditions. The simulations were conducted using the Bellhop ray-tracing model under a range-independent assumption, with the same parameters as Section 3.1. We take the SSP measured by CTD at 9:31 on 10 August. The simulation frequency was set to 110 Hz, corresponding to the center frequency of the 20–200 Hz experimental band. We assume a flat bottom in the modeling because the maximum distance between the seafloor-moored hydrophones analyzed here is approximately 1.5 km, within which the seafloor variation is minimal.
Figure 9 compares the experimental NCF obtained from hydrophone pair D–F with the simulated arrival times. The NCF is shown as black (P-NCF) and red (N-NCF) curves, while the simulated arrivals are represented as color-coded stems. Three distinct peaks in the NCF align well with the simulated arrivals, indicating that the extracted paths correspond closely to physical multipath propagation. The first arriving peak corresponds to the eigenray striking the bottom once, the second peak corresponds to the direct path, and the third peak corresponds to the eigenrays striking both the surface and bottom once. In this SSP configuration, a bottom-reflected path arrives earlier than the direct path. When SSP changes, the time delay of the bottom reflection path may be close to that of the direct path, forming a peak together. This is typical for shallow-water and short spacing of seafloor hydrophones; the propagation times of the respective bottom-reflected path and direct path are very close, making it difficult to perform ray identification and to be used successively for POAT. Considering the variation in the shallow sea SSP, it is far from sufficient to efficiently distinguish different ray paths through Bellhop ray model simulation alone. In the next section, time delays of different arrival paths will be transfered with the arrival time delay differences of different ray paths to better perform path identification.
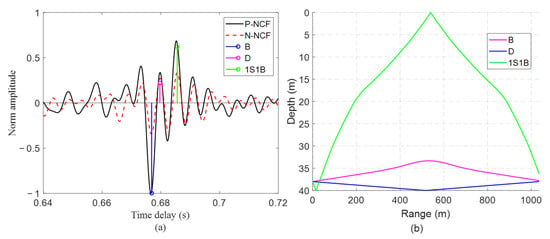
Figure 9.
(a) Comparison of ray-based time arrivals (colorful stem pattern) with NCF extracted from hydrophone pair D–F (black and red line) on August 10th (9:00–12:00). Experiment results are calculated for 20–200 Hz and ray-based for 110 Hz. (b) Ray-based simulated eigenrays corresponding to the ray paths in (a).
4.3. Ray Path Identification
This section presents a comparative analysis of experimental results across three hydrophone pairs. As discussed in Section 3.2, once the arrival time of a reference path (here, the direct path D) is determined, the time delay differences with respect to the reference path are less sensitive to the SSP perturbation and thus more suitable for the path identification. The main procedure is illustrated in Figure 10. The detailed implementation steps and pseudocode are provided in Appendices Appendix A and Appendix B. HYCOM SSP inputs drive Bellhop simulation to generate theoretical arrivals (D, 1S1B, 2S2B, 3S3B, etc.). Cross-correlation of pressure signals between seafloor hydrophones yields coherent wavefronts with multiple peaks. Each peak’s arrival time is extracted for path identification.
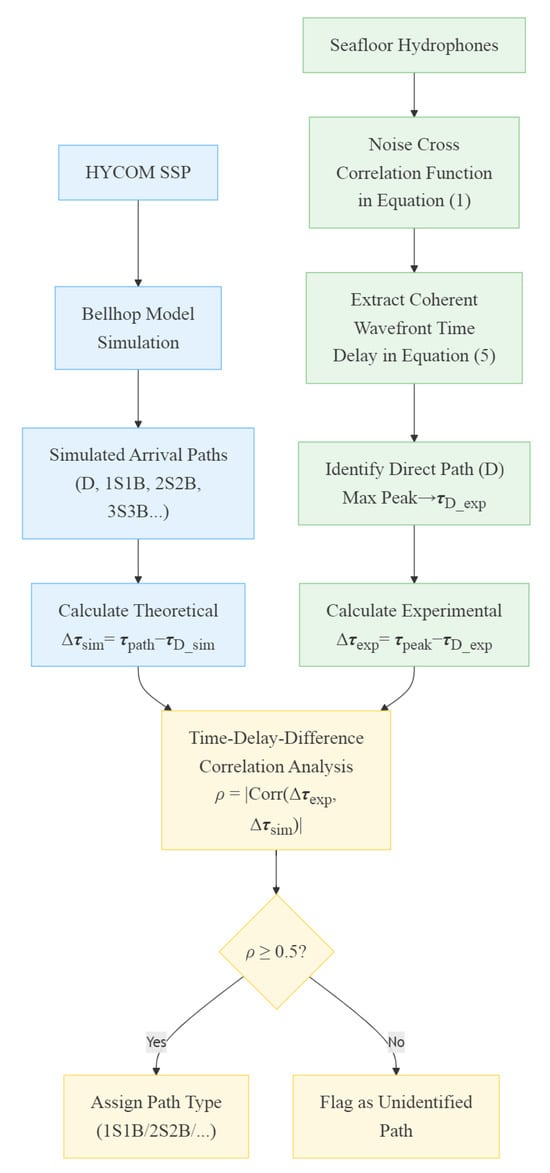
Figure 10.
Ray path identification flowchart.
4.3.1. Hydrophone Pair D–F
Figure 11 compares experimental and simulated arrival delays for the coherent wavefront extracted from hydrophone pair D–F under different accumulation times. In Figure 11a, the red, black, blue, and green lines represent the arrival delays of the dominant peak (typically corresponding to the direct or bottom-reflected path) extracted from the NCF using accumulation times of 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, and 12 h, respectively. The magenta line shows the simulated arrival time of the direct path obtained from Bellhop using HYCOM SSP. The results indicate that longer accumulation times yield smoother delay curves, as they average over more SSP variations and reduce the influence of transient fluctuations. In contrast, shorter accumulation times exhibit greater delay variability, likely due to increased sensitivity to interference and instantaneous SSP perturbations.
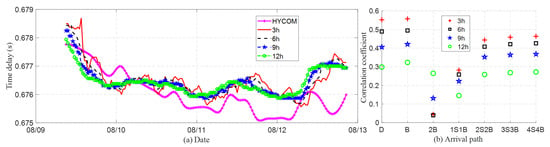
Figure 11.
(a) Comparison of the arrival times of the maximum coherent peak extracted from hydrophone pair D–F under different accumulation times (red, black, blue, and green lines for 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, and 12 h, respectively) with the simulated direct path arrival time from Bellhop using HYCOM SSP (magenta line). The ambient noise is segmented into consecutive short intervals, each lasting 5 s, with a 2.5 s overlap between adjacent snapshots. The final plotted time points are spaced at half-hour intervals. (b) Correlation analysis between the experimental and simulated arrival delays shown in (a), across different ray paths. The horizontal axis indicates the path type, and the vertical axis shows the correlation coefficient.
The direct path (D) usually has the shortest travel time and highest energy, appearing as the earliest and strongest peak in the NCF. However, for seafloor hydrophones in shallow water, the arrival times of D and the bottom-reflected path (B) can differ by just milliseconds, especially with closely spaced hydrophones. The correlation coefficients (Figure 11b) for arrival paths of D and B are very close, making separation between the two paths infeasible. Since the two cannot be reliably distinguished in time, we treat this combined peak as the reference arrival for computing delay differences used in subsequent path identification. This approach avoids the ambiguity of separating D and B and focuses instead on identifying paths with more distinct delay offsets, such as 1S1B and 2S2B.
Figure 12 presents a comparison between the second prominent peak extracted at different accumulation times in the experiment and the Bellhop-simulated arrival time of the 1S1B path using HYCOM data on 10 August. Each data point in Figure 12 corresponds to a single coherent arrival time estimate derived from the full accumulation interval, and no repeated or independent measurements are available to compute statistical error bars. As shown in Figure 12a, although the simulated arrival delay differs from the experimental result by less than 2 ms, their temporal variation trends are inconsistent. This discrepancy likely stems from SSP mismatch between the HYCOM-predicted profile and the actual ocean environment, which affects the absolute arrival time of each path.
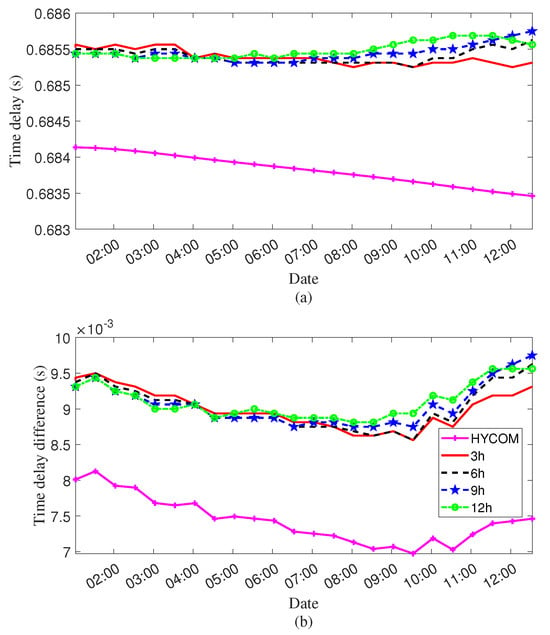
Figure 12.
Comparison of the second peak arrival time extracted from the coherent wavefront of hydrophone pair D–F under different accumulation times (red, black, blue, and green lines correspond to 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, and 12 h, respectively) with the Bellhop-simulated arrival of the single surface-bottom reflection arrival (1S1B) path using HYCOM SSP on August 10 (magenta line). (a) Conventional absolute arrival time. (b) Arrival time difference relative to the 3 h accumulated direct path delay shown in Figure 11a.
To mitigate this issue, we calculate relative time delay differences by subtracting the arrival time of the reference path (the direct path derived from the 3-h accumulated results in Figure 11a) from each individual arrival. While the absolute error between the simulation and experiment of time delay (Figure 12a) and time delay difference (Figure 12b) remains similar, Figure 12b exhibits a much better temporal alignment, indicating that inter-path delay differences are less sensitive to SSP mismatches and provide more reliable features for path identification.
To quantitatively verify this observation, Figure 13 presents a correlation analysis comparing the simulation and experimental results using both absolute arrival times and delay differences. The results show that delay differences consistently yield higher correlation coefficients, demonstrating their superiority for robust path discrimination under uncertain environmental conditions. Also, correlation analysis using time delay differences between the experimental and HYCOM-simulated arrivals consistently identifies the second peak in the coherent wavefront (extracted from hydrophone pair D–F) as the 1S1B path, across accumulation times of 3 h, 6 h, and 9 h. In contrast, correlation analysis based on absolute arrival times yields weaker and less consistent results. Notably, the 3 h accumulation yields a correlation coefficient exceeding 0.6, further supporting this classification and demonstrating the robustness of using delay differences for path identification.
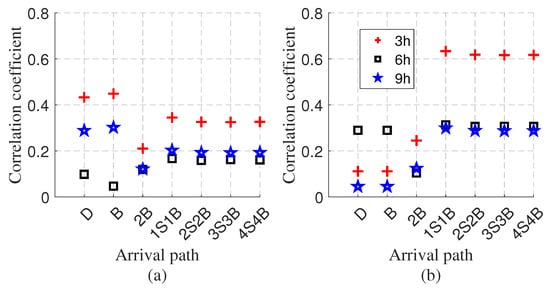
Figure 13.
Correlation analysis between HYCOM-simulated multipath arrivals and the experimental results shown in Figure 12, based on (a) conventional absolute arrival times and (b) delay differences relative to the direct path.
4.3.2. Hydrophone Pairs C–D and C–B
Similar to the previous section, this part extends the correlation analysis to two additional hydrophone pairs: C–D (Figure 14) and C–B (Figure 15). For both pairs, the maximum peak in the coherent wavefront is consistently identified across different accumulation times, showing strong correlation with the Bellhop-simulated arrival time of the direct path. The correlation coefficients exceed 0.6 in all cases, with trends similar to those observed for hydrophone pair D–F. These results indicate that the maximum peak can be reliably associated with the direct path (D).
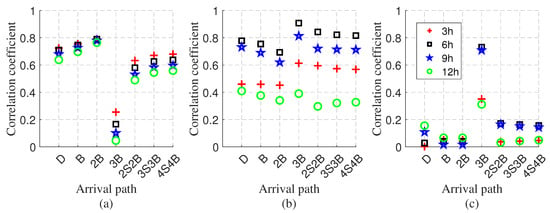
Figure 14.
Correlation analysis between simulated multipath arrivals from HYCOM and experimental results by hydrophone pair C–D on August 10. (a) The maximum peak time delay. (b) The second peak time delay (conventional). (c) The second peak time delay difference.
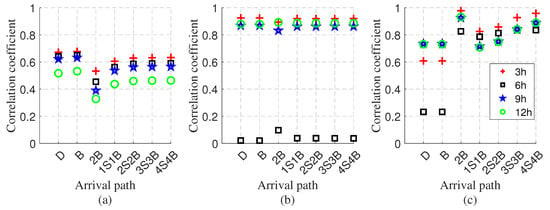
Figure 15.
Correlation analysis between simulated multipath arrivals from HYCOM and experimental results by hydrophone pair C–B on August 10. (a) The maximum peak time delay. (b) The second peak time delay (conventional). (c) The second peak time delay difference.
While longer accumulation improves coherent wavefront extraction from ambient noise, environmental changes (SSP variations) and moving interference sources (vessel traffic) increasingly affect path determination accuracy with extended periods. All 3 h accumulation results exceeded correlation values of 0.6, outperforming other accumulation times (Figure 14a and Figure 15a).
After identifying the direct wave, we next analyze the second coherent wavefront peak in the experimental data. For hydrophone pair C–D, both time delay correlation (Figure 14b) and time delay difference correlation (Figure 14c) consistently identify this peak as the 3B path. In contrast, for hydrophone pairs D–F and C–B, time delay correlation (Figure 13a and Figure 15b) fails to provide reliable identification, whereas time delay difference correlation successfully identifies the second peak as a specific multipath arrival, with correlation coefficients exceeding 0.6 (Figure 13b and Figure 15c). The second peak, having lower energy than the primary arrival, is more susceptible to environmental interference, which leads to less consistent correlation results across different accumulation periods. In addition, differences between HYCOM SSP and actual SSP introduce errors in absolute arrival times. However, the relative time delay differences between propagation paths are less affected by such mismatches and show better agreement with experimental observations.
These findings demonstrate that once the arrival time delay of a specific reference path (such as the direct path) is determined, the relative time delay differences between this path and other arrivals offer a more reliable approach for path identification. In this experimental setting involving shallow water and short-range hydrophone spacing (less than 1.5 km), the number of distinguishable multipath arrivals is relatively limited. Although distinguishing between the direct path and the bottom-reflected path is difficult due to their similar arrival times, reliable identification of other arrival paths can still be achieved using time delay difference correlation.
Time delay difference is more robust to environmental variability, particularly changes in SSP, as the use of relative delays cancels out both clock synchronization errors and hydrophone location uncertainties. It allows for more stable labeling of multipath arrivals, especially in shallow-water, short-range scenarios where overlapping paths are common. However, the method also has several limitations: The approach assumes the direct path is identifiable and can be used as a reference; in environments where the direct path is absent or ambiguous, performance may degrade. The correlation-based path assignment depends on a threshold (e.g., 0.5), which may need adjustment depending on environmental variability and data quality. Overall, the method is well-suited for use in passive acoustic tomography scenarios where ambient noise is sufficiently rich in angular diversity and where at least a rough environmental model is available for simulating reference delays.
5. Conclusions
This study proposes a path identification method based on time delay difference relative to a reference arrival, in order to effectively improve the robustness of passive ocean acoustic tomography (POAT) in shallow-water environments. Field experiments in the East China Sea demonstrate that correlation analysis using time delay difference provides more reliable identification of multipath arrivals compared to using absolute time delay. This method remains effective across different hydrophone pairs and accumulation times, especially for identifying lower-energy multipath components that are otherwise difficult to classify. A key advantage lies in its substantially reduced sensitivity to both clock synchronization errors and hydrophone location uncertainties. Regarding computational complexity, both methods require calculating travel-time delays for all candidate paths across multiple SSPs. The time delay difference method additionally involves computing correlations with experimental delay differences. However, these processes can be executed offline and are compatible with parallelization, resulting in relatively low computational complexity. This favorable trade-off makes the time delay difference technique particularly suitable for practical oceanic applications where environmental stability and precise instrumentation cannot be guaranteed.
Future work will focus on applying the identified multipath structures to improve tomography accuracy and validating the proposed method under more complex sea conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.M., T.Z. and W.X.; methodology, T.M. and T.Z.; software, T.M.; validation, T.M.; formal analysis, T.M. and T.Z. investigation, T.M. and T.Z.; resources, T.M. and T.Z.; data curation, T.M. and T.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, T.M.; writing—review and editing, T.M., T.Z. and W.X.; visualization, T.M.; supervision, W.X.; project administration, W.X.; funding acquisition, W.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61831020).
Data Availability Statement
This study utilizes output from the Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM), developed by the HYCOM Consortium, which is available at https://www.hycom.org/ (accessed on 15 August 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Description | Mathematical Symbols | Description |
| POAT | Passive Ocean Acoustic Tomography | c | Sound speed |
| OAT | Ocean Acoustic Tomography | Correlation coefficient of time delay | |
| NCF | Noise Cross-correlation Function | Correlation coefficient of time delay difference | |
| EGF | Empirical Green’s Function | t | Time delay |
| TDGF | Time-domain Green’s Function | Time delay difference | |
| CIR | Coherent-to-Incoherent Ratio | p | Sound pressure |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio | Correlation time | |
| SSP | Sound Speed Profile | Recording duration | |
| HYCOM | Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model | r | Hydrophone pair spacing |
| D | Direct arrival | a | Amplitude |
| B | Single bottom-reflected arrival | C | Noise cross-correlation function |
| 2B | Double bottom-reflected arrival | G | Green’s function |
| 3B | Triple bottom-reflected arrival | ||
| 1S1B | Single surface-bottom reflection arrival | ||
| 2S2B | Double surface-bottom reflection arrival | ||
| 3S3B | Triple surface-bottom reflection arrival | ||
| 4S4B | Quadruple surface-bottom reflection arrival |
Appendix A
Implementation steps of Figure 10:
- 1.
- The direct path (D) arrival time delay is identified by maximizing correlation between:
- Simulated D arrival time delay (Bellhop).
- Experimental peak time delay .
- 2.
- Time delay differences ( for experiment, for simulation) are computed for all other arrival paths relative to D.
- 3.
- Experimental values are correlated with Bellhop-simulated , where , , and is time delay of simulated arrival path except D. The correlation coefficient . is the number of SSP at different time instants.
- 4.
- Each experimental peak is assigned a path label (e.g., 1S1B, 2S2B) based on the correlation coefficient between and . A threshold (e.g., 0.5) is used to determine reliable matches.
Appendix B
Ray path identification algorithm pseudocode of Figure 10:
Input:
: Experimental arrival peak time.
: Simulated direct path time delay (from Bellhop).
: Simulated time delay for candidate path p.
N: Number of SSPs at different time instants.
Procedure:
1. Identify direct path (D) from experiment: Set with the highest peak amplitude.
2. For each time sample to N: Compute experimental delay difference: ; For each candidate path p: Compute simulated delay difference: .
3. For each candidate path p: Compute correlation coefficient: .
4. If (e.g., 0.5), assign label p to experimental peak. Else, mark as unidentified.
Output:
Identified path label (e.g., D, 1S1B, 2S2B) or flagged as unidentified.
References
- Tan, T.; Godin, O.A. Rapid emergence of empirical Green’s functions from cross-correlations of ambient sound on continental shelf. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 3784–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Gan, W. Passive ocean acoustic tomography in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 2823–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, S.E.; Kuperman, W.A.; Sabra, K.G.; Roux, P. Extracting the local Green’s function on a horizontal array from ambient ocean noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, EL183–EL188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, L.A.; Gerstoft, P. Green’s function approximation from cross-correlations of 20–100 Hz noise during a tropical storm. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin, O.A. Accuracy of the deterministic travel time retrieval from cross-correlations of non-diffuse ambient noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, EL183–EL189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.G.; Godin, O.A.; Williams, N.J.; Zabotin, N.A.; Zabotina, L.; Banker, G.J. Acoustic Green’s function extraction from ambient noise in a coastal ocean environment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5555–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, R.; Froment, B.; Campillo, M. On the correlation of non-isotropically distributed ballistic scalar diffuse waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, O.A. Cross-correlation function of acoustic fields generated by random high-frequency sources. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, O.A.; Zabotin, N.A.; Goncharov, V.V. Ocean tomography with acoustic daylight. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarsoulis, E.; Cornuelle, B. Cross-correlation of shipping noise: Refraction and receiver-motion effects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 3003–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarsoulis, E.; Cornuelle, B. Cross-correlation sensitivity kernels with respect to noise source distribution. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin, O.A. Ocean tomography with acoustic daylight. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, P.; Kuperman, W.A.; Group, N. Extracting coherent wavefronts from acoustic ambient noise in the ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 116, 1995–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sabra, K.G.; Roux, P.; Kuperman, W.A. Arrival-time structure of the time-averaged ambient noise cross-correlation function in an oceanic waveguide. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 116, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siderius, M.; Harrison, C.H.; Porter, M.B. A passive fathometer technique for imaging seabed layering using ambient noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siderius, M.; Song, H.; Gerstoft, P. Adaptive passive fathometer processing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, C.; Lani, S.; Sabra, K.G. Enhancing the emergence rate of coherent wavefronts from ocean ambient noise correlations using spatio-temporal filters. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, S.E.; Walker, S.C.; Hodgkiss, W.S.; Kuperman, W.A. Measuring the effect of ambient noise directionality and split-beam processing on the convergence of the cross-correlation function. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lani, W.; Sabra, K.G.; Hodgkiss, W.S.; Kuperman, W.A.; Philippe, R. Coherent processing of shipping noise for ocean monitoring. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, EL108–EL113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfe, K.F.; Lani, S.; Sabra, K.G.; Kuperman, W.A. Monitoring deep-ocean temperatures using acoustic ambient noise. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2878–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, L.G.; Wapenaar, K.; Heaney, K.D.; Snellen, M. Deep ocean sound speed characteristics passively derived from the ambient acoustic noise field. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 210, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.; Wunsch, C.; Heaney, K.D.; Snellen, M. Ocean acoustic tomography: A scheme for large scale monitoring. Deep Sea Res. Part A 1979, 26, 123–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, D.; Birdsall, T.; Brown, M.; Cornuelle, B.; Heinmiller, R.; Knox, R.; Metzger, K.; Munk, W.; Spiesberger, J.; Spindel, R. A demonstration of ocean acoustic tomography. Nature 1982, 299, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.H.; Worcester, P.; Wuncsh, C. Ocean Acoustic Tomography; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, E.C. Ocean acoustic tomography based on adiabatic mode theory. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 4, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoy, A.; Diachok, O. Low frequency acoustic tomography using matched field processing. In Proceedings of the Engineering in the Ocean Environment, Washington, DC, USA, 24–26 September 1990; pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y. Passive ocean acoustic thermometry with machine learning. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 181, 108167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, V.; Shurup, A.; Godin, O.; Zabotin, N.; Vedenev, A.; Sergeev, S.; Brown, M.G.; Shatravin, A. Tomographic inversion of measured cross-correlation functions of ocean noise in shallow water using ray theory. Acoust. Phys. 2016, 62, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeev, S.; Shurup, A.; Godin, O.; Vedenev, A.; Goncharov, V.; Mukhanov, P.Y.; Zabotin, N.; Brown, M.G. Separation of acoustic modes in the Florida Straits using noise interferometry. Acoust. Phys. 2017, 63, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, O.A. Recovering the acoustic Green’s function from ambient noise cross correlation in an inhomogeneous moving medium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 054301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, K.G.; Roux, P.; Thode, A.M.; D’Spain, G.L.; Hodgkiss, W.S.; Kuperman, W.A. Emergence rate of the time-domain green’s function from the ambient noise cross-correlation function. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, K.G.; Roux, P.; Kuperman, W.A. Using ocean ambient noise for array self-localization and self-synchronization. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 2005, 30, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medwin, H.; Clay, C.S.; Stanton, T.K. Fundamentals of acoustical oceanography. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 4, 2065–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.B.; Bucker, H.P. Gaussian beam tracing for computing ocean acoustic fields. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Porter, M.B. Computational Ocean Acoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zabotin, N.A.; Godin, O.A. Emergence of acoustic Green’s functions from time averages of ambient noise. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2011, 97, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, O.A.; Brown, M.G.; Zabotin, N.A.; Zabotina, L.Y.; Williams, N.J. Passive acoustic measurement of flow velocity in the Straits of Florida. Geosci. Lett. 2014, 1, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.W.; Godin, O.A.; Brown, M.G.; Zabotin, N.A. Characterizing the seabed in the Straits of Florida by using acoustic noise interferometry and time warping. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.W.; Godin, O.A.; Katsnelson, B.; Yarina, M. Passive geoacoustic inversion in the Mid-Atlantic Bight in the presence of strong water column variability. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 125, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).