Abstract
Real-time nitrogen (N) management based on the leaf color chart (LCC) is considered a potential alternative to traditional farmer practices. However, its physiological mechanisms for enhancing rice N utilization and its effects on paddy field N balance remain unclear. We aimed to elucidate the potential enzymatic mechanisms underlying LCC’s influence on rice N use and quantify the impact of LCC on paddy field N balance. In 2022 and 2023, a single-factor randomized block design experiment was conducted during the rice planting season. Four N treatments: no N (ONF), farmers’ conventional practices + urea [FNR] as the control, LCC + urea [SSNM1], LCC + controlled-release urea [SSNM2] were administered. Rice yield and N uptake were positive correlations with nitrate reductase (NR), glutamine synthetase (GS), glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT), glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) activities, which were higher under SSNM1 and SSNM2 compared with FNR, but were negative correlation with proteinase activity. Moreover, SSNM1 and SSNM2 increased rice yield by 9.2% and 9.4%, N uptake by 15.4% and 15.3%, and N use efficiency by 46.9% and 65.0%, and reduced reactive N losses by 46.2% and 66.7%, respectively. The annual net soil N inputs under FNR, SSNM1, and SSNM2 were 12.6, 8.9, and 4.2 kg N ha−1, respectively. LCC-based N management increased N uptake and rice yield by enhancing the activities of NR, GS, GPT, GOT, and GDH while reducing protease activity. Moreover, LCC maintained soil N supply capacity even with reduced nitrogen fertilizer application.
1. Introduction
Rice is a vital food crop and a major consumer of nitrogen (N) fertilizers [1]. According to the fertilizer use by crops report, N fertilizer application in rice fields accounted for approximately 16% of the total N input in farmland in 2018 [2]. In particular, farmers in China tend to overuse N fertilizer as an “insurance” against yield losses, primarily due to the lack of access to advanced N management information and technology [3,4,5]. This practice has resulted in substantial reactive nitrogen (RN) losses in gaseous forms (ammonia [NH3], nitrous oxide [N2O], nitric oxide [NO]), leaching, and runoff, thereby reducing N use efficiency [6,7,8]. Moreover, the imbalance between N inputs (fertilizer application, atmospheric deposition, irrigation) and outputs (crop uptake and RN losses) in rice fields disrupts the N cycle, further exacerbating environmental issues such as water eutrophication and soil acidification [9]. Therefore, adopting more efficient N management practices to reduce RN losses, enhance N uptake by rice, and restore the N balance in rice fields is one of the global priorities for achieving sustainable development [10].
The Leaf Color Chart (LCC), initially developed by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), was designed to provide farmers with a simple, cost-effective, and practical tool to dynamically monitor N nutrition in rice, optimizing both the timing and amount of N fertilizer application [11,12,13]. In recent years, the LCC has been increasingly recognized as a promising technology for N management in rice and has been implemented in various regions [14]. Using LCC-based N management in rice cultivation not only reduces N fertilizer application but also maintains or even increases rice yields. Previous reports suggest that depending on threshold settings, fertilizer type, and environmental factors, LCC can reduce N fertilizer use by 2–27%, improve N use efficiency by 11–45%, and increase grain yield by 4–28% [13,15,16]. These beneficial effects are often simplistically attributed to better synchronization of N supply with crop demand [17], with limited exploration of the underlying physiological mechanisms, such as changes in enzyme activities related to N metabolism. Furthermore, LCC-based N management has been shown to reduce RN losses in rice fields [11,18,19,20]. However, while some environmental impacts of LCC have been preliminarily assessed, these studies often present a fragmented focus on N balance in rice fields. Key components of the N cycle are inadequately considered. For example, gaseous N emissions tend to focus on N2O while overlooking NO or NH3, or soil N inputs and outputs, along with losses through leaching and runoff, lack detailed quantification. In summary, comprehensive assessments of the effects of LCC on N balance in rice fields, particularly studies encompassing all major N input and output pathways, remain scarce. This lack of holistic research limits our understanding of how LCC management practices influence the N cycle in rice fields and their environmental sustainability.
We hypothesized that LCC-based N management would enhance leaf N metabolic enzyme activity, reduce reactive N losses, and restore N balance in rice fields by synchronizing fertilizer inputs with crop demand. To test these hypotheses, a two-years of field experiments, used the local farmers’ conventional practices as a control to analyze the effects of LCC-based urea and slow-release urea management on rice yield, N metabolism-related enzyme activity in leave, N use efficiency, gaseous N losses (NH3, N2O and NO), N leaching and runoff, and soil N inputs and outputs. Additionally, N inputs from atmospheric deposition and irrigation water were measured, with a no-N treatment set as a baseline to represent background N inputs and outputs. Our study provides new insights into the mechanisms by which LCC influences N utilization in rice and further quantifies its impact on N balance in paddy fields. The findings hold significant potential for accelerating the adoption of LCC as a sustainable rice cultivation technology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Field Site
The experimental site is located at the farm in Shanhe Town of Wuchang City, Heilongjiang Province, China (44.73° N, 127.23° E). This region has a temperate monsoon climate, with characteristics of a cold temperate humid continental climate. The average temperatures during the rice growth period in 2022 and 2023 were 17.6 and 17.8 °C, respectively, with total rainfall amounts of 669.0 and 783.7 mm, respectively (Figure 1). The main soil (silty clay loam) properties (0–20 cm depth) were as follows: bulk density (BD) of 1.08 g cm−3, soil pH of 6.3, soil organic carbon (SOC) and total N (TN) contents of 28.63 and 1.52 g kg−1, nitrate (NO3−) of 14.36 mg kg−1, ammonium (NH4+) of 17.11 mg kg−1, available phosphorus (Olsen P) of 16.32 mg kg−1, and available potassium (AK) of 95.63 mg kg−1.
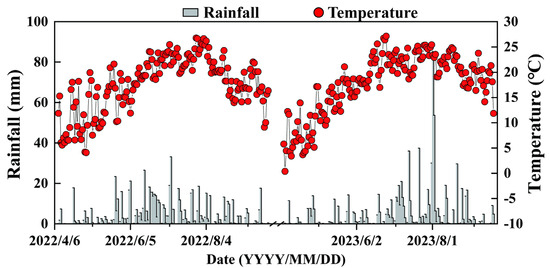
Figure 1.
Temperature and rainfall gathered throughout the rice growth season in 2022 and 2023.
Only one season of rice (Oryza sativa L.) is planted each year, and the cultivated variety is Daohuaxiang No. 2. Fertilizers applied during the rice growth period included urea (46% N), Controlled-release urea (CRU) (44% N), potassium chloride (60% K2O), and superphosphate (12% P2O5). The CRU (Controlled-Release Urea) was provided by Dongkai Green Treasure Pearl (Shandong) Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. (Heze, China) with polyurethane as the coating material. Its release characteristics are detailed in Supplementary Table S1. The Leaf Color Chart (LCC) from the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) was used to assess the color of rice leaves and guide fertilization management. LCC has four green strips, with color ranging from yellow green to dark green (2 to 5).
2.2. Experimental Design and Agronomic Management
In 2022 and 2023, four N fertilizer management methods (FNR, SSNM1, SSNM2, ONF) were designed using random blocks with three replicates. FNR, the local farmers’ urea application practice as the control, involved applying 80 kg N ha−1 one day before transplanting, 60 kg N ha−1 at 7 days after transplanting (DAT), and 60 kg N ha−1 at 42 DAT (the panicle initiation stage). SSNM1 involved applying 80 kg N ha−1 of urea one day before transplanting, followed by measuring the LCC value every 7 days until 42 DAT. Additional 20 kg N ha−1 of urea was applied only when the LCC value < 3. SSNM2 was based on SSNM1, with urea replaced by CRU. ONF denoted the absence of N fertilizer application. All treatments were applied with 60 kg P2O5 ha−1 and 120 kg K2O ha−1 one day before rice transplanting. Rice was sown on 9 April 2022, and 6 April 2023; transplanted on 11 May 2022, and 7 May 2023; and harvested on 22 September 2022, and 19 September 2023. The manual transplanting density was 30 cm × 16 cm, with two seedlings per hill. Each plot was separated by ridges (35 cm wide and 35 cm high) that were covered with plastic film. The area of each plot was 30 m2 (5 m × 6 m). For the four experimental treatments, irrigation and application of pesticide were the same. According to the local conventional irrigation-drainage practices, rice fields were maintained under deep water irrigation (5–10 cm depth) after transplanting until the end of the tillering stage, when fields were drained. From the booting stage to one week before harvest, alternate wetting and drying irrigation management was implemented. In accordance with local practices, rice straw is typically harvested, baled, and reserved for subsequent use; consequently, straw was removed from the experimental plots in this study. Under similar management practices as described above, pre-trials conducted in 2021 determined that the optimal LCC threshold for reducing N fertilizer input while increasing yield was 3 (Supplementary Figure S1).
2.3. Leaf Color Chart Value
At least 10 disease-free rice plants were randomly selected per plot, ensuring a uniform plant population. The topmost, youngest, fully expanded leaf from each hill or plant was selected for measurement. The middle part of each leaf was placed against the LCC, and its color was compared with the chart’s color panels. Measurements were taken under shade to avoid direct sunlight, which could affect readings. When the leaf color fell between two shades, the average of the two values was recorded (e.g., a color between 3 and 4 was recorded as 3.5). LCC measurements were conducted every 7 days starting from the beginning of tillering (7 DAT) and continued until after panicle initiation (42 DAT).
2.4. Enzyme Activities
At the initiation tillering stage (ITS), peak tillering stage (PTS), booting stage (BS), grain filling stage (GFS), and maturity stage (MS), the fully expanded top three leaves of the main stem of rice were collected, with 10 g of samples stored at –80 °C. Each experimental treatment was performed in triplicate. Before enzyme activity determination, leaf samples were homogenized following the method of [21]. Nitrate reductase (NR) activity was measured according to the method of [22] and expressed as the amount of nitrite ions (nmol) produced per gram of fresh weight (FW) per minute through the reduction in nitrate ions. Glutamine synthetase (GS) activity was measured following the method of [21] and expressed as the amount of L-glutamate γ-monohydroxamate (µmol) produced per gram of FW per minute. The activities of Glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) and glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT) were determined using a colorimetric activity assay following the method of Ning et al. (2012) [23]. The activities were expressed as the amount of pyruvate (µmol) produced per gram of FW within 30 min. In addition, the activity of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) was determined using a quartz cuvette-based microplate assay provided by the kit (BIOSS, Beijing, China) (http://www.bioss.com.cn/upload/datasheet/AK079_201.pdf) (accessed on 5 February 2021). The GDH activity was expressed as the amount of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) (µmol) consumed per gram of FW per hour. One unit (1 U) of protease activity is defined as the activity of enzyme that increases the absorbance at 280 nm (A280) by 0.01 per hour. Protease activity is expressed per milligram of protein, and the protein content in enzyme extracts was determined using the Bradford method (1976) [24].
2.5. Grain Yield and Nitrogen Uptake
After rice matured, an area of about 3 m2 was selected from the central part of each plot for grain yield measurement. and then the moisture content of rice grains was measured with a PM-8188-A portable grain moisture (Kett Electric Laboratory, Tokyo, Japan). The rice grains were weighed and converted into the yield at 14% water content. Moreover, the fifth hill of representative plants was selected, killed at 105 °C, and dried to constant weight at 80 °C. The samples dried were crushed and the N contents of rice leaves, stems and roots (0–20 cm depth) were measured by the ECS 4024 CHNSO Classic Analyzer (Costech Analytical Technologies, Milan, Italy). The rice N uptake (NP) was calculated as the sum of the N content in each organ multiplied by its corresponding dry biomass. Each treatment had three biological repeats. N use efficiency (NUEdiff) using the N difference approach were calculated using the following equations [7]:
where NPt and NP0 represent the rice N uptake (kg N ha−1) in plots with N fertilization and without N fertilization, respectively. Yt and Y0 are the rice yield (kg ha−1) in plots with N fertilization and without N fertilization, respectively. Moreover, Nrate is the N fertilizer application rate under the fertilized plots.
2.6. Gaseous Nitrogen Emissions
The samples of N2O and NO were collected with a static closed chamber at intervals of 3–10 days (8:00–10:00 a.m.) after rice transplantation. After the seedlings had been transplanted, the gases were continuously sampled until the rice had been harvested. During the sampling period, two rings were inserted for each plot into the soil at a depth of ~5 cm surrounding two rice plants, and the chambers were temporarily placed in the groove of the rings. The chamber was sealed by manually adding water to the base when it was unsubmerged. After the chamber had been closed for 0, 8, 16 and 24 min, the gas samples were collected successively with a 20 mL syringe and then transferred to 20 mL vacuum glass bottles. Moreover, after the chamber had been closed for 0, 24 and 48 min, 2 L of air were collected into gas sampling bags using a pump. The gas samples were stored for no longer than 2–3 days before they were measured. The concentrations of N2O were analyzed using a gas chromatograph (Shimadzu GC-14 B, Kyoto, Japan). The measurement parameters of gas chromatograph and calculation methods of N2O emission flux and cumulative emissions in this study were consistent with those reported by Tang et al. (2025) [25]. Using dark chamber sampling and aluminized film gas bags for sample storage can prevent the photolysis of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) to NO. However, NO can be oxidized to NO2 by the initial ozone (O3), hydroperoxyl (H2O2), and organic peroxy radicals (RO2) present in the chamber. Therefore, the sum of NO and NO2 fluxes was used to represent the final NO flux [26]. The concentrations of NO and NO2 were measured using a chemiluminescence nitrogen oxide analyzer (42C, Thermo Electron Corporation, Waltham, MA, USA). The sample flow rate was set to 800 mL min−1 to ensure sufficient sample volume and maintain optimal reaction efficiency. Ozone, generated by the internal ozone generator, was supplied at a concentration of 250 ppm to react with NO. The reaction chamber temperature was maintained at 45 °C to optimize the chemiluminescence reaction. NO2 was converted to NO in a molybdenum converter heated to 325 °C, with a conversion efficiency above 95%. Data acquisition was performed at 1 Hz, with an optional 10 s average to reduce short-term fluctuations. The NO emission flux and cumulative emissions were also calculated using the methodology described in Tang et al. (2025) [25]. Similarly, the sampling frequency for NH3 was consistent with that for N2O and NO, and the batch-type airflow enclosure method [25] was used to measure NH3 volatilization. The calculation of NH3 volatilization flux and cumulative emissions followed the methodology described by Tang et al. (2025) [25].
2.7. Nitrogen Content in Paddy Soil, Nitrogen Leaching and Runoff
The lysimeter was made of PVC with a pipe diameter of 10 cm and a length of 80 cm. The bottom of the pipe was sealed, and the top was fitted with a removable cap. Three rows of small holes (6 mm in diameter) were drilled evenly within a 15 cm section, starting 15 cm from the bottom of the pipe. Each row contained five holes, and the pipe was wrapped with two layers of nylon mesh to prevent sediment intrusion. The lysimeter was buried 60 cm into the soil, with the perforated section positioned below 30 cm underground, ensuring that all holes were located beneath the plow pan of the paddy field. This setup allowed for the collection of water samples passing through the plow pan. Leachate samples from the paddy field were collected at regular intervals of 7–14 days during the rice growing season. A PVC container was used to collect runoff generated by rainfall and irrigation. The collector had an area of 2 m × 2 m, with 30 cm buried underground and 50 cm above ground. The collector was connected to the field ridge through a PVC pipe, ensuring that when the water depth in the plot exceeded 30 cm, the excess water would flow into the collector. During the rice-growing period, a total of 16 runoff events occurred. After each event, the runoff volume was recorded, and water samples were collected. Leachate and runoff water samples were stored at 4 °C. The concentrations of TN, NH4+, and NO3− were determined using the alkaline potassium persulfate digestion ultraviolet visible (UV) spectrophotometric method (GB 1184-89) [27], the indophenol blue colorimetric method (GB/T 8538-1995) [28], and the UV spectrophotometry method (HJ/T 346-2007) [29], respectively. The cumulative N leaching (NLtotal) and runoff (NRtotal) volume were calculated using the following equations:
where Ci and CSi represent the N concentrations (mg N L−1) in the leachate and runoff samples collected during each event, respectively. Vi and VSi denote the recorded volumes (L) of leachate and runoff for each event, respectively. B is a constant (159,155) used to convert the leachate volume collected by the lysimeter into leachate volume per hectare [30]. Similarly, BS is a constant (333) used to convert the runoff volume collected by the runoff collector into runoff volume per hectare.
Paddy soil from a depth of 0–20 cm was collected from each plot before rice transplanting and after harvest using the five-point sampling method. The soil samples in each plot were mixed with three replications, and put into centrifuge tubes. The suspensions in the tubes, considered as the soil solution samples, were collected after centrifuging at 4500× g at 24 °C for 30 min. The remaining solid soil without suspensions were extracted with 2 mol L−1 potassium chloride (KCl) for 1 h at 24 °C. The soil solution and extract were refrigerated at 4 °C after filtering through a microporous membrane (0.45 μm). Moreover, the soil TN was extracted by digesting the soil with alkaline potassium persulfate solution (5 g L−1 potassium persulfate [K2S2O8] containing 10 g L−1 sodium hydroxide [NaOH]) at high temperature (121 °C, 30 min). After cooling, the extract was centrifuged and filtered following the same procedure described above, and the supernatant was stored for subsequent analysis. The methods for determining TN, NH4+, and NO3− in the soil extract were the same as those used for water samples.
2.8. Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition and Nitrogen Content in Irrigation Water
The atmospheric N deposition was collected using an automatic wet and dry deposition sampler (APS-3A, Changsha Xianglan Scientific Instrument, Changsha, China). The precipitation volume in the dustfall collector was recorded and collected monthly. During sampling, rainwater was used to rinse the inner walls of the polyurethane foam to simultaneously collect both wet and dry deposition nitrogen. Moreover, ZJPVC-BT01-DN80 irrigation flow meter (Zhongjiang Energy Saving Electronics, Shunde, China) installed in the irrigation pipeline was used for irrigation monitoring and control. The total seasonal water input was calculated as the sum of irrigation water from transplanting to harvest. The TN content in rainwater (TN1) and irrigation water (TN2) was determined using the methods described above (Section 2.7), and the calculation equations are as follows:
where Zi and ZSi represent the N concentrations (mg N L−1) in the rainwater and irrigation water collected during each event, respectively. Pi and PSi denote the recorded volumes of rainwater (mm) and irrigation water (m3) for each event, respectively. K is a constant (10,000) used to convert rainfall (mm) into rainfall volume (L) per hectare. KS is a constant (3.3 × 105) used to convert irrigation water (m3) per plot into irrigation water (L) per hectare.
2.9. Statistical Analysis of Data
All statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS 17.0 analytical software package. The effects of fertilization methods on rice yield, enzyme activities, rice N utilization, gaseous N emissions, N leaching and runoff were evaluated through one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Mean differences among multiple groups were compared using the least significant difference (LSD) test, with a significance level set at 0.05. A one-sample t-test was used to assess changes in soil nitrogen content before and after rice cultivation under different fertilization treatments, with significance levels set at 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001. Additionally, the contribution of N fertilizer to rice yield, rice N utilization, gaseous N emissions, N leaching and runoff was calculated as the difference between treatments with and without N fertilization. The contribution of fertilizer to soil N input was defined as the difference between N fertilizer application rate and other N outputs (including rice N uptake, gaseous N losses, N leaching and runoff). All data met ANOVA assumptions (normality by Shapiro–Wilk test, p > 0.05; homogeneity of variance by Levene’s test, p > 0.05) without requiring transformations. Net ecosystem economic benefit (NEEB) and N loss per unit yield are shown in Supplementary Text S1, Table S2 and Figure S2.
3. Results
3.1. Leaf Color Chart (LCC) Value and Nitrogen Reduction Amount
In 2022 and 2023, the LCC values (3.3–3.4) of SSNM1 were above 3.0 only at 14 DAT, while during other periods they ranged from 2.2 to 2.7 (Figure 2a,b). In contrast, the LCC values (3.1–3.6) of SSNM2 exceeded 3.0 at 7 and 21 DAT, while remaining between 2.5 and 2.9 at other sampling times (Figure 2a,b). Compared with FNR, the N application rates in SSNM1 and SSNM2 were reduced by 10% and 20%, respectively, over the two years (Figure 2c,d).
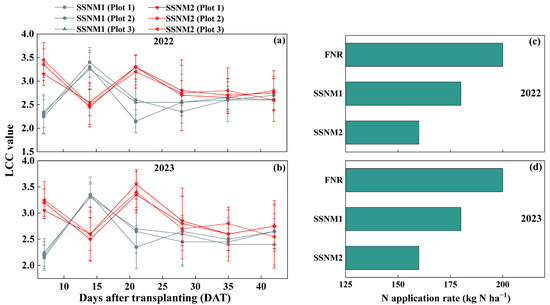
Figure 2.
The application rate of nitrogen fertilizer based on the leaf color chart (LCC). Spatial variations in (a) 2022 LCC, (b) 2023 LCC, (c) 2022 nitrogen application, and (d) 2023 nitrogen application rates. FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD).
3.2. Nitrogen Metabolism-Related Enzyme Activities in Rice Leaves
In 2022 and 2023, compared to ONF, N application treatments (FNR, SSNM1, and SSNM2) increased the activities of NR, GS, GPT, GOT, and GDH while reducing proteinase activity throughout the growth stages (p < 0.05) (Figure 3a–l). There were no significant differences in the activities of NR, GS, GPT, GOT, GDH, and proteinase between SSNM1 and SSNM2 (p > 0.05) (Figure 3a–l). At ITS, the activities of NR, GS, GPT, GOT, and GDH under SSNM1 and SSNM2 were lower than those under FNR, while proteinase activity was higher. However, this trend was reversed during other growth stages (Figure 3a–l). Specifically, compared with FNR, the activities of NR, GS, GPT, GOT, and GDH under SSNM1 were 35.7%, 34.5%, 34.5%, 35.2%, and 30.0% lower at ITS, respectively, while proteinase activity was 53.9% higher (mean of two years) (p < 0.05). Compared with FNR, the activities of NR, GS, GPT, GOT, and GDH under SSNM1 were 16.3–26.6%, 25.2–52.3%, 19.4–54.0%, 17.1–28.7%, and 20.3–25.6% higher in the subsequent growth stages, respectively, while proteinase activity was 19.6–31.8% lower (averaged across two years) (p < 0.05). Similarly, compared with FNR, the activities of NR, GS, GPT, GOT, and GDH under SSNM2 were 36.2%, 32.2%, 33.6%, 34.2%, and 29.4% lower at ITS, respectively, while proteinase activity was 52.9% higher (mean of two years) (p < 0.05). Compared with FNR, the activities of NR, GS, GPT, GOT, and GDH under SSNM2 were 16.7–31.4%, 24.9–53.3%, 19.7–51.1%, 15.2–27.4%, and 21.0–33.9% higher during the remaining growth stages, respectively, while proteinase activity was 18.1–29.8% lower (averaged across two years) (p < 0.05).
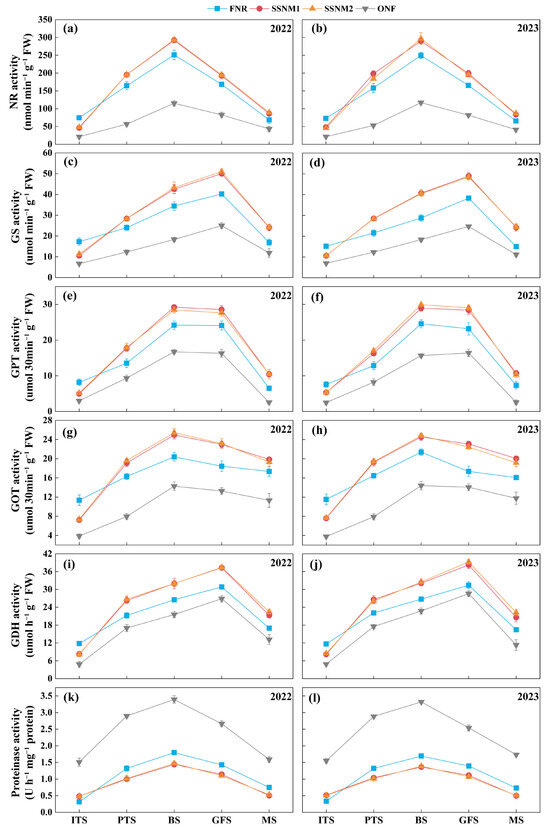
Figure 3.
Changes in the activity of enzymes associated with nitrogen metabolism in rice leaves based on the leaf color chart (LCC). Enzyme activities across 2022 (a,c,e,g,i,k) and 2023 (b,d,f,h,j,l), including nitrate reductase (NR), glutamine synthetase (GS), glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT), glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT), glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), and proteinase. FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC; ITS, Initial tillering stage; PTS, Peak tillering stage; BS, Booting stage; GFS, Grain filling stage; MS, maturity stage. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD).
3.3. Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
Over the two years, soil and fertilizer contributed 49.3–61.5% and 38.5–50.7% of rice yield, respectively, and 42.5–54.6% and 45.4–57.5% of plant N uptake (Figure 4a,b). There were no significant differences in rice yield and plant N uptake between SSNM1 and SSNM2 (p > 0.05) (Figure 4a–c). However, both treatments increased rice yield, plant N uptake, and ANE compared with FNR (Figure 4a–c). Specifically, the two-year average rice yield, plant N uptake, and NUEdiff under SSNM1 were 9.2%, 15.4%, and 46.9% higher than those under FNR, respectively (p < 0.05). Similarly, the two-year average rice yield, plant N uptake, and NUEdiff under SSNM2 were 9.4%, 15.3%, and 65.0% higher than those under FNR, respectively (p < 0.05).
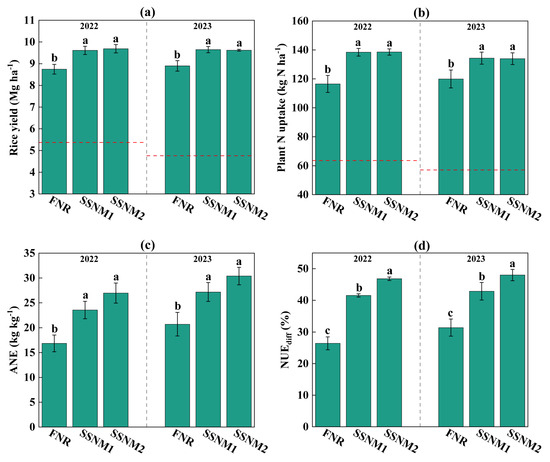
Figure 4.
Rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency based on the leaf color chart (LCC). (a) Rice yield, (b) plant nitrogen uptake, (c) agronomic nitrogen efficiency (ANE), and (d) nitrogen use efficiency based on difference (NUEdiff). FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC. The red lines indicate no N fertilizer application level. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences at the 5% level.
Pearson correlation analysis showed that rice yield and N uptake were positive correlations with NR, GS, GPT, GOT and GDH activities, but were negative correlation with proteinase activity (Table 1).

Table 1.
The Pearson correlation coefficient between enzyme activities and rice yield and N uptake (n = 8).
3.4. Gaseous Nitrogen Emissions from Rice Fields
The peak fluxes of NH3, N2O, and NO emissions occurred after each topdressing application and subsequently declined (Figure 5a–f). Compared to FNR, SSNM1 and SSNM2 exhibited higher frequencies of NH3, N2O, and NO emissions peaks but with lower peak values (Figure 5a–f). Over the two years, the peak emission fluxes of NH3, N2O, and NO under FNR were 1.8–2.8 kg N ha−1 d−1, 121.4–203.0 µg N m−2 h−1, and 66.7–125.6 µg N m−2 h−1, respectively. In comparison, the peak emission fluxes under SSNM1 were 0.3–0.9 kg N ha−1 d−1, 64.9–164.6 µg N m−2 h−1, and 30.1–42.6 µg N m−2 h−1, respectively. Lastly, and with the lowest values, the peak emission fluxes under SSNM2 were 0.3–0.4 kg N ha−1 d−1, 58.3–95.9 µg N m−2 h−1, and 25.0–40.8 µg N m−2 h−1, respectively.
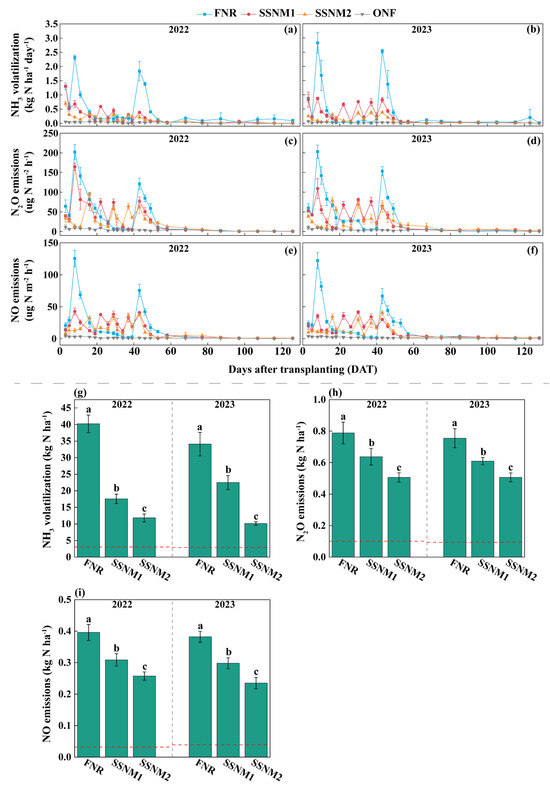
Figure 5.
Gaseous nitrogen emissions from rice fields based on the leaf color chart (LCC). Ammonia (NH3) volatilization flux in (a) 2022 and (b) 2023; nitrous oxide (N2O) emission flux in (c) 2022 and (d) 2023; nitric oxide (NO) emission flux in (e) 2022 and (f) 2023; NH3 (g), N2O (h), NO (i) cumulative emissions during the rice-growing season. FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC. The red dashed line represents the baseline gaseous nitrogen emissions from rice fields without nitrogen fertilizer application (ONF). The red lines indicate no N fertilizer application level. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences at the 5% level.
Over the two years, soil and fertilizer contributed 7.6–28.6% and 71.4–92.4% of the cumulative NH3 emissions, 12.4–19.9% and 80.1–87.6% of the cumulative N2O emissions, and 8.2–16.5% and 83.5–91.8% of the cumulative NO emissions, respectively (Figure 5g–i). The cumulative emissions of NH3, N2O, and NO in 2022 and 2023 followed a consistent pattern: SSNM2 < SSNM1 < FNR (p < 0.05) (Figure 5g–i). Compared with FNR, the two-year average NH3, N2O, and NO emissions under SSNM1 were reduced by 45.2%, 19.2%, and 22.0%, respectively. Furthermore, over two years, the average NH3, N2O, and NO emissions under SSNM2 were 70.4%, 34.4%, and 36.7% lower, respectively, than those under FNR.
3.5. Nitrogen Leaching and Runoff in Rice Fields
Across the two years, soil and fertilizer contributed 4.5–20.5% and 79.5–95.5% of NH4+ leaching, 4.6–16.8% and 83.2–95.4% of NO3− leaching, and 4.8–17.3% and 82.7–95.2% of TN leaching, respectively (Figure 6a,b). The leaching amounts of NH4+, NO3−, and TN in 2022 and 2023 followed the consistent trend: SSNM2 < SSNM1 < FNR (p < 0.05) (Figure 6a,b). Compared to FNR, the two-year average leaching amounts of NH4+, NO3−, and TN under SSNM1 were reduced by 55.6%, 54.0%, and 54.9%, respectively. Under SSNM2, the NH4+, NO3−, and TN leaching amounts (mean of two years) were 71.3%, 69.2%, and 69.0% lower, respectively, than those under FNR.
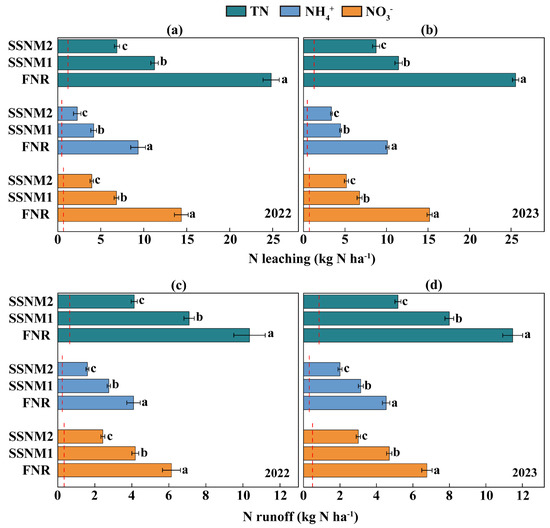
Figure 6.
Nitrogen leaching and runoff in rice fields based on the leaf color chart (LCC). Nitrogen leaching in (a) 2022 and (b) 2023; nitrogen runoff in (c) 2022 and (d) 2023. FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC. The red dashed line represents the baseline nitrogen leaching and runoff in rice fields without nitrogen fertilizer application (ONF). The red lines indicate no N fertilizer application level. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences at the 5% level.
The N runoff in paddy fields was lower than the RN loss through leaching (Figure 6a–d). Over the two years, soil and fertilizer contributed 5.9–15.8% and 84.2–94.1% of NH4+ runoff, 5.6–16.4% and 83.6–94.4% of NO3− runoff, and 6.2–16.5% and 83.5–93.8% of TN runoff, respectively (Figure 6c,d). The runoff amounts of NH4+, NO3−, and TN in both years followed the trend SSNM2 < SSNM1 < FNR (p < 0.05) (Figure 6c,d). Compared with FNR, the NH4+, NO3−, and TN runoff under SSNM1 were reduced by 31.6%, 31.2%, and 30.9%, respectively, on average over the two years. Moreover, NH4+, NO3−, and TN runoff (mean of two years) under SSNM2 were reduced by 58.4%, 58.0%, and 57.5%, respectively, compared with FNR.
3.6. Nitrogen Content in Paddy Soil
Compared with the pre-cultivation levels in 2022, the soil NH4+ content under the ONF treatment decreased by 36.5% and 62.3% after harvest in 2022 and 2023, respectively, while the NO3− content decreased by 17.0% and 41.0%, respectively (p < 0.05) (Figure 7). However, the TN content only showed a reduction of 3.9% after harvest in the second year (p < 0.05). Additionally, the three fertilization treatments (FNR, SSNM1, and SSNM2) did not significantly affect soil NH4+, NO3−, and TN content (p > 0.05).
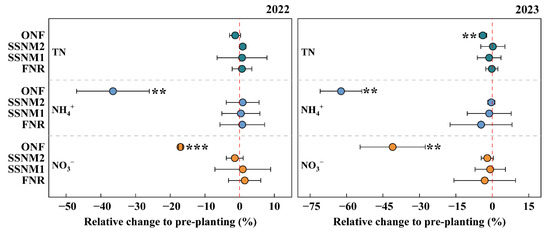
Figure 7.
Changes in soil nitrogen content in rice fields based on the leaf color chart (LCC). FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC; ONF, Omission of nitrogen fertilizer. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (CIs). A total of 95% CIs that overlap with zero indicate no significant difference from the pre-planting levels in 2022. The red dashed line marks the point of no relative change (zero). ** p < 0.01. *** p < 0.001.
3.7. Nitrogen Balance in Rice Fields
In 2022 and 2023, RN loss from paddy fields (gaseous N emissions, N leaching, and runoff) primarily derived from fertilizers (77.3–93.5%) rather than from soil (6.5–22.7%) (Figure 8a–f). Compared with FNR, both SSNM1 and SSNM2 reduced fertilizer RN losses (Figure 8a–f). Specifically, fertilizer RN losses averaged 34.7% (69.4 kg N ha−1), 19.3% (34.8 kg N ha−1), and 12.3% (19.6 kg N ha−1) under FNR, SSNM1, and SSNM2, respectively, over the two years. Gaseous N emissions were the primary pathway of fertilizer RN loss, accounting for 48.2%, 26.1%, and 14.3% under FNR, SSNM1, and SSNM2, respectively. Moreover, under the FNR treatment, soil contributed more to rice N uptake than fertilizers, whereas the opposite was observed under SSNM1 and SSNM2 (Figure 8a–f). Furthermore, the soil N input and output under FNR, SSNM1, and SSNM2 treatments were nearly balanced, with a net input of only 4.2–13.4 kg N ha−1 over the two years. The contributions of atmospheric N deposition and irrigation water to soil N inputs were only 6.2–9.2% of the contributions from fertilizers (Figure 8a–f).
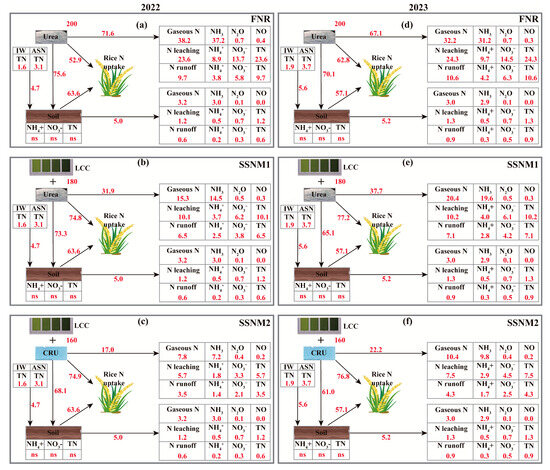
Figure 8.
Nitrogen balance in rice fields based on the leaf color chart (LCC). (a–c) show the nitrogen input and output of paddy fields under FNR, SSNM1, and SSNM2 treatments in 2022, respectively; (d–f) display the corresponding data for 2023. FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC; ONF, Omission of nitrogen fertilizer; IW, Nitrogen content in irrigation water; ASN, Atmospheric nitrogen deposition. The red numbers represent nitrogen inputs and outputs (kg N ha−1). ns indicates no significant difference compared with the pre-planting levels in 2022.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Leaf Color Chart-Based N Management on Enzyme Activities, N Utilization and Rice Yield
Plants primarily acquire inorganic N from the soil in the forms of NO3− and NH4+ [31]. NR and GS are key enzymes in N assimilation. NR catalyzes the reduction of NO3−, marking the first step of N assimilation in plants [32], while GS facilitates the combination of NH4+ with glutamate to form glutamine, which subsequently generates more glutamate through the glutamine synthetase–glutamate synthase (GS-GOGAT) cycle [33]. Additionally, NH4+ can be directly converted to glutamate via GDH [34]. GOT and GPT are the most active transaminases, catalyzing the formation of aspartate and alanine from glutamate, respectively [35]. These enzymes work synergistically through shared substrates and products to complete N assimilation and transformation. Adequate supplies of NO3− and NH4+ may stimulate the activity of these enzymes to meet the increased N demands of plants. Therefore, treatments (SSNM1 and SSNM2) with higher N uptake rates maintained consistently high activities of NR, GS, GOT, GPT and GDH throughout most growth stages (Tabel 1 and Figure 3a–j). In contrast, proteinase activity, which decomposes proteins to supplement amino acids and other metabolites under N deficiency or stress conditions [21,36], showed an opposite trend compared to the activities of NR, GS, GOT, GPT, and GDH (Table 1). Notably, at 7 DAT, the FNR treatment received a substantial N application of 60 kg N ha−1, whereas SSNM1 received only 20 kg N ha−1, and SSNM2 received none (Figure 2a,b). As a result, FNR exhibited higher activities of NR, GS, GOT, GPT and GDH than SSNM1 and SSNM2 at the ITS, whereas proteinase activity showed the opposite trend (Figure 3). In this study, N management based on the LCC aimed to maintain appropriate N levels in rice. Since SSNM1 and SSNM2 used the same leaf color thresholds, there were no significant differences in the six enzyme activities or N uptake between these treatments, despite differences in N fertilizer types (Figure 3 and Figure 4b). However, compared to urea, CRU has a longer fertilizer release cycle at the same N application rate [37]. This characteristic enabled SSNM2 to require the least amount of N fertilizer while achieving the highest NUEdiff (Figure 2b,c and Figure 4c). Furthermore, N is a key component of nucleic acids, proteins, and other nitrogenous compounds and serves as the foundation of carbon metabolism in crops [31]. Consequently, similar to the differences in N uptake between fertilization treatments, there was no significant difference in grain yield between SSNM1 and SSNM2, both of which outperformed FNR (Figure 4a,b). These results align with the positive correlation between rice yield and nitrogen uptake [38,39]. In summary, LCC-based N management enhances rice N uptake and grain yield by sustaining high levels of NR, GS, GOT, GPT and GDH enzyme activities over the long term while maintaining low protease activity. Moreover, combining LCC with controlled-release N fertilizer was more advantageous in improving N use efficiency.
4.2. Effects of Leaf Color Chart-Based N Management on Reactive N Losses in Rice Fields
Reactive nitrogen (RN), defined as all forms of N compounds excluding N2, primarily escapes from farmlands into the atmosphere and freshwater systems through pathways such as NH3 volatilization, N2O and NO emissions, runoff, and leaching [9,40]. In this study, RN loss to the environment under the FNR treatment accounted for 34.7% of N fertilizer (Figure 8a,d), which approaches the upper limit of RN loss from Chinese rice fields (15.3–34.6%) [41]. However, under the SSNM1 treatment, the two-year average RN loss from fertilizers was reduced to only 19.3%, with gaseous N emissions decreasing from 17.6% to 9.9% (Figure 8b,e). During the rice growth period, most gaseous N emissions typically occurred after fertilizer application [42,43]. Excessive N fertilization resulted in an exponential rather than linear increase in gaseous N emissions, due to competition for N between crops and soil microbes [26,44]. Therefore, reducing the amount of N applied per application is critical for mitigating gaseous N emissions. The LCC-based management approach not only reduced the total amount of urea applied but also optimizes its application timing (Figure 2), thereby lowering the peak emissions of NH3, N2O and NO. This strategy promoted greater N uptake by the crop rather than leading to its loss to the atmosphere. Regarding N pollution in water bodies, NO3−, being highly soluble and weakly adsorbed by soil, is the primary form of N lost through leaching and runoff [45]. As a result, NO3− losses were most significantly reduced under the SSNM1 treatment, with the largest decreases observed in leaching and runoff. Based on the estimated leaching and runoff coefficients for N fertilizer in rice fields, reducing N application by 20 kg was expected to decrease leaching by 0.6 kg N and runoff by 0.5 kg N [41]. However, reductions of 13.8 kg N in leaching and 3.4 kg N in runoff were observed under the SSNM1, exceeding expectations. This may result from a synergistic effect between increased rice N uptake and reduced urea application. Compared to SSNM1, SSNM2 further reduced RN losses due to the use of urease inhibitors, which lowered the amount of N fertilizer required, slowed the urease decomposition rate, and inhibited both nitrification and denitrification rates [38,46]. Overall, N management based on the LCC effectively reduced RN losses from rice fields, and its benefits were further enhanced when combined with controlled-release N fertilizers.
4.3. Effects of Leaf Color Chart-Based N Management on Soil N Balance
Soil N is an essential source of N required for crop growth. Even with N fertilizer application, more than half of the N accumulated by crops still obtained from the soil [47]. Therefore, maintaining soil N balance or even enhancing soil N supply capacity is critical for ensuring sustainable crop production. In this study, changes in soil N reserves were determined by the relative quantities of N inputs (atmospheric deposition, irrigation water and fertilizer) and outputs (plant N uptake and RN losses) (Figure 8). Without N fertilizer application, soil NH4+ and NO3− content decreased year by year, and soil TN significantly declined in the second year after planting (Figure 7). soil NH4+ and NO3−, being readily available nutrients, could undergo significant short-term changes due to anthropogenic or environmental influences [48,49]. In contrast, TN was relatively stable because it contained organic N encapsulated within soil aggregates [33,50]. Fertilizer served as the primary pathway for soil N inputs in 2022 and 2023, average accounting for 93.4% under FNR, 93.0% under SSNM1, and 92.6% under SSNM2 (Figure 8). These values are higher than those reported by [51], likely because crop residues were removed in this study. Our findings also demonstrated that rice N uptake was the dominant pathway for soil N outputs, average accounting for 92.2% of the total (Figure 8). Furthermore, although the N fertilizer application rates decreased in the order of FNR, SSNM1, and SSNM2, the differences between soil N inputs and outputs among the three treatments were minimal (Figure 7 and Figure 8), achieving a dynamic balance [10]. This may be attributed to the soil N retention capacity reaching its maximum under all three fertilization scenarios or the benefits of split fertilizer applications, which promote soil N fixation and compensate for the reduction in fertilizer N [52]. Our findings highlight the value of LCC-based N fertilizer management in sustainable agriculture, as it reduces N fertilizer use while maintaining soil N balance.
4.4. Uncertainty and Limitations
Our study focuses on a mechanistic interpretation of how LCC influences N balance in paddy fields. However, we acknowledge that the findings may be region-specific due to the lack of multi-site validation, which limits our ability to assess uncertainties arising from environmental heterogeneity (e.g., climatic and soil property variations). Nevertheless, this research serves as a critical foundation for understanding LCC’s role in rice field nitrogen management. Furthermore, we compared the NEEB of two LCC-based approaches with FNR, revealing similar gains. While this information can support localized decision-making, fluctuations in rice grain market prices may introduce significant variability in NEEB outcomes.
5. Conclusions
Rice leaf enzyme activity was closely related to N uptake. LCC-based N management increased rice N uptake by 15.3–15.4% and grain yield by 9.2–9.4% through sustaining high levels of NR, GS, GOT, GPT and GDH enzyme activities over the long term while maintaining low protease activity. Moreover, this method effectively reduced N fertilizer application by 10–20% and RN losses by 46.2–66.7% in rice fields. Combining LCC with controlled-release N fertilizer proved to be more effective in improving N use efficiency and reducing RN losses compared with conventional urea. While LCC-based N management did not significantly alter soil N content in the short term, this outcome can be seen as a positive indication, given that soil N inputs are steadily accumulating at a low annual rate (8.9 or 4.2 kg N ha−1). Based on this, we predict that LCC will further reduce N fertilizer application rates in the future as soil N content may gradually increase. Therefore, a long-term field observation is essential to validate our hypothesis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15171861/s1, Figure S1: Rice yield response to varied leaf color chart (LCC) thresholds. FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences at the 5% level; Figure S2: Nitrogen loss per unit yield under three management measures. FNR, Farmer’s customary nitrogen application practices; SSNM1, Urea application based on LCC; SSNM2, Controlled-release urea (CRU) application based on LCC. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences at the 5% level; Table S1: Controlled-release fertilizer project specifications; Table S2: Net ecosystem economic benefit (NEEB) under leaf color chart (LCC)-optimized and farmers’ conventional practices (FNR). Supplementary Text S1 documents the calculation methodology of NEEB [53,54,55].
Author Contributions
J.T.: Investigation, Writing—original draft. W.Z.: Investigation. X.N.: Investigation. C.L.: Writing—review & editing. C.C.: Writing—review & editing. D.X.: Supervision, Writing—review & editing, Methodology. Y.Z.: Writing—review & editing, Data curation. J.Q.: Conceptualization. B.W.: Conceptualization. T.L.: Writing—review & editing, Investigation, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We are grateful for grants from National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD2300600), Basic Research Support Program of Outstanding Young Teachers in Heilongjiang Provincial Undergraduate Universities (YQJH2023181), National Natural Science Foundation of China (42407423) and Talent Introduction Project of Northeast Agricultural University (114-54960612).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jichao Tang was employed by the company Wuhan Tanhe International Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, J.S.; Zhang, F.P.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, J.P.; Cai, M.L.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Emissions of N2O and NH3, and nitrogen leaching from direct seeded rice under different tillage practices in central China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludemann, C.I.; Gruere, A.; Heffer, P.; Dobermann, A. Global data on fertilizer use by crop and by country. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowder, S.K.; Skoet, J.; Raney, T. The number, size, and distribution of farms, smallholder farms, and family farms worldwide. World Dev. 2016, 87, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xi, X.; Tang, X.; Luo, D.; Gu, B.; Lam, S.K.; Vitousek, P.M.; Chen, D. Policy distortions, farm size, and the overuse of agricultural chemicals in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7010–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanter, D.R.; Bell, A.R.; Mcdermid, S.S. Precision agriculture for smallholder nitrogen management. One Earth 2019, 1, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.K.; Xing, X.M.; Ding, Y.F.; Ke, J.; Liu, Z.H.; Tang, S.; Ding, C.Q.; Wang, S.H.; Li, G.H. Yield and nitrogen uptake of bowl-seedling machine-transplanted rice with slow-release nitrogen fertilizer. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Xin, Z.; Fang, Y.; Davidson, E.A. Different quantification approaches for nitrogen use efficiency lead to divergent estimates with varying advantages. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Xiao, S.; Liu, S.; Ciais, P.; Zou, J. Data-driven estimates of fertilizer-induced soil NH3, NO and N2O emissions from croplands in China and their climate change impacts. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1008–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Zhang, X.; Lam, S.K.; Yu, Y.; van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Wang, S.; Duan, J.; et al. Cost-effective mitigation of nitrogen pollution from global croplands. Nature 2023, 613, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Ying, H.; Cassman, K.G.; Cong, W.; Tian, X.; He, K.; Wang, Y.; et al. A steady-state N balance approach for sustainable smallholder farming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2106576118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Pathak, H.; Jain, N.; Singh, P.K.; Tomer, R. Greenhouse gas mitigation in rice–wheat system with leaf color chart-based urea application. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, T.; Lu, Z.; Cao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, X. Chlorophyll meter–based nitrogen fertilizer optimization algorithm and nitrogen nutrition index for in-season fertilization of paddy rice. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Bhaduri, D.; Swain, C.K.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, R.; Shahid, M.; Behera, K.K.; Pathak, H. Real-time application of neem-coated urea for enhancing N-use efficiency and minimizing the yield gap between aerobic direct-seeded and puddled transplanted rice. Field Crop. Res. 2021, 264, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogendra, N.D.; Kumara, B.H.; Chandrashekar, N.; Prakash, N.B.; Anantha, M.S.; Shashidhar, H.E. Real-time nitrogen management in aerobic rice by adopting leaf color chart (LCC) as influenced by silicon. J. Plant Nutr. 2017, 40, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Bagchi, B.; Hossain, M. Adoption of leaf color chart for nitrogen use efficiency in rice: Impact assessment of a farmer-participatory experiment in West Bengal, India. Field Crop. Res. 2007, 103, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Karim, M.R.; Ladha, J.K. Integrating best management practices for rice with farmers’ crop management techniques: A potential option for minimizing rice yield gap. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 144, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivenge, P.; Sharma, S.; Bunquin, M.A.; Hellin, J. Improving nitrogen use efficiency—A key for sustainable rice production systems. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 737412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Swain, C.K.; Tripathi, R.; Sethi, S.K.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Kumar, A.; Raja, R.; Shahid, M.; Panda, B.B.; Lal, B.; et al. Nitrate leaching, nitrous oxide emission and N use efficiency of aerobic rice under different N application strategy. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 64, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, W.; Yan, T.; Yang, L. Sustained rice yields and decreased N runoff in a rice-wheat cropping system by replacing wheat with Chinese milk vetch and sharply reducing fertilizer use. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajbonshi, M.P.; Mitra, S.; Bhattacharyya, P. Agro-technologies for greenhouse gases mitigation in flooded rice fields for promoting climate smart agriculture. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 350, 123973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Chao, Y.Y.; Kao, C.H. Exposure of rice seedlings to heat shock protects against subsequent Cd-induced decrease in glutamine synthetase activity and increase in specific protease activity in leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales, E.P.; Iannone, M.F.; Groppa, M.D.; Benavides, M.P. Polyamines modulate nitrate reductase activity in wheat leaves: Involvement of nitric oxide. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, S.J.; Cheng, X.F.; Zhang, G.Y.; Wei, D.Z. Changes in the activity and dynamics of enzymes associated with nitrogen metabolism in flag-leaves of hybrid rice at the late developmental stage. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2012, 20, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, C.; Cao, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, W.; Cheng, B.; Xiong, D.; Liu, T.; et al. Air injection in paddy soil reduces N2O and NH3 emissions and regulates the nitrogen cycle. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X.; Liang, W.; Hu, R. Effects of the applied amount of wheat straw on methane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and nitric oxide fluxes of a bare soil in South Shanxi. Clim. Environ. Res. 2012, 17, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 1184-89; Determination of Total Nitrogen—Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- GB/T 8538-1995; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonium Nitrogen—Indophenol Blue Colorimetric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1995.
- HJ/T 346-2007; Water Quality—Determination of Nitrate nitrogen—Ultraviolet Spectrophotometric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, W.; Ge, C.; Chen, W. Measurement difference in paddy field nitrogen leakage by using different type lysimeters. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Mostofa, M.G.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Zhou, Y.; Adeel, M.; Mehmood, S.; Ahmad, M.A.; Javedi, R.; Imtiaz, M.; Aziz, O.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide enhances rice tolerance to nickel through the prevention of chloroplast damage and the improvement of nitrogen metabolism under excessive nickel. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.L.; Lv, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C.X.; Tan, R.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhong, L.Y.; Gao, Y.Q.; Chao, Z.F.; et al. Decreasing nitrogen assimilation under drought stress by suppressing DST-mediated activation of Nitrate Reductase 1.2 in rice. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sha, Z.; Qin, Q.; Sun, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, S.; Xue, Y.; Cao, L. Soil aggregate-associated organic nitrogen pools, enzyme activities, and microbial community fertilized with food waste-derived organic fertilizer. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Yan, B.; Li, B.; Sun, J.; Guo, S.; Tezuka, T. Bottle gourd rootstock-grafting affects nitrogen metabolism in NaCl-stressed watermelon leaves and enhances short-term salt tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.G.; Chen, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, G.L.; Tian, L. High temperature at grain-filling stage affects nitrogen metabolism enzyme activities in grains and grain nutritional quality in rice. Rice Sci. 2011, 18, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Han, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Qu, Y.; He, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Effects of tillering and heading nitrogen fertilization ratio on compound content and enzyme activity and gene expression to rice leaf senescence. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2018, 49, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Gu, J.; Guo, R.; Li, L. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice. Effects on dry matter accumulation, yield, water and nitrogen use. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 144, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, B. Effects of nitrification and urease inhibitors on ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms, denitrifying bacteria, and greenhouse gas emissions in greenhouse vegetable fields. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Deng, F.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Hu, H.; Pu, S.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Tao, Y.; et al. Polypeptide urea increases rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency through root growth improvement. Field Crop. Res. 2024, 313, 109415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.W. How ammonia feeds and pollutes the world. Science 2021, 374, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Ying, H.; Tian, X.; Cui, Z. Updated loss factors and high-resolution spatial variations for reactive nitrogen losses from Chinese rice paddies. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 358, 120752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q. Abiotic and biotic effects of long-term straw retention on reactive nitrogen runoff losses in a rice–wheat cropping system in the Yangtze Delta region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 305, 107162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Liao, B.; Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Liu, B.; Cui, Y.; Liu, F.; Shi, L. Simultaneous optimization of water and nitrogen management demonstrates effective and robust performance in nitrogen footprint reduction within the double-season rice system. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 469, 143154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbak, I.; Millar, N.; Robertson, G.P. Global metaanalysis of the nonlinear response of soil nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions to fertilizer nitrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9199–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review of emerging adsorbents for nitrate removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Dai, F.; Wu, Y.; Chapman, S. Nitrification and urease inhibitors improve rice nitrogen uptake and prevent denitrification in alkaline paddy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 154, 103665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Cai, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhao, X.; Yan, X. Soil nitrogen supply and retention capacity determine the effect and utilization rate of nitrogen fertilizer in paddy field. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Wang, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J. Distribution of soil available nutrients and their response to environmental factors based on path analysis model in arid and semi-arid area of northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugai, J.; Takashima, N.; Muto, K.; Kaku, T.; Nakayama, H.; Asagi, N.; Komatsuzaki, M. Effects of cover crops on soil inorganic nitrogen and organic carbon dynamics in paddy fields. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, E.; Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, W.; Dai, W.; Jiang, P. A meta-analysis of experimental warming effects on terrestrial nitrogen pools and dynamics. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X. Tracing the fate of nitrogen with 15N isotope considering suitable fertilizer rate related to yield and environment impacts in paddy field. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, M.; Zheng, G.; Yao, Y.; Tao, R.; Zhu, M.; Ding, J.; Li, C.; Guo, W.; Zhu, X. Twice-split application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer met the nitrogen demand of winter wheat. Field Crop. Res. 2021, 267, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y. Evaluating the potential health and economic effects of nitrogen fertilizer application in grain production systems of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Peng, Z.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Dai, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Hu, R.; Luo, Y.; Cui, Y. Can optimizing nitrogen management improve net ecosystem economic benefits in rice cultivation? J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 437, 140756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shen, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S. FeIII-tannic acid-modified waterborne polymer-coated urea has agronomic, environmental and economic benefits in flooded rice paddy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 129013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).