Abstract
It is crucial to clarify the relationship between ecological industry development and ecological civilization construction, as well as their driving forces, to promote high-quality local development. The ecological environment of the karst region is fragile, and it faces a contradiction between ecological preservation and economic advancement. Coordinating the relationship between economic development and ecological protection is crucial for achieving sustainable development in rural karst regions. This study identified karst characteristics in Guizhou province, China, by constructing an index system for ecological industry development and civilization construction. It employed the entropy weight method to calculate a comprehensive score and utilized a coupling coordination model to analyze interactions and symbiotic coordination. Finally, a linear regression analysis model was employed to analyze the impact of ecological industrial development on the construction of ecological civilization. The results indicate the following: (1) The ecological industry and ecological civilization construction levels exhibited a relatively stable growth trajectory across three research areas from 2011 to 2021, with the ecological civilization construction index outperforming the ecological industry development index. (2) The correlation analysis indicated a relationship between the two indices in the research areas, and the divergence trend among the three research areas rose in a uniform direction, indicating a strong positive correlation between the two indices. From the perspective of the coupling degree (C), the degree of coupling between ecological industry and ecological civilization construction in the three research areas exceeded 0.9, indicating a high level of coordination. This suggests that ecological civilization construction and ecological industry in these research areas are effectively coordinated and exist in a state of harmonious co-promotion. There were differences from the coupling coordination degree (D) perspective, but they increased in the three research areas. (3) The regression analysis results indicate that the per capita agricultural output value, per capita forestry output value, per capita forage industry output value, industrial solid waste utilization rate, energy consumption per unit of GDP, tourism income, rocky desertification level, and proportion of the labor force population with a high school education or higher significantly contribute to the development of ecological civilization. The per capita forestry output value greatly advances ecological civilization, significantly enhancing ecological culture and security. The coefficients are 0.0354 and 0.0393, respectively, indicating that a 1% rise in the per capita forestry output value results in increases of 0.0354% and 0.0393% in the ecological culture and security indices.
1. Introduction
Karst is a distinct landscape type formed on soluble rocks that covers approximately 15% of the Earth’s surface [1]. China possesses the largest and most extensively distributed karst region, including an area of 3.44 million km2, accounting for approximately one-third of the country’s land area [2]. Karst regions, deserts, cold deserts, and loess represent four fragile ecological areas in China [3]. The karst region exhibits a binary hydrological structure. The soil formation rate is gradual. The ecological environment is fragile, and human activities consistently destroy the vegetation in this area. Large-scale steep-slope reclamation has led to surface exposure, and the karst soil in the mountains is relatively thin, facilitating bedrock exposure. Soil erosion following a rainstorm leads to progressive rock exposure, resulting in karst desertification [4]. Karst desertification is one of China’s three most serious ecological problems, and it significantly hinders the development of rural karst regions. The rural karst region is the main underdeveloped area in China. The fragility of the karst ecosystem restricts regional economic and social development [5], necessitating more stringent requirements for the development trajectory of this region.
The concept of “ecological industry” has emerged alongside humanity’s ecological awakening. It enhances and transforms the developmental mode of traditional industries, serving as an important node for humanity’s transition from an agricultural and industrial civilization to an ecological civilization. Research on ecological industry originated from traditional industry, and the transformation of its development model is mainly reflected in production methods and technical means. The origins of ecological industry can be traced back to 1969, when the American scholar R.U. Ayres first proposed the concept of “industrial metabolism”. In 1972, he proposed the epoch-making concept of “industrial ecology” [6]. In 1989, Harvard University professors Frosch and Gallopoulos published “sustainable industry development strategy” in the journal Scientific American, introducing the concept of “industrial ecology” [7]. They believed the industrial system should emulate natural systems, transforming the traditional resources–product–waste model into a more comprehensive model called the industrial ecosystem. The first “Industrial Ecology” forum was jointly organized by the National Academy of Sciences and Bell Laboratory in 1991, providing a systematic summary of industrial ecology’s concept, connotation, methods, and application prospects [8]. Traditional linear industries are repeatedly transformed through the ecological production organizational model, forming an ecological industrial composition and structure. An ecological industry is a networked and evolutionary industry characterized by efficient economic processes and harmonious ecological functions organized according to ecological economic principles, ecological engineering technologies, and ecological regulations. The process of product input, production, output, circulation, and consumption embodies the core characteristics of “low carbon, circulation, and high efficiency”, aligning with the principles promoted by low-carbon economy theory and circular economy theory.
In the last century, the rapid development of industrialization promoted rapid global economic growth. Along with the rapid growth of the global population, urbanization, economic globalization, and social wealth have increased sharply. This has resulted in global resource depletion, environmental deterioration, and an ecological crisis, seriously threatening human life and development [9]. Ecological civilization is China’s framework for responding to the planet’s ecological and human developmental problems and building a community with a shared future for humanity amidst profound reflection on the traditional industrial development model and the ecological crisis [10]. Ma expanded ecological research from natural ecosystems to human-centered artificial ecosystems. He introduced the theory of the complex global social–economic–natural ecosystem [11]. In the 1980s, Professor Ye Qianji proposed the concept of “ecological civilization” and the necessity of ecological civilization construction. In 1995, a famous American writer and critic, Roy Morrison, introduced the concept of ecological civilization in the modern sense, perceiving it as a successor to industrial civilization [12]. Liu Zongchao first proposed the “Global Ecological Civilization View” in 1997, which is based on the information proliferation law of the Earth’s surface system [13]. Ecological civilization began with ecological environment construction [14], encompassing the coordinated advancement of ecology, economy, and social issues. The construction of ecological civilization aims to achieve the coordinated development of the economy, society, the population, and nature as a stage of advanced civilization. The assertion is that respecting the objective laws of nature, protecting nature, and advancing humanity allow the internal unity of material and spiritual civilization. With a profound cultural heritage and scientific theoretical basis, ecological civilization aims to promote the green transformation of production methods and lifestyles, achieving mutual development and progress for humanity, nature, and society.
Karst’s unique and fragile geographical environment has no indicator system to assess the development levels of ecological industries and civilization. Furthermore, is there a correlation between ecological industry and ecological civilization? Can ecological industry effectively advance the process of ecological civilization construction? What is its impact? These challenges pertain to the effectiveness of ecological civilization construction and the strategic trajectory of sustainable regional development in rural karst areas. At present, relevant studies have not provided a clear answer. Therefore, this study investigated the influence of ecological industry on the development of ecological civilization in the rural karst area, using Guizhou province, a prime example of a karst landform, as a research sample to empirically analyze the driving mechanisms involved. The marginal contribution of this study mainly encompasses three aspects: (1) In the unique geographical conditions of the karst area, an evaluation index system for ecological industry and ecological civilization was constructed based on local conditions, and the overall score of its complete development level was calculated using the entropy method. (2) This study focused on the rural karst area, analyzing the degree of coordination between ecological industry and ecological civilization construction under varying economic and environmental conditions utilizing a coupling coordination measurement model based on relevant research on ecological industry and ecological civilization development indices. Exploring their connection from the perspective of system symbiosis was advantageous. (3) Utilizing the correlation analysis of ecological industry and ecological civilization, along with research on coupling and the coordination degree, linear regression analysis was applied to explore the driving factors of industrial development on ecological civilization construction while assessing the strength of their driving effect in combination with spatial relationships. Constructing ecological civilization in ecologically fragile areas is crucial for achieving a synergistic effect between the economy and ecology, facilitating regional sustainable development.
2. Methods and Indicator System
2.1. Indicator System Construction
We referenced regulations issued by relevant national departments and existing research on ecological civilization and ecological industries, both domestically and internationally. We utilized the indicator systems of Yang [15], Liu [16], Wang [17], Chen [18], Cheng [19], Yuan [20], etc., and considered the regional characteristics and actual conditions of the rural karst areas to construct the indicator system. This approach considers the level of development in the ecological industry as the primary objective, which comprises two system-level indicators: ecological industrialization (EI) and industrial ecology (IE). Below the system level, there are 10 criterion-level and 11 element-level indicators. The comprehensive objective framework of the construction evaluation system for ecological civilization comprises five system-level indicators: ecological economy (EE), ecological institution (EI), ecological culture (EC), ecological safety (ES), and ecological responsibility (ER). The evaluation method for ecological civilization construction has five system-level indicators, which are all aligned with the overarching objective level: ecological economy (EE), ecological institution (EI), ecological culture (EC), ecological security (ES), and ecological responsibility (ER). The system layer has 10 criterion layers and 13 element layer indicators. The specific criteria are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The evaluation index system for the levels of ecological industry and ecological civilization construction.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Comprehensive Evaluation Model
Hierarchical analysis methods, the coefficient of variation, and entropy methods are often used to determine index weights. Compared to other methods, entropy methods are widely used. Combined with the characteristics of the indicators used in this study, the entropy method was employed to assign index weights, thereby avoiding errors caused by subjective assessment. This study used the entropy method to assign weights to ecological industry and ecological civilization construction. First, the data were standardized. Then, the index weight was obtained according to the information entropy, and the comprehensive development level of ecological industry and ecological civilization construction was measured by the linear weighting method.
EIDL denotes the ecological industry development level; ECCI denotes the ecological civilization construction index; wij and vij are the weights of ecological industry and ecological civilization construction, respectively, corresponding to the jth index of the ith system; and uij and pij are the corresponding normalized values.
2.2.2. Coupling Coordination Method
“Coupling” denotes the strength and coordination of the intercorrelation among systems. It is widely used in academia to study the coupling and coordination relationships between two systems. Then, the coupling and a coordination degree model are employed to assess their respective degrees of coupling and coordination. According to relevant research results [21,22], the coupling coordination degree model represents the interaction and correlation between ecological civilization construction and ecological industry.
- (1)
- The coupling degree (C).
The coupling degree (C) value interval is [0, 1]. The higher the C value, the lower the dispersion. Conversely, if the value is lower, a lower coupling degree exists between the subsystems.
- (2)
- The comprehensive coordination index (T).
T = α × EIDL + β × ECCI
Here, α and β denote coefficients. α and β total 1. Given the significance of ecological industry in relation to ecological civilization in this study, α and β were assigned values of 0.5.
- (3)
- The coupling coordination degree (D).
D denotes the degree of synergistic development and correlation. The larger the value, the stronger the degree of mutual influence and the higher the synergistic effect.
2.2.3. Regression Analysis Model
- The basic form of the regression analysis model
A two-way fixed-effect (TWFE) model was constructed to study the impact of ecological industry on the sub-indicators of ecological civilization, namely ecological economy (EE), ecological institution (EI), ecological culture (EC), ecological security (ES), and ecological responsibility (ER). Before constructing the TWFE model, we identified the 5 ecological industry variables most pertinent to the sub-indicators of ecological civilization as explanatory variables based on their connections with ecological civilization indicators: First, the Pearson correlation coefficient between the independent variable and the dependent variable was computed, resulting in the selection of the top five independent variables exhibiting the highest correlations with the dependent variable. Next, using the combination of variables with the highest relevance, we reconstructed the regression models separately for each dependent variable (EE, EI, EC, ES, and ER) while optimizing the variable selection process. Equations (6)–(10), respectively, represent the baseline TWFE models encompassing ecological economy, ecological institution, ecological culture, ecological security, and ecological responsibility, as presented below:
where a variable with as subscripts denotes the corresponding variable of the th region in the th year; denotes the fixed effect of region; denotes the fixed effect of time; and ε denotes the randomized perturbation term. EE denotes ecological economy; EI denotes ecological institution; EC denotes ecological culture; ES denotes ecological security; ER denotes ecological responsibility; URIS represents the utilization rate of industrial solid waste; RM denotes the roadway mileage; PFPE represents the proportion of the labor force population with a high school education or higher; PCAO denotes the per capita agricultural output value; PCOF represents the per capita output value of the forage industry; ECGDP denotes the energy consumption per unit of GDP; RTGDP represents the ratio of tertiary industry GDP; PCFO denotes the per capita forestry output value; TI represents tourism income; LRD denotes the level of rocky desertification; and CRFF represents compensation for returning farmland to forests. We estimated Equations (6)–(10) using OLS and clustered standard errors at the regional level, where , , , , and were parameter vectors that required estimation.
- 2.
- Modeling verification
The following primary index models were used to evaluate the regression model’s
R-squared (R2)
Formula of computation:
R2 = 1 − RSS/TSS
RSS: residual sum of squares; TSS: total sum of squares. The closer the value of R-squared is to 1, the better the model fit.
Adjusted R-squared
Adjusted R2 was used to balance model complexity with fitting efficacy, preventing spurious enhancement of R2 due to the addition of variables. Then, the computational formula was as presented below:
where n is the number of samples and k is the number of independent variables.
Residual independence
We employed the Durbin–Watson test to detect autocorrelation in the regression model’s residuals. This analysis employed the durbin_watson function from statsmodels to calculate this index. DW ∈ [0, 4], and ideally, DW ≈ 2. DW < 2 indicates a possible positive residual correlation, and DW > 2 indicates a possible negative correlation.
Homoscedasticity
If the residuals were randomly distributed and had no obvious pattern, the assumption of homoscedasticity was satisfied. Verification of the presence of heteroscedasticity was performed using the Breusch–Pagan test. If the p-value was <0.05, it indicated heteroscedasticity.
Residual normality
We employed the Shapiro–Wilk test to ascertain if the residuals conformed to a normal distribution. If the residuals did not conform to a normal distribution, a nonlinear transformation of the variables (such as a log transformation, square-root transformation, etc.) may have been required.
Model evaluation results
The validation of the regression model (Figure 1) indicates that the R2 and adjusted R2 values approached 1, demonstrating an improved model fit. All Durbin–Watson tests approximated 2, all Breusch–Pagan and Shapiro–Wilk test p-values were >0.05, and the overall models successfully passed the main hypothesis tests, including variance, residual normality, and autocorrelation.
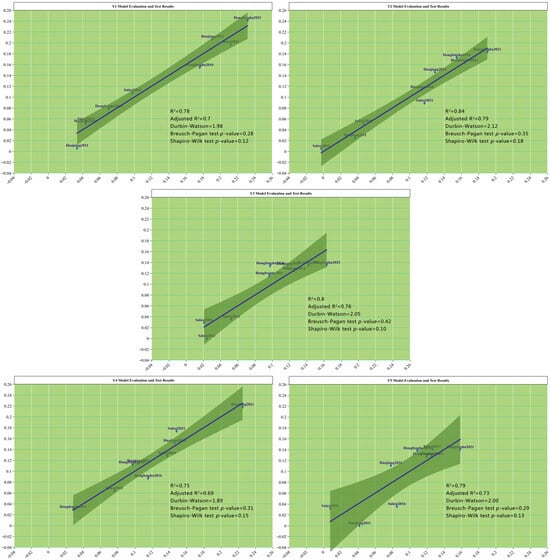
Figure 1.
The results of the model evaluation tests.
3. Introduction to the Study Area and the Data Sources
3.1. Introduction to the Study Area
The southwest karst region is one of the three major concentrations of karst topography globally, encompassing an area of approximately 5.4 × 105 km2 [23]. Guizhou province is located in the center of the South China karst. The karst landform is highly developed and distinctly characteristic. The areas selected for this study are located in the plateau mountains of northwest Guizhou, the plateau valleys of southwest Guizhou, and the plateau basins of central Guizhou, exemplifying the typical landforms of the karst plateau (Figure 2). The Salaxi study area is located in the northwest of Guizhou province (105° 01′10″–105° 08′39″ E, 27° 11′08″–27° 17′30″ N), encompassing a total area of 108.98 km2. This region exemplifies the warm, cool, dry, and wet hydrological conditions of the Liuchong River in the upper reaches of the Wujiang River and is characterized by potential mild rocky desertification within the karst plateau mountains (a 0.2 km2 area with a rock exposure rate of 20-50%). The contradiction between humanity and the land is evident, and land use is extremely unreasonable. The Huajiang research area is located in the southwest of Guizhou (105°36′30″–105°46′30″ E, 25°39′13″–25°41′00″ N), encompassing a total area of 65.77 km2. The rock exposure rate is extremely high. The soil is mostly distributed in rocky areas, exhibiting drought tolerance and water retention capabilities. This area exemplifies a moderate-intensity rocky desertification zone in a dry, hot karst valley (a 0.2 km2 area of spotted rock with an exposure rate of 51–90%). Beipanjiang Town in Zhenfeng County is located on the left, and Huajiang Town in Guanling County is located on the right, representing the regional characteristics of the most severe rocky desertification levels in Guizhou and the entire nation. The Hongfenghu research area is located on both sides of the Youmaweng River basin in the southwestern region of Qingzhen city, with coordinates of 106°18′16″–106°23′16″ east and 26°27′55″–26°34′46″ north. The total size of the study region is 54.68 km2. It is part of the karst area’s mild-to-moderate rocky desertification and represents the karst plateau basin region. The plateau possesses a humid climate with abundant rainfall, providing favorable water conditions for the soil in the research area. Hongfeng Lake Reservoir is the largest artificial lake on a plateau in Guizhou province. It emphasizes ecological tourism and animal husbandry, with significant differences among villages.
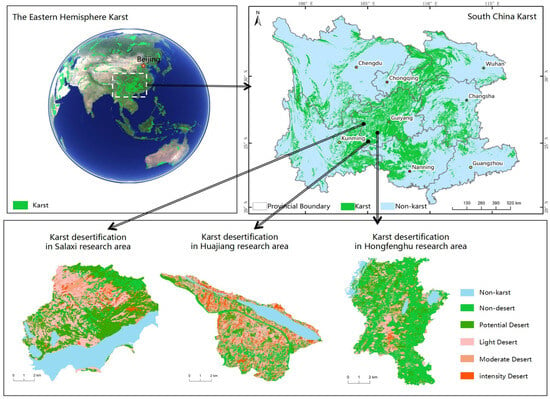
Figure 2.
Location of research area.
3.2. Sources of Data
This study’s data sample period spanned from 2011 to 2021, mainly due to the increasing emphasis on ecological industry and ecological civilization construction since 2010, alongside enhanced policies pertaining to these areas. Data sources regarding the ratio of tertiary industry GDP; roadway mileage; proportion of the senior middle school workforce; per capita agricultural output value; per capita forestry output value; per capita output value of the forage industry; value-added ratio of primary industry; total value of the agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery industries; per capita net income; public environmental education coverage rate; tourism income; population density; drinking water quality rate; proportion of ecological assessment coverage; and soil erosion rate were derived from primary data obtained through social and economic surveys conducted by the research group in the demonstration area in 2011, 2016, and 2021. The data sources for the utilization rate of industrial solid waste, energy consumption per unit of GDP, harmless treatment rate of domestic waste, sewage treatment rate, and forest acreage were derived from the official websites of relevant authorities, including the National Bureau of Statistics, environmental bulletins, water resource bulletins, soil erosion bulletins, government reports from relevant departments, and the statistical yearbook of the study area. Data regarding the rocky desertification levels were derived from the study group’s 11th, 12th, and 13th five-year plans, namely the 15th major special plans for rocky desertification control. The ecological environment index was obtained from the China High-Resolution Ecological Environmental Quality Data Set (CHEQ), which interprets historical ecological environmental quality (EEQ) data with a 500 m resolution from 2011 to 2021. Some missing data were processed by linear interpolation.
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of Ecological Civilization Construction Index and Ecological Industry Development Level Index
Constructing a comprehensive index involves summing the weight of each index alongside standardized data. The comprehensive assessment scores of the three study areas from 2011, 2016, and 2021 were computed using the entropy method per the index evaluation system for ecological industry and ecological civilization construction, and the results are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
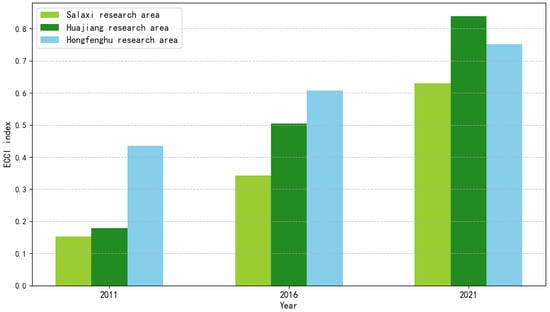
Figure 3.
Comprehensive evaluation score chart of ecological industry.
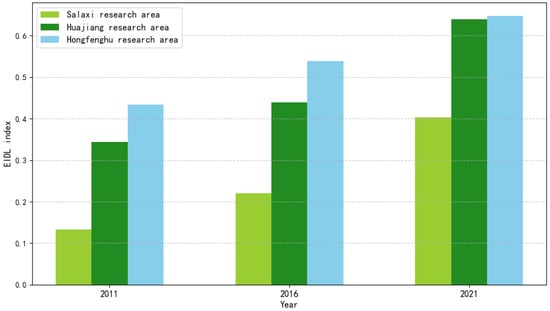
Figure 4.
Comprehensive evaluation score chart of ecological civilization.
From 2011 to 2021, the complete assessment index indicates an increasing trend in the ecological industry and ecological civilization construction index in the Salaxi, Huajiang, and Hongfenghu demonstration regions. It demonstrates that all regional industries and civilizational construction achieved significant results and exhibited a reasonable growth trend. Overall, the ECCI surpassed the EIDL, indicating that the performance of ecological civilization construction in the research area exceeded that of ecological industry development, with a higher growth rate for ecological civilization construction compared to the development level of ecological industry. Horizontally, when comparing the three research areas, the ecological industry index values for the Hongfenghu demonstration area were 0.4336, 0.5387, and 0.6470, respectively, indicating the highest development level during this period. From this point of view, Hongfenghu has achieved notable results in its ecological and economic development strategy, and as a provincial capital, it benefits from advantageous policies, resources, and talent. Regarding ecological civilization construction, the ecological civilization development index fluctuated the most in Huajiang, ranging from 0.1782 in 2011 to a record high of 0.8382 in 2016.
4.2. Analysis of the Coupling Degree, Coordination Index, and Coupling Coordination Degree Results
We applied Formulas (3), (4), and (5) to the EIDL and ECCI values of the three demonstration areas from 2011 to 2021 and subsequently derived the coupling degree (C), coordination index (T), and coupling coordination degree (D) for each year.
Figure 5 illustrates that the coupling degree (C) of ecological industry and ecological civilization construction in the three research areas from 2011 to 2016 and 2021 exceeded 0.9, indicating a high level of coordination. This indicates that during this period, the ecological civilization construction and ecological industry in the three research areas were properly coordinated and in harmony. Secondly, regarding the coordination index (T), the developmental levels of the two indices across the three research areas from 2011 to 2021 were low; nonetheless, there was a general rising trajectory from primary development to high-quality development. The overall progress was obvious. For example, Huajiang rose from 0.2627 in 2011 to 0.7392 in 2021, indicating that ecological industries and ecological civilization construction achieved remarkable results over those 10 years; however, there was still a large gap in achieving high-quality development. The coordination index was relatively high in the Hongfenghu area, whereas it was the lowest in the Salaxi area. Finally, from the coupling coordination degree (D) perspective, the degree of coupling coordination between ecological industry development and ecological civilization construction in the three research areas increased overall. The Salaxi area increased from 0.3768 at the beginning of the period to 0.7098, and four gradients transitioned from mild to moderate coordination coupling. The coupling degree in the Huajiang area was the highest, surpassing that of Salaxi, rising from 0.4973 in 2011 to 0.8559 in 2021, and transitioning from near imbalance to good coordination. The data indicate that the ecological civilization construction and ecological industry in the three research areas were mutually promoted and developed throughout the sample period. The industrial structure was optimized and modernized while maintaining the overall quality of the ecological environment. It is important to acknowledge that the coupling degree score exceeded the threshold for high-quality coupling and that we must sustain the current developmental trajectory.
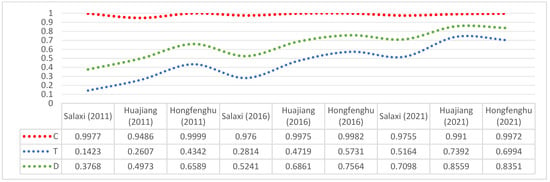
Figure 5.
The coupling degree, coordination index, and coupling coordination degree in the research area from 2011 to 2021.
4.3. Results of Regression Analysis
4.3.1. Regression Analysis of the Influencing Factors of Ecological Economy
After carrying out an analysis of the return impact of ecological industry development on ecological economy, five indicators were selected as independent variables: the utilization rate of industrial solid waste, the roadway mileage, the proportion of the labor force population with a high school education or higher, the per capita agricultural output value, and the per capita output value of the forage industry. Figure 6 indicates that all independent variables positively correlated with the ecological economy. Among them, the per capita agricultural output value and the per capita output value of the forage industry significantly promoted the development of ecological economy at 1% and 10%, respectively. Specifically, for 1 unit of per capita agricultural output value, the ecological economy increased by 0.0347 units, and when the per capita output value of the forage industry increased by 1 unit, the ecological economy increased by 0.0361 units. This indicates that increasing the per capita output value of agriculture and the per capita output value of the forage grass industry plays a significant role in promoting the growth of the eco-economy in the rural karst area. Agriculture, a crucial component of the ecological economy, can enhance farmers’ income through increased output value and can stimulate growth in related industries via expansion of the industrial chain, thereby positively influencing the overall ecological economy in the rural karst region. Similarly, in the rural karst area, the development of the forage industry as an important economic sector cannot be ignored, as it is capable of driving the coordinated development of related industries such as animal husbandry, forming a virtuous industrial cycle and providing strong support for the stable growth of the ecological economy.
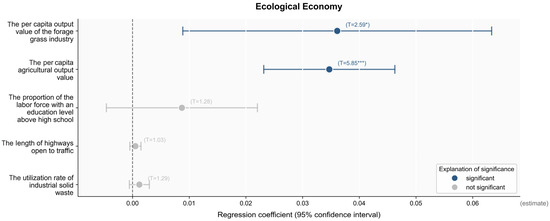
Figure 6.
The results of the regression analysis of eco-economic influencing factors. Note: The values in parentheses represent the standard errors. *** p < 0.01; * p < 0.1.
4.3.2. Regression Analysis of the Influencing Factors of the Ecological System
Regarding the regression effect of ecological industry development on ecological institutions, this study selected five indicators as independent variables for the regression analysis: the utilization rate of industrial solid waste, the energy consumption per unit of GDP, the proportion of the labor force population with a high school education or higher, the per capita agricultural output value, and the per capita grassland industry output value. The regression results (Figure 7) indicate that in addition to a negative correlation between energy consumption per unit of GDP and the ecological system, the utilization rate of industrial solid waste, the proportion of the labor force with a high school education or higher, the per capita agricultural output value, and the per capita output value of the forage industry were all positively correlated with the ecological system. Among them, the utilization rate of industrial solid waste, the energy consumption per unit of GDP, and the per capita output value of the forage industry significantly promoted the development of the ecological system at a value of 10%. Specifically, for each 1-unit increase in the utilization rate of industrial solid waste and the per capita output value of the forage industry, the ecological system correspondingly increased by 0.0016 and 0.03207 units, and the ecological system increased by 0.0116 units for each unit of GDP energy consumption reduction. Therefore, the reduction in energy consumption per unit of GDP in the rural karst area had a significant positive impact on the ecological system, emphasizing the importance of energy conservation, emission reduction, and improving energy utilization efficiency in promoting the construction of an ecological civilization. The improvement in the utilization rate of industrial solid waste also significantly promoted the development of the ecological system, indicating that resource recycling and reducing waste discharge are key links in ecological system construction. The positive impact of the per capita output value of the forage grass industry on the ecological system reflects the penetration and effectiveness of sustainable agricultural development and awareness of ecological protection in animal husbandry in the rural karst area.
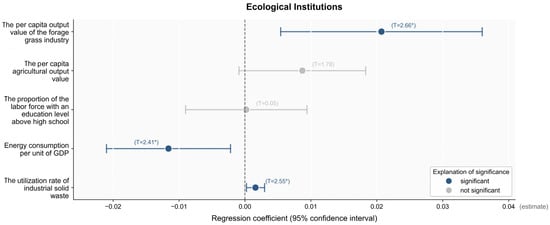
Figure 7.
The results of the regression analysis of factors influencing ecological institutions. Note: The values in parentheses represent the standard errors. * p < 0.1.
4.3.3. Regression Analysis of the Influencing Factors of Ecological Culture
In this study on the influence of ecological industry development on ecological culture, the ratio of tertiary industry GDP, roadway mileage, the proportion of the labor force with a high school education or higher, the per capita forestry output value, and tourism income were selected as independent variables by a principal component analysis (PCA). Regression analysis was conducted, as indicated in Figure 8. Notably, at the 10% significance level, the per capita forestry output value and tourism income significantly promoted the development of ecological culture. When the per capita forestry output value and tourism income increased by one unit, ecological culture increased by 0.0354 and 0.0057 units, respectively. These results highlight the key role of forestry and tourism in promoting ecological culture in the rural karst area. In the rural karst area, forestry provides valuable ecological resources and enriches ecological culture through forest tourism and ecological education [24,25]. At the same time, the rich tourism resources contained in the rural karst area, through the development of tourism activities, can promote the prosperity of local cultural festivals, traditional handicrafts, folk performances, and other ecological cultural activities; attract more tourists to participate in the experience; and promote the inheritance and development of karst ecological culture. In addition, tourism income growth provides the necessary financial support for protecting and developing ecological culture, contributing to in-depth development and extensive dissemination.
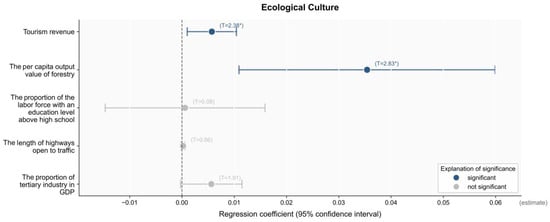
Figure 8.
The results of the regression analysis of factors influencing ecological culture. Note: The values in parentheses represent the standard errors. * p < 0.1.
4.3.4. Regression Analysis of the Influencing Factors of Ecological Security
Given the regression effect of ecological industry development on ecological security, five indicators, including the rocky desertification degree, energy consumption per unit of GDP, per capita agricultural output value, per capita forestry output value, and compensation for returning farmland to forest, were selected as independent variables for the regression analysis. According to the analysis results in Figure 9, rocky desertification and energy consumption per unit of GDP were negatively correlated with ecological security, while the other indicators were positively correlated with ecological security. The energy consumption per unit of GDP and the per capita forestry output value played a positive role in promoting the development of ecological security at significance levels of 10% and 5%, respectively. For every 1-unit decrease in the energy consumption per unit of GDP, the level of ecological security increased by 0.0145 units, and for every 1-unit increase in the per capita forestry output value, the level of ecological security increased by 0.0393 units. A decrease in energy consumption per unit of GDP in rural karst areas usually means an improvement in energy efficiency, which can not only help reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in rural karst areas but also promotes the transformation of the regional economy in the green and low-carbon direction, thus creating favorable conditions for the construction of ecological security in rural karst areas. Undoubtedly, in the role of karst restoration, the increase in forestry output per capita indicates rational utilization of forestry resources and effective management. This can not only increase the karst forest area and improve forest coverage but can also enhance the stability and resistance of the ecosystem to effectively maintain ecological security in rural karst areas.
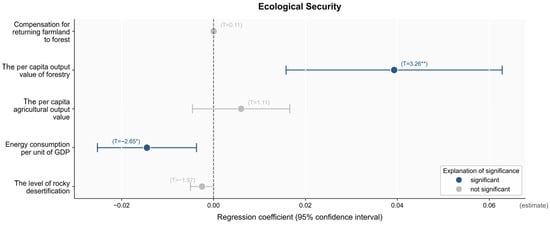
Figure 9.
The results of the regression analysis of factors influencing ecological safety. Note: The values in parentheses represent the standard errors. ** p < 0.05; * p < 0.1.
4.3.5. Regression Analysis of the Influencing Factors of Ecological Responsibility
In order to study the influence of ecological industry development on ecological responsibility, five indicators, including the rocky desertification degree, energy consumption per unit of GDP, roadway mileage, the proportion of the labor force population with a high school education or above, and the per capita output value of forestry, were selected as independent variables for regression analysis. The results showed that all indicators were positively correlated with ecological responsibility except the rocky desertification level (Figure 10). Among the five independent variables examined, the level of rocky desertification and the proportion of the labor population with an education above the high school level were two important factors that significantly affected the development of ecological responsibility at the 10% level. For each reduction in the rocky desertification level, the ecological responsibility level increased by 0.0028 units. For each increase in the proportion of the high school population, the ecological responsibility level increased by 0.0108 units. In the rural karst area, the level of rocky desertification was reduced, which means that land degradation and ecological destruction were contained. This is conducive to fulfilling our ecological responsibility and improving the ecological environment. The increase in the proportion of the highly educated workforce means an improvement in the population quality in this region, enhancing the public’s awareness of environmental protection and ecological responsibility. People have more awareness and ability related to ecological protection and can more effectively participate in the construction of ecological responsibility, which is conducive to providing talent guarantees for implementing ecological responsibility.
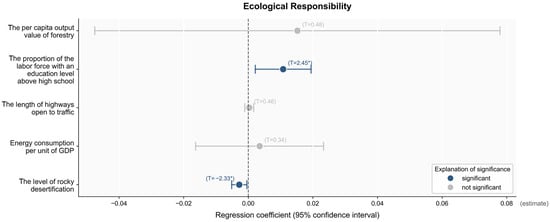
Figure 10.
The results of the regression analysis of factors influencing ecological responsibility. Note: The values in parentheses represent the standard errors. * p < 0.1.
5. Conclusions and Discussion
5.1. Conclusions
The next 10 to 20 years will be a period of strategic opportunities for China’s economic and social development, the transformation of the development model, and the realization of ecological progress. The rural karst region is an important part of the global ecosystem that provides valuable resources and development space for the sustainable development of ecological civilization with harmonious coexistence between man and nature. This study investigated the driving mechanism of ecological industry for ecological civilization construction and selected panel data from three research areas in Guizhou province from 2011 to 2021. Then, a comprehensive evaluation system was built for ecological industry and ecological civilization. The entropy method was used to evaluate the two systems. A coupling and coordination model was used to calculate the coupling and coordinated development relationship between ecological industry and the ecological civilization comprehensive index. A regression model revealed the driving mechanism of industry for ecological civilization construction. The following conclusions are drawn:
(1) There is a strong relationship between ecological industry and ecological civilization in rural karst areas. Both have achieved remarkable accomplishments in rural karst areas in recent years, showing a reasonable growth trend. On the whole, the construction of ecological civilization is more effective than the development of ecological industry. They are strongly related and develop in a coordinated way. From the perspective of the coordination degree (C), the coordination degree of ecological industry and ecological civilization construction in the three research areas from 2011 to 2016 to 2021 was above 0.9, which indicates high-quality coordination. From the perspective of the development degree (T), the development degree of the two indices was at a low level, but the overall trend is rising. From the point of view of the coupling degree (D), the coupling degree of ecological industry development and ecological civilization construction increased. This shows that the development level of ecological industry and ecological civilization construction is low in rural karst areas but the degree of coordination is high. Under the joint action of policy and market guidance, deep integration and coordinated development are gradually being realized.
(2) The regression impact analysis results show that the development of ecological industry can significantly promote the construction of ecological civilization. Variables such as the per capita agricultural output value, per capita forestry output value, per capita forage industry output value, utilization rate of industrial solid waste, energy consumption per unit of GDP, tourism income, rocky desertification level, and proportion of the labor force population with a high school education or higher all distinctly affect the development of ecological civilization. Specifically, the per capita agricultural output value and per capita industry output value promote ecological economic development, while industrial solid waste utilization, energy consumption per unit of GDP, and the per capita industry output value affect the development of the ecological system. The per capita forestry output value and tourism income significantly impact the development of ecological culture. Energy consumption per unit of GDP and the per capita forestry output value play a positive role in promoting the development of ecological security. The level of rocky desertification and the proportion of the labor force with a high school education or higher are two important factors that significantly affect the development of ecological responsibility.
5.2. Discussion
This study has a critical limitation: its empirical foundation rests on a constrained sample of three study areas over three years. This study selected three rural karst areas with different degrees of rocky desertification (Salaxi, Huajiang, and Hongfenghu) to research ecological industry and ecological civilization construction. However, karst ecosystems exhibit high heterogeneity due to lithology, hydrology, and anthropogenic pressure variations. The three-year period (2011–2016–2021) temporarily captured China’s policy shifts but missed continuous feedback loops. While this design allowed for in-depth qualitative and quantitative analysis, the findings must be interpreted cautiously regarding their generalizability. It is important to recognize that the scope of this study is limited and may not fully encompass the complexity and variability in karst environments. Though they are representative of certain conditions, the selected areas may not represent all karst landscapes, especially those with different geological compositions or those subjected to varying levels of human activity. The temporal constraints of this study also mean that while it provides insights into the immediate effects of policy changes, it does not account for long-term ecological responses or potential delayed impacts.
Future research will be carried out on the following aspects: Firstly, it is essential to explore the robustness of the observed mechanisms further by incorporating a broader range of case studies. Specifically, including non-karst regions and international examples will provide a more comprehensive comparison, allowing us to test the universality versus the specificity of the mechanisms identified in this study. For example, by comparing Mediterranean and East Asian models, we can analyze whether China’s “ecological civilization” policy framework has unique political and economic driving factors not found elsewhere. Secondly, there is a need to refine and enhance the indicator system used in this study. This can be achieved by incorporating new indicators that reflect emerging issues and trends in ecological civilization construction. For instance, indicators related to the circular economy, green finance, and sustainable urbanization could be included to provide a more holistic view of the progress. Additionally, the weightings assigned to each indicator should be re-evaluated based on the latest research findings and expert opinions to ensure that they accurately reflect the importance of each factor in driving ecological civilization construction. Lastly, future research should focus on the practical application of the findings from this study. This includes exploring how the identified mechanisms and indicators can be integrated into policy-making and decision-making processes at different levels of governance by working closely with policymakers and practitioners who can ensure that the research findings are academically sound as well as actionable and impactful.
Author Contributions
H.H.: investigation, writing, review, and editing. K.X.: project administration and methodology. J.Y.: map-making and software. Y.L.: formal analysis and data analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Philosophy and Social Science Planning Key Project of Guizhou Province (No. 21GZZB43), the Major Special Project of the Provincial Science and Technology Program of Guizhou Province (No. 6007 2014 QKHZDZXZ), and the China Overseas Expertise Introduction Project for Discipline Innovation (No. D17016).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ford, D.; Williams, P.W. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.X. Modern Karstology and Global Change Study. Earth Sci. Front. 1997, 4, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.J.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, S.J.; Cheng, A.Y.; Dan, W.L. Comparison of ecological significance of landscape diversity changes in Karst mountains: A case study of 4 typical Karst area in Guizhou Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3882–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Xiong, K.N. A review of agroforestry ecosystem services and its enlightenment on the ecosystem improvement of rocky desertification control. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 856, 158538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.H.; Jiang, Z.C.; Yuan, D.X.; Xia, R.Y.; Zhang, C. The progress in the study of the karst dynamic system and global changes in the past 30 years. Geol. China 2017, 44, 874–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.U. Production, Consumption, and Externalities. Am. Econ. Rev. 1969, 59, 282–297. [Google Scholar]
- Frosch, R.A.; Gallopoulos, N.E. Strategies for Manufacturing. Sci. Am. 1989, 261, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.K. Industrial Ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 798–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.J. Change the development model- -building ecological civilization. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 5, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.F.; Xu, Q.H. Integrating China’s eclolgical civilization building and 2030 agenda for sustainable development. Glob. Rev. 2021, 13, 134–151+157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.J.; Wang, R.S. The Social-Economic-Natural Complex Ecosystem. Ecol. Econ. 1984, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M. Ecological Democracy; South End Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.C. Global ecological civilization view Earth surface information proliferation model. Chin. J. Nat. 1993, Z3, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, Q. Progress and prospect of the study on “making great efforts to promote ecological civilization construction”. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2015, 25, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M. Research on the dynamic change of China’s Industrial ecological level and Industry Classification in China. Enterp. Econ. 2018, 37, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.R.; Han, S.F. Research on the Evaluation of Western Region Industrial Ecology. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 33, 90–94+99. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.Y.; Zhang, W.G. Cross-provincial Differences in Determinants of Agricultural Eco-efficiency in China: An Analysis Based on Panel Data from 31 Provinces in 1996-2015. Chin. Rural Econ. 2018, 1, 46–62. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Theoretical and Empirical Study on Coordinated Development of Provincial Eco-industrialization and Industrial Ecology—A Case Study on Guizhou. Guizhou Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, X.T.; Sun, Y.X.; Chen, Y.B. Evolution Characteristics and Its Influencing Factors of Industrial Ecologicalization in the Coastal Areas of China. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.C. Research on the Evaluation of Industrial Ecological Level in Guizhou Province. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Wang, H.J.; Zheng, P. Coupling and Coordinated Development of Circular Economy and Green Finance in Guizhou. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Kong, W.; Ren, L.; Zhi, D.D. Research on misuses and modification of coupling coordination degree model in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, M.M. Karst in China: Its Geomorphology and Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.H.; Xiong, K.N.; Yu, Y.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Kong, L.W.; Zhang, Y.A. Review of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs/Synergies: Enlightenment for the Optimization of Forest Ecosystem Functions in Karst Desertification Control. Forests 2023, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.N.; He, C.; Zhang, M.S.; Pu, J.B. A New Advance on the Improvement of Forest Ecosystem Functions in the Karst Desertification Control. Forests 2023, 14, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).