Abstract
Potassium (K) use efficiency in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis production is relatively low, and the excessive use of K fertilization has negative environmental impacts. Bacterial isolates can effectively alleviate this situation. The present work aimed to analyze the effects of different combinations of three potassium-solubilizing bacteria (KSB) (Bacillus thuringiensis, B. polymyxa, and Paenibacillus amylolyticus) on K in soil and P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis. The results showed that the contents of different forms of K were increased after the application of KSB. Compared with the control group, the maximum increases of slow-acting K, available K, quick-acting K, exchangeable K, and water-soluble K were 32.6% under inoculation with both P. amylolyticus and B. polymyxa, 73.5% with B. thuringiensis, 114.0% with B. thuringiensis, 83.2% with P. amylolyticus, and 210.0% with B. thuringiensis, respectively. This promoted the conversion of soil K to the form of K with high plant availability. Pseudo-protodiosgenin and diosgenin H contents were improved by KSB inoculations, which promoted medicinal quality of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Correlation analysis showed that there were significantly positive correlations among the five forms of K in the soil in all experimental groups. In conclusion, the inoculation of KSB effectively improved the plant availability of soil K and medicinal quality of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis, providing a path for sustainable production of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
1. Introduction
Soils contain substantial reserves of total potassium (K), but the majority exists in the insoluble form and cannot be utilized by plants [1]. K is the third most important primary macronutrient, playing a very important role in improving plant quality, enhancing stress resistance, and increasing yield [2,3]. Deficiency of K in the soil can lead to plants with slow growth rate, poorly developed roots, and low seed production and yield, and, thus, becomes one of the major constraints to crop production. As an important carrier for plant growth and development, soils are the main source of K for plants. K in the soil is present in exchangeable, non-exchangeable, water-soluble (solution K), and mineral or structural forms [3]. Among them, K from exchangeable and water-soluble pools is directly available for plant uptake. The availability of K to the soil by plants is dependent on the form and distribution of K in the rhizosphere and the degree of K absorption by plants. Most of K in the rhizosphere is present in non-exchangeable K or mineral forms, not available for plants. Earlier studies have shown that rhizospheric microorganisms can effectively promote the growth and development of Fenugreek and maize, increase their metabolic levels, and improve plant growth and soil health, which results in increased crop productivity [4,5]. Potassium-solubilizing bacteria (KSB) as a class of bacteria that can decompose silicate primary minerals such as potassium feldspar and mica, are ubiquitous in soils, and promote the transformation of organic and inorganic forms of K by different mechanisms [1,6].
Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, a traditional Chinese medicinal material, is rich in active ingredients, including polysaccharoses, flavonoids, steroid saponins, and aliphatic acids in its rhizomes [7]. In addition, P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis is used for pain relief and detoxification. Chinese Pharmacopoeia (CP) (2020 edition) has stipulated that polyphyllin I, II, and VII are the indicator of quality evaluation in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis [8,9]. Steroidal saponins isolated from P. Polyphylla var. yunnanensis can inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells, regulate the expression levels of some genes and proteins, and convey antitumor and immune-stimulating properties [10]. In addition, steroidal saponins have been applied to cure liver cancer [11]. Studies revealed that inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) increased the content of polyphyllin I, II, III, IV, and total polyphyllin in the rhizomes of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis [12], and accelerated the absorption of macronutrient (e.g., K, P, and Ca) and micronutrient (e.g., Fe, Cu, and Zn) in the root of Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) [13]. Application of Funneliformis mosseae into Polygonum cuspidatum plants distinctly accelerated polydatin and resveratrol contents in leaves and chrysophanol, emodin, polydatin, and resveratral contents in roots [14,15]. As a result, AMF acts as a friendly biostimulant to improve the medicinal quality of medicinal plants.
K use efficiency in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis production is relatively low, and the excessive use of K fertilization has negative environmental impacts. Bacterial isolates can increase leaf area, plant height, fresh weight ratio of plants, and improve plant growth and metabolism, and promote plant development. However, there were few studies about successful inoculation of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis with KSB. The objective of the study was to determine the ability of KSB to enhance the growth of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis plants by measuring different state potassium content in the rhizosphere and steroidal saponins content in the rhizomes of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis to find out the most suitable KSB or combination for the growth of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Culture and Experimental Design
The potted experiment was carried out in the greenhouse of Anshun College (Anshun City, Guizhou Province, China), and four-year-old P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis seedlings were used. The test soil was collected from the campus of Chongqing Three Gorges University. The provenance was preserved by a single plant to ensure the stability and uniformity of germplasm resources. The test soil was passed through an 8 mm soil sieve, and was autoclaved at 121 °C for 2 h. The tested strains were the three dominant species of potassium-solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus thuringiensis, MH497155.1; B. polymyxa, M15817.1; Paenibacillus amylolyticus, KC462533.1) in the rhizosphere soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis which were isolated, cultured, and activated. To examine the effect of KSB on the growth of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis seedlings, the pre-propagated stable KSB strain was adjusted with sterile saline to adjust the concentration of the bacterial suspension to 1 × 106 CFU/mL. From 12 to 20 July 2020, 30 mL of each inoculum was supplied near roots of corresponding plants. Transplanted seedlings were watered once every three days to reach around 70%–80% of field water capacity in soils. During the cultivation period, routine management was carried out according to the potted cultivation of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis. The experiment was consisted of 7 treatment (S1~S7) and a CK by a completely randomized block design with ten replicates per treatment. The inoculation information of each treatment was shown in Table 1. The rhizosphere soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis was collected, air-dried naturally at room temperature, and then ground and passed through an 80-mesh sieve for use. The contents of fast-acting potassium, available potassium, slow-acting potassium, and soluble potassium were determined for 10 individual plants in different treatments. From 21 to 30 November 2020, the rhizomes of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis were selected for quality analysis (at 45 °C to constant weight, 80-mesh sieve). The content of pseudoprotodioscin, polyphyllin VII, polyphyllin H, polyphyllin II, dioscin, and polyphyllin I was determined for 10 individual plants in different treatments.

Table 1.
Inoculated strains in different treatments.
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
Rhizosphere soil was collected at plant maturity stage. The content of fast-acting K in the rhizosphere soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis was determined by 1 mol/L neutral ammonium acetate leaching method. After exchanging cations in soil colloid with ammonium ions, the content was determined by a flame photometry [16]. Available K was extracted using 2 mol/L cold nitric acids as the leaching solution and determined by flame photometry method and molybdate blue method [17]. A 5-g sample of air-dried soil was passed through 1 mm sieve. A volume of 1 mL of the culture supernatant was made up to 50 mL with distilled water and mixed thoroughly. A standard curve was prepared using various contents of KCl solution. The content of water-soluble K was determined by the method of Grewal and Kanwar [18] by a flame photometry. Slow-acting potassium in soil was extracted using 1 mol/L hot nitric acid, and then analyzed using flame photometry method [16]. The potassium extracted by this method was mostly biotite, illite, intermediates decomposed by hydrous mica and K+ was fixed by the clay mineral lattice. The measured value minus the content of available potassium was the content of slow-acting potassium. The content of total potassium was determined by microwave digestion of the sample and then by flame spectrophotometry as illustrated by Sugumaran and Janarthanam [17]. The experiment was replicated five times. KCl solution was used to prepare the standard curve. The results were reported as means ± standard deviation for each treatment.
2.3. Rhizome Sampling and Analysis
The healthy rhizomes of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis were collected in different treatments. For determination of pseudoprotodioscin, polyphyllin VII, polyphyllin H, polyphyllin II, dioscin, and polyphyllin I content by liquid chromatography, rhizome samples (0.5 g) were homogenized in 10 mL of methanol, ultrasonicated for 30 min after weighing, and then centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 15 min [8]. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 µm microporous membrane and used for later use. Chromatographic separation was conducted by an ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 column (150 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 µm). The chromatographic conditions included acetonitrile as the mobile phase A and water as the mobile phase B. The linear gradient elution was carried out as follows: 20~40% A, 0~7 min; 40~58% A, 7~16 min; 58~65% A, 16~20 min; 65% A, 20~21 min; the total running was 32 min, the reequilibration time was 4 min, and then the flow rate of mobile phase was 0.2 mL/min. The effluents from the column were detected by the UV detector where the detection wavelength was set at 203 nm, and the column temperature was 30 °C. The injection volume was 3 µL, and the wash solvent was 10% methanol in water. After accurately weighing the appropriate amounts of the reference substances (pseudoprotodioscin, polyphyllin VII, polyphyllin H, polyphyllin II, dioscin and polyphyllin I), they were dissolved in methanol to prepare the concentrations of 2.134, 2.062, 1.894, 1.890, 1.568, and 1.672 mg/mL, respectively, and stored in a 4 °C refrigerator for later use. The chromatogram was shown in Figure 1. The purity of polyphyllin I (batch no. 50773-41-6), polyphyllin II (batch no. 50773-42-7), polyphyllin VI (batch no. 68124-04-9), polyphyllin H (batch no. 81917-50-2), dioscin (batch no. 19057-60-4), and pseudoprotodioscin (batch no. 102115-79-7) was determined to be over 98%, purchased from Chinese National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products (Beijing, China).
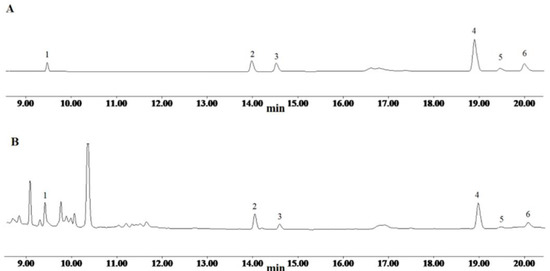
Figure 1.
The chromatogram of reference substances (A) and Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis (B). 1. Pseudoprotodioscin; 2. Polyphyllin VII; 3. Polyphyllin H; 4. Polyphyllin II; 5. Dioscin; 6. Polyphyllin I.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The experimental data were processed by Excel 2010 software, statistical analysis was conducted using the SPSS 21.0 software with one-way ANOVA, and the figures were drawn by the Origin Pro 9.1 software.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of KSB on Available Potassium in Rhizosphere Soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis
In all groups, the content of exchangeable K was higher than that of water-soluble K, and the content of exchangeable K and water-soluble K was significantly different between groups (p < 0.05) (Figure 2). Except for the S5 (inoculation with both B. thuringiensis and B. polymyxa) treatment, the content of available K in all other treatment was higher than that in the CK (inoculation without any KSB). The content of available K in S1 (inoculation with B. thuringiensis) was the highest among all treatment, which was 312.379 mg/kg, an increase of 113.90% compared with the CK. The change trend of exchangeable K and water-soluble K content was consistent with the change trend of available K content. The content of exchangeable K in S2 (inoculation with P. amylolyticus) was the highest, which was 190.084 mg/kg, an increase of 83.20% compared with the CK. The contents of available K, water-soluble K, and exchangeable K in S5 were lower than those in the CK, with a decrease of 9.5%, 7.3%, and 10.4%, respectively. In general, the inoculation of KSB significantly increased the content of available K in the soil, which is beneficial to the absorption and utilization of K by plants, and improved the plant availability of soil K.
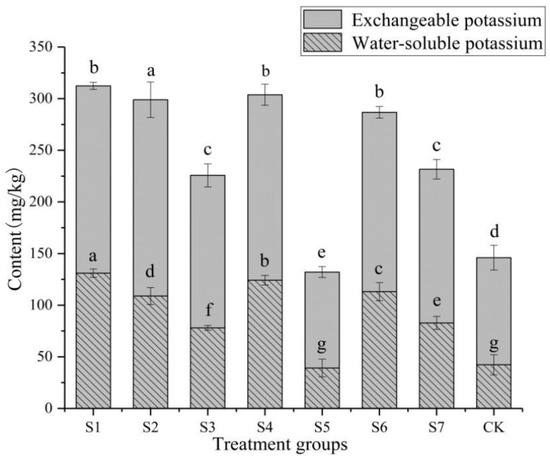
Figure 2.
Effects of potassium-solubilizing bacteria on available potassium in rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Data (means ± SE, n = 10) followed by different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between treatments. The same as below.
3.2. Effects of KSB on Available Potassium and Slow-Available Potassium in Rhizosphere Soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis
The contents of available K and slowly-available K in the rhizosphere soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis were affected by different KSB, and there was a significant difference between the treatments (p < 0.05) (Figure 3). Except for the S5 treatment, the contents of available K and slowly-available K in the rhizosphere soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis in all other treatment were significantly higher than those in the CK. The slow-acting K content of S6 (inoculation with both P. amylolyticus and B. polymyxa) in all treatments was the highest, 1581.26 mg/kg, an increase of 32.60% compared with the CK. The content of available K was the highest in S1, 1136.76 mg/kg, an increase of 73.5% compared with the CK. The contents of available K and slow-acting K in S5 were lower than those in the CK, with a decrease of 7.80% and 10.60%, respectively. In general, the inoculation of KSB had a promoting effect on the content of available K and slow-acting K in the soil.
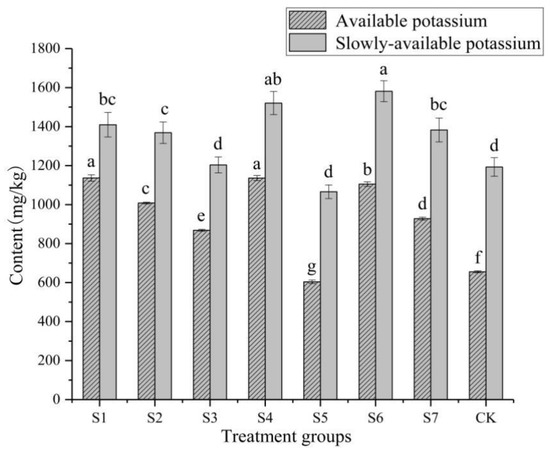
Figure 3.
Effects of potassium-solubilizing bacteria on available potassium and slow-available potassium in rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. a–g: Different letters indicate significant difference between each other (p < 0.05).
3.3. Effects of KSB on Potassium Absorption in Rhizosphere Soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis
The absorption of K in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis was affected by inoculation of KSB (Figure 4). Among all treatment, the total K content of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis in S1, S2, S4 (inoculation with both B. thuringiensis and P. amylolyticus), S5, and S6 was higher than that in the CK, ranging from 16.486 g/kg to 23.707 g/kg. The total K content of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis in S1 was the highest, which was 46.8% higher than that in the CK. The total K content of soil in all experimental groups was 14.358 g/kg (CK)–16.642 g/kg (S4), and the difference between groups was smaller than the total K content in the rhizome of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
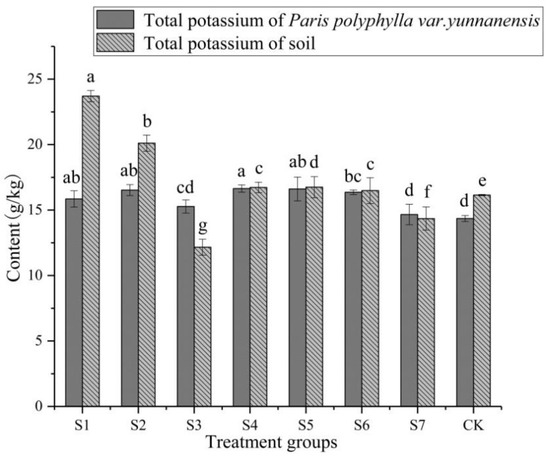
Figure 4.
Effects of potassium-solubilizing bacteria on potassium absorption in rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. a–g: Different letters indicate significant difference between each other (p < 0.05).
3.4. Effects of KSB on the Proportion of Potassium Content in Rhizosphere Soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis
Inoculation of different KSB had a certain effect on the proportion of water-soluble K, exchangeable K, available K, available K, and slow-acting K in the total soil K in the rhizosphere of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis, thus affecting the uptake and utilization of K in the rhizosphere soil (Table 2). After applying different KSB, the proportion of different forms of K in the soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis was changed to a certain extent, and the proportion of K content in the total K in the soil all was showed an upward trend. The proportion of water-soluble K in the rhizosphere soil of all treatment was the highest in S1 (0.83%), an increase of 180.8%, compared with the CK. The highest proportion of exchangeable K was in S2 (1.15%), an increase of 59.2%, compared with the CK. The highest proportion of available K was in S1 (1.97%), an increase of 93.8%, compared with the CK. The highest proportion of available K was in S1 (7.17%), an increase of 57.2% compared with the CK. Only the soil water-soluble K, exchangeable K, available K, and available K ratios in S5 was 0.24%, 0.56%, 0.80%, and 3.64% lower than those of the CK, respectively. The proportion of soil slow-acting K in S1, S4, S6, and S7 (inoculation with B. thuringiensis, P. amylolyticus and B. polymyxa) was higher than that in the CK. The slow-acting K in S6 accounted for the highest proportion of 9.66%, an increase of 16.3% compared with the CK, and the lowest proportion was in S5 (6.42%), a decrease of 22.7% compared with the CK.

Table 2.
Effects of KSB on the proportion of potassium content in rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
3.5. Correlation among Various Forms of Potassium in Soil
There was a significantly positive correlation between water-soluble K and exchangeable K, available K, available K, and slow-acting K in the rhizosphere soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis (Table 3). There was a significantly positive correlation between exchangeable K and quick-acting K, available K, and slow-acting K. There was a significant positive correlation between fast-acting K, and available K and slow-acting K, along with a significant positive correlation between available K and slow-acting K.

Table 3.
Correlation among various forms of potassium in the rhizosphere soil of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
3.6. Effects of KSB on Steroidal Saponins in the Rhizome of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis
An appropriate amount of the stock solution, including polyphyllin I, polyphyllin II, polyphyllin VII, polyphyllin H, dioscin, and pseudoprotodioscin, was placed in a 50 mL volumetric flask, diluted with methanol to the mark, and then 28.453, 137.467, 37.880, 20.160, 10.453, and 11.147 µg/mL of the respective reference substance mixed solution was obtained. The above mixed standard solution was diluted step by step, and measured according to the chromatographic conditions. Taking the concentration of the reference substance as the abscissa (X) and the peak area as the ordinate (Y), we drew a standard curve (Table 4). The results showed that the six steroidal saponins had a good linear relationship within the prepared concentration.

Table 4.
Standard regression equation of six steroidal saponins.
Inoculation of KSB represented different effects on the content of six steroidal saponins in the rhizome of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis (Table 5). There were significant differences in the contents of six steroidal saponins in all experimental groups. The content of pseudoprotodiosgenin ranged from 0.289 mg/g to 1.071 mg/g, and compared with the CK, it showed an overall increasing trend, with a maximum increase of 222.6% (S7). Compared with the CK, the content of polyphyllin VII ranged from 1.650 mg/g to 6.853 mg/g, with only S5 and S6 showing an increasing trend, followed by a maximum increase of 54.0% (S5). Compared with the CK, the content of polyphyllin H ranged from 0.769 mg/g to 2.296 mg/g, showing an overall increasing trend, with a maximum increase of 90.7% (S5). The content of polyphyllin H varied from 5.457 mg/g to 11.808 mg/g, and compared with the CK, only S2, S5, and S6 showed an increasing trend, and the maximum increase was 40.0% (S5). The content of diosgenin ranged from 0.612 mg/g to 1.557 mg/g, only S5 showed an increasing trend, and the maximum increase was 36.3% compared with the CK. Compared with the CK, the content of polyphyllin I ranged from 0.612 mg/g to 1.557 mg/g, coupled with an increasing trend under only S2 and S5 (46.7%). Inoculation with KSB had varying effects on the total amount (11.305 mg/g~27.626 mg/g) of six steroidal saponins in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis, with only S5 and S6 showing an increasing trend, and the largest increase of 46.6% (S5) compared to the CK.

Table 5.
Contents of 6 steroidal saponins in the rhizome of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. (mg/g, ± s, n = 10).
The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2020 edition) proposed that the total amount of polyphyllin I, polyphyllin II, and polyphyllin VII is not less than 0.60%, calculated as a dry product. Inoculation of KSB affected the content of polyphyllin, and the content range is 9.059 mg/g–23.484 mg/g. Compared with the CK, only S5 and S6 showed an increasing trend, and the maximum increase was 45.2% (S5).
3.7. Principal Component Analysis
In this study, the aim of this study for PCA was used to distinguish the different content of steroidal saponins according to the data of UHPLC chromatography. As shown in Table 6, samples were separated depending on the first three principal components (PC) 1 and PC2. The first two PC accounted for the 84.75% of the total variance to classify the sample. The PC 1 mainly reflected the information of polyphyllin II, dioscin, and polyphyllin I; its characteristic value was 3.991 and the contribution rate was 66.52%. The PC 2 mainly reflected the information of pseudoprotodioscin, polyphyllin VII, and polyphyllin H; its characteristic value was 1.094 and the contribution rate was 18.23%.

Table 6.
Principal Component Analysis Matrix of Steroidal Saponins in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
Scores were calculated and ranked for the two principal components obtained, and the results are shown in Table 7. For the PC 1 of the six steroidal saponins in the rhizome of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, the highest score was the S1 treatment, the highest score in the PC2 was the S5 treatment, and the highest comprehensive score was the S5 treatment. To sum up, in PC1, polyphyllin II, dioscin, and polyphyllin I had relatively large main component score coefficients, which could be regarded as the characteristic steroidal saponins of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Among them, the S5 treatment had the most abundant six kinds of steroidal saponins.

Table 7.
Principal component scores of steroidal saponins in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
3.8. Correlation Analysis of Six Steroidal Saponins in the Rhizome of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis
Polyphyllin VII was significantly positively correlated with polyphyllin H in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis (Table 8). There was a positive correlation between polyphyllin II and dioscin in the medicinal materials of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Dioscin was positively correlated with polyphyllin I.

Table 8.
Correlation Analysis of Six Steroidal Saponins in the rhizome of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
4. Discussion
K plays a role in maintaining cell turgor pressure, enzyme activation, transportation of sugars and starches, photosynthesis, protein synthesis, increasing resistance against pests and diseases, helping crops on stress conditions, and improving quality [19]. There is a dynamic balance among various K forms in the soil. The conversion rate between water-soluble K and exchangeable K is much higher than that between exchangeable K and non-exchangeable K, which is also an important factor in determining the amount of K fertilizer applied [20]. The ability of KSB as a bio-fertilizer to enhance K availability in soils by solubilizing some silicate minerals is well known [21,22]. KSB has the characteristics of plant growth promotion, soil fertilization, and environmental friendliness, which, thus, plays an important role in plant growth and improving soil nutrient status [23]. Ding et al. [6] found that the content of water-soluble K and exchangeable K were increased, while the content of non-exchangeable K decreased, along with an increase of 79% in K acquisition by the application of KSB, compared to the results of CK. Bashir et al. [1], who found that the use of KSB as inoculants increased K uptake by plants and thus played a significant role in plant nutrition. Similar results were found in ryegrass [22], cotton [21], and maize [24]. There have been many medicinal studies on steroidal saponins in which the proliferation of human hepatoma SMMC-7221 cells was significantly inhibited and promoted their apoptosis by Polyphyllin I and Polyphyllin D [25,26], anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic effects on hepatoma cells by Polyphyllin VII [27]. In this study, the content of different K forms in the rhizosphere soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis was listed as the trend of slow-acting K > available K > exchangeable K > water-soluble K in a decreasing order. Compared with the CK, the contents of different K showed an overall increasing trend. The maximum increases of slow-acting K, available K, exchangeable K, and water-soluble K were 32.6% (S6), 73.5% (S1), 114.0% (S1), 83.2% (S2), and 210.0% (S1), respectively. Available K is usually used to characterize the K supply capacity of soil. The main reason why exogenous inoculation of KSB can increase the content of available K is that it can decompose and convert K-containing minerals in soil into available K and other forms of K that can be absorbed and utilized by plants through mechanisms such as organic acid production, exopolysaccharide production, and biofilm formation. However, more work is still needed to reveal how KSB promotes plant K uptake, at least in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis. The total K content of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis was increased, compared with the CK, which showed that the application of KSB could promote the absorption of K in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis to a certain extent, increased the content of total K, and thereby improved the plant availability of soil K. This is in agreement with the finding of Xiao [22], Narula [21], and El-Azab and El-Dewiny [24].
The content of active components in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis was significantly affected by inoculation with KSB. The contents of pseudo-protodiosgenin and diosgenin H were shown an overall increasing trend, and there were different trends in the contents of stenoside VII, stegoside II, stegoside I, and diosgenin, compared with the CK. The principal component analysis showed that the score coefficients of polyphyllin I, polyphyllin II, and dioscin were relatively higher, and they were the characteristic steroidal saponins in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Correlation analysis showed that there was a very significant positive correlation among the five forms of K in the rhizosphere soil of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis in all experimental groups, but the correlation with total soil K was not significant. This is consistent with the conclusion of He et al. [20] on the form and spatial distribution of K in farmland soil. Sun et al. [15] also confirmed that endophytic fungi dramatically up-regulated expressions of associated genes in the synthesis path of medicinal components, thereby resulting in increased medicinal component levels. Therefore, whether KSB also changes the level of pseudo-protodiosgenin and diosgenin H by influencing the expression level of associated genes remains to be further studied.
5. Conclusions
After inoculation with KSB, the content of steroidal saponins in P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis was affected to a certain extent. All inoculated groups of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis were met the pharmacopoeia standard, indicating that the inoculation of KSB would not reduce the qualification rate of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis, and would promote the improvement of the medicinal quality of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis in a certain extent. Inoculation of KSB could effectively improve the plant availability of soil K, promote the absorption and utilization of soil K by plants, and provided a new path for environmental protection and reducing the use of K fertilizers during the artificial planting of P. polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-X.Z. and N.Z.; methodology, S.-X.Z. and J.-J.Z.; data curation and statistical analysis, S.-X.Z., Y.-B.X. and Q.-S.W.; investigation, S.-X.Z., Q.-S.D., G.-L.L. and C.-Y.J.; writing— original draft preparation, S.-X.Z.; writing—review and editing, N.Z., J.-J.Z. and Q.-S.W.; supervision, N.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Chongqing Natural Science Foundation Project (cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0115 and cstc2022ycjh-bgzxm0226), the “Shuangcheng Economic Circle Construction in Chengdu-Chongqing Area” Scientific and Technological Innovation Project (KJCX2020046), Chongqing Key Laboratory Project of Chongqing Three Georges Medical College (sys20210007), and the Natural Drug Antitumor Innovation Group Project of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (CXQT20030).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data supporting the findings of this study are included in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bashir, Z.; Zargar, M.Y.; Baba, Z.A.; Mohiddin, F.A. Effect of potassium and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria on growth parameters of chilli (Capsicum annuum L.) under Kashmir climatic conditions. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2017, 5, 692–695. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Zargar, M. Characterization of potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB) in rhizospheric soils of apple (Malusdomestica Borkh.) in temperate kashmir. J. Appl. Life Sci. Int. 2017, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Chatopadhaya, N.; Mandal, J.; Mandal, N.; Ghosh, M. Effect of potassium solubilizing bacteria and waste mica on potassium uptake and dynamics in maize rhizosphere. J. Ind. Soc. Soil Sci. 2021, 68, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Sharma, A.; Chaudhary, P.; Khati, P. Management of plant vigor and soil health using two agriusable nanocompounds and plant growth promotory rhizobacteria in Fenugreek. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.; Khati, P.; Chaudhary, A.; Gangola, S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A. Bioinoculation using indigenous Bacillus spp. improves growth and yield of Zea mays under the influence of nanozeolite. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.L.; Ali, E.F.; Almaroai, Y.A.; Eissa, M.A.; Abeed, H.A. Effect of potassium solubilizing nacteria and humic acid on faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants grown on sandy loam soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.C.; Gao, W.Y.; Yan, X.D.; Ying, W.; Xiao, P.G. Chemical constituents of plants from the genus Paris. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 1277–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Zhang, J.; Jin, H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Z. Quantitative analysis in combination with fingerprint technology and chemometric analysis applied for evaluating six species of wild paris using UHPLC-UV-MS. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 3, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Yang, M.; Shen, Y.X.; Zhang, D.Q. A comparative study of the population genetics of wild and cultivated populations of Paris polyphylla var yunnanensis based on amplified fragment length polymorphism markers. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 10707–10722. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.F.; Yan, C.; Huang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Nie, Z.; Wang, L.F.; Yan, B.Z.; Tang, Y.L.; Yang, L. Immuno-stimulating properties of diosgenyl saponins isolated from Paris polyphylla. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2408–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.C.; Tan, J.; Wang, B.C.; Guan, L.H.; Liu, Y.P.; Zheng, C. In-vitro antitumor activity and antifungal activity of pennogenin steroidal saponins from Paris Polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Xu, L.F.; Yang, M.; Guo, D.Q.; Gan, Q.X.; Zhao, J.J. Mycorrhizal fungal effects on growth, antioxidant capacity, and medicine quality of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Phyton 2021, 90, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.J.; Lee, D.J.; Chi, D.W.; Hong, L.K.; Yong, H.C.; Ju, S.C.; Bo, K.S. Effects of AMF inoculation on growth of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer seedlings and on soil structures in mycorrhizosphere. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 122, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.T.; Feng, X.C.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhou, N.; Feng, H.D.; Liu, Y.M.; Hashem, A.; Al-Arjani, A.; Abd, E.F.; Wu, Q.S. Root endophytic fungi regulate changes in sugar and medicinal compositions of Polygonum cuspidatum. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 818–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.T.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Feng, X.C.; Zhou, N.; Feng, H.D.; Liu, Y.M.; Harsonowati, W.; Hashem, A.; Abd, E.F.; Wu, Q.S. Endophytic fungi accelerate leaf physiological activity and resveratrol accumulation in Polygonum cuspidatum by up-regulating expression of associated genes. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Agricultural Chemistry Analysis of Soil; China Agricultural Science and Technology: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sugumaran, P.; Janarthanam, B. Solubilization of potassium containing minerals by bacteria and their effect on plant growth. World J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 3, 350–355. [Google Scholar]
- Grewal, J.S.; Kanwar, J.S. Forms of potassium in Punjab soils. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1996, 14, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, V.S.; Maurya, B.R.; Verma, J.P.; Aeron, A.; Bajpai, V.K. Potassium solubilizing rhizobacteria (KSR): Isolation, identification, and K-release dynamics from waste mica. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Yang, L.P.; Xu, X.P.; Zhao, S.; Chen, F.; Li, S.; Tu, S.; Jin, J.; Johnston, A.M. Temporal and spatial variation of soil available potassium in China (1990–2012). Field Crop. Res. 2015, 173, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, N.; Saharan, B.S.; Kumar, V.; Bhatia, R.; Bishnoi, L.K.; Lather, B.S.; Lakshminarayana, K. Impact of the use of biofertilizers on cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) crop under irrigated agro-ecosystem. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2005, 51, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. Isolation and identification of three potassium-solubilizing bacteria from rape rhizospheric soil and their effects on ryegrass. Geomicrobiol. J. 2017, 34, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhu, X.Y.; Chen, G.W.; Wan, X.M.; Wang, G. Advances on potassium-solubilizing bacteria and their microscopic potassium solubilizing mechanisms. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 334–348. [Google Scholar]
- El-Azab, M.E.; El-Dewiny, C.Y. Effect of bio and mineral nitrogen fertilizer with different levels on growth, yield and quality of maize plants. JIPBS 2018, 5, 2349–2759. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.M.; Yang, L.; Geng, Y.D. Polyphyllin I induced-apoptosis is enhanced by inhibition of autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngai, B.H.; Loo, J.; Kong, S.K. Abstract 3048: Study of mitochondria in multi-drug resistance and Polyphyllin D anti-cancer effect in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.R.; Qin, G.Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, C.W. Anti-angiogenesis and anti-metastasis effects of Polyphyllin VII on Hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).