Abstract
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is a lipid mediator involved in several allergic reactions. It is released from multiple cells of the immune system, such as eosinophils, neutrophils, and mast cells, and also exerts its effect on most of them upon specific binding to its receptor, becoming a pleiotropic mediator. PAF is considered a potential relevant mediator in allergic rhinitis, with a key role in nasal congestion and rhinorrhoea due to its effect on vascular permeability. Interestingly, despite its potential relevance as a therapeutic target, no specific PAF inhibitors have been studied in humans. However, rupatadine, a second-generation antihistamine with dual antihistamine and anti-PAF effects has shown promising results by both blocking nasal symptoms and inhibiting mast cell activation induced by PAF, in comparison to antihistamine receptor drugs. In conclusion, the inhibition of PAF may be an interesting approach in the treatment of allergic rhinitis as part of a global strategy directed at blocking as many relevant inflammatory mediators as possible.
1. Introduction
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) was originally described in 1974 by Jacques Benveniste as a mediator released by basophils in an IgE-dependent manner, capable of inducing platelet aggregation [1]. PAF is a lipid mediator synthesized in two steps. First, membrane phosphocholine is transformed into lyso-PAF by the actions of cytosolic phospholipase A2; after that, PAF is synthesized from its precursor, lyso-PAF, by acetyl-CoA lyso-PAF acetyltransferase [2]. PAF can be rapidly released (30 s) upon cell stimulation, but it is also produced in the late phase of allergic reactions (Figure 1) [3,4]. PAF has a short half-life (3–13 min) and its degradation is catalyzed by PAF acetyl-hydrolase (PAF-AH) [5]. PAF plasma levels are maintained as low as 54 ± 40 pg/mL in healthy individuals in order to maintain the homeostatic functions [6], but are increased in some diseases such as liver cirrhosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation [6] or acute anaphylaxis [7,8]. PAF-AH deficiency has been related to allergic diseases, and a correlation between PAF-AH serum levels and anaphylaxis severity has also been described [8].
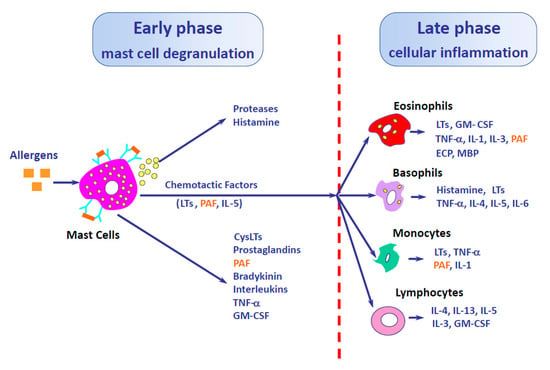
Figure 1.
Importance of platelet-activating factor (PAF) in the early and late phases of allergic response. Adapted from [4] with permission.
PAF is released by several cell types, including mast cells, eosinophils, platelets, neutrophils, monocytes, basophils, epithelial and endothelial cells [9]. Indeed, most of these cell types express PAF receptors (PAF-r) [10]. PAF-r is a seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor that, following activation, becomes rapidly desensitized. This refractory state is dependent on PAF-r phosphorylation, internalization, and down-regulation [9]. PAF-r binding induces different effects, and mediators release depending on the activated cell type or its characteristics. While PAF induces histamine and PGD2 release in human lung mast cells (MC) or MC derived from peripheral progenitors, it has no effect in human skin MC due to a lack of PAF-r expression [11]. In eosinophils, PAF is an extremely potent chemoattractant and promotes chemokine generation, as well as eosinophils activation or prostaglandin production (Figure 2) [12,13]. The ability of PAF to promote eosinophil migration is significantly increased in asthmatic subjects in comparison to healthy individuals [14]. Neutrophils are major producers of PAF [15], which is released in vitro upon FcγR binding (IgG receptor) [16]. Several studies have reported that neutrophils, in an IgG-dependent manner and with PAF as a main mediator, are involved in mouse anaphylaxis [17,18], but also in humans [19]. PAF is also a neutrophil chemoattractant, and some studies have shown neutrophil recruitment into the human nasal airway after a nasal challenge with PAF, although this recruitment is faster in atopic individuals, thereby suggesting a different sensitivity to PAF effects [20] (Figure 1).
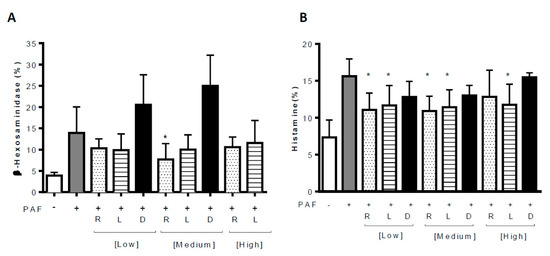
Figure 2.
Effect of rupatadine, levocetirizine and desloratadine on PAF-induced (A) β-hexosaminidase and (B) histamine release in LAD2 cell line. R: rupatadine; L: levocetirizine; D: desloratadine. [Low]: 5 µM, [Medium]: 10 µM, [High]: 25 µM. * p < 0.05. (+) experimental condition with PAF. (−) experimental condition without PAF.
2. Role of PAF in Allergic Diseases
2.1. PAF in Allergic Rhinitis
The role of PAF in allergic rhinitis (AR) has also been suggested. PAF is considered the strongest inducer of vascular permeability, and therefore plays a key role in rhinorrhoea and nasal congestion [21,22]. Similar to asthma, increased levels of both PAF and its precursor lyso-PAF have been found in nasal lavages and plasma samples in AR patients [23]. Indeed, nasal challenge with allergens (pollen) has been shown to increase lyso-PAF and PAF-AH levels in nasal lavage samples, peaking at 10 min and returning to baseline levels at 60 min [23]. Nasal challenge with PAF, similar to asthma, reproduces rhinitis symptoms, and also decreases nasal patency, increases eosinophilic and neutrophilic infiltration, as well as nasal hyperreactivity [20,22,24]. It has also been proposed that PAF plays a role in the priming phenomenon, understood as the influence of one stimulus to a subsequent stimulus (enhancing its effect). In line with that, there are studies showing a greater nasal response after nasal challenge with histamine or bradykinin, if PAF has been administered previously [25]. PAF receptors have recently been found expressed in lung human mast cells [26] as well as in healthy and inflamed upper airway mucosa [27].
Contradictory conclusions regarding the differential effects of PAF in AR and healthy individuals can be found in the literature. Whereas some authors, such as Klementsson et al. [28] have only observed symptoms in AR patients after nasal challenge with PAF, others such as Leggiere et al. [25] and Muñoz-Cano et al. [22] have demonstrated an effect in both AR and healthy individuals. This discrepancy could highlight an interesting aspect, because, as seen in other diseases and models, allergic patients may be more sensitive to the effect of PAF than healthy individuals [29]. Muñoz-Cano et al. [22] observed that the symptoms in allergic patients, measured using a Likert and visual-analogue scale (VAS), were more intense than in the healthy control group, although the differences were not statistically significant. However, none of the published studies directly address the possible differences in the sensitivity to PAF.
There are several studies using PAF nasal challenges aiming to unravel the pathogenesis of AR. Nasal challenge with PAF induces AR symptoms, and its peak is reached 30–120 min after PAF instillation and lasts up to 240 min [22,25,28]. The symptoms’ peak depends on the dose and schedule of the PAF used for the challenge. Most studies use a single dose of PAF, ranging from 30 to 600 nM, observing the peak at 30 min [25,28]. Another study, using progressively increasing doses (100 nM, 200 nM, 400 nM every 30 min), with a cumulative dose of 700 nM, observed the symptoms peak at 60 min after the last dose (120 min after the first dose) [22]. These discrepancies are difficult to explain. Considering PAF’s priming effect, the study using the cumulative schedule should have observed the symptoms in an earlier time point, compared to the single dose schedule. However, the magnitude of the symptoms may be different depending on the dose. Therefore, the “peak” observed in one study may be lower than the “peak” of another study that uses higher doses of PAF. For the same reason, depending on the concentration of PAF used for the nasal challenge, the duration of the effects may be different. However, Leggieri et al. [25] observed almost a resolution of the symptoms, just 60 min after instillation, of 600 nM of PAF. Muñoz-Cano et al. [22], conversely, with a similar dose (700 nM), observed it 240 min after instillation. Although those two studies had similar doses, they each used a different schedule, namely single dose vs. cumulative. Therefore, in the single dose study the effect of PAF vanished rapidly after its instillation, whereas in the cumulative schedule the effect last 240 min after the first dose and 90 min after the last one, suggesting a priming effect.
PAF has been demonstrated to induce a wide range of nasal symptoms, but nasal congestion seems to be one of the most important. Actually, in one study the authors only observed nasal blockage, but no sneezing or itching, and a very mild rhinorrhoea [22]. That means that nasal congestion seems to be strongly related to PAF, although the role of other mediators needs to be considered. This is a good therapeutic opportunity, considering that nasal blockage is the most bothersome symptom in AR and antihistamines has a limited effect, and nasal corticosteroids are often then required to treat this symptom [30]. Although nasal corticosteroids are safe and very useful drugs in AR [31], there is a lack of adherence to the treatment, mostly related to corticophofia and some local side effects [32]. Therefore, the development of drugs targeting PAF may be an alternative to nasal corticosteroids for the treatment of the nasal congestion in AR patients.
Despite the observed involvement of PAF in AR, the PAF receptor antagonist has only been studied in animal models (with promising results), and no human studies have been performed [33,34]. However, there are several studies with rupatadine, a second-generation antihistamine, that has shown a dual effect on H1 histamine and PAF receptors [35,36,37]. Rupatadine has been successfully used in patients with allergic rhinitis (and urticaria), and clinical trials have demonstrated its safety and efficacy [4,37,38]. A systematic review/meta-analysis examined the efficacy of rupatadine by pooling data from ten randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies involving more than 2500 patients. This meta-analysis showed that rupatadine was significantly better than the placebo in controlling allergy rhinitis, mainly nasal congestion as well as conjunctival symptoms. As a result of this analysis, a robust level of evidence was found, and a recommendation for use of rupatadine in allergic rhinoconjunctivitis was made.
Rupatadine has demonstrated several anti-allergic effects, blocking mast cell degranulation, eosinophil and neutrophil chemotaxis, as well as cytokine production (IL-5, IL-8, GM-CSF and TNF-α) [4,38]. In order to demonstrate that the combined inhibition of PAF and histamine may be a better strategy to treat patients with AR, Muñoz-Cano et al. [39] designed a proof of concept randomized, double-blind crossover placebo-controlled study. Nasal challenge with PAF was performed in patients that were previously treated (during 4 days) with levocetirizine (H1 antagonist) or rupatadine (H1 and PAF antagonist). They compared seasonal allergic rhinitis (grass or tree pollen allergy) patients with healthy individuals, out of pollen season. The results showed that rupatadine, but not levocetirizine, significantly reduced PAF-induced symptoms in patients with AR (Figure 3). Rupatadine produced a significant 54% reduction in the area under the curve for the total 4 nasal symptoms scores (T4SS) induced by PAF, which includes mainly nasal congestion and rhinorrhoea, and in smaller proportion, itching and sneezing. Rupatadine caused a 73% decrease of the T4SS at 60 min after nasal challenge, compared to the 23% decrease observed with levocetirizine.
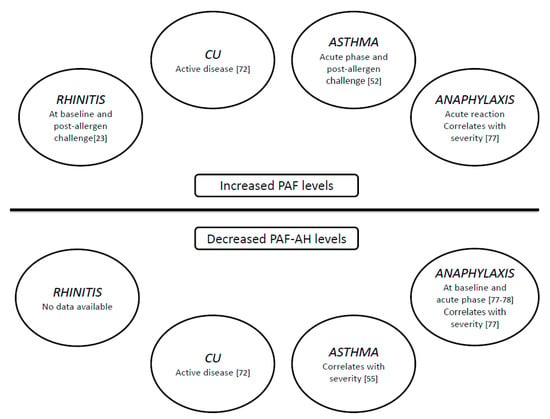
Figure 3.
PAF and PAF-AH levels in respiratory diseases, anaphylaxis and chronic urticaria.
The same authors, using an in vitro approach, showed again that rupatadine, but not any of the other tested antihistamines (without PAF effect), significantly inhibited PAF-induced mast cell activation [26]. Mast cells from the human cell line LAD2 and primary human lung mast cells were incubated with PAF and either rupatadine, levocetirizine, desloratadine, PAF receptor antagonists CV6209, BN52021 or WEB2086. Mast cell degranulation was evaluated using both β-hexosaminidase and histamine assays. Rupatadine inhibited LAD2 β-hexosaminidase release, but neither levocetirizine nor desloratadine showed any significant effect (Figure 2A). Interestingly, levocetirizine inhibited histamine release in LAD2, similar to rupatadine (Figure 2B). Finally, in lung mast cells, only rupatadine blocked mast cell degranulation. Among the PAF receptor antagonists, BN52021 and WEB2086 failed to show any inhibitory effect, whereas CV6209 inhibited mast cell degranulation (both histamine and β-hexosaminidase) in all the tested cell types. Finally, these authors suggest a comparable effect on inhibiting mast cell activation when comparing rupatadine and CV6209.
Kajiwara et al. [11] showed a similar activation pattern, but used a lower concentration of PAF (1nM vs. 10 µM in Muñoz-Cano et al.). The different cell types used (progenitor-derived mast cells vs. LAD2 or human lung mast cells) in the studies may account for those differences. Similar to the previous study, the compound CV6209 also demonstrated an inhibitory effect on PAF-induced histamine release.
Finally, Alvezios et al. [40] demonstrated the inhibitory effect of rupatadine on PAF-induced histamine and cytokine release using the LAD2 model. Those authors compared rupatadine with an old antihistamine with no PAF effect (diphenhydramine). Indeed, rupatadine, but not diphenhydramine, inhibited mast cell mediator release.
Several other antihistamines have also shown, in vitro, an anti-PAF effect including azelastine, oxatomide, ketotifen and epinastine. Shindo et al. showed that both azelastine [41] and oxatomide [42] inhibited PAF release in neutrophils obtained from either asthmatic patients and healthy individuals. Other authors have demonstrated that epinastine [43] and ketotifen [44] suppressed rabbit platelet aggregation induced by PAF at higher concentrations. Ketotifen also inhibited beta-hexosaminidase release from mouse mast cells derived from bone marrow [45].
In summary, PAF plays an important role in allergic rhinitis, and in contrast to the observation in asthma, blocking this mediator seems to improve rhinitis symptoms, and therefore may be considered a therapeutic target. However, PAF is only one of the several inflammatory mediators involved in allergic rhinitis. In our opinion, we propose that anti-PAF drugs may contribute to a better control of nasal symptoms, such as nasal congestion or rhinorrhea, compared to the use of antihistamines with no other anti-inflammatory properties. The in vivo studies using the only commercially available antihistamines with known anti-PAF activity, such as rupatadine [38], azelastine [46], ketotifen [47] or epinastine [48], have demonstrated their efficacy and safety as a daily treatment for allergic rhinitis. Among those, rupatadine is the only compound that has demonstrated their capacity for an inhibition of PAF release in nasal airways, in several in vitro and in vivo studies. This may suggest that PAF blockage may be usefully included in a strategy aimed at inhibiting as many mediators as possible. However, further clinical studies are needed with anti-PAF compounds in AR patients.
2.2. PAF in other Respiratory, Cutaneous and Allergic Diseases
2.2.1. PAF in Asthma
Current evidence suggests that PAF plays a role in the immune and inflammatory response in asthma. Several studies have shown that PAF, in bronchial challenge, induces bronchoconstriction and increases airway hyperreactivity [49]. Moreover, it has also been shown that PAF favors mucus production and increases vascular permeability of pulmonary blood vessels [50]. Interestingly, inhaled PAF stimulates the production of cysteinyl leukotrienes, and it is likely that the effects of PAF in the lungs may be mediated by some of these products [51]. PAF is produced in response to several pro-inflammatory stimulus, such as allergens but also during infections [12]. Increased PAF levels in sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage samples of asthmatics patients have been found during an asthma attack and after allergen challenge [52]. Interestingly, smooth muscle proliferation induced by salbutamol is mediated by PAF. Indeed, salbutamol induces PAF synthesis and inhibits its catabolism [53]. It has also been speculated that PAF may inhibit the response to beta-adrenergic agonists [54].
Furthermore, similar to anaphylaxis, PAF-AH levels inversely correlate with asthma severity in Japanese children; a missense mutation in the PAF-AH gene results in inactive PAF-AH and occurs in 4% of the Japanese population [51]. Stafforinie et al. found that a deficiency in PAF-AH may constitute a risk factor for the development of asthma and also asthma attacks, being the subjects with a complete deficiency, at risk of developing severe asthma [55].
Even though it is the suggested role of PAF in this disease, most PAF receptor inhibitors have failed to show any significant beneficial effect in asthma symptoms in humans [51]. Y-24180, a PAF receptor antagonist, improved bronchial hyperreactivity measured by methacholine. However, the randomized clinical trials failed to demonstrate its utility as a routine asthma treatment [51]. Another PAF antagonist, WEB2086, could not attenuate either the early or the late asthmatic response induced by an allergen. No effects on lung function, rescue medication or inhaled corticosteroids dose were observed [56]. Regrettably, several studies with different PAF antagonists had the same outcomes as the previously described, not showing sufficient beneficial effects for the regular treatment of asthmatic patients [51].
Considering that PAF-AH deficiency may be related to asthma and its severity, another interesting approach could be the administration of recombinant PAF-AH. Although promising results in the murine models and the pre-clinical studies showed a decrease of inflammation, PAF-AH failed to attenuate neither the early nor the late allergic response in mild asthma patients [57,58].
There is not only one inflammatory mediator involved in asthma, and therefore, strategies targeting PAF and other mediators as histamine have also been considered. Azelastine, oxatomide and epinastine, dual PAF and histamine antagonists, have shown a remarkable effect of blocking PAF-induced bronchoconstriction in guinea pigs and rats [59,60,61] and its use is approved for asthma patients in Japan as an add-on treatment [62]. Ketotifen, also included in the Japanese asthma guidelines [62], has shown to improve asthma control and wheezing in children with mild and moderate asthma [63]. Conversely, the studies with another dual antagonist, Sch37370, showed an effective blockage of the bronchospasm induced by histamine, PAF, antigen or serotonin, as well as antigen-induced eosinophilia, in guinea pigs [64]. However, as far as we know, no studies in humans have been performed. Finally, rupatadine has been successfully used in rhinitis and urticaria patients, but not in asthmatics [4,37].
In conclusion, despite the important role of PAF in asthma, the blockage of this mediator alone does not seem to have a significant effect on asthma symptoms. Considering the complex networks and signaling pathways involved in asthma pathogenesis, PAF seems to be just a downstream mediator. It may be, for this reason, that corticosteroids are still the first-line treatment, because of its capacity of blocking upstream signals, and therefore, creates the effect of multiple mediators on multiple cells types and tissues [65].
2.2.2. PAF in Chronic Urticaria and Food Allergy
Chronic urticaria (CU) is an inflammatory skin disorder, which is defined by recurrent itchy wheals, associated or not with angioedema, and would have been continuously or intermittently present for at least 6 weeks [66]. In most cases, chronic urticaria is related to idiopathic mechanisms, and in some cases, to immunological non-allergic and exceptionally to allergic mechanisms [66,67]. Mast cells are considered the most important cells in the pathogenesis of CU, and histamine is the predominant mediator [68]. However, other cell types such as basophils [69], and mediators such as cysteinyl leukotrienes, serotonin, TNF-α and PAF are also thought to play a part in urticaria [12,66,68]. PAF effects on urticaria seem to be related to the increase of vascular permeability, particularly in skin capillaries, enhancing the effect of other mediators and the development of wheals [12,21,70]. A recent study published in 2019 by Ullambayar et al. [71] has shown that patients with spontaneous CU have higher levels of PAF and lower levels of PAF-AH, the enzyme degrading PAF, in comparison to a group of healthy individuals. Those authors also compared a subgroup of CU patients who had not responded to antihistamines (up to fourfold) after 3 months, with a group of patients who were responding to the antihistamine. Interestingly, they found that non-responders had higher PAF levels and lower PAF-AH levels. Finally, a multivariate analysis showed that PAF serum levels >5000 pg/mL could be a significant predictor of a poor response to antihistamine treatment.
Another interesting result from the Ullambayar study was the inverse correlation found between PAF-AH and the urticaria duration [71]. This suggests that PAF-AH may be a part of a compensatory mechanism that could explain why there is a resolution of the symptoms in up to 50% of CU patients after 3 years of symptoms [72]. At some point, PAF-AH may increase enough to block the effect of PAF, reducing the PAF-related enhancement of histamine release and therefore resolving the urticaria symptoms. However, there is a need for studies to assess PAF-AH levels at different time points in CU patients, comparing those who achieve a symptom-free situation with those that are still symptomatic after 3 years.
Finally, a further interesting analysis in the Ullambayar study showed a positive correlation between triglyceride, total cholesterol and body mass index (BMI), and PAF-AH levels, only in the CU patients [71]. The active form of PAF-AH, also known lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, circulates as a complex with low-density lipoproteins (LDL) [5]. Plasma PAF-AH concentration has been shown to directly correlate with LDL levels in a cohort of 240 normolipidemic individuals [73]. This means that lowering LDL in plasma results in reduced levels of PAF-AH, and therefore, a longer half-life for PAF [73], that could increase the risk for severe anaphylaxis or, perhaps, other allergic reactions. This relationship between cholesterol metabolism and PAF has previously been described by Perelman [7] in a group of children who demonstrated peanut allergy. They studied 63 children between 2–19 years that had urticaria with or without angioedema related to peanuts, with positive skin tests (≥8 mm wheal) and/or peanut-specific IgE ≥ 14 kU/L. A strong correlation between PAF-AH and plasma concentration of Apoprotein B, considered as a good surrogate to measure LDL concentration [5], was found. However, no healthy individuals were used as a control, thereby limiting the interpretation of these results.
2.2.3. PAF in Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe, immediate, life-threatening reaction often related to allergic mechanisms, i.e., food, drug or insect allergy. There are no treatments to prevent these reactions, and only drugs for acute management are available [72]. Several mediators are released during an anaphylactic reaction from several cell types, although mast cells and basophils are the principal cells involved in those reactions [74]. Tryptase is protease mostly released by mast cells, widely used as a marker of mast cell activation and clonal expansion [75]. However, neither tryptase nor histamine correlates with the severity of anaphylactic reactions. Interestingly, Vadas et al. showed that PAF, compared to tryptase and histamine, correlates more accurately with anaphylaxis severity [76]. PAF is related to the increase of the vascular permeability; therefore, these authors compared PAF levels in patients who developed angioedema during anaphylaxis, with those that had hypotension, and found higher levels in the latter patients.
In 2008 Vadas et al. showed, for the first time, the positive correlation between anaphylaxis severity and PAF levels, and the negative correlation between severity and PAF-AH levels. The authors compared PAF and PAF-AH levels in patients with fatal peanut anaphylaxis, healthy controls (both adult and children), children with peanut allergy (urticaria/angioedema) at baseline, and non-fatal peanut acute anaphylaxis. Fatal anaphylaxis was related to the lowest PAF-AH levels, but there were no differences between the other groups. However, the number of patients with a decrease PAF-AH activity (≤20 nmol/mL/min) was higher in the anaphylaxis group, and most importantly, in grade 3 anaphylaxis individuals. Surprisingly, there is no data regarding PAF or PAF-AH levels at baseline in the anaphylaxis group. It could be that the patients with more severe anaphylaxis may have lower baseline levels of PAF-AH and this could thus be used as a biomarker. A study from Pravettoni et al. [77] addressed this matter in a group of patients allergic to hymenoptera venom. They found that basal PAF-AH levels inversely correlated with anaphylaxis grades, suggesting that PAF-AH levels may predict anaphylaxis severity in the future.
The relevance of PAF in anaphylaxis was demonstrated in a PAF receptor knockout (KO) mouse model [78]. PAFr KO mice suffered from less severe anaphylaxis, none of them fatal, compared to normal animals. The authors suggested that, among the different mediators involved in an anaphylaxis that includes histamine or eicosanoids, PAF has the most important role. Similarly, Kajiwara et al. [11] suggested that the relevance of PAF in anaphylaxis may be related to its capacity to amplify the allergic reaction (from local to systemic). Also using a mouse model, Jordana et al. showed that PAF antagonists significantly attenuated the magnitude and duration of the anaphylaxis [17]. However, neither histamine nor leukotriene blockage significantly affected any of those parameters. While 83% of PAF antagonist-treated mice recovered within 120 min after the peanut challenge, only 43% of the untreated ones did it, and 50% of the treated mice developed either no or mild anaphylactic reactions. Indeed, a greater protective effect was achieved when using a dual strategy, blocking histamine and PAF, compared to blocking PAF alone. The beneficial effect of a concomitant blockade of multiple mediators has previously been demonstrated by Brandt et al. [79], blocking PAF and serotonin in an ovalbumin-induced allergic diarrhea model. Actually, it was also observed in the Jordana et al. [17] model that combined therapy was associated with a significant decrease in vascular leakage and release of vasoactive mediators.
3. Conclusions
Compared to the research performed in asthma, PAF has been less studied in AR and its potential role as a therapeutic target is therefore less known. This lack of strong evidence, and the failure of PAF inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in asthma, may account for the lack of interest in performing studies with PAF inhibitors in AR. However, the failure of PAF inhibition in asthma does not necessarily correlate with a lack of efficacy in AR. Antihistamines are widely and effectively used in AR and are useless in asthma. So, despite the concept of “one airway, one disease” still being valid, some drugs may target the upper and the lower airways differently, and therefore, be useful in some diseases and not in others. Further research is needed in the field of AR, because it seems obvious that targeting more than one inflammatory mediator would provide a better control of the inflammation, and therefore, of the symptoms.
A summary of PAF actions, and PAF and PAF-AH profile in different diseases has been pictured in Table 1 and Figure 3, respectively.

Table 1.
PAF in allergic diseases.
Author Contributions
R.M.M.-C. wrote the manuscript while R.C.-S., P.R., I.B., A.V.S. and J.M. reviewed it and gave approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
R.M.M.-C. is a recipient of a Juan Rodes fellowship (JR16/00016), from Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias (FIS), Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCiii), Spain.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Benveniste, J. Platelet-activating factor, a new mediator of anaphylaxis and immune complex deposition from rabbit and human basophils. Nature 1974, 249, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindou, H.; Ishii, S.; Uozumi, N.; Shimizu, T. Roles of cytosolic phospholipase A(2) and platelet-activating factor receptor in the Ca-induced biosynthesis of PAF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 271, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, R.; Shindou, H.; Tarui, M.; Shimizu, T. Rapid production of platelet-activating factor is induced by protein kinase Cα-mediated phosphorylation of lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 2 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15566–15576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullol, J.; Bousquet, J.; Bachert, C.; Canonica, W.G.; Gimenez-Arnau, A.; Kowalski, M.L.; Martí-Guadaño, E.; Maurer, M.; Picado, C.; Scadding, G.; et al. Rupatadine in allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria. Allergy 2008, 63, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafforini, D.M. Biology of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH, lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2). Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2009, 23, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugatani, J.; Miwa, M.; Komiyama, Y.; Murakami, T. Quantitative analysis of platelet-activating factor in human plasma. Application to patients with liver cirrhosis and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 166, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, B.; Adil, A.; Vadas, P. Relationship between platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase activity and apolipoprotein B levels in patients with peanut allergy. Allergy Asthma. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadas, P.; Gold, M.; Perelman, B.; Liss, G.M.; Lack, G.; Blyth, T.; Simons, F.E.R.; Simons, K.J.; Cass, D.; Yeung, J. Platelet-activating factor, PAF acetylhydrolase, and severe anaphylaxis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braquet, P.; Rola-Pleszcynski, M. Platelet-activating factor and cellular immune responses. Immunol. Today 1987, 8, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.; Olson, M.S. Platelet-activating factor: Receptors and signal transduction. Biochem. J. 1993, 292 Pt 3, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiwara, N.; Sasaki, T.; Bradding, P.; Cruse, G.; Sagara, H.; Ohmori, K.; Saito, H.; Ra, C.; Okayama, Y. Activation of human mast cells through the platelet-activating factor receptor. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pałgan, K.; Bartuzi, Z. Platelet activating factor in allergies. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2015, 28, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Kita, H.; Tachibana, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Tsuchida, Y.; Kimura, H. Dual signaling and effector pathways mediate human eosinophil activation by platelet-activating factor. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 134, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giembycz, M.A.; Lynch, O.T.; De Souza, P.M.; Lindsay, M.A. Review: G-protein-coupled receptors on eosinophils. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 13, 195–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotner, G.Z.; Lynch, J.M.; Betz, S.J.; Henson, P.M. Human neutrophil-derived platelet activating factor. J. Immunol. 1980, 124, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, F.; Mancardi, D.A.; Zhao, W.; Kita, Y.; Iannascoli, B.; Khun, H.; van Rooijen, N.; Shimizu, T.; Schwartz, L.B.; Daëron, M.; et al. Human FcγRIIA induces anaphylactic and allergic reactions. Blood 2012, 119, 2533–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, K.; Baig, M.; Colangelo, M.; Chu, D.; Walker, T.; Goncharova, S.; Coyle, A.; Vadas, P.; Waserman, S.; Jordana, M. Concurrent blockade of platelet-activating factor and histamine prevents life-threatening peanut-induced anaphylactic reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, F.; Mancardi, D.A.; Kita, Y.; Karasuyama, H.; Iannascoli, B.; Van Rooijen, N.; Shimizu, T.; Daëron, M.; Bruhns, P. Mouse and human neutrophils induce anaphlaxis. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 1484–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, F.; de Chaisemartin, L.; Granger, V.; Gouel-Chéron, A.; Gillis, C.M.; Zhu, Q.; Dib, F.; Nicaise-Roland, P.; Ganneau, C.; Hurtado-Nedelec, M.; et al. An IgG-induced neutrophil activation pathway contributes to human drug-induced anaphylaxis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, A.; Palumbo, G.; Milazzo, N.; Miadonna, A. Nasal neutrophilia and eosinophilia induced by challenge with platelet activating factor. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 93, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, V. Role of histamine and platelet-activating factor in allergic rhinitis. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 60, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Cano, R.; Valero, A.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Bartra, J.; Sanchez-Lopez, J.; Mullol, J.; Picado, C. Platelet-activating factor nasal challenge induces nasal congestion and reduces nasal volume in both healthy volunteers and allergic rhinitis patients. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2013, 27, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touqui, L.; Herpin-Richard, N.; Gene, R.M.; Jullian, E.; Aljabi, D.; Hamberger, C.; Vargaftig, B.B.; Dessange, J.F. Excretion of platelet activating factor-acetylhydrolase and phospholipase A2 into nasal fluids after allergenic challenge: Possible role in the regulation of platelet activating factor release. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, C.E.; Foreman, J.C. The effect of platelet-activating factor on the responsiveness of the human nasal airway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 110, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggieri, E.; Tedeschi, A.; Lorini, M.; Bianco, A.; Miadonna, A. Study of the effects of paf-acether on human nasal airways. Allergy 1991, 46, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Cano, R.; Ainsua-Enrich, E.; Torres-Atencio, I.; Martin, M.; Sánchez-Lopez, J.; Bartra, J.; Picado, C.; Mullol, J.; Valero, A. Effects of Rupatadine on Platelet- Activating Factor–Induced Human Mast Cell Degranulation Compared With Desloratadine and Levocetirizine (The MASPAF Study). J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 27, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Roca-Ferrer, J.; Callejas, F.D.B.; Fuentes, M.; Pérez-González, M.; Alobid, I.; Muñoz-Cano, R.; Valero, A.; Izquierdo, I.; Mullol, J. Expression PAF receptor in cells and tissues from healthy and inflamed upper airway mucosa (Rinopaf-1 study). Allergy 2018, 73, 756. [Google Scholar]
- Klementsson, H.; Andersson, M. Eosinophil chemotactic activity of topical PAF on the human nasal mucosa. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992, 42, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocklin, R.E.; Thistle, L.; Audera, C. Decreased sensitivity of atopic mononuclear cells to prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and prostaglandin D2 (PGD2). J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 2033–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Benninger, M. Diagnosis and Management of Nasal Congestion: The Role of Intranasal Corticosteroids. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 121, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozek, J.L.; Bousquet, J.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Bonini, S.; Canonica, G.W.; Casale, T.B.; van Wijk, R.G.; Ohta, K.; Zuberbier, T.; Schünemann, H.J.; et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromer, L.M.; Ortiz, G.; Ryan, S.F.; Stoloff, S.W. Insights on allergic rhinitis from the patient perspective. J. Fam. Pract. 2012, 61, S16–S22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albert, D.H.; Malo, P.E.; Tapang, P.; Shaughnessy, T.K.; Morgan, D.W.; Wegner, C.D.; Curtin, M.L.; Sheppard, G.S.; Xu, L.; Davidsen, S.K.; et al. The role of platelet-activating factor (PAF) and the efficacy of ABT-491, a highly potent and selective PAF antagonist, in experimental allergic rhinitis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 284, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misawa, M.; Iwamura, S. Platelet-activating factor (PAF)-induced rhinitis and involvement of PAF in allergic rhinitis in guinea pigs. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 54, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queralt, M.; Merlos, M.; Giral, M.; Puigdement, A. Dual effect of rupatadine on enema induced by PAF and histamine in dogs: Comparison with antihistamines and PAF antagonists. Drug Dev. Res. 1996, 39, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlos, M.; Giral, M.; Balsa, D.; Ferrando, R.; Queralt, M.; Puigdemont, A.; Garcia-Rafanell, J.; Forn, J.; García-Rafanell, J.; Forn, J. Rupatadine, a new potent, orally active dual antagonist of histamine and platelet-activating factor (PAF). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González-Núñez, V.; Bachert, C.; Mullol, J. Rupatadine: Global safety evaluation in allergic rhinitis and urticaria. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullol, J.; Bousquet, J.; Bachert, C.; Canonica, G.W.; Giménez-Arnau, A.; Kowalski, M.L.; Simons, F.E.; Maurer, M.; Ryan, D.; Scadding, G. Update on rupatadine in the management of allergic disorders. Allergy 2015, 70, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Cano, R.; Valero, A.; Izquierdo, I.; Sánchez-López, J.; Doménech, A.; Bartra, J.; Mullol, J.; Picado, C. Evaluation of nasal symptoms induced by platelet activating factor, after nasal challenge in both healthy and allergic rhinitis subjects pretreated with rupatadine, levocetirizine or placebo in a cross-over design. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevizos, M.; Karagkouni, A.; Vasiadi, M.; Sismanopoulos, N.; Makris, M.; Kalogeromitros, D.; Theoharides, T.C. Rupatadine inhibits inflammatory mediator release from human laboratory of allergic diseases 2 cultured mast cells stimulated by platelet-activating factor. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, K.; Fukumura, M.; Hirai, Y.; Koide, K. Effect of azelastine hydrochloride on release and production of platelet activating factor in human neutrophils. Prostaglandins. Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 1997, 56, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, K.; Fukumura, M. Oxatomide inhibits synthesis and release of platelet-activating factor in human neutrophils. Prostaglandins. Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 1998, 58, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, C.; Mio, M.; Kitazumi, K.; Tsujimoto, S.; Yoshida, T.; Adachi, Y.; Tasaka, K. Antiallergic Effect of Epinastine (WAL 801 CL) on Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions: (II) Antagonistic Effect of Epinastine on Chemical Mediators, Mainly Antihistamine and Anti-PAF Effects. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 1992, 14, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devillier, P.; Arnoux, B.; Lalau Keraly, C.; Landes, A.; Marsac, J.; Benveniste, J. Inhibition of human and rabbit platelet activation by Ketotifen. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 1990, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, F.; Bessou, G.; Benveniste, J.; Ninio, E. Ketotifen inhibits paf-acether biosynthesis and β-hexosaminidase release in mouse mast cells stimulated with antigen. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1987, 144, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeely, W.; Wiseman, L.R. Intranasal Azelastine. Drugs 1998, 56, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S.M.; Goa, K.L.; Fitton, A.; Sorkin, E.M. Ketotifen. Drugs 1990, 40, 412–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, M.; Hashiguchi, K.; Okubo, K. Efficacy of Epinastine Hydrochloride for Antigen-Provoked Nasal Symptoms in Subjects with Orchard Grass Pollinosis. Allergol. Int. 2011, 60, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuitert, L.; Barnes, N. PAF and asthma—Time for an appraisal? Clin. Exp. Allergy 1995, 12, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuss, F.M.; Dixon, C.M.; Barnes, P.J. Effects of inhaled platelet activating factor on pulmonary function and bronchial responsiveness in man. Lancet (London, England) 1986, 2, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperska-Zajac, A.; Brzoza, Z.; Rogala, B. Platelet-activating factor (PAF): A review of its role in asthma and clinical efficacy of PAF antagonists in the disease therapy. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2008, 2, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan-Yeung, M.; Lam, S.; Chan, H.; Tse, K.S.; Salari, H. The release of platelet-activating factor into plasma during allergen-induced bronchoconstriction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 87, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, R.; Arteaga, A.; Raj, J.U.; Ibe, B.O. Albuterol isomers modulate platelet-activating factor synthesis and receptor signaling in human bronchial smooth muscle cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 158, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Bewtra, A.K.; Hopp, R.J.; Nair, N.; Townley, R.G. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic-receptor systems in bronchial asthma and in subjects without asthma: Reduced mononuclear cell beta-receptors in bronchial asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 86, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafforini, D.M.; Numao, T.; Tsodikov, A.; Vaitkus, D.; Fukuda, T.; Watanabe, N.; Fueki, N.; McIntyre, T.M.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Makino, S.; et al. Deficiency of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase is a severity factor for asthma. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 103, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitag, A.; Watson, R.M.; Matsos, G.; Eastwood, C.; O’Byrne, P.M. Effect of a platelet activating factor antagonist, WEB 2086, on allergen induced asthmatic responses. Thorax 1993, 48, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Henig, N.R.; Aitken, M.L.; Liu, M.C.; Yu, A.S.; Henderson, W.R. Effect of recombinant human platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, W.R.; Lu, J.; Poole, K.M.; Dietsch, G.N.; Chi, E.Y. Recombinant human platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase inhibits airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in mouse asthma model. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 3360–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaka, K.; Kamei, C.; Nakamura, S. Inhibitory effect of epinastine on bronchoconstriction induced by histamine, platelet activating factor and serotonin in guinea pigs and rats. Arzneimittelforschung 1994, 44, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pretolani, M.; Lefort, J.; Venco, C.; Perrisoud, D.; Vargaftig, B.B. Inhibition by azelastine of the effects of platelet-activating factor in lungs from actively sensitised guinea-pigs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 216, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijkamp, F.P.; Folkerts, G.; Beetens, J.R.; De Clerck, F. Suppression of PAF-induced bronchoconstriction in the guinea-pig by oxatomide: Mechanism of action. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 1989, 340, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinose, M.; Sugiura, H.; Nagase, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Inoue, H.; Sagara, H.; Tamaoki, J.; Tohda, Y.; Munakata, M.; Yamauchi, K.; et al. Japanese guidelines for adult asthma 2017. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, D.; Mitra, A.A.; Ducharme, F.M.; Forster, J.; Schwarzer, G. Ketotifen alone or as additional medication for long-term control of asthma and wheeze in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billah, M.M.; Egan, R.W.; Ganguly, A.K.; Green, M.J.; Kreutner, W.; Piwinski, J.J.; Siegel, M.I.; Villani, F.J.; Wong, J.K. Discovery and preliminary pharmacology of Sch 37370, a dual antagonist of PAF and histamine. Lipids 1991, 26, 1172–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Corticosteroids. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2016, 42, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Lang, D.M.; Khan, D.A.; Craig, T.; Dreyfus, D.; Hsieh, F.; Sheikh, J.; Weldon, D.; Zuraw, B.; Bernstein, D.I.; et al. The diagnosis and management of acute and chronic urticaria: 2014 update. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.P. Chronic urticaria: Pathogenesis and treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennino, A.; Bérard, F.; Guillot, I.; Saad, N.; Rozières, A.; Nicolas, J.-F. Pathophysiology of urticaria. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 30, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luquin, E.; Kaplan, A.P.; Ferrer, M. Increased responsiveness of basophils of patients with chronic urticaria to sera but hypo-responsiveness to other stimuli. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2005, 35, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spickett, G. Urticaria and angioedema. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2014, 44, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulambayar, B.; Yang, E.-M.; Cha, H.-Y.; Shin, Y.-S.; Park, H.-S.; Ye, Y.-M. Increased platelet activating factor levels in chronic spontaneous urticaria predicts refractoriness to antihistamine treatment: An observational study. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozel, M.M.; Mekkes, J.R.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Bos, J.D. Natural course of physical and chronic urticaria and angioedema in 220 patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caslake, M.J.; Packard, C.J.; Suckling, K.E.; Holmes, S.D.; Chamberlain, P.; Macphee, C.H. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2), platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase: A potential new risk factor for coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2000, 150, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.F.; Cotterell, C.; Isbister, G.K.; Holdgate, A.; Brown, S.G.A. Emergency Department Anaphylaxis Investigators Elevated serum cytokines during human anaphylaxis: Identification of potential mediators of acute allergic reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, U.R. Elevated baseline serum tryptase, mastocytosis and anaphylaxis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadas, P.; Perelman, B.; Liss, G. Platelet-activating factor, histamine, and tryptase levels in human anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pravettoni, V.; Piantanida, M.; Primavesi, L.; Forti, S.; Pastorello, E.A. Basal platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase: Prognostic marker of severe Hymenoptera venom anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Kuwaki, T.; Nagase, T.; Maki, K.; Tashiro, F.; Sunaga, S.; Cao, W.-H.; Kume, K.; Fukuchi, Y.; Ikuta, K.; et al. Impaired Anaphylactic Responses with Intact Sensitivity to Endotoxin in Mice Lacking a Platelet-activating Factor Receptor. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, E.B.; Strait, R.T.; Hershko, D.; Wang, Q.; Muntel, E.E.; Scribner, T.A.; Zimmermann, N.; Finkelman, F.D.; Rothenberg, M.E. Mast cells are required for experimental oral allergen-induced diarrhea. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 112, 1666–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).