Abstract
Claudin 1 is a small transmembrane protein responsible for maintaining the barrier function that exists between epithelial cells. A tight junction protein that regulates the paracellular transport of small ions across adjacent cells, claudin 1 maintains cellular polarity and plays a major role in cell-cell communication and epithelial cell homeostasis. Long considered to be a putative tumor suppressor in human breast cancer, new studies suggest a role much more complex. While most invasive breast cancers exhibit a down regulation or absence of claudin 1, some aggressive subtypes that exhibit high claudin 1 levels have now been described. Furthermore, a causal role for claudin 1 in breast cancer progression has recently been demonstrated in some breast cancer cell lines. In this review we highlight new insights into the role of claudin 1 in breast cancer, including its involvement in collective migration and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT).
1. Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women and the second leading cause of cancer death in women worldwide [1]. A difficulty in treating this disease is attributed to the heterogeneous nature of breast cancer, which can be classified into a growing number of molecular subtypes (10 to date), many poorly characterized [2]. Of these, the most characterized are the luminal A, luminal B, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) over expressing, the basal-like, and more recently, the claudin-low subtype [3]. Each subtype is defined by the presence/absence of unique molecular markers and exhibits unique prognostic features [4,5,6,7]. The luminal subtypes, luminal A and luminal B, express the estrogen receptor (ER) and are deemed ER positive (ER+). They are more differentiated and more responsive to hormonal treatment, and as such are less aggressive and have more favorable prognosis. Whereas estrogen receptor negative (ER−) tumors, the HER2 overexpressing, the basal-like and the “claudin low” are more aggressive and have less favorable outcomes. Yet still a further subgroup of breast cancer is the triple negative breast cancers (TNBC), of which there are now at least six types with unique characteristics identified to date [8]. In addition to being ER−, these tumors are progesterone receptor negative (PR−) and HER2− as well.
1.1. Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis
Metastasis of breast cancer to secondary sites in bone, liver, brain and lungs is largely incurable and is the principle cause of death in breast cancer patients [9,10,11,12]. It is a complex multistep process which involves the dissemination of cancer cells from the primary tumor mass to anatomically distant organs [13]. The metastatic cascade is a succession of cell-biological events that involve local invasion through the extracellular matrix and stroma cell layer, intravasation into the systemic circulation, survival during transportation through the vasculature, extravasation into distant tissues, establishment of micrometastasis in distant organs and finally colonization of these cells to form secondary tumors [14].
To achieve metastatic potential, a few cancer cells initially acquire the ability to evade and survive the homeostatic mechanisms of the organism. These cells are selected from the genetically heterogeneous lineages of cancer cells within the microenvironment of the tumor’s origin and continue to proliferate [15]. The continuous expansion of these rare tumor cells that express the genes necessary to initiate the metastatic cascade gives rise to clonal descendants that comprise the metastatic lesion [16,17].
1.2. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
As epithelial cells convert from the non-invasive to the invasive phenotype, cells become anchorage independent and exhibit enhanced motility as well as increased aggressiveness. Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) is thought to be a major mechanism for this conversion [16,18]. During EMT, epithelial cells acquire a mesenchymal-like phenotype via disruption of intercellular adhesion and resulting in enhanced motility (for review, [18,19,20]). Driving the EMT process are several transcription factors, such as Slug, Snail, Twist, Zeb1 and Zeb2 [20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Up regulation of these transcription factors may cause dysfunctional cell-cell adhesion and loss of cell-cell junctions, thereby allowing the dissemination of tumor cells from the primary sites [19]. While the mechanism for the induction of EMT has clearly shown repression of the junctional adhesion molecules such as E-cadherin, definitive involvement of the tight junction (TJ) proteins has not been demonstrated until recently [19,21]. Emerging evidence now show that TJ proteins as well, may also be key players in the EMT process in many cancers including breast cancer [27,28,29].
2. Tight Junction (TJ) Proteins: The Claudins
TJs form the closest contacts between adjacent cells along the apical border of the epithelial cell membrane [30]. They are comprised of a network of strands that encircle the cells, resulting in a barrier that separates apical and basolateral fluid compartments on opposite sides of the epithelial cell layer, thereby preventing paracellular movement of substances. This “paracellular seal” therefore, separates the extracellular fluid from the lumen (Figure 1). Additionally, TJs regulate the flow of nutrients and small ions between cells. They are also involved in maintaining the integrity and architecture of the cell and forms connections to the actin cytoskeleton [31,32]. A disruption of TJs during tumorigenesis generally leads to invasiveness, loss of cohesion, and lack of differentiation in cancer cells (for review, [33]).
The claudins are a family of integral membrane proteins (24 identified to date), central to the formation of TJs [34,35]. By regulating the passage of small ions and nutrients between cells, they maintain cell homeostasis and cell-cell communication [36]. Additionally, the claudins are critical for the maintenance of cellular polarity and are also involved in cellular growth and differentiation [37]. Several family members have been shown to be involved in cellular signaling [38,39]. Members of this family of proteins possess four transmembrane domains with two extracellular loops, with an amino and carboxyl terminal tail extending into the cytoplasm [39]. The extracellular loops are essential for maintaining TJ function and epithelial barrier integrity [40]. Moreover, the first extracellular loop of the claudin family has been identified as an important region of the protein for regulating paracellular ion permeability [41]. Variations in this first extracellular loop give rise to differences in the paracellular charge selectivity among members of the claudin family, whereas the C-terminus interacts with many signaling pathways and tight junction proteins through a PDZ domain. Through this domain, claudins interact with multiple TJ proteins [42,43]. The dysregulation of claudins in several cancers is now well documented (for review, [38,44,45,46,47,48,49]).
3. Claudin 1
Claudin 1, the first claudin family member identified, forms the backbone of the TJ strand [36,50]. Knockdown experiments of claudin 1 in mice have definitively demonstrated that it is essential for the epidermal barrier function [36]. The first extracellular loop possesses a key sequence motif capable of regulating TJ structure and function and is critical for epithelial barrier integrity [40]. As with all claudin family members, a PDZ binding domain is found within the intracellular C-terminal of the claudin 1 protein [39,51]. In claudin 1, this PDZ domain has been shown to interact with the zona occludins (ZO1 and ZO2), which connect to several signaling pathways. Interestingly, this domain in claudin 1 has been demonstrated to be important for and a target for different viral oncoproteins [52,53,54]. Further, the first extracellular loop of claudin 1 was shown to mediate uptake of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) [55], and more recently, the Dengue virus [56], thus identifying the claudin 1 protein as a receptor for viruses. Such a role has implications for claudin 1 as a potential target for antibody treatment of viral diseases, as well as in cancer therapy [57,58,59].
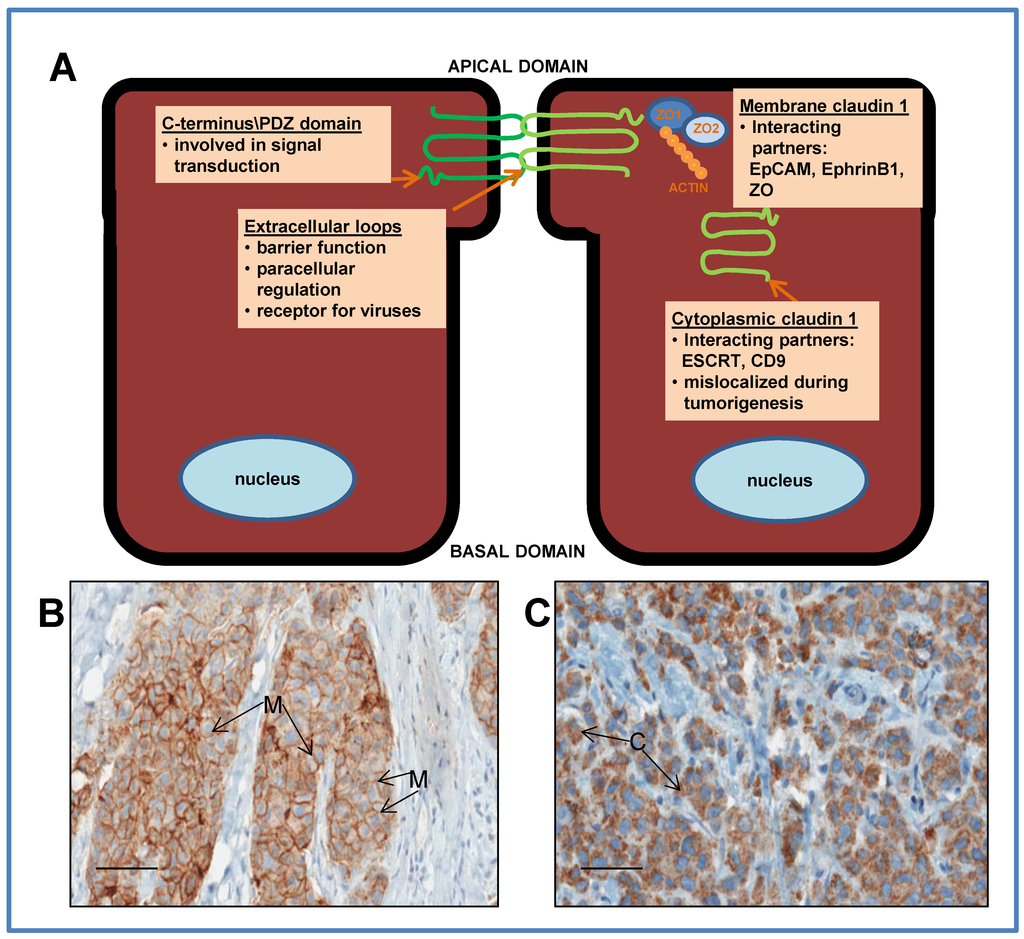
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of ductal epithelial cells, depicting the relative location and function of the claudin 1 protein in the membrane at the tight junction, and in the cytoplasm. The protein has 4 transmembrane domains with 2 extracellular loops with amino and carboxy terminal tails extending into the cytoplasm. The extracellular loops are essential for maintaining tight junction function, epithelial barrier integrity and regulating paracellular ion permeability. The C-terminus interacts with many signaling pathways through a PDZ domain. Through this domain, claudin 1 interacts with other tight junction proteins such as zona occludins (ZO). In addition to a tight junction function, membrane claudin 1 may act as a tumor facilitator by promoting collective migration during breast cancer progression; (B) Immunostaining of a breast tumor with claudin 1 antibody depicting membrane (M) staining and (C) depicting cytoplasmic (C) staining. Bars = 50 μm.
3.1. Dysregulation of Claudin 1 in Cancer
A dysregulation of claudin 1 in cancer has been well documented, and both a loss and gain has been associated with several cancers including oral, lung, prostate and gastric carcinoma as well as breast cancer [60,61,62,63,64,65]. In oral squamous cell carcinoma [44] and in breast cancer [61], the loss of claudin 1 has been associated with higher recurrence status and shorter disease free survival. In lung adenocarcinomas and hepatocellular carcinoma, enhanced invasiveness has also been demonstrated in association with claudin 1 loss [62,63]. In the latter, a down-regulation of claudin 1 has been associated with poor differentiation, portal invasion and low patient survival rates [63]. Conversely, the over expression of claudin 1 has been reported and was shown to increase cell invasion in colon [45,66,67], colorectal [68,69,70], oral squamous cell carcinoma [71] and melanoma [47]. Collectively, these studies provide evidence that claudin 1 can both promote or suppress tumorigenesis.
Interestingly, aberrant expression of claudin 1 has been observed not only in different cancers but in different histological subtypes of the same cancer. The over expression of claudin 1 in type II seropapillary endometroid carcinoma can distinguish it from type I which exhibits low claudin 1 expression [72].
3.2. A Putative Tumor Suppressor Role in Invasive Human Breast Cancer
Although not definitively proven, claudin 1 has long been postulated to be a tumor suppressor in breast cancer, as it was observed to be frequently down regulated or absent during disease progression. To lend further support to this hypothesis, a correlation between down regulation of claudin 1 and disease recurrence was also reported in a study involving 83 patients (57 patients with non-recurrent breast cancer and 26 patients with recurrent disease) [61]. More recently, in a much larger study using tissue microarray (TMA) strategies, Blanchard et al. [73], showed that only a small percentage of ER+ breast cancers were positive for claudin 1 whereas a significantly higher level of ER− tumors exhibited claudin 1 positivity. Further, in vitro studies showed that re-expression of claudin 1 alone was sufficient to induce apoptosis in a human breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB361 [74], and a loss of expression led to neoplastic transformation of mammary epithelial cells [75]. Claudin 1 has also been shown to be sufficient to exert TJ-mediated paracellular sealing in metastatic breast cancer cells in the absence of other TJ proteins [76].
There have been many speculations about the mechanisms responsible for claudin 1 loss in ER+ breast cancers. A search for mutations in the promoter or coding region of the claudin 1 gene has been futile as an explanation for the down regulation of claudin 1 in breast cancer [77]. Recent reports show that epigenetic factors, specifically transcriptional repression by methylation of the claudin 1 promoter near the CpG islands, may be partly responsible for claudin 1 down regulation [78,79]. As well, miRNA regulation may be another possible mechanism by which claudin 1 is deregulated in breast cancer. A down regulation of both claudin 1 mRNA and protein by miR-155 in ovarian cancer cells [80] was recently reported. Interestingly, miR-155 was found to be elevated in the blood of breast cancer patients and was associated with tumor progression [81,82]. It is therefore plausible that miR-155 may play a role in down regulating claudin 1 in breast cancer.
3.3. A Promoter of EMT, Cell Migration and Invasion
Claudin 1 involvement in EMT has also been well documented in several cancers [28,32]. Claudin 1 has been shown to have a causal role in EMT and malignant progression [32,45,66,83]. It has the ability to directly promote EMT through its interaction with defined EMT-related transcription factors and signaling pathways [23]. For example, in human liver cells, claudin 1 induced EMT through the activation of the transcription factors Slug and Zeb, which were regulated via the c-Abl/Raf/Ras/ERK signaling axis [32,84]. In colon cancer, modulation of β-catenin/Tcf signaling and E-cadherin expression and localization has been shown to play an important role in claudin 1-dependent regulation of EMT [85]. In breast cancer, a claudin-low subtype has been one of the more recent molecular subtypes identified. Claudin-low tumors characteristically exhibit low expression of claudins 1, 3, 4, and 7 [7,86], an up regulation of EMT markers and are enriched in stem-like cells [6,87]. In an earlier study, Sarrio et al. [88] suggested that in breast cancer, EMT likely occurs within a specific genetic context, the basal-like phenotype. In a large TMA study consisting of 479 patient biopsies, dysregulation of EMT markers, as well as an overexpression of proteins involved in extracellular matrix remodeling and invasion, was associated with the basal-like phenotype of breast cancers. In human breast cancer cell lines we have shown that either overexpression or inhibition of claudin 1 can alter the expression of EMT related molecules [27,89]. It has also been previously demonstrated that claudin 1 is a target for EMT markers, such as beta-catenin and Slug/Snail [90,91,92,93,94]. The latter, shown to bind to the E boxes in the claudin 1 promoter [23] and repress transcription. Recently, Hou et al. [95] further demonstrated that claudin 1 can also promote EMT in vivo. These authors showed that Stanniocalcin 2 (STC2) promoted breast cancer metastasis in mice through its interaction with claudin 1, which directly led to an alteration of the expression of the EMT molecules including Zeb1, Slug, and Twist [95].
3.4. Interaction with the Extracellular Matrix
The matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of zinc-dependent endopeptidases which can degrade and remodel the extracellular matrix (ECM) and its constitutive proteins, during both normal processes (such as morphogenesis and tissue repair), and pathological processes (such as the facilitation of cell migration and invasion) during EMT [96]. However, in the normal intestinal epithelium, independent of TJs, claudin 1 and 7 can form complexes with α2 integrin to regulate cell-matrix interactions and increase the expression of MMPs [97]. Claudin 1 interaction with the MMPs in the extracellular matrix also demonstrates its involvement in invasion and tumor progression. In cancer, claudin 1 increased cell motility and invasiveness through its deregulation of MMPs such as MMP1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 directly [71,98].
In breast cancer claudin 1 co-localized and directly interacted with membrane type MMP-1 and pro-MMP-2 and mediated its activation [98]. MMP-2 cleaved ECM proteins such as collagen I and collagen IV [96], as well as laminin-5 [71], by binding to integrin, an ECM receptor to facilitate cell invasion. This activation of MMPs by claudin 1 does not appear to be related to its TJ functions as the co-localization of claudin 1 with membrane type MMP-1 was not found at TJ strands but instead was located diffusely in the membrane and primarily in the cytoplasm [98].
This suggests a dual role for claudin 1 in its interactions with the ECM. Claudin 1 may form complexes with ECM proteins to stabilize cell-matrix interactions, and/or assist in the degradation of the ECM through MMPs during cell invasion.
4. New Insights into the Role of Claudin 1 in Breast Cancer
4.1. A Leading Role in Collective Migration
Both in vitro and in vivo studies reveal an emerging role for claudin 1 in breast cancer. The concept that there are two main patterns by which cancer cells migrate, collective migration or single cell migration, has been described several years ago, but the mechanisms are not well understood. Single cell migration, as the name implies, refers to the detachment of single epithelial cells from the tumor, and, facilitated by the acquisition of mesenchymal characteristics, then proceed to navigate through the ECM to metastasize to distal sites [11,99]. Collective cell migration, however, is characterized by the migration of whole groups of cells interconnected by adhesion molecules and other communication junction proteins [100]. This collection of cells then detaches from the tumor mass and penetrates into the surrounding tissues. During collective migration, the “group” is observed to have a “leading front” and utilizes integrins and proteases to facilitate migration. Strikingly, clear differences in gene expression exist between “leader” cells and “followers” [101,102,103]. Collective migration has now been demonstrated in several cancers, including breast cancer, and can occur through partial EMT mechanisms or can occur totally independently of EMT [102,104].
Claudin 1 plays a key role in facilitating the collective migration of tumor cells. Work by Giampieri et al. [102] showed the involvement of claudin 1 in migration was through partial EMT mechanisms. In rat mammary carcinoma, cancer cells displayed single cell migration under high transient expression of TGFβ, leading to blood-borne metastasis. However, following the inhibition of TGFβ expression, the cancer cells moved collectively and lead to lymphatic invasion. Importantly, it was also demonstrated that the expression of TGFβ was tightly regulated by claudin 1, such that, when claudin 1 levels were high, TGFβ expression was inhibited, leading to collective migration. More recently, Fortier et al. [105], showed that claudin 1 had the potential to induce collective migration, independent of EMT pathways. Using cervical carcinoma cells, they showed that knockdown of keratin (K8/18), a marker of epithelial cells, increased the collective migration and invasiveness of the cancer cells without modulating EMT markers. Once again, they identified claudin 1 as a major player in this process. They also observed that sub-confluent sheets of cells along the leading edge exhibited intense cytoplasmic and nuclear staining for claudin 1, while “follower cells” demonstrated a continuous membrane-staining pattern. As well, claudin 1 simultaneously exhibited high levels of expression in some cells while low levels of expression were observed in neighboring cells, depending on their position in the “pack”. Based on such positioning, it was proposed that cytoplasmic claudin 1 plays a role in cell motility, while junctional claudin 1 facilitates increased cell cohesion and consequently, and in so doing, facilitated collective cell migration.
4.2. More Than a Tumor Suppressor? “Claudin High” Breast Cancers
Despite the fact that many laboratories, including our own, suggest that claudin 1 is a tumor suppressor in invasive breast cancer, our studies also suggest that this is not the case for all breast cancers [83]. We have additionally shown that ER− tumors exhibited a significantly higher frequency of positivity for claudin 1, while ER+ tumors often exhibit very diminished or complete loss of claudin 1 expression [73]. Furthermore, we identified a significantly high association with claudin 1 and the basal-like subtype of breast cancers [73], an aggressive form of breast cancer, which to date remains poorly characterized [106]. In support of these observations, Lu et al. [86], also recently showed high levels of claudin 1 in the basal-like subtype. These authors also identified high claudin 1 levels in a small percentage of luminal and HER2 subtypes, further highlighting the heterogeneous nature of this disease and the need to better characterize molecular subtypes already identified. Moreover, we also showed that there was a positive relationship between high claudin 1 protein levels in the tumor and patient age [27]. However, we were unable to identify any significant association between claudin 1 levels and patient survival. Interestingly, increased levels of claudin 1 have also been reported for medullary and BRCA1-type breast cancers as well, and it was further proposed that claudin 1 expression can be used to discriminate mutation carriers from sporadic breast cancer cases [107], (Figure 2).
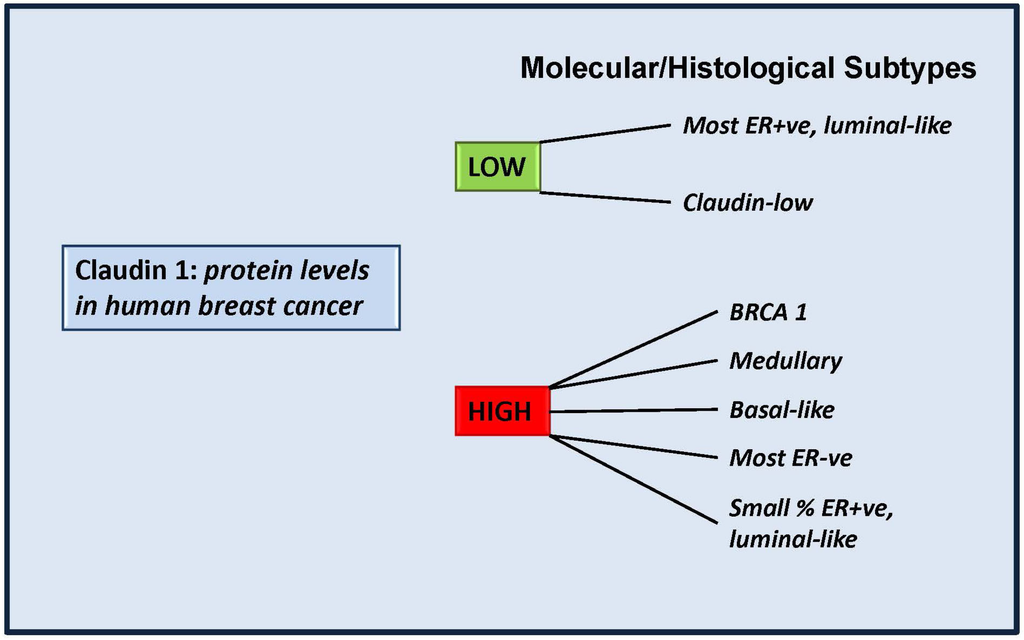
Figure 2.
Claudin 1 levels in molecular/histological subtypes of breast cancer. Some molecular subtypes of human invasive breast cancer have been shown to exhibit low levels of claudin 1, in line with studies which suggest claudin 1 plays a tumor suppressor role in those tumors. However some aggressive forms exhibit high endogenous levels of claudin 1 and it is still to be determined whether in these tumors, claudin 1 is playing a tumor-facilitating role. BRCA1: a hereditary breast cancer. Patients carry a mutation of the breast cancer 1 (BRCA1) gene. Medullary: a subset of basal-like carcinomas that exhibit a high rate of p53 mutations [108].
Indeed it could be speculated that the high levels of claudin 1 observed in breast cancer may be attributed to a “bystander effect” and do not contribute or participate in tumorigenesis. However a direct role for claudin 1 in altering the migration and proliferation rates of several human breast cancer cell lines, has now been demonstrated [27,89]. In particular, we showed that the knockdown of claudin 1 in a basal-like subtype human breast cancer cell line, resulted in reduced cancer cell migration [27]. Thus, the high levels of claudin 1 expression in some basal-like breast cancers has led to further speculations that claudin 1 may be a tumor-facilitator in this breast cancer subtype [83], as has been shown for claudin 1 in melanomas, colon cancer, and oral squamous cell carcinomas [45,47,66,67,71]. Further support for such speculations comes from studies by Suh et al. [32], who recently demonstrated that in hepatic carcinoma cells claudin 1 directly participated in the molecular signaling that contributes to tumor malignancy. This may also be the case in breast cancer.
4.3. Cytoplasmic Mislocalization in Breast Cancer
The appropriate subcellular localization of proteins is essential in providing a physiological context to their function. However, subcellular mislocalization of membrane proteins can often occur at the onset and progression of various human cancers. The mislocalization of claudin 1 to the cytoplasm, has been observed in several cancers [27,28,45,47,73,109,110]. For example, in colon, oral squamous cancer and melanomas, the subcellular localization of claudin 1 in cytoplasm has been associated with tumor progression [45,47,66,67,71]. Cytoplasmic localization was found to enhance tumor progression and the metastatic potential of the cancer cells. Interestingly, in melanoma, when claudin 1 was found in the nucleus it appeared to have no impact on invasion and metastasis [47].
It was hypothesized that the PDZ-binding motif within the C-terminal was the structural component of claudins integral to their correct localization. However, this was shown not to be the case as it was demonstrated that claudin 1 mutants bearing a mutated PDZ binding domain, were still incorporated into apical TJs [111]. However, the removal of the entire C-terminal tail resulted in its mislocalization to the cytoplasm, suggesting that it was the cytoplasmic juxta membrane region, not the PDZ-binding domain, that was structurally essential for claudin 1 localization to the TJ [111]. Moreover, it was determined that the carboxyl-terminal region contained numerous phosphorylation sites that may contribute to that process [28]. Mimicking constitutive phosphorylation at Protein Kinase A (PKA)/Protein Kinase C (PKC) sites, was shown to cause cytoplasmic claudin 1 localization [112].
4.4. Interaction with Unique Subcellular Partners
Recently, a number of claudin 1 interacting proteins have been identified that may play a direct role in the amount, function and subcellular localization of claudin 1 in breast cancer (Table 1).

Table 1.
Putative interacting partners of claudin 1 in breast cancer.
| Protein | Description | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ephrin B1 | A transmembrane protein involved in intrinsic cell signaling | Membrane | [113,114] |
| ESCRT | Required for proper protein transport and maintenance of epithelial cell polarity | Cytoplasm | [115] |
| CD9 | A transmembrane protein that plays a role in cell fusion and invasion | Membrane | [116] |
| EpCAM | A transmembrane surface glycoprotein | Membrane | [117] |
Ephrins: The Ephrin (Eph) family receptors (protein tyrosine kinases), and its ligands can induce bidirectional signaling in epithelial cells via cell-cell contact [118]. Claudin 1 has been shown to have a unique relationship with Ephrin B1 [114], a transmembrane protein involved in intrinsic cell signaling [118]. The extracellular domains of claudin 1 have been shown to facilitate the phosphorylation of Ephrin B1 interaction through binding of both domains to Ephrin B1 resulting in cell-cell contact. This interaction with claudin 1 mediates the tyrosine phosphorylation of Ephrin B1 in its cytoplasmic region in a manner dependent on claudin 1. The phosphorylation of Ephrin B1 further mediates cell migration and invasion through the downstream exocytosis of matrix metalloproteinases ultimately leading to changes in levels of cell-cell adhesion [118]. Interestingly, interrogation of the claudin 1 amino acid sequence has revealed conserved Eph phosphorylation sites [113], which indicates that the claudins in turn may also be phosphorylated by members of the Eph family, revealing that the relationship between claudin 1 and the Ephrin family may not be as straightforward as it first appears. Moreover, it has been observed that Eph receptors are frequently overexpressed in cancerous tissues [119]. Understanding the interactions of the Eph family, their ligands and claudin 1 will be an important novel area of study with regards to breast cancer progression.
The ESCRT machinery: It has been shown that the intracellular accumulation of claudin 1 can occur as a result of defective interactions with the Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport (ESCRT) machinery, a collection of cytosolic proteins required for proper protein transport and maintenance of epithelial cell polarity [120]. ESCRT aids in maintaining cell polarity by regulating the recycling and trafficking of membrane-bound proteins, including claudin 1, via endocytic mechanisms [115]. Thus, ESCRT plays an important role in claudin 1 transport to the membrane. Inhibition of ESCRT function causes claudin 1 to accumulate in the cytoplasm. This leads to weakening and disassembly of TJs and loss of cellular polarity. In epithelial cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma and pancreatic tumors, components of ESCRT show reduced expression [115]. Moreover, loss of ESCRT function in cancer cells has been associated with increased proliferation, together with the acquisition of a less stable tissue architecture [115], two of the key features acquired by tumor cells [121]. Such observations suggest that ESCRT may facilitate the tumor-suppressive role of claudin 1 in breast cancer.
CD9: The tetraspanin CD9 has recently been identified as an interacting partner of claudin 1. Claudin 1 is one of a few known interacting partners of CD9. Tetraspanins are transmembrane proteins that typically reside on cell surface and do not generally function as ligands or receptors [116]. Rather, they assemble themselves with other proteins to form microdomains [122,123,124,125]. Tetraspanins act to regulate cell fusion, invasion, migration and differentiation [126].
In breast cancer, the interaction of claudin 1 with CD9 has been shown to coincide with its subcellular co-localization in breast cancer. This has now been demonstrated in multiple cell lines, including the human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB231 (basal-like subtype) and MCF7 (luminal A subtype) [116]. Interestingly, CD9-claudin-complexes do not appear to reside in TJs, but rather in the cytoplasm and may be indicative of a role for claudin 1 other than that of a TJ protein. CD9 was shown to have a destabilizing effect on claudin 1. Depletion of CD9 diminished the half-life of non-junctional claudin 1 by approximately 50% [116]. It has also been suggested that CD9 prevents claudin 1 from associating with the TJ [116]. This could indeed reflect a normal regulating process, or is a contributing factor to the increased EMT and consequently migration that results from TJ disruption. If indeed CD9 prevents claudin 1 from associating with the TJ, then this could promote tumor progression. In support of such a hypothesis, it has been shown that the over expression of CD9 in human breast cancer promotes the development of bone metastases [127].
EpCAM: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), also known as CD326, is a transmembrane surface glycoprotein found expressed in epithelia and some invasive carcinomas [128]. EpCAM is generally localized to the lateral interfaces of polarized epithelial cells, but does not co-localize with TJs [117]. EpCAM exhibits pro-oncogenic activity, by promoting cell proliferation and motility and metastasis [129]. As a result, the therapeutic potential of EpCAM antibodies is being actively explored.
EpCAM has recently been shown to play an important role in regulating the composition and function of TJs through specific interaction with claudin 1. Wu et al. [117] recently demonstrated a physical interaction between claudin 1 and EpCAM in epithelial cells. They showed that this relationship protected claudin 1, which is continually trafficked from the membrane to the lysosome, from degradation and regulates its amount and function in the cell. Moreover, this physical contact was shown as necessary for the stabilization of claudin 1. The importance of such interfacing was further highlighted by experiments, which demonstrated that knocking down EpCAM in cancer cells resulted in increased overall TJs in the membrane and diminished intercellular claudin 1. An interaction between EpCAM and claudin 1 has not yet been demonstrated in breast cancer but a similar interaction may account for one of the mechanisms by which high levels of claudin 1 accumulate in the cytoplasm of some aggressive breast cancer cell lines and tumors, and warrants further investigation.
5. Future Perspectives
The void in our knowledge about the ever-emerging breast cancer molecular subtypes presents an insurmountable challenge to finding effective strategies for managing this disease. In the healthy mammary gland, TJ permeability can be reproduced readily in response to a number of physiological stimuli [130], and thus tight regulation of cell permeability is critical for maintaining homeostasis. Enhancing our understanding of the regulation of TJ permeability, or lack of it thereof, in pathological states is critical. Indeed, research into the development of approaches to modulate barrier function for efficient drug delivery continues to receive much attention [131], as dysregulation of the claudin family of TJ proteins leads to tumor progression [33,132].
The loss of cell-cell adhesion is a crucial step in EMT, and thus strategies to overcome the altered expression of TJ proteins in cancerous tissues are attractive as they could eventually lead to the development of effective therapeutic management for treating and possibly preventing human cancers.
Claudin 1 is of particular interest in the quest to identify new targets for breast cancer therapy as, (1) increasingly it has been shown to have direct involvement in the migration and proliferation rates in several cancers, including breast [44,45,47,112] and (2), it is a receptor, and thus, a port of entry for viruses [55,133]. Recently the HCV gene E2 was shown to be mainly involved in viral entry into the host via claudin 1 [134]. Such knowledge of this interaction between host cell surface receptors and viral factors may offer new therapeutic options in patients with aggressive tumors that exhibit high claudin 1 levels. Furthermore, it has been suggested that the identification of a critical claudin 1 extracellular loop motif (claudin-1 53–80) [40], capable of regulating TJ structure and function, may offer a useful adjunct to treatment that require drug delivery across the epithelial barrier.
As well, the pattern of expression of claudin 1 in different molecular subtypes indicates that claudin 1 may be a useful biomarker for the detection, diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer and may also serve as a tool for predicting disease progression. [27,73]. It has recently been shown that when claudin 1 was used in conjunction with four other markers, this cohort of markers was a useful predictive indicator for breast cancer patients [135], suggesting it may have utility as a potential biomarker for breast cancer. Decreased claudin 1 expression is positively correlated with frequency of recurrence and shorter disease-free intervals in breast cancer [61]. High claudin 1 levels have also been shown to be associated with some aggressive forms of breast cancers, including inflammatory breast cancers, hereditary breast cancer, some high grade invasive ductal carcinoma [86] and the basal-like subtypes. Collectively, these observations suggest the potential value of claudin 1 in identifying specific groups of breast cancer patients and present new opportunities for developing effective therapeutic strategies for managing breast cancer.
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by the Canadian Breast Cancer Foundation (Prairies-NWT). The authors thank Molly Pind for reading and editing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Canadian Cancer Society, Canadian Cancer Statistics 2014. Available online: http://www.cancer.ca (accessed on 15 November 2014).
- Curtis, C.; Shah, S.P.; Chin, S.F.; Turashvili, G.; Rueda, O.M.; Dunning, M.J.; Speed, D.; Lynch, A.G.; Samarajiwa, S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 2012, 486, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitt, S.J. Classification and prognosis of invasive breast cancer: From morphology to molecular taxonomy. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, S60–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sorlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de, R.M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorlie, T.; Perou, C.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Aas, T.; Geisler, S.; Johnsen, H.; Hastie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10869–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prat, A.; Parker, J.S.; Karginova, O.; Fan, C.; Livasy, C.; Herschkowitz, J.I.; He, X.; Perou, C.M. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herschkowitz, J.I.; Simin, K.; Weigman, V.J.; Mikaelian, I.; Usary, J.; Hu, Z.; Rasmussen, K.E.; Jones, L.P.; Assefnia, S.; Chandrasekharan, S.; et al. Identification of conserved gene expression features between murine mammary carcinoma models and human breast tumors. Genome Biol. 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Sarrio, D.; Honrado, E.; Hardisson, D.; Calero, F.; Benitez, J.; Palacios, J. Prognostic significance of basal-like phenotype and fascin expression in node-negative invasive breast carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimann, R.; Lan, F.; McBride, R.; Hellman, S. Separating favorable from unfavorable prognostic markers in breast cancer: The role of E-cadherin. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weigelt, B.; Peterse, J.L.; vanʼt Veer, L.J. Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Sosnoski, D.M.; Mastro, A.M. Breast cancer metastasis to the bone: Mechanisms of bone loss. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlen, P.; Puisieux, A. Metastasis: A question of life or death. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.F.; Groom, A.C.; MacDonald, I.C. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.P.; Massagué, J. Cancer metastasis: Building a framework. Cell 2006, 127, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, I.J. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: The “seed and soil” hypothesis revisited. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, I.J.; Talmadge, J.E. Evidence that intravenously derived murine pulmonary melanoma metastases can originate from the expansion of a single tumor cell. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 5167–5171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumour invasion. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, M.; Rubino, B.; Ballabio, G. The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology. Pathology 2007, 39, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinos, M.I.; Wafai, R.; Wong, M.K.; Newgreen, D.F.; Thompson, E.W.; Waltham, M. Vimentin and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer—Observations in vitro and in vivo. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 185, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, D.; Niu, G.; Huber, P.; Carter, W.B. Tumor-induced upregulation of twist, snail, and slug represses the activity of the human ve-cadherin promoter. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 482, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Estrada, O.M.; Culleres, A.; Soriano, F.X.; Peinado, H.; Bolos, V.; Martinez, F.O.; Reina, M.; Cano, A.; Fabre, M.; Vilaro, S. The transcription factors slug and snail act as repressors of claudin-1 expression in epithelial cells. Biochem. J. 2006, 394, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironchik, Y.; Winnard, P.T.; Vesuna, F.; Kato, Y.; Wildes, F.; Pathak, A.P.; Kominsky, S.; Artemov, D.; Bhujwalla, Z.; Van Diest, P.; et al. Twist overexpression induces in vivo angiogenesis and correlates with chromosomal instability in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10801–10809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, S.E.; Perez, D.; Pan, T.-C.; Sarkisian, C.J.; Portocarrero, C.P.; Sterner, C.J.; Notorfrancesco, K.L.; Cardiff, R.D.; Chodosh, L.A. The transcriptional repressor snail promotes mammary tumor recurrence. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Mani, S.A.; Donaher, J.L.; Ramaswamy, S.; Itzykson, R.A.; Come, C.; Savagner, P.; Gitelman, I.; Richardson, A.; Weinberg, R.A. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 2004, 117, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, A.A.; Ma, X.; Dueck, K.J.; Penner, C.; Cooper, S.C.; Mulhall, D.; Murphy, L.C.; Leygue, E.; Myal, Y. Claudin 1 expression in basal-like breast cancer is related to patient age. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.J. Emerging roles of claudins in human cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18148–18180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zou, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhao, G.; Gray, H.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Yue, J. Lentiviral vector mediated claudin1 silencing inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Viruses 2015, 7, 2965–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.M.; Balda, M.S.; Fanning, A.S. The structure and regulation of tight junctions. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 1993, 5, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartsock, A.; Nelson, W.J. Adherens and tight junctions: Structure, function and connections to the actin cytoskeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, Y.; Yoon, C.H.; Kim, R.K.; Lim, E.J.; Oh, Y.S.; Hwang, S.G.; An, S.; Yoon, G.; Gye, M.C.; Yi, J.M.; et al. Claudin-1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of the c-Abl-ERK signaling pathway in human liver cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4873–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leech, A.O.; Cruz, R.G.; Hill, A.D.; Hopkins, A.M. Paradigms lost—An emerging role for over-expression of tight junction adhesion proteins in cancer pathogenesis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero-Esparza, A.; Jiang, W.G.; Martin, T.A. The claudin family and its role in cancer and metastasis. Front. Biosci. (Landmark. Ed.) 2011, 16, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales-Mariscal, L. Tight Junctions, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Furuse, M.; Hata, M.; Furuse, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Haratake, A.; Sugitani, Y.; Noda, T.; Kubo, A.; Tsukita, S. Claudin-based tight junctions are crucial for the mammalian epidermal barrier: A lesson from claudin-1-deficient mice. J. Cell. Biol. 2002, 156, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, P.J. Claudin proteins in human cancer: Promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9603–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, K.J.; Agarwal, R.; Morin, P.J. The claudin gene family: Expression in normal and neoplastic tissues. BMC Cancer 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, K.; Furuse, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Tsukita, S. Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain protein components of tight junction strands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrsny, R.J.; Brown, G.T.; Gerner-Smidt, K.; Buret, A.G.; Meddings, J.B.; Quan, C.; Koval, M.; Nusrat, A. A key claudin extracellular loop domain is critical for epithelial barrier integrity. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colegio, O.R.; Van Itallie, C.; Rahner, C.; Anderson, J.M. Claudin extracellular domains determine paracellular charge selectivity and resistance but not tight junction fibril architecture. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 284, C1346–C1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, M.; Furuse, M.; Morita, K.; Kubota, K.; Saitou, M.; Tsukita, S. Direct binding of three tight junction-associated maguks, zo-1, zo-2, and zo-3, with the cooh termini of claudins. J. Cell. Biol. 1999, 147, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahraoui, A.; Louvard, D.; Galli, T. Tight junction, a platform for trafficking and signaling protein complexes. J. Cell. Biol. 2000, 151, F31–F36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Mori, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, Z.; Olaru, A.V.; Hamilton, J.P.; David, S.; Selaru, F.M.; Yang, J.; Abraham, J.M.; et al. Silencing of claudin-11 is associated with increased invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B.; Deane, N.G.; No, Y.; Shiou, S.-R.; Schmidt, C.; Neff, J.; Washington, M.K.; Beauchamp, R.D. Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Argani, P.; Korz, D.; Evron, E.; Raman, V.; Garrett, E.; Rein, A.; Sauter, G.; Kallioniemi, O.-P.; Sukumar, S. Loss of the tight junction protein claudin-7 correlates with histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2021–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leotlela, P.D.; Wade, M.S.; Duray, P.H.; Rhode, M.J.; Brown, H.F.; Rosenthal, D.T.; Dissanayake, S.K.; Earley, R.; Indig, F.E.; Nickoloff, B.J.; et al. Claudin-1 overexpression in melanoma is regulated by pkc and contributes to melanoma cell motility. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3846–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michl, P.; Barth, C.; Buchholz, M.; Lerch, M.M.; Rolke, M.; Holzmann, K.H.; Menke, A.; Fensterer, H.; Giehl, K.; Lohr, M.; et al. Claudin-4 expression decreases invasiveness and metastatic potential of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6265–6271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.B.; Dhawan, P. Claudins and cancer: Fall of the soldiers entrusted to protect the gate and keep the barrier intact. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 42, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M. Claudin-based barrier in simple and stratified cellular sheets. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2002, 14, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamazaki, Y.; Itoh, M.; Sasaki, H.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Multi-PDZ domain protein 1 (MUPP1) is concentrated at tight junctions through its possible interaction with claudin-1 and junctional adhesion molecule. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, I.J.; Roh, M.H.; Frese, K.K.; Weiss, R.S.; Margolis, B.; Javier, R.T. Viral oncoprotein-induced mislocalization of select PDZ proteins disrupts tight junctions and causes polarity defects in epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4283–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunbhakdi-Craig, V.; Craig, L.; Machleidt, T.; Sontag, E. Simian virus 40 small tumor antigen induces deregulation of the actin cytoskeleton and tight junctions in kidney epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2807–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, M.; Sakurai, M.; Higuchi, M.; Mori, N.; Fukushi, M.; Oie, M.; Coffey, R.J.; Yoshiura, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Uchiyama, M.; et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein induces and interacts with a multi-PDZ domain protein, MAGI-3. Virology 2004, 320, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.J.; von Hahn, T.; Tscherne, D.M.; Syder, A.J.; Panis, M.; Wölk, B.; Hatziioannou, T.; McKeating, J.A.; Bieniasz, P.D.; Rice, C.M. Claudin-1 is a hepatitis c virus co-receptor required for a late step in entry. Nature 2007, 446, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, P.; Tang, H.; Li, Q. The interaction between claudin-1 and dengue viral prM/M protein for its entry. Virology 2013, 446, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offner, S.; Hekele, A.; Teichmann, U.; Weinberger, S.; Gross, S.; Kufer, P.; Itin, C.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Kohleisen, B. Epithelial tight junction proteins as potential antibody targets for pancarcinoma therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2005, 54, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayrolles-Torro, A.; Vezzio-Vie, N.; Denis, V.; Boissiere-Michot, F.; Garambois, V.; Busson, M.; Ait Arsa, I.; Mollevi, C.; Pugniere, M.; Bibeau, F.; et al. Abstract b245: Claudin-1 (CLDN1) as a new therapeutic target in colorectal cancer: Inhibition of cell growth and survival by an anti-CLDN1 monoclonal antibody. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fofana, I.; Krieger, S.E.; Grunert, F.; Glauben, S.; Xiao, F.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Soulier, E.; Royer, C.; Thumann, C.; Mee, C.J.; et al. Monoclonal anti-claudin 1 antibodies prevent hepatitis C virus infection of primary human hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kusumi, T.; Sato, F.; Kawasaki, H.; Shibata, S.; Ohashi, M.; Hakamada, K.; Sasaki, M.; Kijima, H. Decreased expression of claudin-1 is correlated with recurrence status in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Res. 2008, 29, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohashi, S.; Kusumi, T.; Sato, F.; Odagiri, H.; Chiba, H.; Yoshihara, S.; Hakamada, K.; Sasaki, M.; Kijima, H. Decreased expression of claudin-1 correlates with recurrence status in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Y.C.; Pan, S.H.; Yang, S.C.; Yu, S.L.; Che, T.F.; Lin, C.W.; Tsai, M.S.; Chang, G.C.; Wu, C.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; et al. Claudin-1 is a metastasis suppressor and correlates with clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Sakaguchi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Baba, S.; Reinecker, H.-C.; Nakamura, S.; Konno, H. Loss of claudin-1 expression correlates with malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 139, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, T.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Murata, M.; Son, S.; Imamura, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Osanai, M.; Chiba, H.; Himi, T.; et al. Transforming growth factor-β induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition by down-regulation of claudin-1 expression and the fence function in adult rat hepatocytes. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soini, Y.; Tommola, S.; Helin, H.; Martikainen, P. Claudins 1, 3, 4 and 5 in gastric carcinoma, loss of claudin expression associates with the diffuse subtype. Virchows Arch. 2006, 448, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, J.L.; Ahmad, R.; Bhat, A.A.; Washington, M.K.; Singh, A.B.; Dhawan, P. Claudin-1 overexpression in intestinal epithelial cells enhances susceptibility to adenamatous polyposis coli-mediated colon tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takehara, M.; Nishimura, T.; Mima, S.; Hoshino, T.; Mizushima, T. Effect of claudin expression on paracellular permeability, migration and invasion of colonic cancer cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, S.S.; de Oliveira, I.M.; de Souza, W.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A. Claudins upregulation in human colorectal cancer. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 6179–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinugasa, T.; Huo, Q.U.N.; Higashi, D.; Shibaguchi, H.; Kuroki, M.; Tanaka, T.; Futami, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Hachimine, K.E.N.; Maekawa, S.; et al. Selective up-regulation of claudin-1 and claudin-2 in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3729–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, N.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S.; Niikawa, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Furukawa, Y. Involvement of claudin-1 in the β-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway and its frequent upregulation in human colorectal cancers. Oncol. Res. 2001, 12, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oku, N.; Sasabe, E.; Ueta, E.; Yamamoto, T.; Osaki, T. Tight junction protein claudin-1 enhances the invasive activity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by promoting cleavage of laminin-5 gamma2 chain via matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and membrane-type MMP-1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5251–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, G.; Nemeth, J.; Kiss, A.; Lotz, G.; Szabo, I.; Udvarhelyi, N.; Schaff, Z.; Paska, C. Claudin 1 differentiates endometrioid and serous papillary endometrial adenocarcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 103, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, A.A.; Skliris, G.P.; Watson, P.H.; Murphy, L.C.; Penner, C.; Tomes, L.; Young, T.L.; Leygue, E.; Myal, Y. Claudins 1, 3, and 4 protein expression in er negative breast cancer correlates with markers of the basal phenotype. Virchows Arch.: Int. J. Pathol. 2009, 454, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoevel, T.; Macek, R.; Swisshelm, K.; Kubbies, M. Reexpression of the TJ protein CLDN1 induces apoptosis in breast tumor spheroids. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulawiec, M.; Safina, A.; Desouki, M.M.; Still, I.; Matsui, S.I.; Bakin, A.; Singh, K.K. Tumorigenic transformation of human breast epithelial cells induced by mitochondrial DNA depletion. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoevel, T.; Macek, R.; Mundigl, O.; Swisshelm, K.; Kubbies, M. Expression and targeting of the tight junction protein CLDN1 in CLDN1-negative human breast tumor cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 191, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, F.; White, K.; Kubbies, M.; Swisshelm, K.; Weber, B.H. Genomic organization of claudin-1 and its assessment in hereditary and sporadic breast cancer. Hum. Genet. 2000, 107, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Cello, F.; Cope, L.; Li, H.; Jeschke, J.; Wang, W.; Baylin, S.B.; Zahnow, C.A. Methylation of the claudin 1 promoter is associated with loss of expression in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myal, Y.B.A. Tight junctions in cancer: Multifaceted players in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. In Tight Junctions in Cancer Metastasis; Martin, T., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, W.; Ren, Q.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Microrna-155 is a novel suppressor of ovarian cancer-initiating cells that targets CLDN1. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Analysis of miR-205 and miR-155 expression in the blood of breast cancer patients. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 25, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roth, C.; Rack, B.; Muller, V.; Janni, W.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating micrornas as blood-based markers for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myal, Y.; Leygue, E.; Blanchard, A.A. Claudin 1 in breast tumorigenesis: Revelation of a possible novel “claudin high” subset of breast cancers. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebbing, J.; Filipovic, A.; Giamas, G. Claudin-1 as a promoter of emt in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4871–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.B.; Sharma, A.; Smith, J.J.; Krishnan, M.; Chen, X.; Eschrich, S.; Washington, M.K.; Yeatman, T.J.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Dhawan, P. Claudin-1 up-regulates the repressor ZEB-1 to inhibit E-cadherin expression in colon cancer cells. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 2140–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Singh, K.; Mangray, S.; Tavares, R.; Noble, L.; Resnick, M.B.; Yakirevich, E. Claudin expression in high-grade invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: Correlation with the molecular subtype. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, B.T.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.-M.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Gilcrease, M.Z.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Lee, J.-S.; Fridlyand, J.; Sahin, A.; Agarwal, R.; Joy, C.; et al. Characterization of a naturally occurring breast cancer subset enriched in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem cell characteristics. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4116–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrió, D.; Rodriguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Hardisson, D.; Cano, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Palacios, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Blanchard, A.; Wang, N.; Ma, X.; Han, J.; Schroedter, I.; Leygue, E.; Myal, Y. Claudin 1 promotes migration and increases sensitivity to tamoxifen and anticancer drugs in luminal-like human breast cancer cells MCF7. Cancer Investig. 2015, 33, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, E.; Sancho, E.; Franci, C.; Dominguez, D.; Monfar, M.; Baulida, J.; Garcia De, H.A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2000, 2, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolos, V. The transcription factor slug represses e-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal transitions: A comparison with snail and E47 repressors. J. Cell. Sci. 2002, 116, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakihara, T.; Saitoh, M.; Miyazono, K. Differential regulation of epithelial and mesenchymal markers by δEF1 proteins in epithelial mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-β. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 3533–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comijn, J.; Berx, G.; Vermassen, P.; Verschueren, K.; van Grunsven, L.; Bruyneel, E.; Mareel, M.; Huylebroeck, D.; van Roy, F. The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol. Cell. 2001, 7, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesuna, F.; van Diest, P.; Chen, J.H.; Raman, V. Twist is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Yang, L.; Yu, X.; Yang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Meng, J.; Feng, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. Stanniocalicin 2 suppresses breast cancer cell migration and invasion via the PKC/claudin-1-mediated signaling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimes, R.T.; Quigley, J.P. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 is an interstitial collagenase. Inhibitor-free enzyme catalyzes the cleavage of collagen fibrils and soluble native type I collagen generating the specific 3/4- and 1/4-length fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5872–5876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Lu, Z.; Foreman, O.; Tatum, R.; Lu, Q.; Renegar, R.; Cao, J.; Chen, Y.H. Inflammation and disruption of the mucosal architecture in claudin-7-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamori, H.; Takino, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tokai, H.; Itoh, Y.; Seiki, M.; Sato, H. Claudin promotes activation of pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 mediated by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 28204–28211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, J.H.; Yang, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 2192–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakhmal, N.V.; Zavyalova, M.V.; Denisov, E.V.; Vtorushin, S.V.; Perelmuter, V.M. Cancer invasion: Patterns and mechanisms. Acta Nat. 2015, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, P.; Gilmour, D. Collective cell migration in morphogenesis, regeneration and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampieri, S.; Manning, C.; Hooper, S.; Jones, L.; Hill, C.S.; Sahai, E. Localized and reversible TGFβ signalling switches breast cancer cells from cohesive to single cell motility. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2009, 11, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Christofori, G. Mechanisms of motility in metastasizing cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl, P.; Noble, P.B.; Walton, P.A.; Laird, D.W.; Chauvin, P.J.; Tabah, R.J.; Black, M.; Zanker, K.S. Migration of coordinated cell clusters in mesenchymal and epithelial cancer explants in vitro. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 4557–4560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortier, A.-M.; Asselin, E.; Cadrin, M. Keratin 8 and 18 loss in epithelial cancer cells increases collective cell migration and cisplatin sensitivity through claudin1 up-regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11555–11571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toft, D.J.; Cryns, V.L. Minireview: Basal-like breast cancer: From molecular profiles to targeted therapies. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerma van Voss, M.R.; van Diest, P.J.; Smolders, Y.H.; Bart, J.; van der Wall, E.; van der Groep, P. Distinct claudin expression characterizes BRCA1-related breast cancer. Histopathology 2014, 65, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent-Salomon, A.; Gruel, N.; Lucchesi, C.; MacGrogan, G.; Dendale, R.; Sigal-Zafrani, B.; Longy, M.; Raynal, V.; Pierron, G.; de, M.I.; et al. Identification of typical medullary breast carcinoma as a genomic sub-group of basal-like carcinomas, a heterogeneous new molecular entity. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soini, Y. Expression of claudins 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 in various types of tumours. Histopathology 2005, 46, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokés, A.-M.; Kulka, J.; Paku, S.; Szik, A.; Páska, C.; Novák, P.K.; Szilák, L.; Kiss, A.; Bögi, K.; Schaff, Z. Claudin-1, -3 and -4 proteins and mrna expression in benign and malignant breast lesions: A research study. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffer, C.; Gerke, V. The C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of claudins 1 and 5 but not its PDZ-binding motif is required for apical localization at epithelial and endothelial tight junctions. Eur. J. Cell. Biol. 2004, 83, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, A.D.; Fiori, J.L.; Camilli, T.C.; Leotlela, P.D.; OʼConnell, M.P.; Frank, B.P.; Subaran, S.; Indig, F.E.; Taub, D.D.; Weeraratna, A.T. PKC and PKA phosphorylation affect the subcellular localization of claudin-1 in melanoma cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales-Mariscal, L.; Garay, E.; Quiros, M. Regulation of claudins by posttranslational modifications and cell-signaling cascades. In Current Topics in Membranes; Elsevier Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 65, pp. 113–150. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Kamata, R.; Sakai, R. Phosphorylation of ephrin-B1 via the interaction with claudin following cell-cell contact formation. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukes, J.D.; Fish, L.; Richardson, J.D.; Blaikley, E.; Burns, S.; Caunt, C.J.; Chalmers, A.D.; Whitley, P. Functional escrt machinery is required for constitutive recycling of claudin-1 and maintenance of polarity in vertebrate epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2011, 22, 3192–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, O.V.; Yang, X.H.; Hemler, M.E. A novel cysteine cross-linking method reveals a direct association between claudin-1 and tetraspanin cd9. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.J.; Mannan, P.; Lu, M.; Udey, M.C. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) regulates claudin dynamics and tight junctions. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12253–12268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Sasaki, K.; Kamata, R.; Sakai, R. The C-terminus of ephrin-B1 regulates metalloproteinase secretion and invasion of cancer cells. J. Cell. Sci. 2007, 120, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, H.Q.; Wu, X.S.; Wei, B.; Chen, L. Eph receptors and ephrins as targets for cancer therapy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 2894–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, O.; Teis, D. The escrt machinery. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R116–R120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berditchevski, F.; Odintsova, E. Tetraspanins as regulators of protein trafficking. Traffic 2007, 8, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemler, M.E. Tetraspanin proteins mediate cellular penetration, invasion, and fusion events and define a novel type of membrane microdomain. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2003, 19, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemler, M.E. Tetraspanin functions and associated microdomains. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nydegger, S.; Khurana, S.; Krementsov, D.N.; Foti, M.; Thali, M. Mapping of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains that can function as gateways for HIV-1. J. Cell. Biol. 2006, 173, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucheix, C.; Rubinstein, E. Tetraspanins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1189–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kischel, P.; Bellahcene, A.; Deux, B.; Lamour, V.; Dobson, R.; de Pauw, E.; Clezardin, P.; Castronovo, V. Overexpression of cd9 in human breast cancer cells promotes the development of bone metastases. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 5211–5220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Gires, O. Epcam (cd326) finding its role in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Gun, B.T.; Melchers, L.J.; Ruiters, M.H.; de Leij, L.F.; McLaughlin, P.M.; Rots, M.G. Epcam in carcinogenesis: The good, the bad or the ugly. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.E.; Kanyicska, B.; Lerant, A.; Nagy, G. Prolactin: Structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1523–1631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Itoh, M.; Bissell, M.J. The organization of tight junctions in epithelia: Implications for mammary gland biology and breast tumorigenesis. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2003, 8, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.A.; Jiang, W.G. Loss of tight junction barrier function and its role in cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 872–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Shen, L.; Turner, J.R.; Coyne, C.B.; Wang, T. Tight junction proteins claudin-1 and occludin control hepatitis c virus entry and are downregulated during infection to prevent superinfection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2011–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, S.; Khaliq, S.; Samreen, B.; Ijaz, B.; Khan, M.; Ahmad, W.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Hassan, S. Effect of combined siRNA of HCV E2 gene and HCV receptors against HCV. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpin, C.; Tavassoli, F.; Secq, V.; Giusiano, S.; Villeret, J.; Garcia, S.; Birnbaum, D.; Bonnier, P.; Lavaut, M.N.; Boubli, L.; et al. Validation of an immunohistochemical signature predictive of 8-year outcome for patients with breast carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E236–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).