Endoanal Ultrasound in Perianal Crohn’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. EAUS Technique
- -
- Deep plane: The proximal anal canal, characterized by the U-shaped sling of the puborectalis muscle.
- -
- Intermediate plane: The hypoechoic internal anal sphincter, the perineal body, and the transverse perineal muscle.
- -
- Superficial plane: The distal canal, including the submucosal portion of the external anal sphincter.
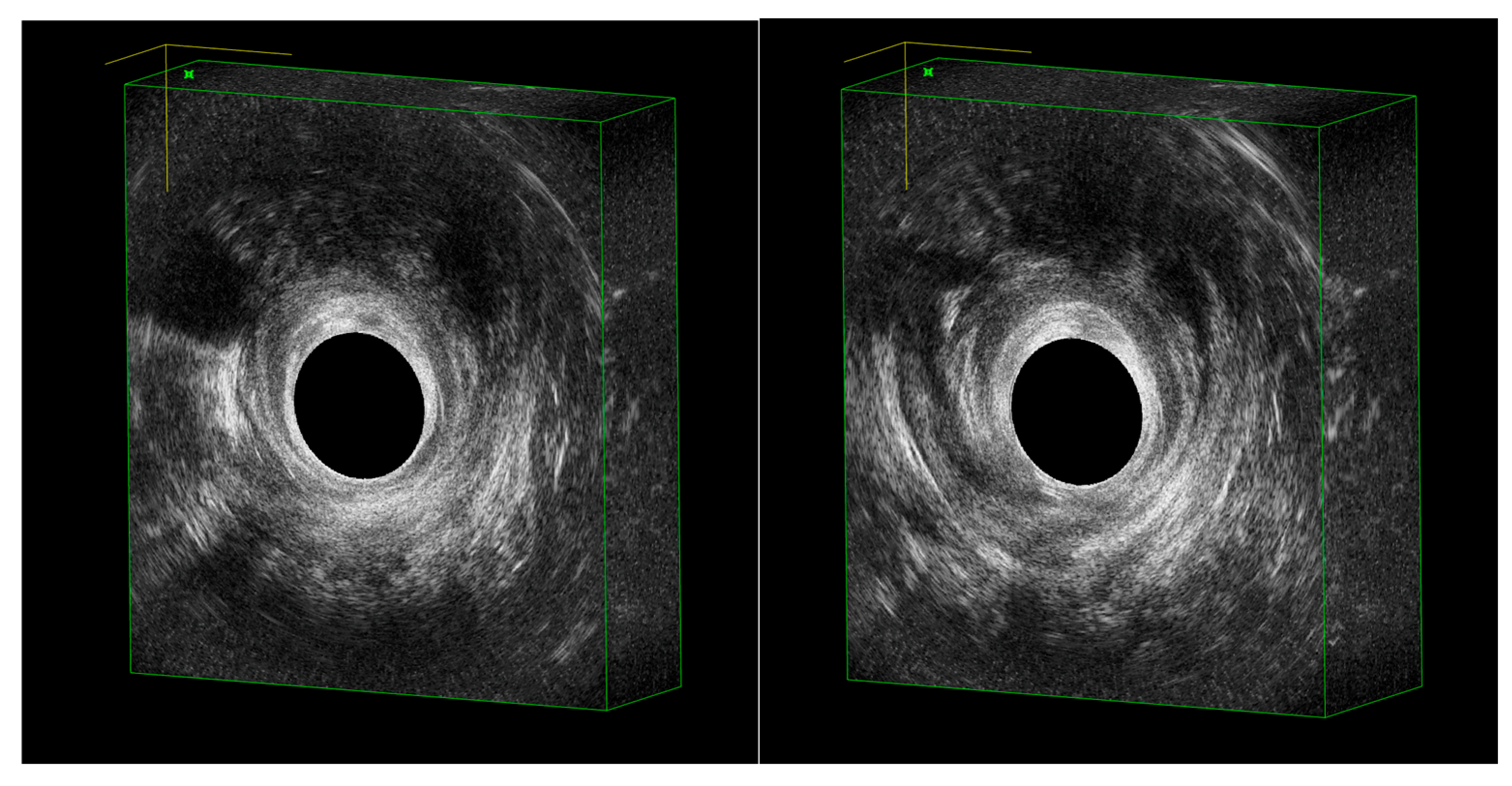
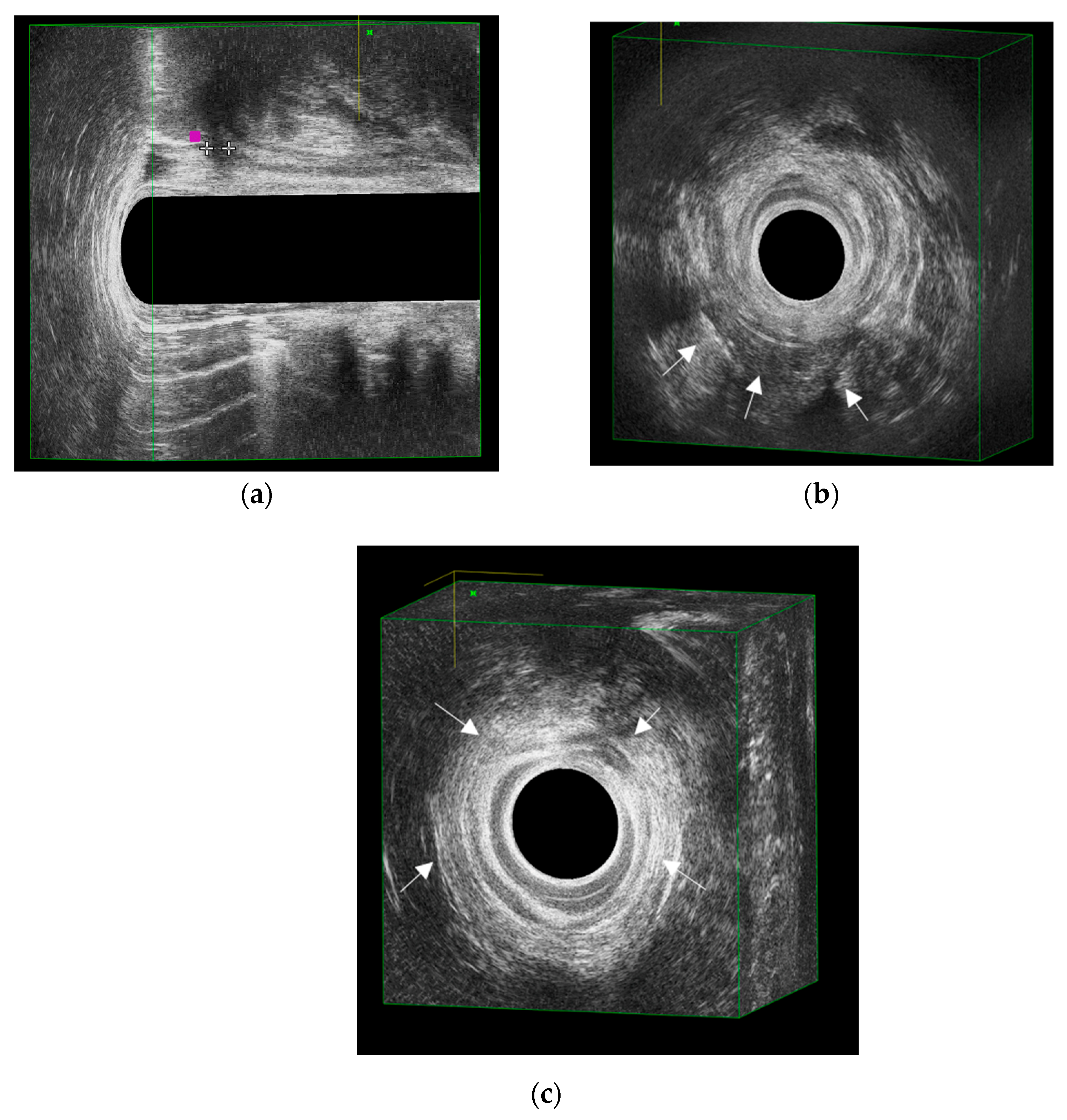
3. Diagnosis with EAUS
Typical EAUS Signs of pCD
4. Disease Activity and Management with EAUS
5. Comparative Roles: EAUS vs. MRI
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| EAUS | Endoanal ultrasound |
| T2T | Treat-to-target |
| TPUS | Transperineal ultrasound |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| pCD | Perianal Crohn’s disease |
| CUFS | Crohn’s Ultrasound Fistula Sign |
| SWE | Shear wave elastography |
References
- Tsai, L.; McCurdy, J.D.; Ma, C.; Jairath, V.; Singh, S. Epidemiology and Natural History of Perianal Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Cohorts. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eglinton, T.W.; Barclay, M.L.; Gearry, R.B.; Frizelle, F.A. The Spectrum of Perianal Crohn’s Disease in a Population-Based Cohort. Dis. Colon Rectum 2012, 55, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; McC Mortensen, N.J.; Jewell, D.P.; George, B. Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Br. J. Surg. 2004, 91, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zallot, C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Clinical Risk Factors for Complicated Disease: How Reliable Are They? Dig. Dis. 2012, 30, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Aniwan, S.; Scott Harmsen, W.; Tremaine, W.J.; Lightner, A.L.; Faubion, W.A.; Loftus, E.V. Update on the Natural Course of Fistulizing Perianal Crohn’s Disease in a Population-Based Cohort. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, A.; Yanai, H.; Girardi, P.; Milicevic, S.; Carvello, M.; Maroli, A.; Avedano, L. The Impact of Crohn’s Perianal Fistula on Quality of Life: Results of an International Patient Survey. Crohn’s Colitis 360 2023, 5, otad036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide Incidence and Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the 21st Century: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crohn, B.B. Regional Ileitis: A Pathologic and Clinical Entity. JAMA 1984, 251, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coremans, G.; Dockx, S.; Wyndaele, J.; Hendrickx, A. Do Anal Fistulas in Crohn’s Disease Behave Differently and Defy Goodsall’s Rule More Frequently Than Fistulas That Are Cryptoglandular in Origin? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 2732–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecse, K.B.; Bemelman, W.; Kamm, M.A.; Stoker, J.; Khanna, R.; Ng, S.C.; Panés, J.; Van Assche, G.; Liu, Z.; Hart, A.; et al. A Global Consensus on the Classification, Diagnosis and Multidisciplinary Treatment of Perianal Fistulising Crohn’s Disease. Gut 2014, 63, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathallah, N.; Pagano, M.; Haouari, M.A.; Barré, A.; Atanasiu, C.; Chambenois, E.; Nion-Larmurier, I.; Morisset, S.; Kirchgesner, J.; De Parades, V. Effectiveness and Safety of Advanced Dual-Targeted Therapy in Refractory Perianal Crohn’s Disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halligan, S.; Tolan, D.; Amitai, M.M.; Hoeffel, C.; Kim, S.H.; Maccioni, F.; Morrin, M.M.; Mortele, K.J.; Rafaelsen, S.R.; Rimola, J.; et al. ESGAR Consensus Statement on the Imaging of Fistula-in-Ano and Other Causes of Anal Sepsis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4734–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombel, J.-F.; D’haens, G.; Lee, W.-J.; Petersson, J.; Panaccione, R. Outcomes and Strategies to Support a Treat-to-Target Approach in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombel, J.-F.; Panaccione, R.; Bossuyt, P.; Lukas, M.; Baert, F.; Vaňásek, T.; Danalioglu, A.; Novacek, G.; Armuzzi, A.; Hébuterne, X.; et al. Effect of Tight Control Management on Crohn’s Disease (CALM): A Multicentre, Randomised, Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; Vermeire, S.; D’Haens, G.; Panés, J.; Dignass, A.; Magro, F.; Nazar, M.; Le Bars, M.; Lahaye, M.; Ni, L.; et al. Treat to Target versus Standard of Care for Patients with Crohn’s Disease Treated with Ustekinumab (STARDUST): An Open-Label, Multicentre, Randomised Phase 3b Trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, P.J.; Bartram, C.I. Anal Endosonography: Technique and Normal Anatomy. Gastrointest. Radiol. 1989, 14, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-M.; Kye, B.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Yoo, N. Standardizing the 3D-Endoluminal Ultrasound Procedure: Optimal Delineation of Anorectal Anatomy. J. Surg. Ultrasound 2024, 11, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasinghe, D.; Samarasekera, D.N. Comparison of Preoperative Endoanal Ultrasonography with Intraoperative Findings for Fistula In Ano. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudoł-Szopińska, I.; Garg, P.; Mellgren, A.; Spinelli, A.; Breukink, S.; Iacobellis, F.; Kołodziejczak, M.; Ciesielski, P.; Christian, J.; SMART Collaborative Group; et al. Structured Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Endoanal Ultrasound Anal Fistulas Reporting Template (SMART): An Interdisciplinary Delphi Consensus. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2024, 16, 3288–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maconi, G.; Greco, M.; Asthana, A. Transperineal Ultrasound for Perianal Fistulas and Abscesses—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ultraschall Der Med.-Eur. J. Ultrasound 2017, 38, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tto, T.L.; Mulder, C.J.J.; Wijers, O.B.; Sars, P.R.A.; Tytgat, G.N.J. Endosonography of Peri-Anal and Pericolorectal Fistula and/or Abscess in Crohn’s Disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1990, 36, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsoni, P.; Barthet, M.; Portier, F.; Panuel, M.; Desjeux, A.; Grimaud, J.C. Prospective Comparison of Endosonography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Surgical Findings in Anorectal Fistula and Abscess Complicating Crohn’s Disease. J. Br. Surg. 1999, 86, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Wiersema, M.J.; Dudiak, K.M.; Fletcher, J.G.; Clain, J.E.; Tremaine, W.J.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Norton, I.D.; Boardman, L.A.; Devine, R.M.; et al. A Comparison of Endoscopic Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Exam under Anesthesia for Evaluation of Crohn’s Perianal Fistulas. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.R.S.; Ashrafian, H.; Tozer, P.; Daulatzai, N.; Burling, D.; Hart, A.; Athanasiou, T.; Phillips, R.K. A Diagnostic Accuracy Meta-Analysis of Endoanal Ultrasound and MRI for Perianal Fistula Assessment. Dis. Colon. Rectum 2012, 55, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losco, A.; Viganò, C.; Conte, D.; Cesana, B.M.; Basilisco, G. Assessing the Activity of Perianal Crohn’s Disease: Comparison of Clinical Indices and Computer-Assisted Anal Ultrasound. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, J.B.; Kane, R.A.; Morrin, M.M. Peroxide-Enhanced Anal Endosonography: Technique, Image Interpretation, and Clinical Applications. RadioGraphics 2001, 21, S173–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsankov, T.; Tankova, L.; Deredjan, H.; Kovatchki, D. Contrast-Enhanced Endoanal and Transperineal Sonography in Perianal Fistulas. Hepatogastroenterology 2008, 55, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.; Faisal, M.F. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Transrectal Drainage of Perirectal Abscess in a Patient with Crohn Disease. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e930698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, F.D.L.; León-Jiménez, E.; Cisneros, N.; Rada, R.; Flikier, B.; Vega, J.; Hugo Maldonado, V. Use of Anorectal Ultrasounds in Perianal Crohn’s Disease: Consistency with Clinical Data. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2006, 98, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, J.; Nyström, P.O.; Gunnarsson, U.; Strigård, K. Endoanal Ultrasonography May Distinguish Crohn’s Anal Fistulae from Cryptoglandular Fistulae in Patients with Crohn’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Tech. Coloproctol. 2011, 15, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawadzki, A.; Starck, M.; Bohe, M.; Thorlacius, H. A Unique 3D Endoanal Ultrasound Feature of Perianal Crohn’s Fistula: The ‘Crohn Ultrasound Fistula Sign’. Color. Dis. 2012, 14, e608–e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbar, A.P.; Horesh, N.; Bucholtz, V.; Zmora, O.; Beer-Gabel, M.; Carter, D. Are There Specific Endosonographic Features in Crohn’s Patients with Perianal Fistulae? J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luglio, G.; Giglio, M.C.; Rispo, A.; Bucci, C.; Sollazzo, V.; Castiglione, F.; De Palma, G.D.; Bucci, L. Diagnostic Accuracy of 3-Dimensional Endoanal Ultrasound in Identifying Perianal Crohn’s Fistulas. Dis. Colon. Rectum 2018, 61, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Portilla, F.; Sojo, V.; Vázquez-Monchul, J.M.; Pintor-Tortolero, J.; Dios, S.; Reyes-Díaz, M.L. Description of a New Ultrasound Sign to Distinguish Crohn’s Anal Fistula from Cryptoglandular Fistula: The Rosary Sign. Color. Dis. 2023, 25, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamina, M.; Minozzi, S.; Warusavitarne, J.; Buskens, C.J.; Chaparro, M.; Verstockt, B.; Kopylov, U.; Yanai, H.; Vavricka, S.R.; Sigall-Boneh, R.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Surgical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, 18, 1556–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradlin, N.M.; Wise, P.E.; Herline, A.J.; Muldoon, R.L.; Rosen, M.; Schwartz, D.A. A Randomized Prospective Trial of Endoscopic Ultrasound to Guide Combination Medical and Surgical Treatment for Crohn’s Perianal Fistulas. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, D.M.; Beaulieu, D.; Slaughter, J.C.; Horst, S.; Wagnon, J.; Duley, C.; Annis, K.; Nohl, A.; Herline, A.; Muldoon, R.; et al. Use of Endoscopic Ultrasound to Guide Adalimumab Treatment in Perianal Crohn’s Disease Results in Faster Fistula Healing. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillantino, A.; Iacobellis, F.; Di Sarno, G.; D’Aniello, F.; Izzo, D.; Paladino, F.; De Palma, M.; Castriconi, M.; Grassi, R.; Di Martino, N.; et al. Role of Tridimensional Endoanal Ultrasound (3D-EAUS) in the Preoperative Assessment of Perianal Sepsis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2015, 30, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Moulton, D.E.; Koyama, T.; Morgan, W.M.; Morrow, S.E.; Herline, A.J.; Muldoon, R.L.; Wise, P.E.; Polk, B.D.; Schwartz, D.A. Endoscopic Ultrasound to Guide the Combined Medical and Surgical Management of Pediatric Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, L.; Ratto, C.; Semeraro, S.; Roberto, I.; De Vitis, I.; Papa, A.; Marzo, M.; Parello, A.; Foglietto, G.; Doglietto, G.B.; et al. Combined Therapy with Infliximab and Seton Drainage for Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease with Anal Endosonographic Monitoring: A Single-Centre Experience. Tech. Coloproctol. 2008, 12, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, K.L.; Meima-van Praag, E.M.; Bossuyt, P.M.; D’Haens, G.R.; Gecse, K.B.; Horsthuis, K.; Snijder, H.J.; Tielbeek, J.A.W.; Buskens, C.J.; Stoker, J. Fibrosis and MAGNIFI-CD Activity Index at Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Predict Treatment Outcome in Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease Patients. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.; Liu, W.-Y.; Zhang, J.-L.; Qian, K.; Liu, J.; Ye, X.-J.; Zeng, F.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, K.-G. Assessment of Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease Activity with Endoanal Ultrasound: A Retrospective Cohort Study. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2024, 16, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindryckx, P.; Jairath, V.; Zou, G.; Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J.; Stoker, J.; Khanna, R.; Stitt, L.; Van Viegen, T.; Shackelton, L.M.; et al. Development and Validation of a Magnetic Resonance Index for Assessing Fistulas in Patients With Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1233–1244.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, E.J. Usual Therapy Improves Perianal Crohn’s Disease as Measured by a New Disease Activity Index. McMaster IBD Study Group. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1995, 20, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feuerstein, J.D.; Ho, E.Y.; Shmidt, E.; Singh, H.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Sultan, S.; Terdiman, J.P.; Sultan, S.; Cohen, B.L.; Chachu, K.; et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Medical Management of Moderate to Severe Luminal and Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2496–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Fazio, V.W.; Feagan, B.G.; Hanauer, S.B. AGA Technical Review on Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1508–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.A.; White, C.M.; Wise, P.E.; Herline, A.J. Use of Endoscopic Ultrasound to Guide Combination Medical and Surgical Therapy for Patients With Crohn’s Perianal Fistulas. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2005, 11, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aho Fält, U.; Zawadzki, A.; Starck, M.; Bohe, M.; Regnér, S.; Johnson, L.B. Postoperative Three-Dimensional Endoanal Ultrasound Findings and Relation to Anal Fistula Plug Failure. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, M.M.F.; Almutairi, S.F.M.; Alarjani, N.O.; Alghaylan, M.Y.A.; Aljawhari, M.S.M.; Alkhulaifi, A.A.S. Advancements in AI-Driven Diagnostic Radiology: Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency. Int. J. Health Sci. 2024, 8, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelebi, F.; Tuncer, O.; Oral, M.; Duymaz, T.; Orhan, T.; Ertaş, G. Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Breast Ultrasound: A Comparative Analysis of Decision Support Among Radiologists With Various Levels of Expertise. Eur. J. Breast Healh 2025, 21, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturi, B.; Dulal, S.; Sayana, S.B.; Ibrahim, A.; Ramakrishna, M.; Chinta, V.; Sharma, A.; Ravipati, H. Revolutionizing Cardiology: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Echocardiography. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabiso, M.E.; Iasiello, F.; Pellino, G.; Iacomino, A.; Roberto, L.; Pinto, A.; Riegler, G.; Selvaggi, F.; Reginelli, A. 3D-EAUS and MRI in the Activity of Anal Fistulas in Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkenbosch, J.H.C.; Van Ruler, O.; De Vries, A.C.; Van Der Woude, C.J.; Dwarkasing, R.S. The Role of MRI in Perianal Fistulizing Disease: Diagnostic Imaging and Classification Systems to Monitor Disease Activity. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 50, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felt-Bersma, R.J.F. Endoanal Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Cryptoglandular Anal Fistulas and Abscesses. In Anal Fistula and Abscess; Ratto, C., Parello, A., Litta, F., De Simone, V., Campennì, P., Eds.; Coloproctology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–23. ISBN 978-3-030-30902-2. [Google Scholar]
- Abdool, Z.; Sultan, A.H.; Thakar, R. Ultrasound Imaging of the Anal Sphincter Complex: A Review. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, G.; Halligan, S.; Williams, A.; Cohen, C.R.G.; Tarroni, D.; Phillips, R.K.; Bartram, C.I. Effect of MRI on Clinical Outcome of Recurrent Fistula-in-Ano. Lancet 2002, 360, 1661–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundi, N.; Bozchelouei, J.K.; Abrishami, A.; Frootan, M.; Siami, A.; Alimadadi, E.; Saba, G.B.; Rezazadeh, E.; Amerifar, M.; Eghdami, E. Comparison of MRI and Endoanal Ultrasound in Assessing Intersphincteric, Transsphincteric, and Suprasphincteric Perianal Fistula. J. Ultrasound Med. 2023, 42, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsamis, N.; Kosmidis, C.; Chatzimavroudis, G.; Apostolidou Kiouti, F.; Efthymiadis, C.; Lalas, V.; Mystakidou, C.M.; Sevva, C.; Papadopoulos, K.; Anthimidis, G.; et al. Preoperative Assessment of Perianal Fistulas with Combined Magnetic Resonance and Tridimensional Endoanal Ultrasound: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Section | Items to Report |
|---|---|
| Patient/Indication/Date | Basic demographics, indication for EAUS, and examination date |
| Technique | Probe MHz; 360° rotation; 2D/3D mode; Doppler/SWE use; patient tolerance |
| Internal Openings | N, clock face position; distance from anal verge (cm) |
| Primary Tract Type | Intersphincteric/Transsphincteric/Suprasphincteric/Extrasphincteric; laterality; level (low/mid/high) |
| Secondary Extensions | Horseshoe (anterior/posterior); contralateral spread; supralevator extension (if suspected) |
| Collections | N; size (mm); compartments; proximity to skin/mucosa |
| Activity Markers | Tract width (mm); internal echoes/debris; Doppler grade (0–2); SWE values (m/s or kPa, if available) |
| Sphincters | IAS/EAS integrity; presence of scars/defects; risk to continence |
| Devices/Surgery | Setons (number and path); drains; stomas |
| Synthesis/Impact | Overall impression with Parks classification; actionable next steps (e.g., drainage, seton placement, MRI, interval for repeat EAUS) |
| First Author (Year) | EAUS Sign(s) | Diagnostic Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Blom, J. (2011) [30] | Bifurcation/secondary tracts; width > 3 mm; debris | Suggested CD, but without detailed sensitivity/specificity |
| Zawadzki, A. (2012) [31] | CUFS 1 | Specificity 98%; Sensitivity 69%; κ = 0.77 |
| Zbar, A.P. (2013) [32] | CUFS 1 | Specificity 97%; Sensitivity 43%; κ = 0.85 |
| Luglio, G. (2018) [33] | CUFS 1 + tract width > 4 mm | Specificity 88–100%; Sensitivity up to 100%; κ = 0.84 |
| de la Portilla, F. (2022) [29] | Rosary sign 2 | Specificity 71%; Sensitivity 49%; κ = 0.27 |
| Feature | EAUS | MRI |
|---|---|---|
| Availability and logistics | Outpatient, cost-effective, quick (15–20 min) | Higher cost, limited access, requires scheduling |
| Contraindications | Minimally invasive, but limited in stenosis or severe anal pain | Non-invasive, but contraindicated in claustrophobia, metal implants, or gadolinium restriction |
| Field of view | High-resolution imaging of anal canal, sphincter complex, and intersphincteric space | Panoramic multiplanar imaging of entire pelvis, including supralevator and extrapelvic disease |
| Internal opening detection | Excellent, especially with 3D probes and hydrogen peroxide enhancement | Reliable, but may be less precise than EAUS for fine sphincteric detail |
| Secondary extensions | Good for low and intersphincteric tracts; limited for very lateral or supralevator disease | Superior for complex, high, and recurrent tracts; comprehensive mapping |
| Abscess detection | Accurate for perianal and intersphincteric abscesses; limited in deep pelvis | Excellent sensitivity for deep pelvic and supralevator collections |
| Validated scoring systems | None validated; candidate parameters under study (tract width, echoes, Doppler, SWE) | Several validated indices (Van Assche, MAGNIFI-CD, mVAI) used in trials and monitoring |
| Role in clinical pathway | First-line, bedside triage, perioperative seton guidance, serial monitoring | Reference standard for complex/recurrent disease, surgical planning, and research endpoints |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagano, M.; Litta, F.; Parello, A.; Marra, A.A.; Campennì, P.; Ratto, C. Endoanal Ultrasound in Perianal Crohn’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6867. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196867
Pagano M, Litta F, Parello A, Marra AA, Campennì P, Ratto C. Endoanal Ultrasound in Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6867. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196867
Chicago/Turabian StylePagano, Mario, Francesco Litta, Angelo Parello, Angelo Alessandro Marra, Paola Campennì, and Carlo Ratto. 2025. "Endoanal Ultrasound in Perianal Crohn’s Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6867. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196867
APA StylePagano, M., Litta, F., Parello, A., Marra, A. A., Campennì, P., & Ratto, C. (2025). Endoanal Ultrasound in Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6867. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196867






