Elastic Compression Dressing after Total Hip Replacement Slightly Reduces Leg Swelling: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
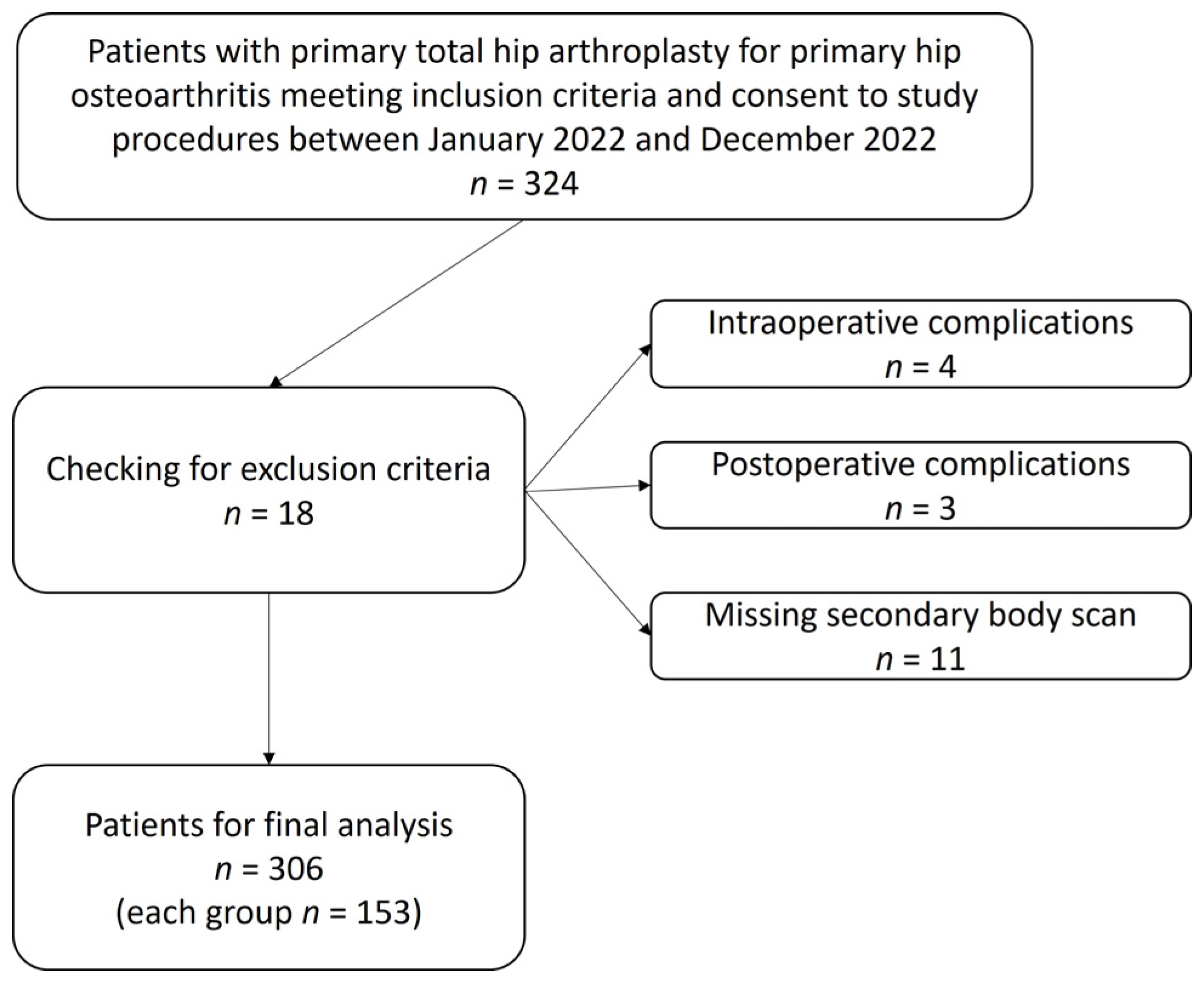
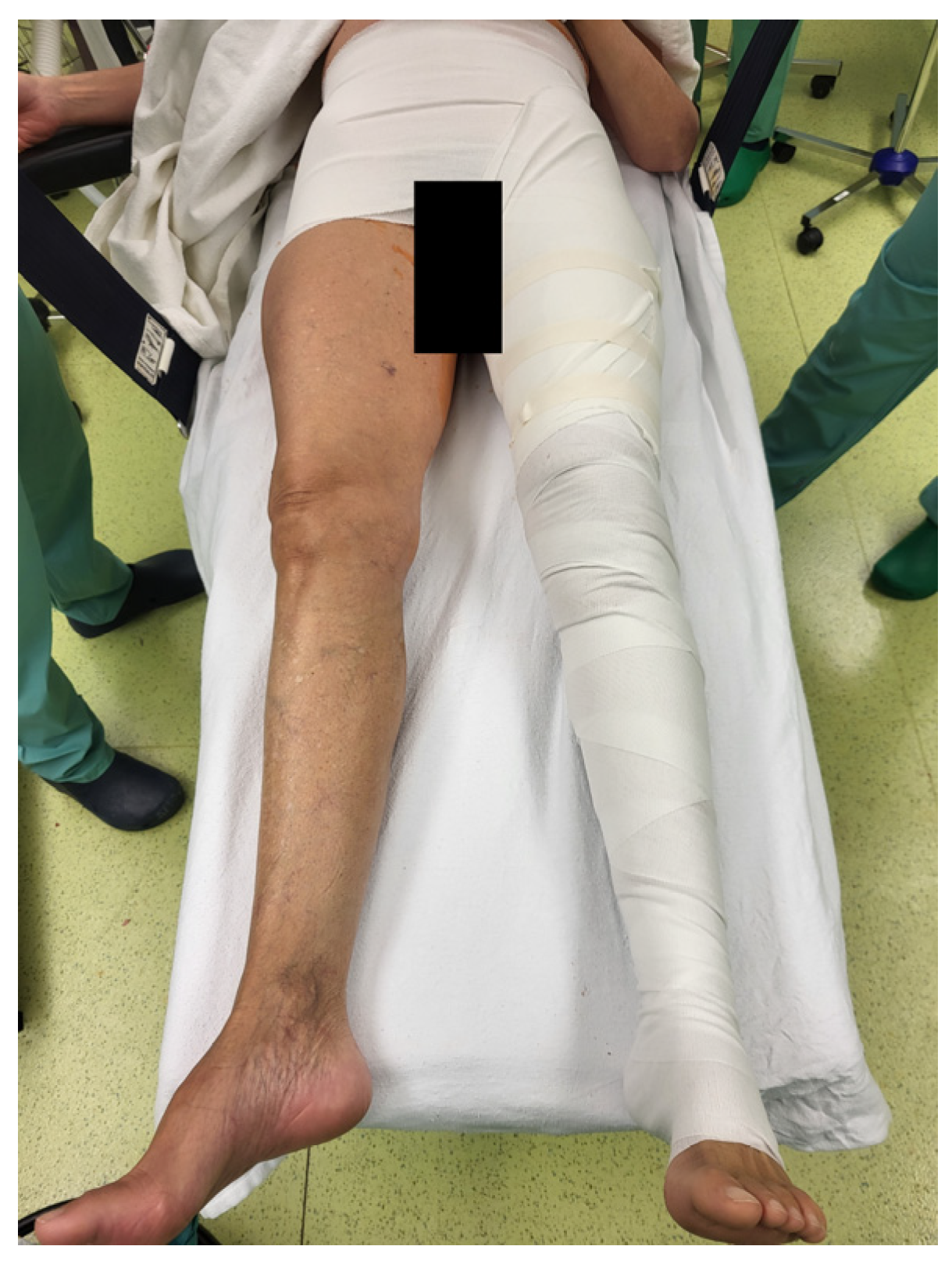
2. Materials and Methods
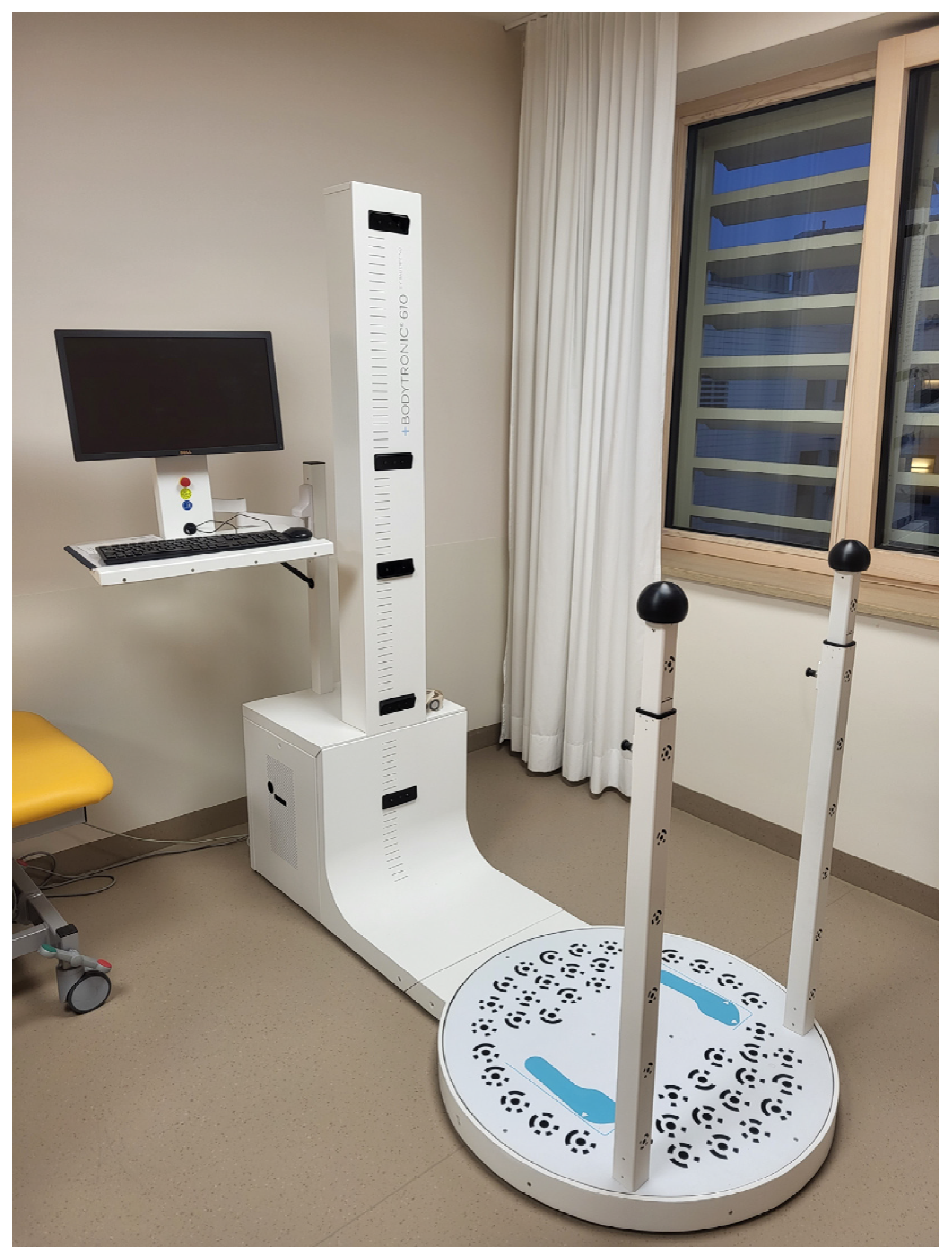
2.1. Leg Swelling
2.2. Blood Loss
2.3. Sample Size and Power
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
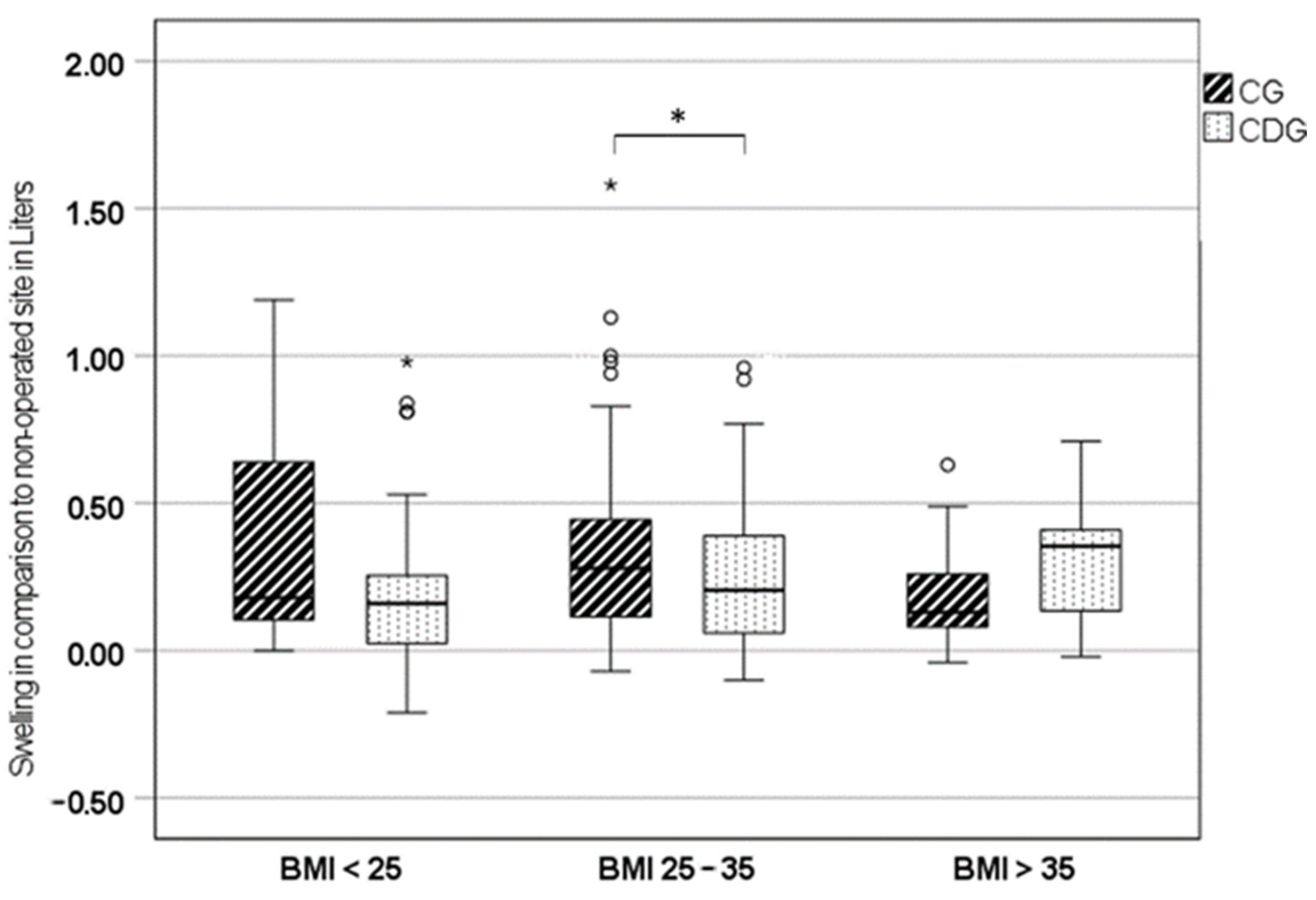
3.1. Leg Swelling
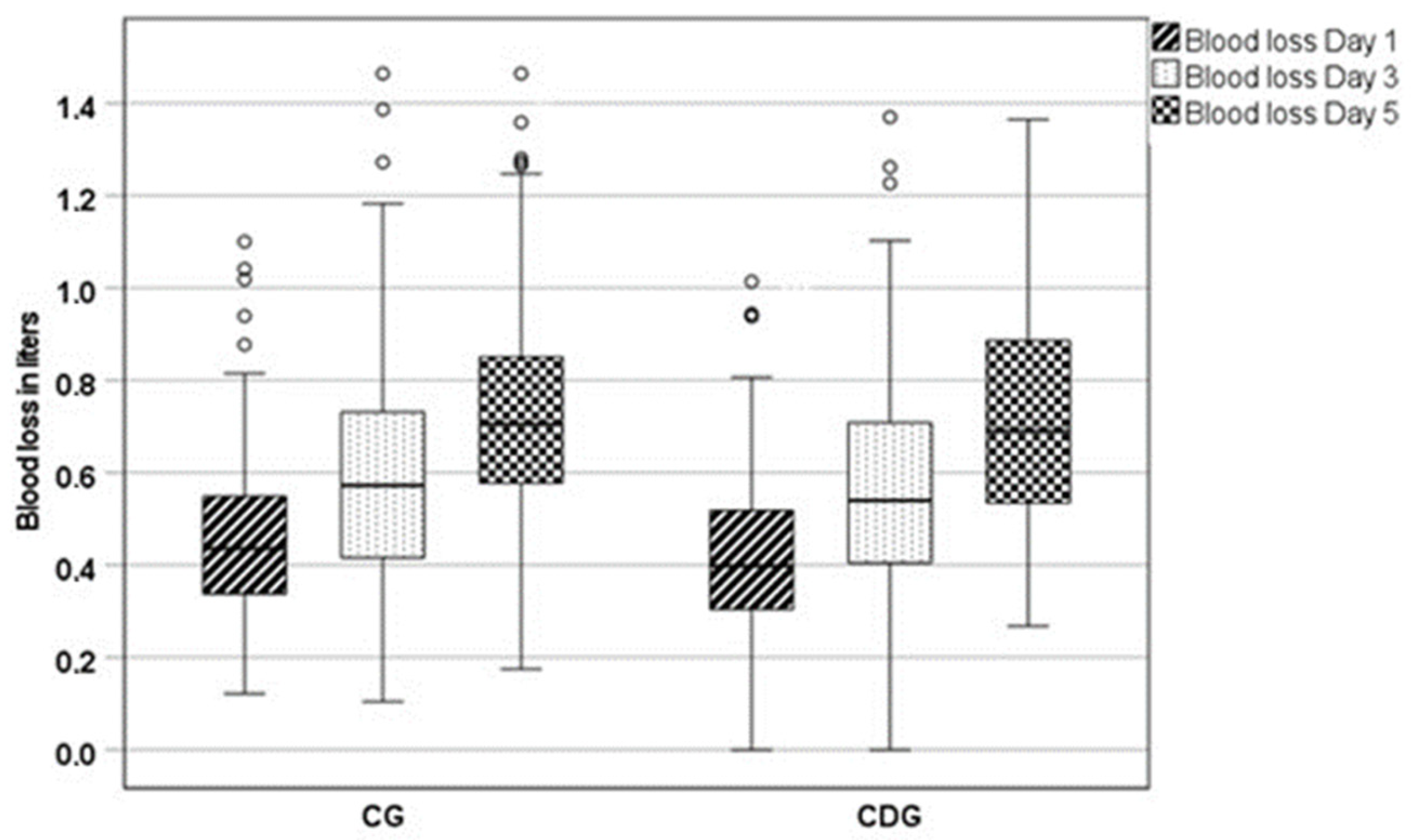
3.2. Blood Loss
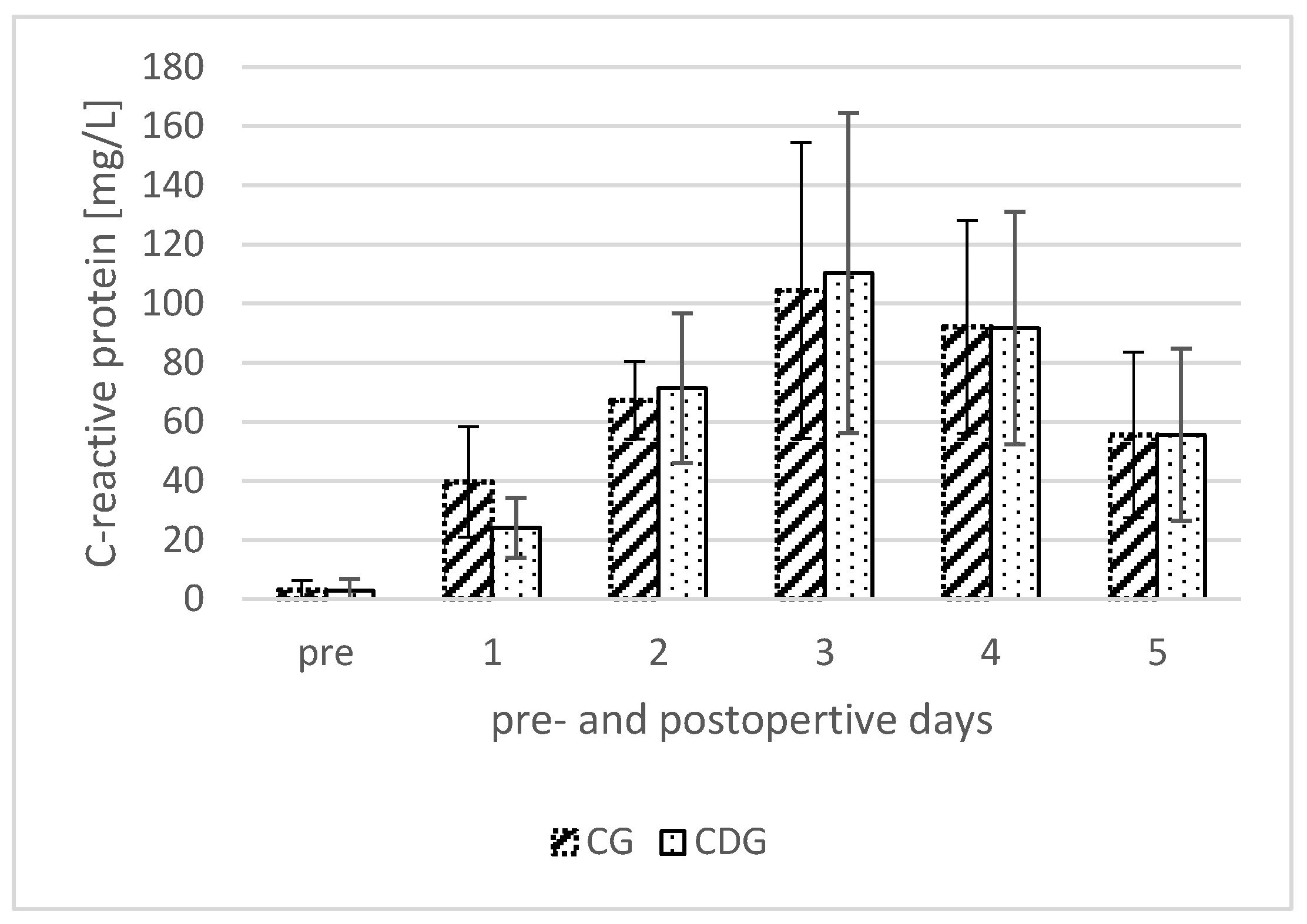
3.3. C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rainer, W.G.; Kolz, J.M.; Wyles, C.C.; Houdek, M.T.; Perry, K.I.; Lewallen, D.G. Lymphedema Is a Significant Risk Factor for Failure After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2022, 104, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everhart, J.S.; Sojka, J.H.; Mayerson, J.L.; Glassman, A.H.; Scharschmidt, T.J. Perioperative Allogeneic Red Blood-Cell Transfusion Associated with Surgical Site Infection After Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2018, 100, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, K.T.; Best, M.J.; Skolasky, R.L.; Ponnusamy, K.E.; Sterling, R.S.; Khanuja, H.S. Lupus and Perioperative Complications in Elective Primary Total Hip or Knee Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akti, S.; Zeybek, H.; Bilekli, A.B.; Çelebi, N.Ö.; Erdem, Y.; Çankaya, D. The effect of tranexamic acid on hidden blood loss in total hip arthroplasty. Jt. Dis. Relat. Surg. 2022, 33, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Biagini, M.; Rath, B.; Meisen, N.; Tingart, M.; Eschweiler, J. Total hip arthroplasty: Minimally invasive surgery or not? Meta-analysis of clinical trials. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, T.; Pettersson, L.-G.; Lisander, B. Tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty saves blood and money: A randomized, double-blind study in 100 patients. Acta Orthop. 2005, 76, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, B. Hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2011, 26, 1100–1105.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, J.F.; Walters, T.J.; Baer, D.G.; Fox, C.J.; Wade, C.E.; Salinas, J.; Holcomb, J.B. Practical use of emergency tourniquets to stop bleeding in major limb trauma. J. Trauma 2008, 64, S38–S49; discussion S49–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolz, J.M.; Rainer, W.G.; Wyles, C.C.; Houdek, M.T.; Perry, K.I.; Lewallen, D.G. Lymphedema: A Significant Risk Factor for Infection and Implant Failure After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grada, A.A.; Phillips, T.J. Lymphedema: Diagnostic workup and management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, T.; Engquist, M.; Pettersson, L.-G.; Lisander, B. Blood loss after total hip replacement: A prospective randomized study between wound compression and drainage. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörnberg, I.; Bengtsson, A.; Bergman, B. Kompressionsförband minskar behovet av allogent blod vid höftproteskirurgi. Lakartidningen 2002, 99, 397–399. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Wu, T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Fan, Z.; Guo, X. Hemostasis effect of compression dressing therapy after total hip arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 2016, 30, 416–420. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, G.J.; Grant, D.; Bartke, C.; McCartin, J.; Carn, R.M. Wound complications after hip surgery using a tapeless compressive support. Orthop. Nurs. 1999, 18, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, K.J.; Egol, K.A.; Hiebert, R.; Spratt, K.F. Tape blisters after hip surgery: Can they be eliminated completely? Am. J. Orthop. 2007, 36, 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Rothfusz, C.A.; Emara, A.K.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Molloy, R.M.; Krebs, V.E.; Piuzzi, N.S. Wound Dressings for Hip and Knee Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Narrative Review. JBJS Rev. 2021, 9, e20.00301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; Khan, M.A.; Nizam, I.; Haddad, F.S. Peri-operative interventions producing better functional outcomes and enhanced recovery following total hip and knee arthroplasty: An evidence-based review. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, W.M.; Branson, J.J. Posterior-lateral approach to minimal incision total hip arthroplasty. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 35, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartzband, M.A. Posterolateral minimal incision for total hip replacement: Technique and early results. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 35, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röttinger, H. Minimalinvasiver Zugang zum Hüftgelenk (OCM) zur Implantation von Hüftendoprothesen. Oper. Orthop. Traumatol. 2010, 22, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischer, T.; Oye, S.; Wolf, A.; Feldhege, F.; Jacksteit, R.; Mittelmeier, W.; Bader, R.; Mau-Moeller, A. Measuring lower limb circumference and volume—Introduction of a novel optical 3D volumetric measurement system. Biomed. Tech. 2020, 65, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, S.B.; Hidalgo, J.H.; Bloch, T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery 1962, 51, 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, R.L.; Lostis, E.; Jones, I.; Whitehouse, M.R. Estimation of blood volume and blood loss in primary total hip and knee replacement: An analysis of formulae for perioperative calculations and their ability to predict length of stay and blood transfusion requirements. J. Orthop. 2021, 24, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumaier, M.; Metak, G.; Scherer, M.A. C-reactive protein as a parameter of surgical trauma: CRP response after different types of surgery in 349 hip fractures. Acta Orthop. 2006, 77, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Ji, W. C-reactive protein levels after 4 types of arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2009, 80, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykov, K.; Reininga, I.H.F.; Sietsma, M.S.; Knobben, B.A.S.; Have, B.L.E.F. ten. Posterolateral vs Direct Anterior Approach in Total Hip Arthroplasty (POLADA Trial): A Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Differences in Serum Markers. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 3652–3658.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholen, D.W.; Linnet, K.; Kondratovich, M. Protocols for Determination of Limits of Detection and Limits of Quantitation; Approved Guideline, 2nd ed.; NCCLS: Wayne, PA, USA, 2004; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Rohe, S.; Röhner, E.; Windisch, C.; Matziolis, G.; Brodt, S.; Böhle, S. Sex Differences in Serum C-Reactive Protein Course after Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, C.N.; Chen, A.F.; Daryoush, T.; Rothman, R.H.; Maltenfort, M.G.; Hozack, W.J. Does an Elastic Compression Bandage Provide Any Benefit After Primary TKA? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Mu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Guo, W. Should compression bandage be performed after total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, A.C.; Belczak, C.E.Q.; Campos, M.B.; Campos, R.B.; Harada, D.S. The impact of obesity on venous insufficiency. Phlebology 2015, 30, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rij, A.M.; de Alwis, C.S.; Jiang, P.; Christie, R.A.; Hill, G.B.; Dutton, S.J.; Thomson, I.A. Obesity and impaired venous function. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2008, 35, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenberg, T.; Clemens, R.; Haegeli, L.M.; Amann-Vesti, B.; Baumgartner, I.; Husmann, M. The influence of abdominal pressure on lower extremity venous pressure and hemodynamics: A human in-vivo model simulating the effect of abdominal obesity. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 41, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, G.-C.; Zhu, X.-R.; Wang, L.; Li, H.-W. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in primary total hip arthroplasty performed using the direct anterior approach: A one-center retrospective observational study. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2022, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Z.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Pei, F. The efficacy and safety of multiple-dose oral tranexamic acid on blood loss following total hip arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CDG | CG | p-Value | p-Value (Adjusted *) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 153 | 153 | 1.00 | |
| Male sex | 71 (46.4%) | 65 (42.5%) | 0.49 | |
| Age [y] | 64.07 ± 0.99 | 64.57 ± 11.75 | 0.81 | |
| Obesity | 38 (24.8%) | 34 (22.2%) | 0.59 | |
| Overweight | 118 (77.1%) | 116 (75.8%) | 0.87 | |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 28.66 ± 4.95 | 28.96 ± 5.34 | 0.31 | |
| Diabetes | 22 (14.4%) | 21 (13.7%) | 0.87 | |
| Renal failure | 6 (3.9%) | 11 (7.2%) | 0.21 | |
| Osteoporosis | 12 (7.8%) | 11 (7.2%) | 0.83 | |
| Hypertension | 97 (63.4%) | 91 (59.5%) | 0.48 | |
| Coronary disease | 8 (5.2%) | 8 (5.2%) | 1.00 | |
| Length of stay [d] | 5.93 ± 0.67 | 5.91 ± 0.84 | 0.38 | |
| Surgery time [min] | 51.39 ± 17.39 | 55.40 ± 21.76 | 0.04 | |
| Anterolateral approach | 130 (85.0%) | 132 (86.3%) | 0.87 | |
| Dorsolateral approach | 23 (15.0%) | 21 (13.7%) | 0.81 | |
| Blood transfusion | 0 | 0 | - | |
| p.o. Leg swelling [L] | 0.24 ± 0.23 | 0.31 ± 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| EBV [L] | 5.01 ± 1.04 | 4.85 ± 0.97 | 0.09 | - |
| EBL p.o. day 1 [L] | 0.43 ± 0.19 | 0.46 ± 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.24 |
| EBL p.o. day 3 [L] | 0.56 ± 0.25 | 0.61 ± 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.24 |
| EBL p.o. day 5 [L] | 0.72 ± 0.26 | 0.73 ± 0.23 | 0.38 | - |
| CDG | CG | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI < 25 kg/m2 [n] | 35 | 36 | |
| Leg swelling [L] | 0.22 ± 0.28 | 0.35 ± 0.34 | 0.04 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 1 [L] | 0.34 ± 0.16 | 0.45 ± 0.17 | 0.01 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 3 [L] | 0.50 ± 0.24 | 0.61 ± 0.21 | 0.06 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 5 [L] | 0.62 ± 0.24 | 0.68 ± 0.17 | 0.14 |
| BMI 25–35 kg/m2 [n] | 96 | 106 | |
| Leg swelling [L] | 0.24 ± 0.22 | 0.32 ± 0.28 | 0.02 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 1 [L] | 0.45 ± 0.19 | 0.46 ± 0.18 | 0.33 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 3 [L] | 0.56 ± 0.23 | 0.60 ± 0.26 | 0.10 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 5 [L] | 0.72 ± 0.24 | 0.72 ± 0.23 | 0.47 |
| BMI > 35 kg/m2 [n] | 12 | 21 | |
| Leg swelling [L] | 0.31 ± 0.21 | 0.20 ± 0.18 | 0.06 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 1 [L] | 0.49 ± 0.20 | 0.49 ± 0.17 | 0.49 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 3 [L] | 0.68 ± 0.38 | 0.63 ± 0.31 | 0.33 |
| Blood loss p.o. day 5 [L] | 0.98 ± 0.27 | 0.82 ± 0.25 | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rohe, S.; Böhle, S.; Matziolis, G.; Layher, F.; Brodt, S. Elastic Compression Dressing after Total Hip Replacement Slightly Reduces Leg Swelling: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082207
Rohe S, Böhle S, Matziolis G, Layher F, Brodt S. Elastic Compression Dressing after Total Hip Replacement Slightly Reduces Leg Swelling: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(8):2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082207
Chicago/Turabian StyleRohe, Sebastian, Sabrina Böhle, Georg Matziolis, Frank Layher, and Steffen Brodt. 2024. "Elastic Compression Dressing after Total Hip Replacement Slightly Reduces Leg Swelling: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 8: 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082207
APA StyleRohe, S., Böhle, S., Matziolis, G., Layher, F., & Brodt, S. (2024). Elastic Compression Dressing after Total Hip Replacement Slightly Reduces Leg Swelling: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(8), 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082207








