Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Arterial Re-Occlusion After Successful Mechanical Thrombectomy for Emergent Intracranial Large Vessel Occlusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
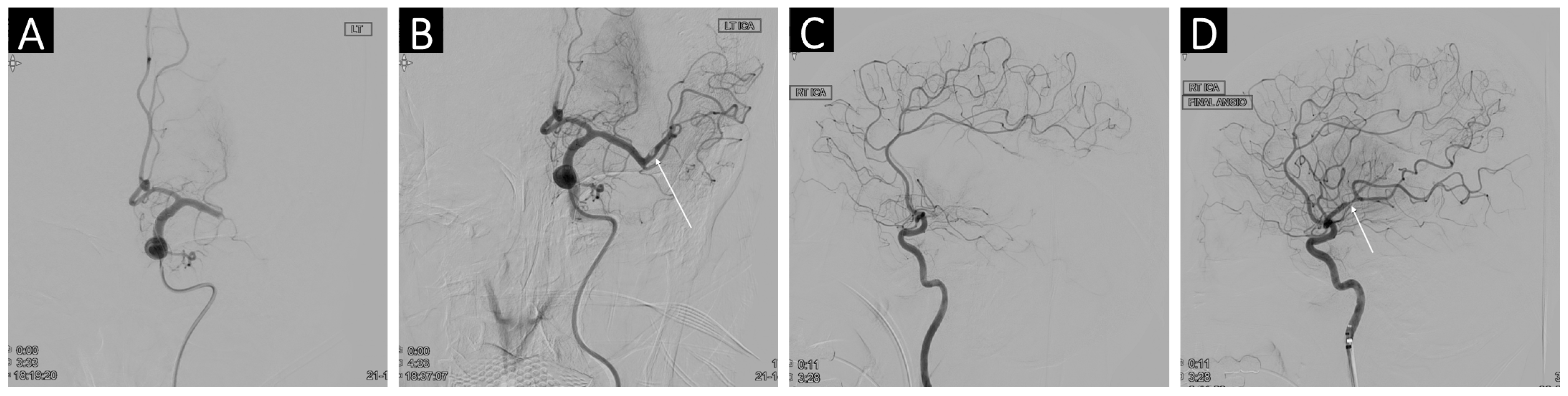
2.3. Thrombectomy Procedure and Medication
2.4. Angiographic and Clinical Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
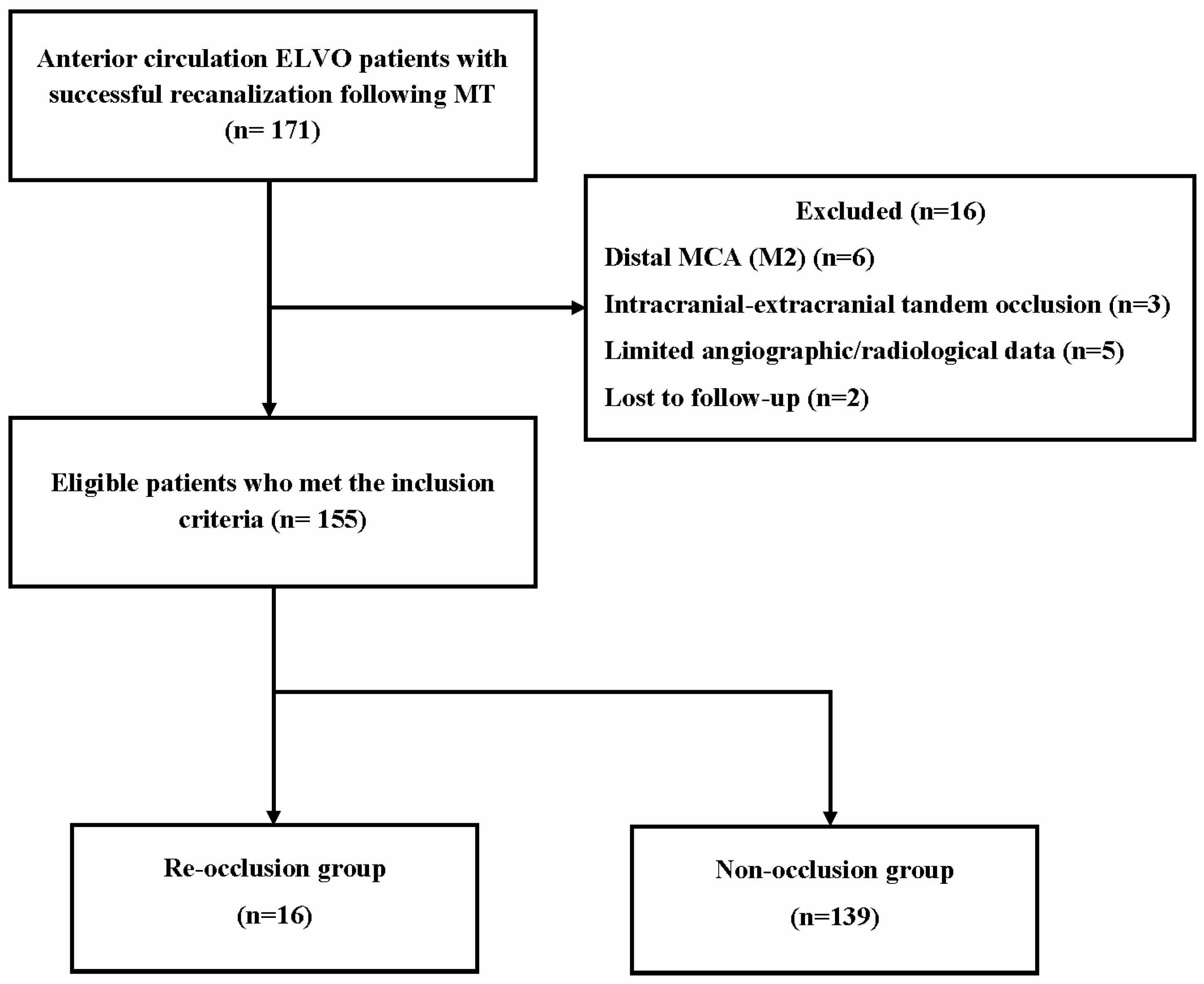
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Risk Factors for Re-Occlusion
3.3. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.S.; Beumer, D.; van den Berg, L.A.; Lingsma, H.F.; Yoo, A.J.; Schonewille, W.J.; Vos, J.A.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Wermer, M.J.H.; et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Menon, B.K.; Van Zwam, W.H.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Mitchell, P.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Dávalos, A.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; van der Lugt, A.; de Miquel, M.A.; et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016, 387, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Mitchell, P.J.; Kleinig, T.J.; Dewey, H.M.; Churilov, L.; Yassi, N.; Yan, B.; Dowling, R.J.; Parsons, M.W.; Oxley, T.J.; et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.O.A.; Cheung, I.H.W.; Lau, K.K.; Brinjikji, W.; Kallmes, D.F.; Krings, T. Outcomes of stent retriever versus aspiration-first thrombectomy in ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassélius, J.; Hall, E.; Ramgren, B.; Andersson, T.; Ullberg, T. Procedural factors associated with successful recanalization in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with endovascular thrombectomy—A nationwide register-based observational study. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2024, 15910199241248268 , Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmeier, L.; Faizy, T.D.; Broocks, G.; Meyer, L.; Heitkamp, C.; Brekenfeld, C.; Thaler, C.; Steffen, P.; Schell, M.; Deb-Chatterji, M.; et al. Association between recanalization attempts and functional outcome after thrombectomy for large ischemic stroke. Stroke 2023, 54, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajthia, O.; Almallouhi, E.; Ali, H.; Essibayi, M.A.; Bass, E.; Neyens, R.; Anadani, M.; Chalhoub, R.; Kicielinski, K.; Lena, J.; et al. Failed mechanical thrombectomy: Prevalence, etiology, and predictors. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 139, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gu, F.; Ding, J.; Bian, J.; Wang, N.; Shu, R.; Li, Q.; Xu, X. The predictors and prognosis for unexpected reocclusion after mechanical thrombectomy: A meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ding, J.; Sui, X.; Qi, Z.; Wu, L.; Sun, C.; Ji, K.; Ma, Q.; Ji, X.; Liu, K.J. Prognosis and risk factors for reocclusion after mechanical thrombectomy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marto, J.P.; Strambo, D.; Hajdu, S.D.; Eskandari, A.; Nannoni, S.; Sirimarco, G.; Bartolini, B.; Puccinelli, F.; Maeder, P.; Saliou, G.; et al. Twenty-four–hour reocclusion after successful mechanical thrombectomy: Associated factors and long-term prognosis. Stroke 2019, 50, 2960–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhoisne, M.; Puy, L.; Bretzner, M.; Bricout, N.; Behal, H.; Cordonnier, C.; Henon, H. Early reocclusion after successful mechanical thrombectomy for large artery occlusion–related stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 18, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosimann, P.J.; Kaesmacher, J.; Gautschi, D.; Bellwald, S.; Panos, L.; Piechowiak, E.; Dobrocky, T.; Zibold, F.; Mordasini, P.; El-Koussy, M.; et al. Predictors of unexpected early reocclusion after successful mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke patients. Stroke 2018, 49, 2643–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, M.; Remollo, S.; Quesada, H.; Renú, A.; Tomasello, A.; Minhas, P.; Pérez de la Ossa, N.; Rubiera, M.; Llull, L.; Cardona, P.; et al. Vessel patency at 24 hours and its relationship with clinical outcomes and infarct volume in REVASCAT trial (randomized trial of revascularization with solitaire Fr device versus best medical therapy in the treatment of acute stroke due to anterior circulation large vessel occlusion presenting within eight hours of symptom onset). Stroke 2017, 48, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Hwang, Y.H.; Park, S.P.; Kim, Y.S.; Baik, S.K. Instant reocclusion following mechanical thrombectomy of in situ thromboocclusion and the role of low-dose intra-arterial tirofiban. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 37, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Kang, D.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Liebeskind, D.S. Impact of target arterial residual stenosis on outcome after endovascular revascularization. Stroke 2016, 47, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Yoo, A.J.; Khatri, P.; Tomsick, T.A.; von Kummer, R.; Saver, J.L.; Marks, M.P.; Prabhakaran, S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Fitzsimmons, B.F.M.; et al. Recommendations on angiographic revascularization grading standards for acute ischemic stroke: A consensus statement. Stroke 2013, 44, 2650–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Correia, M.A.; Marto, J.P.; Carvalho Dias, M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Nguyen, T.N.; Nogueira, R.G.; Aboul-Nour, H.; Marin, H.; Bou Chebl, A.; et al. Reocclusion after successful endovascular treatment in acute ischemic stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, 15, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.B.; Yoon, W.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Baek, B.H.; Kim, J.T.; Park, M.S. Predictors and impact of hemorrhagic transformations after endovascular thrombectomy in patients with acute large vessel occlusions. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Yoo, J.S.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Kang, D.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hong, J.M.; Choi, J.W.; et al. Prognosis of acute intracranial atherosclerosis-related occlusion after endovascular treatment. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Kim, B.M. Angiographical identification of intracranial, atherosclerosis-related, large vessel occlusion in endovascular treatment. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, D.J.; Heo, J.H.; Nam, H.S.; Song, D.; Bang, O.Y. Importance of truncal-type occlusion in stentriever-based thrombectomy for acute stroke. Neurology 2016, 87, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A.C.O.; Orru, E.; Klostranec, J.M.; Yang, I.H.; Lau, K.K.; Tsang, F.C.P.; Lui, W.M.; Pereira, V.M.; Krings, T. Thrombectomy outcomes of intracranial atherosclerosis-related occlusions. Stroke 2019, 50, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Chang, C.H. Feasibility and safety of the strategy of first stenting without retrieval using Solitaire FR as a treatment for emergent large-vessel occlusion due to underlying intracranial atherosclerosis. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 135, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Tong, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, B.; Huo, X.; Luo, G.; Ma, N.; et al. Necessity and timing of angioplasty in acute large-vessel occlusion strokes due to intracranial atherosclerotic disease: A cohort analysis with data from the angel-ACT registry. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1087816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hong, J.M.; Lee, K.S.; Suh, H.I.; Demchuk, A.M.; Hwang, Y.H.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, J.S. Endovascular therapy of cerebral arterial occlusions: Intracranial atherosclerosis versus embolism. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2074–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, S.; Matouk, C.; Casaubon, L.K.; Silver, F.L.; Krings, T.; Mikulis, D.J.; Mandell, D.M. Vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in acute ischemic stroke: Effects of embolism and mechanical thrombectomy on the arterial wall. Stroke 2014, 45, 2330–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arturo Larco, J.; Abbasi, M.; Liu, Y.; Madhani, S.I.; Shahid, A.H.; Kadirvel, R.; Brinjikji, W.; Savastano, L.E. Per-pass analysis of recanalization and good neurological outcome in thrombectomy for stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2022, 28, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Re-Occlusion (n = 16) | Non-Occlusion (n = 139) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male | 8 (47.1) | 66 (47.5) | 0.855 |
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 69.3 ± 14.4 | 69.9 ± 11.9 | 0.857 |
| Medical history | |||
| Hypertension | 7 (43.8) | 66 (47.5) | 0.785 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 7 (43.8) | 36 (25.9) | 0.133 * |
| Dyslipidemia | 5 (31.3) | 44 (31.7) | 0.975 |
| Current smoking | 4 (25.0) | 36 (25.9) | 0.940 |
| Coronary heart disease | 4 (25.0) | 33 (23.7) | 0.916 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 3 (18.8) | 43 (30.9) | 0.315 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 3 (18.8) | 19 (13.7) | 0.634 |
| Anticoagulant pretreatment | 3 (18.8) | 24 (17.3) | 0.890 |
| Antiplatelet pretreatment | 3 (18.8) | 51 (36.7) | 0.156 * |
| Baseline NIHSS score, median (IQR) | 17.5 (11.5–21.5) | 17 (11–20) | 0.801 |
| ASPECTS, median (IQR) | 8 (7–9) | 8 (8–9) | 0.706 |
| Site of occlusion | 0.208 | ||
| Intracranial ICA | 8 (50.0) | 45 (32.4) | |
| MCA - M1 | 8 (50.0) | 94 (67.6) | |
| Stroke etiology | |||
| Large-artery atherosclerosis | 8 (50.0) | 33 (23.7) | 0.024 * |
| Cardioembolic | 8 (50.0) | 94 (67.6) | 0.208 |
| Other or unknown | 0 (0) | 8 (5.8) | 0.328 |
| Procedure-related data | |||
| IVT | 9 (56.3) | 95 (68.3) | 0.379 |
| Use of balloon guiding catheter | 10 (62.5) | 86 (61.9) | 0.962 |
| Use of aspiration catheter | 4 (25.0) | 36 (25.9) | 0.940 |
| Time metrics | |||
| Onset-to-puncture, min, mean (SD) | 274.4 ± 41.4 | 262.7 ± 54.6 | 0.316 |
| Onset-to-IVT, min, mean (SD) | 176.7 ± 25.6 | 167.4 ± 47.7 | 0.566 |
| IVT-to-puncture, min, mean (SD) | 98.3 ± 17.3 | 87.3 ± 28.6 | 0.258 |
| Procedure time, min, mean (SD) | 51.6 ± 13.3 | 47.8 ± 17.8 | 0.318 |
| Number of device passes, mean (SD) | 2.4 ± 1.3 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 0.004 * |
| Number of device passes > 2 | 6 (37.5) | 23 (16.5) | 0.046 |
| Residual thrombus or stenosis | 7 (43.8) | 27 (19.4) | 0.026 * |
| Permanent stenting | 2 (12.5) | 28 (20.1) | 0.416 |
| Variables | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes mellitus | 2.465 (0.708–8.585) | 0.156 |
| Antiplatelet pretreatment | 0.463 (0.112–1.916) | 0.288 |
| Large-artery atherosclerosis | 3.942 (1.247–12.464) | 0.020 * |
| Number of device passes | 2.509 (1.352–4.654) | 0.004 * |
| Residual thrombus or stenosis | 4.123 (1.267–13.415) | 0.019 * |
| Re-Occlusion (n = 16) | Non-Occlusion (n = 139) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIHSS scores at discharge, median (IQR) | 15 (9.75–22) | 8 (4–12) | <0.001 * |
| mRS scores at 3 months, median (IQR) | 3 (2–5) | 2 (1–3) | 0.017 * |
| Functional independence | 5 (31.3) | 83 (59.7) | 0.037 * |
| Mortality | 3 (18.8) | 14 (10.1) | 0.296 |
| Any ICH | 5 (31.3) | 38 (27.3) | 0.759 |
| Symptomatic ICH | 2 (12.5) | 10 (7.2) | 0.555 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, I.-H.; Ha, S.-K.; Lim, D.-J.; Choi, J.-I. Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Arterial Re-Occlusion After Successful Mechanical Thrombectomy for Emergent Intracranial Large Vessel Occlusion. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247640
Lee I-H, Ha S-K, Lim D-J, Choi J-I. Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Arterial Re-Occlusion After Successful Mechanical Thrombectomy for Emergent Intracranial Large Vessel Occlusion. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(24):7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247640
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, In-Hyoung, Sung-Kon Ha, Dong-Jun Lim, and Jong-Il Choi. 2024. "Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Arterial Re-Occlusion After Successful Mechanical Thrombectomy for Emergent Intracranial Large Vessel Occlusion" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 24: 7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247640
APA StyleLee, I.-H., Ha, S.-K., Lim, D.-J., & Choi, J.-I. (2024). Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Arterial Re-Occlusion After Successful Mechanical Thrombectomy for Emergent Intracranial Large Vessel Occlusion. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(24), 7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247640






