Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy is becoming the standard of care for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. However, T-cell activation by ICIs frequently induces a flare-up of preexisting autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are increasingly used in the treatment of RA, but they could interfere with the efficacy of ICIs by inhibiting interferon signaling. Case Report: Here, we describe a case in which upadacitinib, a JAK1-selective inhibitor, was used to manage a severe RA flare-up occurring during ICI therapy with pembrolizumab, an anti-programmed cell death protein-1 antibody. A 54-year-old man with RA was diagnosed with grade IV lung squamous cell carcinoma. The patient had maintained RA remission for 4 years at the time of lung cancer diagnosis. After seven cycles of pembrolizumab therapy, the size of the primary tumor was markedly reduced, but a severe RA flare-up and organizing pneumonia (OP)-like pulmonary lesions occurred. Considering the severity of the flare-up, pembrolizumab was discontinued. Upadacitinib induced swift recovery from the RA flare-up and OP. Eleven months after the last pembrolizumab use, almost all metastatic lesions in the body had disappeared. We did not observe recurrence of lung cancer for more than 1 year during upadacitinib therapy. Conclusions: Upadacitinib could be a safe and effective option to treat severe RA flare-ups occurring during anti-PD-1 ICI therapy.
1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by persistent synovitis and progressive damage to multiple joints [1]. Over the past two decades, significant advances have been made in the management of RA. Immunomodulatory therapies with conventional, biological, and nonbiological targeted disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) have reduced the disease burden of RA [2]. Given the role of the immune system in tumor surveillance, however, these drugs could increase the risk of developing malignancies. Additionally, RA itself causes disturbances of the immune system, which can affect the risk of certain malignancies [3,4,5].
Lung cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers worldwide and remains the leading cause of cancer-related death [6]. Recent population-based cohort studies have shown that RA patients are 1.4 to 1.8 times more likely to develop lung cancer compared with the non-RA population [7,8,9,10,11]. In the US Veterans cohort from 2000 to 2017, RA patients had a 23% increased risk of all-cause mortality, and approximately 15% of excess deaths in RA patients were attributed to lung cancer [12]. In our cohort study, the standardized incidence rate compared with the general population was 2.5 for male RA patients, and the risk of lung cancer-related death was 2.5 times higher in RA patients than in non-RA patients between 2006 and 2021 [13,14].
Substantial improvements in our understanding of lung cancer biology at the molecular level have led to the development of new and effective immunotherapies for patients with lung cancer, especially those with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [15]. The most progress has been made in immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, which is becoming the standard of care for the treatment of advanced NSCLC. The expression of immune checkpoint proteins, such as programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)/programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), downregulates T-cell activation and promotes T-cell apoptosis. This mechanism helps to protect the body from autoimmunity in physiological conditions, but tumor cells utilize it to evade the host immune system [16,17]. Monoclonal antibodies against PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 are most commonly used as ICIs in the treatment of a wide range of malignancies. In many clinical trials for advanced NSCLC, these ICIs, whether as monotherapy or in combination, have shown a significant survival benefit [18,19].
However, T-cell activation by ICIs frequently induces a broad spectrum of immune-related adverse events (irAEs). In particular, patients with preexisting autoimmune disease are 1.3 to 1.7 times more likely to report irAEs than those without this condition [20,21]. The pooled occurrence rates of irAEs such as flare-ups and new-onset irAEs were 35% to 50% and 23% to 34%, respectively [21,22,23,24]. Most irAEs were manageable with oral glucocorticoid therapy, but some cases required methotrexate (MTX) or biological DMARDs such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors or interleukin (IL)-6 inhibitors [17,25]. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, nonbiological targeted DMARDs, are increasingly used in the treatment of RA [26,27]. However, JAK inhibitors might interfere with the efficacy of ICIs by inhibiting interferon (IFN) signaling [28,29]. The use of JAK inhibitors for the management of flare-ups in RA patients receiving ICI therapy has rarely been reported in the medical literature.
In this study, we report on a case in which upadacitinib, a JAK1-selective inhibitor, was used to manage a severe RA flare-up occurring in a patient receiving ICI therapy with the anti-PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab against stage IV lung squamous cell carcinoma.
2. Case Presentation
In August 2011, a 54-year-old Japanese man with a tobacco smoking history of 35 pack-years was diagnosed with seropositive RA. The patient simultaneously developed biopsy-proven organizing pneumonia (OP). The patient exhibited high levels of disease activity for RA, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (anti-CCP Abs), and rheumatoid factor (RF). Pulmonary conditions improved markedly following a 1-month course of high-dose steroid therapy. During the tapering-off of the steroid, MTX monotherapy was introduced as the first-line DMARD for RA. No relapse of OP occurred after the start of steroid tapering. The patient’s RA activity was well controlled thereafter. Seven years later, the patient experienced a flare-up of articular symptoms, but the introduction of peficitinib, a JAK inhibitor, produced favorable outcomes and maintained remission for 4 years. The patient’s health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) score was zero.
On 6 December 2022, the patient presented with chest pain. Chest radiography revealed a mass (approximately 70 mm × 60 mm in diameter) in the right upper lobe and pleural effusion (Figure 1A). Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) revealed multiple abnormal uptakes (Figure 2). A large solid mass (65 mm in diameter) in the right upper lobe and separate nodules in the right middle and right lower lobes were observed. The maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax) in the pulmonary mass was 11.8. PET-CT also detected metastatic pleural nodules and malignant pleural effusion in the right lung. High metastatic activity was observed in hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes on both sides (SUVmax, 9.8), multiple bones (breastbone, vertebral bodies, bilateral ribs, left scapula, and bilateral iliac bones; SUVmax, 13.7), and the right adrenal gland (SUVmax, 9.3). The clinical tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage was IVB (c-T4N3M1ac). Transbronchial biopsy of the pulmonary lesion revealed that the histological type was squamous cell carcinoma. Molecular genetic testing of biopsy samples did not detect epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangement (fusion), c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS-1) gene rearrangement (fusion), or Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog G12C (KRASG12C) mutation. PD-L1 expression according to the tumor proportion score (TPS) was >75%.
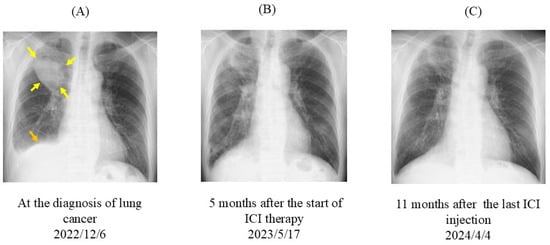
Figure 1.
Chest radiographs. (A) At lung cancer diagnosis, a large mass (yellow arrows) and pleural effusion (orange arrow) were observed in the right lung. (B) Five months after the start of chemotherapy and ICI therapy, the tumor size had reduced. (C) Eleven months after the last ICI injection, tumor expansion was not observed. ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor.
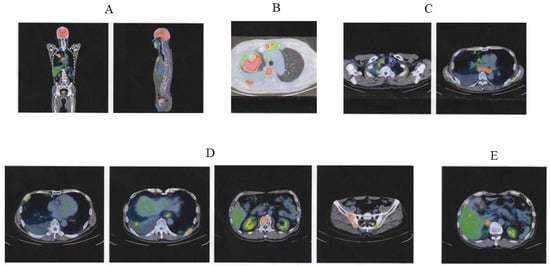
Figure 2.
PET-CT images at lung cancer diagnosis. (A) Multiple abnormal signals were observed. (B) A large mass with strong abnormal uptake was prominent in the right upper lobe of the lung. Abnormal uptakes were also detected in pleural effusion and nodules in the right lung and multiple bones (breastbone and vertebral bodies). (C) High metastatic activity was observed in hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes on both sides. (D) Multiple bone metastases were detected in vertebral bodies, bilateral ribs, and bilateral iliac bones. (E) Abnormal uptake was detected in the right adrenal gland. PET, positron emission tomography; CT, computed tomography; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor.
A clinical course with relevant care is presented in Figure 3. On 21 December 2022, the patient started carboplatin (area under the curve, 5 mg/mL/min on day 1) and nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel, 100 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15) every 3 weeks for four cycles as the first-line chemotherapy, and concomitantly commenced ICI therapy with pembrolizumab, an anti-PD-1 antibody, at 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks. When ICI therapy was started, the patient’s RA had been in remission for 4 years under peficitinib therapy. Peficitinib was discontinued because of concern that a JAK inhibitor could reduce the efficacy of ICI therapy.
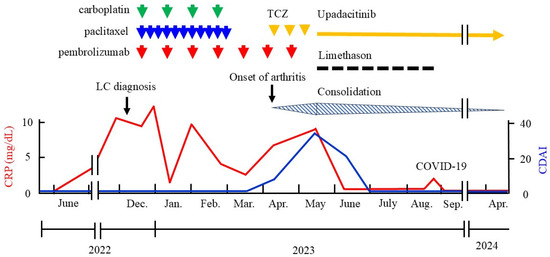
Figure 3.
Clinical course with relevant treatment. During upadacitinib therapy, the patient suffered from COVID-19 infection (23 August 2023), but his symptoms were mild. The red line represents serum CRP values and the blue line represents CDAI values. TCZ, tocilizumab; LC, lung cancer; CRP, C-reactive protein; CDAI, clinical disease activity index; COVID-19, coronavirus infectious disease-19.
On 9 April 2023, the patient complained of pain and swelling of the right knee; serum C-reactive protein (CRP) level had increased to 6.5 mg/dL. Along with the occurrence of knee arthritis, a small consolidation appeared in the right lower lobe (S6) (Figure 4A). Sputum was negative for bacterial cultures and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for Pneumocystis jirovecii. Antibiotics were not effective. The patient had previously suffered from biopsy-proven OP at RA onset, and OP often follows an RA flare-up [30]. Because RA flare-up and RA-associated OP were suspected, tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, was introduced as a monotherapy via subcutaneous injection of 162 mg every other week.
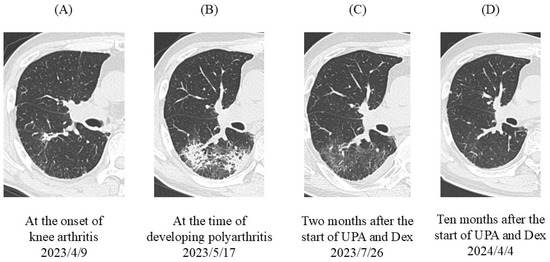
Figure 4.
Chest HRCT scans. (A) At the onset of knee arthritis, a small consolidation appeared in the right lower lobe (S6). (B) At the time the patient developed polyarthritis, patchy consolidations and ground-glass opacities spread from S6 to S10. (C) Two months after the start of UPA and Dex therapies, consolidation was improved but ground-glass attenuation remained. (D) Ten months after the start of UPA and Dex therapies, abnormal shadows completely disappeared. HRCT, high-resolution computed tomography; UPA, upadacitinib; Dex, dexamethasone.
On 17 May 2023, despite the use of tocilizumab, the patient developed polyarthritis with a high clinical disease activity index (CDAI score, 35) and severe functional disability (HAQ score 1.75). Serum CRP was highly elevated (9.1 mg/dL). The results of the synovial fluid test were as follows: Rivalta reaction, positive; total cell count, 12,220/mL; segmented leukocytes, 75%; lymphocytes, 20%; protein, 4.3 g/dL; glucose, 77 mg/dL; and lactate dehydrogenase, 723 U/mL. The consolidation in the right lung spread from S6 to S10 (Figure 4B). The severity of the RA flare-up was grade 3 according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (version 5.0). Limethason, a lipid emulsion containing dexamethasone, was started at a dose equivalent to 2.5 mg of dexamethasone intravenously every 2 weeks (a total of eight times). Tocilizumab was switched to the JAK1 inhibitor upadacitinib (15 mg/day orally). Considering the severity of the RA flare-up, ICI therapy was discontinued; a total of seven cycles were completed. Following upadacitinib therapy, serum CRP was markedly decreased. The patient achieved remission within 6 weeks. Two months later, consolidation was improved (Figure 4C). As of 4 April 2024, the patient’s OP lesions were completely resolved (Figure 4D) and his RA remained in remission.
On 17 May 2023, the size of the primary tumor was markedly reduced on chest radiography (Figure 1B). Eleven months after the last ICI injection, no change in tumor size was observed (Figure 1C). On 8 April 2024, PET-CT revealed that the abnormal signal in the primary tumor had markedly diminished (SUVmax, 2.1) and the separate nodules in the lung had disappeared (Figure 5). Residual small uptake was seen in the right hilar lymph node (SUVmax 3.6), but other abnormal signals were absent.
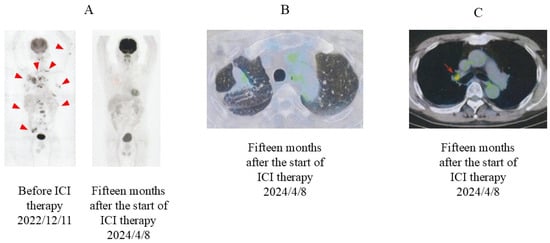
Figure 5.
PET and PET-CT images after ICI therapy. (A) PET images (not combined with CT), taken before and 15 months after the start of ICI therapy. Before the start of ICI therapy, multiple abnormal signals were observed (red arrowheads). (B) PET-CT image taken 15 months after the start of ICI therapy. Abnormal uptake diminished in the primary tumor and disappeared in other multiple lesions. (C) PET-CT image taken 15 months after the start of ICI therapy. Residual small uptake remained in the right hilar lymph node (red arrow). PET, positron emission tomography; CT, computed tomography; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor.
3. Discussion
In the current study, we describe a severe RA flare-up during ICI therapy with the anti-PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab for advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma. The patient had maintained remission for 4 years with peficitinib at lung cancer diagnosis, and this JAK inhibitor was discontinued at the start of ICI therapy. Sixteen weeks later, an RA flare-up and OP-like lesions appeared. Tocilizumab monotherapy failed to control these conditions. The use of upadacitinib together with the intravenous injection of dexamethasone induced the remission of RA within 6 weeks, and OP lesions also improved. Although pembrolizumab was discontinued following the flare-up, the patient had no recurrence of lung cancer for more than 1 year during upadacitinib therapy.
Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have shown that RA patients are more susceptible to ICI-related disease flare-ups than patients with other preexisting rheumatic autoimmune diseases: the pooled relative risk is 1.35 [23,24]. In a retrospective cohort study of RA patients with malignancies, McCarter et al. showed that flare-ups occurred in 46% (46 of 100 patients) after starting ICI therapy. In their study, 82% of patients were in remission or had low disease activity at the start of ICI therapy, and 25% were on glucocorticoids and 35% were receiving any DMARDs during ICI therapy. Among these patients, most did not change their anti-RA therapies after starting ICI therapy. Patient characteristics at the start of ICI therapy, including RA disease activity, RA treatment, deformities, and cancer type, were not associated with the risk of flare-up. Most flare-up cases were not severe (grade 1 or 2) and were manageable with oral glucocorticoids. Approximately 20% of patients discontinued ICI therapy following a flare-up [31]. In a single-center retrospective analysis, Efuni et al. showed that RA flare-up occurred in 55% (12 of 20 patients) after the initiation of ICI therapy. When ICI therapy was introduced, 86% of patients had inactive RA, and 73% were receiving glucocorticoids and/or any DMARDs. Patients on glucocorticoid therapies continued their current dose after the start of ICI therapy. Approximately 80% of patients experiencing disease flare-up were successfully treated with oral glucocorticoids, and most patients continued to receive ICI therapy despite flare-up [32]. In our case, the patient had maintained remission for 4 years during peficitinib therapy, and functional disability was not observed at the time of starting ICI therapy. We cannot entirely exclude the possibility that the discontinuation of peficitinib simultaneously with the start of ICI therapy might have resulted in RA flare-up independently of immune activation by ICI therapy. However, the flare-up that occurred after the start of ICI therapy was more severe than a previous flare-up before the development of lung cancer, and it was not resolved by tocilizumab therapy. Although the precise mechanism of irAEs remains unclear, the administration of ICIs leads to aberrant cytotoxic T-cell activation, increased autoantibody production, and production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-17, and IL-6, which can facilitate the emergence of irAEs [33]. Therefore, targeted inhibition of IL-6 signaling by tocilizumab is considered a rational therapy to treat rheumatic irAEs. In the present case, however, tocilizumab was not effective in the treatment of the RA flare-up following ICI therapy. This can be explained by the idea that disease-associated immune responses involve a complex interaction of multiple cytokines in RA and rheumatic irAEs. Therefore, the blockage of a single cytokine does not necessarily lead to remission in all RA patients [27].
In our case, upadacitinib was effective in managing the RA flare-up occurring after the introduction of ICI therapy. Additionally, the antitumor response continued during upadacitinib therapy, even after discontinuation of ICI therapy. Upadacitinib is a JAK1-selective inhibitor, which interferes with the membrane-to-nucleus signaling of multiple cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-10, IL-2, and type I and type II IFNs, by blocking intracellular JAK-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathways [27,34]. Among these cytokines, type I and type II IFNs are considered key mediators in the generation of antitumor action, including direct effects on tumor cells and activation of antitumor immune response [28,35]. In contrast, under conditions of persistent antigen exposure and prolonged IFN signaling, IFNs can have suppressive effects on antitumor immunity. IFNγ, a single type II IFN, has feedback inhibitory effects that avoid the potential toxicity associated with excessive response, which can attenuate antitumor effect. Upon tumor antigen recognition by T cells, prolonged IFNγ production by T cells increases the expression of PD-L1 on tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages. PD-L1 interacts with its cognate inhibitory receptor PD-1 expressed on tumor-infiltrating T cells, which leads to exhaustion of the T cells and immune evasion of tumor cells. Blocking this negative feedback is a major therapeutic effect of ICI therapy with anti-PD-1 antibodies [29,36,37]. IFNγ upregulates PD-L1 expression on solid tumor cells [38], and the blockade of JAK1 signaling by upadacitinib leads to inhibition of the expression of multiple cytokines (including IFNγ). Thus, it is logical to hypothesize that upadacitinib may play a critical role in the management of ICI-related irAEs. Given the importance of IFNs in the generation of antitumor immune response and the upregulation of PD-L1, however, we were concerned that the use of upadacitinib to treat the RA flare-up might impede the antitumor effect of anti-PD-1 antibody therapy by inhibiting IFN signaling. Nevertheless, recurrence of lung cancer was not observed in our patient during upadacitinib therapy.
Acquired resistance to ICI therapy is common in patients with NSCLC treated with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. Memon et al. showed an association of chronic and upregulated IFN signaling with acquired resistance in tumors from NSCLC patients who developed resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 blocking therapy [39]. Using in vivo mouse models, Benci et al. showed that prolonged IFNγ signaling in tumor cells can augment the expression of IFN-stimulated genes and ligands for multiple T-cell inhibitory receptors on tumor cells, which increases PD-L1-dependent and PD-L1-independent resistance to immune checkpoint blockage through multiple inhibitory pathways. Both type I and type II IFNs maintain this resistance program. Therefore, blocking IFN signaling via JAK inhibitors can improve immune function of distinct exhausted T-cell populations and restore antitumor responses [40]. In our case, durable antitumor response and RA remission continued for more than 1 year during upadacitinib therapy, which may be explained by this mechanism. In a recent phase 1 clinical trial of the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib with the anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab, Zak et al. found that the combination of agents yielded the best overall response rate in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma who were refractory or relapsed after prior ICI therapy. Ruxolitinib was shown to rescue the function of exhausted T cells and enhance the efficacy of ICI blockade in preclinical solid tumor and lymphoma models [41]. Mathew et al. showed that administration of the JAK1 inhibitor itacitinib after ICI therapy with the anti-PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab improved immune function and antitumor response in mice and also resulted in high response rates in a phase 2 clinical trial for metastatic NSCLC. The patients failed to respond to initial ICI therapy with anti-PD-1 antibody but responded well after addition of the JAK1 inhibitor [42]. These studies demonstrated the therapeutic potential of JAK inhibition in combination with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy.
Information about PD-L1 expression levels at the tumor site will contribute to guiding and optimizing PD-1/PD-L1 blocking immunotherapy, especially if this therapy is used in combination with JAK inhibitors. Recently, Mishra et al. reported an accurate and non-invasive PD-L1 quantification tool using PET molecular imaging with two new radiolabeled peptides, which is useful for quantifying total PD-L1 levels at baseline and monitoring accessible PD-L1 levels during therapy. PET monitoring of PD-L1 could provide valuable insights into correlating changes in PD-L1 expression levels with observed responses throughout therapy [43,44].
Murray et al. reported a case in which the use of the pan-JAK inhibitor tofacitinib resulted in rapid and sustained remission from inflammatory arthritis that had occurred after 6 months of ICI therapy with pembrolizumab for lung adenocarcinoma. The patient remained in full remission from arthritis and lung cancer 75 weeks after commencing tofacitinib and discontinuing pembrolizumab [45]. In a recent retrospective observational study, Liu et al. showed that short-term treatment with tofacitinib (for a median of 52.5 days) induced promising clinical efficacy in 47 out of 53 patients (88.7%) experiencing irAEs (including myocarditis, myositis, and hepatitis) during ICI therapies, mainly with anti-PD-1 antibody. ICI therapy was permanently discontinued in 98% of patients, but the antitumor efficacy of ICIs seemed not to be compromised by tofacitinib therapy [46]. Tofacitinib is a first-generation JAK inhibitor, which inhibits JAK1, JAK 3, and partially JAK2. Although peficitinib successfully controlled a previous RA flare-up and maintained remission for 4 years in our case, it is also a non-selective pan-JAK inhibitor. Upadacitinib is a next-generation JAK inhibitor, and thus has higher selectivity than tofacitinib. Considering the risk of unwanted side effects, upadacitinib may be safer for the treatment of RA patients with advanced malignancies [27]. Therefore, in our case, we chose upadacitinib to treat an RA flare-up during ICI therapy for lung cancer. Nevertheless, we should keep in mind that head-to-head direct comparison studies about the safety of different JAK inhibitors are lacking and, therefore, it is not established whether increased selectivity will reduce the risk of malignancies [34].
In the present case, the patient had a tobacco smoking history of 35 pack-years at the time of RA diagnosis. For the treatment of a disease flare-up occurring during MTX monotherapy before the development of lung cancer, we introduced the JAK inhibitor peficitinib. In the oral surveillance study, RA patients aged ≥50 years with one additional cardiovascular risk factor who were receiving tofacitinib 10 mg two times daily had an increased risk for lung cancer compared with those receiving TNF inhibitors. The risk of lung cancer was also increased in current and past smokers who were receiving tofacitinib 10 mg two times a day compared with patients who had never smoked, although these risks were not observed at the currently approved dosage for RA [47]. These data may influence the choice of treatment when the decision is between a JAK inhibitor and a TNF inhibitor, particularly in patients who are at increased risk of lung cancer (i.e., current and past smokers). However, it is not clear whether the increased risk of lung cancer associated with tofacitinib therapy observed in the oral surveillance study may be generalized to other JAK inhibitors [2]. Although it may be hard to justify the use of a JAK inhibitor as a first-line advanced therapy in the majority of RA patients [48], our patient had poor prognostic factors for RA, namely high disease activity and high levels of serum CRP, anti-CCP Abs, and RF, at the first disease flare-up despite long-term MTX therapy. Severe functional disability was also observed. Additionally, the patient desired a DMARD that can be administered orally. In our prospective cohort study, we found that although tofacitinib is an effective treatment option for MTX-refractory RA patients, its effect is significantly lower in patients with previous failure to biological DMARD therapy compared with that in biological DMARD-naive patients [49]. Using our ongoing real-world registries consisting of MTX-refractory RA patients, we also found that tofacitinib can induce greater improvements in biological DMARD-naive patients compared with tocilizumab, but this difference was not observed in previous biological DMARD-failure patients [50]. Considering these points, we chose the JAK inhibitor to treat an RA flare-up that occurred before the lung cancer diagnosis.
4. Conclusions
JAK inhibitors are increasingly used in the treatment of RA. Given the role of IFN signaling in upregulating PD-L1 expression, the use of JAK inhibitors might induce tumor resistance to anti-PD-1 antibody by inhibiting IFN signaling. Nevertheless, in the present case, upadacitinib induced the rapid resolution of a severe RA flare-up occurring during anti-PD-1 ICI therapy for advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma. Antitumor response continued during upadacitinib therapy, even after discontinuation of the anti-PD-1 ICI therapy. To date, we have not observed tumor recurrence or RA relapse for more than 1 year in our patient. To our knowledge, this is the first case in which upadacitinib successfully controlled a severe RA flare-up and maintained the antitumor immune response after anti-PD-1 ICI therapy for advanced lung cancer. Upadacitinib can be a safe and effective option to treat severe RA flare-up following anti-PD-1 ICI therapy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M. and K.N.; data curation, S.M., K.N., M.S. and K.O.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.; writing—review and editing, S.M., K.N., M.S. and K.O.; visualization, S.M. and K.N.; supervision, S.M. and K.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the nature of the publication (case report), which did not involve interventions on the patient other than routine clinical care and scientifically informed decisions based on the available data.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings are available from the Human Research Ethics Committee of NHO Kumamoto Saishun Medical Center for interested researchers who meet the criteria for access to confidential data. Because these data include patients’ personal information, the Committee does not recommend that such data be shared publicly. Please contact Mr. Masahiro Hamaguchi, the Control Manager of the Committee, at 616-syol@mail.hosp.go.jp to request data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewe, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilton, K.M.; Matteson, E.L. Malignancy incidence, management, and prevention in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Ther. 2017, 4, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cock, D.; Hyrich, K. Malignancy and rheumatoid arthritis: Epidemiology, risk factors and management. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Li, C.I. Impact of rheumatoid arthritis and biologic and targeted synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic agents on cancer risk and recurrence. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung cancer 2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidionysiou, K.; di Giuseppe, D.; Soderling, J.; Catrina, A.; Askling, J. Risk of lung cancer in rheumatoid arthritis and in relation to autoantibody positivity and smoking. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.J.; Nam, E.S.; Min, K.W.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; et al. Potential cancer risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A longitudinal Korean population-based analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Palmer, N.; Fox, K.; Liao, K.P.; Yu, K.H.; Kou, S.C. Large-scale real-world data analyses of cancer risks among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 153, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydon, M.; Pinto, S.; De Rycke, Y.; Fautrel, B.; Mariette, X.; Seror, R.; Tubach, F. Risk of cancer for patients with rheumatoid arthritis versus general population: A national claims database cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 35, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.H.; Cho, J.H.; Eun, Y.; Han, K.; Jung, J.; Cho, I.Y.; Yoo, J.E.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Park, S.Y.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and risk of lung Cancer: A nationwide cohort study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.M.; Yang, Y.; Roul, P.; Sauer, B.C.; Cannon, G.W.; Kunkel, G.; Michaud, K.; Baker, J.F.; Mikuls, T.R.; England, B.R. A narrowing mortality gap: Temporal trends of cause-specific mortality in a national matched cohort study in US veteranswith rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Ueki, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Nakamura, K.; Nakashima, K.; Hidaka, T.; Ishii, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Miyamura, T. Impact of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema on lung cancer risk and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Sakai, F.; Nakashima, K.; Nakamura, K. Incidence of and predictive factors for lung cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective long-term follow-up study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2024, roae084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamdani, H.; Matosevic, S.; Khalid, A.B.; Durm, G.; Jalal, S.I. Immunotherapy in lung cancer: Current landscape and future directions. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 823618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Callahan, M.K.; Flores-Chavez, A.; Keegan, N.; Khamashta, M.A.; Lambotte, O.; Mariette, X.; Prat, A.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, A.; Garaud, S.; Chiche, L.; Cornec, D.; Kostine, M. Immune-checkpoint inhibitor use in patients with cancer and pre-existing autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoi, K.; Chihara, Y.; Uchino, J.; Shimamoto, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Iwasaku, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Yamada, T.; Takayama, K. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for lung cancer treatment: A review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Qin, C.; Hu, H.; Liu, T.; He, Y.; Guo, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Zhou, H. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: Progress, challenges, and prospects. Cells 2022, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Huo, G.W.; Zhu, F.Y.; Yue, P.; Yuan, D.Q.; Chen, P. Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced cancer patients with autoimmune disease: A meta-analysis. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2145102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Olivo, M.A.; Kachira, J.J.; Abdel-Wahab, N.; Pundole, X.; Aldrich, J.D.; Carey, P.; Khan, M.; Geng, Y.; Pratt, G.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and uncontrolled trials reporting on the use of checkpoint blockers in patients with cancer and pre-existing autoimmune disease. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 207, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Wahab, N.; Shah, M.; Lopez-Olivo, M.A.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E. Use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of patients with cancer and preexisting autoimmune disease: A systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 168, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Huang, H.; Xiao, S.; Fan, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z. Immune checkpoint inhibitors therapies in patients with cancer and preexisting autoimmune diseases: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, S.; Ke, L.; Cui, H. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with rheumatologic preexisting autoimmune diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, J.A. Pre-existing autoimmune diseases and immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer treatment: Considerations about initiation, flares, immune-related adverse events, and cancer progression. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2024, 50, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadina, M.; Johnson, C.; Schwartz, D.; Bonelli, M.; Hasni, S.; Kanno, Y.; Changelian, P.; Laurence, A.; O’Shea, J.J. Translational and clinical advances in JAK-STAT biology: The present and future of jakinibs. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Kastrati, K.; Ghoreschi, K.; Gadina, M.; Heinz, L.X.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; O’Shea, J.; Laurence, A. Selectivity, efficacy and safety of JAKinibs: New evidence for a still evolving story. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.S.; Rautela, J.; Hertzog, P.J. Antitumour actions of interferons: Implications for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B. IFNgamma: Signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Koga, Y.; Sugimoto, M. Organizing pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A case-based review. Clin. Med. Insights Circ. Respir. Pulm. Med. 2015, 9, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarter, K.R.; Arabelovic, S.; Wang, X.; Wolfgang, T.; Yoshida, K.; Qian, G.; Kowalski, E.N.; Vanni, K.M.M.; LeBoeuf, N.R.; Buchbinder, E.I.; et al. Immunomodulator use, risk factors and management of flares, and mortality for patients with pre-existing rheumatoid arthritis after immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2024, 64, 152335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efuni, E.; Cytryn, S.; Boland, P.; Niewold, T.B.; Pavlick, A.; Weber, J.; Sandigursky, S. Risk of toxicity after initiating immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Q.M.; Watanabe, R.; Shiomi, M.; Fukumoto, K.; Nobashi, T.W.; Okano, T.; Yamada, S.; Hashimoto, M. Rheumatic immune-related adverse events due to immune checkpoint inhibitors: A 2023 update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.C.; Choy, E.; Baraliakos, X.; Szekanecz, Z.; Xavier, R.M.; Isaacs, J.D.; Strengholt, S.; Parmentier, J.M.; Lippe, R.; Tanaka, Y. Differential properties of Janus kinase inhibitors in the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, K.L.; Brockwell, N.K.; Parker, B.S. JAK-STAT signaling: A double-edged sword of immune regulation and cancer progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Diaz, A.; Shin, D.S.; Moreno, B.H.; Saco, J.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Sun, L.; Hugo, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Interferon receptor signaling pathways regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minn, A.J.; Wherry, E.J. Combination cancer therapies with immune checkpoint blockade: Convergence on interferon signaling. Cell 2016, 165, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, K.; Teh, J.L.; Okayama, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Kua, L.F.; Koh, V.; Smoot, D.T.; Ashktorab, H.; Oike, T.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. PD-L1 expression is mainly regulated by interferon gamma associated with JAK-STAT pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, D.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Ye, D.; Fromm, G.; Rizvi, H.; Zhang, X.; Keddar, M.R.; Mathew, D.; Yoo, K.J.; Qiu, J.; et al. Clinical and molecular features of acquired resistance to immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 209–224.e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benci, J.L.; Xu, B.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, T.J.; Dada, H.; Twyman-Saint Victor, C.; Cucolo, L.; Lee, D.S.M.; Pauken, K.E.; Huang, A.C.; et al. Tumor interferon signaling regulates a multigenic resistance program to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 2016, 167, 1540–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, J.; Pratumchai, I.; Marro, B.S.; Marquardt, K.L.; Zavareh, R.B.; Lairson, L.L.; Oldstone, M.B.A.; Varner, J.A.; Hegerova, L.; Cao, Q.; et al. JAK inhibition enhances checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma. Science 2024, 384, eade8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, D.; Marmarelis, M.E.; Foley, C.; Bauml, J.M.; Ye, D.; Ghinnagow, R.; Ngiow, S.F.; Klapholz, M.; Jun, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Combined JAK inhibition and PD-1 immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer patients. Science 2024, 384, eadf1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Kumar, D.; Gupta, K.; Lofland, G.; Sharma, A.K.; Banka, D.S.; Hobbs, R.F.; Dannals, R.F.; Rowe, S.P.; Gabrielson, E.; et al. Gallium-68-labeled peptide PET quantifies tumor exposure of PD-L1 therapeutics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Gupta, K.; Kumar, D.; Lofland, G.; Sharma, A.K.; Solnes, L.B.; Rowe, S.P.; Forde, P.M.; Pomper, M.G.; Gabrielson, E.W.; et al. Non-invasive PD-L1 quantification using [(18)F]DK222-PET imaging in cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, K.; Floudas, A.; Murray, C.; Fabre, A.; Crown, J.; Fearon, U.; Veale, D. First use of tofacitinib to treat an immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced arthritis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e238851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Zou, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Jiao, X.; et al. Tofacitinib for the treatment of immune-related adverse events in cancer immunotherapy: A multi-center observational study. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.R.; Yamaoka, K.; Chen, Y.H.; Bhatt, D.L.; Gunay, L.M.; Sugiyama, N.; Connell, C.A.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Menon, S.; et al. Malignancy risk with tofacitinib versus TNF inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the open-label, randomised controlled ORAL Surveillance trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.; Harkins, P.; Conway, R. Janus kinase inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis: An update on the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Yoshitama, T.; Ueki, Y. Tofacitinib therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: A direct comparison study between biologic-naïve and experienced patients. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Urata, Y.; Yoshitama, T.; Ueki, Y. Tofacitinib versus tocilizumab in the treatment of biological-naive or previous biological-failure patients with methotrexate-refractory active rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).