Combined Neuro-Humoral Modulation and Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
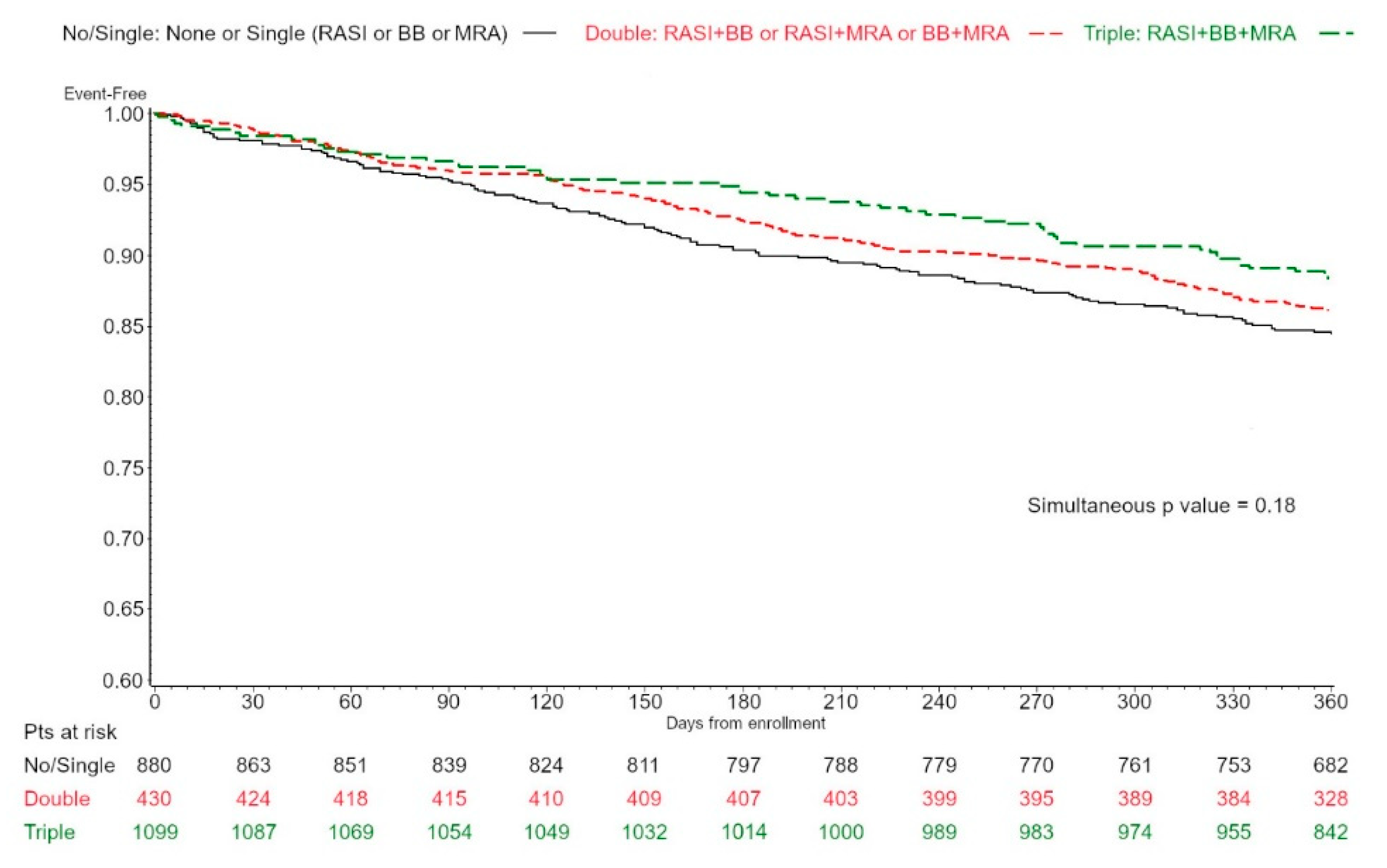
3.1. NHM Prescription and Distribution
3.2. Clinical Characteristics According to NHM
3.3. NHM and Outcome
4. Discussion
4.1. NHM Prescription in HF with EF > 40%
4.2. Factors Underlying Benefits of Combined NHM in HF with LVEF > 40%
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Conrad, N.; Judge, A.; Tran, J.; Mohseni, H.; Hedgecott, D.; Crespillo, A.P.; Allison, M.; Hemingway, H.; Cleland, J.G.; McMurray, J.J.V.; et al. Temporal trends and patterns in heart failure incidence: A population-based study of 4 million individuals. Lancet 2018, 391, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Choi, D.J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. EMPEROR-Preserved Trial Investigators. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, L.H.; Claggett, B.; Liu, J.; Lam, C.S.; Jhund, P.S.; Rosano, G.M.; Swedberg, K.; Yusuf, S.; Granger, C.B.; Pfeffer, M.A.; et al. Heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction in CHARM: Characteristics, outcomes and effect of candesartan across the entire ejection fraction spectrum. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.D.; Claggett, B.; Lewis, E.F.; Desai, A.; Anand, I.; Sweitzer, N.K.; O’Meara, E.; Shah, S.J.; McKinlay, S.; Fleg, J.L.; et al. TOPCAT Investigators. Influence of ejection fraction on outcomes and efficacy of spironolactone in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Jhund, P.S.; Claggett, B.L.; Packer, M.; Widimský, J.; Seferovic, P.; Rizkala, A.; Lefkowitz, M.; Shi, V.; McMurray, J.J.V.; et al. A putative placebo analysis of the effects of sacubitril/valsartan in heart failure across the full range of ejection fraction. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Bewarder, Y.; Kindermann, I. Ejection fraction in heart failure revisited- where does the evidence start? Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2363–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 4–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, e263–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maria, R.; Gori, M.; Marini, M.; Gonzini, L.; Benvenuto, M.; Cassaniti, L.; Municinò, A.; Navazio, A.; Ammirati, E.; Leonardi, G.; et al. Temporal trends in characteristics, treatment, and outcomes of heart failure in octogenarians over two decades. Rev. Española Cardiol. 2022, 75, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, M.; Marini, M.; De Maria, R.; Gonzini, L.; Gorini, M.; Cassaniti, L.; Benvenuto, M.; Municinò, A.; Navazio, A.; Ammirati, E.; et al. Italian Network on Heart Failure (IN-HF) Investigators. Age-related changes in clinical characteristics and outcomes of chronic heart failure outpatients in a cardiology setting. A report from the Italian Network on Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 346, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavazzi, L.; Senni, M.; Metra, M.; Gorini, M.; Cacciatore, G.; Chinaglia, A.; Di Lenarda, A.; Mortara, A.; Oliva, F.; Maggioni, A.P. IN-HF (Italian Network on Heart Failure) Outcome Investigators. Multicenter prospective observational study on acute and chronic heart failure: One-year follow-up results of IN-HF (Italian Network on Heart Failure) outcome registry. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Men, Ageing and Health: Achieving Health across the Life Span. 2001. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/66941 (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Anand, I.S.; Ge, J.; Lam, C.S.P.; Maggioni, A.P.; Martinez, F.; Packer, M.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Pieske, B.; et al. PARAGON-HF Investigators and Committees. Angiotensin-Neprilysin Inhibition in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, S.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Swedberg, K.; Granger, C.B.; Held, P.; McMurray, J.J.; Michelson, E.L.; Olofsson, B.; Ostergren, J. CHARM Investigators and Committees. Effects of candesartan in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved left- ventricular ejection fraction: The CHARM-Preserved Trial. Lancet 2003, 362, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Assmann, S.F.; Boineau, R.; Anand, I.S.; Claggett, B.; Clausell, N.; Desai, A.S.; Diaz, R.; Fleg, J.L.; et al. TOPCAT Investigators. Spironolactone for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, M.; Senni, M.; Gupta, D.K.; Charytan, D.M.; Kraigher-Krainer, E.; Pieske, B.; Claggett, B.; Shah, A.M.; Santos, A.B.; Zile, M.R.; et al. PARAMOUNT Investigators. Association between renal function and cardiovascular structure and function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 3442–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, E.; Vaduganathan, M.; Gori, M.; Gavazzi, A.; Butler, J.; Senni, M. Role of biomarkers in cardiac structure phenotyping in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Critical appraisal and practical use. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, G.; Gori, M.; Iorio, A.; D’Elia, E.; Moon, J.C.; Iacovoni, A.; Burocchi, S.; Schelbert, E.B.; Brambilla, P.; Sironi, S.; et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Myocyte, interstitium, microvascular, and metabolic abnormalities. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, M.; Lam, C.S.; Gupta, D.K.; Santos, A.B.; Cheng, S.; Shah, A.M.; Claggett, B.; Zile, M.R.; Kraigher-Krainer, E.; Pieske, B.; et al. PARAMOUNT Investigators. Sex-specific cardiovascular structure and function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarese, G.; Stolfo, D.; Sinagra, G.; Lund, L.H. Heart failure with mid-range or mildly reduced ejection fraction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, P.; Stolfo, D.; Merlo, M.; Gregorio, C.; Cannatà, A.; Ramani, F.; Nuzzi, V.; Lund, L.H.; Savarese, G.; Sinagra, G. Transient versus persistent improved ejection fraction in non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, B.P.; Wassall, R.; Lota, A.S.; Khalique, Z.; Gregson, J.; Newsome, S.; Jackson, R.; Rahneva, T.; Wage, R.; Smith, G.; et al. Withdrawal of pharmacological treatment for heart failure in patients with recovered dilated cardiomyopathy (TRED-HF): An open-label, pilot, randomised trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.L.; de Boer, R.A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.P.; Martinez, F.; et al. Baseline Characteristics of Patients with HF With Mildly Reduced and Preserved Ejection Fraction: DELIVER Trial. JACC Heart Fail. 2022, 10, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenewegen, A.; Rutten, F.H.; Mosterd, A.; Hoes, A.W. Epidemiology of heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1342–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, P.; Jackson, A.; Lam, C.S.P.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Zannad, F.; Pitt, B.; Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V. Interactions between left ventricular ejection fraction, sex and effect of neurohumoral modulators in heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPRINT Research Group; Lewis, C.E.; Fine, L.J.; Beddhu, S.; Cheung, A.K.; Cushman, W.C.; Cutler, J.A.; Evans, G.W.; Johnson, K.C.; Kitzman, D.W.; et al. Final Report of a Trial of Intensive versus Standard Blood-Pressure Control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Deng, Y.; Wu, S.; Ren, J.; Sun, G.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.D.; et al. STEP Study Group. Trial of Intensive Blood-Pressure Control in Older Patients with Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiade, M.; Peterson, E.D. Improving postdischarge outcomes in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure syndromes. JAMA 2011, 305, 2456–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.L.; Inciardi, R.M.; Fonarow, G.C.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D. Estimating the benefits of combination medical therapy in heart failure with mildly reduced and preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 2022, 145, 1741–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amario, D.; Rodolico, D.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Dahlström, U.; Crea, F.; Lund, L.H.; Savarese, G. Association between dosing and combination use of medications and outcomes in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Data from the Swedish Heart Failure Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
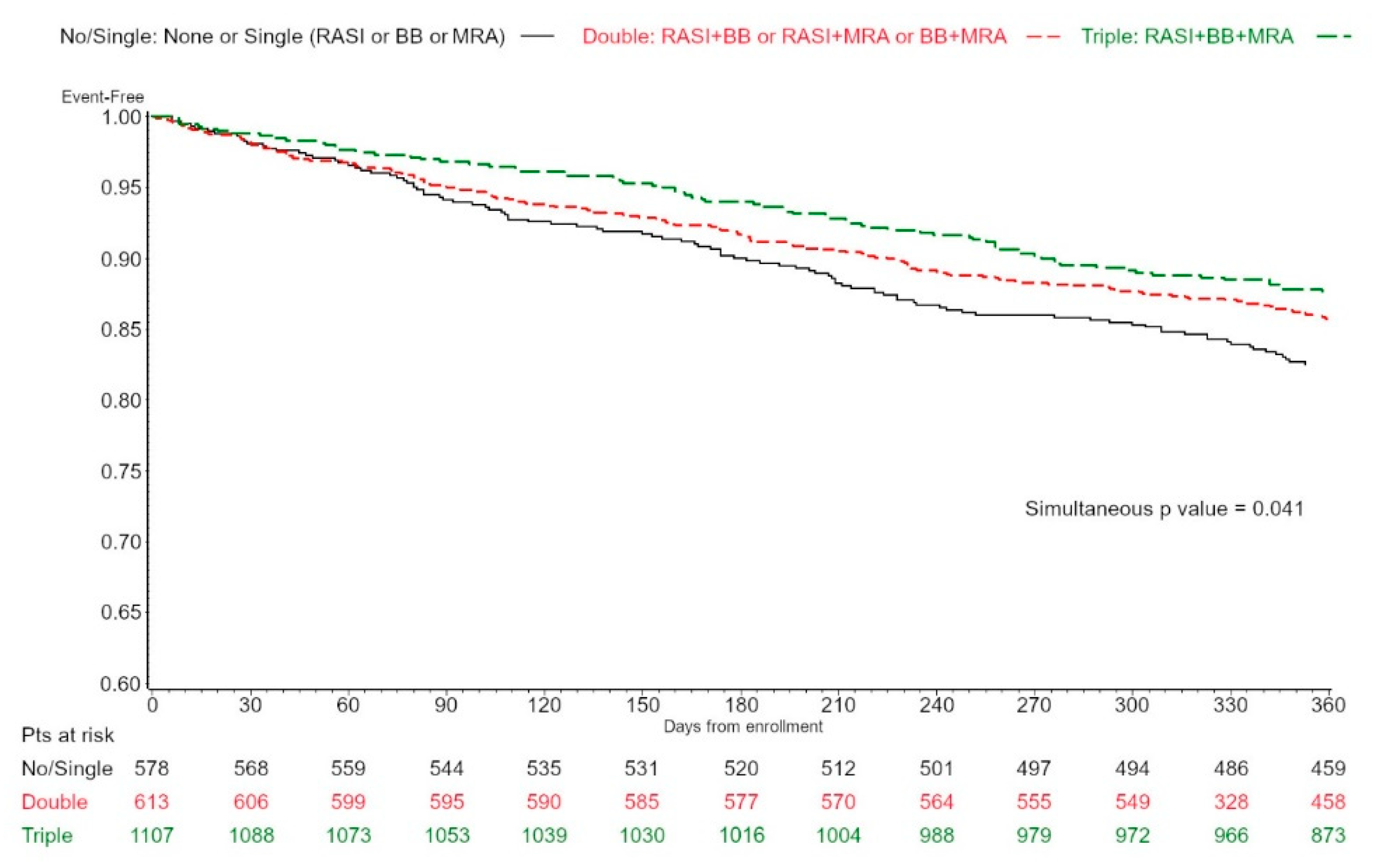
| LVEF 41–49% | All 2298 | No-Single 578 (25.1) | Double 1107 (48.2) | Triple 613 (26.7) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 67 ± 14 | 68 ± 15 | 67 ± 13 | 67 ± 13 | 0.009 |
| Age < 65 | 854 (37.2) | 181 (31.3) | 436 (39.4) | 237 (38.7) | 0.003 |
| Age 65–79 | 1057 (46.0) | 285 (49.3) | 485 (43.8) | 287 (46.8) | 0.09 |
| Age 80+ | 387 (16.8) | 112 (19.4) | 186 (16.8) | 89 (14.5) | 0.08 |
| Female Sex | 663 (28.9) | 164 (28.4) | 320 (28.9) | 179 (29.2) | 0.95 |
| Epoch 1999–2005 | 782 (34.0) | 299 (51.7) | 381 (34.4) | 102 (16.6) | <0.0001 |
| Epoch 2006–2011 | 572 (24.9) | 128 (22.1) | 302 (27.3) | 142 (23.2) | 0.04 |
| Epoch 2012–2018 | 944 (41.1) | 151 (26.1) | 424 (38.3) | 369 (60.2) | <0.0001 |
| HF admissions (previous year) | 752 (32.7) | 195 (33.7) | 313 (28.3) | 244 (39.8) | <0.0001 |
| HF history >6 months | 1396 (60.8) | 314 (54.3) | 670 (60.5) | 412 (67.2) | <0.0001 |
| History of hypertension | 1349 (58.7) | 309 (53.5) | 667 (60.3) | 373 (60.9) | 0.01 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 665 (28.9) | 166 (28.7) | 293 (26.5) | 206 (33.6) | 0.007 |
| Ischemic etiology | 908 (39.5) | 235 (40.7) | 453 (40.9) | 220 (35.9) | 0.10 |
| At least one cardiac comorbidity with an indication for NHM # | 1839 (80.0) | 456 (78.9) | 901 (81.4) | 482 (78.6) | 0.29 |
| Diabetes | 665 (28.9) | 163 (28.2) | 313 (28.3) | 189 (30.8) | 0.48 |
| Previous stroke/TIA | 163 (7.1) | 46 (8.0) | 82 (7.4) | 35 (5.7) | 0.27 |
| Body mass index | 27.2 ± 4.8 | 26.6 ± 4.7 | 27.1 ± 4.5 | 28.1 ± 5.3 | <0.0001 |
| LVEF% | 44.6 ± 2.2 | 44.9 ± 2.3 | 44.6 ± 2.1 | 44.2 ± 2.1 | <0.0001 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 130 ± 20 | 133 ± 21 | 130 ± 21 | 125 ± 18 | <0.0001 |
| Heart rate | 70 ± 14 | 72 ± 15 | 70 ± 14 | 69 ± 13 | <0.0001 |
| NYHA class III–IV | 307 (13.4) | 103 (17.8) | 126 (11.4) | 78 (12.7) | 0.001 |
| Furosemide | 1603 (69.8) | 350 (60.6) | 715 (64.6) | 538 (87.8) | <0.0001 |
| Non-NHM polypharmacy | 418 (18.2) | 101 (17.5) | 187 (16.9) | 130 (21.2) | 0.07 |
| LVEF ≥ 50% | All 2409 | No-Single 880 (36.5) | Double 1099 (45.6) | Triple 430 (17.9) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 70 ± 14 | 69 ± 16 | 71 ± 14 | 72 ± 13 | 0.007 |
| Age < 65 | 701 (29.1) | 281 (31.9) | 309 (28.1) | 111 (25.8) | 0.04 |
| Age 65–79 | 1017 (42.2) | 372 (42.3) | 458 (41.7) | 187 (43.5) | 0.81 |
| Age 80+ | 691 (28.7) | 227 (25.8) | 332 (30.2) | 132 (30.7) | 0.06 |
| Female Sex | 1097 (45.5) | 388 (44.1) | 511 (46.5) | 198 (46.1) | 0.55 |
| Epoch 1999–2005 | 668 (27.7) | 347 (39.4) | 279 (25.4) | 42 (9.8) | <0.0001 |
| Epoch 2006–2011 | 631 (26.2) | 231 (26.3) | 311 (28.3) | 89 (20.7) | 0.01 |
| Epoch 2012–2018 | 1110 (46.1) | 302 (34.3) | 509 (46.3) | 299 (69.5) | <0.0001 |
| HF admissions previous year | 803 (33.3) | 261 (29.7) | 366 (33.3) | 176 (40.9) | 0.0003 |
| HF history >6 months | 1589 (66.0) | 562 (63.9) | 727 (66.2) | 300 (69.8) | 0.10 |
| History of hypertension | 1504 (62.4) | 467 (53.1) | 730 (66.4) | 307 (71.4) | <0.0001 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 986 (40.9) | 337 (38.3) | 449 (40.9) | 200 (46.5) | 0.02 |
| Ischemic etiology | 513 (21.3) | 161 (18.3) | 247 (22.5) | 105 (24.4) | 0.02 |
| At least one cardiac comorbidity with an indication for NHM # | 1951 (81.0) | 650 (73.9) | 929 (84.5) | 372 (86.5) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes | 624 (25.9) | 215 (24.4) | 283 (25.8) | 126 (29.3) | 0.17 |
| Previous stroke/TIA | 182 (7.6) | 70 (8.0) | 87 (7.9) | 25 (5.8) | 0.32 |
| Body mass index | 27.1 ± 5.0 | 26.7 ± 4.9 | 27.2 ± 4.9 | 27.5 ± 5.3 | 0.01 |
| LVEF% | 57.1 ± 6.3 | 58.1 ± 6.7 | 56.8 ± 6.1 | 55.8 ± 5.6 | <0.0001 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 130 ± 21 | 132 ± 21 | 130 ± 21 | 127 ± 19 | 0.001 |
| Heart rate | 72 ± 15 | 72 ± 15 | 71 ± 15 | 71 ± 14 | 0.24 |
| NYHA class III–IV | 473 (19.6) | 184 (20.9) | 217 (19.8) | 72 (16.7) | 0.20 |
| Furosemide | 1694 (70.3) | 528 (60.0) | 781 (71.1) | 385 (89.5) | <0.0001 |
| Non-NHM polypharmacy | 470 (19.5) | 161 (18.3) | 214 (19.5) | 95 (22.1) | 0.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gori, M.; Marini, M.; Gonzini, L.; Carigi, S.; De Gennaro, L.; Gentile, P.; Leonardi, G.; Orso, F.; Tinti, D.; Lucci, D.; et al. Combined Neuro-Humoral Modulation and Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226627
Gori M, Marini M, Gonzini L, Carigi S, De Gennaro L, Gentile P, Leonardi G, Orso F, Tinti D, Lucci D, et al. Combined Neuro-Humoral Modulation and Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226627
Chicago/Turabian StyleGori, Mauro, Marco Marini, Lucio Gonzini, Samuela Carigi, Luisa De Gennaro, Piero Gentile, Giuseppe Leonardi, Francesco Orso, Denitza Tinti, Donata Lucci, and et al. 2022. "Combined Neuro-Humoral Modulation and Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226627
APA StyleGori, M., Marini, M., Gonzini, L., Carigi, S., De Gennaro, L., Gentile, P., Leonardi, G., Orso, F., Tinti, D., Lucci, D., Iacoviello, M., Navazio, A., Ammirati, E., Municinò, A., Benvenuto, M., Cassaniti, L., Tavazzi, L., Maggioni, A. P., & De Maria, R., on behalf of the Italian Network on Heart Failure (IN-HF) Investigators. (2022). Combined Neuro-Humoral Modulation and Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6627. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226627









