Abstract
Menstrual pain is consequent to intense uterine contraction aimed to expel menstrual flow through downstream uterine cervix. Herein it was evaluated whether characteristics of uterine cervix are associated with intensity of menstrual pain. Ultrasound elastography was used to analyze cervix elasticity of 75 consecutive outpatient women. Elasticity was related to intensity of menstrual pain defined by a Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). Four regions of interest (ROI) were considered: internal uterine orifice (IUO), anterior (ACC) and posterior cervical (PCC) compartment and middle cervical canal (MCC). Tissue elasticity, evaluated by color score (from 0.5 = blue/violet (low elasticity) to 3.0 = red (high elasticity), and percent tissue deformation was analyzed. Elasticity of IUO was lower (p = 0.0001) than that of MCC or ACC, and it was negatively related (R2 = 0.428; p = 0.0001) to menstrual VAS (CR −2.17; 95%CI −3.80, −0.54; p = 0.01). Presence of adenomyosis (CR 3.24; 95% CI 1.94, 4.54; p = 0.0001) and cervix tenderness at clinical examination (CR 2.74; 95% CI 1.29, 4.20; p = 0.0004), were also independently related to menstrual VAS. At post hoc analysis, women with vs. without menstrual pain had lower IUO elasticity, expressed as color score (0.72 ± 0.40 vs. 0.92 ± 0.42; p = 0.059), lower percent tissue deformation at IUO (0.09 ± 0.05 vs. 0.13 ± 0.08; p = 0.025), a higher prevalence of cervical tenderness at bimanual examination (36.2% vs. 9.5%; p = 0.022) and a higher prevalence of adenomyosis (46.5% vs. 19.9%; p = 0.04). These preliminary data indicate that IUO elasticity is associated with the presence and the intensity of menstrual pain. Mechanisms determining IUO elasticity are useful to be explored.
1. Introduction
Almost 85% of young women suffer from some degree of menstrual pain [1]. Pain intensity can be evaluated by a visual analogue scale (VAS) [2,3], and is called dysmenorrhea when it is intense, impacts on daily activities and requires medical treatment [1,4,5]. Even in its more severe forms, menstrual pain is very common and represents an important disturbance, capable of influencing a woman’s quality of life [1,6]. It is the consequence of intense myometrial contractions stimulated by endometrial prostaglandins [4]. Prolonged menstrual pain induces changes in brain activity resembling features of chronic pain [7,8] that may lead to persistence of disease and to insurgence of chronic pelvic pain [8,9,10]. Contractions increase intrauterine pressure aimed to expel menstrual blood through downstream uterine cervix [11]. A stiff cervix may obstacle menstrual flow more than an elastic one, possibly causing intense and painful contractions. Ultrasound elastography was used to evaluate tissue stiffness/elasticity of breast and muscle [12], thyroid [13], liver [14], prostate [14], pancreas [15], uterine myomas and adenomyosis [16,17,18]. Application of elastography to uterine cervix has been mainly confined to obstetrics [19,20,21,22], stiffness modifications being used to define the risk of preterm birth [23,24] or to set the time for labor induction [25]. Rarely, elastography was used to investigate uterine cervix outside pregnancy [26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. In the present study, we evaluated whether elasticity of the uterine cervix is related to the intensity of menstrual pain.
2. Experimental Section
An observational study was performed between October 2017 and July 2018 in women of an outpatient service for contraception at a University Hospital. The study did not involve any intervention outside common clinical practice, but each woman signed a written informed consent for the anonymous use of her data in clinical research. The Institutional Review Board IRB gave consent to direct data publication. Cycling women, 18 to 45 years of age were included. Women who were pregnant, with any type of oncological disease, with an intrauterine device, or on hormonal contraception were excluded. Among 99 screened women, 20 women were on hormonal contraceptives and were excluded. The remaining 79 were considered.
Demographic and clinical data were collected for each woman. Presence of heavy menstrual bleeding identified as menstrual blood loss >80 mL, was later confirmed by the pictorial method [33]. A 10 cm VAS was used to measure intensity of menstrual pain, perceived by women in the last 3 menstrual cycles with the use of no medication [1,6]. Each woman underwent vaginal bimanual examination, to evaluate cervical stiffness and tenderness at passive mobilization. Presence of gynecological diseases such as uterine myomas, adenomyosis and endometriosis were evaluated by patient history, bimanual examination and ultrasonography. Ultrasonographic criteria for the diagnosis of ovarian and pelvic endometriosis [34,35,36], uterine myomas and adenomyosis [37] were used. Ultrasound investigations were performed by an expert trained practitioner (A.X.), who was blind about the woman menstrual pain, using a Voluson E10 General Electric (GE, General Electric Company, Boston, Massachusetts, USA) instrument with a transvaginal probe (TSV) GE RIC 59D) and a proper software for elastography (Voluson E10 BT16, General Elcetric Company, Boston Massachussetts, USA). For each woman, longitudinal (L), transverse (T) and antero-posterior (AP) diameter of the uterus, length and transverse diameter of the cervix, and elasticity of different cervical compartments was obtained. Uterus volume (cm3) was calculated by the ellipsoid formula (L × T × AP × 0.5223). Tissue elasticity was obtained by strain elastography (SE)(Figure 1). SE is based on differences in elasticity of various tissues in both physiological and pathological conditions [31,32]. It measures tissue deformation or displacement generated by an applied pressure. During image acquisition, vaginal probe was positioned in the anterior vaginal fornix and a B-Mode sagittal view of the cervix was obtained and displayed alongside to facilitate images interpretation [30]. The operator performed a series of about 5 compression and decompression cycles, using sub-centimetric excursions perpendicular to the axis of the cervical canal [19,25]. A control bar of the ultrasound processing program indicated, in real time, optimal compression force (Figure 1). Regions of interest (ROIs) with a circular area of 19.6 mm2 were placed in the middle of the anterior cervical compartment (ACC), in the middle of the posterior cervical compartment (PCC), in the middle portion of the cervical canal (MCC) and at the internal uterine orifice (IUO) (Figure 1). SE evaluations were recorded on clips and analyzed afterwards. Results were calculated at optimal compression force. Tissue elasticity coded with a scale ranging from violet/blue (low) to red (high), with yellow/green as intermediate elasticity, was evaluated by three independent scorers, who were blind about menstrual VAS value. A predefined value was assigned on the basis of the colorimetric scale on the whole spectrum (from the value 0.5 = blue/violet to the value 3.0 = red) [31,32]. Mean value of the 3 scorers was used. The SE software, (General Electrics Company, Boston, Massachussets, USA in use also provided a numerical index of the ROI’s percent tissue deformation (Figure 1). This value was also considered in statistical analysis. Ratios of both color score elasticity and percent tissue deformation of different ROIs were calculated and compared.
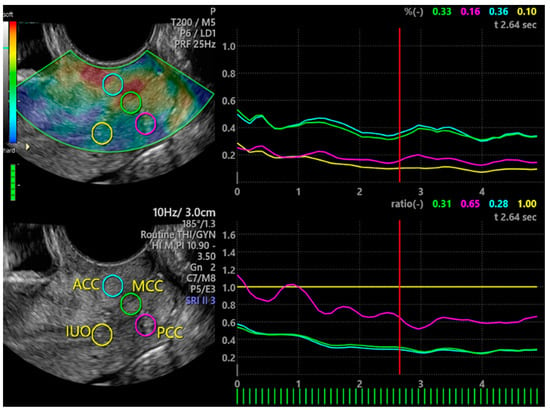
Figure 1.
Elastography of uterine cervix. On the left, the two vertical bars indicate the colorimetric scale (upper bar) and the control bar (lower bar) that when full green indicates optimal compression force. Circles indicate ROIs. On the right are the numerical index and graphical representation of ROI’s percent tissue deformation (upper panel) and numerical index and graphical representation of ratio between IUO percent tissue elasticity (as reference) and other ROIs. ACC = anterior cervical compartment; PCC = posterior cervical compartment; IUO = internal uterine orifice; MCC = middle cervical canal.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for repeated measures with subjects as replicates was used to compare elasticity of the different cervix compartments. Linear regression analysis was used to test the relation of menstrual pain VAS value (dependent variable) and factors (independent) expressed by continuous or categorical data. Continuous data were age (years), age at menarche (years), uterine volume (cm3), cervix length and diameter (cm), color score of elasticity and percent deformation of the four cervical ROIs. Ratios of color score elasticity or percent deformation of different ROIs were also considered. Categorical data entered as dummy variables, were previous pregnancy vs. no, previous caesarean section vs. no, cervical stiffness at bi-manual investigation vs. no, tenderness at cervix mobilization during bi-manual investigation vs. no, presence of heavy menstrual periods vs. no, presence of endometriosis, myoma, or adenomyosis vs. no. Variables, that at simple regression analysis were significantly related to menstrual pain, were entered in a multiple regression model in order to define those factors that were independently related to intensity of menstrual pain. At a post hoc analysis, 59 women were suffering and 21 were not suffering from menstrual pain (VAS = 0). Values of women with any intensity of menstrual pain were compared to those of women without menstrual pain. Means of the two groups were compared by the Student’s t-test, while frequencies were compared by contingency tables and the Chi-squared test.
Many studies investigating cervix elasticity included from 20 to 74 women [20,23,30,31,32]. We estimated that a similar number of women was sufficient to define elasticity of the cervix and its relation to the intensity of menstrual pain. Statistical analysis was performed with the StatView program (SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC, USA). Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). A p-value < 0.05 was considered as significant.
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants
Data of study participants are reported in Table 1. Mean VAS value of menstrual pain was 4.55 ± 3.7 in the whole sample of women, but it was 6.19 ± 2.9 in women with pain and by definition it was 0 in women without menstrual pain. Among women with menstrual pain, 13 women had a VAS < 4, 18 had a VAS between 4 and 7, and 27 had a VAS ≥ 7. There was no difference between women with and without menstrual pain, but in the former a higher rate of adenomyosis, and cervix tenderness at bimanual examination was obtained (p = 0.022) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Mean (± SD) values of enrolled women, also divided at post hoc analysis in women with and without menstrual pain. Significance of comparison between the two groups is reported.
3.2. Elastography of the Cervix
Compartments of the cervix showed a different elasticity (Table 2). IUO had a lower elasticity (p = 0.0001) than MCC and ACC.

Table 2.
Mean (± SD) color score elasticity, percent tissue deformation and ratios of different regions of interest of the cervix: Data of women with and without menstrual pain are also reported along with their comparison.
At linear regression analysis, intensity of menstrual pain was negatively related to color score elasticity of IUO, PCC, and elasticity ratio of IUO/MCC, IUO/ACC, and PCC/ACC (Table 3). Menstrual pain was also negatively related to percent tissue deformation of IUO and to the percent tissue deformation ratio IUO/ACC (Table 3). In addition, intensity of menstrual pain was positively related to the presence of adenomyosis, pelvic endometriosis, heavy menstrual bleeding, and cervical tenderness at clinical examination (Table 3).

Table 3.
Results of single and multiple linear regression analyses (R2 = 0.428; p = 0.0001) performed between intensity of menstrual pain expressed as visual analogue scale (VAS) value and related factors, among which include tissue color score elasticity and tissue percent deformation.
When these single factors were entered into multiple regression analysis, only IUO elasticity at color score (CR −2.17; 95% CI −3.80, −0.54; p = 0.01), cervix tenderness (CR 2.74; 95% CI 1.29, 4.20; p = 0.0004), and presence of adenomyosis (CR 3.24; 95% CI 1.94, 4.54; p = 0.0001) remained significantly related to the intensity of menstrual pain (R2 0.428; p = 0.0001) (Table 3).
3.3. Post Hoc Groups Comparison
Heterogeneity of cervix elasticity was different in women with (n = 58) and without (n = 21) menstrual pain. In women with menstrual pain, IUO had a lower elasticity than both MCC and ACC (p = 0.0001), while in women with no menstrual pain, IUO had a lower elasticity of MCC only (p = 0.046).
Comparisons between groups showed that IUO color score elasticity (p = 0.059) and percent tissue deformation (p = 0.025) was lower in women with than without menstrual pain (Table 2). Ratio IUO/MCC of color score elasticity (p = 0.021) or percent tissue deformation (p = 0.05) was also lower in women with than without menstrual pain (Table 2). Similarly, ratio IUO/ACC of color score elasticity (p = 0.015) or percent tissue deformation (p = 0.035) was lower in women with than without menstrual pain (Table 2).
4. Discussion
The present study indicates that intensity of menstrual pain is related to elasticity of IUO, higher pain being present with lower IUO elasticity. Additional related factors to intensity of menstrual pain are the presence of adenomyosis and a tender cervix, at bimanual examination.
SE allows evaluation of tissue elasticity by measuring ROIs tissue deformation during compressive and decompressive forces [31,32]. Elasticity of uterine cervix was seldom investigated in gynecological conditions, and it emerged that elasticity of various cervical area or ROIs is different [27,29,30,31,38]. In our study, ROIs of uterine cervix showed a different tissue elasticity, the inner part of tissue around the IUO showing a lower elasticity than other areas, particularly the MCC and ACC. Besides possible confounding related to the method of investigation, it is likely that difference in elasticity is the consequence of a different anatomical conformation of the cervix at the IUO. The presence of radial collagen fibers, along with a robust bundle of circular collagen fibers, is peculiar of this anatomical area [39]. In addition, 50% of this area tissue is composed by circular muscular cells responsive to oxytocin and neurotransmitters [40]. These peculiarities make the IUO mechanically apt to containment. It represents an area that, more than others, counteracts dilatative forces exerted by the fetus, during pregnancy [39,40,41] and likely, by menstrual blood, during menses. Lower elasticity at the IUO indicates a structure harder to deform by an external force, but also by an internal dilatative force, as previously reported in pregnancy [21,41]. The present study shows that a lower elasticity at the IUO is present in women suffering from menstrual pain, with an inverse linear relation between the degree of elasticity and the intensity of pain. This relation was not observed for other ROIs, including the MCC. IUO/MCC, or even IUO/ACC elasticity ratios, were lower in women with than without menstrual pain. These differences indicate that heterogeneity of tissue elasticity within the cervix is magnified in women with menstrual pain.
Elasticity of IUO was independently related to intensity of menstrual pain even when other risk factors, such as heavy menstrual bleeding, endometriosis or adenomyosis, were considered. Interestingly, when elasticity of IUO was taken into account, most risk factors lost their relations with menstrual pain. Only adenomyosis remained independently related to pain intensity.
There are several weaknesses in this study. Elastography was applied to different ROIs and multiple comparisons were made. Accordingly, some of them can be significant only by chance. SE does not allow absolute quantification of elasticity, that can only be appropriately evaluated on cervix tissue specimens in vitro. SE results are conditioned by the force the operator applies during the evaluation [31,32]. Analysis was optimized by performing the evaluation at optimal compression, as indicated in real time by the software in use. Data obtained at IUO were confirmed by performing ratios between IUO and other ROIs. Assuming that the applied external force is equivalent across the cervix, ratio values are independent on the applied external force [42]. In addition, it has been reported that evaluation of IUO’s elasticity is less variable than that of other areas of the cervix [19]. The results are rather consistent and in agreement with published studies showing that this area has an anatomical composition different from other regions of the cervix [39,40]. Independent readings of the 3 examiners were used as a mean value and not separately. Accordingly, we did not evaluate interrater reliability. This is going to be evaluated in future studies.
5. Conclusions
Overall, the data indicate that menstrual pain is associated with a lower elasticity of the cervical tissue around the IUO. Stability over time of these preliminary data should be tested and confirmed in additional studies. Whether confirmed, mechanisms determining IUO elasticity may be useful to be explored.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.X., G.S. and A.C. (Angelo Cagnacci); methodology, A.X., S.V. and G.T.; formal analysis, A.X.; investigation, A.X., G.S. and S.V.; data management G.S., S.V., G.T. and A.C. (Angelo Cagnacci); writing draft manuscript A.C. (Alessandra Chiodini) and M.F.F.; review and editing, A.X. and A.C. (Angelo Cagnacci); supervision, A.X.; project administration, A.C. (Angelo Cagnacci). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was an observational investigation conducted according to normal clinical practice without any intervention arm. The Institutional Review Board of the Azienda Sanitaria Universitaria di Udine gave consent to direct data publication (protocol code 20/26 date 18 September 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Grandi, G.; Ferrari, S.; Xholli, A.; Cannoletta, M.; Palma, F.; Romani, C.; Volpe, A.; Cagnacci, A. Prevalence of menstrual pain in young women, what is dysmenorrhea. J. Pain Res. 2012, 5, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.I.; Rangel-Flores, E.; Carrillo-Alarcòn, L.C.; Veras-Godoy, H.A. Prevalence and impact of primary dysmenorrhea among Mexican high school students. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2009, 107, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, A.; Celik, H.; Gurates, B.; Kaya, D.; Nalbant, M.; Kavak, E.; Hanay, F. Prevalence of primary dysmenorrhea in young adult female university students. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2009, 279, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.Y. Dysmenorrhea and prostaglandins, Pharmacological and therapeutic considerations. Drugs 1981, 22, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozerdogan, N.; Sayiner, D.; Ayranci, U.; Unsal, A.; Giray, S. Prevalence and predictors of dysmenorrhea among students at a university in Turkey. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2007, 107, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, G.; Xholli, A.; Ferrari, S.; Cannoletta, M.; Volpe, A.; Cagnacci, A. Intermenstrual pain, quality of life and pain. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 2013, 75, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, K.; Warnaby, C.; Stagg, C.J.; Moore, J.; Kennedy, S.; Tracey, I. Dysmenorrhoea is associated with central changes in otherwise healthy women. Pain 2011, 152, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, K.M.; Roth, G.E.; Dillane, K.E.; Garrison, E.F.; Oladosu, F.A.; Clauw, D.J.; Frank, F.T. Dysmenorrhea subtypes exhibit differential quantitative sensory assessment profiles. Pain 2020, 161, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.H.; Niddam, D.M.; Chao, H.T.; Liu, R.S.; Hwang, R.J.; Yeh, T.C.; Hsieh, J.-C. Abnormal cerebral metabolism during menstrual pain in primary dysmenorrhea. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, L.A.; Seidman, L.C.; Sim, M.-S.; Rapkin, A.J.; Naliboff, B.D.; Zeltzer, L.K. Experimental evaluation of central pain processes in young women with primary dysmenorrhea. Pain 2019, 160, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnacci, A.; Grandi, G.; Cannoletta, M.; Xholli, A.; Piacenti, I.; Volpe, A. Intensity of menstrual pain and estimated angle of uterine flexion. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2014, 93, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cespedes, I.; Ophir, J.; Ponnekanti, H.; Maklad, N. Elastography, Elasticity imaging using ultrasound with application to muscle and breast in vivo. Ultrason. Imaging 1993, 15, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, U.; Dighe, M.; Dubinsky, T.; Minoshima, S.; Shamdasani, V.; Kim, Y. Ultrasound thyroid elastography using carotid artery pulsation, Preliminary study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2007, 26, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudea, S.M.; Giurgiu, C.R.; Dumitriu, D.; Chiorean, A.; Ciurea, A.; Botar-Jid, C.; Coman, I. Value of ultrasound elastography in the diagnosis and management of prostate carcinoma. Med. Ultrasond 2011, 13, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Menten, R.; Leonard, A.; Clapuyt, P.; Vincke, P.; Nicolae, A.C.; Lebecque, P. Transient elastography in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2010, 40, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoelinga, B.; WHehenkamp, W.J.K.; Br¨Olmann, H.A.M.; Huirne, J.A. Real-time elastography for assessment of uterine disorders. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 43, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, S.; Millar, E.; Mitkova, M.; Mitkov, V. Value of ultrasound shear wave elastography in the diagnosis of adenomyosis. Ultrasound 2016, 24, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wasnik, A.P.; Masch WRRubin, J.M.; Carlos, R.C.; Quint, E.H.; Maturen, K.E. Transvaginal ultrasound shear wave elastography for the evaluation of benign uterine pathologies. A prospective pilot study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Andrade, E.; Hassan, S.S.; Ahn, H.; Korzeniewski, S.J.; Yeo, L.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Romero, R. Evaluation of cervical stiffness during pregnancy using semiquantitative ultrasound elastography. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 41, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, K.M.; Feltovich, H.; Mazza, E.; Vink, J.; Bajka, M.; Wapner, R.J.; Hall, T.J.; House, M. The mechanical role of the cervix in pregnancy. J. Biochem. 2015, 48, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, L.C.; Hall, T.J.; Rosado-Mendeza, I.M.; Palmeri, M.L.; Feltovich, H. Detection of changes in cervical softness using shear wave speed in early vs. late pregnancy, An in vivo cross-sectional study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruscalzo, A.; Londero, A.P.; Fröhlich, C. Quantitative elastography for cervical stiffness assessment during pregnancy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Andrade, E.; Garcia, M.; Ahn h Korzeniewski, S.J.; Saker, H.; Yeo, L.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Hassan, S.S.; Romero, R. Strain at the internal cervical os assessed with quasi-static elastography is associated with the risk of spontaneous preterm delivery at ≤34 weeks of gestation. J. Perinat. Med. 2015, 43, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Xiang, X.; Wen, J.; Yi, M.; He, B.; Hu, B. Diagnostic accuracy of cervical elastography in predicting preterm delivery. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, 29.e16449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, L.; Rasmussen, C.K.; Schlutter, J.M.; Sandager, P.; Uldbjerg, N. Quantitative sono-elastography of the uterine cervix prior to induction of labor as a predictor of cervical dilation time. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2014, 93, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, F.S.; Go’ Mez, L.F.; Florido, J.; Padilla, M.C.; Nicolaides, K.H. Quantification of cervical elastography, A reproducibility study. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 39, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, L.C.; Feltovich, H.; Palmeri, M.L.; Dahl, J.J.; Munoz del Rio, A.; Hall, T.J. Estimation of shear wave speed in the human uterine cervix. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 43, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanziano, A.; Caringella, A.M.; Cantatore, C.; Trojano, G.; Caroppo, E.; D’Amato, G. Evaluation of the cervix tissue homogeneity by ultrasound elastography in infertile women for the prediction of embryo transfer ease, A diagnostic accuracy study. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2017, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, S.; Zelesco, M.; Sun, Z. Shear Wave Elastography on the uterine cervix. technical development for the transvaginal approach. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemici, A.A.; Gulsever, A.B.; Tunca, A.F.; Hocaoglu, E.; Inci, E. Shear wave elastography of the uterine cervix under different conditions with inter-operator agreement analysis. Pol. J. Radiol. 2020, 85, e245–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltovich, H.; Drehfal, L. New techniques in evaluation of the cervix. Semin. Perinatol. 2017, 41, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, L. Overview of the methods available for biomechanical testing of the uterine cervix in vivo. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2014, 93, 1219–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, K.M.; Dimmock, P.W.; Walker, T.J.; O’Brien, P.M. Determination of total menstrual blood loss. Fertil. Steril. 2001, 76, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelli, L. Transvaginal sonography for the assessment of ovarian and pelvic endometriosis: How deep is our understanding? Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 33, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerriero, S.; Condous, G.; van den Bosch, T.; Valentin, L.; Leone, F.P.; Van Schoubroeck, D.; Exacoustos, C.; Installé, A.J.; Martins, W.P.; Abrao, M.S.; et al. Systematic approach to sonographic evaluation of the pelvis in women with suspected endometriosis, including terms, definitions and measurements, A consensus opinion from the International Deep Endometriosis Analysis (IDEA) group. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xholli, A.; Filip, G.; Previtera, F.; Cagnacci, A. Modification of endometrioma size during hormone therapy containing dienogest. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bosch, T.; Dueholm, M.; Leone, F.P.; Valentin, L.; Rasmussen, C.K.; Votino, A.; Van Schoubroeck, D.; Landolfo, C.; Installé, A.J.; Guerriero, S.; et al. Terms, definitions and measurements to describe sonographic features of myometrium and uterine masses, A consensus opinion from the Morphological Uterus Sonographic Assessment (MUSA) group. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 46, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltovich, H.; Hall, T.J.; Berghella, V. Beyond cervical length, Emerging technologies for assessing the pregnant cervix. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 207, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Gan, Y.; Myers, K.M.; Vink, J.Y.; Wapner, R.J.; Hendon, C.P. Collagen fiber orientation and dispersion in the upper cervix of non-pregnant and pregnant women. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.Y.; Qin, S.; Brock, C.O.; Zork, N.M.; Feltovich, H.M.; Chen, X.; Urie, P.; Myers, K.M.; Hall, T.J.; Wapner, R.; et al. A new paradigm for the role of smooth muscle cells in the human cervix. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 478.e1–478.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Houseb, M.; Jambawalikarc, S.; Zork, N.; Vink, J.; Wapner, R.; Myers, K. Investigating the mechanical function of the cervix during pregnancy using finite element models derived from high resolution 3D MRI. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 2016, 19, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, A.; Grajo, J.R.; Dhyani, M.; Anthony, B.W.; Samir, A.E. Principles of ultrasound elastography. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).