Abstract
Small-for-gestational-age (SGA) infants have been associated with increased risk of adverse perinatal outcomes (APOs). In this work, we assess the predictive ability of the ultrasound-estimated percentile weight (EPW) at 35 weeks of gestational age to predict late-onset SGA and APOs, according to six growth standards, and whether the ultrasound–delivery interval influences the detection rate. To this purpose, we analyze a retrospective cohort study of 9585 singleton pregnancies. EPWs at 35 weeks were calculated to the customized Miguel Servet University Hospital (MSUH) and Figueras standards and the non-customized MSUH, Fetal Medicine Foundation (FMF), INTERGROWTH-21st, and WHO standards. As results of our analysis, for a 10% false positive rate, the detection rates for SGA ranged between 48.9% with the customized Figueras standard (AUC 0.82) and 60.8% with the non-customized FMF standard (AUC 0.87). Detection rates to predict SGA by ultrasound–delivery interval (1–6 weeks) show higher detection rates as intervals decrease. APOs detection rates ranged from 27.0% with FMF to 7.9% with the Figueras standard. In conclusion, the ability of EPW to predict SGA at 35 weeks is good for all standards, and slightly better for non-customized standards. The APO detection rate is significantly greater for non-customized standards.
1. Introduction
Screenings for fetal growth abnormalities are essential components of antenatal care, and fetal ultrasound plays a key role in the assessment of these conditions [1,2,3]. Small-for-gestational-age (SGA) infants—those with a birth weight below the 10th percentile according to the standards [4]—have been associated with increased risk of adverse perinatal outcomes (APOs) [5].
These fetuses are the leading cause of stillbirth [6,7,8], and have more risks of both neonatal morbidity [9] and mortality [10,11]. Recent studies have shown that an early diagnosis of SGA in the third trimester can help to reduce APOs, reflecting the benefit of prenatal diagnosis in these cases [12,13], although the time to perform the ultrasound is not clearly established.
Several studies customized or not to maternal and fetal physiological variables have been proposed to predict SGA [14]; these fetal growth standards [15,16,17] are based on Hadlock et al.’s methodology [18,19], or on new multilevel models [20,21,22], and can be customized to maternal and fetal physiological variables [23]. The estimation of the percentile adjusted for maternal and fetal characteristics is the property that postulates customized standards as better detectors of adverse perinatal outcomes than population-based standards (non-customized (NC)) [24]. The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (RCOG) [25] recommends the use of customized birthweight curves to identify SGA fetuses; the adjustment of fetal weight should be performed individually, and not by population—although some studies have questioned the superiority of the EPW by customized standards and its association with APOs [26,27], and SGA with APOs [28].
Furthermore, new standards have recently been published by EFW [29], including international standards from the World Health Organization (WHO) [17] and the INTERGROWTH-21st project [20,21], and local standards from the Fetal Medicine Foundation (FMF) [22]. According to the recent review by McCowan et al. (2018), international population ultrasound standards still require more comparative studies for validation [5].
Since the controversy arose about the most appropriate method to predict SGA, and the lack of comparative assessment for the cited approaches, the objective of this study is to compare the ability of EPW—according to six growth standards, by ultrasound at 35 weeks, including population, population-customized, and international references—to predict late-onset SGA, defined as a birth weight below the 10th percentile at term delivery. The secondary objective is to determine whether the ultrasound–delivery interval influences the detection rate of SGA newborns.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This was a retrospective cohort study of births assisted at the Miguel Servet University Hospital (MSUH), between March 2012 and December 2016. The inclusion criteria were as follows: live singleton pregnancies controlled in MSUH from the first trimester of gestation; fetal ultrasound assessment at gestational age of 35 (range 34–36) weeks; and deliveries between 37 and 42 weeks of gestational age of fetuses without stillbirth associated with malformations or chromosomal abnormalities. Of the 19,310 consecutive deliveries assisted in our hospital in the period studied, the 9585 cases that fulfilled the specific inclusion criteria—such as data availability to estimate percentile weights by standards—were considered for the analysis. Study participants’ selection samples are detailed in Figure 1.
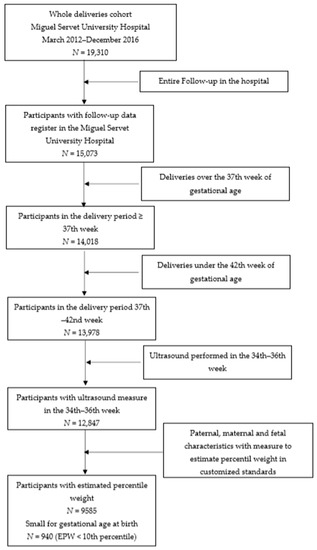
Figure 1.
Flowchart of patient recruitment; EPW: estimated percentile weight.
The last menstrual period was adjusted by first trimester ultrasound [30]. Universal ultrasound screening was performed at 35 weeks (range 34–36 weeks) at the Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnosis Unit using either a Voluson 730 Expert, E6, E8 ultrasound machine (General Electric, Healthcare, Zipf, Austria) or an Aloka Prosound SSD-5000 (Hitachi Aloka Medical Systems, Tokyo, Japan). This ultrasound corresponds to the one that is routinely performed in all pregnancies at our center to try to increase the detection of fetal growth alterations [5].
EFW was calculated with the formula of each standard to which it was built. We used Hadlock et al.’s [19] formula, which combines biparietal diameter, cephalic and abdominal circumference, and femur length, for the MSHU, Figueras et al., and WHO standards; and the version that uses cephalic and abdominal circumference and femur length for the Fetal Medicine Foundation (FMF) standard. In addition, Stirnemann et al.’s formula [20], including only cephalic and abdominal circumference, was used to estimate percentile weight for the INTERGROWTH-21st standard.
For the calculation of the EPW, we collected in the study the maternal age and body mass index (BMI) at the beginning of pregnancy, parity, maternal and paternal height, maternal ethnic origin, smoking habits, infant gender, birth weight, and ultrasound EFW. We also collected perinatal outcomes in order to analyze APOs in SGA infants at delivery, defined as the occurrence of a 5-min Apgar score < 7, instrumental or cesarean delivery for non-reassuring fetal status, arterial cord blood pH < 7.10, and stillbirth.
2.2. Estimated Percentile Weight
EPWs were calculated according to 6 different customized and NC growth standards, including population, population-customized, and international references. For the customized standards, the methodologies of Hadlock et al. [18] and Gardosi et al. [23] were used for (1) the MSUH standard customized for parity, age, BMI, maternal height, paternal height, and fetal gender, built using a modified version of Hadlock et al.’s growth charts adjusted to our population, with a coefficient of variation that changes with gestational age (Saviron-Cornudella et al. [16]); (2) and the Barcelona Clinic Hospital (Figueras et al. [15]). For the NC standards, we used (3) an NC version of the MSUH standard (Saviron-Cornudella et al. [16]); (4) the international population INTERGROWTH–21st [20,21]—a multilevel mixed model whose main characteristic is that it includes pregnant women without pathology; (5) the international WHO fetal growth standard [17], and (6) the FMF local growth multilevel mixed model (Nicolaides at al [22]).
To assess ultrasound weight measures in the third trimester, EPWs were estimated between 34 and 36 weeks of gestational age. The WHO EPW was calculated by interpolation of the 5th, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, and 95th percentiles.
As a gold standard for the analysis, SGA was defined as a birth weight below the 10th percentile, using a growth reference for the Spanish population based on 9362 birthweights [31]. We did not focus our analysis on intrauterine growth-restricted fetuses (IUGRs). As we did not perform Doppler ultrasound universally (only in cases of estimated fetal weight < 10th percentile), we did not study the subgroup of SGA fetuses at delivery with altered Doppler ultrasound. This is because a significant percentage of SGA fetuses at delivery did not present an estimated fetal weight <10th percentile by ultrasound.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Data were descriptively analyzed using medians and interquartile ranges for continuous variables, and absolute and relative frequencies for categorical variables. The ability of EPW provided by the six standards to predict SGA was analyzed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) [32]. Sensitivity (detection rate) was established for false positive rates (FPR) of 5, 10, 15, and 20%. The percentile threshold point corresponding to the FPR values was also calculated. AUCs were compared using the DeLong test, and sensitivities through a proportion comparison test.
In addition, we built logistic regression models to estimate the OR and 95% confidence interval that correspond to an increase of 1% in the EPW at 35 weeks, as a predictor for SGA at delivery, performing a subanalysis for different ultrasound–delivery intervals (1–6 weeks).
We analyzed the diagnostic ability of the EPW 10th percentile and SGA birthweights to detect the following adverse perinatal outcomes: 5-min Apgar score < 7, instrumental delivery for non-reassuring fetal status (NRFS), cesarean delivery for NRFS, arterial cord blood pH < 7.10, and stillbirth. Comparison between APOs predicted by standards was performed using a proportion test.
Analyses were performed using R version 3.6.2 language programming (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) [33].
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Results
Table 1 shows the descriptive characteristics of the pregnant women, and also displays medians and percentiles 10 (P10) and 90 (P90) among groups for the six studied standards for EFWs by ultrasound at 35 weeks (range from 34+0 to 36+6 weeks). WHO and FMF standards show an underestimation of the median expected value (50%) by ultrasound (median values 43.1%, P10–P90 range 7.5–74.9, and 37.6%, P10–P90 range 2.7–89.9, respectively), while the Figueras standard shows an overestimation by ultrasound (median values 59.3%, P10–P90 range 18.1–93.5).

Table 1.
Parental baseline characteristics (top), pregnancy (middle), and perinatal characteristics (bottom) of pregnancies. Data are reported as n (%) or medians (interquartile range); MSUH: Miguel Servet University Hospital; NRFS: non-reassuring fetal status; WHO: World Health Organization.
EPW distributions are detailed in Figure 2, where a comparison of the percentage of SGA is shown for each standard. The rate of SGA at birth in our cohort was 9.4% (n = 902).
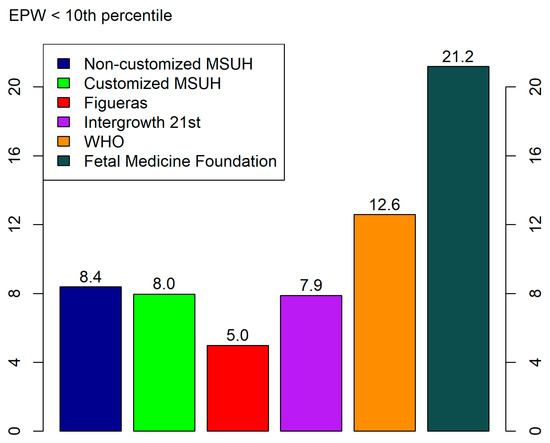
Figure 2.
Percentage of small for gestational age (estimated percentile weight (EPW) <10th percentile) cases provided by standards at the third trimester (34th–36th week). Growth standards: non-customized Miguel Servet University Hospital (MSUH)16, customized MSUH, Figueras et al., INTERGROWTH-21st, World Health Organization (WHO), and Fetal Medicine Foundation.
Regarding APOs, Table 2 shows that SGA deliveries included 21.6% (n = 139) APOs, 28.6% (n = 12) 5-min Apgar scores < 7, 19.9% (n = 32) instrumental deliveries for NRFS, 26.8% (n = 71) cesarean deliveries for NRFS, 17.7% (n = 45) neonatal acidemia (pH cord blood pH < 7.10), and 26.3% (n = 5) stillbirth.

Table 2.
Diagnosis of adverse perinatal outcomes (APOs); EPW: estimated percentile weight at 35 weeks (range 34–36 weeks); MSUH: Miguel Servet University Hospital; NRFS: non-reassuring fetal status; WHO: World Health Organization.
3.2. Comparison of Standards
Table 3 displays values of AUCs and sensitivities plus the percentile threshold points for different FPRs to predict SGA at delivery by ultrasound at 35 weeks (range 34+0–36+6 weeks). For a 10% FPR, the detection rates for SGA for all standards ranged between 48.9% with the Figueras standard (AUC: 0.82; 95% CI: 0.80–0.83) to 60.8% with the Fetal Medicine Foundation standard (AUC: 0.87; 95% CI: 0.85–0.88). These values were obtained with percentile threshold points below 17.3%, 16.3%, 22.9%, 17.3%, 11.1% and 5.3% for NC MSUH, customized MSUH, Figueras, INTERGROWTH-21st, WHO, and FMF standards, respectively. For a 20% FPR, the detection rates were between 66.4 and 78.92%, using 28.5%, 28.1%, 34.6%, 28.1%, 19.1%, and 13.1% as percentile threshold points for the abovementioned standards, respectively.

Table 3.
Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and sensitivity analyses to detect small for gestational age cases by ultrasound at 35 weeks (range 34–36 weeks) for different false positive rate (FPR) percentages; MSUH: Miguel Servet University Hospital; Pc: percentile; WHO: World Health Organization. * Sensitive threshold percentile (Thr): percentile point that corresponds to a false positive rate value.
Figure 3 illustrates the receiver operating characteristic curve comparison and AUC for the prediction of SGA at delivery by ultrasound at 35 weeks. Figure 4 displays the results of the logistic regression model with the ORs and 95% CIs to predict SGA by ultrasound at 35 weeks, according to the standards.
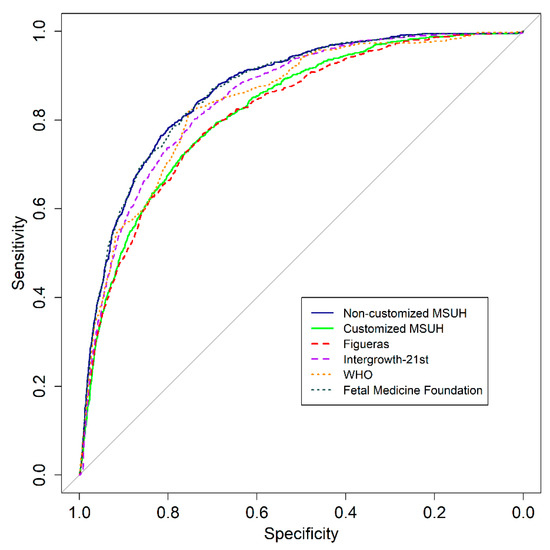
Figure 3.
Receiver operating characteristic curves: comparison of fetal growth standards and area under the curve (95% CIs) for prediction of small for gestational age newborns, using estimated percentile weight by ultrasound at 35 weeks. Growth standards: non-customized Miguel Servet University Hospital (MSUH), customized MSUH, Figueras et al., INTERGROWTH-21st, World Health Organization (WHO), and Fetal Medicine Foundation.
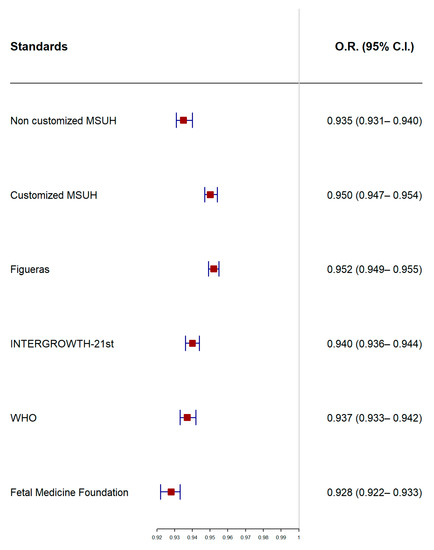
Figure 4.
Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of standards in to predict small for gestational age according to estimated percentile weight by ultrasound at 35 weeks; MSUH: Miguel Servet University Hospital; WHO: World Health Organization.
p-values of the comparisons of the standard AUC values and sensitivity for a 90% specificity are shown in Table 4. The Fetal Medicine Foundation and the non-customized MSUH standards showed no statistically significant differences between them, with greater SGA prediction ability than the Intergrowth-21st, Figueras, and WHO standards. Moreover, in the comparison, the Intergrowth-21st and WHO standards showed significant differences from the customized MSHU and Figueras standards. Finally, customized standards did not show differences between them.

Table 4.
Results of p-value tests to compare standards: area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and sensitivities (specificity 90%) to predict small for gestational age; and percentage of adverse perinatal outcome (APO) diagnosis; NC: non-customized; C: customized; MSUH: Miguel Servet University Hospital; WHO: World Health Organization.
Regarding APO prediction by EPW < 10, in Table 2 we show that the Fetal Medicine Foundation and WHO standards reached the greatest detection rates—27.0% and 17.4% respectively—with statistically significant differences between them and the rest of standards. No statistically significant differences were detected in the any of the possible comparisons between the non-customized MSUH (11.8%), INTERGROWTH-21st (10.7%), customized MSUH (9.6%), and Figueras (7.9%) standards, with the unique exception of the significant difference between the non-customized MSUH and Figueras standards. The instrumental deliveries for NRFS, cesarean deliveries for NRFS, and neonatal acidemia APOs might explain those differences. p-values of all comparisons are illustrated in Table 4.
3.3. Ultrasound-Delivery Interval: Comparison of Standards
Table 5 displays values of AUCs and sensitivities for different FPRs to predict SGA by ultrasound–delivery interval (range 1–6 weeks). The observed results show higher detection rates as the interval decreases. Figure 5 shows the prediction of small for gestational age cases, by standard, by ultrasound–delivery interval (1–6 weeks), for a 10% false positive rate.

Table 5.
Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and sensitivity analyses to predict small for gestational age newborns using estimated percentile weight by ultrasound at 35 weeks (range 34–36 weeks), for different false positive rate (FPR) percentages and ultrasound–delivery intervals (1–6 weeks); MSUH: Miguel Servet University Hospital; WHO: World Health Organization.
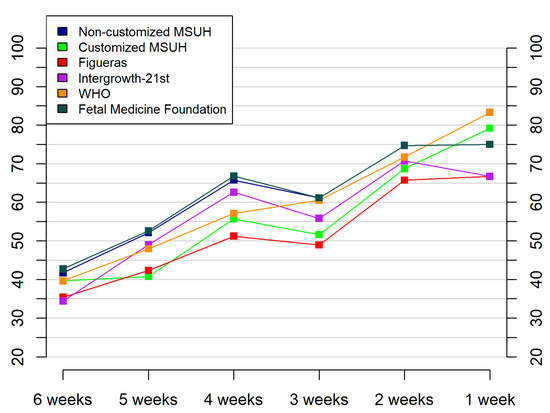
Figure 5.
Prediction of small for gestational age cases, by standard and by ultrasound–delivery interval (1–6 weeks), for a 10% false positive rate. Growth standards: non-customized Miguel Servet University Hospital (MSUH), customized MSUH, Figueras et al., INTERGROWTH-21st, World Health Organization (WHO), and Fetal Medicine Foundation.
Figure 6 displays odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals of the standards in order to predict SGAs by ultrasound–delivery interval (range 1–6 weeks). Figure 7 illustrates the receiver operating characteristic curve comparison of fetal growth standards for the prediction of SGA newborns according to the ultrasound–delivery interval (range 1–6 weeks).
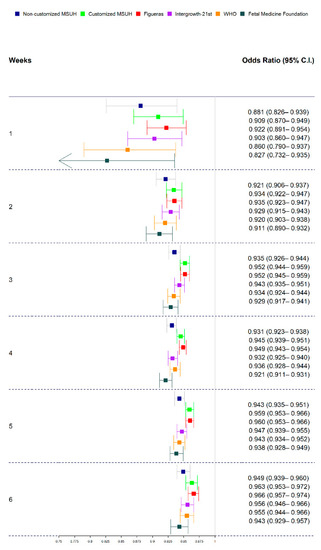
Figure 6.
Odds ratios (ORs), 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and p-values of standards, in order to predict small for gestational age (SGA) fetuses by standard and ultrasound–delivery interval delivery date (1–6 weeks). Growth standards: non-customized Miguel Servet University Hospital (MSUH), customized MSUH, Figueras et al., INTERGROWTH-21st, World Health Organization (WHO), and Fetal Medicine Foundation.
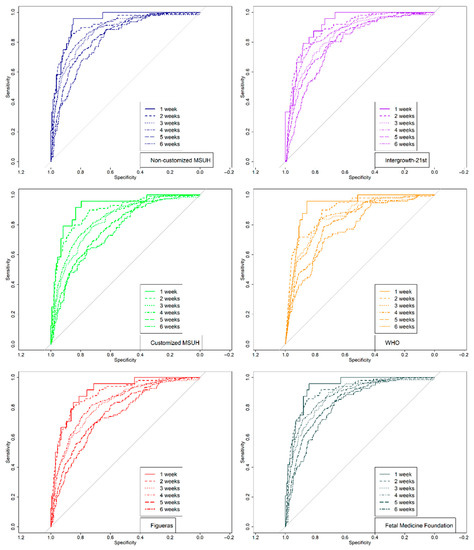
Figure 7.
Receiver operating characteristic curves: comparison of fetal growth standards and area under the curve for prediction of small for gestational age (SGA) by standard and by ultrasound–delivery interval (1–6 weeks). Growth standards: non-customized Miguel Servet University Hospital (MSUH), customized MSUH, Figueras et al., INTERGROWTH-21st, World Health Organization (WHO), and Fetal Medicine Foundation.
4. Discussion
4.1. Principal Findings
We have demonstrated the utility of EPW by ultrasound at 35 weeks (range 34+0–36+6 weeks) as a predictor of SGA fetuses at delivery at term. Adjusting the percentile threshold points, the growth standards showed a similar good predictive ability, but with a significant advantage for the non-customized MSUH and Fetal Medicine Foundation standards, and a disadvantage for both the customized MSUH and Figueras standards, for SGA fetuses.
In our results, we found an underestimation of 10th percentile, by ultrasound at 35 weeks (range 34–36 weeks) with the WHO (7.5%) and FMF (2.7%) standards, and an overestimation with the Figueras (18.1%) standard; for that, we can conclude that these standards have a lack of calibration for our study population. The MSHU (NC (11.9%) and customized (12.2%)) and INTERGROWTH-21st (12.7%) standards fit better to the 10th percentile, with a minimum error, probably for the exclusion of premature deliveries.
When we analyzed the APO-predictive ability of the six standards by percentile weight <10 at 35th week of gestational age, the customized Fetal Medicine Foundation and WHO standards showed the greatest diagnostic ability, with statistically significant differences from the rest of standards. The main reason for this lies in the greater proportion of 10th percentile EPW for the Fetal Medicine Foundation (21.2%) and WHO (12.6%) standards, In any case, with similar proportions of EPW < 10, the non-customized MSUH and INTERGROWTH-21st standards show a better APO-predictive ability than the customized MSUH and Figueras standards. A previous study did not find any significant differences between the customized and non-customized standards when analyzing the predictive ability of EPW to detect APOs; by contrast, using EPW > 90th percentile, we detected significant differences [34].
4.2. Prediction by Fetal Biometry and Ultrasound–Delivery Interval
There is no international consensus on performing a universal ultrasound in the third trimester; two international guidelines—the RCOG [35], and the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) [36]—do not recommend universal ultrasound to detect fetal growth anomalies. Sovio el al [37], however, found that universal third trimester ultrasound in nulliparous women, compared with selected ultrasound, tripled the detection of SGA < P10 infants, and could identify FGR fetuses at increased risk of neonatal morbidity.
The EPW at third trimester ultrasound over 32 weeks has been shown to be a good predictive model (AUC > 0.85) for the detection of SGA at delivery in several studies, although with detection rates limited for late-onset SGA births [4,38,39]. For gestational time, the detection rate of SGA at delivery by ultrasound between 33–34 weeks is approximately 52%, and between 36–37 weeks it is approximately 60% (FPR of 10%) [40,41,42]. According to several studies, therefore, detection is higher the later the ultrasound is performed [14,43,44]. In our case, the predictive capacity for SGA at delivery by ultrasound at 35 weeks is also limited for the six growth standards, and generally, a shorter ultrasound–delivery interval is correlated with better prediction rates. In any case, the cutoff points of the 10th percentiles by ultrasound at 35 weeks are moderate for the prediction of SGA at delivery.
4.3. Prediction by Fetal Biometry and Ultrasound–Delivery Interval: Comparison of Standards
Blue et al., in 2018 [45], compared the RCOG and ACOG standards for the detection of SGA at delivery, with a mean birth of 37.7 weeks and ultrasounds performed in the previous 2 weeks, and showed that both standards had a moderate predictive capacity (AUCs of 0.78 and 0.76, respectively). In another study by Blue in 2019 [46], the Hadlock and INTERGROWTH-21st standards for the detection of SGA, with deliveries at 37 weeks on average and ultrasound in the previous two weeks, showed good predictive capabilities (>0.90), with cutoff points of the optimal percentile at 15% for the Hadlock standard and 22% for the INTERGROWTH-21st standard. Both studies are not comparable to ours; although they show the minimum differences in SGA prediction regardless of the standard used, neither of them studied customized standards.
In two studies by Odibo et al. in 2018 [47] and 2019 [48], using the same sample obtained for the three different standards compared (INTERGROWTH-21st, a local customized standard, and the Hadlock standard), a moderate predictive capacity for SGA at delivery was achieved (0.67, 0.62, and 0.69, respectively), although with ultrasound performed between 26 and 36+6 weeks, and an average ultrasound–delivery interval of 6.7 weeks—also different from our study.
Reboul et al., in 2017 [49], found that the Hadlock and the customized Gardosi standards had a moderate predictive capacity for SGA at delivery (0.768 and 0.708, respectively), with the detection rates somewhat higher for the Hadlock standard, although with an average of performing ultrasound at 32 weeks—lower than ours, which could justify the lower predictive capacity.
4.4. Clinical and Research Implications
In clinical practice we can say that more important than the choice of the growth standard is its calibration before clinical use, both by ultrasound and delivery, in the reference population. The physiological and non-pathological characteristics of each population are those that will allow us to calibrate the standard to be used.
There are several factors for which ultrasound in the third trimester presents limitations when predicting SGA and FGRs at delivery, and some of them are unavoidable—especially the systematic error of ultrasound at the time of EFW calculation [50]. With the current studies carried out on the timing of performing the third trimester ultrasound and the ultrasound–delivery interval, together with our comparative study of standards, we can affirm that the timing that better predicts SGA cases is the one closest to delivery; however, we cannot delay ultrasound universally to 37 weeks, since we would not detect early FGRs. As we are not currently able to make that prediction, it will continue to be the subject of future research.
According to our results, it would be appropriate to raise the ultrasound-estimated weight percentile cutoff point above 10 for fetal growth control. This is because the 10th percentile has been shown to be insufficient, and with low predictive capacity for SGA at delivery and, therefore, fetuses that can potentially be IUGR even before delivery can escape control and, thus, increase their morbidity and mortality. Our recommendation, in the ultrasound during the third trimester, between 35 and 36 weeks, could be to raise the cutoff point at least from the 10th to the 20th percentile for strict control of fetal growth.
4.5. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
Our study has several strengths, including the wide sample size close to 10,000 pregnancies. Ultrasound measurements were performed in routine clinical practice; thus, weight estimations were more concentrated over specific weeks of gestational age. Limitations of our investigation are that our data came from a single hospital, and their retrospective nature could limit the generalization of our standards. Furthermore, the information of the ultrasound was available to the obstetricians, which could mean a bias in the management of the pregnancies. A small percentage of labors are inductions of labor or cesarean sections programmed by IUGR, and they could act as confounding factors in the study. Similarly, other cases of early termination due to other causes have not been taken into account.
5. Conclusions
In summary, even with limited detection rates, the growth standards showed a similar good predictive ability, with a statistically significant improvement by the use of non-customized standards, for SGA at delivery by ultrasound at 35 weeks. Generally, a shorter ultrasound delivery interval for the different standards was correlated with better prediction rates for small gestational age cases. When focusing on the use of EPW < 10th percentile at week 35 for the prediction of APOs, non-customized standards also demonstrated an advantage over customized standards.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.-C., L.M.E. and M.T.-D.; methodology, R.S.-C., L.M.E. and F.R.P.-L.; software, L.M.E., R.A.-G. and G.S.; validation, R.S.-C., P.D.-P. and J.M.C.; resources, G.S. and J.M.C.; data curation, R.S.-C., L.M.E., R.A.-G., P.D.-P. and B.C.-L.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S.-C. and L.M.E.; writing—review and editing, R.A.-G., P.D.-P., J.M.C., F.R.P.-L., B.C.-L., G.S. and M.T.-D.; funding acquisition, G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by project MTM2017-83812-P of MINECO.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Aragon (PI20/414).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived, as due to the retrospective observational nature of this study, data could be fully anonymized.
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed were retrieved from the Miguel Servet University Hospital database.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank all the staff of the Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnosis Unit of the Miguel Servet University Hospital (Zaragoza, Spain) for their help in the acquisition and management of data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Jelks, A.; Cifuentes, R.; Ross, M.G. Clinician bias in fundal height measurement. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 110, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.P.; Magann, E.F. Screening for fetal growth restriction. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 49, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Agudelo, A.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Kennedy, S.H.; Villar, J. Novel biomarkers for predicting intrauterine growth restriction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG 2013, 120, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Triunfo, S.; Crispi, F.; Gratacos, E.; Figueras, F. Prediction of delivery of small-for-gestational age neonates and adverse perinatal outcome by fetoplacental Doppler at 37 weeks' gestation. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 49, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCowan, L.M.; Figueras, F.; Anderson, N.H. Evidence-based national guidelines for the management of suspected fetal growth restriction: Comparison, consensus, and controversy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, S855–S868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardosi, J.; Giddings, S.; Buller, S.; Southam, M.; Williams, M. Preventing stillbirths through improved antenatal recognition of pregnancies at risk due to fetal growth restriction. Public Health 2014, 128, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardosi, J.; Madurasinghe, V.; Williams, M.; Malik, A.; Francis, A. Maternal and fetal risk factors for stillbirth: Population based study. BMJ 2013, 346, f108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, N.A.; Bukowski, R.; Thomas, A.M.; Cantonwine, D.; Zera, C.; Robinson, J.N. Identification of pathologically small fetuses using customized, ultrasound and population-based growth norms. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 44, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, S.; Glinianaia, S.V.; Torrioli, M.G.; Platt, M.J.; Miceli, M.; Jouk, P.S.; Johnson, A.; Hutton, J.; Hemming, K.; Hagberg, G.; et al. Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe (SCPE) collaboration of European Cerebral Palsy Registers. Cerebral palsy and intrauterine growth in single births: European collaborative study. Lancet 2003, 362, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kady, S.; Gardosi, J. Perinatal mortality and fetal growth restriction. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2004, 18, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasak, B.; Koenen, S.V.; Koster, M.P.; Hukkelhoven, C.W.; Franx, A.; Hanson, M.A.; Visser, G.H. Human fetal growth is constrained below optimal for perinatal survival. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 45, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindqvist, P.G.; Molin, J. Does antenatal identification of small-for-gestational age fetuses significantly improve their outcome? Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 25, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovio, U.; Smith, G.C.S. The effect of customization and use of a fetal growth standard on the association between birthweight percentile and adverse perinatal outcome. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, S738–S744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caradeux, J.; Martinez-Portilla, R.J.; Peguero, A.; Sotiriadis, A.; Figueras, F. Diagnostic performance of third-trimester ultrasound for the prediction of late-onset fetal growth restriction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 220, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras, F.; Meler, E.; Iraola, A.; Eixarch, E.; Coll, O.; Figueras, J.; Francis, A.; Gratacos, E.; Gardosi, J. Customized birthweight standards for a Spanish population. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2008, 136, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviron-Cornudella, R.; Esteban, L.M.; Lerma, D.; Cotaina, L.; Borque, Á.; Sanz, G.; Castán, S. Comparison of fetal weight distribution improved by paternal height by Spanish standard versus Intergrowth 21st standard. J. Perinat. Med. 2018, 46, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiserud, T.; Piaggio, G.; Carroli, G.; Widmer, M.; Carvalho, J.; Neerup Jensen, L.; Giordano, D.; Cecatti, J.G.; Abdel Aleem, H.; Talegawkar, S.A.; et al. The World Health Organization Fetal Growth Charts: A Multinational Longitudinal Study of Ultrasound Biometric Measurements and Estimated Fetal Weight. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002220. [Google Scholar]
- Hadlock, F.P.; Harrist, R.B.; Martinez-Poyer, J. In utero analysis of fetal growth: A sonographic weight standard. Radiology 1991, 181, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadlock, F.P.; Harrist, R.B.; Sharman, R.S.; Deter, R.L.; Park, S.K. Estimation of fetal weight with the use of head, body, and femur measurements: A prospective study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1985, 151, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirnemann, J.; Villar, J.; Salomon, L.J.; Ohuma, E.; Ruyan, P.; Altman, D.G.; Nosten, F.; Craik, R.; Munim, S.; Cheikh Ismail, L.; et al. International estimated fetal weight standards of the INTERGROWTH-21st project. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 49, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villar, J.; Cheikh Ismail, L.; Victora, C.G.; Ohuma, E.O.; Bertino, E.; Altman, D.G.; Lambert, A.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Carvalho, M.; Jaffer, Y.A.; et al. International standards for newborn weight, length, and head circumference by gestational age and sex: The newborn cross-sectional study of the INTERGROWTH-21st project. Lancet 2014, 384, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaides, K.H.; Wright, D.; Syngelaki, A.; Wright, A.; Akolekar, R. Fetal Medicine Foundation fetal and neonatal population weight charts. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 52, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardosi, J.; Chang, A.; Kalyan, B.; Sahota, D.; Symonds, E.M. Customised antenatal growth charts. Lancet 1992, 339, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardosi, J.; Francis, A. Controlled trial of fundal height measurement plotted on customized antenatal growth charts. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1999, 106, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Small-for-Gestational-Age Fetus, Investigation and Management (Green-top Guideline No. 31), 2nd ed.; The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Savirón-Cornudella, R.; Esteban, L.M.; Tajada-Duaso, M.; Castán-Mateo, S.; Dieste-Pérez, P.; Cotaina-Gracia, L.; Lerma-Puertas, D.; Sanz, G.; Perez-Lopez, F.R. Detection of Adverse Perinatal Outcomes at Term Delivery Using Ultrasound Estimated Percentile Weight at 35 Weeks of Gestation: Comparison of Five Fetal Growth Standards. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2020, 47, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, D.; Romero, R.; Gudicha, D.W.; Hernandez-Andrade, E.; Pacora, P.; Benshalom-Tirosh, N.; Tirosh, D.; Yeo, L.; Erez, O.; Hassan, S.S.; et al. Prediction of adverse perinatal outcomes by fetal biometry: A comparison of customized and population-based standards. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 55, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheon, J.A.; Zhang, X.; Platt, R.W.; Cnattingius, S.; Kramer, M.S. The case against customised birthweight standards. Pediatric Perinat. Epidemiol. 2011, 25, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuma, E.O.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methodology for constructing gestational age-related charts using cross-sectional and longitudinal data: THE INTERGROWTH-21st Project as a case study. Stat. Med. 2019, 38, 3507–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Committee on Obstetric Practice and American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Committee Opinion No 700: Methods for Estimating the Due Date. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 129, e150–e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, A.; Fernández, J.M.; Ferrández, A.; López-Siguero, J.P.; López, D.; Sánchez, E.; Colaborador, G. Estudios españoles de crecimiento 2010. Rev. Esp. Endocrinol. Pediatric 2011, 2, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Languaje and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Savirón-Cornudella, R.; Esteban, L.M.; Dieste-Pérez, P.; Pérez-López, F.R.; Castán-Larraz, B.; Sanz, G.; Tajada-Duaso, M. Prediction of Large for Gestational Age by Ultrasound at 35 Weeks and Impact of Ultrasound-Delivery Interval: Comparison of 6 Standards. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2021, 48, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Collaborating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health (NCC-WCH) on behalf of the National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Antenatal Care (NICE Clinical Guideline 62); National Institute of Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 101: Ultrasonography in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 113, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovio, U.; White, I.R.; Dacey, A.; Pasupathy, D.; Smith, G.C. Screening for fetal growth restriction with universal third trimester ultrasonography in nulliparous women in the Pregnancy Outcome Prediction (POP) study: A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2015, 386, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, J.; Rodriguez-Lopez, M.; Triunfo, S.; Sairanen, M.; Kouru, H.; Parra-Saavedra, M.; Crovetto, F.; Figueras, F.; Crispi, F.; Gratacós, E. Prediction of fetal growth restriction using estimated fetal weight vs a combined screening model in the third trimester. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 50, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadigas, C.; Saiid, Y.; Gonzalez, R.; Poon, L.C.; Nicolaides, K.H. Prediction of small for gestational age neonates: Screening by fetal biometry at 35–37 weeks. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 45, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, N.J. A systematic review of the ultrasound estimation of fetal weight. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 25, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degani, S. Fetal biometry: Clinical, pathological, and technical considerations. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2001, 56, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, L.K.; Rushworth, V.; Shah, P.S.; Keunen, J.; Windrim, R.; Ryan, G.; Kingdom, J. Incorporation of femur length leads to underestimation of fetal weight in asymmetric preterm growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 35, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souka, A.P.; Papastefanou, I.; Pilalis, A.; Michalitsi, V.; Panagopoulos, P.; Kassanos, D. Performance of the ultrasound examination in the early and late third trimester for the prediction of birth weight deviations. Prenat. Diagn. 2013, 33, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, E.; Arnau, A.; Berdala, R.; Bergos, C.; Montesinos, J.; Figueras, F. Ultrasound screening for fetal growth restriction at 36 vs 32 weeks' gestation: A randomized trial (ROUTE). Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 46, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blue, N.R.; Beddow, M.E.; Savabi, M.; Katukuri, V.R.; Mozurkewich, E.L.; Chao, C.R. A Comparison of Methods for the Diagnosis of Fetal Growth Restriction Between the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 131, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blue, N.R.; Savabi, M.; Beddow, M.E.; Katukuri, V.R.; Fritts, C.M.; Izquierdo, L.A.; Chao, C.R. The Hadlock Method Is Superior to Newer Methods for the Prediction of the Birth Weight Percentile. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odibo, A.O.; Nwabuobi, C.; Odibo, L.; Leavitt, K.; Obican, S.; Tuuli, M.G. Customized fetal growth standard compared with the INTERGROWTH-21st century standard at predicting small-for-gestational-age neonates. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2018, 97, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nwabuobi, C.; Odibo, L.; Camisasca-Lopina, H.; Leavitt, K.; Tuuli, M.; Odibo, A.O. Comparing INTERGROWTH-21st Century and Hadlock growth standards to predict small for gestational age and short-term neonatal outcomes. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, Q.; Delabaere, A.; Luo, Z.C.; Nuyt, A.M.; Wu, Y.; Chauleur, C.; Fraser, W.; Audibert, F. Prediction of small-for-gestational-age neonate by third-trimester fetal biometry and impact of ultrasound-delivery interval. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 49, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lappen, J.R.; Myers, S.A. The systematic error in the estimation of fetal weight and the underestimation of fetal growth restriction. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).