Abstract
A majority of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) develops in the setting of persistent chronic inflammation as immunological mechanisms have been shown to play a vital role in the initiation, growth and progression of tumours. The index review has been intended to highlight ongoing immunological changes in the hepatic parenchyma responsible for the genesis and progression of HCC. The in-situ vaccine effect of radiofrequency (RF) is through generation tumour-associated antigens (TAAs), following necrosis and apoptosis of tumour cells, which not only re-activates the antitumour immune response but can also act in synergism with checkpoint inhibitors to generate a superlative effect with intent to treat primary cancer and distant metastasis. An improved understanding of oncogenic responses of immune cells and their integration into signaling pathways of the tumour microenvironment will help in modulating the antitumour immune response. Finally, we analyzed contemporary literature and summarised the recent advances made in the field of targeted immunotherapy involving checkpoint inhibitors along with RF application with the intent to reinstate antitumour immunity and outline future directives in very early and early stages of HCC.
1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver malignancy; according to GLOBOCAN 2018 database, the figure of estimated annual incidence is approximately 841,000 and mortality of 782,000, labeling the entity as the sixth most commonly encountered and fourth most lethal cancer of the globe [1]. The HCC begins over the background of chronic inflammation of the liver, which occurs owing to several attributes, notably hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis leading to cirrhosis [2,3,4].
Despite the recent advancement in the management of HCC, it continues to remain a significant burden on global health owing to late presentation, higher recurrence and metastasis. The disease prognosis is highly related to its stage at presentation; in an early stage with localised disease, hepatic resection or transplantation can be an option; a five-year survival is 40–70%; however, patients with advanced disease that is not amenable to locoregional therapy have a median survival rate between 3–11 months [5,6,7].
HCCs are classical archetypes of inflammation-associated malignancy as these tumours are arising in the context of hepatic inflammation and the resultant fibrosis. The risk factors of HCC lead to a chronic inflammatory state and proclivities of proinflammatory cells present within the tumour microenvironment engender carcinogenesis and dysregulated growth [8,9,10]; studies have outlined that continued expression of cytokines and recruitment of immune cells on the background of chronic inflammatory state cause DNA damage leading to genetic mutations and neoplastic transformation [11,12,13].
Typically, the host immune system perceives and eliminates any aberrant changes; however, that is not always the case and the inflammatory state of liver brings significant alteration in the tumour microenvironment to dodge the immune surveillance, secondary to changes in molecular and cellular pathways necessitated in antigen processing, presentation and degradation of HCC cells [14,15,16]. These changes bring a paradigm shift in the immune response from antitumour to the state of tumour tolerance, leading to genesis and progress of HCC [17,18,19]. Hence, there is a great deal of interest in understanding the immunopathogenesis of HCC in order to enhance the antitumour immune response or inhibit the suppressive effect of immunity as a potential source of immunotherapy. The present review has aimed to discern the main attributes of the very intricate and heterogeneous landscape of HCC, pivoting on the dynamic interplay between malignant and immune cells within the tumour microenvironment. On account of the fact that specific immune compositions may extend tumour growth, an improved understanding of the functioning of immune cells and better knowledge of diverse mechanisms of immune evasion will help in formulating various therapeutic approaches to modulate antitumour immune response in the management of very early and early-stage HCC tumours.
2. Immune Response and Tolerance in the Hepatic Parenchyma
The hepatic parenchyma performs multitudes of responsibilities such as removal of environmental or bacterial agents from the alimentary tract, elimination of bloodborne pathogens, and metabolizing and excreting various toxic substances. Concurrently, hepatic parenchyma has been exposed to loads of antigens, causing an enormous amount of immune response, which can cause collateral damage to the normal liver tissue. However, it gets countervailed through the intrinsic mechanism of hepatic parenchyma to tolerate the immune response [20,21,22].
The hepatic innate immune system, Kupffer cells, and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) play an important role in the induction of local immunosuppression [23]. The immune response includes differentiation of T cells into memory-like T-cells and generation effector T-cells following reactivation by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) as dendritic cells (DCs) and through activation of cytotoxic T--cells; however, in the situation of chronic inflammation and ongoing exposure of antigens induce tolerogenic hepatic priming [24,25]. The priming of hepatic parenchyma manifests with defective antigen processing by LSECs, undermines antigen-specific immune surveillance and declines in expression of co-stimulatory molecules B7-1 (CD80) & B7-2 (CD86) on CD4+ T-cells and CD137 on CD8+ and NK (Natural Killer) cells [26,27].
The CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) molecules present on different types of APCs play essential roles in the signaling of immune checkpoint pathways B7-CD28/CTLA-4. The interactions of B7 with the CD28 receptor on T-cells relay co-stimulatory signals to antigen-primed T-cells or may incur co-inhibitory signals following binding with the inhibitory checkpoint receptor, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) present on T-cells [20,28].
Further, the immunosuppressive role of CTLA-4 has been elucidated through the induction of immune tolerance in recipient following liver transplantation via expression of CTLA-4 molecule on Foxp3+CD25+CD4+ T-regulatory cells (Tregs), which indicates its applicability in the regulation of immune activity in liver transplantation [29,30].
Additionally, the PD-L1 molecules are present on hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), LSECs, and Kupffer cells, which help in the genesis of immune tolerance through induction of T-cell dysfunction or apoptosis [31,32]. PD-L1/PD-L2/PD-1 (programmed death-ligand 1 or 2/programmed cell death 1 receptor) immune checkpoint pathway is involved in the inhibition of immune activity in the hepatic milieu, particularly in instances of chronic inflammation of the liver where the physiologic expression of PD-L1, along with PD-L2 and PD-1, get enhanced [28,33].
The main purpose of these tolerogenic responses is protection through avoidance of unnecessary inflammatory response against harmless antigens; however, they become inimical in a situation of chronic inflammation where immune tolerance to tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) contributes to onset and progression of HCC (Figure 1).
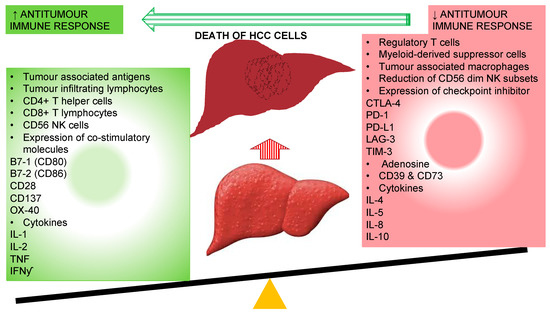
Figure 1.
Immunological alteration associated with improved antitumour immune response with the resolution of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. CD: cluster of differentiation; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4; IFNγ: interferon-gamma; IL: interleukin; LAG-3: lymphocyte-activation gene 3; PD-1: programmed cell death-1; PD-L1: programmed cell death-ligand1; NK: natural killer cells; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3.
3. Tumour Microenvironment and Immunosuppression in HCC
The tumour microenvironment incites a multitude of changes for the genesis of HCC, involving immune cells and cytokines to elude the antitumour immune surveillance. Contemporary literature uncovered varied mechanisms of immune suppression and crosstalk between tumour cells, immune cells and microenvironment in modulating the process of liver fibrosis, hepatocarcinogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), tumour invasion, and distant spread [34,35,36]. Below we have outlined mechanisms employed to alter the antitumour immune response during the onset of HCC.
The interactive immunosuppressive microenvironment interferes in detection of tumour antigen by DCs via downregulation of tumour associated antigen (TAA) and MHC molecules; secretion of inhibitory factors (IL-10, TGF-b, and VEGF) by tumour and tumour-associated macrophages to rivet suppressor cells in tumour microenvironment including Tregs cells, TAM, MDSC and immature DCs; VEGF mediated inhibition of differentiation and function of immune cells during hematopoiesis; inhibition of helper CD4+ T-cells; induction of MDSCs and Tregs secondary to secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines and release indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO); inhibition of effector cells through Tregs cells, TAM, and MDSC via production of arginase, ROS, and suppressive cytokines IL-2 and TGF-b; reduced co-stimulatory molecule expression and activation of inhibitory receptors (CTLA-4 and PD-1) through its ligands, vitiating release of inflammatory cytokines IL-2, INF-y, TNF and cytotoxic chemicals perforin and granzyme by CD8+ T-cells [37,38,39,40]. On this account, it has been envisaged that the reinstatement of the antitumour immune response could have the potential of improving survival and decreasing recurrences in HCC (Figure 2).
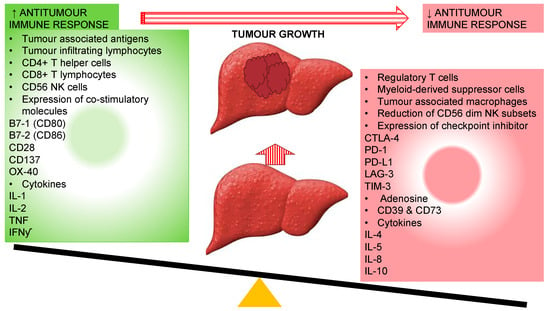
Figure 2.
Different immune responses associated with genesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma owing to the reduction in antitumour immune response. CD: Cluster of differentiation; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4; IFNγ: interferon-gamma; IL: interleukin; LAG-3: lymphocyte-activation gene 3; PD-1: programmed cell death-1; PD-L1: programmed cell death-ligand1; NK: Natural Killer cells; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3.
4. HCC Tumour Microenvironment and Changes in Cytokines Milieu
Despite of enhanced levels of expression of neoantigens in HCC tissue and a reciprocal infiltration of CTLs in tumour tissue, the instigated antitumour immune response is flawed and inadequate [41]. The explicable explanations of diminished immune response include anergy of immune cells secondary to point mutation or insertion/deletion of β2 microglobulin present in MHC I molecules causing a defect in antigens presentation to T-cells; expression of inhibitory immune regulatory receptors, ligands and cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-b. The immune checkpoints are inhibitory immune regulatory molecules, which include PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA-4, TIM3, lymphocyte-activating gene 3 protein and other lymphocyte attenuators. CTLA-4 expression on Tregs is associated with a decline in the production of granzyme B from CTLs, whilst its expression on CD14+ DCs relates with IL-10 and IDO mediated inhibition of T-cell proliferation with the induction of apoptosis. In addition, lowering of antitumour immunity is mediated through cells such as Tregs, MDSC and TAM involved in generating immune tolerance and reduction in hepatic parenchyma infiltrating CD56 dim NK, effector T-cells and CTLs [42,43,44].
To achieve optimal antitumor effects, CTLs must not only migrate to the tumour, but also be competent in functioning to induce lysis of tumour cells. In contrast to the earlier observation that increased density of lymphocytes within the HCC microenvironment is a surrogate marker of good prognosis following hepatic resection and transplantation [45]. Recent studies have highlighted that despite being the presence of adequate density of lymphocytes within HCC tissue, the antitumour immune responses are less than apposite owing to the diminution in the capacity for T-cells to proliferate, to release cytokine and inability to lyse tumour cells [46,47]. The abnormal set of behaviour can be explained by virtue of reduced CTLs activity secondary to suppressive nature of HCC tumour microenvironment and failing to release IFNγ upon stimulation of tumour-infiltrating CD8+ T-cells in contrast to peripheral CD8+ T-cells [48], although the installation of CTLs following isolation and ex-vivo cultivation has exhibited optimum antitumour specific activity [49]. Further research has been made to understand the clinical implication of these changes in immunological parameters in terms of survival. A recent study has outlined poor overall survival in HCC patients with increased levels of Tregs and reduced intra-tumoural and peripheral CD8+ T-cells [50]. Finkelmeier et al. (2016) investigated the prognostic value of soluble PD-L1 with HCC and concluded that higher values are associated with dismal outcomes [51]. Similarly, an increase in levels of immunosuppressive cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-8 and IL-10) or diminution of stimulating cytokines (IL-1, TNF-a, TFN-y) are also considered as a marker of poor prognostic value [52,53,54].
Even though the pathways entailed in HCC associated immune tolerance have not been completely elucidated, contemporary research has outlined the potential of targeted therapy in the reinstatement of antitumour immunity through the interaction of receptors, ligands and instigating immune cells and cytokines level [55].
Tregs cells, one of the important constituents of the HCC tumour microenvironment, cognate with a reduction in density and functioning of CD8+ T-cells, hence a therapeutic measure targeting Tregs would not only help in establishing of antitumour immune responses but can also improve survival [56,57]. Studies have outlined a significant decline in levels of intra-tumoural and circulating Tregs cells following radiofrequency ablation or radiofrequency based resection of HCC tumour and an associated improvement in survival [58].
5. HCC Tumour Microenvironment Immunomodulation
5.1. HCC Tumour Microenvironment Immunomodulation through Radiofrequency Application
Contemporary research has demonstrated that the application of radiofrequency (RF) over HCC nodules not only kills the tumour cells but also releases an abundance of neoantigens and DAMPs, which, in turn, incites CD8+ T-cell infiltration. The CD8+ T-cells then recognise such antigen-producing tumour cells alongside metastatic cells. Such immune-mediated response to locoregional therapy over the tumour nodule was first described in relation to radiation and is known as the “abscopal effect” [59]. The mechanism behind the abscopal effect has not been completely elucidated; a multitude of studies have outlined the potential of combining neoantigen generating locoregional therapy with immunotherapy could further enhance boost such effect. The cellular stress following tumour irradiation generates tumour-associated antigens (TAAs) secondary to necrosis and apoptosis of tumour cells and debris similar to vaccine effect with intent to treat or prevent the development of malignancy [60] (Figure 3). Such effects are observed in various solid tumours, including melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, to name a few. Further, radiofrequency waves are similar to radiation, which can elicit a tumour-specific in situ vaccine effect, resulting in a systemic response. Hence, the application of radiofrequency energy over the HCC tumour facilitates the release of DAMPs with subsequent increase in peripheral and tumour infiltrating CD4+, CTLs and NK cells, which shift the scale of balance towards the antitumour immune response rather than cancer progression [61,62].
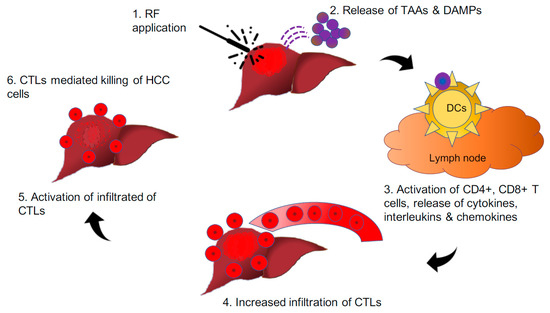
Figure 3.
Pictorial depiction of the hypothesis that “in-situ vaccine effect” through radiofrequency induces the release of neoantigens and DAMPs from HCC nodules, leading to the reinstatement of the antitumour immune response.
5.2. HCC Tumour Microenvironment Immunomodulation through Immunotherapy
As mentioned earlier and demonstrated in various studies, a mere increase in the levels of immune cells is not adequate to generate sufficient immune response owing to anergic T-cells. Hence, immunotherapy targeting co-stimulatory and inhibitory (checkpoint) receptors can reestablish the T-cell priming and effector functioning back to normal [63]. A targeted approach to modulate the activity of T-cells includes antagonism of checkpoint inhibitors. Of the various molecules involved in the immune checkpoint, PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4 have been shown to play important roles in suppression of T-cell activation by malignant cells [64,65]. On continuance, the development of monoclonal antibody targeting these molecules has been found to be highly efficacious in cancer with high immunogenicity, such as malignant melanoma. The last decade has witnessed significant progress in the understanding of the immune system and led to the development of immune checkpoints blockades such as anti-CTLA-4, anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1, which has shown the potential to bring a paradigm shift in management and prognosis of several cancers, including liver cancer [55,65].
The expression of CTLA-4 is increased following the activation of T-cells. The interaction between CTLA-4 and its ligand not only inhibits activity but also inflict anergy to T-cells. The anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies (tremelimumab and ipilimumab) have demonstrated their ability to deplete Tregs cells and reverse exhaustion of T-cells with intent to reinstituting the antitumour immune response. An anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody (tremelimumab) has received FDA approval in 2011 for the treatment of malignant melanoma [66,67,68].
Similarly, PD-1 and PD-L1 get upregulated following the activation of T-cells and the coupling of PD-1 with PD-L1 leads to inactivity of T-cells and NK cells functioning. The notable anti-PD-1 (nivolumab and pembrolizumab) and anti-PD-L1 (atezolimumab and avelumab) have further expanded the applicability of checkpoint inhibitors to various other cancers, including HCC. Presently, several phase III trials are going on, and the scientific community is eagerly waiting to peruse their outcomes and explore future applicability [64,69] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Clinical Trials involving various immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A phase II, non-controlled trial evaluated tremelimumab, a humanised IgG2 monoclonal antibody against CTLA-4 in advanced HCC patients not eligible for surgery or locoregional therapy. A total of 21 patients with advanced HCC with chronic HCV infection and Child–Pugh scores A (57.1%) or B (42.9%) were enrolled. Each patient received 15 mg/kg of tremelimumab every 90 days as a single agent therapy. A partial response was observed in 17.6% with a disease control rate of 76.4% and a median overall survival of 8.2 months. Approximately 45% had transient grade 3 transaminase toxicity following initial dosing of tremelimumab dose, although it did not require systemic steroids. A progressive decline in viral load was observed most of the patients, but a complete viral response was reported in just 3 patients. The analysis of results indicates a dual effect of tremelimumab in terms of antitumour and antiviral activity, suggesting that immune checkpoint treatment can be particularly beneficial in patients with a viral etiology such as HBV or HCV-related HCC [70].
A phase I/II trial studied the safety and preliminary activity of anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab (humanised IgG4 monoclonal antibody) in 262 advanced HCC patients with or without HBV or HCV infection received 0.1–10 mg/kg of nivolumab once every 2 weeks (dose-escalating cohort) or at a dose level of 3 mg/kg once every 2 weeks (expansion cohort). The trial demonstrated a manageable safety profile with a promising efficacy (dose-escalation cohort: response rate of 15%, median survival period of 15 months; expansion cohort: response rate of 20%, duration of response 9.9 months [71]. Further phase III randomised trial (NCT02576509) has compared nivolumab against sorafenib for unresectable HCC as a first-line treatment but did not outline any significant difference in terms of overall survival (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.72–1.02; p = 0.0752); however, further details of analysis by study group are still awaited [72]. Another ongoing trial NCT03383458 is evaluating the efficacy of nivolumab as adjuvant therapy following surgical resection or ablation for HCC tumours [73].
Another phase II trial (KEYNOTE-224, NCT02702414) with anti-PD-1pembrolizumab reported overall response rate (18%) and median survival of 12.9 months in advanced HCC following failed sorafenib treatment. In light of these promising results, the US FDA granted approval to nivolumab and pembrolizumab for treating HCC in patients who had received prior sorafenib, while many other immune checkpoint inhibitors are under evaluation to determine their applicability for treatment in HCC [74] (Table 1).
Studies have advocated that combining anti-CTLA-4 with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 could produce a superlative approach in reestablishing a competent immunity through the mitigation of immunosuppression signals. The interaction of CTLA-4 on T-cells with B7 ligands expressed on DCs or APCs in lymph node limits number and activity T-cells, whereas binding of PD-1 expressed on the activated CTLs to its ligand PD-L1 on tumour cells or TAM, brings inactivity of T-cells [75,76]. Hence, the rationale of combining includes induction of T-cells proliferation through inhibition of CTLA-4 and enhance CTLs activity through PD-1 inhibition.
A phase I/II trial assessed the combination of anti-PD-L1 antibody (durvalumab) and anti-CTLA-4 antibody (tremelimumab) in 40 patients with advanced HCC and demonstrated a response rate of 25%; highlighting the benefit of combined approach over monotherapy with tolerable toxicity profile. Presently, phase III trial (NCT03298451) is evaluating the efficacy of various regimens, including durvalumab monotherapy with two regimens of durvalumab and tremelimumab combination and sorafenib monotherapy. Another ongoing trial (NCT01658878) is assessing the efficacy of combination nivolumab with ipilimumab in contrast to nivolumab alone [74,77].
5.3. HCC Tumour Microenvironment Immunomodulation through Combined Approach
Contemporary research has demonstrated locoregional therapy, particularly radiofrequency (RF) based ablation of HCC nodules, not only kills the tumour cells but also release an abundance of neoantigens and DAMPs and induce CD8+ T-cell infiltration. According to meta-analysis performed by Ding et al., increased density of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) have been significantly associated with improved survival [78]. Additionally, studies have outlined positive immunomodulatory change following the application of RF in terms of Tregs, CD8+ T-cells, TGF-β, IFNγ, IL-10, IL-17, respectively [79,80,81,82].
Further, Tumeh et al. (2014) demonstrated that better tumour response following introduction pembrolizumab in a situation of higher expression of PD-1/PD-L1 on CD8+ T-cells at the margin of melanoma tumours. In addition, observation of significant tumour regression was discerned in association with an increase in CD8+ T-cells from baseline to post-treatment biopsy, specifically at the tumour center and invasive margin. Hence, both baseline and post-treatment CD8+ T-cells may act as important biomarkers in envisaging the tumour response to checkpoint inhibitors [83]. The combined approach involves radiofrequency ablation to generate neoantigens and influx of CD8+ T-cells, along with checkpoint inhibitors to activate these CD8+ T-cells to invigorate an antitumour immune response against HCC cells. Here, RF-induced cellular stress generates tumour-associated antigens (TAAs) through necrosis and apoptosis, which act as vaccines to activate the antitumour immune response, which gets boosted with the simultaneous introduction of checkpoint inhibitors with intent to treat or prevent the development of malignancy and distant metastasis (Figure 4). The same principle has formed the basis of a recent trial done by Duffy et al. (2017), where they evaluated 19 patients of advanced HCC to understand the clinical response of combining ablation with anti-CTLA-4 (tremelimumab). Five (26.3%) of nineteen had a partial response (95% confidence interval, 9.1–51.2%); 12 out of 14 HCC patients also marked quantifiable reduction in HCV viral load following treatment [84]. The plausible explanation of the observed decline in viral load could be because of the simultaneous return of immune response against these hepatotropic viruses too. Although the observed findings are intriguing and require further studies to envisage future applicability.
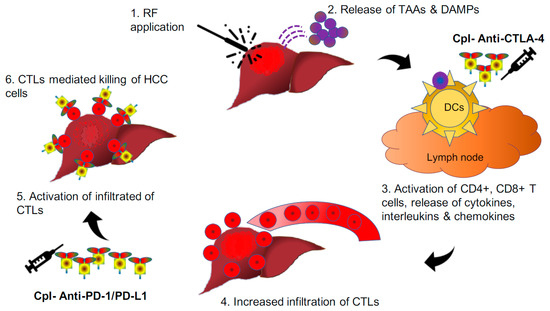
Figure 4.
Pictorial depiction of radiofrequency-induced release of neoantigens and DAMPs from HCC nodules whereupon activation of CD4+ and intratumoural infiltration CD8+ T-cells. The activity of these cells gets further augmented with the introduction of checkpoint inhibitors. CD: cluster of differentiation; CpI: checkpoint inhibitors; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4; DAMPs: damage-associated molecular patterns; PD-1: programmed cell death-1; PD-L1: programmed cell death-ligand1; RF: radiofrequency.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are proved to be beneficial in the treatment of advanced HCC; however, the world of immunomodulation is still not fully explored, particularly in very early and early stages of HCC. Moreover, the identification of predictive markers is of the utmost importance to determine a subgroup of HCC patients who are most likely to be benefitted from checkpoint inhibitors. Research exploring predictive markers for checkpoint treatment response has pointed towards mutational burden, PD-L1 expression, expression of immune regulatory molecules and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [85,86]. Shrestha et al. (2018) [87] reported that HCC patients with higher mutation burden have significantly poor overall survival and progression-free survival than those with a lower mutation burden; however, a study by Mauriello et al. [88] highlighted that high mutation does not correlate with a decline in survival in the absence of immunotherapy. On the contrary, multiple studies have shown that a high mutation burden associated with a better response to checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma patients. The mechanism is not fully understood, but an increased number of neoantigens (potential tumor-specific T-cell targets) generated by a high mutation burden is thought to bring an enhanced response from checkpoint inhibitors. Similarly, PD-L1 expression in HCC has been reported as a predictive biomarker for poor prognosis and can also utilised as an important tool to predict the response to anti-PD-1 antibodies; however, identifying other immune biomarkers could play an important role to further improve patient outcome as PD-L1 levels fluctuate along the course of the disease and only expressed in 30% of HCC tumours [89]. Higher levels of PD-L1 induce EMT in HCC patients with an increase in invasion and metastasis of malignant cells [87,90]. Thus, HCC patients with EMT phenotype are more likely to respond to PD-1/PD-L1 targeted immunotherapy.
6. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Despite advancement in chemotherapy, the observed outcomes in advance HCC tumours are dismal owing to reduced immune recognition of cancer cells and the development of an immunosuppressive microenvironment, rendering the immune system unable to mount an effective antitumour response. The present review has outlined the tumour microenvironment in HCC and summarised the applicability of checkpoint inhibitors and their potential benefits in terms of partial response, reduction in viral load and improved survival in advanced HCC. The same principle could be applicable in very early stages of HCC, where radiofrequency ablation or radiofrequency based resection in early stages to generate neoantigens to reinstate antitumor immunity, which could be boosted with checkpoint inhibitors. The mechanisms behind the diverse clinical responses to mono or a combined regimen of checkpoint inhibitors in advanced HCC patients are insufficiently elucidated. A focus on functional evaluations in the context of patient immunity for novel regimens alongside clinical testing may shed some light on the most effective combinations and the best strategies to reduce adverse effects. However, because of the complexity of the antitumour immune response and the observed heterogeneity, it is improbable to predict wide-ranging clinical benefits without using a wide set of biomarkers. Biomarker development is an area of intense study and remains a considerable clinical challenge. A few notable markers for checkpoint treatment response include the degree of mutational burden, PD-L1 expression, expression of immune regulatory molecules and EMT phenotype; however, further studies are warranted to develop better strategies with checkpoint inhibitors in HCC along with biomarkers in very early and early stages.
Author Contributions
K.J. and R.A. developed the concept and design of the study. K.J. wrote the manuscript. K.W.H., R.A., J.W., M.P., and N.H. critically revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
Prof. Nagy Habib is an inventor of the RF-based device Habib™ 4X. All the other authors have no conflicts of interest, including specific financial interests or relationships and affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript.
Abbreviations
CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4; PD-1: programmed cell death-1; PD-L1: programmed cell death-ligand1; OS: overall survival; DOR: duration of response; PR: partial response; mon: month.
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Yoon, S.K.; Lencioni, R. The Etiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Consequences for Treatment. Oncologist 2010, 15, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, J.H.; Ghouri, Y.A.; Mian, I. Review of hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, etiology, and carcinogenesis. J. Carcinog. 2017, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reccia, I.; Kumar, J.; Akladios, C.; Virdis, F.; Pai, M.; Habib, N.; Spalding, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A sign of systemic disease. Metabolism 2017, 72, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.; Fuster, J.; Bruix, J. The Barcelona approach: Diagnosis, staging, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transplant. 2004, 10, S115–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2017, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, B.; Battal, B.; Sari, S.; Verim, S. Hepatocellular carcinoma review: Current treatment, and evidence-based medicine. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18059–18060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringelhan, M.; Pfister, D.; O’Connor, T.; Pikarsky, E.; Heikenwälder, M. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J. THU-08 Molecular signature of prognosis and outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2013, 45, S236–S237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, D.; Villanueva, A.; Friedman, S.L.; Llovet, J. Liver Cancer Cell of Origin, Molecular Class, and Effects on Patient Prognosis. Gastroenterol. 2017, 152, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Karin, M. Obesity, inflammation, and liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2011, 56, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Gea, V.; Toffanin, S.; Friedman, S.L.; Llovet, J. Role of the microenvironment in the pathogenesis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol. 2013, 144, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capece, D.; Fischietti, M.; Verzella, D.; Gaggiano, A.; Cicciarelli, G.; Tessitore, A.; Zazzeroni, F.; Alesse, E. The Inflammatory Microenvironment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Pivotal Role for Tumor-Associated Macrophages. BioMed Res. Int. 2012, 2013, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, K.L. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Epidemiology and Molecular Carcinogenesis. Gastroenterol. 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Mellman, I. Oncology Meets Immunology: The Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Immun. 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.W.H.; Lo, C.L.R.; Chan, L.K.; Ng, I.O.-L. Molecular Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2016, 5, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravalli, R.N.; Cressman, E.; Steer, C.J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 87, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Gores, G.J.; Mazzaferro, V. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut 2014, 63, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P.; Fried, M.; Labrecque, D.; Bruix, J.; Sherman, M.; Omata, M.; Heathcote, J.; Piratsivuth, T.; Kew, M.; Otegbayo, J.A.; et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knolle, P.A.; Gerken, G. Local control of the immune response in the liver. Immunol. Rev. 2000, 174, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, F.; Tacke, F. Immunology in the liver—From homeostasis to disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubes, P.; Jenne, C. Immune Responses in the Liver. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 247–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, M.K.; Bedrosian, A.S.; Malhotra, A.; Henning, J.R.; Ibrahim, J.; Vera, V.; Cieza-Rubio, N.E.; Hassan, B.U.; Pachter, H.L.; Cohen, S.; et al. In hepatic fibrosis, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells acquire enhanced immunogenicity. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2200–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racanelli, V.; Rehermann, B. The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatol. 2006, 43, S54–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieghs, V.; Trautwein, C. The innate immune response during liver inflammation and metabolic disease. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Paulete, A.R.; Labiano, S.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Azpilikueta, A.; Etxeberria, I.; Bolaños, E.; Lang, V.; Rodriguez, M.; Aznar, M.A.; Jure-Kunkel, M.; et al. Deciphering CD137 (4-1BB) signaling in T-cell costimulation for translation into successful cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Lalor, P.F.; Adams, D.H. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells—Gatekeepers of hepatic immunity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knolle, P.A. Staying local—Antigen presentation in the liver. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 40, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, K.; Onishi, Y.; Prieto-Martin, P.; Yamaguchi, T.; Miyara, M.; Fehervari, Z.; Nomura, T.; Sakaguchi, S. CTLA-4 Control over Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cell Function. Science 2008, 322, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, C.E.; Taylor, A.; Schneider, H. CD28 and CTLA-4 coreceptor expression and signal transduction. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiegs, G.; Lohse, A.W. Immune tolerance: What is unique about the liver. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, H.; Li, K.; Qu, K.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Ye, L.; Dong, Z.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; et al. Liver-Resident NK Cells Control Antiviral Activity of Hepatic T Cells via the PD-1-PD-L1 Axis. Immun. 2019, 50, 403–417.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiskirchen, R.; Tacke, F. Cellular and molecular functions of hepatic stellate cells in inflammatory responses and liver immunology. HepatoBiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, N.A.; Neilson, E.G.; Moses, H.L. Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature 2004, 432, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libra, M.; Leonardi, G.C.; Candido, S.; Cervello, M.; Nicolosi, D.; Raiti, F.; Travali, S.; Spandidos, D. The tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critelli, R.M.; De Maria, N.; Villa, E. Biology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Nakamura, I.; Roberts, L.R. The tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and therapeutic targets. Semin. Cancer Boil. 2010, 21, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Nakashima, O.; Kutami, R.; Yamamoto, O.; Kojiro, M. Clinicopathological study on hepatocellular carcinoma with lymphocytic infiltration. Hepatology 1998, 27, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Mogushi, K.; Akiyama, Y.; Furuyama, T.; Watanabe, S.; Ogura, T.; Ogawa, K.; Ono, H.; Mitsunori, Y.; Ban, D.; et al. Comprehensive molecular and immunological characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Zhao, H.; Ren, X.-B. Relationship of VEGF/VEGFR with immune and cancer cells: Staggering or forward? Cancer Boil. Med. 2016, 13, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.C.; Friedman, S.L. Hepatic Fibrosis and the Microenvironment: Fertile Soil for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development. Gene Expr. 2014, 16, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprinzl, M.F.; Galle, P.R. Immune Control in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Progression: Role of Stromal Cells. Semin. Liver Dis. 2014, 34, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.-X.; Ling, Y.; Wang, H.-Y. Role of nonresolving inflammation in hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. npj Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova-Rusher, O.V.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Duffy, A.G.; Greten, T.F. The yin and yang of evasion and immune activation in HCC. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endig, J.; Buitrago-Molina, L.E.; Marhenke, S.; Reisinger, F.; Saborowski, A.; Schütt, J.; Limbourg, F.; Könecke, C.; Schreder, A.; Michael, A.; et al. Dual Role of the Adaptive Immune System in Liver Injury and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flecken, T.; Schmidt, N.; Hild, S.; Gostick, E.; Drognitz, O.; Zeiser, R.; Schemmer, P.; Bruns, H.; Eiermann, T.; Price, D.A.; et al. Immunodominance and functional alterations of tumor-associated antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell responses in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Seki, E. Inflammation and Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnelo, M.; Tan, A.; Her, Z.; Yeong, J.P.S.; Lim, C.J.; Chen, J.; Lim, K.H.; Weber, A.; Chow, P.; Chung, A.; et al. Interaction between tumour-infiltrating B cells and T cells controls the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2015, 66, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.; Cardoso, A.P.; Gonçalves, R.; Serre, K.; Oliveira, M.J. Interferon-Gamma at the Crossroads of Tumor Immune Surveillance or Evasion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhao, P.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; et al. Increased Regulatory T Cells Correlate With CD8 T-Cell Impairment and Poor Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Gastroenterolgy 2007, 132, 2328–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelmeier, F.; Canli, Ö.; Tal, A.; Pleli, T.; Trojan, J.; Schmidt, M.; Kronenberger, B.; Zeuzem, S.; Piiper, A.; Greten, F.R.; et al. High levels of the soluble programmed death-ligand (sPD-L1) identify hepatocellular carcinoma patients with a poor prognosis. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 59, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.-S.; Gu, X.; Xiong, W.; Guo, W.; Han, L.; Bai, Y.; Peng, C.; Cui, M.; Xie, M. Increased programmed death ligand-1 expression predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 4805–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaggiante, B.; Kazemi, M.; Pozzato, G.; Dapas, B.; Farra, R.; Grassi, M.; Zanconati, F.; Grassi, G. Novel hepatocellular carcinoma molecules with prognostic and therapeutic potentials. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1268–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-G. Isolation of Novel Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by a Subtraction-Enhanced Display Technique. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2003, 45, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hato, T.; Goyal, L.; Greten, T.F.; Duda, D.G.; Zhu, A.X. Immune checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma: Current progress and future directions. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Xiang, L.; Tan, D.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Claret, F.X.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: Tregs is correlated with poor overall survival. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormandy, L.A. Increased Populations of Regulatory T Cells in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Hiraoka, N.; Yamagami, W.; Ojima, H.; Kanai, Y.; Kosuge, T.; Nakajima, A.; Hirohashi, S. FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cells Affect the Development and Progression of Hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, R.H. Whole Body Irradiation—Radiobiology or Medicine? Br. J. Radiol. 1953, 26, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; MacManus, M.P.; Martin, R.F.; Martin, O.A. Abscopal effects of radiation therapy: A clinical review for the radiobiologist. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, J.; Melero, I.; Sangro, B. Immunological landscape and immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, T.F.; Wang, X.W.; Korangy, F. Current concepts of immune based treatments for patients with HCC: From basic science to novel treatment approaches. Gut 2015, 64, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Sprengers, D.; Boor, P.P.; Doukas, M.; Schutz, H.; Mancham, S.; Pedroza-Gonzalez, A.; Polak, W.G.; De Jonge, J.; Gaspersz, M.; et al. Antibodies Against Immune Checkpoint Molecules Restore Functions of Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Gastroenteroloy 2017, 153, 1107–1119.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breous, E.; Thimme, R. Potential of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, N.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Thimme, R. Cellular Immune Responses to Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Lessons for Immunotherapy. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floudas, C.S.; Brar, G.; Greten, T.F. Immunotherapy: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avola, D.; Melero, I.; Sangro, B. Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Immunother. Princ. Pract. 2018, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.J.; El Dika, I.; Abou-Alfa, G.K. Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Primed to make a difference? Cancer 2015, 122, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonaguro, L.; Mauriello, A.; Cavalluzzo, B.; Petrizzo, A.; Tagliamonte, M. Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangro, B.; Gomez-Martin, C.; De La Mata, M.; Iñarrairaegui, M.; Garralda, E.; Barrera, P.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Larrea, E.; Alfaro, C.; Sarobe, P.; et al. A clinical trial of CTLA-4 blockade with tremelimumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.C.C.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, L.A.; Gordan, J.D.; Kelley, R.K. Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, M.P.; Khakoo, S.I. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current and future. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2977–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okusaka, T.; Ikeda, M. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and future perspectives. ESMO Open 2018, 3, e000455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Irving, B.A.; Hodi, F.S. Molecular pathways: Next-generation immunotherapy—Inhibiting programmed death-ligand 1 and programmed death-1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intlekofer, A.M.; Thompson, C.B. At the bench: Preclinical rationale for CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade as cancer immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Boil. 2013, 94, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.K.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Bendell, J.C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Borad, M.J.; Yong, W.-P.; Morse, M.; Kang, Y.; Rebelatto, M.; Makowsky, M.; et al. Phase I/II study of durvalumab and tremelimumab in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Phase I safety and efficacy analyses. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Xu, X.; Qian, Y.; Xue, W.; Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Jin, L.; Tan, Y. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med. 2018, 97, e13301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayant, K.; Sodergren, M.H.; Reccia, I.; Kusano, T.; Zacharoulis, D.; Spalding, D. A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing liver resection with the Rf-based device habibTM-4X with the clamp-crush technique. Cancers. 2018, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-W.; Lee, P.-H.; Kusano, T.; Reccia, I.; Jayant, K.; Habib, N. Impact of cavitron ultrasonic surgical aspirator (CUSA) and bipolar radiofrequency device (Habib-4X) based hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma on tumour recurrence and disease-free survival. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93644–93654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazmishvili, K.; Jayant, K.; Janikashvili, N.; Kikodze, N.; Mizandari, M.; Pantsulaia, I.; Paksashvili, N.; Sodergren, M.H.; Reccia, I.; Pai, M.; et al. Study to evaluate the immunomodulatory effects of radiofrequency ablation compared to surgical resection for liver cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.-W.; Jayant, K.; Lee, P.-H.; Yang, P.-C.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Habib, N.; Sodergren, M. Positive Immuno-Modulation Following Radiofrequency Assisted Liver Resection in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumeh, P.C.; Harview, C.; Yearley, J.H.; Shintaku, I.P.; Taylor, E.J.M.; Robert, L.; Chmielowski, B.; Spasić, M.; Henry, G.; Ciobanu, V.; et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature 2014, 515, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, A.G.; Ulahannan, S.; Makorova-Rusher, O.; Rahma, O.; Wedemeyer, H.; Pratt, D.; Davis, J.L.; Hughes, M.S.; Heller, T.; Elgindi, M.; et al. Tremelimumab in combination with ablation in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 66, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Huang, Z.; Teng, F.; Xing, L.; Yu, J. Predictive biomarkers in PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 515, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, G.T.; Weiner, L.M.; Atkins, M.B. Predictive biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e542–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Prithviraj, P.; Anaka, M.; Bridle, K.R.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Dhungel, B.; Steel, J.; Jayachandran, A. Monitoring Immune Checkpoint Regulators as Predictive Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, A.; Zeuli, R.; Cavalluzzo, B.; Petrizzo, A.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Ceccarelli, M.; Tagliamonte, M.; Buonaguro, L. High Somatic Mutation and Neoantigen Burden Do Not Correlate with Decreased Progression-Free Survival in HCC Patients not Undergoing Immunotherapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, M.; Green, M.; El Naqa, I. Characterizing PD-L1/PD-1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and implications on postresection treatment response. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e15626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocker, M. Biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: What’s new on the horizon? World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3974–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).