Effects of Different Adjuvants on the Protective Efficacy of a Subcellular Vaccine Against Chlamydia abortus Infection in Sheep
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Preparation of C. abortus COMC Antigen and Formulation of Vaccines
2.3. Preparation of C. abortus S26/3 Challenge Inoculum
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Sample Collection and Processing
2.6. Chlamydia abortus Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Analyses of Tissues
2.8. Immunological Analyses
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Outcome
3.2. Estimation and Detection of C. abortus Infection and Pathogen Load
3.3. Histology and Immunohistochemical Analysis
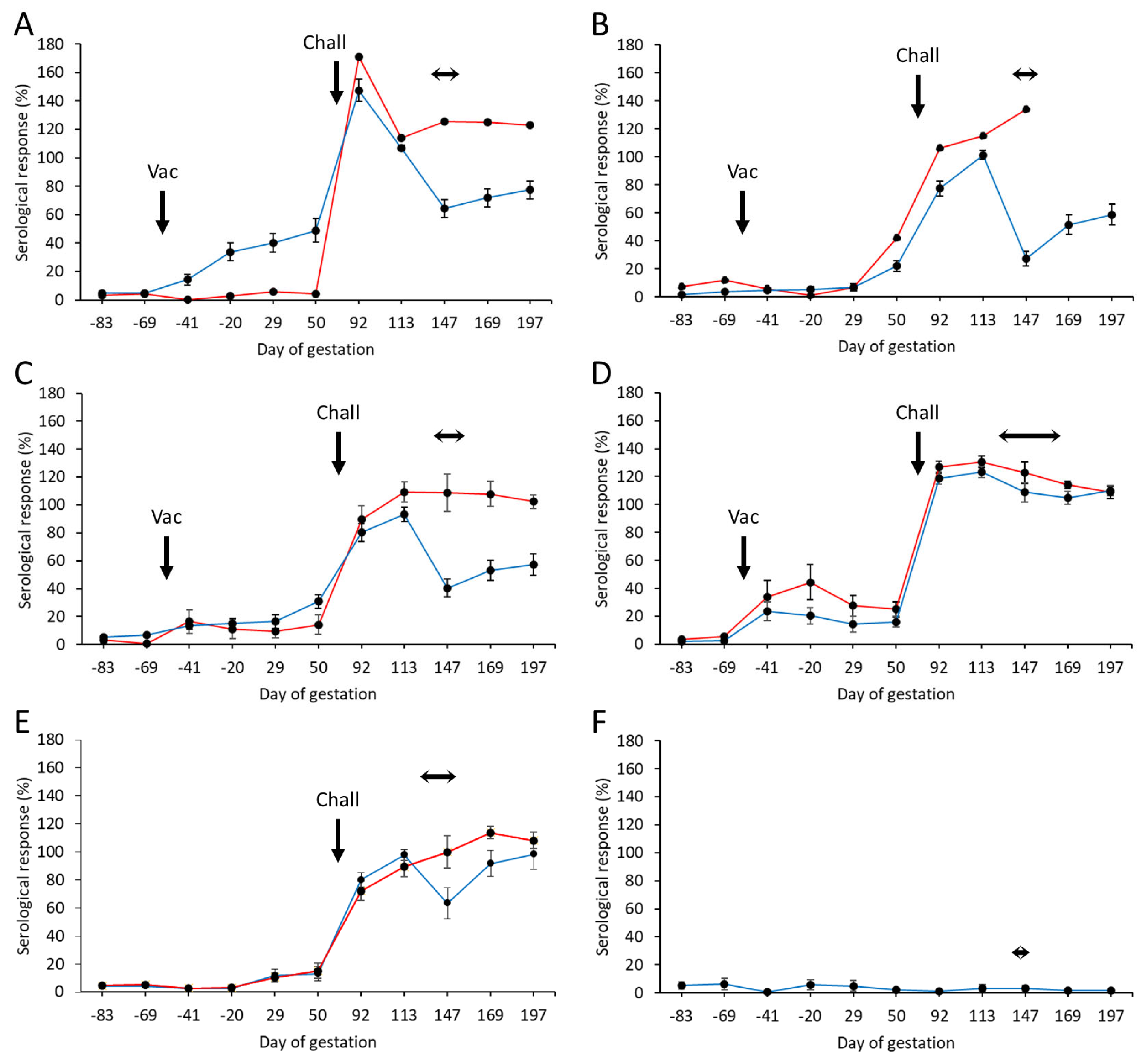
3.4. Serological Responses
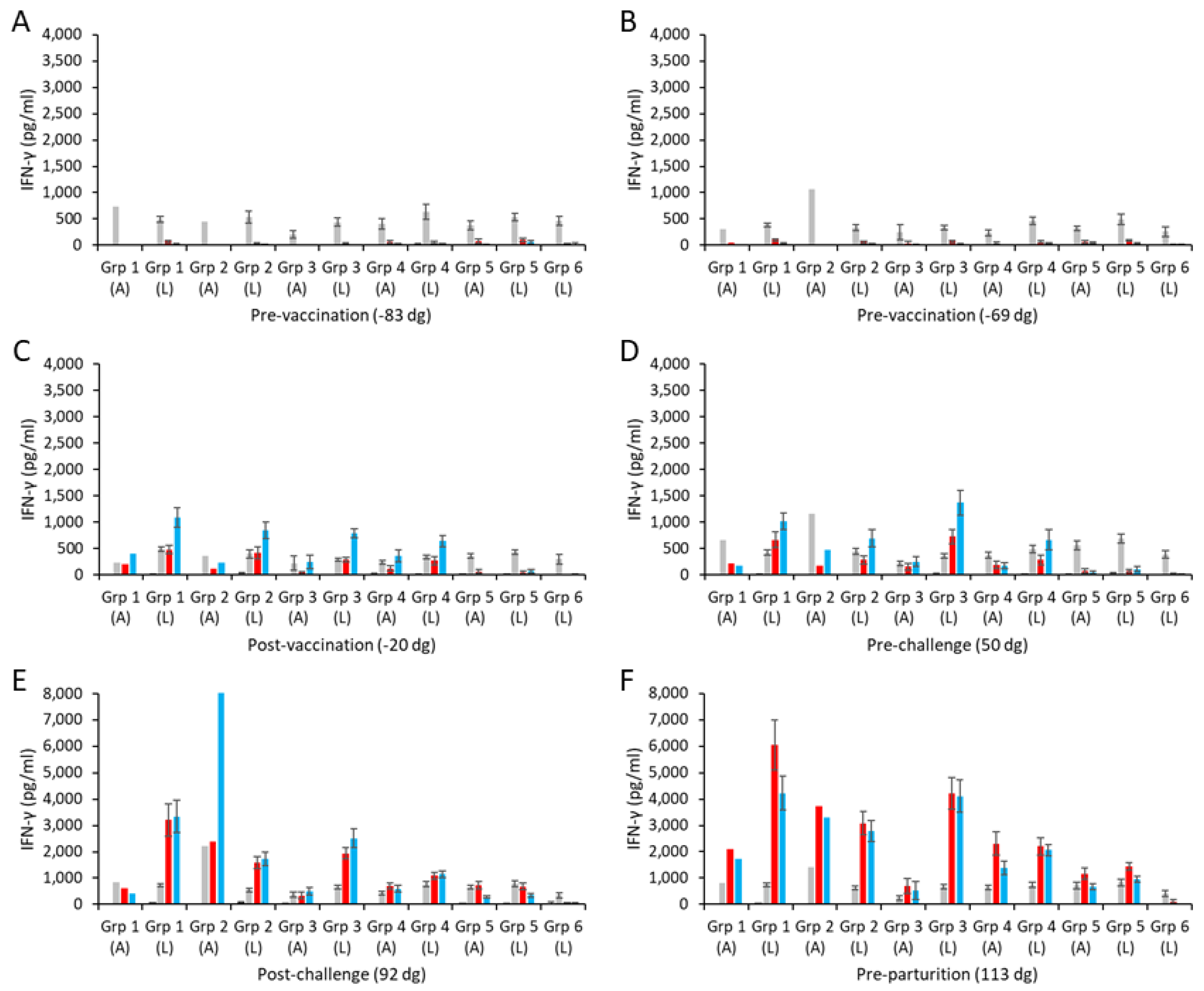
3.5. Cellular Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stamp, J.; McEwen, A.D.; Watt, J.; Nisbet, D. Enzootic abortion in ewes; transmission of the disease. Vet. Rec. 1950, 62, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longbottom, D.; Coulter, L.J. Animal chlamydioses and zoonotic implications. J. Comp. Pathol. 2003, 128, 217–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodolakis, A.; Laroucau, K. Chlamydiaceae and chlamydial infections in sheep or goats. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachse, K.; Grossmann, E. Chlamydial diseases of domestic animals—Zoonotic potential of the agents and diagnostic issues. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2002, 109, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, R. The ‘Direct Costs’ of livestock disease: The development of a system of models for the analysis of 30 endemic livestock diseases in Great Britain. J. Agric. Econ. 2003, 54, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R. Enzootic abortion costs home industry £20m pa. Farmers Wkly. 1992, 117, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Borel, N.; Polkinghorne, A.; Pospischil, A. A Review on Chlamydial Diseases in Animals: Still a Challenge for Pathologists? Vet. Pathol. 2018, 55, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospischil, A.; Thoma, R.; Hilbe, M.; Grest, P.; Gebbers, J.O. Abortion in woman caused by caprine Chlamydophila abortus (Chlamydia psittaci serovar 1). Swiss Med. Wkly. 2002, 132, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wen, Y.; Ding, H.; Zeng, H. Septic shock with Chlamydia abortus infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, N.; Guindre, L.; Laroucau, K.; Cantaloube, M.; Nallatamby, A.; Parreau, S. Chlamydia abortus in Pregnant Woman with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 628–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgener, A.V.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B.; Kern-Baumann, S.; Durovic, A.; Blaich, A.; Menter, T.; Bruder, E.; Roloff, T.; Martinez, A.; Borel, N.; et al. A Case Study of Zoonotic Chlamydia abortus Infection: Diagnostic Challenges from Clinical and Microbiological Perspectives. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turin, L.; Surini, S.; Wheelhouse, N.; Rocchi, M.S. Recent advances and public health implications for environmental exposure to Chlamydia abortus: From enzootic to zoonotic disease. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, B.; Wan, H.; Yu, L. Atypical pneumonia caused by Chlamydia abortus in HIV patient: A case report. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, N.; Caro, M.R.; Gallego, M.C.; Murcia-Belmonte, A.; Alvarez, D.; Del Rio, L.; Cuello, F.; Buendia, A.J.; Salinas, J. Isolation of Chlamydia abortus from a laboratory worker diagnosed with atypical pneumonia. Ir. Vet. J. 2015, 69, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, D.; Barlow, R.M.; Finlayson, J.; Anderson, I.E.; Mackellar, A. Observations on the pathogenesis of Chlamydia psittaci infection of pregnant sheep. J. Comp. Pathol. 1990, 102, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodolakis, A.; Salinas, J.; Papp, J. Recent advances on ovine chlamydial abortion. Vet. Res. 1998, 29, 275–288. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.E.; Anderson, I.E. Chlamydia psittaci: Is tonsillar tissue the portal of entry in ovine enzootic abortion? Res. Vet. Sci. 1988, 44, 260–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsmore, A.J.; Izzard, K.A.; Wilsmore, B.C.; Dagnall, G.J. Breeding performance of sheep infected with Chlamydia psittaci (ovis) during their preceding pregnancy. Vet. Rec. 1990, 126, 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, I.E.; Tan, T.W.; Jones, G.E.; Herring, A.J. Efficacy against ovine enzootic abortion of an experimental vaccine containing purified elementary bodies of Chlamydia psittaci. Vet. Microbiol. 1990, 24, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsmore, A.J.; Izzard, K.A.; Dagnall, G.J.; Wilsmore, B.C.; Woodland, R.M. Protection of ewes vaccinated with A22 strain Chlamydia psittaci (ovis) against challenge in pregnancy with homologous and heterologous strains of the organism. Br. Vet. J. 1990, 146, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.E.; Jones, K.A.; Machell, J.; Brebner, J.; Anderson, I.E.; How, S. Efficacy trials with tissue-culture grown, inactivated vaccines against chlamydial abortion in sheep. Vaccine 1995, 13, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodolakis, A.; Souriau, A. Response of ewes to temperature-sensitive mutants of Chlamydia psittaci (var ovis) obtained by NTG mutagenesis. Ann. Rech. Vet. 1983, 14, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodolakis, A.; Souriau, A. Response of goats to vaccination with temperature-sensitive mutants of Chlamydia psittaci obtained by nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1986, 47, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.W.; Herring, A.J.; Anderson, I.E.; Jones, G.E. Protection of sheep against Chlamydia psittaci infection with a subcellular vaccine containing the major outer membrane protein. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 3101–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Pais, R.; Ohandjo, A.; He, C.; He, Q.; Omosun, Y.; Igietseme, J.U.; Eko, F.O. Comparative evaluation of the protective efficacy of two formulations of a recombinant Chlamydia abortus subunit candidate vaccine in a mouse model. Vaccine 2015, 33, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.M.; Keane, O.M.; Ross, P.J.; Nally, J.E.; Seshu, J.; Markey, B. Evaluation of protective and immune responses following vaccination with recombinant MIP and CPAF from Chlamydia abortus as novel vaccines for enzootic abortion of ewes. Vaccine 2019, 37, 5428–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; He, C. Induction of a protective immune response against swine Chlamydophila abortus infection in mice following co-vaccination of omp-1 DNA with recombinant MOMP. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 56, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, A.D.; Foggie, A. Enzootic abortion in ewes: Prolonged immunity following the injection of adjuvant vaccine. Vet. Rec. 1956, 68, 686–690. [Google Scholar]
- Linklater, K.A.; Dyson, D.A. Field studies on enzootic abortion of ewes in south east Scotland. Vet. Rec. 1979, 105, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, W.S.; Simpson, J.; Lee, S.J.; Baxendale, W. Use of a live chlamydial vaccine to prevent ovine enzootic abortion. Vet. Rec. 1997, 141, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montbrau, C.; Fontseca, M.; March, R.; Sitja, M.; Benavides, J.; Ortega, N.; Caro, M.R.; Salinas, J. Evaluation of the efficacy of a new commercially available inactivated vaccine against ovine enzootic abortion. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroucau, K.; Aaziz, R.; Vorimore, F.; Menard, M.F.; Longbottom, D.; Denis, G. Abortion storm induced by the live C. abortus vaccine 1B strain in a vaccinated sheep flock, mimicking a natural wild-type infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 225, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longbottom, D.; Sait, M.; Livingstone, M.; Laroucau, K.; Sachse, K.; Harris, S.R.; Thomson, N.R.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B. Genomic evidence that the live Chlamydia abortus vaccine strain 1B is not attenuated and has the potential to cause disease. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3593–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.; Lovatt, F. Advice for when enzootic abortion vaccine is unavailable. Vet. Rec. 2024, 195, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Theodor, I.; Peterson, E.M.; de la Maza, L.M. Immunization with an acellular vaccine consisting of the outer membrane complex of Chlamydia trachomatis induces protection against a genital challenge. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3361–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, M.; Aitchison, K.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; Ciampi, F.; Underwood, C.; Paladino, A.; Chianini, F.; Entrican, G.; Wattegedera, S.R.; Longbottom, D. Protective Efficacy of Decreasing Antigen Doses of a Chlamydia abortus Subcellular Vaccine Against Ovine Enzootic Abortion in a Pregnant Sheep Challenge Model. Vaccines 2025, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, M.; Aitchison, K.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; Chianini, F.; Rocchi, M.S.; Caspe, S.G.; Underwood, C.; Flockhart, A.; Wheelhouse, N.; Entrican, G.; et al. Evaluation of the Protective Efficacy of Different Doses of a Chlamydia abortus Subcellular Vaccine in a Pregnant Sheep Challenge Model for Ovine Enzootic Abortion. Animals 2024, 14, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, M.; Wattegedera, S.R.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; Aitchison, K.; Corbett, C.; Sait, M.; Wilson, K.; Chianini, F.; Rocchi, M.S.; Wheelhouse, N.; et al. Efficacy of Two Chlamydia abortus Subcellular Vaccines in a Pregnant Ewe Challenge Model for Ovine Enzootic Abortion. Vaccines 2021, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucouturier, J.; Dupuis, L.; Ganne, V. Adjuvants designed for veterinary and human vaccines. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longbottom, D.; Livingstone, M.; Maley, S.; van der Zon, A.; Rocchi, M.; Wilson, K.; Wheelhouse, N.; Dagleish, M.; Aitchison, K.; Wattegedera, S.; et al. Intranasal infection with Chlamydia abortus induces dose-dependent latency and abortion in sheep. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattegedera, S.R.; Livingstone, M.; Maley, S.; Rocchi, M.; Lee, S.; Pang, Y.; Wheelhouse, N.M.; Aitchison, K.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; Buxton, D.; et al. Defining immune correlates during latent and active chlamydial infection in sheep. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClenaghan, M.; Herring, A.J.; Aitken, I.D. Comparison of Chlamydia psittaci isolates by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Infect. Immun. 1984, 45, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buendia, A.J.; Salinas, J.; Sanchez, J.; Gallego, M.C.; Rodolakis, A.; Cuello, F. Localization by immunoelectron microscopy of antigens of Chlamydia psittaci suitable for diagnosis or vaccine development. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 150, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.F.; Hernandez, J.N.; Machin, C.; Perez-Hernandez, T.; Wright, H.W.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Price, D.R.G.; Matthews, J.B.; McNeilly, T.N.; Nisbet, A.J. Impacts of breed type and vaccination on Teladorsagia circumcincta infection in native sheep in Gran Canaria. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, I.E.; Baxter, T.A. Chlamydia psittaci: Inclusion morphology in cell culture and virulence in mice of ovine isolates. Vet. Rec. 1986, 119, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premium Sheep & Goat Health Schemes. Available online: https://www.sruc.ac.uk/business-services/veterinary-laboratory-services/sheep-goat-health-schemes/premium-sheep-goat-health-schemes/ (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Wilson, K.; Livingstone, M.; Longbottom, D. Comparative evaluation of eight serological assays for diagnosing Chlamydophila abortus infection in sheep. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, M.; Wheelhouse, N.; Maley, S.W.; Longbottom, D. Molecular detection of Chlamydophila abortus in post-abortion sheep at oestrus and subsequent lambing. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspe, S.G.; Livingstone, M.; Frew, D.; Aitchison, K.; Wattegedera, S.R.; Entrican, G.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; McNeilly, T.N.; Milne, E.; Sargison, N.D.; et al. The 1B vaccine strain of Chlamydia abortus produces placental pathology indistinguishable from a wild type infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konietschke, F.; Hothorn, L.; Brunner, E. Rank-based multiple test procedures and simultaneous confidence intervals. Electron. J. Stat. 2012, 6, 738–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammin, D.J.; Markey, B.K.; Quinn, P.J.; McElroy, M.C.; Bassett, H.F. Comparison of Fetal and Maternal Inflammatory Responses in the Ovine Placenta after Experimental Infection with Chlamydophila abortus. J. Comp. Pathol. 2006, 135, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begg, D.J.; Dhungyel, O.; Naddi, A.; Dhand, N.K.; Plain, K.M.; de Silva, K.; Purdie, A.C.; Whittington, R.J. The immunogenicity and tissue reactivity of Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis inactivated whole cell vaccine is dependent on the adjuvant used. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, S.G.; Orr, M.T.; Fox, C.B. Key roles of adjuvants in modern vaccines. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; O’Hagan, D.T. Recent advances in veterinary vaccine adjuvants. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.X.; Xie, Y.; Ye, Y.P. ISCOMs and ISCOMATRIX. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4388–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia de la Fuente, J.N.; Gutierrez-Martin, C.B.; Ortega, N.; Rodriguez-Ferri, E.F.; del Rio, M.L.; Gonzalez, O.R.; Salinas, J. Efficacy of different commercial and new inactivated vaccines against ovine enzootic abortion. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 100, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.T.; Nunn, F.; Nath, M.; Frew, D.; Wells, B.; Marr, E.J.; Huntley, J.F.; McNeilly, T.N.; Nisbet, A.J. A recombinant subunit vaccine for the control of ovine psoroptic mange (sheep scab). Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.L.; Colditz, I.G.; Andrew, M.; Gill, H.S.; Altmann, K.G. Age-dependent immune response in Merino sheep. Res. Vet. Sci. 1994, 57, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Hernandez, T.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Hernandez, J.N.; Machin, C.; Paz-Sanchez, Y.; Hayward, A.D.; Wright, H.W.; Price, D.R.G.; Matthews, J.B.; McNeilly, T.N.; et al. Differences in the protection elicited by a recombinant Teladorsagia circumcincta vaccine in weaned lambs of two Canarian sheep breeds. Vet. Parasitol. 2022, 306, 109722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machin, C.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Hernandez, J.N.; Perez-Hernandez, T.; Hayward, A.D.; Wright, H.W.; Price, D.R.G.; Matthews, J.B.; McNeilly, T.N.; Nisbet, A.J.; et al. Cellular and humoral immune responses associated with protection in sheep vaccinated against Teladorsagia circumcincta. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Těšický, M.; Vinkler, M. Trans-Species Polymorphism in Immune Genes: General Pattern or MHC-Restricted Phenomenon? J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 838035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Feilzer, K.; Caldwell, H.D.; Morrison, R.P. Chlamydia trachomatis genital tract infection of antibody-deficient gene knockout mice. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.; Ananaba, G.A.; Bolier, J.; Bowers, S.; Belay, T.; Eko, F.O.; Igietseme, J.U. Fc receptor regulation of protective immunity against Chlamydia trachomatis. Immunology 2002, 105, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, M.S.; Wattegedera, S.; Meridiani, I.; Entrican, G. Protective adaptive immunity to Chlamydophila abortus infection and control of ovine enzootic abortion (OEA). Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, S.; Sammin, D.J.; Bassett, H.F.; Reid, C.R.; Gutierrez, J.; Marques, P.X.; Nally, J.E.; O’Donovan, J.; Williams, E.J.; Proctor, A.; et al. Interferon-gamma expression in trophoblast cells in pregnant ewes challenged with Chlamydophila abortus. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 90, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.P.; Jones, G.E.; MacLean, M.; Livingstone, M.; Entrican, G. Recombinant ovine interferon gamma inhibits the multiplication of Chlamydia psittaci in ovine cells. J. Comp. Pathol. 1995, 112, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattegedera, S.R.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Pang, Y.; Frew, D.; McNeilly, T.N.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; McInnes, C.J.; Hope, J.C.; Glass, E.J.; Entrican, G. Enhancing the toolbox to study IL-17A in cattle and sheep. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wu, L.; Li, X. IL-17 family: Cytokines, receptors and signaling. Cytokine 2013, 64, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.W.; Rosenkrands, I.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Cheeseman, H.M.; Kristiansen, M.P.; Dietrich, J.; Shattock, R.J.; Follmann, F. Immune signature of Chlamydia vaccine CTH522/CAF(R)01 translates from mouse-to-human and induces durable protection in mice. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Cheng, J.; Gao, X.; Joyee, A.G.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L.; Yao, Z.; Yang, X. IL-17/Th17 promotes type 1 T cell immunity against pulmonary intracellular bacterial infection through modulating dendritic cell function. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5886–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, M.; Waugh, C.; Beagley, K.W.; Timms, P.; Polkinghorne, A. Interleukin 17A is an immune marker for chlamydial disease severity and pathogenesis in the koala (Phascolarctos cinereus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizarraga, D.; Timms, P.; Quigley, B.L.; Hanger, J.; Carver, S. Capturing Complex Vaccine-Immune-Disease Relationships for Free-Ranging Koalas: Higher Chlamydial Loads Are Associated with Less IL17 Expression and More Chlamydial Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 530686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Zeng, H.; Li, Z.; Lei, L.; Yeh, I.T.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, G. Protective immunity against mouse upper genital tract pathology correlates with high IFNgamma but low IL-17 T cell and anti-secretion protein antibody responses induced by replicating chlamydial organisms in the airway. Vaccine 2012, 30, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group 1 | Ewes | Average Length of Gestation | Number of Lambs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Dose/ Adjuvant) | No. Pregnant | No. Lambed (%) | No. Aborted (%) | Lambed | Aborted | Viable | Dead |
| 1 (20/70VG) | 37 | 36 (97.3) | 1 (2.7) | 146.5 | 135.0 | 60 | 5 2 |
| 2 (2.5/70VG) | 31 | 30 (96.8) | 1 (3.2) | 146.1 | 140.0 | 45 | 2 3 |
| 3 (2.5/61VG) | 37 | 34 (91.9) | 3 (8.1) | 146.1 | 136.0 | 58 | 5 |
| 4 (2.5/QuilA) | 38 | 29 (76.3) | 9 (23.7) | 146.0 | 132.7 | 47 | 13 |
| 5 | 38 | 24 (63.2) | 14 (36.8) | 144.7 | 134.7 | 41 | 21 |
| 6 | 7 | 7 (100) | 0 (0) | 146.9 | - | 14 | 0 |
| Group 1 (Dose/ Adjuvant) | Pregnancy Outcome | No. Ewes | Lesions 2 | Smears 3 | Swab qPCR 4 | Swab qPCR Load 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (20/70VG) | Lambed | 36 7 | 1+, 34 | 1+, 34− | 14+, 22− | 107 (1.33) |
| Aborted | 1 | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | n/a 6 | |
| 2 (2.5/70VG) | Lambed | 30 | 4+, 26− | 4+, 26− | 20+, 10− | 240 (1.63) |
| Aborted | 1 | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | n/a 6 | |
| 3 (2.5/61VG) | Lambed | 34 | 0+, 34− | 4+, 30− | 16+, 18− | 196 (1.51) |
| Aborted | 3 | 3+ | 3+ | 3+ | 3,211,854 (2.48) | |
| 4 (2.5/QuilA) | Lambed | 29 7 | 15+, 13− | 17+, 11− | 27+, 2− | 41,402 (1.99) |
| Aborted | 9 7 | 8+, 0− | 8+, 0− | 9+, 0− | 1,070,840 (1.84) | |
| 5 | Lambed | 24 7 | 14+, 9− | 16+, 7− | 23+, 1− | 58,283 (2.15) |
| Aborted | 14 | 13+, 1− | 13+, 1− | 14+, 0− | 2,848,149 (1.32) | |
| 6 | Lambed | 7 | 7− | 7− | 7− | 13 (1.87) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Livingstone, M.; Aitchison, K.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; Caspe, S.G.; Underwood, C.; Hill, H.; Cunnea, C.; Stronach, K.; Chianini, F.; Entrican, G.; et al. Effects of Different Adjuvants on the Protective Efficacy of a Subcellular Vaccine Against Chlamydia abortus Infection in Sheep. Vaccines 2025, 13, 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060609
Livingstone M, Aitchison K, Palarea-Albaladejo J, Caspe SG, Underwood C, Hill H, Cunnea C, Stronach K, Chianini F, Entrican G, et al. Effects of Different Adjuvants on the Protective Efficacy of a Subcellular Vaccine Against Chlamydia abortus Infection in Sheep. Vaccines. 2025; 13(6):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060609
Chicago/Turabian StyleLivingstone, Morag, Kevin Aitchison, Javier Palarea-Albaladejo, Sergio Gastón Caspe, Clare Underwood, Holly Hill, Cameron Cunnea, Kelly Stronach, Francesca Chianini, Gary Entrican, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Different Adjuvants on the Protective Efficacy of a Subcellular Vaccine Against Chlamydia abortus Infection in Sheep" Vaccines 13, no. 6: 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060609
APA StyleLivingstone, M., Aitchison, K., Palarea-Albaladejo, J., Caspe, S. G., Underwood, C., Hill, H., Cunnea, C., Stronach, K., Chianini, F., Entrican, G., Wattegedera, S. R., & Longbottom, D. (2025). Effects of Different Adjuvants on the Protective Efficacy of a Subcellular Vaccine Against Chlamydia abortus Infection in Sheep. Vaccines, 13(6), 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060609








