In the original publication, there was a mistake in Figure 4C as published [1]. The corrected Figure 4 appears below. The authors apologize for any inconvenience caused and state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
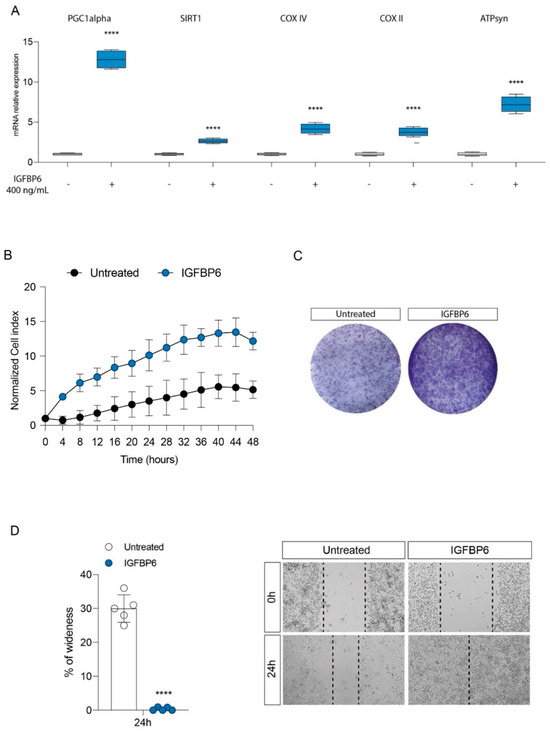
Figure 4.
IGFBP6 modulates mitochondrial metabolism and promotes breast cancer cell proliferation. Evaluation of relative mRNA expression levels of PGC1 alpha, SIRT1, COX IV, COX II and ATPsyn (A), following 24 h of IGFBP6 (400 ng/mL) treatment. The calculated value of 2−ΔΔCt in untreated controls is 1. Effect of IGFBP6 exposure (800 ng/mL) on cell proliferation (B), colony formation capacity (C) and wound healing (D). Data are expressed as mean ± SD of at least four independent experiments. **** p < 0.0001.
Reference
- Longhitano, L.; Forte, S.; Orlando, L.; Grasso, S.; Barbato, A.; Vicario, N.; Parenti, R.; Fontana, P.; Amorini, A.M.; Lazzarino, G.; et al. The Crosstalk between GPR81/IGFBP6 Promotes Breast Cancer Progression by Modulating Lactate Metabolism and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).