In Silico Methodologies to Improve Antioxidants’ Characterization from Marine Organisms
Abstract
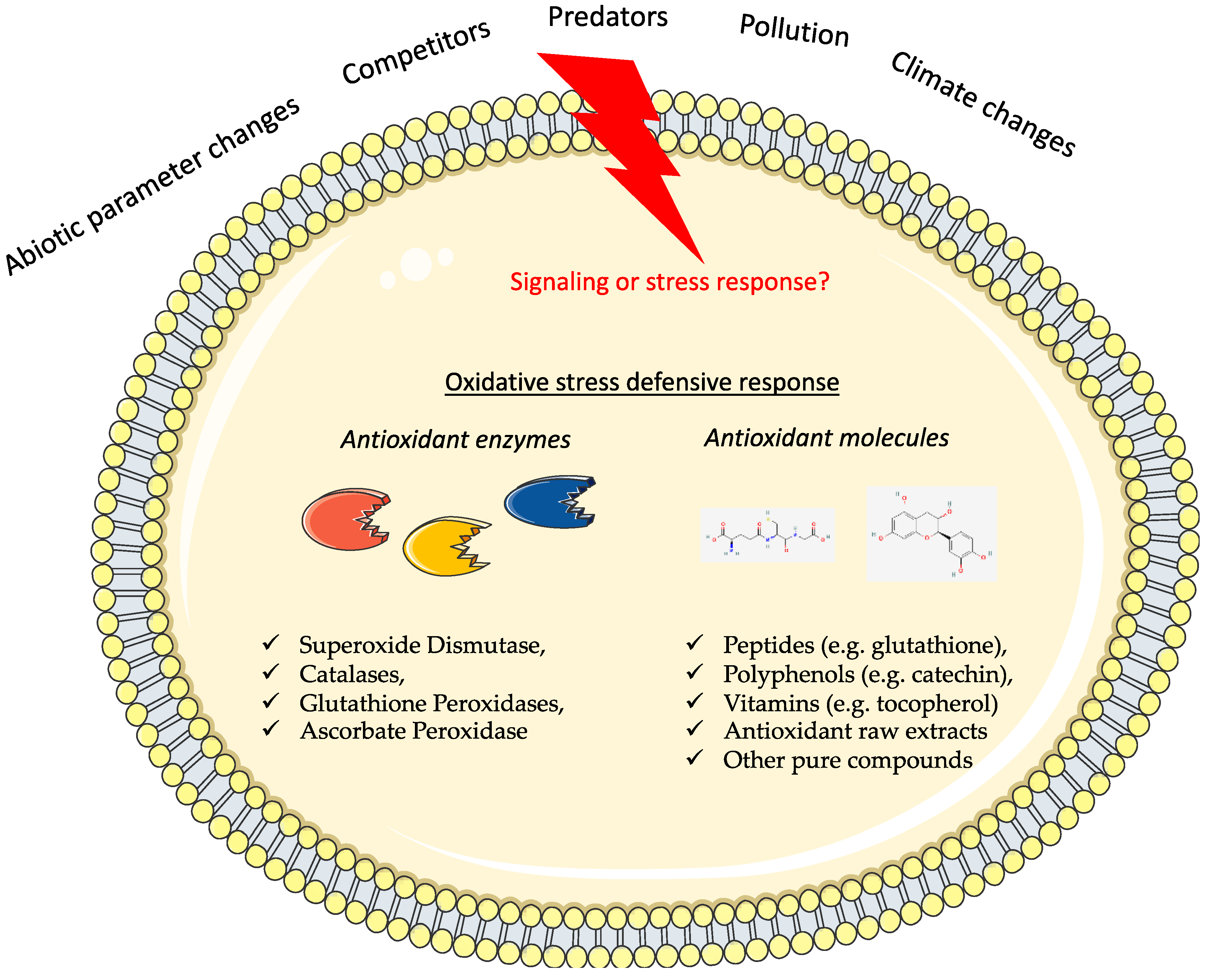
1. Introduction
What Is Already Available on the Market?
2. Overview of Tools for In Silico Prediction of Bioactive Peptides
2.1. Docking Prediction Tools
2.2. Bioactive Compound Prediction Tools
2.3. Protein Structure Prediction Tools
2.4. Pharmacophore Modeling Tools
3. In Silico Analysis and Validation to Discover Antioxidant Properties of Marine Origins
3.1. Molecular Docking Prediction and Validation
3.2. Bioactive Peptides’ Prediction and Validation
3.3. Identification of Marine Protein with Antioxidant Activity and Validation
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harizani, M.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V. The Laurencia Paradox: An Endless Source of Chemodiversity. In Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products 102; Kinghorn, A.D., Falk, H., Gibbons, S., Kobayashi, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 102, pp. 91–252. ISBN 978-3-319-33170-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lauritano, C.; Rizzo, C.; Giudice, A.L.; Saggiomo, M. Physiological and Molecular Responses to Main Environmental Stressors of Microalgae and Bacteria in Polar Marine Environments. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinnan, R.; Steinke, M.; Mcgenity, T.; Loreto, F. Plant Volatiles in Extreme Terrestrial and Marine Environments: Plant Volatiles in Extreme Environments. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 1776–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, C.; Ruocco, M.; Dattolo, E.; Buia, M.C.; Silva, J.; Santos, R.; Olivé, I.; Costa, M.M.; Procaccini, G. Response of key stress-related genes of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica in the vicinity of submarine volcanic vents. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 4185–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivé, I.; Silva, J.; Lauritano, C.; Costa, M.M.; Ruocco, M.; Procaccini, G.; Santos, R. Linking gene expression to productivity to unravel long- and short-term responses of seagrasses exposed to CO2 in volcanic vents. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanganyado, E.; Chingono, K.E.; Gwenzi, W.; Chaukura, N.; Liu, W. Organic pollutants in deep sea: Occurrence, fate, and ecological implications. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, R.K.; Heine, Z.; Milfont, T.L. Public understanding of climate change-related sea-level rise. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, e0254348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servili, A.; Canario, A.; Mouchel, O.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A. Climate change impacts on fish reproduction are mediated at multiple levels of the brain-pituitary-gonad axis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 291, 113439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Llodra, E.; Tyler, P.A.; Baker, M.C.; Bergstad, O.A.; Clark, M.R.; Escobar, E.; Levin, L.A.; Menot, L.; Rowden, A.A.; Smith, C.R.; et al. Man and the Last Great Wilderness: Human Impact on the Deep Sea. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C. Marine Natural Products in Medicinal Chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Costantini, M.; Sansone, C.; Lauritano, C.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A. Marine microorganisms as a promising and sustainable source of bioactive molecules. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, S.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Chemical Ecology of Marine Microbial Defense. J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 1971–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.J.; Freeman, C.J.; Agarwal, V. Chemical Ecology of Marine Sponges: New Opportunities through “-Omics”. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2019, 59, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Caldwell, G.S.; Casotti, R.; Cembella, A.D.; Engström-Öst, J.; Halsband, C.; Sonnenschein, E.; Legrand, C.; Llewellyn, C.A.; et al. The Relevance of Marine Chemical Ecology to Plankton and Ecosystem Function: An Emerging Field. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1625–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, M.P. OXIDATIVE STRESS IN MARINE ENVIRONMENTS: Biochemistry and Physiological Ecology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, C.; Ianora, A. Chemical Defense in Marine Organisms. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, N. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Hypertension–A Current Review. CHYR 2015, 11, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.D.; Huang, B.-W.; Tsuji, Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, M.A.; Loscos, J.; Dietz, K.-J.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M.; Becana, M. Function of antioxidant enzymes and metabolites during maturation of pea fruits. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, T.; Georgieva, N.; Staneva, A.; Gospodinova, D. Recent Progress in Antioxidant Active Substances from Marine Biota. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS Function in Redox Signaling and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, C.; Procaccini, G.; Ianora, A. Gene expression patterns and stress response in marine copepods. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 76, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizdaroglu, M.; Jaruga, P. Mechanisms of free radical-induced damage to DNA. Free. Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 382–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, N.A.; Sharma, P.; Gill, S.S.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Khan, E.A.; Kachhap, K.; Mohamed, A.A.; Thangavel, P.; Devi, G.D.; Vasudhevan, P.; et al. Catalase and ascorbate peroxidase—representative H2O2-detoxifying heme enzymes in plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 19002–19029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abele-Oeschger, D. A comparative study of superoxide dismutase activity in marine benthic invertebrates with respect to environmental sulphide exposure. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 197, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Cho, H.; Lee, Y.-M. Modulation of glutathione S-transferase and superoxide dismutase in response to heavy metals in brackish water flea Diaphanosoma celebensis. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2020, 12, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, X.X.; Zhou, B. Description of a Zostera marina catalase gene involved in responses to temperature stress. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atli, G.; Alptekin; Tükel, S.; Canli, M. Response of catalase activity to Ag+, Cd2+, Cr6+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ in five tissues of freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 143, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; Carotenuto, Y.; Vitiello, V.; Buttino, I.; Romano, G.; Hwang, J.-S.; Ianora, A. Effects of the oxylipin-producing diatom Skeletonema marinoi on gene expression levels of the calanoid copepod Calanus sinicus. Mar. Genom. 2015, 24, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaglioli, C.; Lauritano, C.; Buia, M.C.; Balestri, E.; Capocchi, A.; Fontanini, D.; Pardi, G.; Tamburello, L.; Procaccini, G.; Bulleri, F. Nutrient Loading Fosters Seagrass Productivity Under Ocean Acidification. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, M.; Son, K.-T.; Jeong, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Antioxidant Activity of Marine Algal Polyphenolic Compounds: A Mechanistic Approach. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
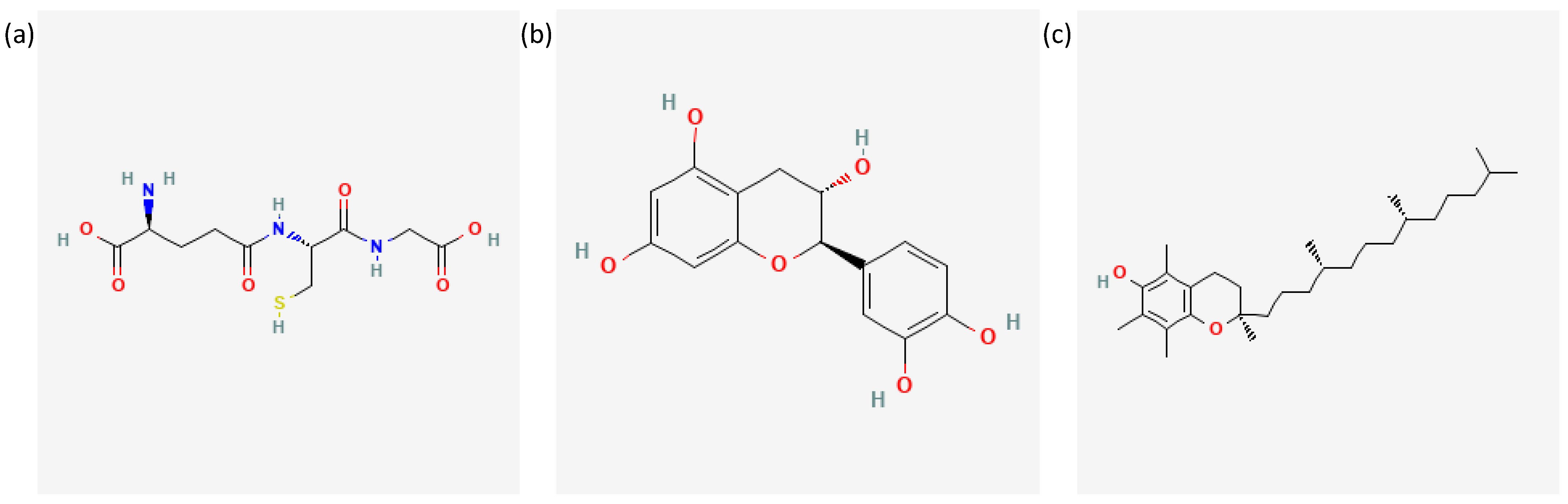
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 124886, Glutathione. 2023. Available online: Https://Pubchem.Ncbi.Nlm.Nih.Gov/Compound/124886#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 9064, Cianidanol. 2023. Available online: Https://Pubchem.Ncbi.Nlm.Nih.Gov/Compound/9064#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 14985, Vitamin E. 2023. Available online: Https://Pubchem.Ncbi.Nlm.Nih.Gov/Compound/14985#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- El-Shafei, R.; Hegazy, H.; Acharya, B. A Review of Antiviral and Antioxidant Activity of Bioactive Metabolite of Macroalgae within an Optimized Extraction Method. Energies 2021, 14, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Abert-Vian, M.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Strube, J.; Uhlenbrock, L.; Gunjevic, V.; Cravotto, G. Green extraction of natural products. Origins, current status, and future challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.; Santos, R.A.; Iglesias, P.; Couto, A.; Serra, C.R.; Gouvinhas, I.; Barros, A.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Díaz-Rosales, P. Effect of extraction method and solvent system on the phenolic content and antioxidant activity of selected macro- and microalgae extracts. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Glenn, K.C.; Gnanasambandam, R.; Johnson, M.G. Natural Antioxidant Extract from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenumgraecum) for Ground Beef Patties. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.-J.; Jung, W.-K.; Nam, K.-S.; Shahidi, F.; Kim, S.-K. Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptides from protein hydrolysate of lecithin-free egg yolk. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K. Marine cosmeceuticals. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2014, 13, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunassee, S.N.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Cytotoxic and antioxidant marine prenylated quinones and hydroquinones. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balboa, E.M.; Conde, E.; Moure, A.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. In vitro antioxidant properties of crude extracts and compounds from brown algae. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1764–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomponi, S.A. The bioprocess–technological potential of the sea. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 70, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Wijesekara, I. Development and biological activities of marine-derived bioactive peptides: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Y. Effect of marine collagen peptides on long bone development in growing rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Mendis, E. Bioactive compounds from marine processing byproducts – A review. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatschek, D.; Schatton, W.; Kellermann, J.; Müller, W.E.G.; Kreuter, J. Marine sponge collagen: Isolation, characterization and effects on the skin parameters surface-pH, moisture and sebum. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 53, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Oliviero, M.; Vitale, G.A.; Lauritano, C.; D’Ambra, I.; Iannace, S.; De Pascale, D. Marine Collagen from Alternative and Sustainable Sources: Extraction, Processing and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Esposito, F.P.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; de Pascale, D. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karawita, R.; Senevirathne, M.; Athukorala, Y.; Affan, A.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, J.-B.; Jeon, Y.-J. Protective Effect of Enzymatic Extracts from Microalgae Against DNA Damage Induced by H2O2. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, X.; Han, L.; Lou, Q. Fatty acids of some algae from the Bohai Sea. Phytochemistry 2002, 59, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.V.; Walsh, N.A. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of extracts from a variety of edible seaweeds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, C.; Galasso, C.; Orefice, I.; Nuzzo, G.; Luongo, E.; Cutignano, A.; Romano, G.; Brunet, C.; Fontana, A.; Esposito, F.; et al. The green microalga Tetraselmis suecica reduces oxidative stress and induces repairing mechanisms in human cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henríquez, V.; Escobar, C.; Galarza, J.; Gimpel, J. Carotenoids in Microalgae. In Carotenoids in Nature; Stange, C., Ed.; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 79, pp. 219–237. ISBN 978-3-319-39124-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yeum, K.-J.; Russell, R.M. CAROTENOID BIOAVAILABILITY AND BIOCONVERSION. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziccarelli, V.E.; Basu, T.K. Anin VivoStudy of the Antioxidant Potentials of a Plant Food Concentrate. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003, 22, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmig-Adams, B.; Adams, W.W. Antioxidants in Photosynthesis and Human Nutrition. Science 2002, 298, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoveská, L.; Ross, M.E.; Stanley, M.S.; Pradelles, R.; Wasiolek, V.; Sassi, J.-F. Microalgal Carotenoids: A Review of Production, Current Markets, Regulations, and Future Direction. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havas, F.; Krispin, S.; Cohen, M.; Loing, E.; Farge, M.; Suere, T.; Attia-Vigneau, J. A Dunaliella salina Extract Counteracts Skin Aging under Intense Solar Irradiation Thanks to Its Antiglycation and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Gostner, J.; Fuchs, J.E.; Chaita, E.; Aligiannis, N.; Skaltsounis, L.; Ganzera, M. Inhibition of Collagenase by Mycosporine-like Amino Acids from Marine Sources. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrapusta, E.; Kaminski, A.; Duchnik, K.; Bober, B.; Adamski, M.; Bialczyk, J. Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids: Potential Health and Beauty Ingredients. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition; Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; et al. Safety of Schizochytrium sp. oil as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283(a). EFSA J. 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocanegra, A.; Bastida, S.; Benedi, J.; Ródenas, S.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J. Characteristics and Nutritional and Cardiovascular-Health Properties of Seaweeds. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 236–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolaore, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Duran, E.; Isambert, A. Commercial applications of microalgae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition; Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; et al. Safety of oil from Schizochytrium sp. (strain ATCC 20889) for use in infant and follow-on formula as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2022, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohinejad, S.; Koubaa, M.; Barba, F.J.; Saljoughian, S.; Amid, M.; Greiner, R. Application of seaweeds to develop new food products with enhanced shelf-life, quality and health-related beneficial properties. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 1066–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Ishimaru, K.; Kawaguchi, S.; Yoshikawa, H.; Hama, Y. Antioxidant activities of phlorotannins isolated from Japanese Laminariaceae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleria, H.A.R.; Osborne, S.; Masci, P.; Gobe, G. Marine-Based Nutraceuticals: An Innovative Trend in the Food and Supplement Industries. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6336–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arct, J.; Pytkowska, K. Flavonoids as components of biologically active cosmeceuticals. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimat, V.; Elabed, N.; Kulawik, P.; Ceylan, Z.; Jamroz, E.; Yazgan, H.; Čagalj, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Özogul, F. Recent Advances in Marine-Based Nutraceuticals and Their Health Benefits. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anraku, M.; Fujii, T.; Kondo, Y.; Kojima, E.; Hata, T.; Tabuchi, N.; Tsuchiya, D.; Goromaru, T.; Tsutsumi, H.; Kadowaki, D.; et al. Antioxidant properties of high molecular weight dietary chitosan in vitro and in vivo. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.; Li, Y.; Li, G. Effect of concentration and temperature on the rheological behavior of collagen solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Gobinet, C.; Feru, J.; -Pasco, S.B.; Manfait, M.; Piot, O. Characterization of Type I and IV Collagens by Raman Microspectroscopy: Identification of Spectral Markers of the Dermo-Epidermal Junction. Spectrosc. Int. J. 2012, 27, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.; Turnay, J.; Fernández-Díaz, M.D.; Ulmo, N.; Lizarbe, M.; Montero, P. Structural and physical properties of gelatin extracted from different marine species: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.; Wolmarans, M.; Park, G. The role of albumin in critical illness. Br. J. Anaesth. 2000, 85, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, I.; Kim, S.-K. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors from Marine Resources: Prospects in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mos, L.; Jack, J.; Cullon, D.; Montour, L.; Alleyne, C.; Ross, P.S. The Importance of Marine Foods to a Near-Urban First Nation Community in Coastal British Columbia, Canada: Toward a Risk-Benefit Assessment. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2004, 67, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.-P.; Yuan, J.; Sun, L.; She, Z.-G.; Wu, J.-H.; Lan, X.-J.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-P. Statistical Research on Marine Natural Products Based on Data Obtained between 1985 and 2008. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turon, X.; Becerro, M.; Agell, G. Siliceous spicules and skeleton frameworks in sponges: Origin, diversity, ultrastructural patterns, and biological functions. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 62, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.J.; Desbois, A.P.; Dyrynda, E.A. Conventional and Unconventional Antimicrobials from Fish, Marine Invertebrates and Micro-algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1213–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibilla, S.; Godfrey, M.; Brewer, S.; Budh-Raja, A.; Genovese, L. An Overview of the Beneficial Effects of Hydrolysed Collagen as a Nutraceutical on Skin Properties: Scientific Background and Clinical Studies. Open Nutraceuticals J. 2015, 8, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijtsma, L.; De Swaaf, M.E. Biotechnological production and applications of the ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Zacharias, M. In Silico Prediction of Binding Sites on Proteins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, P. Gliding to success. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Seukep, A.; Guo, M. Recent Advances in Molecular Docking for the Research and Discovery of Potential Marine Drugs. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, T.J.; Makino, S.; Skillman, A.G.; Kuntz, I.D. DOCK 4.0: Search strategies for automated molecular docking of flexible molecule databases. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2001, 15, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, D.B.; Decornez, H.; Furr, J.R.; Bajorath, J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, J.K.; Law, S.M.; Brooks, C.L. Flexible CDOCKER: Development and application of a pseudo-explicit structure-based docking method within CHARMM: Adding Receptor Flexibility Improves Protein-Ligand Docking Within CDOCKER. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 37, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrusier, N.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. FireDock: Fast interaction refinement in molecular docking. Proteins 2007, 69, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Inbar, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. PatchDock and SymmDock: Servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W363–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Geng, C.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, T.; Tang, J.; Chu, Y.; Zhao, K. Dockey: A modern integrated tool for large-scale molecular docking and virtual screening. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, bbad047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.S.; Karthe, P. Improved docking of peptides and small molecules in iMOLSDOCK. J. Mol. Model. 2022, 29, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M.; Sieniawski, K.; Starowicz, P. BIOPEP database of sensory peptides and amino acids. Food Res. Int. 2016, 85, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM Database of Bioactive Peptides: Current Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senadheera, T.R.L.; Hossain, A.; Dave, D.; Shahidi, F. In Silico Analysis of Bioactive Peptides Produced from Underutilized Sea Cucumber By-Products—A Bioinformatics Approach. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, I.; Naneva, L.; Doytchinova, I.; Bangov, I. AllergenFP: Allergenicity prediction by descriptor fingerprints. Bioinformatics 2013, 30, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Open Source Drug Discovery Consortium; Raghava, G.P.S. In Silico Approach for Predicting Toxicity of Peptides and Proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, F.; Arnold, K.; Künzli, M.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL Repository and associated resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D387–D392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, A.; Patiyal, S.; Lathwal, A.; Arora, C.; Kaur, D.; Dhall, A.; Mishra, G.; Kaur, H.; Sharma, N.; Jain, S.; et al. Pfeature: A Tool for Computing Wide Range of Protein Features and Building Prediction Models. J. Comput. Biol. 2023, 30, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Rao, S.N. PHASE: A Novel Approach to Pharmacophore Modeling and 3D Database Searching. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 67, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2022.02 Chemical Computing Group ULC, 1010 Sherbooke St. West, Suite #910, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3A 2R7, 2023.
- Wolber, G.; Langer, T. LigandScout: 3-D Pharmacophores Derived from Protein-Bound Ligands and Their Use as Virtual Screening Filters. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, R.; Morris, G.M.; Olson, A.J.; Goodsell, D.S. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manak, M.; Jirkovsky, L.; Kolingerova, I. Interactive Analysis of Connolly Surfaces for Various Probes. Comput. Graph. Forum 2017, 36, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto, A. Bioactive Peptides from Food Proteins. In Handbook of Food Products Manufacturing; Hui, Y.H., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–37. ISBN 978-0-470-11355-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, D.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Agyei, D. Antioxidant peptides encrypted in flaxseed proteome: An in silico assessment. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Holton, T.A.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. PeptideLocator: Prediction of bioactive peptides in protein sequences. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the Improved Discovery and Design of Functional Peptides: Common Features of Diverse Classes Permit Generalized Prediction of Bioactivity. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P.S. Peptide Toxicity Prediction. In Computational Peptidology; Zhou, P., Huang, J., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1268, pp. 143–157. ISBN 978-1-4939-2284-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bonvin, A.M. Flexible protein–protein docking. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2006, 16, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, D.; Biancaniello, C.; Argenio, M.A.; Facchiano, A. Drug Design by Pharmacophore and Virtual Screening Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, T.; Wolber, G. Pharmacophore definition and 3D searches. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, I.H.; Bandaranayake, U.; Keerthirathna, L.R.; Manawadu, C.; Silva, R.M.; Mohamed, B.; Rizwan, A.; Peiris, D.C. Integration of in vitro and in-silico analysis of Caulerpa racemosa against antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhaseelan, H.; Dinakaran, V.T.; Sakthivel, B.; Somasundaram, M.; Thanamegam, K.; Devendiran, V.; Dahms, H.-U.; Rathinam, A.J. Bioactive Efficacy of Novel Carboxylic Acid from Halophilic Pseudomonas aeruginosa against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aniello, E.; Iannotti, F.A.; Falkenberg, L.G.; Martella, A.; Gentile, A.; De Maio, F.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Gavagnin, M.; Waxman, J.S.; Di Marzo, V.; et al. In Silico Identification and Experimental Validation of (−)-Muqubilin A, a Marine Norterpene Peroxide, as PPARα/γ-RXRα Agonist and RARα Positive Allosteric Modulator. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, N. A Comprehensive Survey of Prospective Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Early Drug Discovery in the Past Fifteen Years. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Mondo, A.; Vinaccia, A.; Pistelli, L.; Brunet, C.; Sansone, C. On the human health benefits of microalgal phytohormones: An explorative in silico analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, G.-F.; Jiang, W.; Ye, Y.-N.; Wu, F.-X.; Zhu, X.-L.; Guo, F.-B.; Yang, G.-F. ACFIS: A web server for fragment-based drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W550–W556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Liu, Q.; Bao, H.; Wang, X.; Miao, S. Effects of different freshness on the quality of cooked tuna steak. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-S. Impact of processing on stability of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides obtained from tuna cooking juice. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Bao, W.; Wan, H.; Lu, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Cheong, L.; Su, X. In silico analysis and in vivo tests of the tuna dark muscle hydrolysate anti-oxidation effect. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14109–14119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Li, H. Interaction of α-cyperone with human serum albumin: Determination of the binding site by using Discovery Studio and via spectroscopic methods. J. Lumin 2015, 164, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Cho, A.E. Using reverse docking to identify potential targets for ginsenosides. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, C.; Jiang, X.; Trevino, I.; Bender, C.F.; Ferguson, D.A.; Probst, B.; Swinger, K.K.; Stoll, V.S.; Thomas, P.J.; Dulubova, I.; et al. Characterization of novel small-molecule NRF2 activators: Structural and biochemical validation of stereospecific KEAP1 binding. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 2537–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kgk, D.; Kumari, S.; G, S.; Malla, R.R. Marine natural compound cyclo(L-leucyl-L-prolyl) peptide inhibits migration of triple negative breast cancer cells by disrupting interaction of CD151 and EGFR signaling. Chem. Interact. 2020, 315, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.-K.; Kim, I.; Warren, B.; Kim, J.; Jung, K.; Ku, B. Antiviral Activity of Two Marine Carotenoids against SARS-CoV-2 Virus Entry In Silico and In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansone, C.; Pistelli, L.; Del Mondo, A.; Calabrone, L.; Fontana, A.; Noonan, D.M.; Albini, A.; Brunet, C. The Microalgal Diatoxanthin Inflects the Cytokine Storm in SARS-CoV-2 Stimulated ACE2 Overexpressing Lung Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devita, L.; Lioe, H.N.; Nurilmala, M.; Suhartono, M.T. The Bioactivity Prediction of Peptides from Tuna Skin Collagen Using Integrated Method Combining In Vitro and In Silico. Foods 2021, 10, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, G.K.; Suresh, P. Physico-chemical characteristics and fibril-forming capacity of carp swim bladder collagens and exploration of their potential bioactive peptides by in silico approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvitigala, D.A.S.; Whang, I.; Lee, J. Molecular profiling and functional insights of rock bream ( Oplegnathus fasciatus ) thioredoxin reductase 3-like molecule: Investigation of its transcriptional modulation in response to live pathogen stress. Gene 2015, 570, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, N.; Godahewa, G.; Lee, J. Copper-zinc-superoxide dismutase (CuZnSOD), an antioxidant gene from seahorse ( Hippocampus abdominalis ); molecular cloning, sequence characterization, antioxidant activity and potential peroxidation function of its recombinant protein. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 57, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Gross, H.; Goeger, D.E.; Mooberry, S.L.; Gerwick, W.H. Aurilides B and C, Cancer Cell Toxins from a Papua New Guinea Collection of the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotolo, S.; Cervellera, C.; Russo, M.; Russo, G.L.; Facchiano, A. Virtual Screening of Natural Compounds as Potential PI3K-AKT1 Signaling Pathway Inhibitors and Experimental Validation. Molecules 2021, 26, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, P.C.D.; Skillman, A.G.; Nicholls, A. Comparison of Shape-Matching and Docking as Virtual Screening Tools. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciabola, S.; Torella, R.; Nagata, A.; Boehm, M. Critical Assessment of State-of-the-Art Ligand-Based Virtual Screening Methods. Mol. Inform. 2022, 41, 2200103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, W.P.; Wang, R. New Trends in Virtual Screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 4109–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyaningrum, D.; Oktafika, R.A.; Cecilia, D. Microalgae pigments as a promising immunomodulating food ingredient: In silico study. IOP Conf. Series Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 998, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tools | Information | Availability | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Docking | |||
| AutoDock4 | Grid-based flexible docking prediction | Free | [89] |
| AutoDock Vina | Grid-based flexible docking prediction using multithreading | Free | [90] |
| Flexible CDOCKER | Docking prediction exploring the conformational space simultaneously of ligands and protein configurations | Free only for academic, government and nonprofit labs | [91] |
| FireDock | Rescoring and refinement of docking solutions | Free | [92] |
| PatchDock | Predicts protein–protein and protein–small molecule docking | Free | [93] |
| Dockey | Analysis of non-covalent interactions between small molecules and proteins, performing cross-docking with multiple receptors and ligands | Free | [94] |
| iMOLSDOCK | Induced-fit docking algorithm, with improvement of the receptor flexibility | Free | [95] |
| Bioactivity | |||
| BIOPEP-UWM | Database of peptides, proteins, amino acids and allergens | Free | [96,97] |
| PepRank | Predicts bioactivity of a peptide | Free | [98] |
| AllergenFP | Predicts allergenicity of a peptide | Free | [99] |
| ToxinPred | Predicts toxicity of a peptide | Free | [100] |
| Protein structure | |||
| ExPASy | Database of resources from the Swiss Institute of Bionformatics (SIB) | Free | [101] |
| SWISS-MODEL Repository | Generates models based on homology modeling | Free | [102] |
| I-TASSER | Predicts 3D protein structures | Free | [103] |
| Pfeature | Predicts protein residue-level annotation, protein function and chemically modified peptides’ function | Free | [104] |
| AlphaFold | Deep learning algorithm that predicts protein structure, even if there is not a similar one known | Free | [105] |
| Pharmacophore | |||
| Phase | Pharmacophore modeling with tree-based partitioning algorithm | Free | [106] |
| MOE | Pharmacophore modeling, in which for the 3D pharmacophore database, a consensus query can be used from several aligned molecules | Commercial | [107] |
| LigandScout | Pharmacophore modeling, which also allows researchers to compare the common binding modes of pharmacophores and molecules | Commercial | [108] |
| Organism | Antioxidant Compound/Enzyme | In Silico Prediction Tool | Validation Assay | Possible Application Field | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alga Caulerpa racemosa | Crude polyphenolic extract (CPE), caulerpin | AutoDock | DPPH (2, 2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazylhydrate) radical photometric assay | Diabetic conditions, breast cancer | [119] |
| Bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Hexane ethyl acetate (HPAEtOAcE) fraction, 5-(1H-indol-3-yl)-4-pentyl-1,3-oxazole-2-carboxylic acid (Compound 1) | CDOCKER | DPPH (2, 2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazylhydrate) radical photometric assay | Drug against several harmful pathogens, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) | [120] |
| Bacterium Streptomyces mangrovisoli | Cyclo (L-Leucyl-L-Prolyl) peptide/CLP | PatchDock | Co-immunoprecipitation | Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) | [131] |
| Red Sea sponge Diacarnus erythraeanus | (−)-Muqubilin (Muq) | AutoDock Vina (version 1.1.2) | Luciferase assay to validate the agonistic effect | Neurological diseases | [121] |
| Tuna fish | KEFT, EEASA and RYDD peptides | CDOCKER | In vivo administration and evaluation of protein and transcript levels of antioxidant enzymes | Keap1/Nrf2/ARE antioxidant pathway regulation | [138] |
| Seaweeds and diatoms | Fucoxanthin (FX), siphonaxanthin (SX), diatoxanthin (Dt) | AutoDock Vina (version 1.1.2) | In vitro simulation of viral infection | Treatment and/or prevention of severe inflammatory syndrome | [132,133] |
| Tuna bigeye (Thunnus obesus) | Bioactive peptides | BIOPEP | DPPH (2, 2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazylhydrate) radical photometric assay | Food and health applications | [134] |
| Atlantic sea cucumber | Peptide sequence (GPPGPQWPLDF) | BIOPEP and PepRank | DPPH (2, 2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazylhydrate) radical photometric assay | Food industries | [135] |
| Rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus) | RbTrxR-3 | EMBOSS Needle and ClustalW; ExPASy PROSITE; SECISearch; ExPASy ProtParam tool | Thiol-reductase activity | Response to pathogen stress | [136] |
| Hippocampus abdominalis | HaCuZnSOD | ClustalW; ExPASy PROSITE; Motif Scan; I-TASSER; SWISS-MODEL | Xanthine/xanthine oxidase (xanthine/XOD) assay | Host antioxidant defense | [137] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lauritano, C.; Montuori, E.; De Falco, G.; Carrella, S. In Silico Methodologies to Improve Antioxidants’ Characterization from Marine Organisms. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030710
Lauritano C, Montuori E, De Falco G, Carrella S. In Silico Methodologies to Improve Antioxidants’ Characterization from Marine Organisms. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(3):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030710
Chicago/Turabian StyleLauritano, Chiara, Eleonora Montuori, Gabriele De Falco, and Sabrina Carrella. 2023. "In Silico Methodologies to Improve Antioxidants’ Characterization from Marine Organisms" Antioxidants 12, no. 3: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030710
APA StyleLauritano, C., Montuori, E., De Falco, G., & Carrella, S. (2023). In Silico Methodologies to Improve Antioxidants’ Characterization from Marine Organisms. Antioxidants, 12(3), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030710









