Abstract
The current study investigated the effects of the maternal Zn source in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on the growth performance, antioxidant status, Zn concentration, and immune function of the offspring. It also explored whether there is an interaction between maternal Zn and their offspring’s dietary Zn. One-day-old Lingnan Yellow-feathered broilers (n = 800) were completely randomized (n = 4) between two maternal dietary supplemental Zn sources [maternal Zn–Gly (oZn) vs. maternal ZnSO4 (iZn)] × two offspring dietary supplemental Zn doses [Zn-unsupplemented control diet (CON), the control diet + 80 mg of Zn/kg of diet as ZnSO4]. oZn increased progeny ADG and decreased offspring mortality across all periods, especially during the late periods (p < 0.05). The offspring diet supplemented with Zn significantly improved ADG and decreased offspring mortality over the whole period compared with the CON group (p < 0.05). There were significant interactions between the maternal Zn source and offspring dietary Zn with regards to progeny mortality during the late phase and across all phases as a whole (p < 0.05). Compared with the iZn group, the oZn treatment significantly increased progeny liver and serum Zn concentrations; antioxidant capacity in the liver, muscle, and serum; and the IgM concentration in serum; while also decreasing progeny serum IL-1 and TNF-α cytokine secretions (p < 0.05). Similar results were observed when the offspring diet was supplemented with Zn compared with the CON group; moreover, adding Zn to the offspring diet alleviated progeny stress by decreasing corticosterone levels in the serum when compared to the CON group (p < 0.05). In conclusion, maternal Zn–Gly supplementation increased progeny performance and decreased progeny mortality and stress by increasing progeny Zn concentration, antioxidant capacity, and immune function compared with the same Zn levels from ZnSO4. Simultaneously, Zn supplementation in the progeny’s diet is necessary for the growth of broilers.
1. Introduction
Zinc (Zn) is an essential mineral that is usually added to the diets of the breeder to obtain the best reproductive performance. It ensures the development of bones and feathers in birds, as well as fertility and scavenging of oxygen free radicals in animals [1,2]. Additionally, Zn is one of the most important active elements for transforming protein, carbohydrate, nucleic acid, and activating enzyme, which is essential for the proper operation of the immune system [3,4,5].
Maternal effects are one of the most important epigenetic inheritance phenomena, and can directly influence the offspring’s growth, development, nutrient metabolism, and physiological characteristics [6]. Previous studies reported that maternal stress not only influences the birth weight and growth of offspring, but also changes the metabolic parameters and hormone secretion of mammals [7]. Zhu et al. [8] indicated that maternal Zn supplementation, regardless of the source of Zn, can reduce the negative impact of maternal heat stress on the progeny’s growth performance, and maternal organic Zn supplementation can improve the meat quality of offspring. For poultry, hatching eggs are an important pathway for transgenerational nutritional regulation. Maternal dietary Zn supplementation increased the Zn content in egg yolk [9], alleviated progeny intestinal inflammation, and improved the skeletal muscle development of offspring [10,11]. Therefore, as one kind of important feed additive, Zn is widely used in poultry feed. Inorganic Zn (including sulfate, oxide salts, etc.,) is one of several important main forms of Zn supplementation in poultry diets. However, antagonism can occur between inorganic Zn and other inorganic trace minerals [12]. The lower bioavailability of inorganic Zn results in its excessive addition, which causes waste and even environmental pollution [13]; however, organic Zn has a higher bioavailability than inorganic Zn [14,15].
Glycine (Gly) chelate is composed of one to three Gly particles combined with Zn, which determines its strong stability and chemical and physical homogeneity. Therefore, Gly has a better stability constant for Zn, which may facilitate easier uptake by the Zn–Gly complex [16]. Our previous studies found that the optimal dosage for broiler breeders was 80 mg Zn/kg of Zn–Gly [17,18], however, little research has been done about maternal Zn in relation to their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation in broilers. We hypothesized that maternal organic Zn–Gly might have a better effect than inorganic zinc sulfate (ZnSO4) on their offspring’s growth performance, antioxidant status, immune function, etc., and expect to observe an interaction between maternal Zn and their offspring’s dietary Zn. Therefore, in this study, the main purpose was to explore the effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant status, Zn concentration, and immune function of offspring from female breeders subjected to 80 mg of Zn/kg of diet from ZnSO4 and Zn–Gly, respectively. We have also explored whether there is an interaction between maternal Zn and their offspring’s dietary Zn.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design, Birds, and Diets
This study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Zhejiang University. Experimental design and treatments for the maternal broiler breeder phase were discussed in detail in our previous study [18]. A completely randomized design was performed with two maternal dietary supplemental Zn sources [maternal Zn–Gly (oZn) vs. maternal ZnSO4 (iZn)] × two offspring dietary supplemental Zn doses [Zn-unsupplemented control diet (CON), the control diet + 80 mg of Zn/kg of diet from ZnSO4 (80 mg zinc/kg was derived from crystal standard zinc, provided by PANCOSMA, Switzerland). Firstly, a total of 200 39-week-old Lingnan Yellow broiler breeders were randomly divided into two groups—the oZn group and iZn group—with each group containing 5 replicates with 20 birds each. All broiler breeders from the two groups were fed a corn–soybean meal basal diet with 24 mg Zn/kg for four weeks pre-test to consume excess Zn in the body; in the formal feeding period of eight weeks, the iZn group and oZn group were supplemented with 80 mg Zn/kg from ZnSO4 and 80 mg Zn/kg from the Zn–Gly-based basal diet, respectively. All eggs from the last seven days were collected from two breeder groups (oZn group and iZn group) for offspring incubation. Then, 400 healthy offspring chicks from each group were selected and divided into two groups with two offspring dietary supplemental Zn doses (0 or 80 mg Zn/kg). Figure 1 shows the entirety of the experimental design. Table 1 displays the composition and nutrient content of the basal diet for the broiler breeders. The control group received the basal diet without Zn supplementation (negative control), and (iZn-iZn) and Zn–Gly (oZn-oZn) received a basal diet supplemented with 80 mg of Zn/kg of diet from ZnSO4 and Zn–Gly, respectively. Then, all hatched chicks were reared for the 60 day offspring broiler phase. Table 2 shows the composition and nutrient level of the basal diet for the offspring broiler. On days 21 and 60, three male broilers from each replicate were randomly selected and slaughtered. Serum samples from the blood were isolated by centrifuging at 3000× g for 10 min and stored at −80 °C until analysis. Liver and left breast muscle samples were immediately stored at −80 °C after slaughter for further analysis.
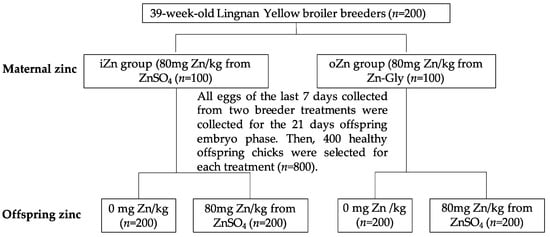
Figure 1.
Experimental design of broilers.

Table 1.
Composition and nutrient level of the basal diet for broiler breeders (%, unless otherwise stated).

Table 2.
Composition and nutrient level of the basal diet for offspring broiler (%, unless otherwise stated).
2.2. Measurement of Growth Performance and Sample Collection
On days 1, 21, and 60 of the experiment, the birds and their diet were weighed per the whole replicate. The variables of the growth performance (final body weight (BW)), average daily feed intake (ADFI), average daily gain (ADG), and feed:gain ratio (F:G) were measured.
2.3. Zn Concentration Determination
As described in our previous study [17], inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (Iris Intrepid; Thermo Elemental, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to determine the concentrations of Zn in serum, liver, and breast muscle after microwave wet digestion in nitric acid (MARS 5; CEM Corp., Matthews, NC, USA) and dilution with distilled water. Calibration of Zn content determination was performed using a series of mixtures containing Zn standard solutions of graded concentrations [19].
2.4. Antioxidant Status Analysis
After combining the liver and muscle of each replicating broiler into a separate sample, the sample was weighed and then homogenized into nine volumes of sodium chloride solution (0.86%) (4000 rpm, 4 °C, 15 min) with Ultra Turrax homogenizer (Tekmar Co., Cincinnati, OH, USA). The homogenates were then centrifuged at 3500 rpm at 4 °C for 15 min and the supernatant was collected for further analysis [18].
As demonstrated in our previous study, the total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) activities, copper zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu-Zn SOD) activities, total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations were evaluated using a commercial analytical kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). The results were standardized with the total protein for internal comparison. The concentrations of liver metallothionein (MT) was determined by the commercial ELISA kit purchased from Shanghai Elisa Technology Co., Ltd. All procedures were carried out according to the instructions of the assay kits [18].
2.5. Chemical and Cytokine Secretions Analyses
Immunoglobulins (IgA, IgG and IgM) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-2, and TNF-α) were determined using the commercial ELISA kit purchased from Shanghai Elisa Technology Co., Ltd. All procedures were carried out according to the instructions of the assay kits.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA using the general linear model procedure of SAS 9.2 (SAS Institute, 2010, Cary, NC, USA). This model combines the main effects of maternal dietary Zn, progeny dietary Zn, and their interaction. The treatment comparisons for significant differences were tested by the LSD method. Each replicate served as the experimental unit for all statistical analyses. Significant differences were set at p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
During days 1–60, oZn increased the progeny ADG and decreased the mortality (p < 0.05), but no significant differences were observed for the ADFI and F/G parameters. The offspring diet supplemented with Zn improved the ADG by 2.55% and significantly decreased mortality compared with the CON group (p < 0.05). Significant interactions between maternal Zn and offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation were observed in progeny mortality during the entire phase (Table 3).

Table 3.
Effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring dietary Zn supplementation on growth performance of day 1–60 in offspring broilers (mean ± S.E.).
3.2. Zn Concentrations
The effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on the serum, liver, and muscle Zn concentrations of offspring broilers are shown in Table 4. Maternal dietary Zn as Zn–Gly rather than ZnSO4 supplementation resulted in higher Zn concentrations in the liver of the offspring at 21 days of age and increased progeny Zn concentrations in serum, liver, and muscle at 60 days of age (p < 0.05). Additionally, the broiler offspring’s dietary 80 mg/kg of Zn supplementation increased the Zn concentrations in the serum, liver, and muscle during the entire phase compared to the CON group (p < 0.05). Significant interactions (p = 0.031) between maternal Zn and offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation were observed in the progeny’s muscle at 60 days of age.

Table 4.
Effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring dietary Zn supplementation on the Zn content in serum, liver, and muscle of offspring broilers (mean ± S.E.).
3.3. Antioxidant Status in Serum
The effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on the serum antioxidant status of offspring broilers are shown in Table 5. Maternal dietary oZn supplementation increased the activities of T-AOC (by 5.66%), T-SOD (by 8.58%), and CuZn-SOD (by 6.24) compared to iZn at 21 days of age, and similar results were also observed in the broiler’s offspring dietary 80 mg Zn/kg supplementation compared with the CON group (p < 0.05). At 60 days of age, T-AOC activity increased by 7.99% in the case of oZn compared to iZn; and the activity of T-AOC (by 21.49%) and CuZn-SOD (by 6.43%) significantly increased when the broiler’s offspring dietary 80 mg Zn/kg supplementation (p < 0.05) compared with the CON group. The MDA content decreased in offspring broilers at 21 and 60 days of age compared to maternal ZnSO4 (p < 0.05). Significant interactions between maternal Zn and offspring dietary Zn supplementation were observed in progeny MDA content at 21 days of age and activity of T-SOD at 60 days of age (p < 0.05).

Table 5.
Effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring dietary Zn supplementation on serum antioxidant indexes in offspring broilers (mean ± S.E.).
3.4. Antioxidant Status in Liver
The effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on the liver antioxidant status of offspring broilers are shown in Table 6. Maternal dietary Zn–Gly supplementation increased the T-SOD activity and MT content in offspring broilers at 21 and 60 days of age and CuZn-SOD activity in offspring broilers at 21 days of age compared with that of maternal ZnSO4 (p < 0.05), whereas maternal Zn supplementation did not affect their offspring regarding the activity of T-AOC in the liver of the progeny (p > 0.05). Additionally, compared with the CON group, offspring broilers dietary 80 mg/kg of Zn supplementation increased progeny T-AOC, T-SOD, and CuZn-SOD activities at 21 days of age, and decreased progeny MDA content and increased MT content at 21 and 60 days of age (p < 0.05). Significant interactions (p < 0.001) between maternal Zn and offspring dietary Zn supplementation were observed in the progeny’s MDA content at 21 days of age and the progeny’s T-AOC, T-SOD, and CuZn-SOD activities at 60 days of age (p < 0.05).

Table 6.
Effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring dietary Zn supplementation on liver antioxidant indexes in offspring broilers (mean ± S.E.).
3.5. Antioxidant Status in Muscle
The effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on the muscle antioxidant status of broiler offspring are shown in Table 7. Maternal dietary Zn as Zn–Gly rather than ZnSO4 supplementation increased T-AOC activity and decreased MDA content at both 21 and 60 days of age (p < 0.05). Furthermore, their offspring broiler’s dietary 80 mg/kg of Zn increased the activities of T-SOD and CuZn-SOD at 21 days of age, and increased the T-AOC activity and decreased MDA content at both 21 and 60 days of age (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, no significant interactions between maternal Zn and offspring dietary Zn supplementation were observed in the antioxidant status of the progeny’s muscle (p > 0.05).

Table 7.
Effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring dietary Zn supplementation on muscle antioxidant indexes in offspring broilers (mean ± S.E.).
3.6. Cytokine Secretion
The effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on the cytokine secretion of offspring broilers are shown in Table 8. Maternal dietary Zn as Zn–Gly rather than ZnSO4 supplementation had no significant effects on progeny IL-1, IL-2, and TNF-α concentrations at 21 days of age while significantly decreasing the IL-1 and TNF-α concentrations of progeny at 60 days of age (p < 0.05). Similar results were observed for offspring broilers dietary 80 mg/kg of Zn. No significant interactions between maternal Zn and dietary Zn supplementation were observed in progeny cytokine secretions at 21 days of age (p > 0.05), whereas significant interactions were observed in progeny IL-1 (p = 0.012) and TNF-α (p = 0.030) concentrations at 60 days of age.

Table 8.
Effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring dietary Zn supplementation on cytokine secretion in serum of offspring broilers (mean ± S.E.).
3.7. Immunoglobulin Content
The effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on the immunoglobulin content of offspring broilers are shown in Table 9. Maternal dietary Zn–Gly rather than ZnSO4 supplementation increased progeny IgM concentrations at both 21 and 60 days of age (p < 0.05). Additionally, offspring dietary supplementation of 80 mg/kg of Zn increased the IgA content of progeny at 21 days and the IgG and IgM concentrations of progeny at 60 days of age (p < 0.05); moreover, no significant interactions between maternal Zn and offspring dietary Zn supplementation were observed in progeny immunoglobulin content (p > 0.05).

Table 9.
Effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with their offspring dietary Zn supplementation on immune indexes in serum of offspring broilers (mean ± S.E.).
3.8. Stress Index
The effects of maternal Zn in combination with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation on the stress index of the broiler’s offspring are shown in Table 10. Maternal Zn–Gly rather than ZnSO4 supplementation had no significant effects on progeny CORT, HSP70, and CK content at 21 days of age; however, it significantly decreased the CORT content of progeny at 60 days of age. Additionally, their broiler’s offspring dietary supplementation of 80 mg/kg of Zn significantly decreased the CORT content at 21 days of age (p < 0.05), and Zn–Gly rather than ZnSO4 supplementation significantly increased the HSP70 content at 60 days of age (p < 0.05). Significant interactions between maternal Zn and offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation were observed in progeny CORT (p = 0.033) and HSP70 (p = 0.021) concentrations at 60 days of age.

Table 10.
Effects of maternal Zn in conjunction with offspring dietary Zn supplementation on stress indexes in serum of offspring broilers (mean ± S.E.).
4. Discussion
Maternal Zn, in combination with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation, had no significant effects on the progeny growth performance during the stage of days 1–21. Furthermore, supplementation of 80 mg Zn/kg from Zn–Gly increased progeny BW at 60 days as well as ADG during the stage of days 22–60, and had a lower mortality rate compared to the same Zn levels from ZnSO4, thereby indicating that maternal dietary organic Zn in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation improved the growth performance of progeny in the final period. Consistent with our findings, several studies reported that dietary organic Zn supplementation increased growth rate, feed intake, and feed efficiency in broiler chicks [20,21,22,23] however, reports showed that low Zn diets will lead to loss of appetite, feed intake, and weight gain [24,25], resulting in decreased hatchability and increased embryonic mortality [26,27] and even further depressed the growth performance of progeny [8]. It is implied that in the current study, maternal dietary Zn supplementation may be transferred to progeny broilers during the stage of embryonic development and showed in the progeny growth performance of the final period.
Dietary Zn supplementation in broiler breeders markedly enhanced the Zn concentrations of eggs [9,28]. In our previous studies, the Zn concentrations in muscle and eggs [17] increased with dietary organic Zn supplementation compared with inorganic Zn and even increased in the livers of developing embryos and one-day-old chicks [18] moreover, we found that maternal 80 mg Zn/kg from Zn–Gly increased the Zn concentration in progeny serum, liver, and muscle compared to the same Zn levels from ZnSO4. This may be because in broilers, dietary organic Zn supplementation had a higher absorption rate and lower excretion rate than inorganic Zn [29], thereby resulting in higher Zn concentrations. Interestingly, the broiler offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation increased Zn concentrations in their liver at 21 days of age and remained stable over time. On the contrary, it returned to initial values or was even lower in serum and muscle at 60 days of age. This may be because broilers were at different growth stages and had different nutritional requirements. The increased deposition of Zn in egg yolk leads to higher Zn availability, which facilitates the growth of chick embryos [30]. Consistent with the results in our present study, Kwiecień et al. [1] indicated that organic Zn addition enhanced the Zn concentrations in the liver of broilers compared to inorganic Zn supplementation, implying that the results of increased egg, progeny tissue, and serum Zn concentrations were from the increased maternal Zn.
Given the better antioxidant properties of Zn, therefore, dietary Zn status is closely related to the antioxidant system [31] it influences antioxidant status by a different mechanism: First, protecting proteins and enzymes against free radical attack or oxidation, and second, preventing free radical formation produced by other metals, such as iron and copper [32]. T-AOC, T-SOD, and MDA are marks of oxidative stress as they participate in the antioxidant defense systems that result in potential damages induced by oxidative stress [33]. Zn is an essential component of CuZn-SOD, and its potential antioxidant effects could be associated with its role in the mechanism of the structural integrity of CuZn-SOD [34]. Additionally, its presence in the Zn metallothionein protects organs and tissues against immune-mediated attacks by ROS [35].
Zn deficiency might cause an increase in the production of free radicals [36], resulting in decreased SOD activity and increased MDA content [37]. However, Zn supplementation enhanced the activities of CuZn-SOD and GSH-Px and decreased the MDA levels in broilers’ livers [38]. Our previous experiment showed that maternal Zn supplementation significantly reduced the content of MDA and enhanced the activity of T-SOD, CuZn-SOD, and T-AOC in the livers of both chick embryos and one-day-old chicks [18]. Further experiments showed that maternal Zn, in conjunction with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation, markedly reduced the MDA concentrations and enhanced the activity of T-AOC and CuZn-SOD in progeny serum, liver, and muscle, and enhanced MT concentrations in the liver of progeny. In addition, maternal organic Zn had better effects on the antioxidant defense of progeny serum and tissue than inorganic Zn. It is implied that maternal Zn, in combination with their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation, had better effects on antioxidant capacity; it reduces the oxidative stress of offspring broilers by increasing the activity of CuZn-SOD and inducing the production of MT, thereby improving the production performance of broilers.
Zn can interact with the immune systems’ components and is thought to be essential for immune response [39]. It binds to enzymes, proteins, and peptides with different binding affinities [40]. A previous study reported that the immune organs, including the thymus, spleen, and bursa of fabricius of three-week-old broilers, were significantly influenced by Zn–Gly levels in their diets [41]. Additionally, Zn supplementation is an adjunctive therapy for treating chronic and inflammatory diseases; modulating TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10; and modifying the gene expression of MT in white blood cells. This highlights the importance of Zn in gene transcription and cell metabolism [42,43]. It can also prevent Salmonella-induced liver injury by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine levels [44]. In the current study, the results indicated that maternal organic Zn and their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation significantly reduced the concentrations of IL-1 and TNF-α, suggesting that the protective effects of Zn on the broiler may be through downregulating the inflammation of the host; moreover, the severity of the inflammatory response is generally inversely proportional to the serum Zn concentration [45]. Hence, the additional possible mediator of Zn, which alleviates the host’s inflammatory response, is caused by the enhanced antioxidant defense and higher Zn concentration.
In the present study, maternal organic Zn and their offspring’s dietary Zn supplementation had significantly higher immunoglobulin concentrations and complements. Consistent with our present results, ample Zn supplementation improves the ability to produce antibodies [46,47]. Fraker et al. [48] showed that supplementing Zn as ZnSO4 to a diet deficient in Zn was effective for total serum IgG concentration, and diets supplemented with Zn as Zn–Gly had higher levels of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, and IgG) in the serum of broilers [41], moreover, Wellinghausen et al. [49] indicated that Zn status in Zn methionine and Zn sulfate affected the total non-specific IgM and IgG concentrations in seven-day-old broilers.
Stressors (such as heat stress and oxidative stress) can increase plasma corticosterone concentration in different tissues of poultry with a concomitant increase in creatine kinase levels [50]. In the present study, offspring dietary Zn supplementation significantly decreased the corticosterone levels, indicating that Zn supplementation can reduce oxidative stress during broiler production, as Zn supplementation increased broiler tissue Zn content—thereby improving its antioxidant status and reducing oxidative stress. However, we also found that Zn supplementation increased the levels of HSP70, which may be because HSP70 is the most important family of heat shock proteins and can produce non-specific tolerance to various stressors [51]. The increased levels of HSP70 in vivo alleviates the stress of environmental stressors on chickens to a certain extent.
In the current study, as this experiment was a 2 × 2 factor experimental design, the offspring broilers were only supplemented with inorganic Zn with different doses (0 or 80 mg Zn/kg). In our future experiments, we will explore the effects of adding different forms of Zn sources (including inorganic Zn and organic Zn) to the offspring broilers.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, maternal Zn–Gly supplementation increased progeny performance and decreased progeny mortality and stress by increasing the progeny Zn concentration, antioxidant capacity, and immune function at the same Zn levels as ZnSO4. At the same time, Zn supplementation in the progeny’s diet is necessary for the growth of broilers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. (Yuanyuan Wang); methodology, Y.W. (Yuanyuan Wang), L.Z. and A.F.; formal analysis, X.D. and Y.W. (Yuanyuan Wang); investigation, L.Z., A.F., Y.X., X.Z. and Y.W. (Yuanyuan Wang); visualization, Y.W. (Yongxia Wang), Y.X.; software, X.D.; validation, Y.W. (Yuanyuan Wang) and X.Z.; resources, X.Z.; data curation, A.F.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W. (Yuanyuan Wang); writing—review and editing, X.Z.; supervision, X.Z. and A.F.; project administration, X.Z. and A.F.; funding acquisition, X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The financial support provided by Anhui Youth Natural Science Foundation (2108085QC133), Zhejiang Province Major Agricultural Technologies Collaborative Extension Plan (2021XTTGXM04), China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-41, Beijing, China), Zhejiang Province Key R&D Program (2013C02010, Hangzhou, China) are gratefully acknowledged.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This experiment was approved by the Zhejiang University Laboratory Animal Welfare and Experimental Ethical Committee (ZJU20160380).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kwiecien, M.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A.; Milczarek, A.; Klebaniuk, R. Biological Response of Broiler Chickens to Decreasing Dietary Inclusion Levels of Zinc Glycine Chelate. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 175, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteiza, P.L.; Olin, K.L.; Fraga, C.G.; Keen, C.L. Oxidant defense systems in testes from zinc-deficient rats. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1996, 213, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Loutsidou, A.C.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Zinc and human health: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteiza, P.I. Zinc and the modulation of redox homeostasis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, A.H.; Prasad, A.S. Zinc and immune function: The biological basis of altered resistance to infection. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 447s–463s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muiruri, H.K.; Harrison, P.C. Effect of Roost Temperature on Performance of Chickens in Hot Ambient Environments. Poult. Sci. 1991, 70, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Monteiro, A.P.A.; Thompson, I.M.; Hayen, M.J.; Dahl, G.E. Effect of late-gestation maternal heat stress on growth and immune function of dairy calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 7128–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Li, W.X.; Lu, L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Ji, C.; Lin, X.; Liu, H.C.; Odle, J.; Luo, X.G. Impact of maternal heat stress in conjunction with dietary zinc supplementation on hatchability, embryonic development, and growth performance in offspring broilers. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lv, Z.P.; Li, C.W.; Yue, Y.S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, F.L.; Guo, Y.M. Maternal Zinc Supplementation Enhanced Skeletal Muscle Development Through Increasing Protein Synthesis and Inhibiting Protein Degradation of Their Offspring. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 162, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Guo, S.S.; Gao, J.; Guo, Y.M.; Du, E.C.; Lv, Z.P.; Zhang, B.B. Maternal high-zinc diet attenuates intestinal inflammation by reducing DNA methylation and elevating H3K9 acetylation in the A20 promoter of offspring chicks. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virden, W.S.; Yeatman, J.B.; Barber, S.J.; Zumwalt, C.D.; Ward, T.L.; Johnson, A.B.; Kidd, M.T. Hen mineral nutrition impacts progeny livability. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2003, 12, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreicher, P.; Cousins, R.J. Copper and zinc absorption in the rat: Mechanism of mutual antagonism. J. Nutr. 1985, 115, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Star, L.; vanderKlis, J.D.; Rapp, C.; Ward, T.L. Bioavailability of organic and inorganic zinc sources in male broilers. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 3115–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H.; Lu, L.; Wang, R.L.; Lei, H.L.; Li, S.F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Luo, X.G. Effects of supplemental zinc source and level on antioxidant ability and fat metabolism-related enzymes of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2686–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virden, W.S.; Yeatman, J.B.; Barber, S.J.; Willeford, K.O.; Ward, T.L.; Fakler, T.M.; Wideman, R.F.; Kidd, M.T. Immune system and cardiac functions of progeny chicks from dams fed diets differing in zinc and manganese level and source. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Additives, E.P.; Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Bastos, M.L.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Durjava, M.F.; Kouba, M. Safety of the feed additive consisting of manganese chelates of lysine and glutamic acid for all animal species (Zinpro Animal Nutrition). EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.X.; Guo, T.Y.; Zhan, X.A. Effects of Zinc Glycinate on Productive and Reproductive Performance, Zinc Concentration and Antioxidant Status in Broiler Breeders. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 178, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.X.; Guo, T.Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhan, X.A. Effects of Maternal Zinc Glycine on Mortality, Zinc Concentration, and Antioxidant Status in a Developing Embryo and 1-Day-Old Chick. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 181, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.J.; Guo, Y.M.; Ma, S.D.; Yuan, J.M.; An, S.Y.; Li, J.H. Dietary Mineral Sources Altered Lipid and Antioxidant Profiles in Broiler Breeders and Posthatch Growth of Their Offsprings. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 145, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.M.; Shirley, R.B.; Dibner, J.J.; Wedekind, K.J.; Yan, F.; Fisher, P.; Hampton, T.R.; Evans, J.L.; Vazquez-Anon, M. Superior growth performance in broiler chicks fed chelated compared to inorganic zinc in presence of elevated dietary copper. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanian, R.; Rasouli, E. Effects of dietary substitution of zinc-methionine for inorganic zinc sources on growth performance, tissue zinc accumulation and some blood parameters in broiler chicks. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, H.M.; Lee, H.R.; Jo, C.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, B.D. Effect of dietary zinc proteinate supplementation on growth performance, and skin and meat quality of male and female broiler chicks. Brit. Poult. Sci. 2012, 53, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanian, R.; Moghaddam, H.N.; Rezaei, A. Improved broiler chick performance by dietary supplementation of organic zinc sources. Asian-Austral. J. Anim. 2008, 21, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Birkhold, S.G.; Kubena, L.F.; Nisbet, D.J.; Ricke, S.C. Review on the role of dietary zinc in poultry nutrition, immunity, and reproduction. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2004, 101, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, P.; Rutz, F.; Anciuti, M.A.; Rech, J.L.; Zauk, N.H.F. Influence of graded levels of organic zinc on growth performance and carcass traits of broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2007, 16, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamberg, D.L.; Blackwood, U.B.; Supplee, W.C.; Combs, G.F. Effect of Zinc Deficiency in Hens on Hatchability and Embryonic Development. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1960, 104, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienholz, E.W.; Turk, D.E.; Sunde, M.L.; Hoekstra, W.G. Effects of zinc deficiency in the diets of hens’. J. Nutr. 1961, 75, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, B.P.; Dozier, W.A.; Wilson, J.L.; Sander, J.E.; Ward, T.L. Reproductive performance and immune status of caged broiler breeder hens provided diets supplemented with either inorganic or organic sources of zinc from hatching to 65 wk of age. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2004, 13, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lu, L.; Wang, R.L.; Xi, L.; Luo, X.G.; Liu, B. Effects of zinc source and phytate on zinc absorption by in situ ligated intestinal loops of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yair, R.; Uni, Z. Content and uptake of minerals in the yolk of broiler embryos during incubation and effect of nutrient enrichment. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Yan, S. Effects of Cd, Zn, or Pb Stress in Populus alba berolinensis on the Antioxidant, Detoxifying, and Digestive Enzymes of Lymantria dispar. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucuk, O. Zinc in a combination with magnesium helps reducing negative effects of heat stress in quails. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 123, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, J.; Ruram, A.A.; Singh, S.S.; Devi, S.B.; Devi, T.I.; Singh, W.G. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant vitamins in urolithasis. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 22, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, T.M.; Bettger, W.J. The Physiological-Role of Zinc as an Antioxidant. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1990, 8, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.G.; McCutchon, T.L.; Boermans, H.J.; DiSilvestro, R.A.; Bray, T.M. Comparison of Zn and vitamin E for protection against hyperoxia-induced lung damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, P.; Garg, M.L.; Dhawan, D.K. Protective effects of zinc on oxidative stress enzymes in liver of protein-deficient rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 28, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.A.; Elfattah, A.A.A. Effect of Dietary Zinc on Lipid-Peroxidation, Glutathione, Protein Thiols Levels and Superoxide-Dismutase Activity in Rat-Tissues. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B 1995, 27, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Tan, S.X.; Xiao, X.Y.; Qiu, X.S.; Pan, J.Q.; Tang, Z.X. Effects of Dietary Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Growth Performance and Antioxidative Status in Broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 160, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellinghausen, N.; Rink, L. The significance of zinc for leukocyte biology. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 64, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocchegiani, E.; Muzzioli, M.; Giacconi, R. Zinc and immunoresistance to infection in aging: New biological tools. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ma, W.Q.; Niu, H.H.; Wu, X.M.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J. Effects of Zinc Glycine Chelate on Growth, Hematological, and Immunological Characteristics in Broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 133, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydemir, T.B.; Blanchard, R.K.; Cousins, R.J. Zinc supplementation of young men alters metallothionein, zinc transporter, and cytokine gene expression in leukocyte populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, P.C.S.; Sena-Evangelista, K.C.M.; Paiva, M.S.M.D.; Ferreira, D.Q.C.; Ururahy, M.A.G.; Rezende, A.A.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; Pedrosa, L.F.C. The beneficial effects of rosuvastatin are independent of zinc supplementation in patients with atherosclerosis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishi, P.; Kaur, P.; Virdi, J.S.; Shukla, G.; Koul, A. Amelioratory effects of zinc supplementation on Salmonella-induced hepatic damage in the murine model. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, R.J.; Leinart, A.S. Tissue-specific regulation of zinc metabolism and metallothionein genes by interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988, 2, 2884–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.B. Antibody production suppressed in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus) by zinc deficiency. Avian Pathol. 1983, 12, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, R.S.; Gershwin, M.E.; Makishima, R.K.; Hurley, L.S. Impaired Immunological Ontogeny in Postnatal Zinc Deprivation. J. Nutr. 1980, 110, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraker, P.J.; King, L.E.; Laakko, T.; Vollmer, T.L. The dynamic link between the integrity of the immune system and zinc status. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1399s–1406s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellinghausen, N.; Kirchner, H.; Rink, L. The immunobiology of zinc. Immunol. Today 1997, 18, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga, C.; Hunter, R.R.; Amat, C.; Planas, J.M.; Mitchell, M.A.; Moreto, M. Heat stress increases apical glucose transport in the chicken jejunum. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R195–R201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Yan, F.F.; Hu, J.Y.; Amen, O.A.; Cheng, H.W. Supplementation of Bacillus subtilis-based probiotic reduces heat stress-related behaviors and inflammatory response in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).