Abstract
Objective: This meta-analysis with a systematic review was undertaken to assess the association between APOE allelic genotypes and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in the Italian population. Methods: The Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus databases were searched until 15 November 2023. The odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated using fixed and random effect models, depending on the I2 statistic value. The systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in agreement with the PRISMA guideline and registered with PROSPERO (CRD42023492580). Results: Our meta-analysis based on 15 studies revealed a higher risk of AD among Italian individuals carrying the APOE ε4 allele (OR = 3.60, 95% CI [2.90–4.47], p < 0.0001). The association of AD genotype APOE ε2ε4 (OR = 1.36, 95% CI [0.76–2.41], p = 0.29) was not statistically significant, while APOE ε3ε4 (OR = 3.43, 95% CI [2.95–3.99], p < 0.0001) has a high risk of AD development; the risk is more notably in the APOE ε4ε4 genotype (OR = 7.08, 95% CI [4.22–11.86], p < 0.0001). The APOE ε2 allele has a protective effect (APOE ε2 (OR = 0.47, 95% CI [0.29–0.74], p = 0.0013)), and similar results were achieved by APOE ε3 (OR = 0.49, 95% CI [0.37–0.65], p < 0.0001). Subgroup analysis of three areas of Italy (southern, northern, and center) revealed that that APOE ε4 allele was a risk factor with a higher OR in northern Italy (OR 4.22; 95% CI [3.46–5.16], p < 0.0001) compared to southern and center Italy (OR 3.02; 95% CI [2.28–4.01], p < 0.0001 and OR 3.97; 95% CI [1.37–11.56], p < 0.0001, respectively). As well, APOE ε4ε4 genotype carriers had a significantly higher OR in northern Italy (OR 9.69; 95% CI [4.94–18.99], p < 0.0001) compared to in southern and center Italy (OR 4.38; 95% CI [1.54–12.47], p < 0.0001 and OR 3.59; 95% CI [0.87–14.86], p < 0.0001, respectively). Conclusions: This systematic review with a meta-analysis of the Italian population on APOE alleles, genotyping, and AD incidence, highlights that individuals harboring APOE ε4 have a higher risk of developing AD compared to those with other alleles. It also supports the protective effect of the APOE ε2 allele against the progress of AD. The qualitative analysis on the complex genetic interactions influencing Alzheimer risk emphasizes the need for further research on genetic and environmental factors for effective prevention strategies.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder and the most common cause of dementia, accounting for 60–80% of cases in elderly individuals [1]. Memory impairment, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes are most often associated with the disease [2,3], although less common clinical presentations are becoming more recognized. The core of AD neuropathology consists of extracellular beta-amyloid plaque deposits in discrete brain areas and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) composed of aggregated tau protein. Additional factors in the pathogenic framework of AD include the presence of neuroinflammatory conditions and vascular dysfunction [4]. Despite extensive research efforts, the etiology of AD remains poorly understood. Studies on familial forms of early-onset AD (EOAD) happening before 65 years of age have highlighted the crucial role of precise mutations in the amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin 1 (PSEN1), and presenilin 2 (PSEN2) genes; however, these rare familial forms of AD account for less than 1% of the cases [5]. More than 95% of AD cases are sporadic or late-onset AD (LOAD), where both environmental and genetic factors play a significant role in its etiology. The APOE gene has been identified as the most potent genetic risk factor in sporadic disease [6]. Located on chromosome 19q13.32, the APOE gene encodes a protein primarily involved in lipid metabolism and transport in the central nervous system [7,8]. Three allelic variants of the gene, namely ε2 (APOE2), ε3 (APOE3), and ε4 (APOE4), have a worldwide frequency of 8.4%, 77.9%, and 13.7%, respectively, and six genotypes (ε2ε2, ε2ε3, ε2ε4, ε3ε3, ε3ε4 and ε4ε4) [9] have been identified in humans. Meta-analyses have shown that the APOE ε4 allele increases the risk of the disease by three times in heterozygotes and by about 15 times in homozygotes [9]. In contrast, the APOE ε2 allele reduces AD risk by almost half, relative to the common APOE ε3 allele [10,11]. Significantly, the APOE ε4 both increases the risk of AD and lowers the age of disease onset in an allele number-dependent manner [12]. The precise molecular mechanism by which the APOE polymorphism determines the risk of AD remains unclear. Evidence advises that human APOE isoforms significantly impact AD pathogenesis through their differential effects on Aβ aggregation and clearance. However, APOE isoforms also affect multiple pathways that are not necessarily dependent on Aβ, with APOE4 revealing either a gain in toxic function or a loss of physiological function [13]. Although the APOE ε4 allele accounts for most of the genetic risk in sporadic AD [14], the contribution of other genes cannot be ruled out. Thanks to GWAS, dozens of genes robustly associated with AD have been recently discovered [15,16]. The heterogenic pathogenetic profile and the multifactorial nature of sporadic AD in which several susceptibility genes act in a complex interplay with environmental factors, might explain this difficulty [17]. Even if several questions are still open on the etiology of AD, the impact of genetic variants represents a key factor in the pathogenetic framework of the disease, as highlighted by several studies in the field. Herein, we conducted a meta-analysis to systematically assess the results of various research on the association among the APOE allele, genotypes, and AD risk for the first time in Italian population.
2. Materials and Methods
The systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [18] and protocol registered at the PROSPERO International Prospective Registry (CRD42023492580). A machine learning approach was used using the MySLR platform [19]. MySRL is a semi-automated tool that implements the Latent Dirichlet Allocation LDA algorithm (https://myslr.unical.it, accessed on 1 November 2023). The LDA algorithm has been applied in some fields to extract topics and identify patterns within the literature [20,21].
2.1. Research Strategy
Two researchers (D.M.A-G and G.F.S) performed literature searches on the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases to identify publications in peer-reviewed journals up to 15 November 2023. The boolean operators “AND” and “OR” were used to combine the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terminology: (“apolipoprotein E” OR “APO E” OR “APOE”) AND (“italian” OR “italy”).
2.2. Paper Analysis and Data Extraction
The inclusion criteria for studies published up to 15 November 2023 were as follows: population: Italian population with AD; exposure: APOE; outcomes: present or absent allele and genotype; and types of study: case–control studies conducted on an Italian population.
Articles were excluded if they were not case–control studies; were studies with an incomplete genotype or allele frequency; were not published in English; were review-based or non-original research; or involved non-human subjects. Disagreements were resolved by discussion or by third reviewer (M.C.C, M.M, and R.C).
Two authors (D.M.A-G and G.F.S) extracted data, and one author (E.C.) checked them. The following data were extracted: authors and publication year, country, study design, participant characteristics, starting sample, diagnostic criteria, genotype and allele frequency, and result.
2.3. Quality Assessment
The risk of bias of each study included was assessed using the NIH Study Quality Assessment Tool of Case–Control Studies (accessed 10 December 2023). Twelve questions were designed to help focus on the key concepts for evaluating each study’s internal validity. A traffic light plot and summary plot were created with the Robvis tool [22].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) and p-value were used to evaluate the relationship of APOE and AD in the following six genotypes and three allele frequencies. A Q test and the I2 were used to assess the heterogeneity of included studies [23]. The I2 test was used to determine the heterogeneity among the studies, and if I2 < 50%, then the studies were considered homogeneous, and the fit-equal model/fixed model (EE) was used to analyze the included data. When I2 ≥ 50% of the studies were considered heterogeneous, the random effect model (RE) was used to analyze the included data. A visual inspection of funnel plots and Egger’s test were used to assess the publication bias [24,25]. All statistical tests in this study were carried out using fixed and random effect designs implemented in the metafor R package, version 3.2.4 [26].
2.5. Results Presentation
The final step of the methodological approach is detailed in the ‘Results’ and ‘Discussion’ Sections. The latter is dedicated to defining and analyzing the results of the MySLR procedure and includes a meticulous review of the relevant literature to clearly describe and discuss the findings.
3. Results
In total, 2093 records were identified from the initial literature search of the three databases (PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science). After excluding duplicate records, 1482 items remained. MySLR removed 294 papers because they were review-based or non-original research. Of the 1188 studies remaining, 1121 were discarded based on their abstracts. After full-text reading and analysis, 52 records were excluded for failing to meet the inclusion/exclusion criteria. Therefore, a total number of 15 studies were considered eligible. The PRISMA flowchart in Figure 1 shows the selection of the studies for this systematic review.
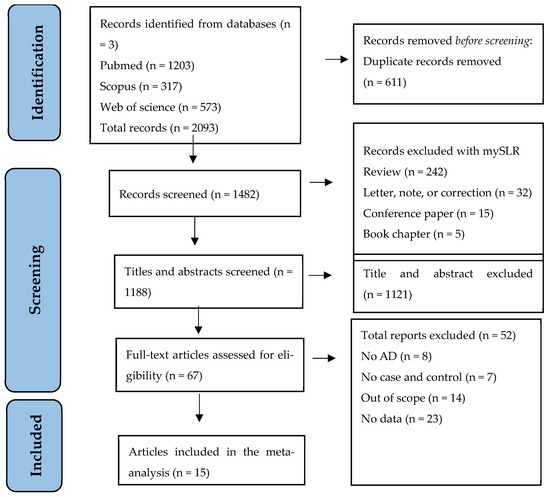
Figure 1.
PRISMA Flow diagram for selecting eligible studies.
3.1. Study Characteristics
The characteristics of the distribution of the selected studies are summarized in Table 1. Fifteen articles were selected, including 2846 cases and 2391 controls from three different areas of Italy: six studies from northern Italy [27,28,29,30,31,32], three studies from the center area [33,34,35], five studies from southern Italy [36,37,38,39,40,41], and only one study from a non-reported geographical area [42]. Blood was used for genomic DNA extraction in 13 articles [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,39,40], and two studies did not report the biological fluid that was used [38,42]. NINCDS-ADRDA was used as diagnostic criteria in 12 articles [27,28,29,30,32,33,35,36,37,38,39,40]. At the same time, three studies used DMS III/IV [35,37,38], and Nacmias et al. used a clinical/neurological examination, a laboratory test, and CT/MRI [31].

Table 1.
Qualitative and quantitative synthesis and characteristics of the studies.
The global cognitive function was report through the Mini-Mental State Evaluation (MMSE) score by eight studies in both groups (case and control) [27,28,30,34,36,37,38] and solely in the control group of Lovati et al. and Bizzarro et al. [29,33]; Nacmias et al. did not report the MMSE score for the control group [31]. The distribution of the genotypes in the groups was consistent with the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE). The distributions of alleles and genotypes in the individual studies are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
APOE allele and genotype frequencies in AD case and control groups.
3.2. Quality Assessment and Publication Bias
The risk of bias assessment is summarized in Figure 2A,B. The total number of studies (100%) described objectives, similar populations, cases clearly defined and distinguished from controls, and the blinding of assessors, and they were judged to have a ‘fair’ and low risk of bias in these areas. No studies reported information about random selection and concurrent controls. Only two studies reported sample size justification [30,36]. All other domains were evaluated to have a low risk of bias.
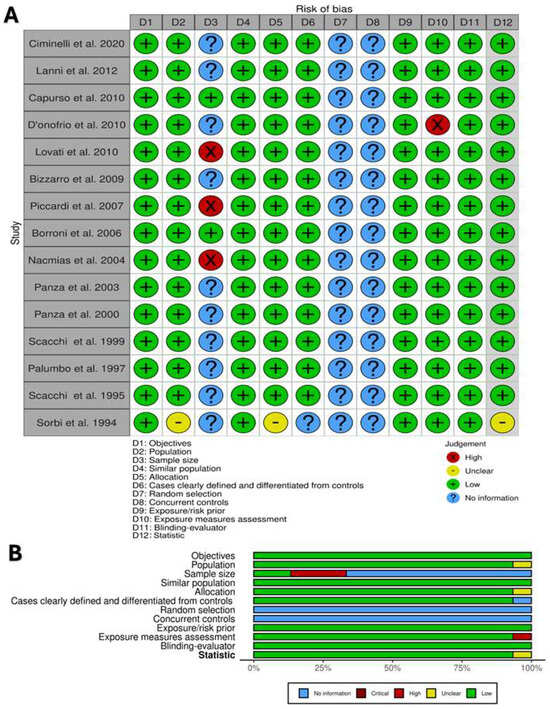
Figure 2.
Risk of bias assessment for included cases and control studies. (A) Review of author’ judgment about each risk-of-bias item. (B) Presented ad percentage across all included studies. Created with Robvis tool.
The distribution of the ORs from individual studies in relation to their respective standard error in funnel plot is shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4A–C. A visual inspection of the funnel plots and Egger’s test for allele ε4 (p = 0.686) and genotypes ε2/ε4 (0.916), ε3/ε4 (p = 0.461), and ε4/ε4 (p = 0.895) revealed no evidence of asymmetry. Thus, there was no possibility of publication bias risk in the meta-analysis.
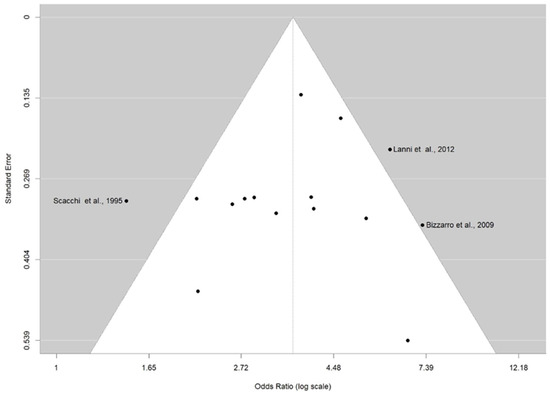
Figure 3.
Funnel plot for publication bias on the association between ε4 allele carriers and AD risk. The x-axis displays the estimated effect size as OR (log scale), and the y-axis represents a measure of study precision as standard error. The horizontal line in the figure represents the overall estimated effects as the odds ratio (log scale). The two diagonal lines represent the 95% confidence limits of the effect estimate.
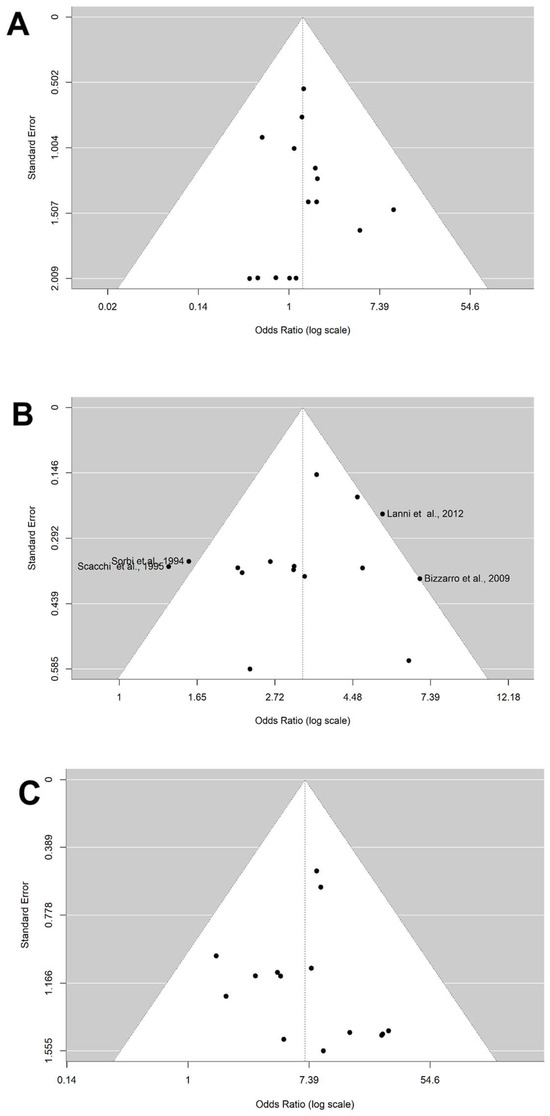
Figure 4.
Funnel plot on the association between genotype carriers ε4 and AD risk. (A) Genotype ε2/ε4. (B) Genotype ε3/ε4. (C) Genotype ε4/ε4. The x-axis displays the estimated effect size as the OR (log scale), and the y-axis represents a measure of study precision as the standard error. The horizontal line in the figure represents the overall estimated effects as the odds ratio (log scale). The two diagonal lines represent the 95% confidence limits of the effect estimate.
3.3. Meta-Analysis of APOE Alleles and AD
The I2 > 50% and Q statistics were significant; thus, heterogeneity between studies was significant (Table 3).

Table 3.
Test of heterogeneity in meta-analysis of allele APOE and risk of AD.
The random effect model (RE) was applied for calculating the pooled OR. The results of each allele of APOE in this meta-analysis are listed in Table 4. The results show a significant association among APOE ε2 (OR = 0.47, 95% CI [0.29–0.74], p = 0.0013), APOE ε3 alleles, and AD (OR = 0.49, 95% CI [0.37–0.65], p < 0.0001), highlighting the lower risk of AD for the ε2 and ε3 alleles.

Table 4.
Pooled OR results in meta-analysis of APOE allele and risk of AD.
All forest plots are included in the Supplementary Material. Overall, this meta-analysis displays that the frequency of the APOE ε4 allele is higher in AD than in the healthy controls and established a statistically significant association among risk factor APOE ε4 allele carriers and AD in the Italian population (OR = 3.60, 95% CI [2.90–4.47], p < 0.0001) (Figure 5).
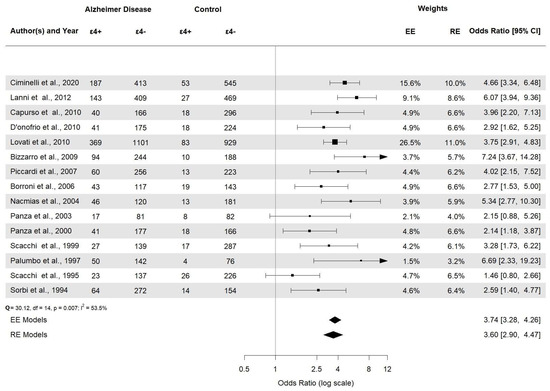
Figure 5.
Forest plot of the association between APOE ε4 alleles and AD risk in Italian population.
3.4. Meta-Analysis of APOE Genotypes and AD
With the exception of the APOE ε2ε2 genotype, APOE ε2ε2, and APOE ε4ε4 homozygotes, all I2 > 50% and Q statistics were significant (Table 5).

Table 5.
Test of heterogeneity in meta-analysis of genotype APOE and risk of AD.
Therefore, the corresponding fit-equal model (EE) and random model (RE) were used for calculating the pooled OR. The results of each allele of APOE in this meta-analysis are listed in Table 6.

Table 6.
Pooled OR results in meta-analysis of APOE genotype and risk of AD.
APOE ε2ε3 was associated with AD (APOE ε2ε3: OR 0.38, 95% CI [0.22–0.66], p = 0.0006). APOE ε2/ε2 and APOE ε2/ε4 (Figure 6) were not statistically significant (p = 0.23 and p = 0.29, respectively). Then, the APOE ε3ε3 and APOE ε3ε4 (Figure 7) genotypes were also significantly associated with AD (APOE ε3ε3: OR 0.47, 95% CI [0.33–0.67], p < 0.0001). Genotype investigation showed a higher frequency of APOE ε3/ε4 genotypes in AD patients (OR 3.43, 95% CI [2.95–3.99], p < 0.0001) and of APOE ε4/ε4 in AD patients compared to controls (OR = 7.08, 95% CI [4.22–11.86]), p < 0.0001), indicating a strong association with AD patients (Figure 8). The OR of APOE ε4ε4 homozygotes was the largest, and that of APOE ε2ε3 was the smallest. All forest plots are included in the Supplementary Material.
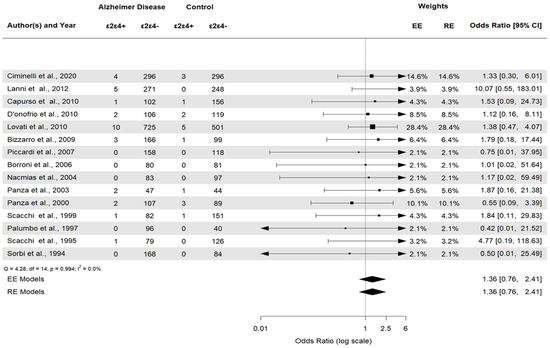
Figure 6.
Forest plot of the association between APOE ε2/ε4 genotypes and AD versus control.
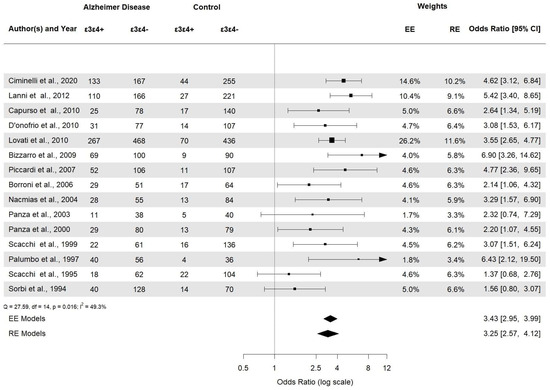
Figure 7.
Forest plot of the association between APOE ε3/ε4 genotypes and AD risk.
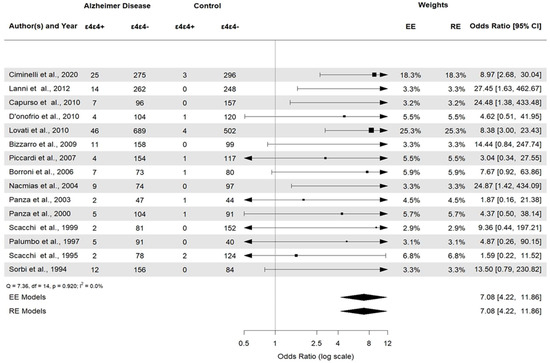
Figure 8.
Forest plot of the association between APOE ε4/ε4 genotypes and AD.
3.5. Subgroup Analysis of APOE ε4 Allele and APOE ε4ε4 Genotype Based on Location
When stratified by location (southern, northern, and center), we used only 14 articles due to Sorbi et al. not reporting an allocation study [42]. APOE ε4 allele carriers significantly had a higher OR in northern Italy (OR 4.22; 95% CI [3.46–5.16], p < 0.0001) compared to southern and center Italy (OR 3.02; 95% CI [2.28–4.01], p < 0.0001 and OR 3.97; 95% CI [1.37–11.56], p < 0.0001, respectively). A forest plot of the subgroup analyses by location is displayed in Figure 9.
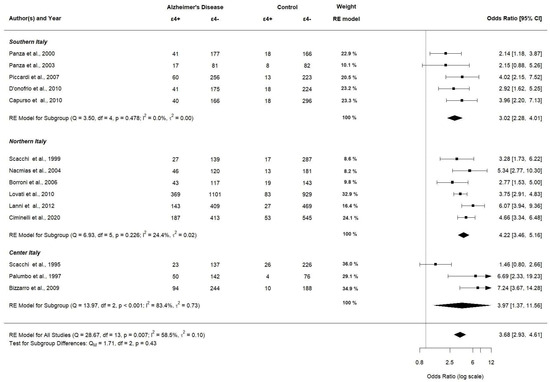
Figure 9.
Subgroup analysis of APOE ε4 allele (assessed in 14 studies).
Figure 10 shows the corresponding results for APOE ε4ε4 genotype carriers significantly having a higher OR in northern Italy (OR 9.69; 95% CI [4.94–18.99], p < 0.0001) compared to southern and center Italy (OR 4.38; 95% CI [1.54–12.47], p < 0.0001 and OR 3.59; 95% CI [0.87–14.86], p < 0.0001, respectively).
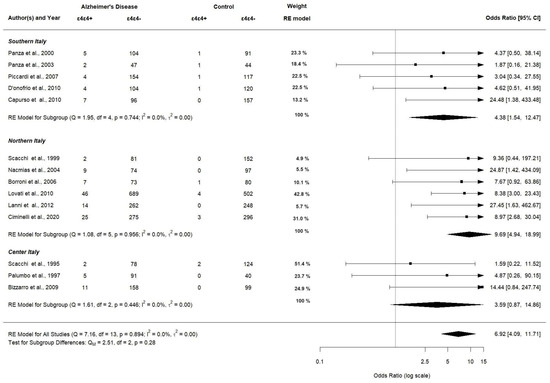
Figure 10.
Subgroup analysis of APOE ε4ε4 allele (assessed in 14 studies).
4. Discussion
AD is a complex neurodegenerative disorder in which genetic variants are implicated in its pathogenesis. While mutations in APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 genes lead to the occurrence of EOAD, variants in lots of other genes have been correlated with an augmented risk of developing a LOAD form of the disease. Among these, APOE ε4 was first described as a major risk factor for AD in 1993 [43]. A study published by Farmer et al. shows that the effects of APOE ε4 induce lipid droplet formation and cholesterol accumulation in astrocytes, which are specialized cells that, among their various functions, supply nutrients to neurons and support the structure of the brain [44,45]. While APOE ε2 has been shown to confer protection against AD-related pathology [13]. According to a previous meta-analysis, the prevalence of the APOE ε4 genotype differs between AD patients by geographical region and sample size [46], with northern Europe having the highest estimates and Asia and southern Europe having the lowest. In Europe, APOE4 frequency increases with latitude from the highest frequencies in Norway (31.0%) to the lowest frequencies in Italy (Sardinia: 5.2%) [46]. Therefore, several meta-analyses have been performed in certain ethnic groups to examine the relation between APOE ε4 and AD. Liu et al. reported that the APOE ε4 allele and APOE ε4ε4 genotype are related with 3.93-fold and 11.76-fold increased risks of developing AD, respectively, in a Chinese population [47]. Also, Agarwal et al. conducted a meta-analysis on an Indian population and showed that the risk of developing AD increased 5.90-fold and 4.81-fold for individuals carrying the APOE ε4 allele or with the APOE ε4ε4 genotype [48]. Similarly, Abyadeh and co-workers suggested an association between the APOE ε4 allele and ε4ε4 genotype and the risk of developing AD in an Iranian population (4.81- and 7.47-fold, respectively), while pointing out a protective role of the APOE ε3 allele [49]. An association between APOE ε4 and increased AD and related dementia risk was recently reported in global Hispanic populations, with the strength of this association varying across Hispanic subgroups [50].
The present meta-analysis included 15 cases and control studies, comprising 2391 patients in the experimental group and 2583 in the control group. Herein, we conducted a meta-analysis of studies exploring the connection between APOE haplotypes and AD in the Italian population. Overall, our results show that the risk of developing AD in ε4 allele carriers was 3.60-fold higher than APOE ε4 noncarriers. We also found a statistically significant association among APOE ε2, APOE ε3, and AD with a low positive rate ((OR = 0.47; 95% CI [0.29–0.74], p = 0.0013; OR = 0.49; 95% CI [0.37–0.65], p < 0.0001, respectively)) for both alleles, thus underscoring their lower risk of developing AD. The results also reveal that the risk of developing AD in individuals with the APOE ε4ε4 genotype was 7.08-fold higher than APOE ε4ε4 genotype non-carriers. Notably, APOE ε4 homozygosity has been recently proposed as another form of genetically determined AD, owing to near-full penetrance, the predictability of symptom onset, and a probable sequence of biomarker and clinical changes [51]. This evidence could lead to a conceptual reshaping of the genetic architecture of AD, which is usually categorized into the sporadic and autosomal dominant forms, with important consequences for public health and genetic counseling. Our results also reveal that APOE ε3 and APOE ε4 heterozygotes show an intermediate OR value (OR = 3.43; 95%CI [2.95–3.99], p < 0.0001) between APOE ε3 (OR = 0.47; 95% CI [0.33–0.67], p < 0.0001) and APOE ε4 homozygotes (OR = 7.08; 95% CI [4.22–11.86], p < 0.0001), suggesting a dose-dependent association among the number of APOE ε4 alleles and the risk of AD in the Italian population. No significant association was found between the APOE ε2ε4 allele and AD risk. Interestingly, although APOE ε2 has been shown to confer protection against AD [52], Insel et al. reported that carrying an APOE ε2 in the presence of APOE ε4 may confer some defense against Aβ accumulation compared to APOE ε3 [53,54,55]. However, other studies found that the OR of APOE ε2ε4 individuals is more comparable to that of APOE ε4 carriers than APOE ε2 carriers [52], suggesting that the increased risk associated with APOE ε4 is more dominant than the protection offered by APOE ε2. Moreover, the relationship between the APOE genotype and AD is not only determined by genetic factors but is also modulated by complex gene–environment interactions such as diet, physical activity, cognitive stimulation, and cardiovascular health, which may modify the risk conferred by the APOE genotype; for example, Panza et al. reported a significant reduction in serum APOE levels from APOE ε2 to ε4 carriers. In addition, serum HDL levels among age groups significantly decreased in ε4 carriers only [39]. Furthermore, Borroni et al. reported that subjects with hypercholesterolemia and heterozygous for the APOE ε4 allele had more than a three-fold risk to develop AD compared with the control group [30], highlighting the importance of adopting preventive strategies. The latter can be recognized in life style and nutrition; in particular, a mediterranean diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 is associated with fewer signs of AD in the brains of older adults [56]. Additionally, supplements with antioxidants and other micronutrients can boost cognitive function [57,58]. Finally, in the subgroup analysis by region, the association of the APOE ɛ4ɛ4 genotype with AD was striking. In the three areas of Italy (southern, northern, and center), the ɛ4 allele was associated with more or less the same risk of AD compared with controls, but the estimates of the association of the ɛ4ɛ4 genotypes by subgroups show an approximately double risk in northern Italy compared with southern and center Italy. In this context, the meta-analysis across the global population of AD patients recruited in southern Europe/Mediterranean appeared to have a significantly lower ε4 carrier status compared to in northern Europe. This difference may be due to the different sample sizes of the studies, to the specific geographical characteristics, or to different gene–environment interactions. According to a national study, southern Italian regions shown high adherence to the Mediterranean diet compared to northern regions [59]. However, in recent years, there has been a progressive decline in adherence to the Mediterranean diet in the South of Italy [60]. Although several environmental factors and lifestyle can also play a part in the modification of AD risk, no single environmental/lifestyle risk factor has been shown to be strongly associated with AD yet [61]. Recently, a Polygenic Risk Score based on 21 SNPs for AD contributed a modifier of risk of the APOE ε4 homozygotes, unlike other factors that contributed more to causality [62,63]. In our systematic review, Bizzarro et al. pointed out that rs449647 A/T and rs405509 T/T genotypes were negative to AD, and rs449647 A/A and rs405509 G/G genotypes were positive. This means that promoter genotypes and APOE haplotypes might have a complex function in AD-associated genetic risk factors [33]. Interestingly, the modifying effect of the rs405509 genotype explained much of the ethnic variability in the AD/APOE ε4 association [64]. In addition, Lanni et al. reported a synergy between the COMT Val158Met GG genotype and APOE ε4, which increased to about a 2–3-fold risk for AD, markedly in males [28]. Finally, Capurso et al. founded no interaction or synergy between GSTO1 SNP and APOE variants [36]. These findings demonstrate the potential impact of rare APOE variants on AD risk.
This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to specifically investigate the effects of APOE alleles and genotypes associated with AD in the Italian population. The quality of the clinical trials was evaluated, and most of the included studies had a good quality. Also, no evidence of publication bias was evidenced. Specific eligibility criteria and controlled queries were applied to the literature search, and we are confident that the search strategy retrieved all relevant studies. However, there are some limitations in this meta-analysis. Firstly is heterogeneity across studies, due to differences in aims. Secondly, eligible studies could not be investigated because of inadequate evidence regarding the potential effects of other parameters such as gender, age, cognitive status, and interactions with environmental factors such as diet or physical activity. Thirdly, the retrospective nature of case–control studies limits causal inference and requires caution in interpreting the results. Finally, few studies have reported total and fractionated cholesterol values, which would provide important information regarding the potential causality of associations between total cholesterol, APOE genotype, and AD risk.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our meta-analysis with a systematic review suggests that APOE ε4 carriers are associated with AD in the Italian population, and supports the protective effect of the APOE ε2 allele against developing AD. In addition, the estimates of the association of the ɛ4ɛ4 genotypes by subgroup analysis show an approximately double risk of AD in the northern Italy population compared with in the south and center.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/brainsci14090908/s1: Table S1: PRISMA 2020 checklist. Figure S1: Forest plot of the association between APOE ε2 allele [65]; Figure S2: Forest plot of the association between APOE ε3 allele; Figure S3: Forest plot of the association between APOE ε2ε2 genotype; Figure S4: Forest plot of the association between APOE ε2ε3 genotype; Figure S5: Forest plot of the association between APOE ε3ε3 genotype; Figure S6: Forest plot of the association between APOE ε3ε4 genotype.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.C.; methodology, D.M.A.-G. and G.F.S.; software, D.M.A.-G.; formal analysis, D.M.A.-G. and E.C.; resources, E.C.; data curation, R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.M.A.-G.; writing—review and editing, E.C., M.C.C. and D.M.A.-G.; visualization, M.M.d.B. and R.C.; supervision, M.C.C.; funding acquisition, E.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Next Generation EU—Italian NRRP, Mission 4, Component 2, Investment 1.5, call for the creation and strengthening of ‘Innovation Ecosystems’, building ‘Territorial R&D Leaders’ (Directorial Decree n. 2021/3277)—project Tech4You—Technologies for climate: ECS0000009.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated/analyzed throughout this research are included in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Crous-Bou, M.; Minguillón, C.; Gramunt, N.; Molinuevo, J.L. Alzheimer’s disease prevention: From risk factors to early intervention. Alzheimers. Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madnani, R.S. Alzheimer’s disease: A mini-review for the clinician. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1178588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindpani, K.; McNamara, L.G.; Smith, N.R.; Vinnakota, C.; Waldvogel, H.J.; Faull, R.L.M.; Kwakowsky, A. Vascular Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Prelude to the Pathological Process or a Consequence of It? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringman, J.M.; Coppola, G. New genes and new insights from old genes: Update on Alzheimer disease. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2013, 19, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montufar, S.; Calero, C.; Vinueza, R.; Correa, P.; Carrera-Gonzalez, A.; Villegas, F.; Moreta, G.; Paredes, R. Association between the APOE ε4 Allele and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease in an Ecuadorian Mestizo Population. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 2017, 1059678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Grau, S.; Initiative, A.D.N.; Hernández, I.; Heilmann-Heimbach, S.; Ruiz, S.; Rosende-Roca, M.; Mauleón, A.; Vargas, L.; Rodríguez-Gómez, O.; Alegret, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Significant Risk Factors on Chromosome 19 and the APOE Locus. Oncotarget. 2018, 15, 24590–24600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.G.; March, Z.M.; Stephenson, R.A.; Narayan, S.P. Apolipoprotein E in lipid metabolism and neurodegenerative disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, L.A.; Cupples, L.A.; Haines, J.L.; Hyman, B.; Kukull, W.A.; Mayeux, R.; Myers, R.H.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Risch, N.; van Duijn, C.M. Effects of Age, Sex, and Ethnicity on the Association Between Apolipoprotein E Genotype and Alzheimer Disease: A Meta-analysis. JAMA 1997, 278, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corder, E.H.; Saunders, A.M.; Risch, N.J.; Strittmatter, W.J.; Schmechel, D.E.; Gaskell, P.C., Jr.; Rimmler, J.B.; Locke, P.A.; Conneally, P.M.; Schmader, K.E.; et al. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat. Genet. 1994, 7, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieden, C.; Garai, K. Structural differences between apoE3 and apoE4 may be useful in developing therapeutic agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8913–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sando, S.B.; Melquist, S.; Cannon, A.; Hutton, M.L.; Sletvold, O.; Saltvedt, I.; White, L.R.; Lydersen, S.; Aasly, J.O. APOE ε4 lowers age at onset and is a highrisk factor for Alzheimer’s disease; A case control study from central Norway. BMC Neurol. 2008, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulin, A.-C.; Doss, S.V.; Trottier, Z.A.; Ikezu, T.C.; Bu, G.; Liu, C.-C. ApoE in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raber, J.; Huang, Y.; Ashford, J.W. ApoE genotype accounts for the vast majority of AD risk and AD pathology. Neurobiol. Aging 2004, 25, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Kucukali, F.; Jansen, I.E.; Kleineidam, L.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Amin, N.; Naj, A.C.; Campos-Martin, R.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Andrade, V.; et al. New insights into the genetic etiology of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 412–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.J.; Renton, A.E.; Fulton-Howard, B.; Podlesny-Drabiniok, A.; Marcora, E.; Goate, A.M. The complex genetic architecture of Alzheimer’s disease: Novel insights and future directions. eBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczyn, A.D.; Grinberg, L.T. Is Alzheimer disease a disease? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammirato, S.; Felicetti, A.M.; Rogano, D.; Linzalone, R.; Corvello, V. Digitalising the Systematic Literature Review process: The MySLR platform. Knowl. Manag. Res. Pract. 2022, 21, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevacqua, E.; Ammirato, S.; Cione, E.; Curcio, R.; Dolce, V.; Tucci, P. The Potential of MicroRNAs as Non-Invasive Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Systematic Literature Review Based on a Machine Learning Approach. Cancers 2022, 14, 5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, G.F.; Abrego-Guandique, D.M.; Cannataro, R.; Caroleo, M.C.; Cione, E. Machine Learning Approach to Identify Case-Control Studies on ApoE Gene Mutations Linked to Alzheimer’s Disease in Italy. BioMedInformatics 2024, 4, 600–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huedo-Medina, T.B.; Sánchez-Meca, J.; Marín-Martínez, F.; Botella, J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I 2 Index? Psychol. Methods 2006, 11, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminelli, B.M.; Menduti, G.; Benussi, L.; Ghidoni, R.; Binetti, G.; Squitti, R.; Rongioletti, M.; Nica, S.; Novelletto, A.; Rossi, L.; et al. Polymorphic Genetic Markers of the GABA Catabolism Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 77, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanni, C.; Garbin, G.; Lisa, A.; Biundo, F.; Ranzenigo, A.; Sinforiani, E.; Cuzzoni, G.; Govoni, S.; Ranzani, G.N.; Racchi, M. Influence of COMT Val158Met Polymorphism on Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Italian Patients. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 32, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovati, C.; Galimberti, D.; Albani, D.; Bertora, P.; Venturelli, E.; Cislaghi, G.; Guidi, I.; Fenoglio, C.; Cortini, F.; Clerici, F. APOE ε2 and ε4 influence the susceptibility for Alzheimer’s disease but not other dementias. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2010, 1, 193. [Google Scholar]
- Borroni, B.; Grassi, M.; Costanzi, C.; Archetti, S.; Caimi, L.; Padovani, A. APOE Genotype and Cholesterol Levels in Lewy Body Dementia and Alzheimer Disease: Investigating Genotype–Phenotype Effect on Disease Risk. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 14, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacmias, B.; Piccini, C.; Bagnoli, S.; Tedde, A.; Cellini, E.; Bracco, L.; Sorbi, S. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, apolipoprotein E genetic variants and cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 367, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbo, R.M.; Scacchi, R. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) allele distribution in the world. Is APOE*4 a ‘thrifty’ allele? Ann. Hum. Genet. 1999, 63, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarro, A.; Seripa, D.; Acciarri, A.; Matera, M.G.; Pilotto, A.; Tiziano, F.D.; Brahe, C.; Masullo, C. The complex interaction between APOE promoter and AD: An Italian case–control study. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 17, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, B.; Parnetti, L.; Nocentini, G.; Cardinali, L.; Brancorsini, S.; Riccardi, C.; Senin, U. Apolipoprotein-E genotype in normal aging, age-associated memory impairment, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia patients. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 231, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scacchi, R.; De Bernardini, L.; Mantuano, E.; Donini, L.M.; Vilardo, T.; Corbo, R.M. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) allele frequencies in late-onset sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (AD), mixed dementia and vascular dementia: Lack of association of ϵ4 allele with AD in Italian octogenarian patients. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 201, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, C.; Panza, F.; Seripa, D.; Frisardi, V.; Imbimbo, B.P.; Verdile, G.; Vendemiale, G.; Pilotto, A.; Solfrizzi, V. Polymorphisms in Glutathione S-Transferase Omega-1 Gene and Increased Risk of Sporadic Alzheimer Disease. Rejuvenation Res. 2010, 13, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, G.; Panza, F.; Seripa, D.; Sancarlo, D.; Paris, F.; Cascavilla, L.; Urbano, M.; Gravina, C.; Fontana, A.; Solfrizzi, V.; et al. The APOE polymorphism in Alzheimer’s disease patients with neuropsychiatric symptoms and syndromes. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2011, 26, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, M.; Congiu, D.; Squassina, A.; Manconi, F.; Putzu, P.F.; Mereu, R.M.; Chillotti, C.; Del Zompo, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Case-control association study of polymorphisms in ACHE, CHAT, and BCHE genes in a Sardinian sample. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2007, 144B, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Solfrizzi, V.; Colacicco, A.M.; Basile, A.M.; D’Introno, A.; Capurso, C.; Sabba, M.; Capurso, S.; Capurso, A. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) polymorphism influences serum APOE levels in Alzheimer’s disease patients and centenarians. Neuroreport 2003, 14, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Solfrizzi, V.; Torres, F.; Mastroianni, F.; Colacicco, A.M.; Basile, A.M.; Capurso, C.; D’Introno, A.; Del Parigi, A.; Capurso, A. Apolipoprotein E in Southern Italy: Protective effect of ε2 allele in early- and late-onset sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 292, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Solfrizzi, V.; Torres, F.; Mastroianni, F.; Del Parigi, A.; Colacicco, A.M.; Basile, A.M.; Capurso, C.; Noya, R.; Capurso, A. Decreased frequency of apolipoprotein E ε4 allele from Northern to Southern Europe in Alzheimer’s disease patients and centenarians. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 277, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorbi, S.; Nacmias, B.; Forleo, P.; Latorraca, S.; Gobbini, I.; Bracco, L.; Piacentini, S.; Amaducci, L. ApoE allele frequencies in Italian sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 177, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strittmatter, W.J.; Saunders, A.M.; Schmechel, D.; Pericak-Vance, M.; Enghild, J.; Salvesen, G.S.; Roses, A.D. Apolipoprotein E: High-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, B.C.; Kluemper, J.; Johnson, L.A. Apolipoprotein E4 Alters Astrocyte Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Formation. Cells 2019, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, J.W.; Akay, L.A.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; von Maydell, D.; Mathys, H.; Davidson, S.M.; Effenberger, A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Maner-Smith, K.; Hajjar, I.; et al. APOE4 impairs myelination via cholesterol dysregulation in oligodendrocytes. Nature 2022, 611, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.; Crean, S.; Mercaldi, C.J.; Collins, J.M.; Boyd, D.; Cook, M.N.; Arrighi, H.M. Prevalence of apolipoprotein E4 genotype and homozygotes (APOE e4/4) among patients diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 2012, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bian, C.; Zhang, J.; Wen, F. Apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese population: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Tripathi, C.B. Association of Apolipoprotein E Genetic Variation in Alzheimer’s Disease in Indian Population: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2014, 29, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyadeh, M.; Djafarian, K.; Heydarinejad, F.; Alizadeh, S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Association between Apolipoprotein E Gene Polymorphism and Alzheimer’s Disease in an Iranian Population: A Meta-Analysis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, L.K.L.; Min, S.H.; Kaplan, S.; Wei, J.; Welsh-Bohmer, K.; Xu, H. Meta-analysis of variations in association between APOE ɛ4 and Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias across Hispanic regions of origin. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 93, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortea, J.; Pegueroles, J.; Alcolea, D.; Belbin, O.; Dols-Icardo, O.; Vaqué-Alcázar, L.; Videla, L.; Gispert, J.D.; Suárez-Calvet, M.; Johnson, S.C.; et al. APOE4 homozygozity represents a distinct genetic form of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, T.E.; Huey, E.D.; Devanand, D.P. Association of APOE e2 genotype with Alzheimer’s and non-Alzheimer’s neurodegenerative pathologies. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4727–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniewski, T.; Drummond, E. APOE-amyloid interaction: Therapeutic targets. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 138, 104784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A.; Alkon, D.L.; Nelson, T.J. Apolipoprotein E3 (ApoE3) but Not ApoE4 Protects against Synaptic Loss through Increased Expression of Protein Kinase Cϵ. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15947–15958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, P.S.; Hansson, O.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N. Association between apolipoprotein E ε2 vs ε4, age, and β-amyloid in adults without cognitive impairment. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Leurgans, S.E.; Agrawal, S.; Aggarwal, N.T.; Cherian, L.J.; James, B.D.; Dhana, K.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Schneider, J.A. Association of Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay and Mediterranean Diets with Alzheimer Disease Pathology. Neurology 2023, 100, e2259–e2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrego-Guandique, D.M.; Bonet, M.L.; Caroleo, M.C.; Cannataro, R.; Tucci, P.; Ribot, J.; Cione, E. The Effect of Beta-Carotene on Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elechi, J.O.G.; Guandique, D.M.A.; Cannataro, R. Creatine in Cognitive Performance: A Commentary. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2024, 17, e18761429272915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, E.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Costanzo, S.; Persichillo, M.; Bracone, F.; Cerletti, C.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G.; Iacoviello, L.; Bonaccio, M. Socioeconomic and psychosocial determinants of adherence to the Mediterranean diet in a general adult Italian population. Eur. J. Public Health 2019, 29, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Notarnicola, M.; Cisternino, A.M.; Inguaggiato, R.; Guerra, V.; Reddavide, R.; Donghia, R.; Rotolo, O.; Zinzi, I.; Leandro, G.; et al. Trends in adherence to the Mediterranean diet in South Italy: A cross sectional study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tan, L.; Wang, H.-F.; Jiang, T.; Tan, M.-S.; Tan, L.; Zhao, Q.-F.; Li, J.-Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.-T. Meta-analysis of modifiable risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huq, A.J.; Fulton-Howard, B.; Riaz, M.; Laws, S.; Sebra, R.; Ryan, J.; Consortium, A.D.G.; Renton, A.E.; Goate, A.M.; Masters, C.L.; et al. Polygenic score modifies risk for Alzheimer’s disease in APOE ε4 homozygotes at phenotypic extremes. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2021, 13, e12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.J.; Fulton-Howard, B.; O’Reilly, P.; Marcora, E.; Goate, A.M.; Consortium, C.; Farrer, L.A.; Haines, J.L.; Mayeux, R.; Naj, A.C. Causal associations between modifiable risk factors and the Alzheimer’s phenome. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Gunasekaran, T.I.; Kang, S.; Lee, W.; Jeong, J.; Lim, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Won, S.-Y.; et al. APOE Promoter Polymorphism-219T/G is an Effect Modifier of the Influence of APOE ε4 on Alzheimer’s Disease Risk in a Multiracial Sample. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).